A&P: Anatomy of the Neck
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
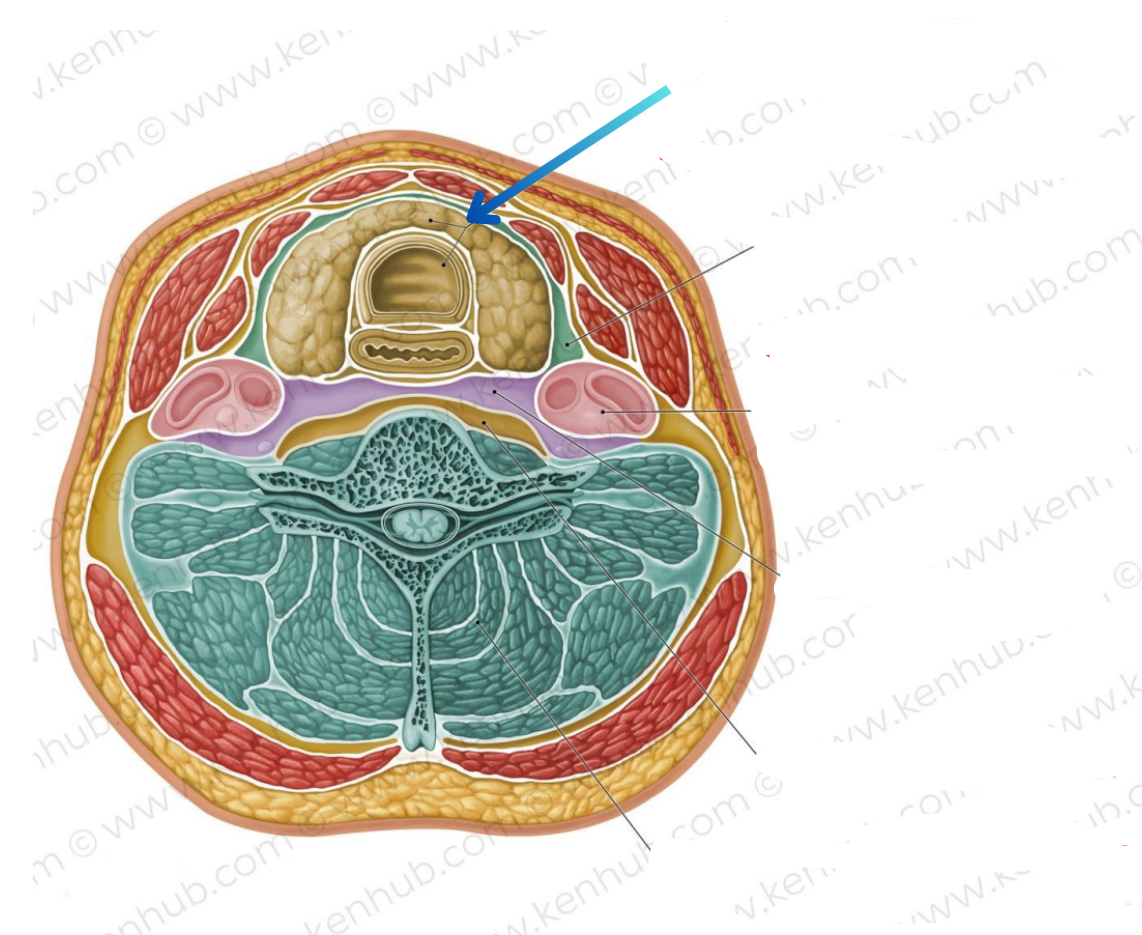
Visceral compartment
Contains glands, larynx, pharynx, and trachea
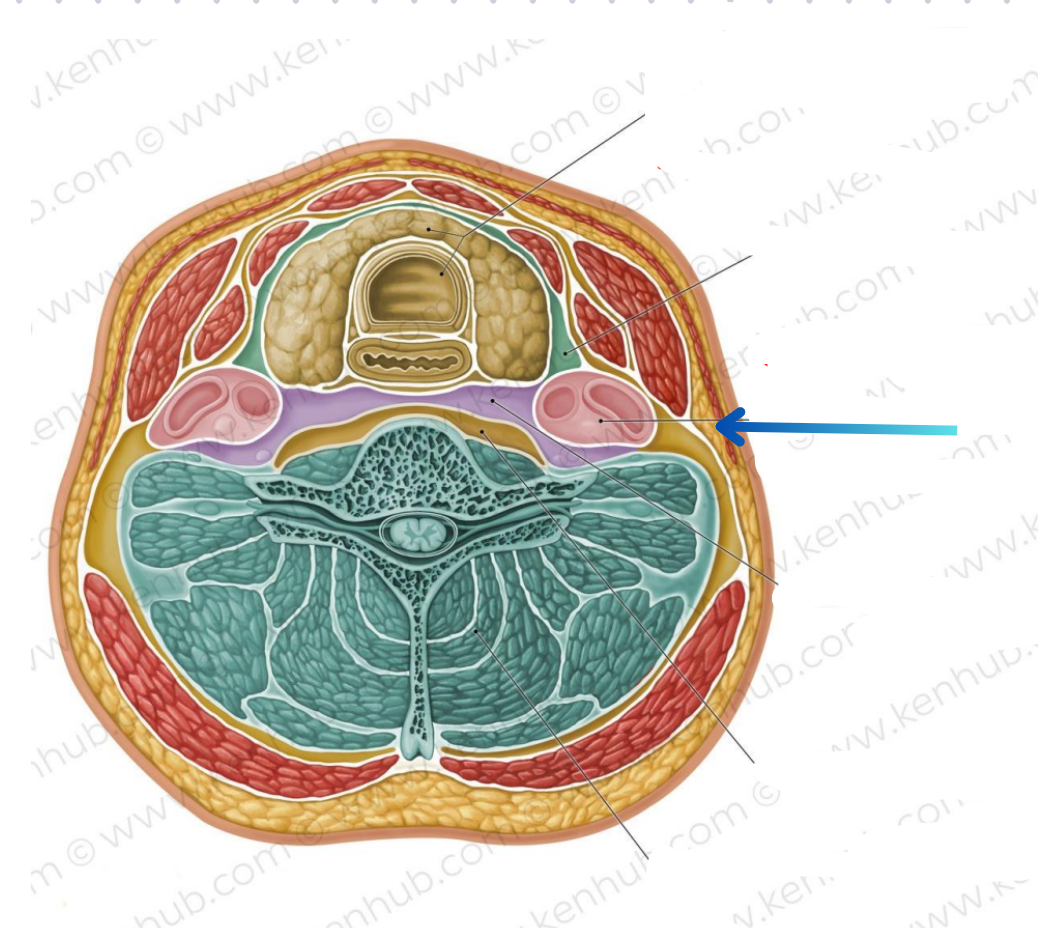
Vascular compartments (2)
Contains common carotid artery, internal jugular vein, and vagus nerve
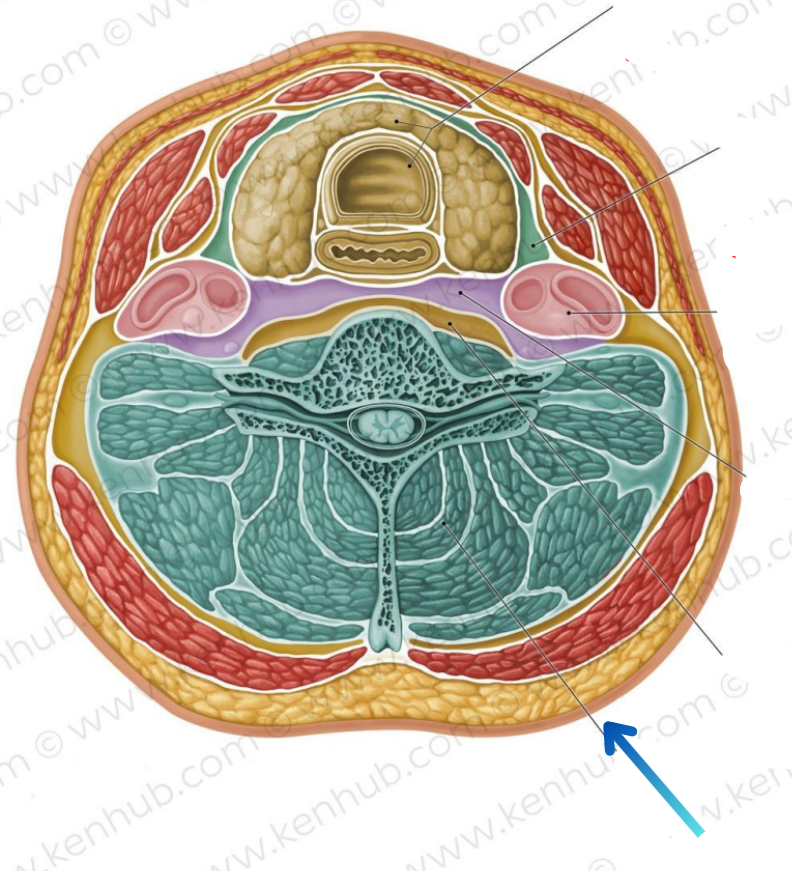
Vertebral compartment
Contains cervical vertebrae and postural muscles
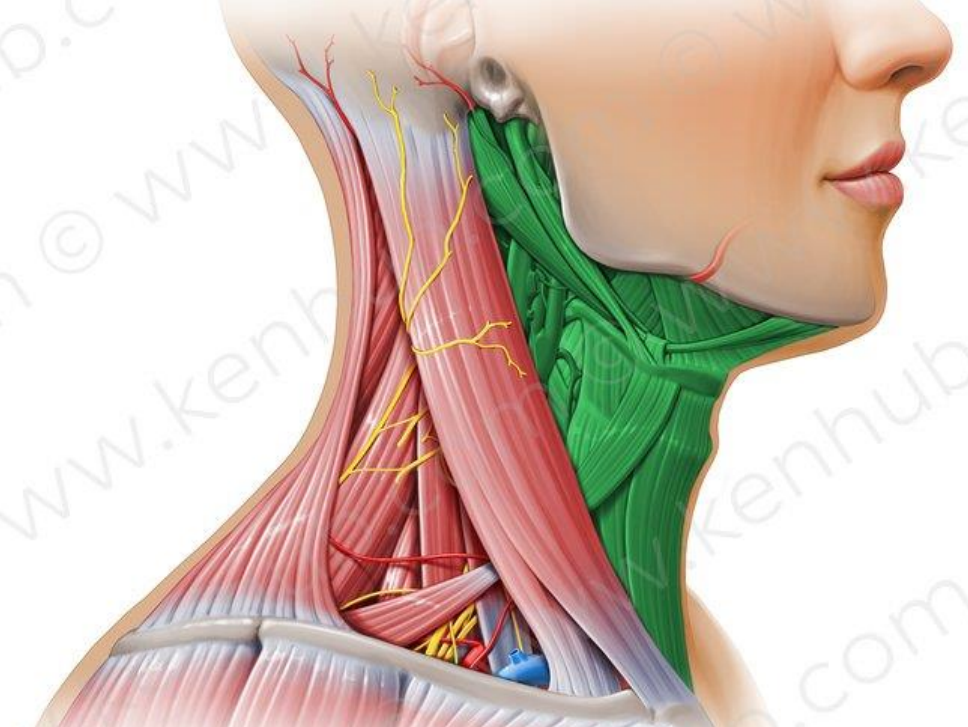
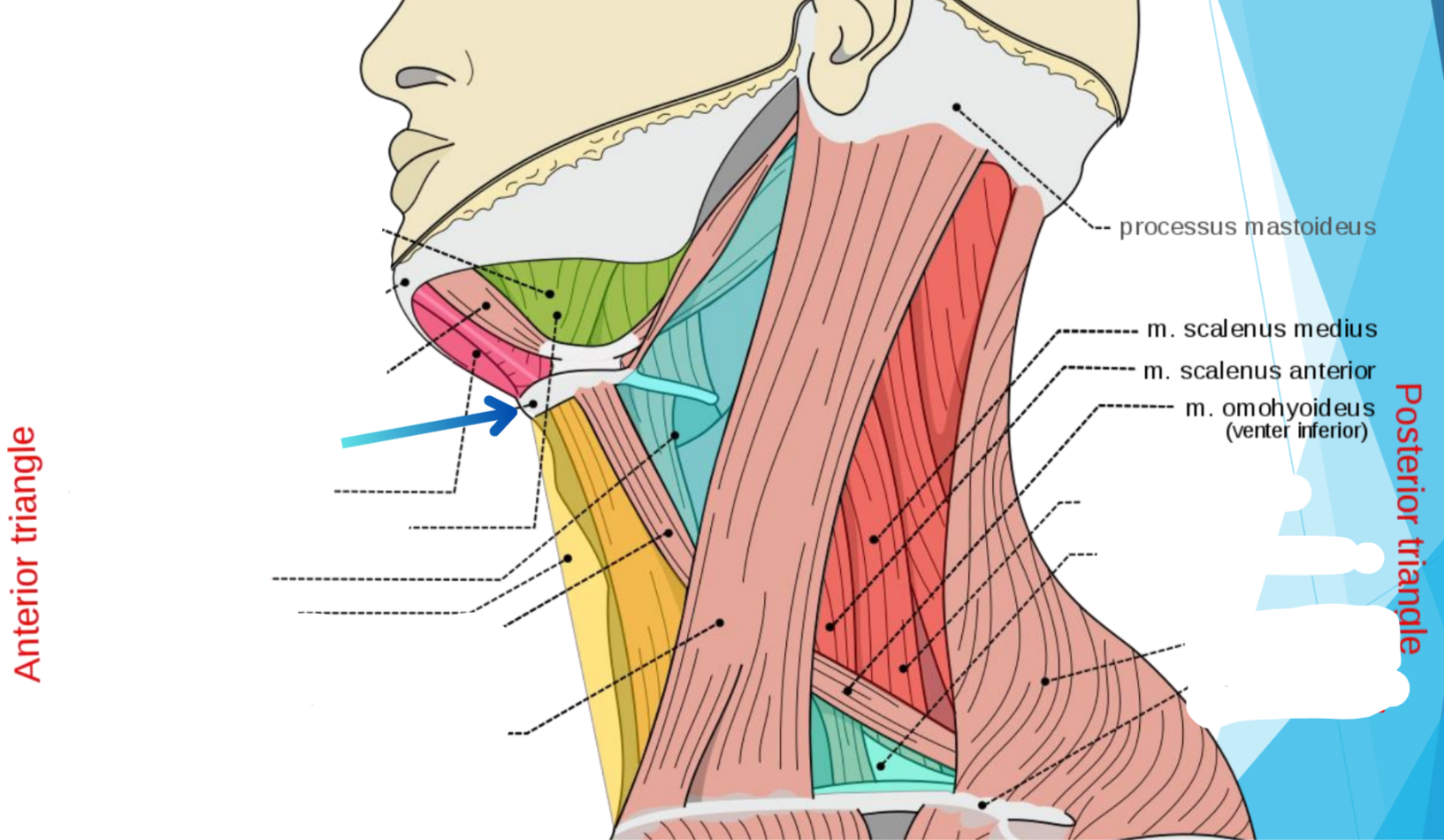
In green
Anterior triangle
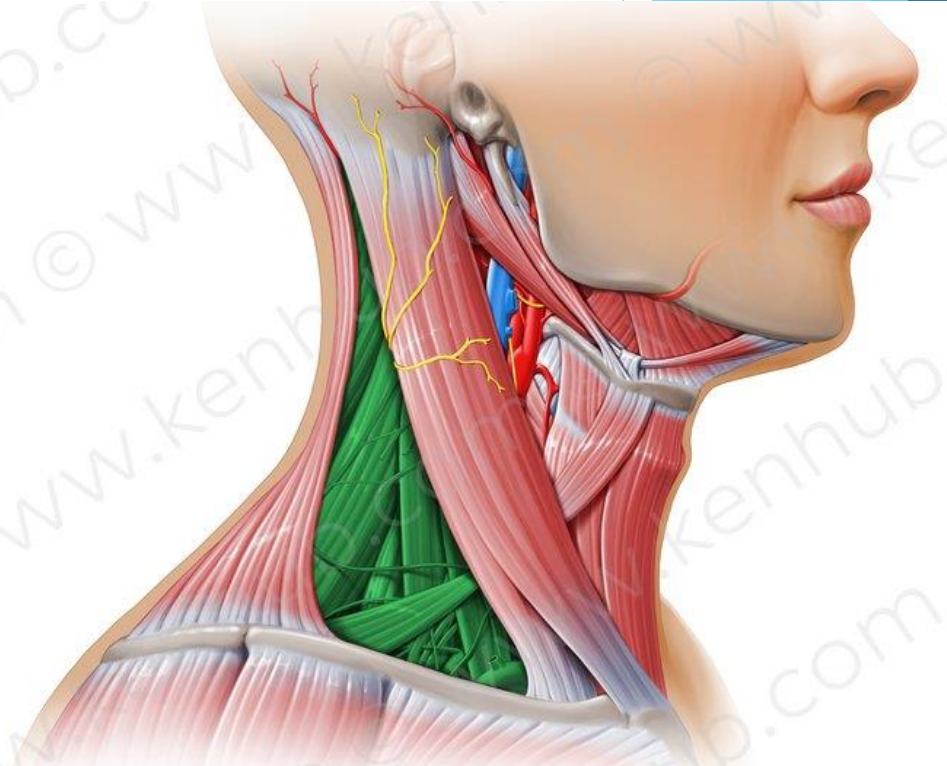
In green
Posterior triangle
Mandibula
Mylohyoideus muscle
Digastricus muscle
Hyoideum bone
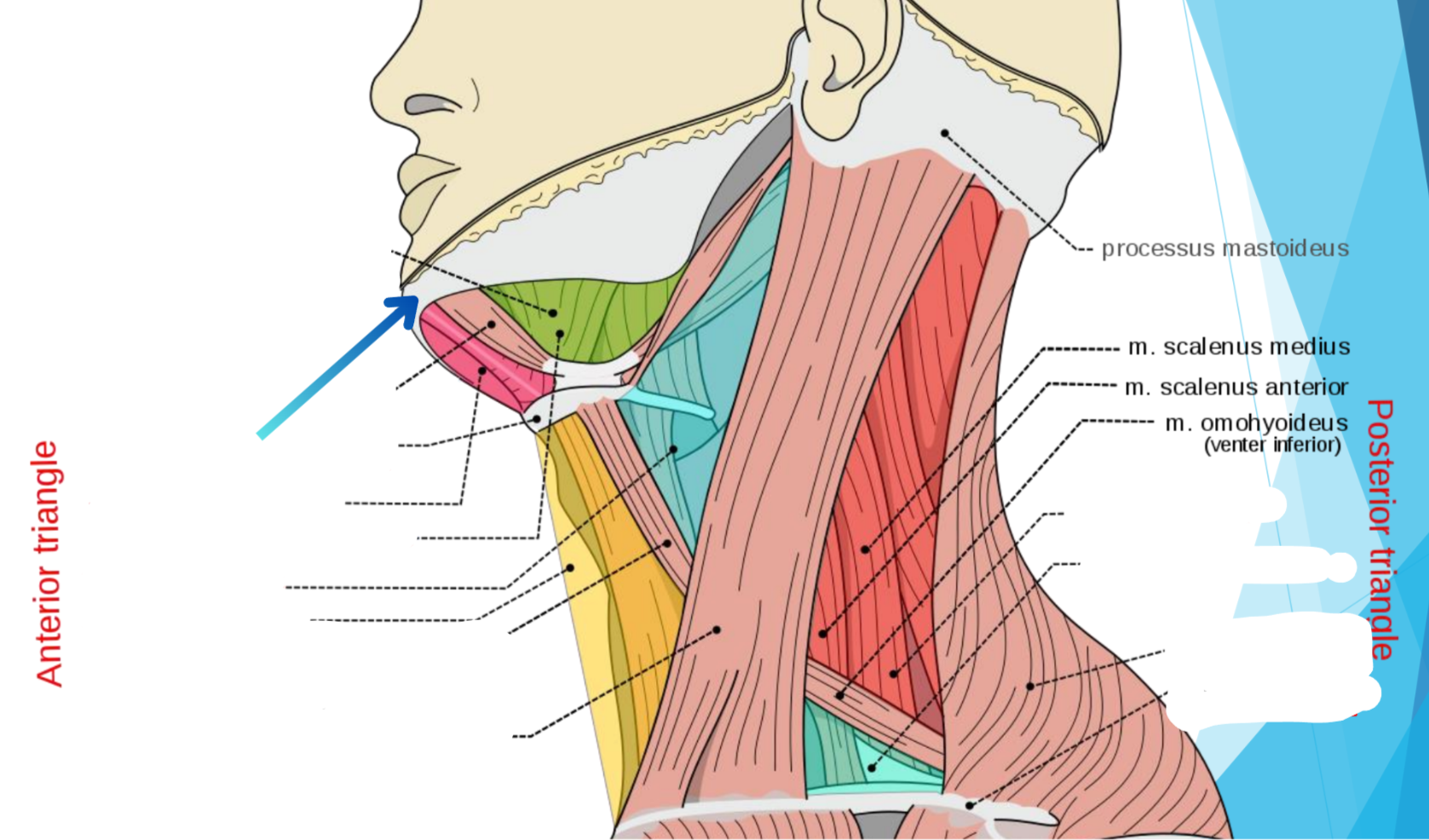
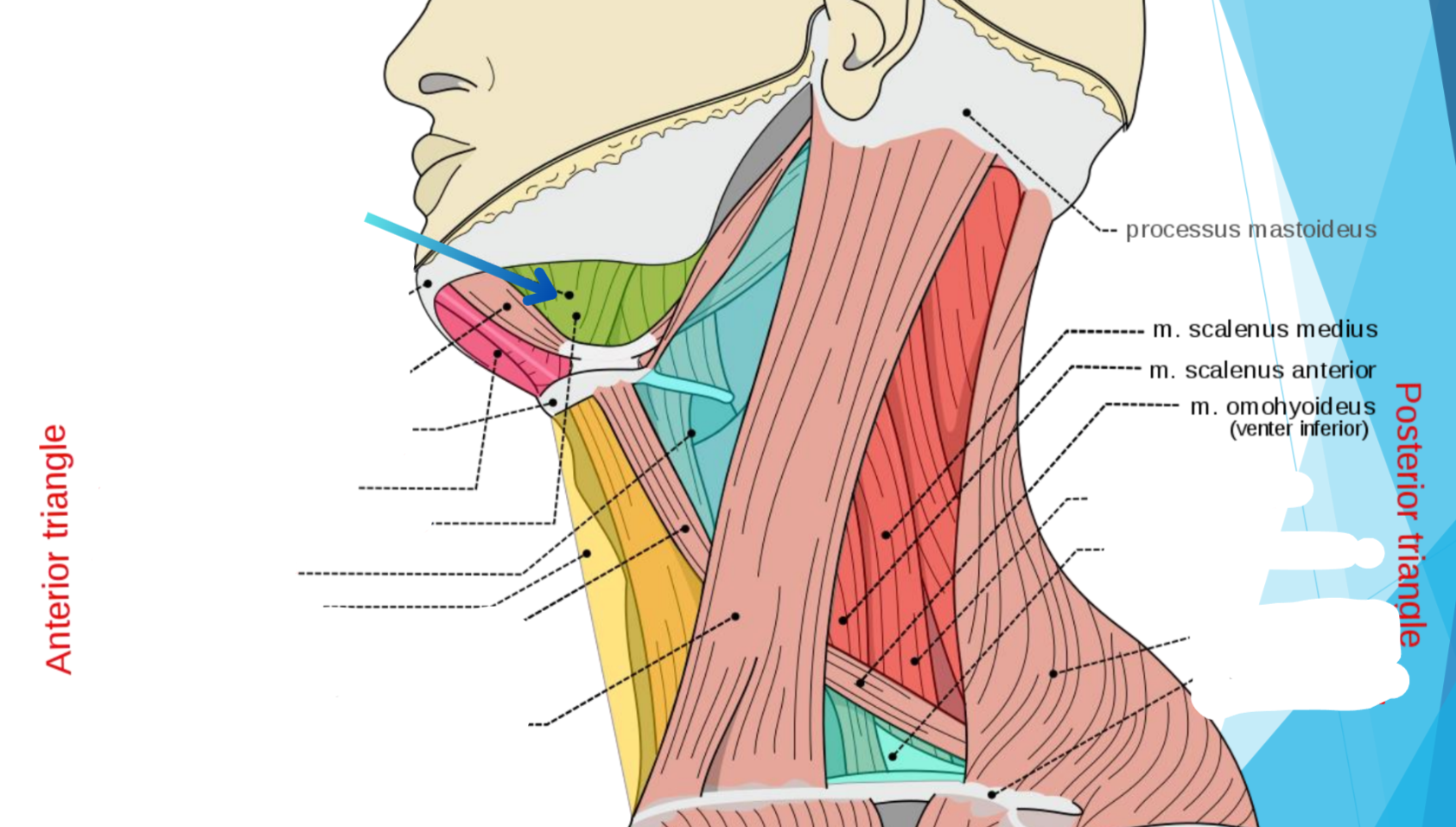
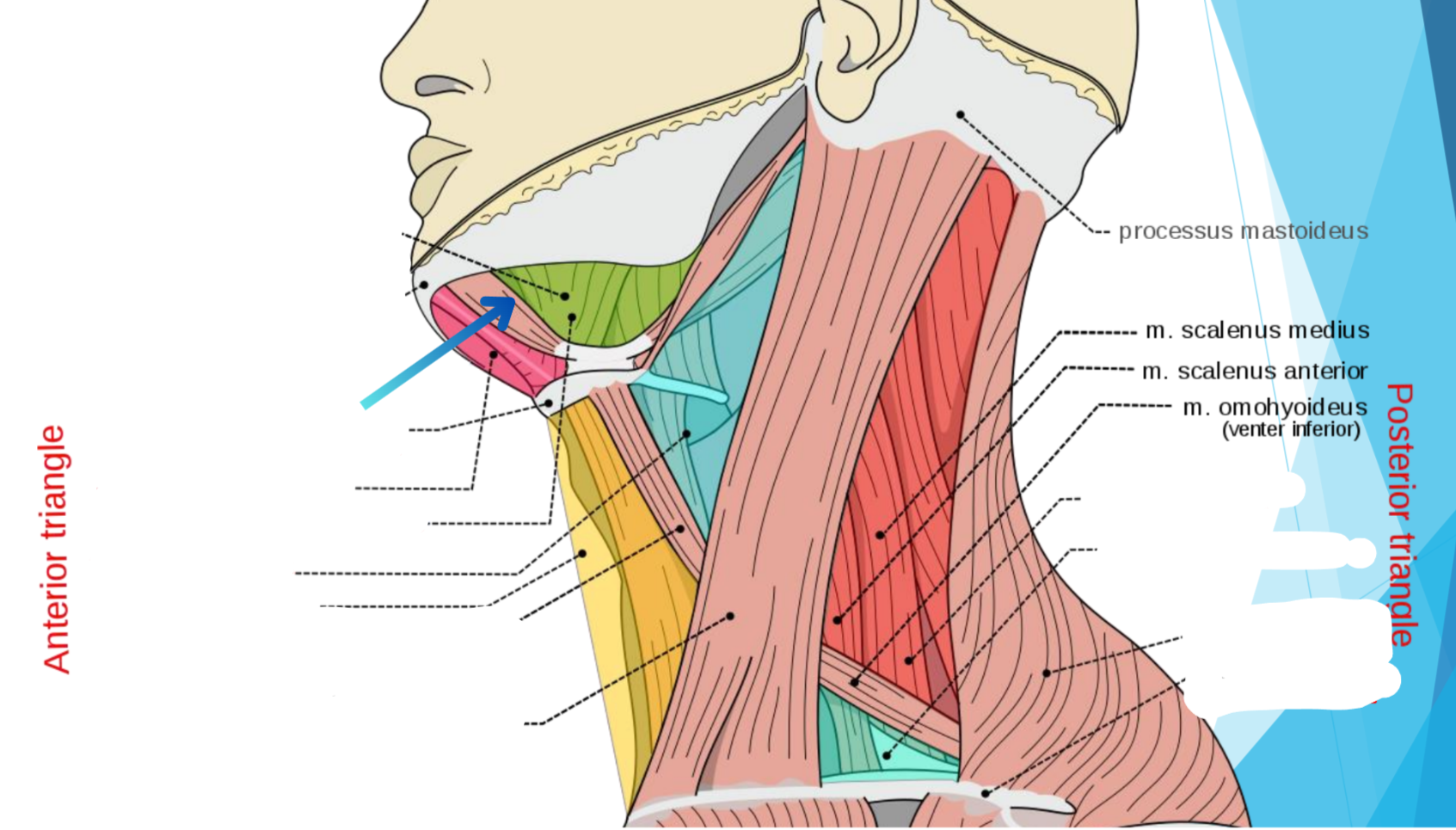
What triangle does hot pink show?
Submental triangle
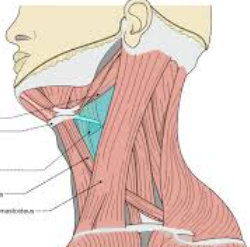
What triangle does green show?
Submandibular triangle
Carotid triangle
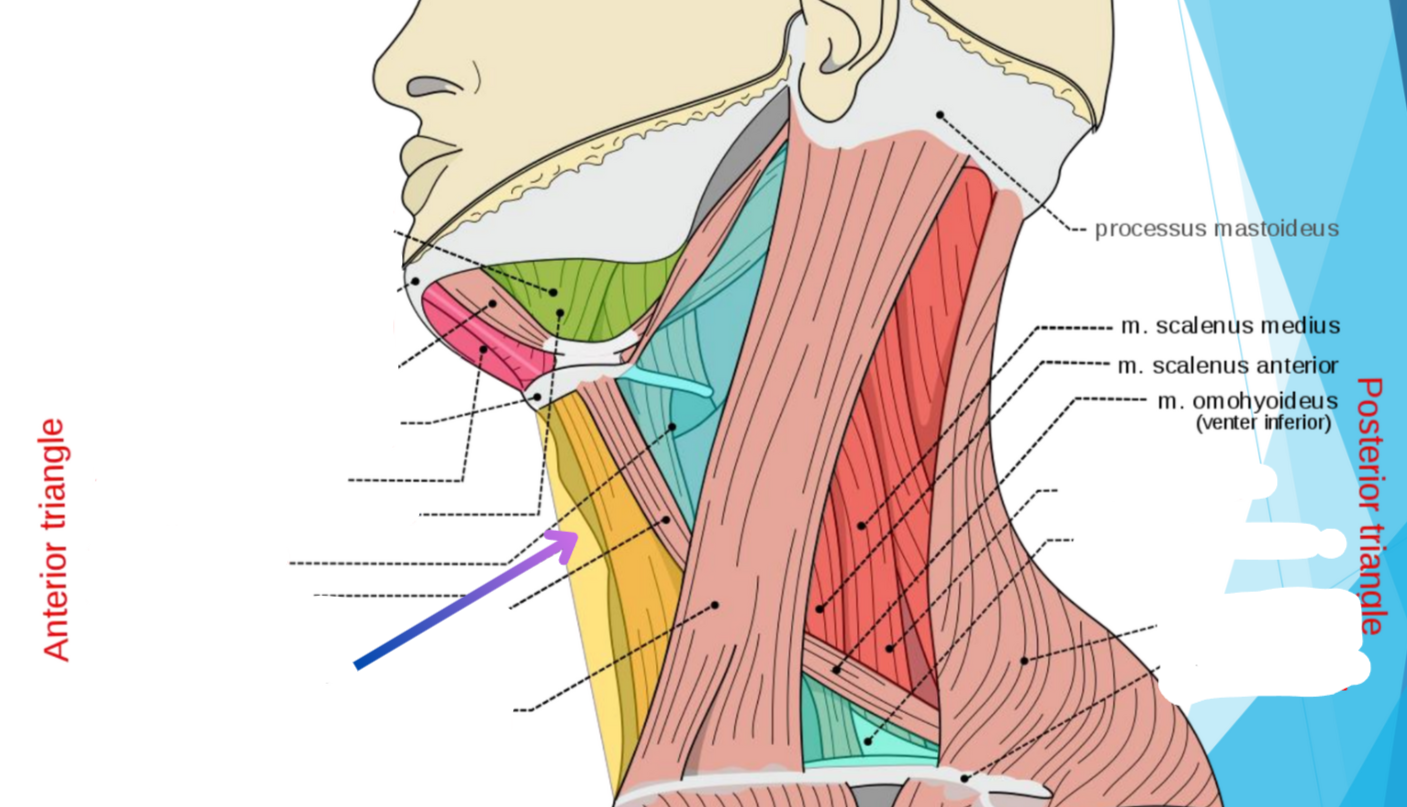
What triangle does yellow show?
Muscular triangle
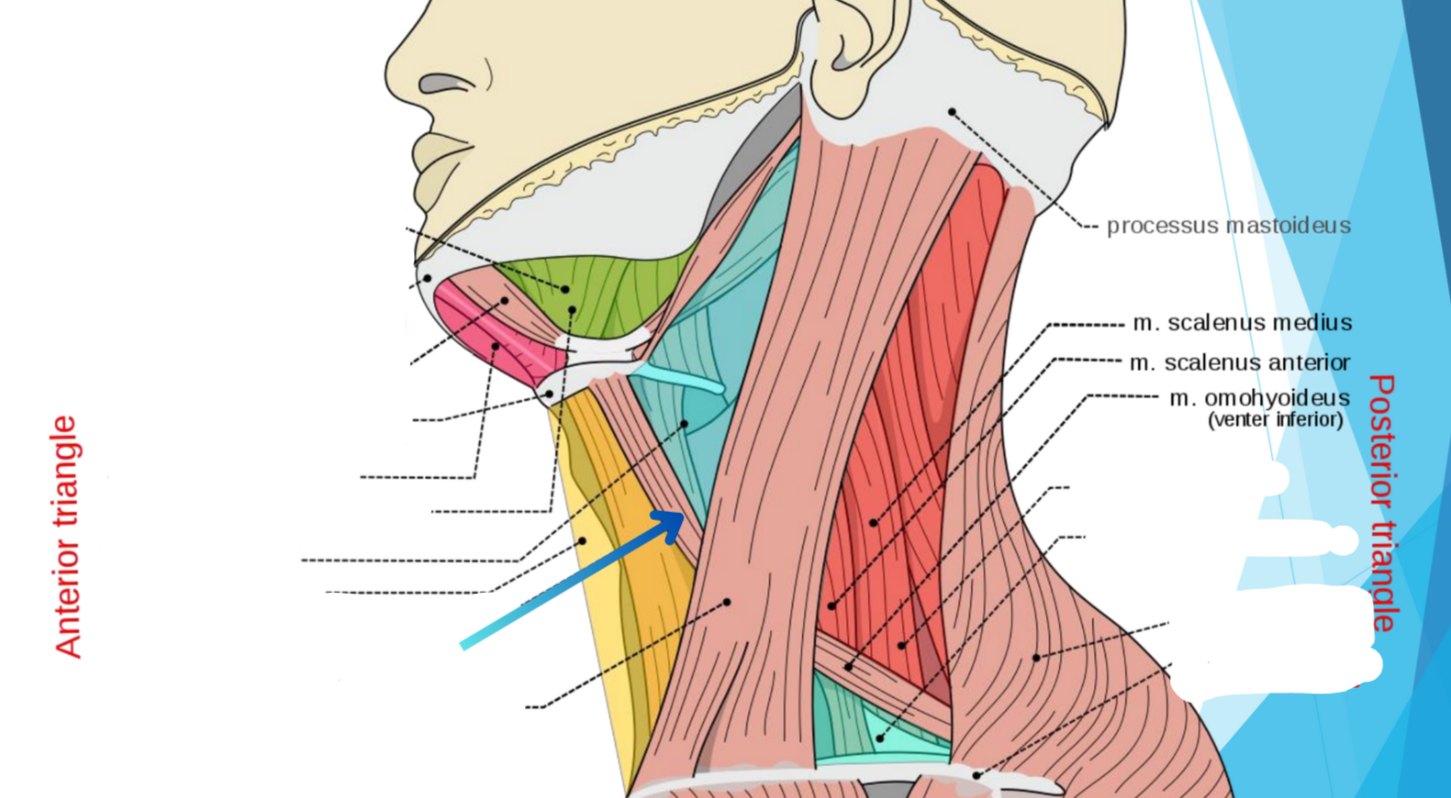
Omohyoideus muscle
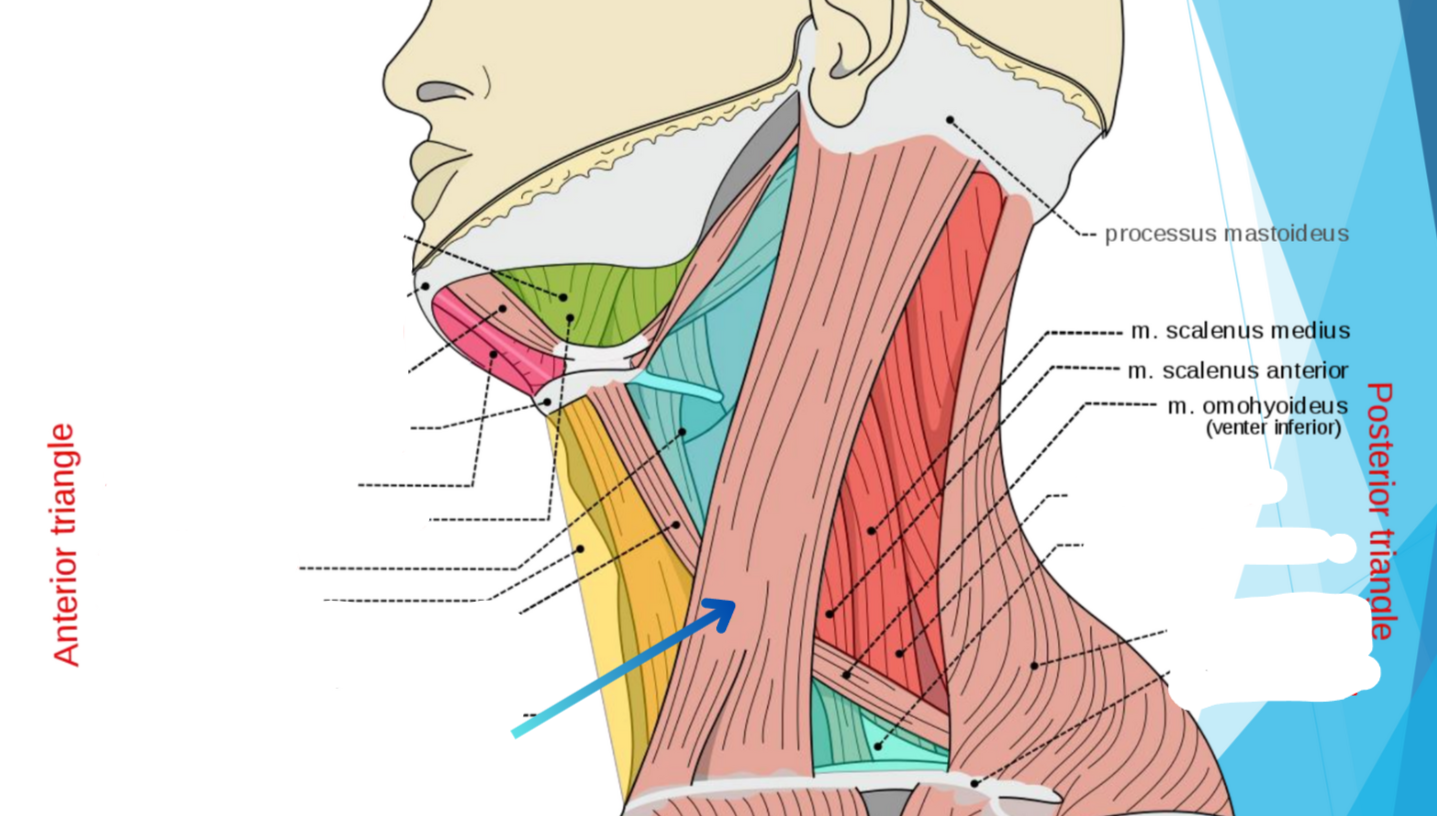
Sternocleidomastoideus muscle
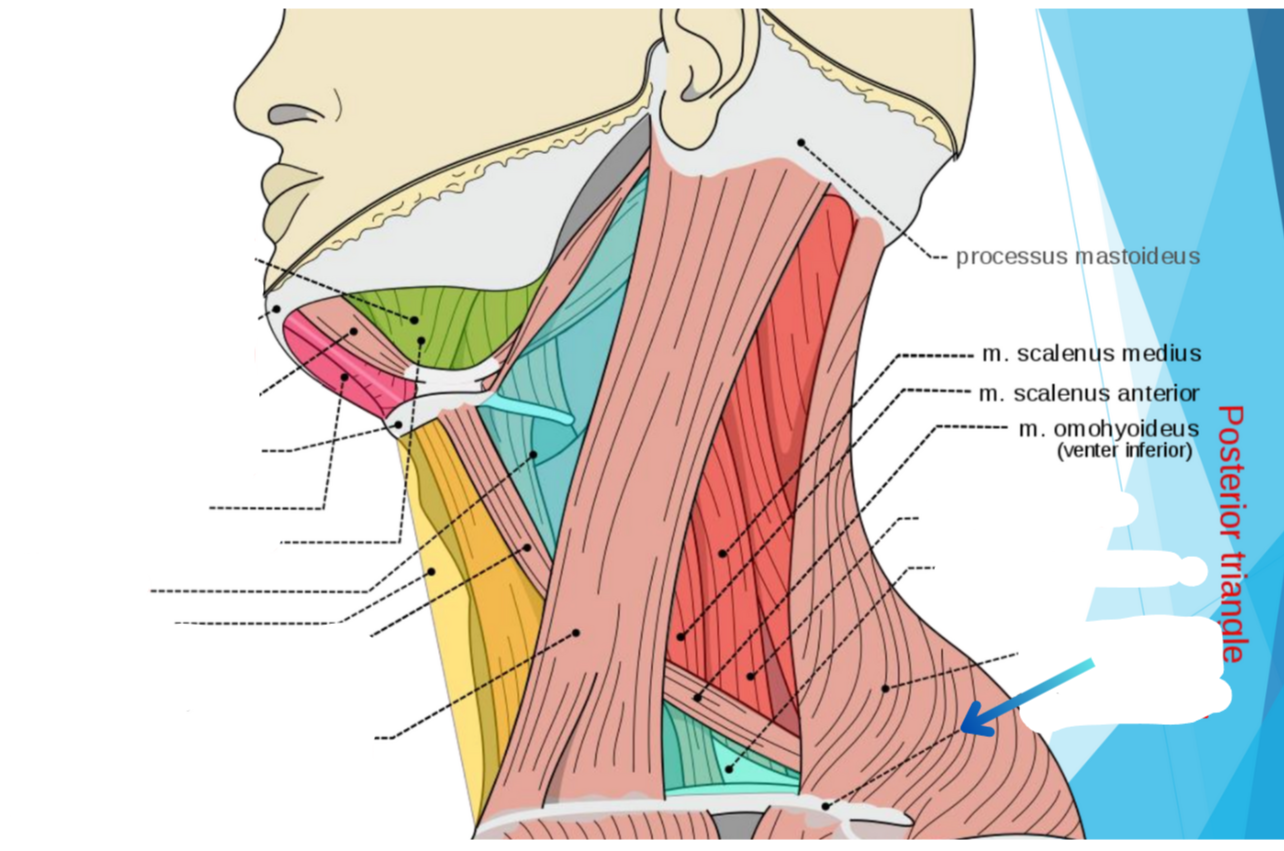
What triangle does dark red show?
Occipital triangle
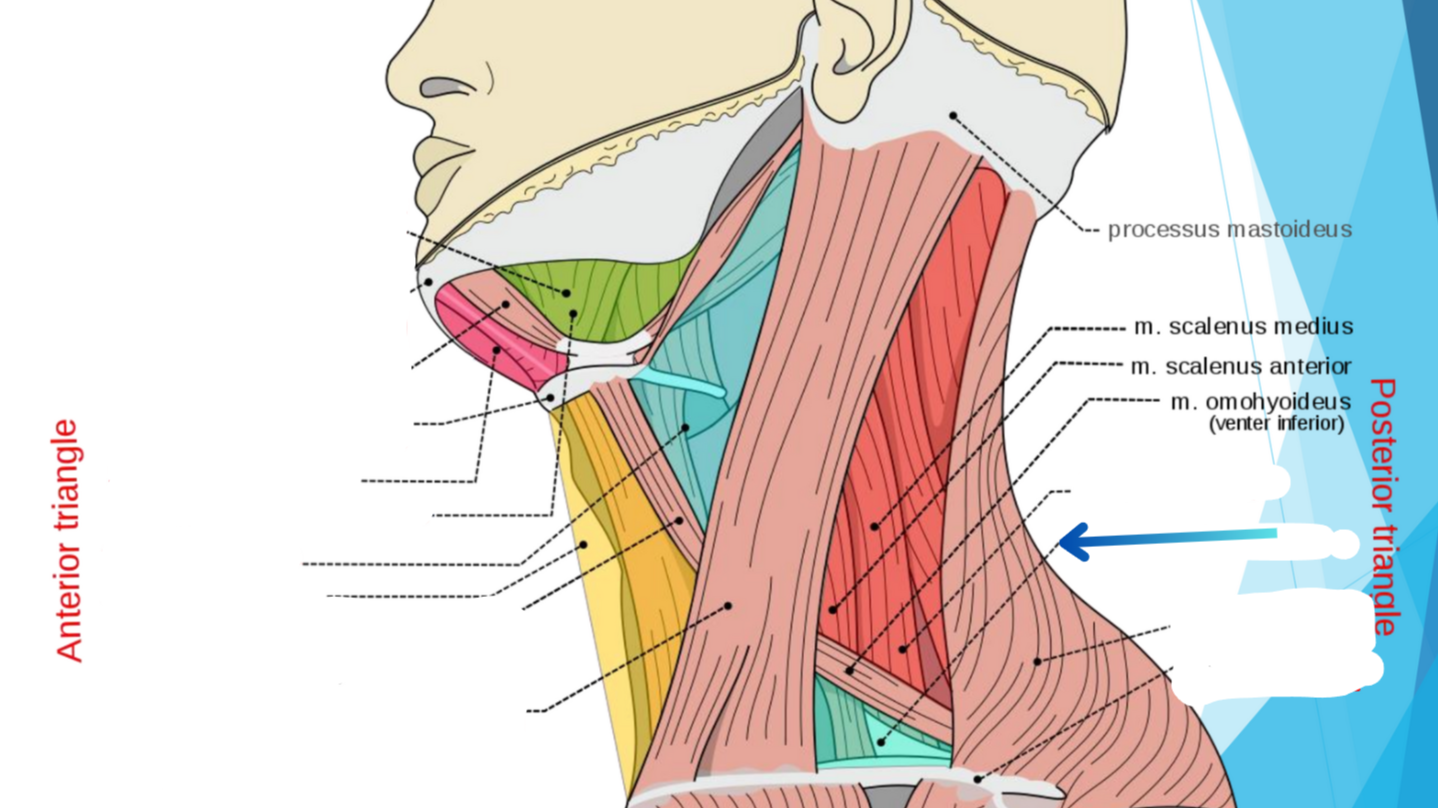
What triangle does teal show? (Lower blue)
Subclavian triangle
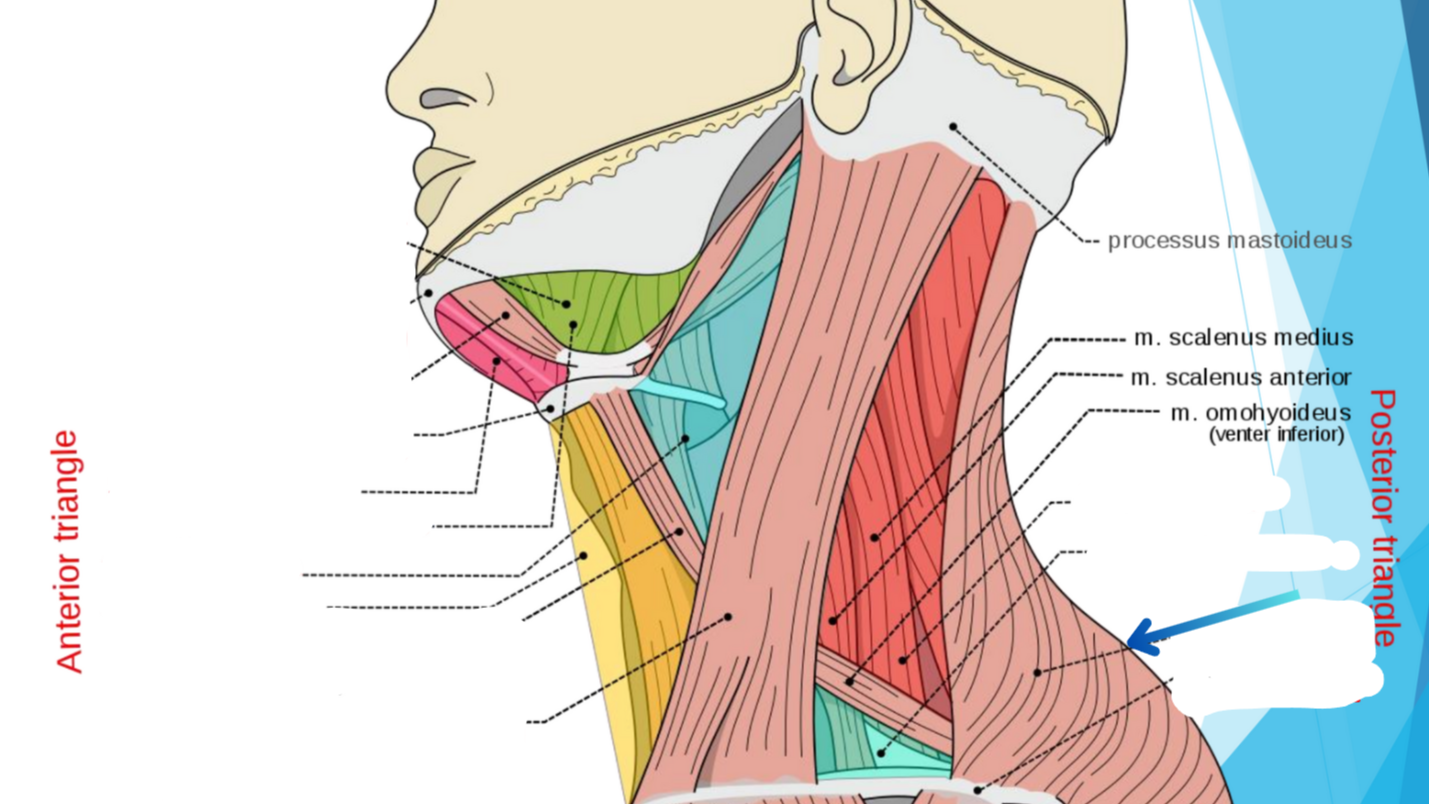
M. Trapezius
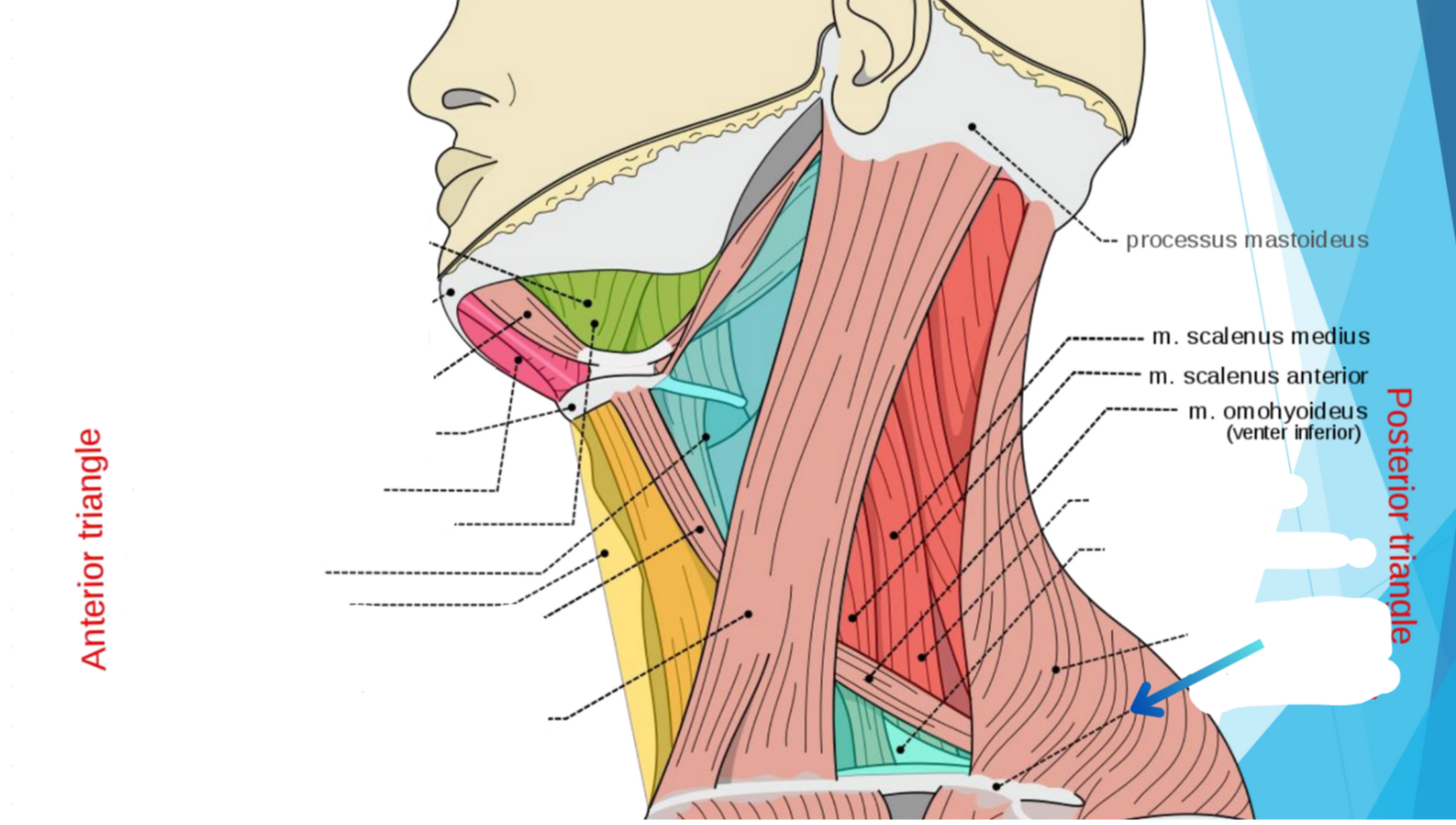
Clavicula
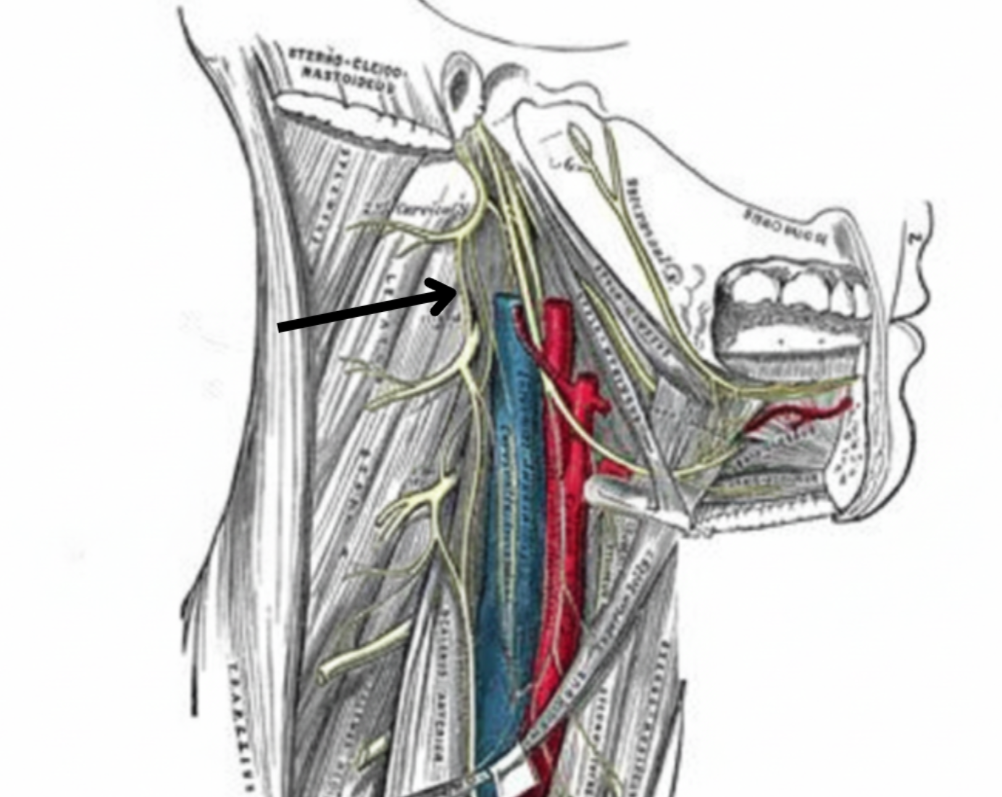
CI, CII, CIII (Ansa cervicalis)
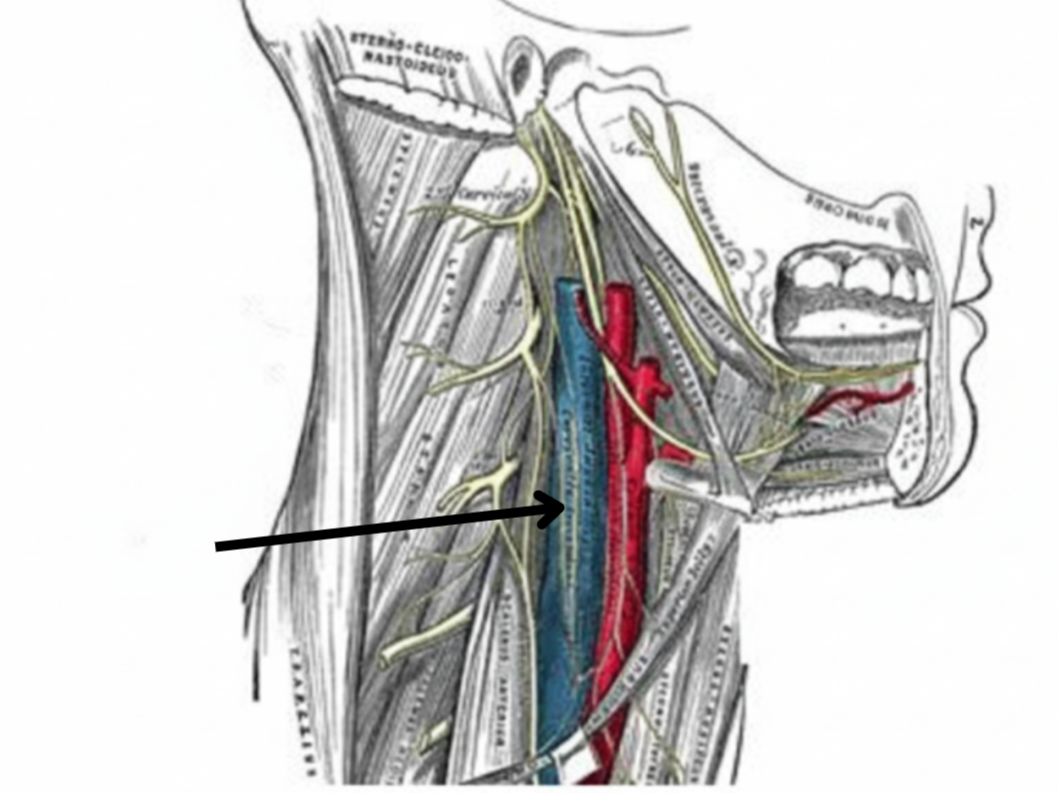
Internal jugular vein
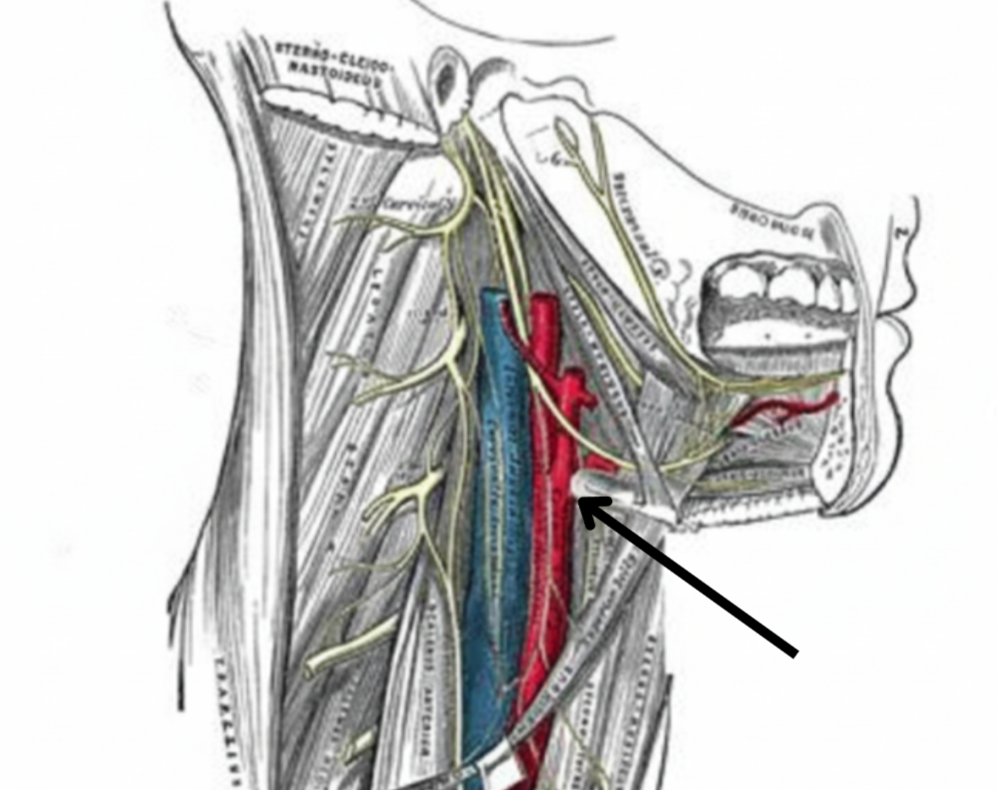
Internal and external carotid arteries
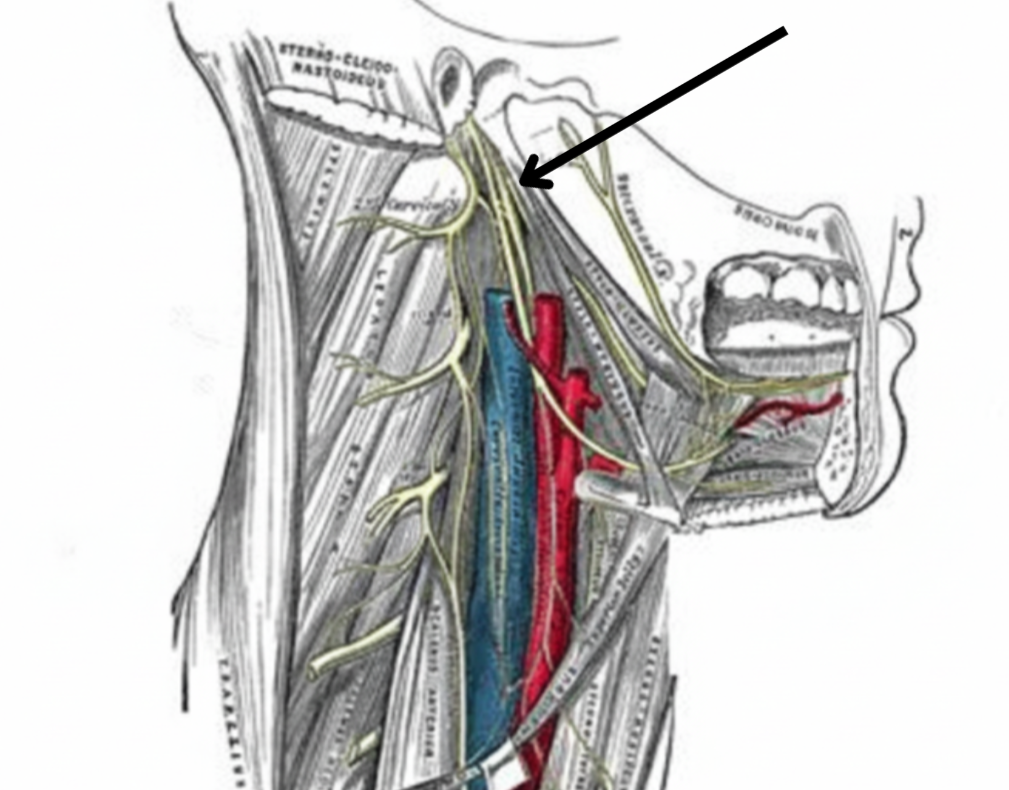
CN X, XI, and XII
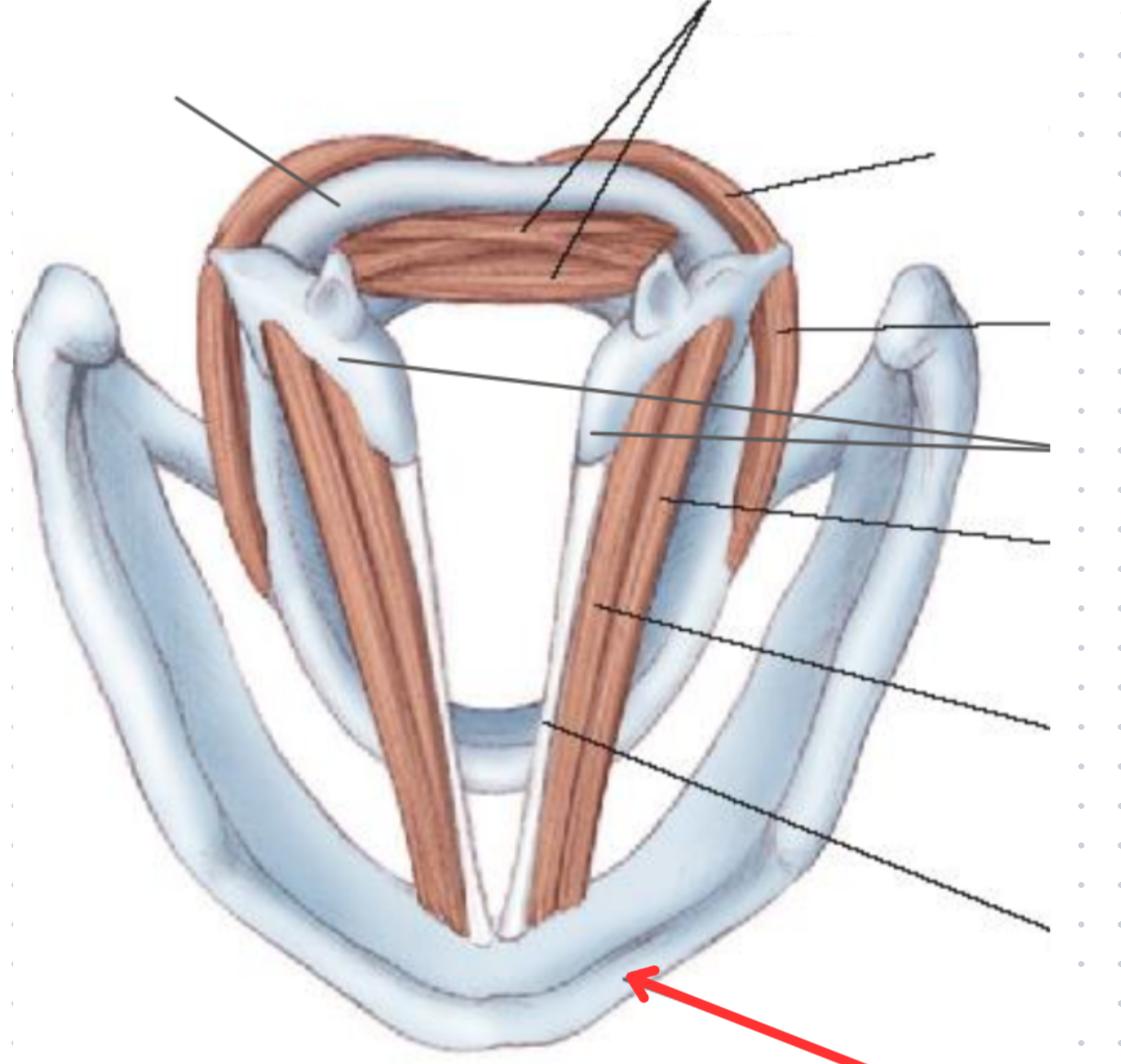
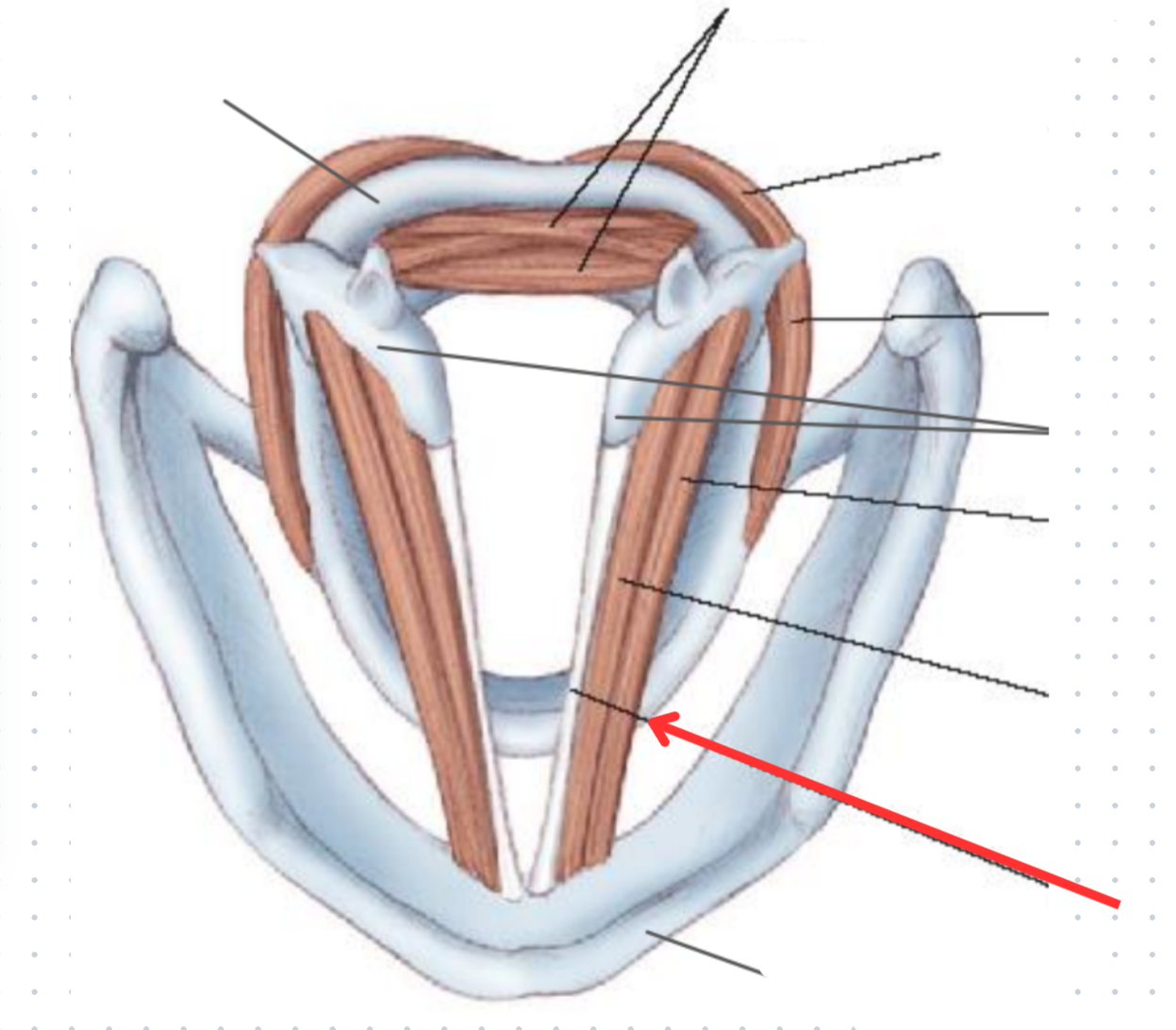
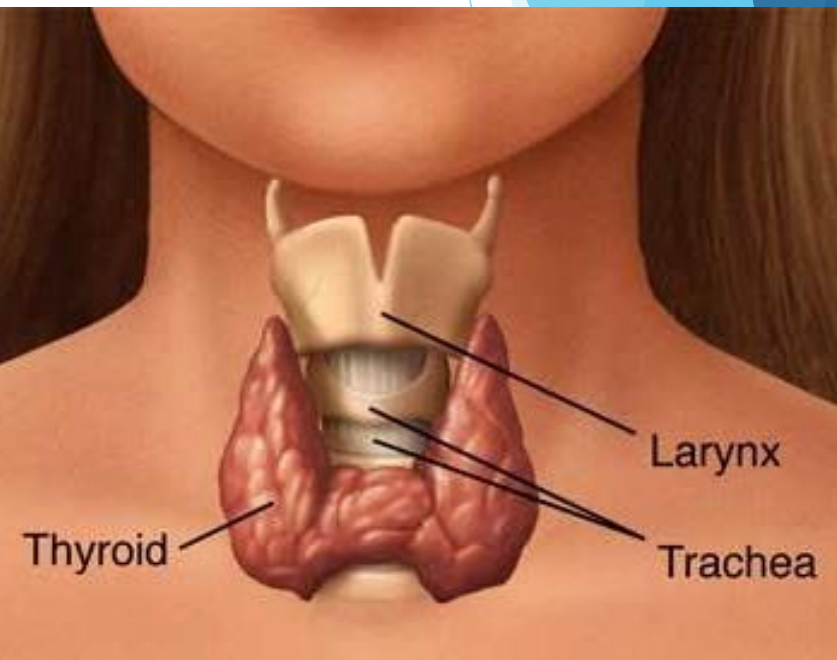
The larynx
Cartilaginous skeleton
Lets air pass from throat → trachea
Contains vocal chords
Prevents food from entering trachea
Paried vs. unpaired cartilages
Paired: Bilateral pairs of cartilage that are not connected
Unapaired: Symmetrical pairs of cartilage connected
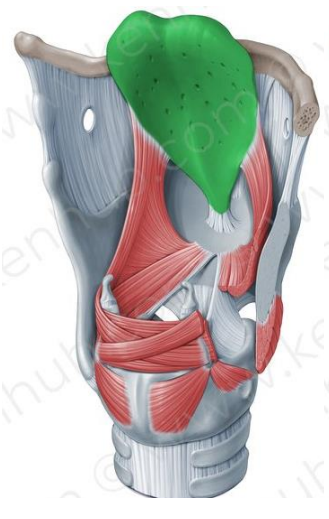
Epiglottis
Unpaired, elastic cartilage
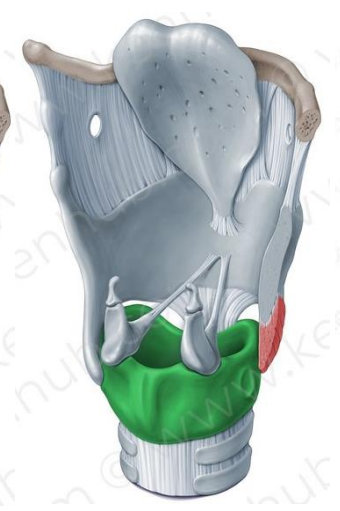
Cricoid cartilage
Hyaline, unpaired cartilage
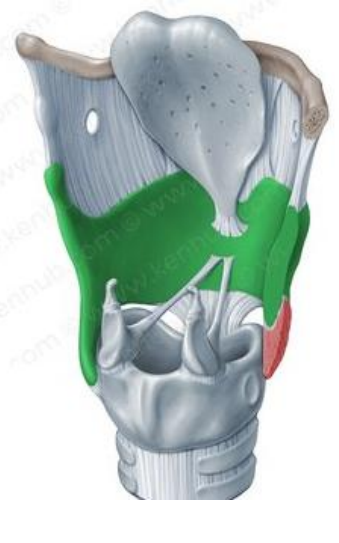
Thyroid cartilage
Hyaline, unpaired cartilage
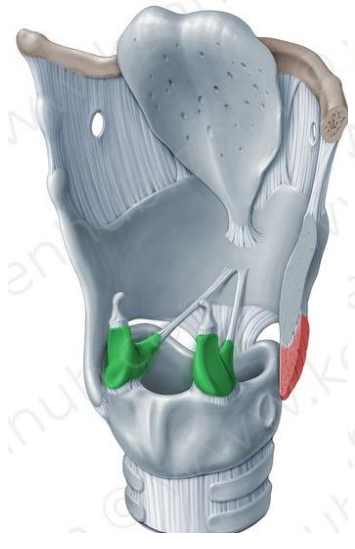
Arytenoid cartilages
Paired, elastic cartilage
Role in vocal processes
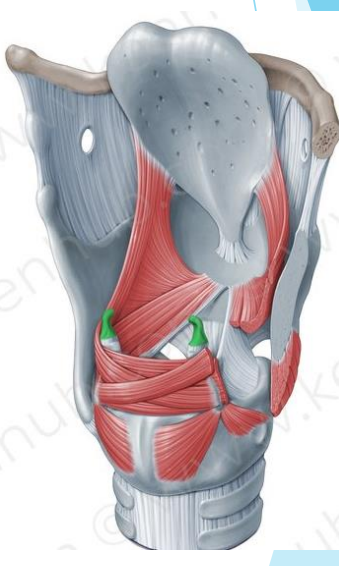
Corniculate cartilages
Paired, elastic cartilage
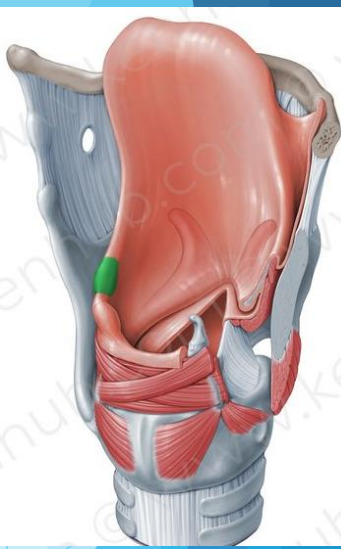
Cuneiform cartilages
Paired, elastic cartilage
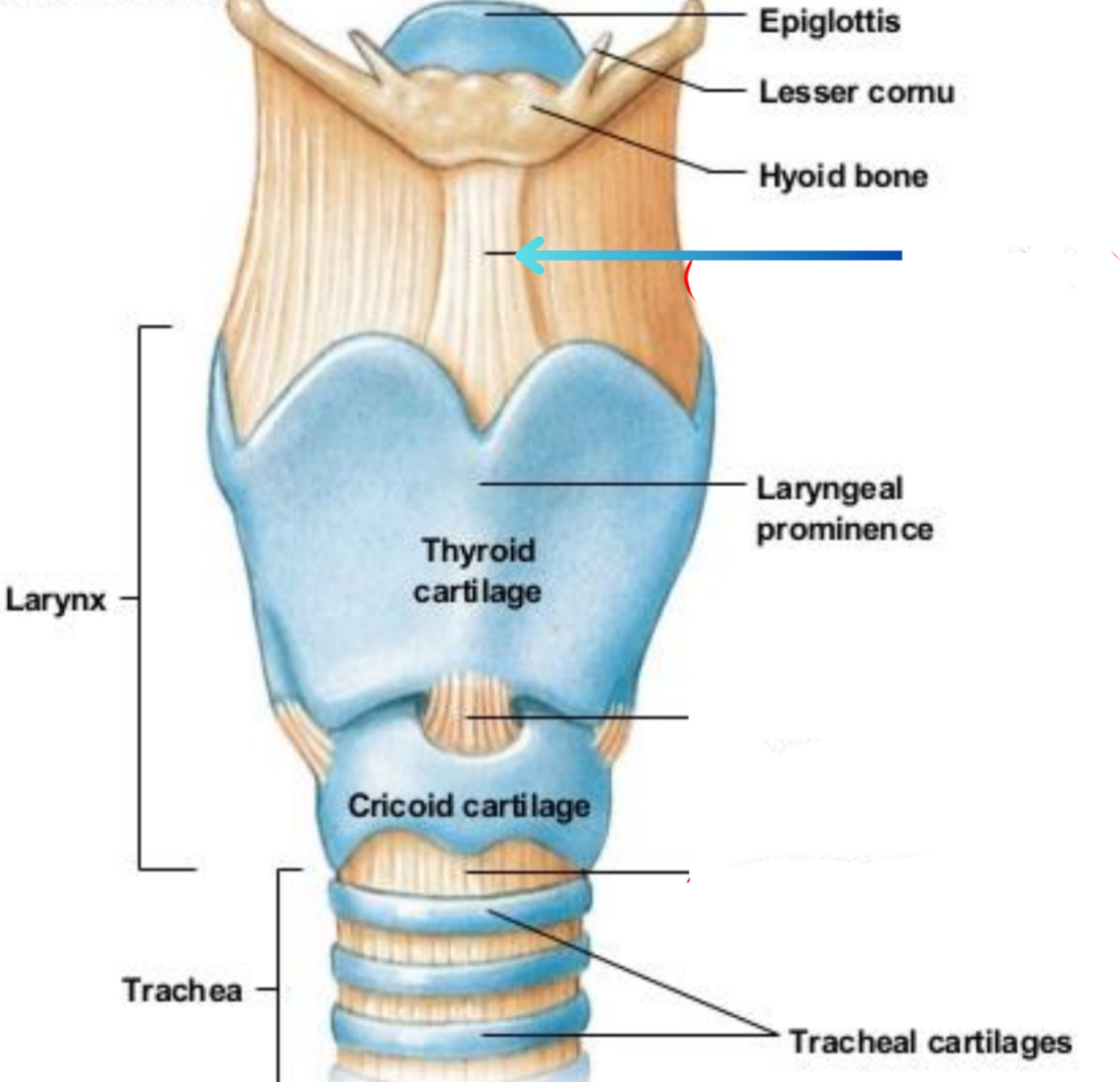
Thyroid ligament (extrinsic)
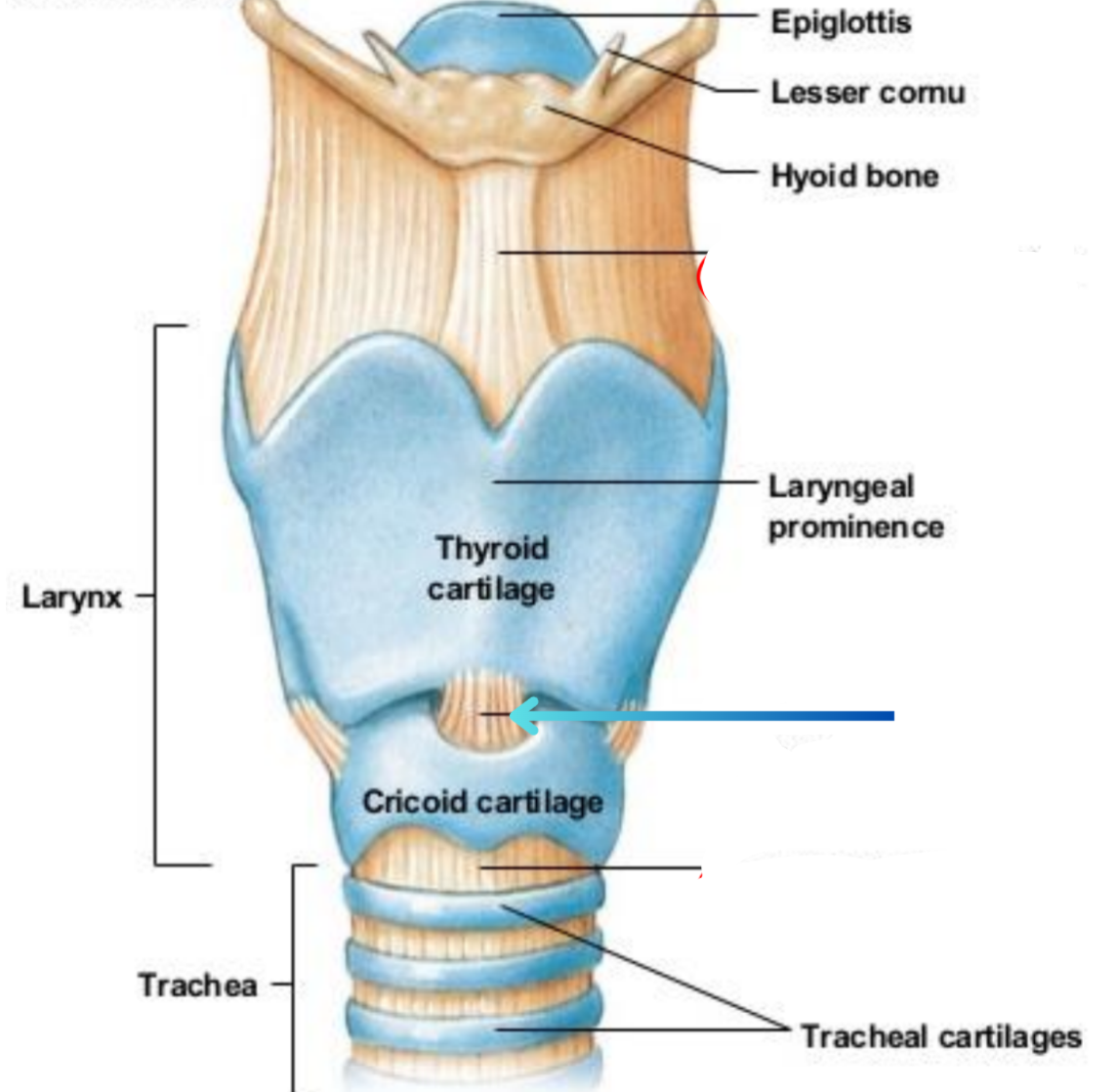
Cricothyroid ligament (Intrinsic)
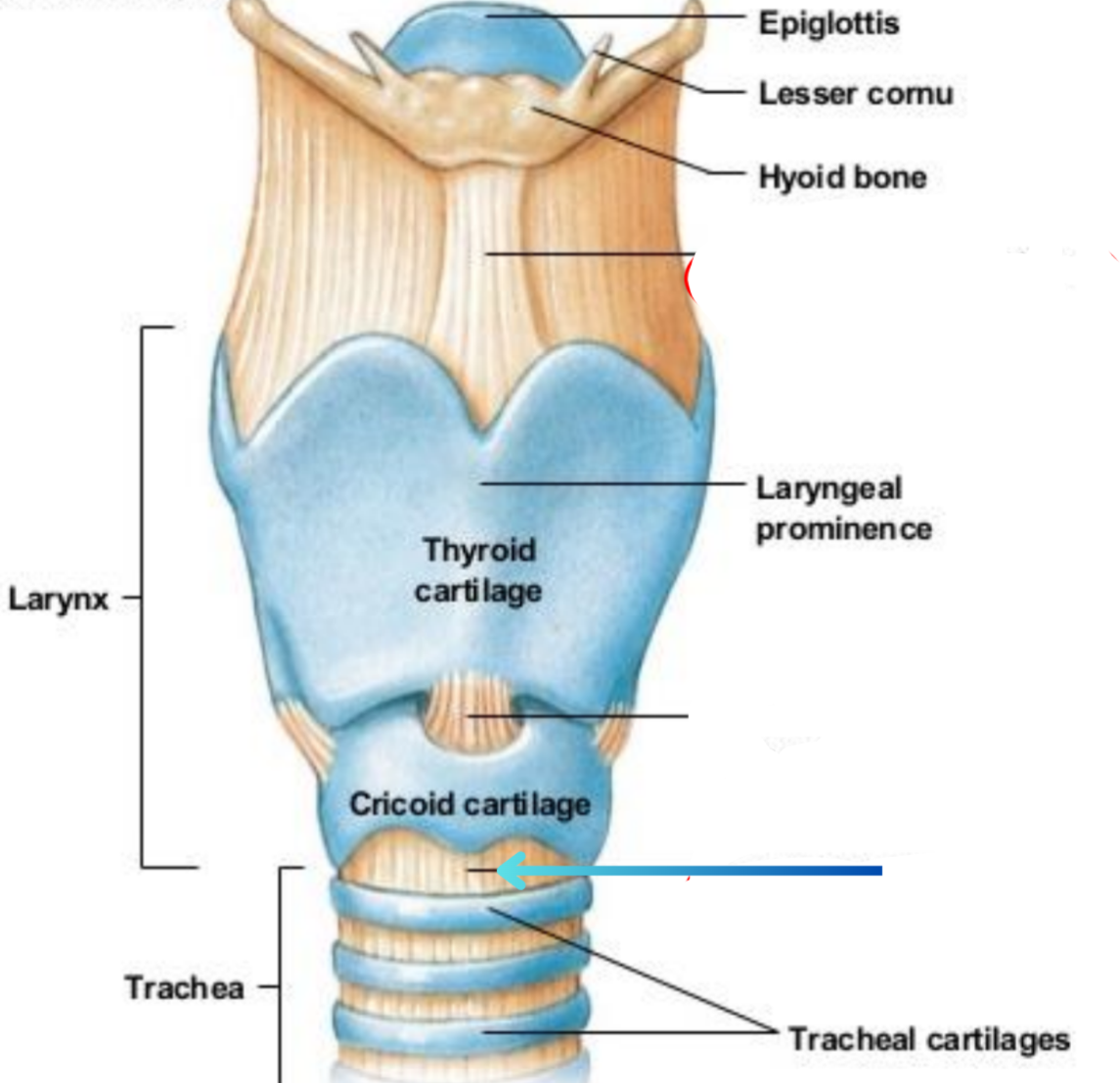
Cricotracheal ligament (Extrinsic)
What tissue type is the structure of the larynx
Cartilage
Function of larynx ligaments
Connect areas of cartilage
Attach larynx to nearby structures
What do muscles do for the larynx
Move larynx while swallowing
Help with breathing and produce vocal sounds
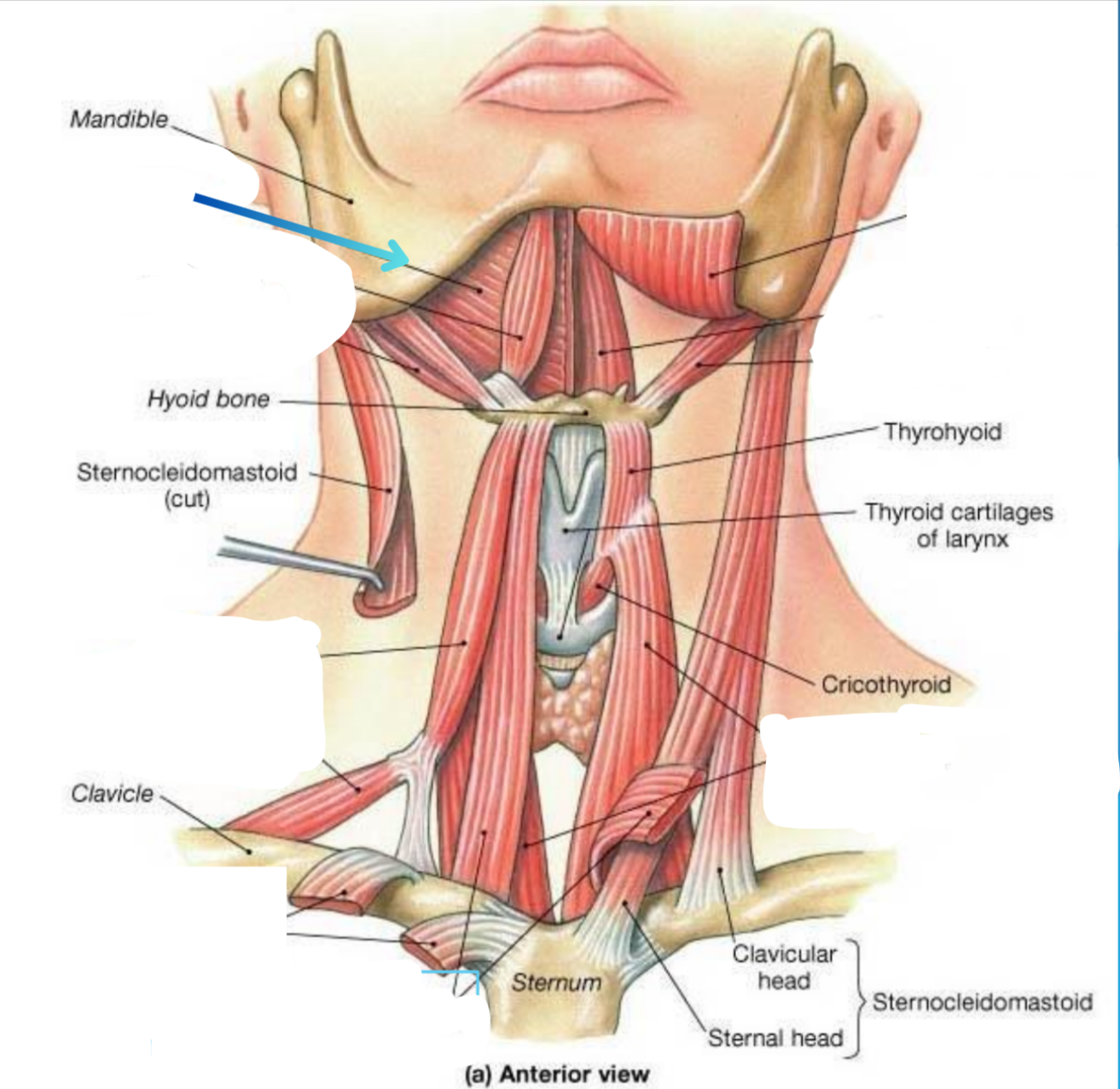
Mylohyoid muscle
Elevator
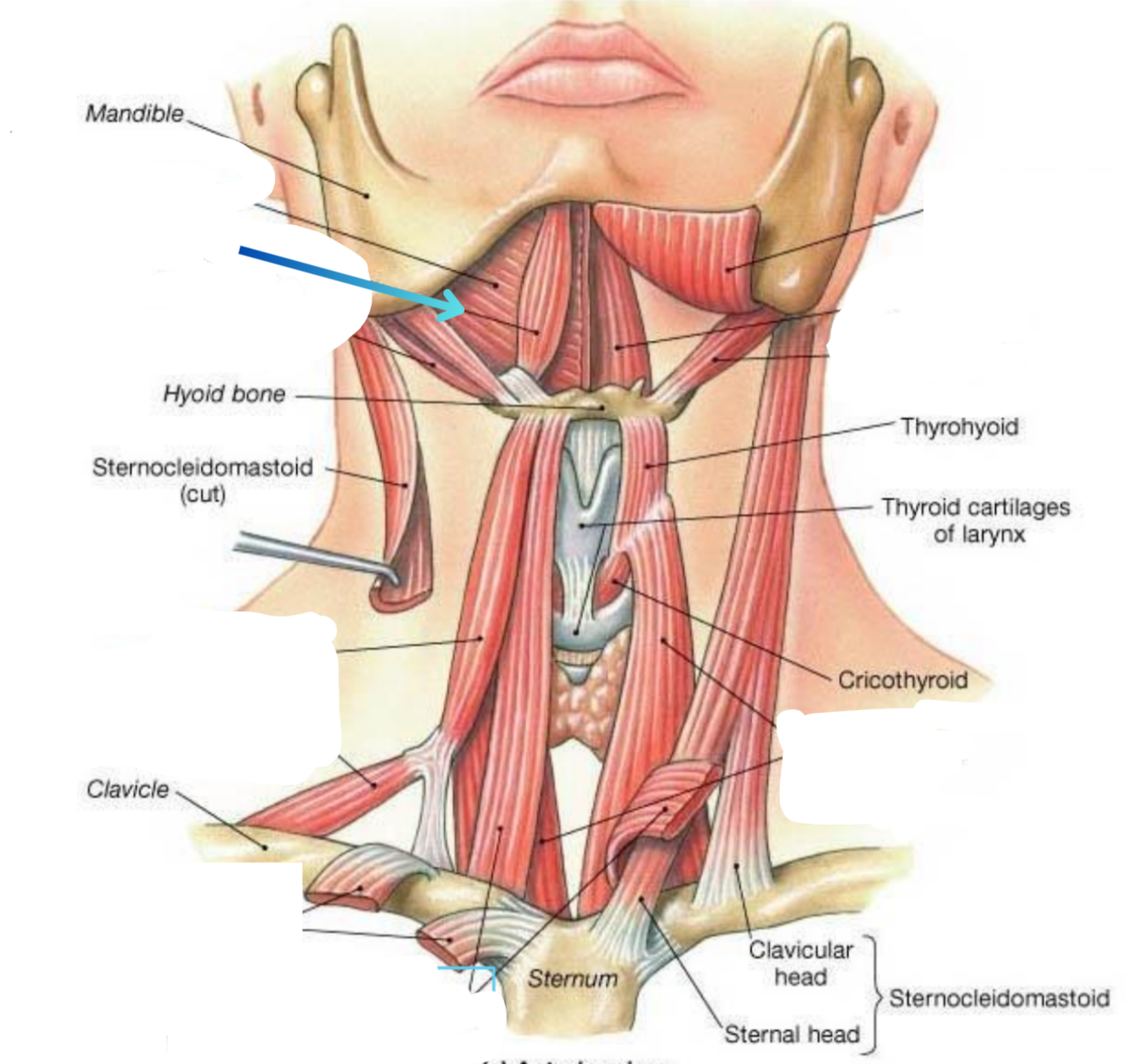
Anterior digastric muscle
Elevator
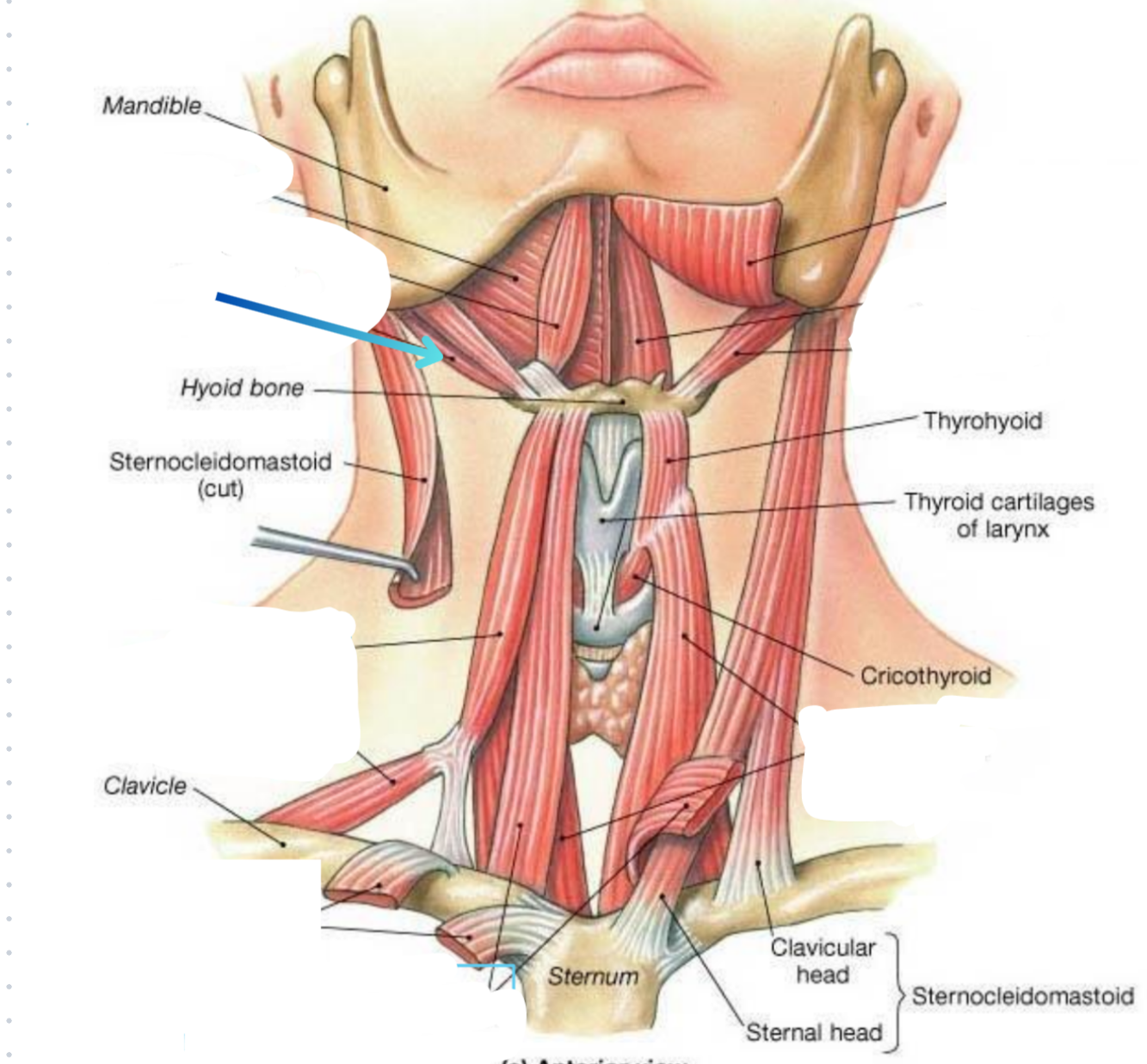
Posterior digastric muscle
Elevator
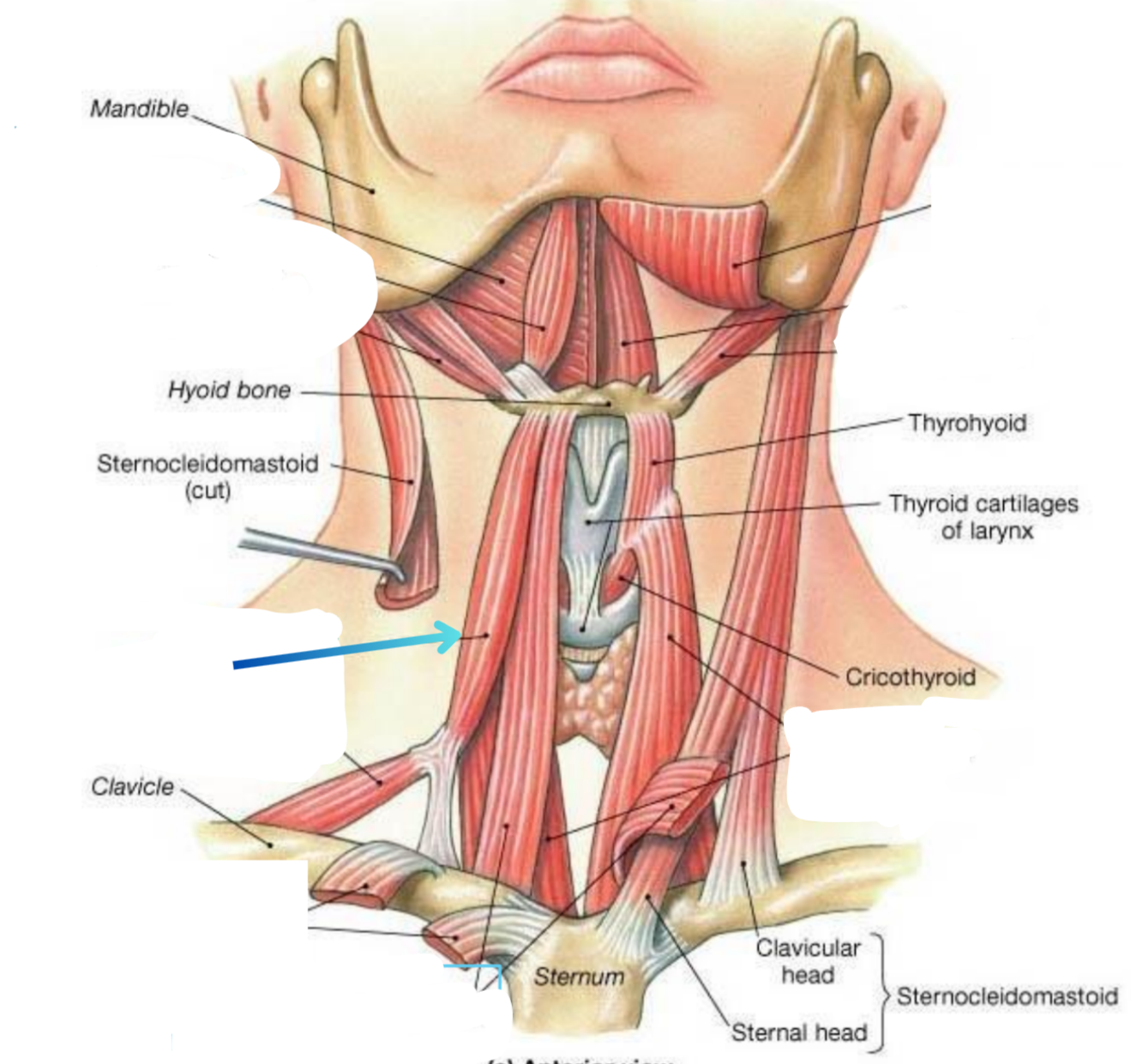
Superior belly of the omohyoid
Depressor
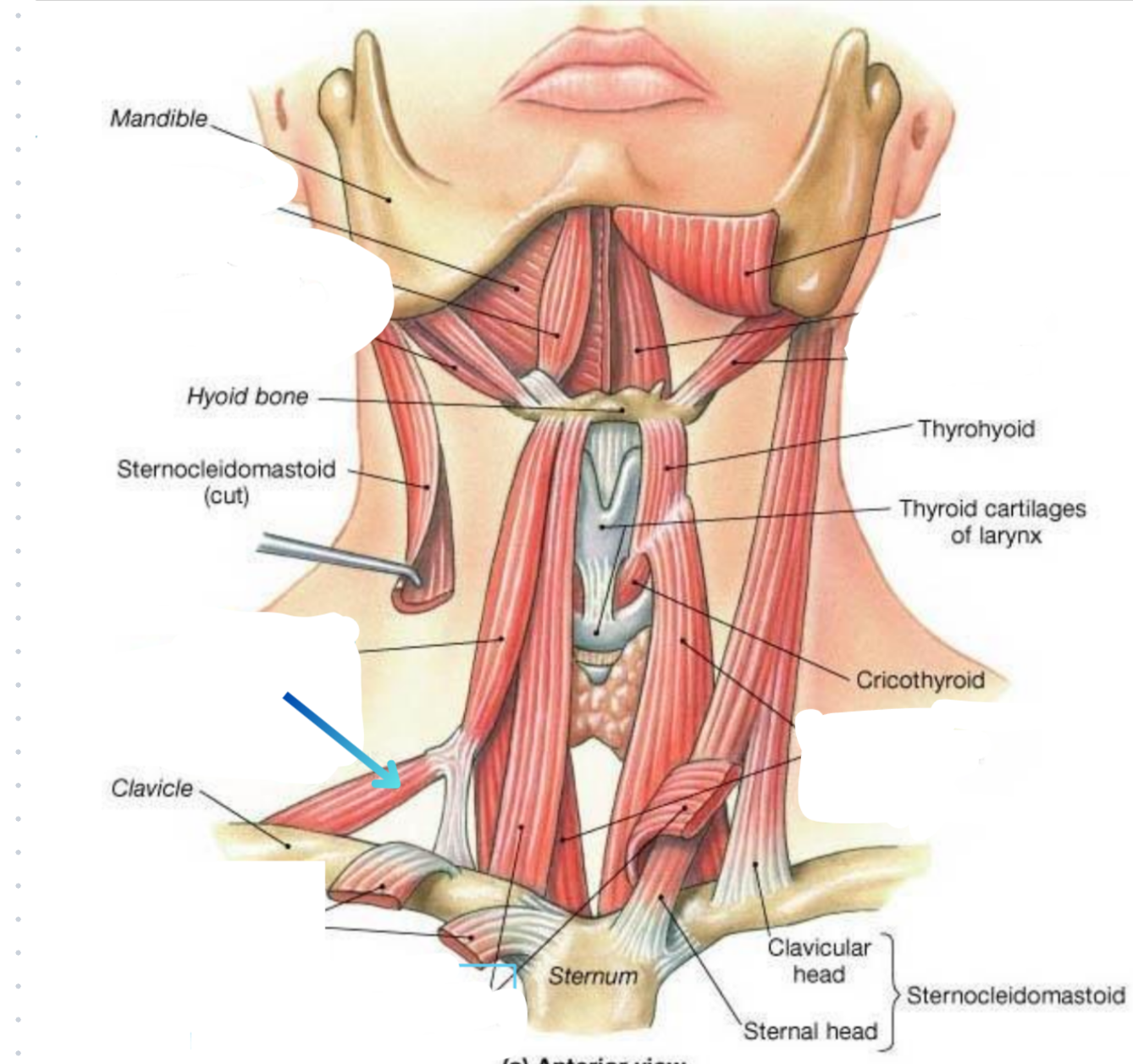
Inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle
Depressor
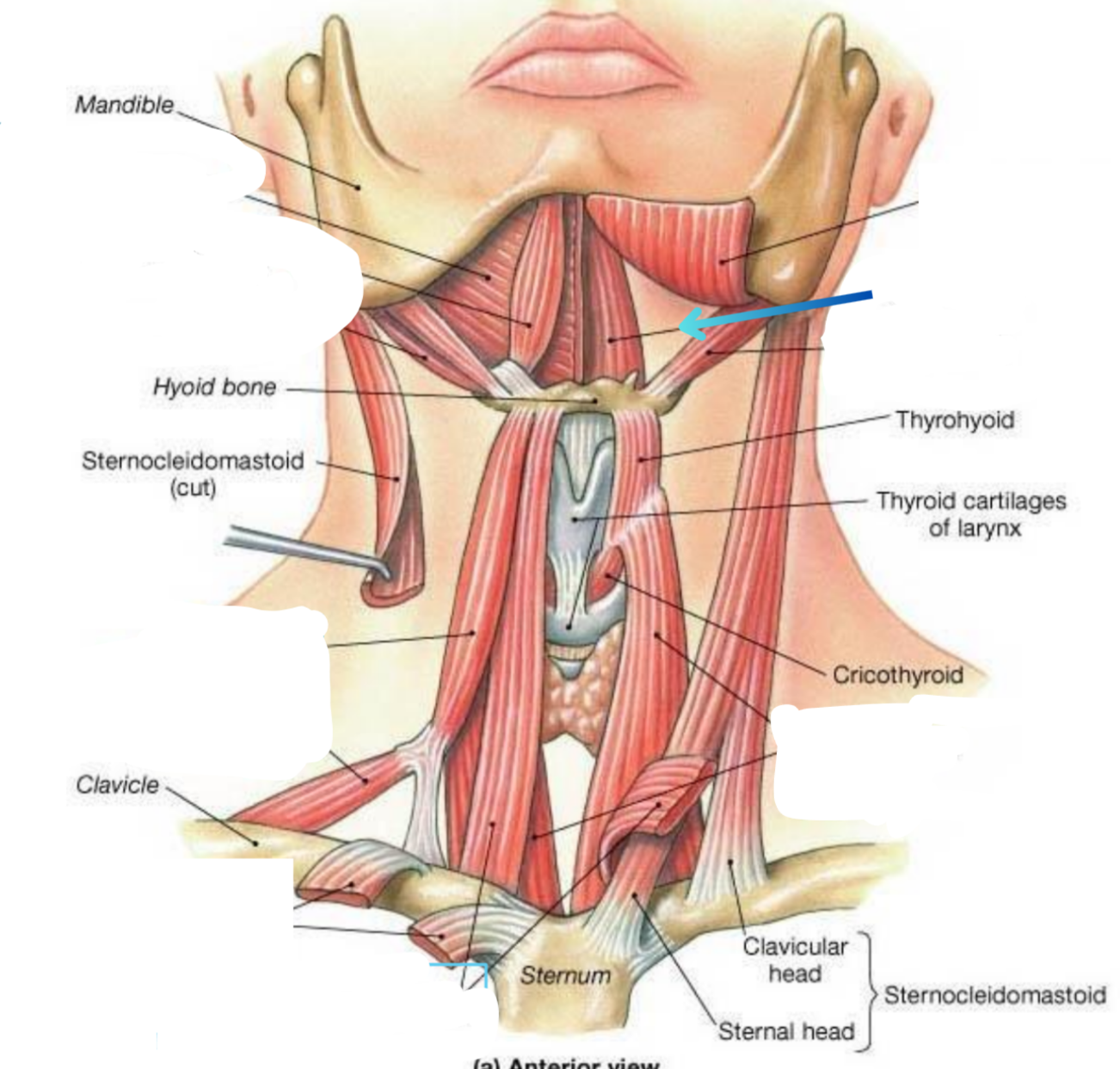
Geniohyoid
Elevator
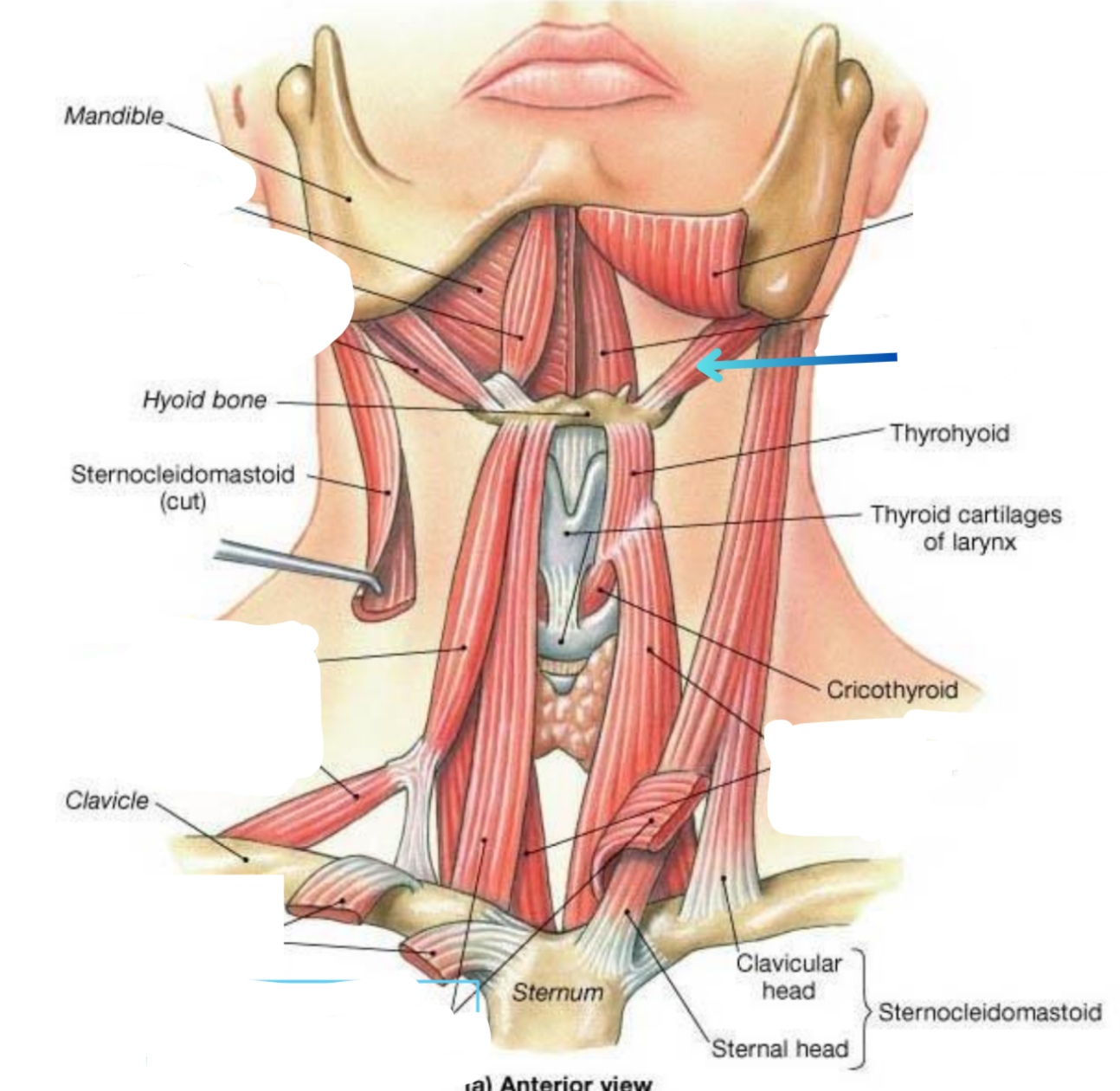
Stylohyoid
Elevator
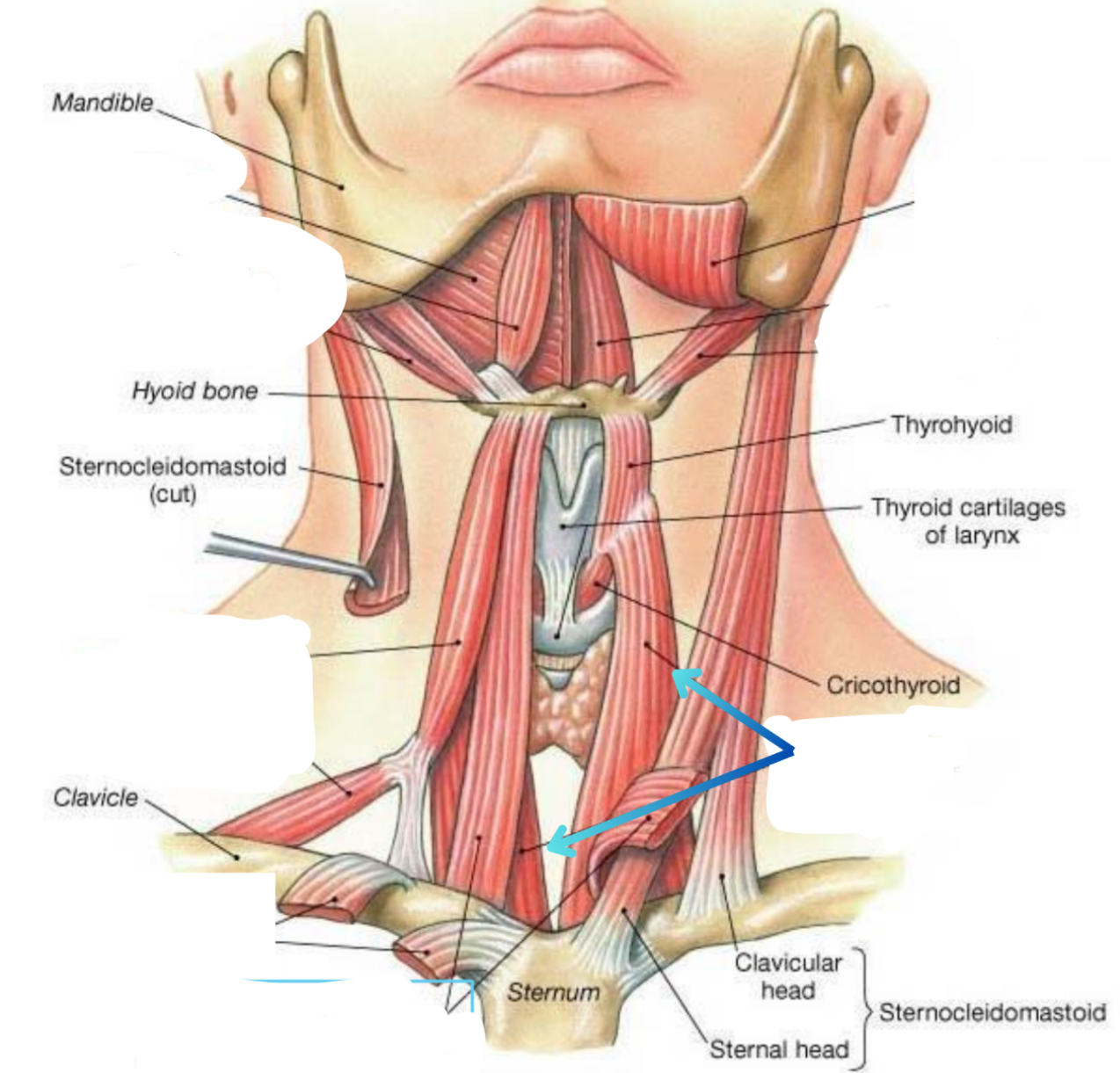
Sternothyroid
Depressor
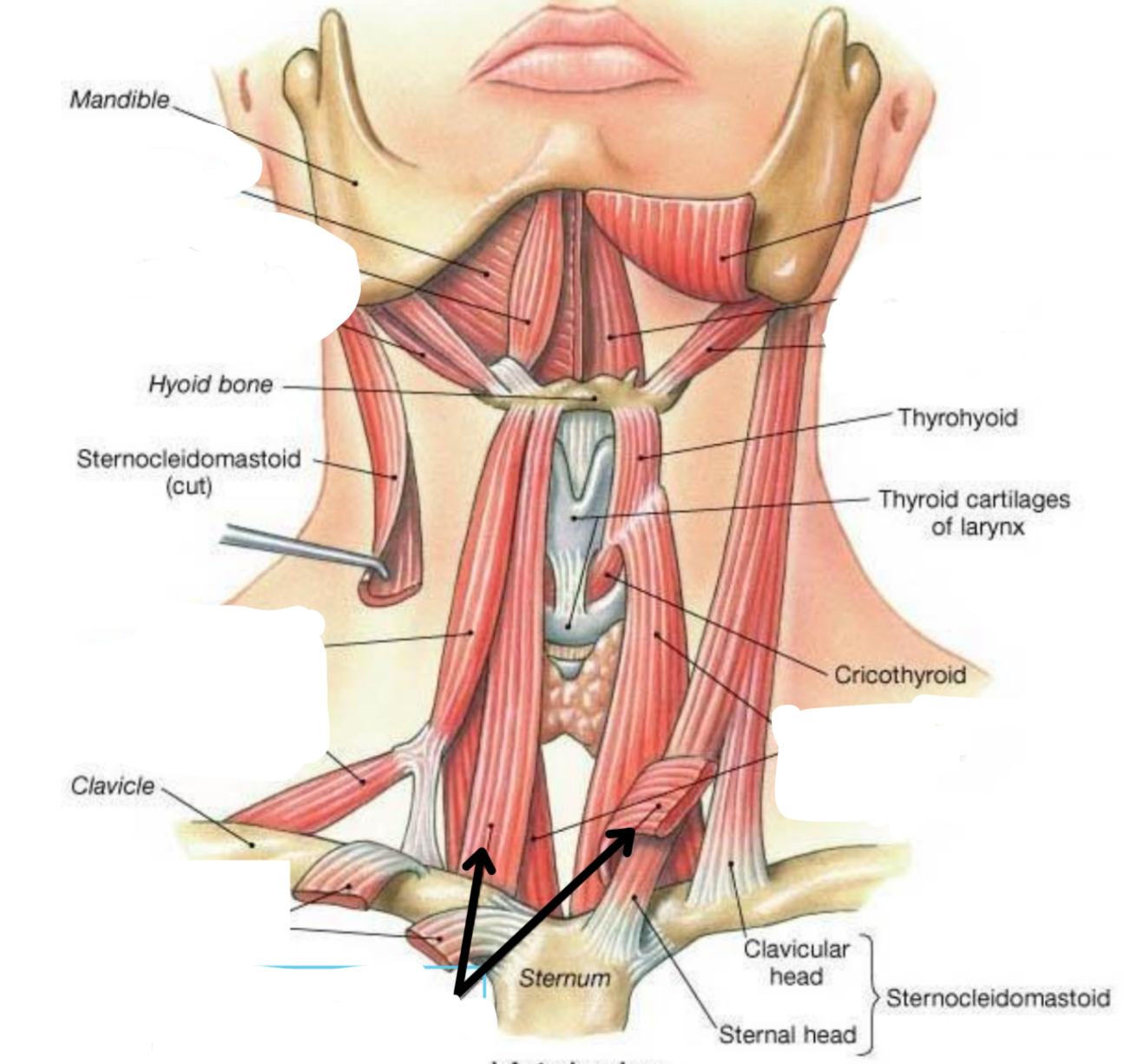
Sternohyoid
Depressor
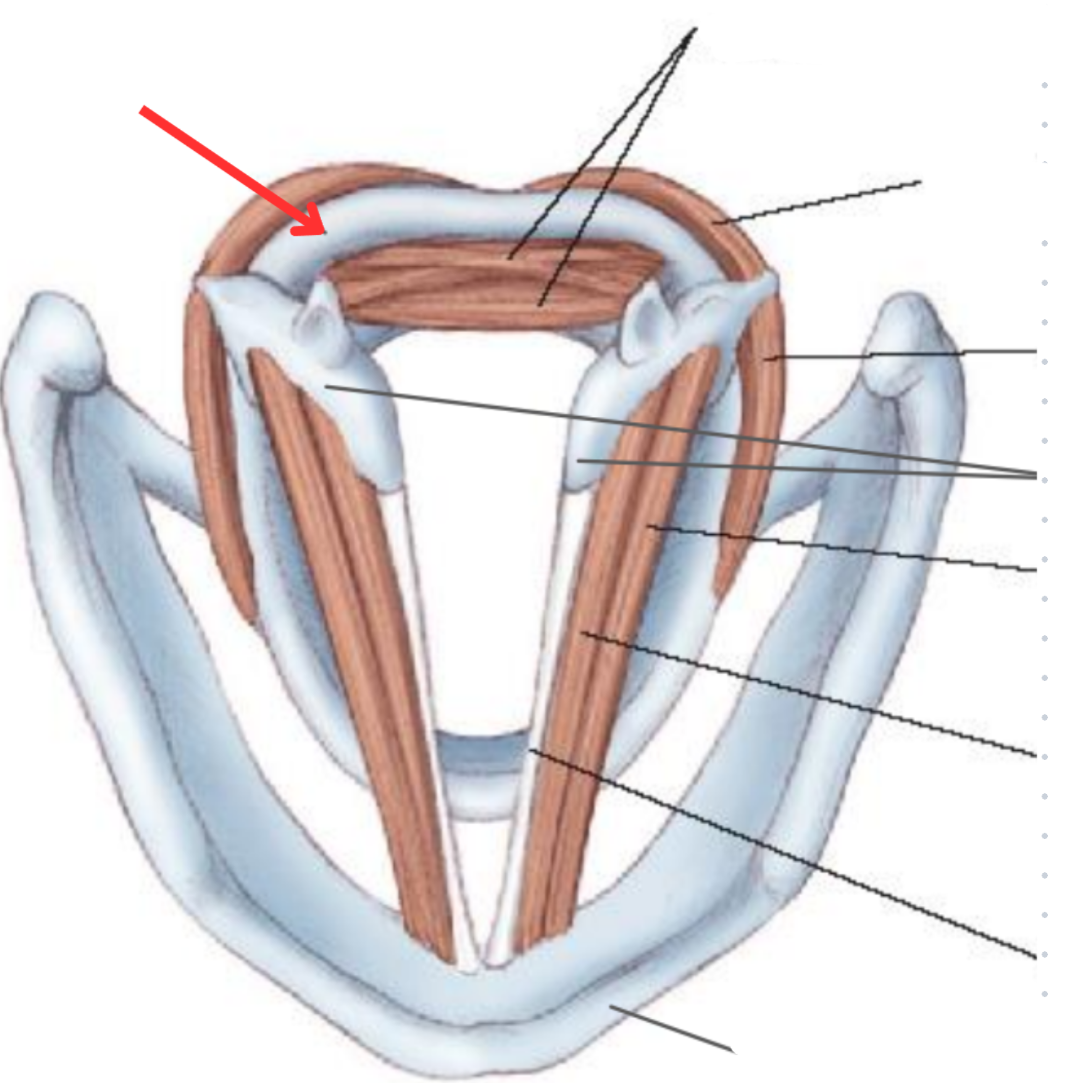
Cricoid cartilage
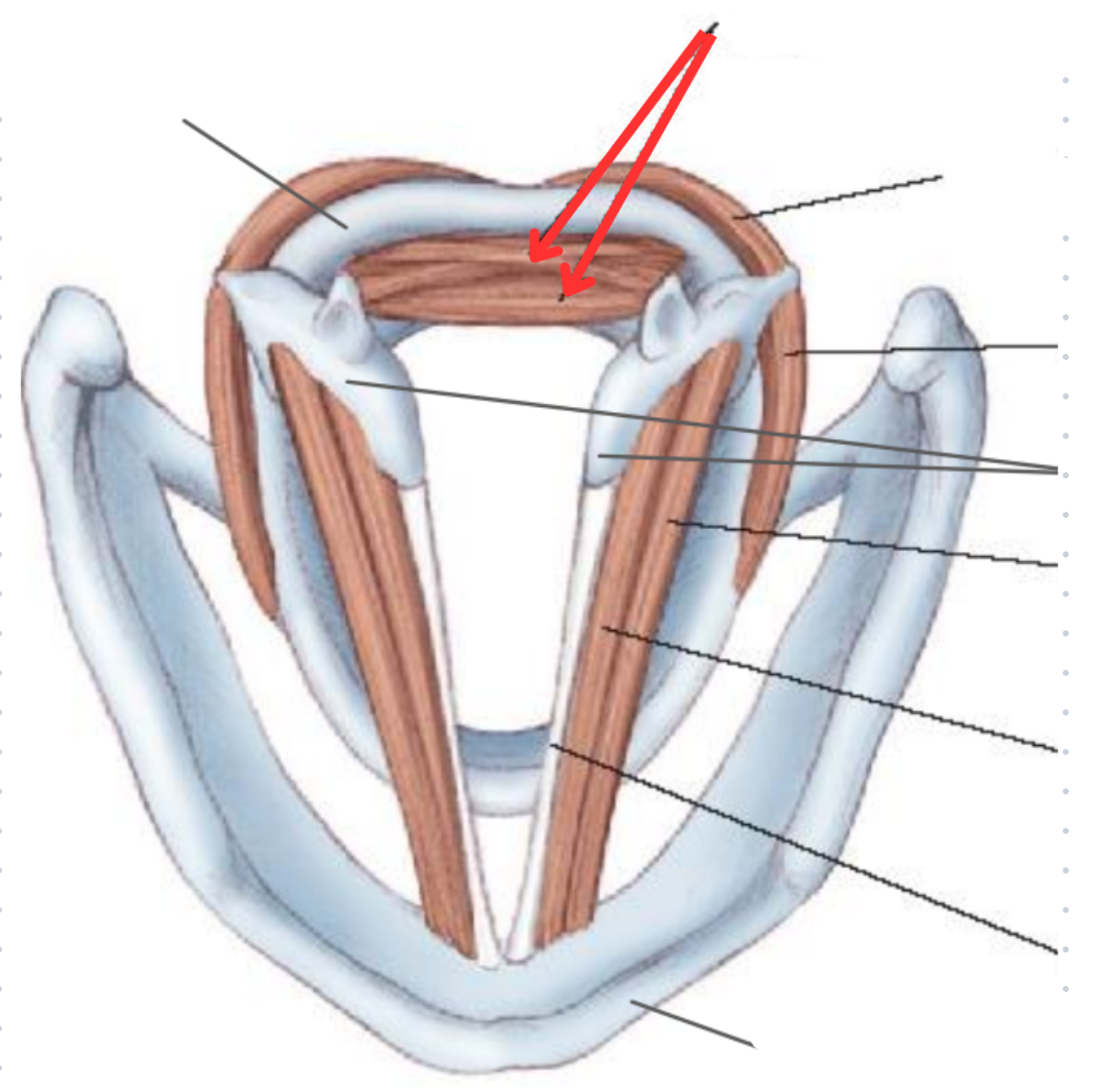
Transverse and oblique arytenoid muscle
Voca ladductor
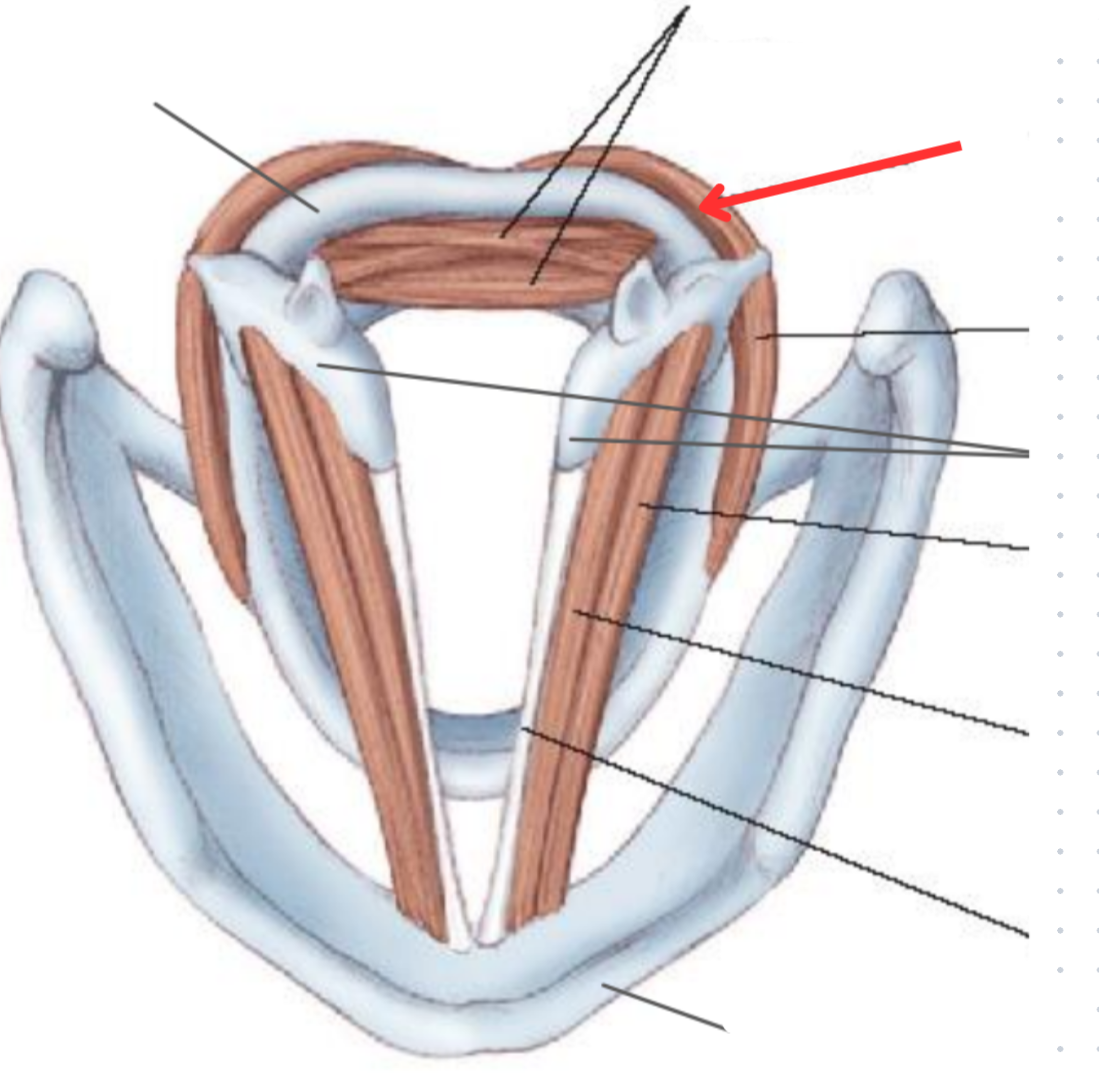
Posterior cricoarytenoid muscle
Vocal abductor
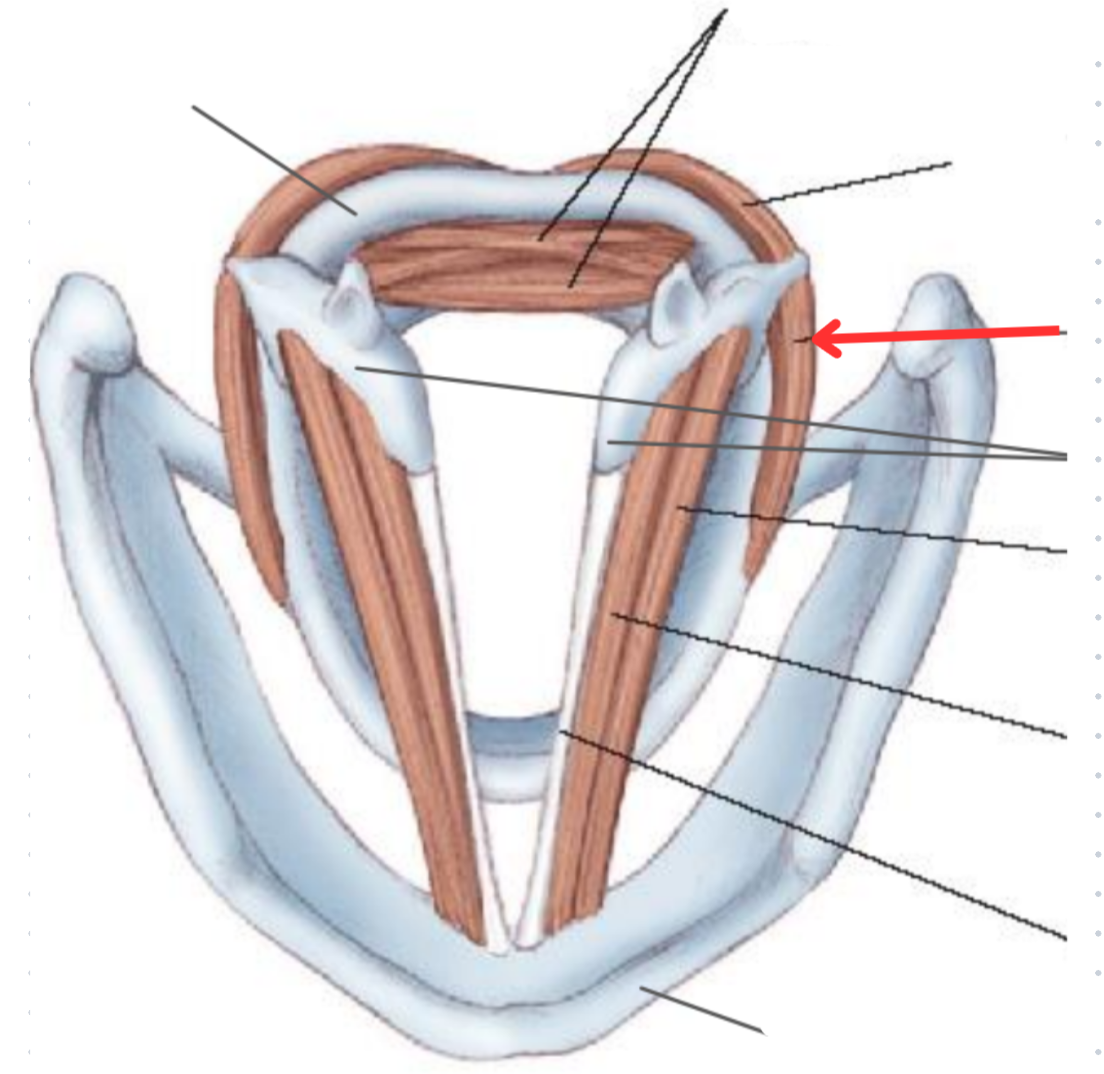
Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle
Vocal adductor
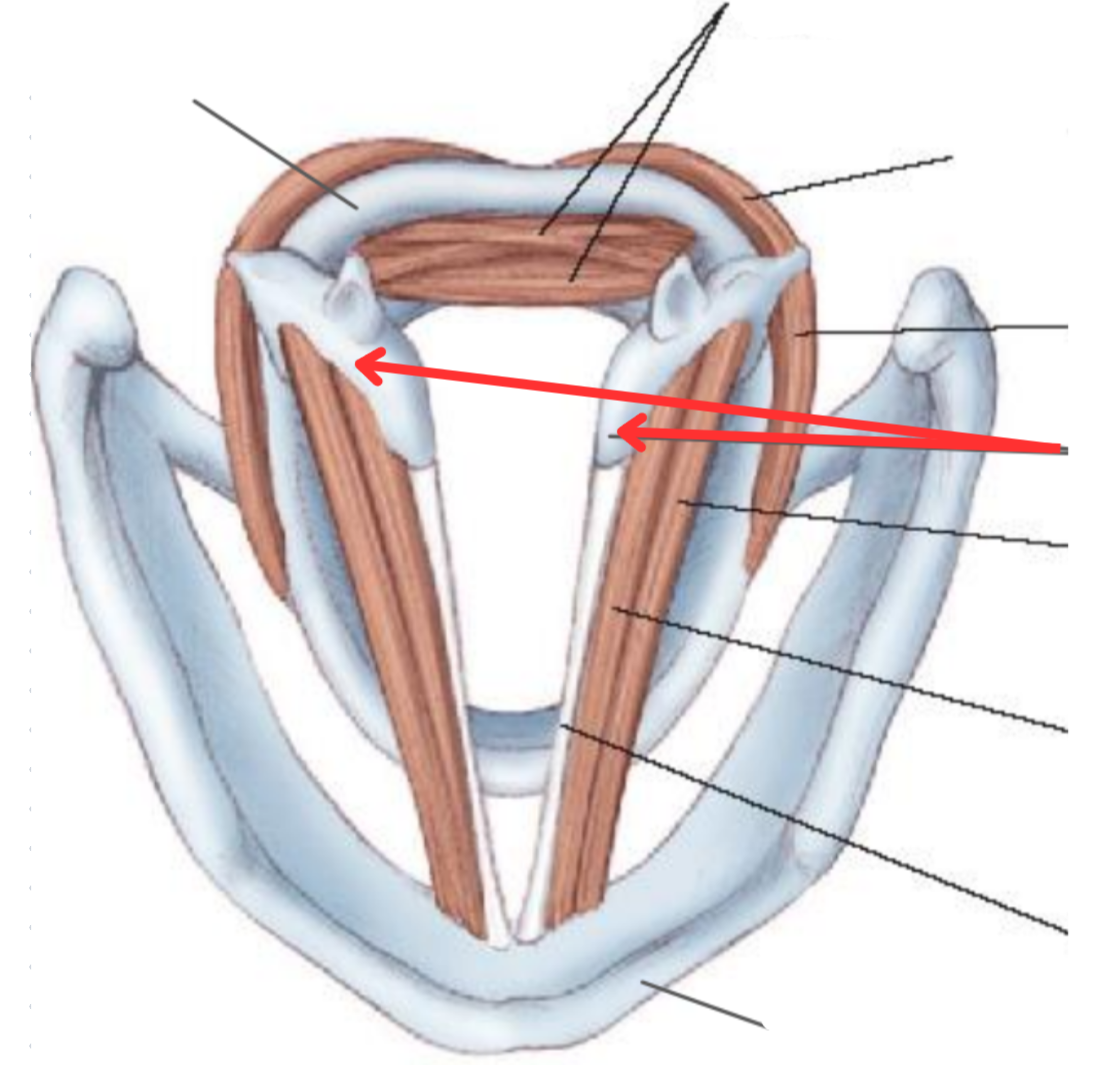
Arytenoid cartilage
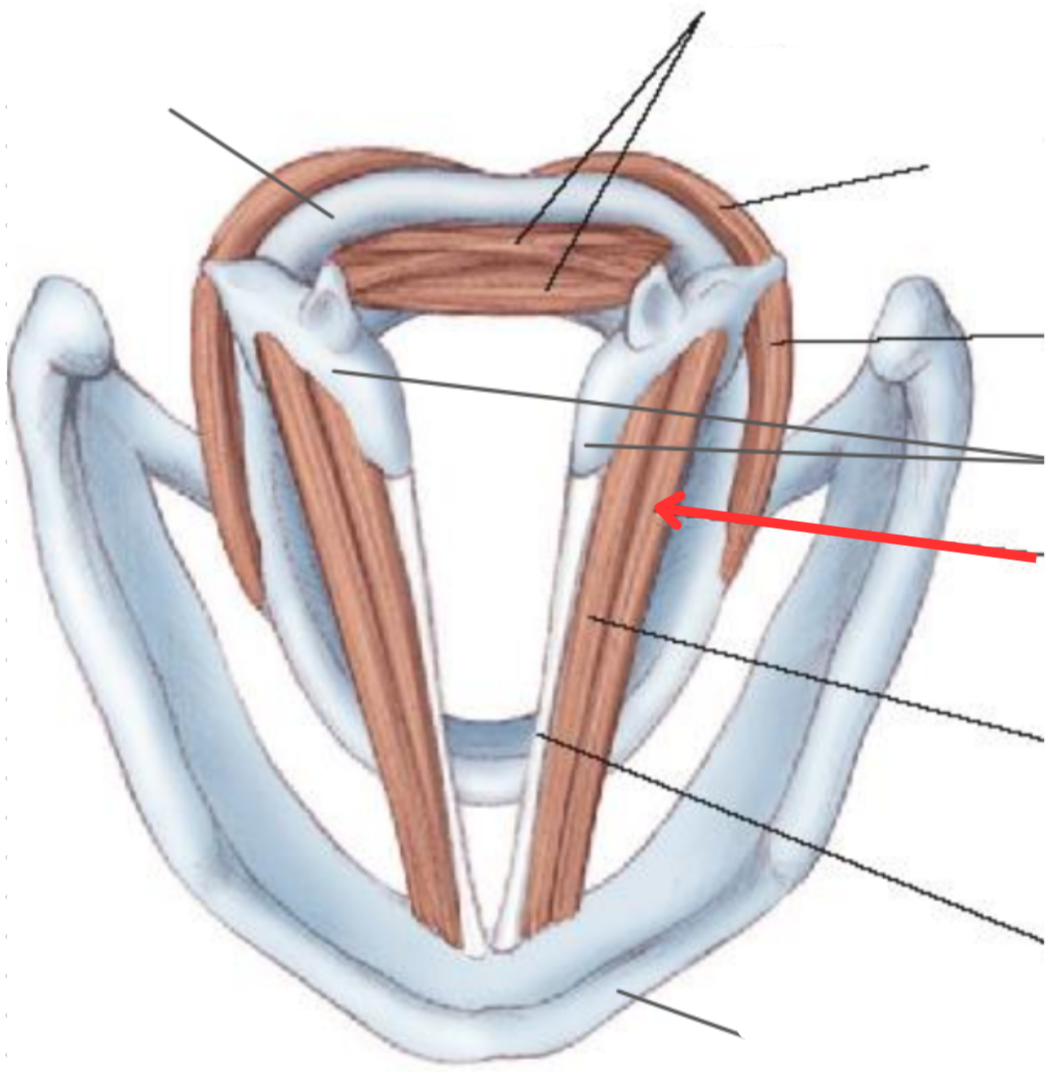
Thyroarytenoid muscle
Origin: Inner surface of thyroid cartilage
Insertion: Anterolateral surface ofarytenoid cartilage
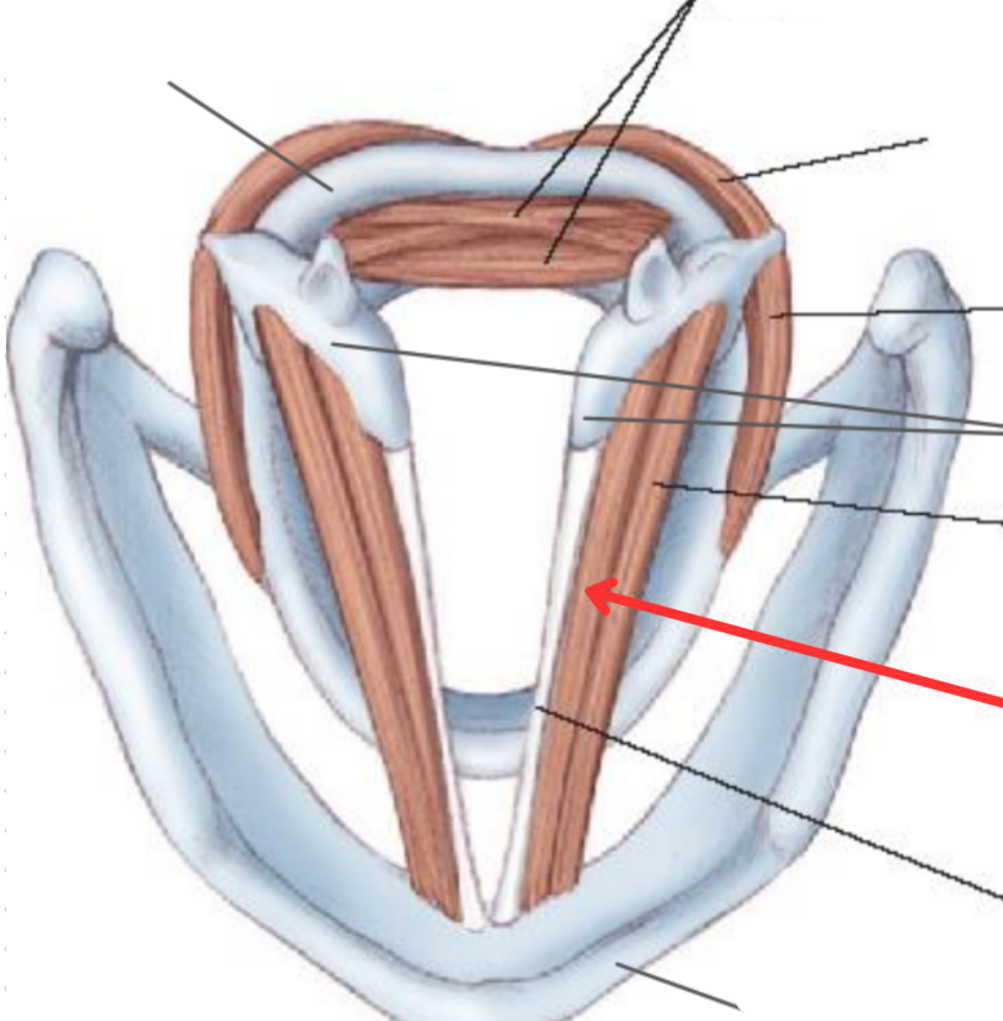
Vocalis muscle
Sits parallel to the vocal ligament
Crucial part in controlling tonal quality of voice
Vocal ligament
Thyroid cartilage
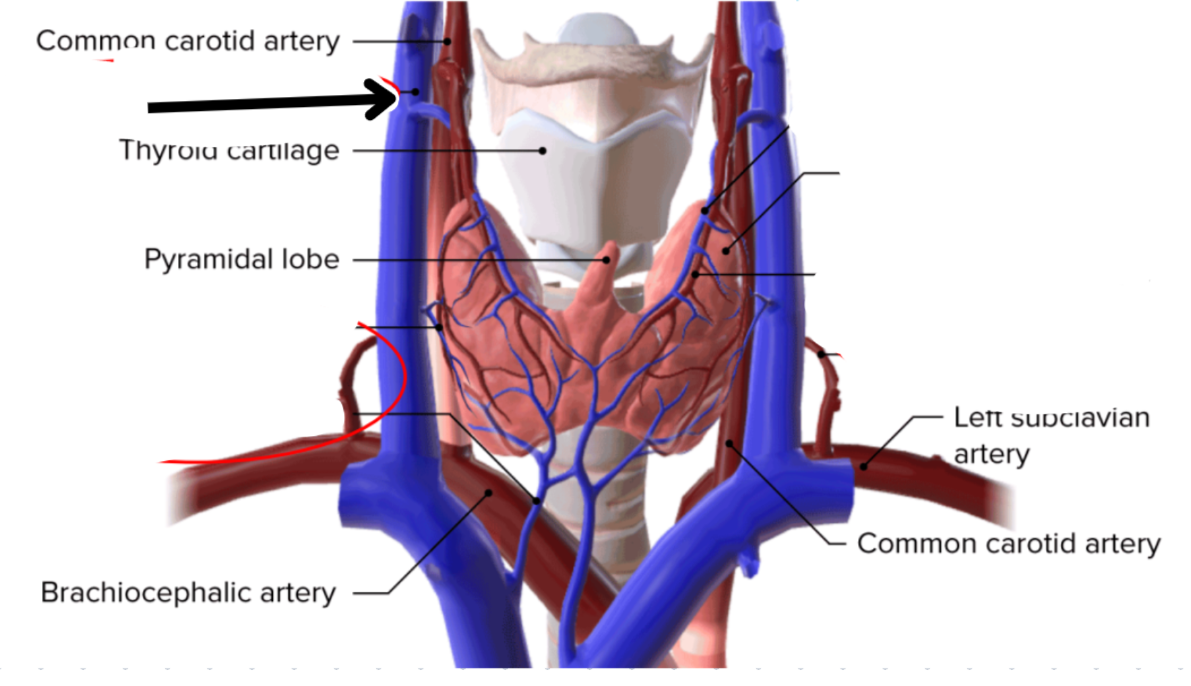
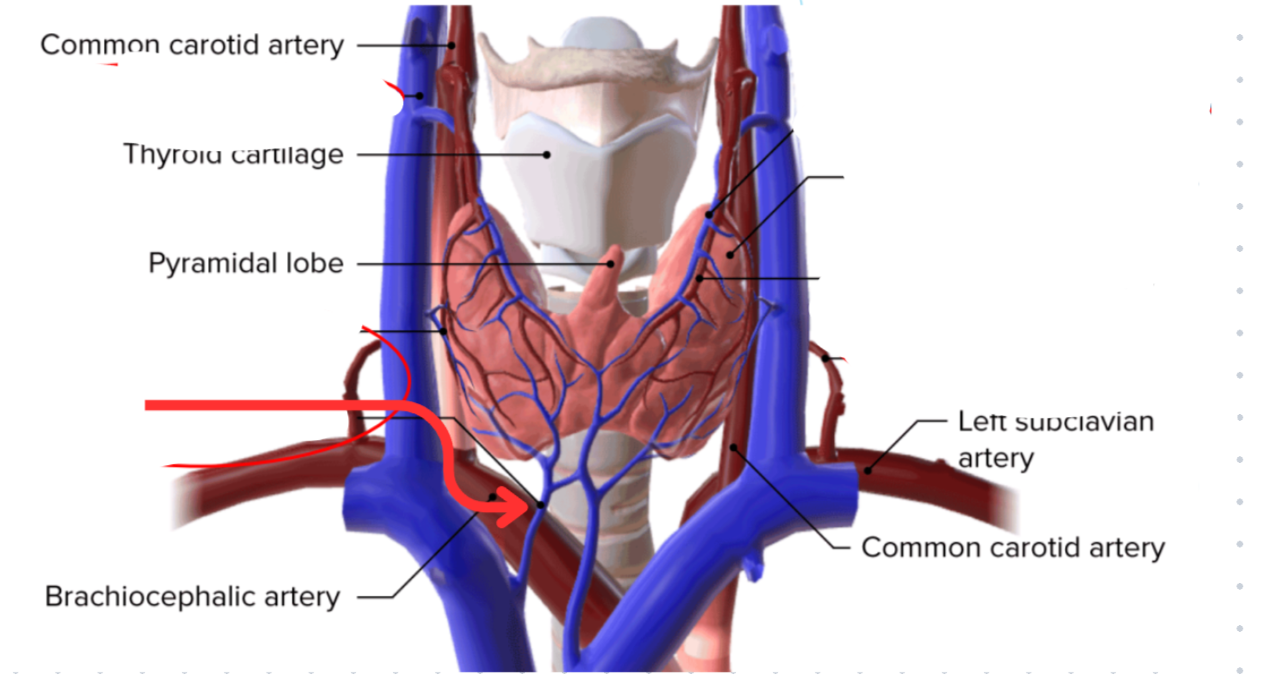
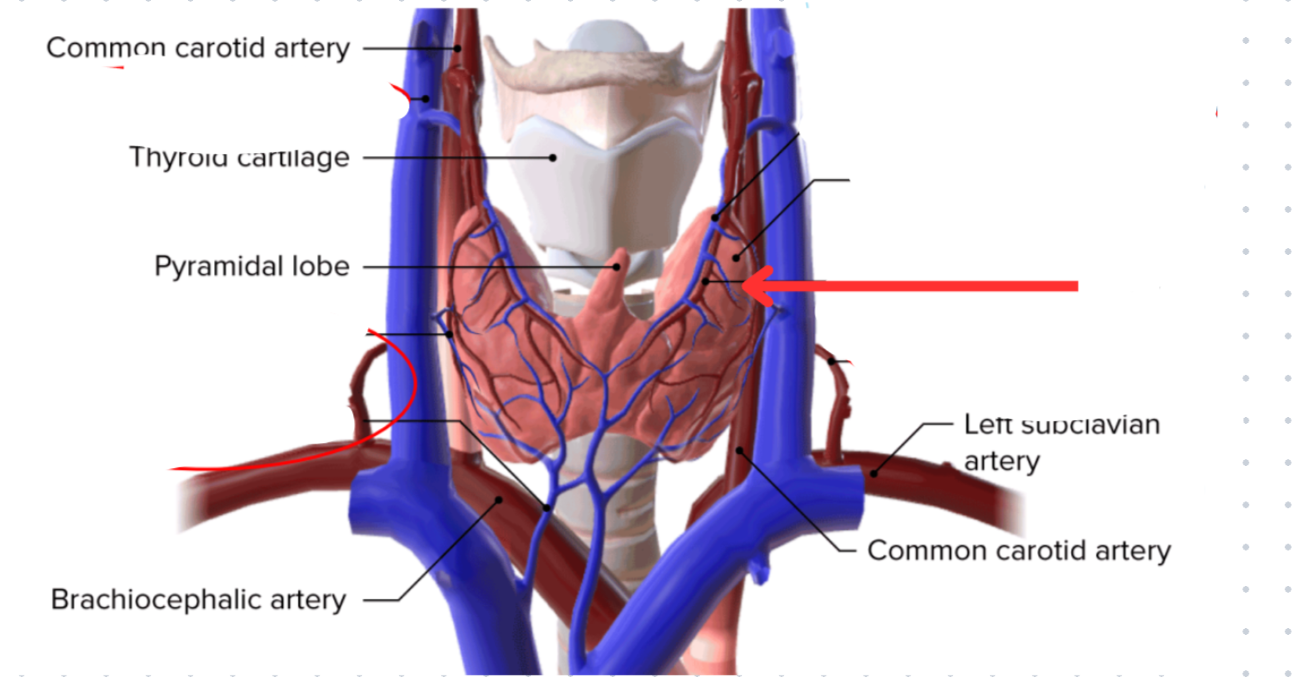
Thyroid gland
Butterfly shaped, two connected lobes
Anterior to the trachea
20-60 grams
Larger in women, increases size during pregnancy
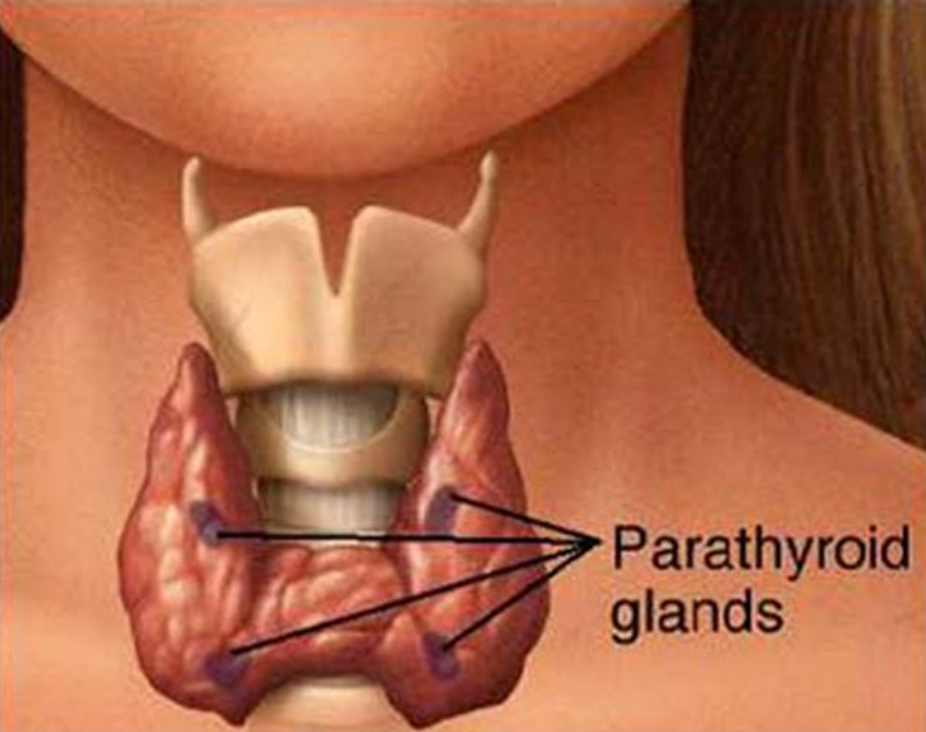
Parathyroid gland
Four of them, two on each side
6mm in length, 3-4 mm in width
T3 and T3 hormones
Made in follicular epithelial cells of thyroid
Iodine is main building block (Need to eat some)
Stimulates body tissues to produce proteins and increase amount of O2
Calcitonin
Made by c-cells of thyroid gland
What % of hormones made by the thyroid are T4 and T3
80% T3 and 20% T4
Function of the thyroid
Regulates body’s metabolism
Parathyroid hormone (pTH)
Regulates level of calcium in blood
Released in response to decreased calcium levels
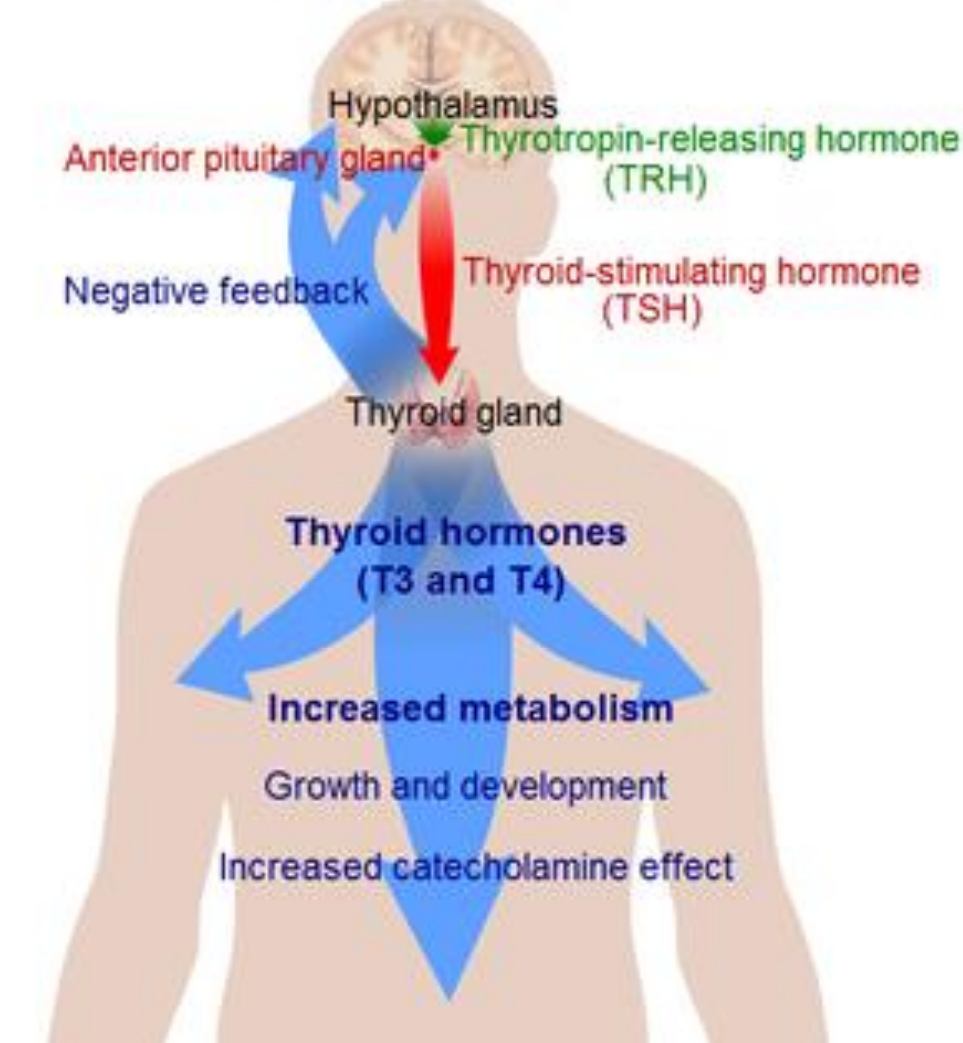
Negative inhibition in thyroid hormone production
Hypothalamus → TRH → Anterior pituitary gland → TSH → Thyroid gland → T3 + T4
T3 + T4 → Hypothalamus + Anterior pituitary gland to stop making TRH and TSH
Right Vagus nerve
Provides main sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers to the larynx
No role in hormones, mainly influences vasculature (Indirectly effects hormones)
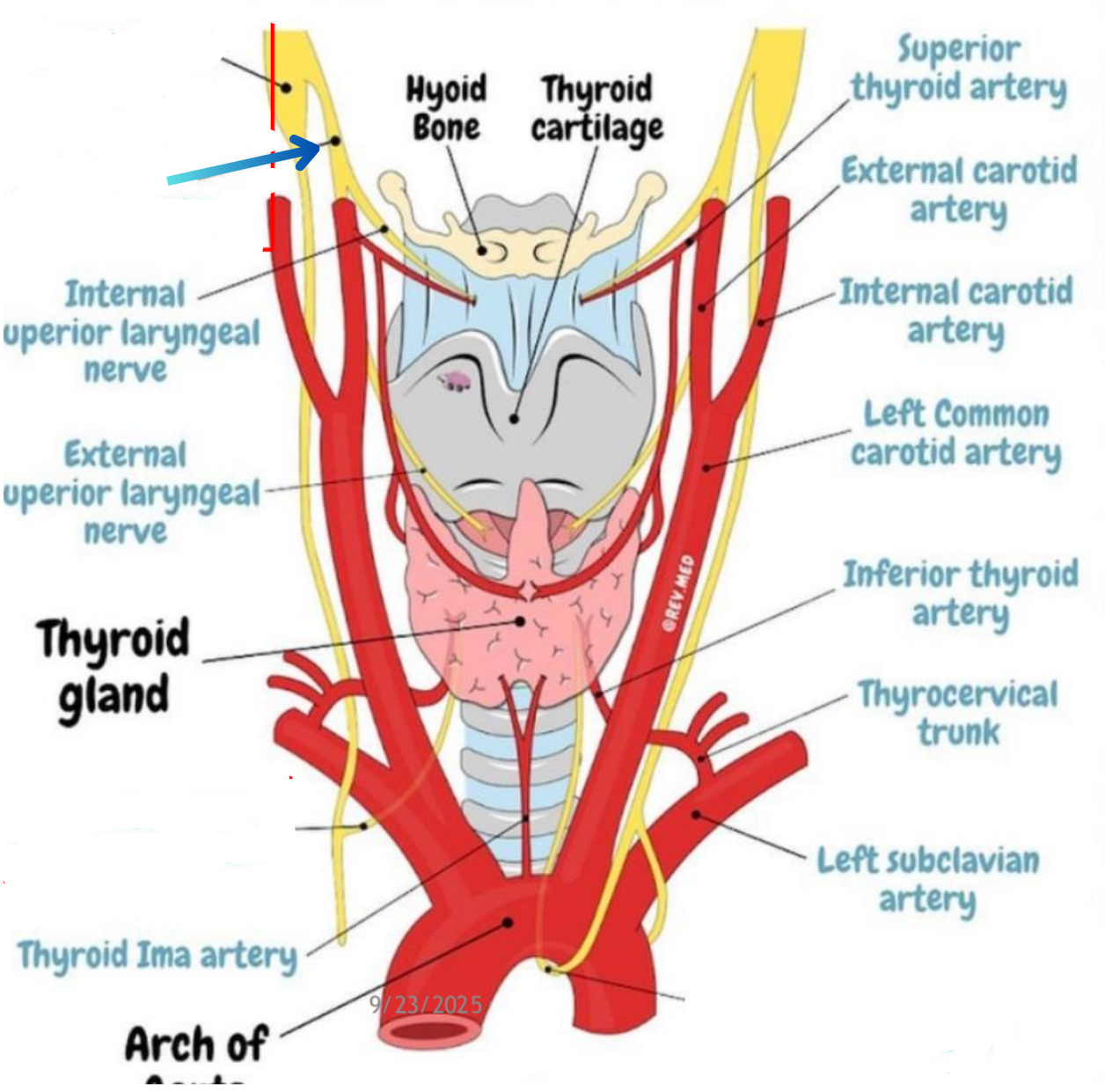
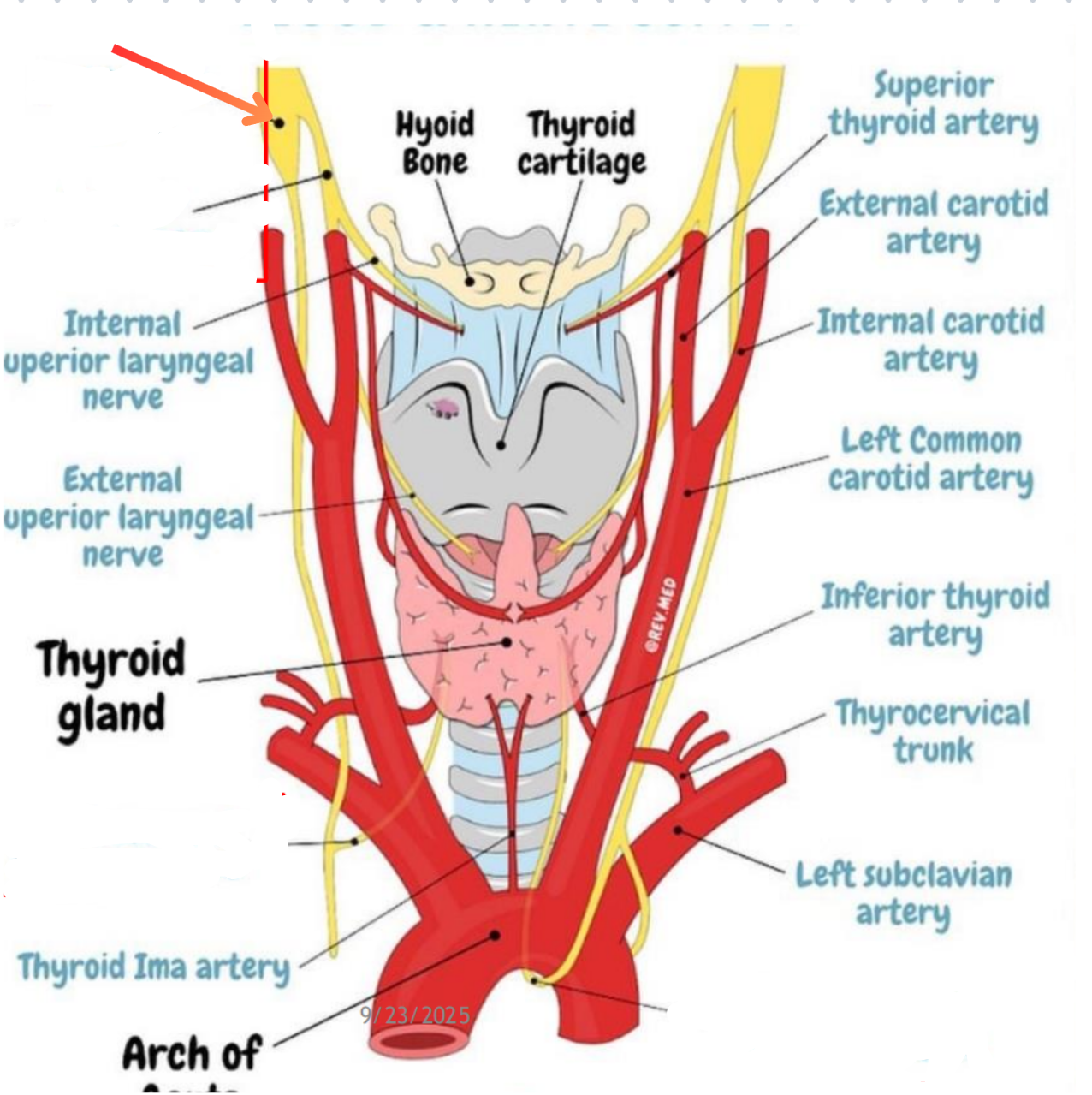
Superior laryngeal nerve
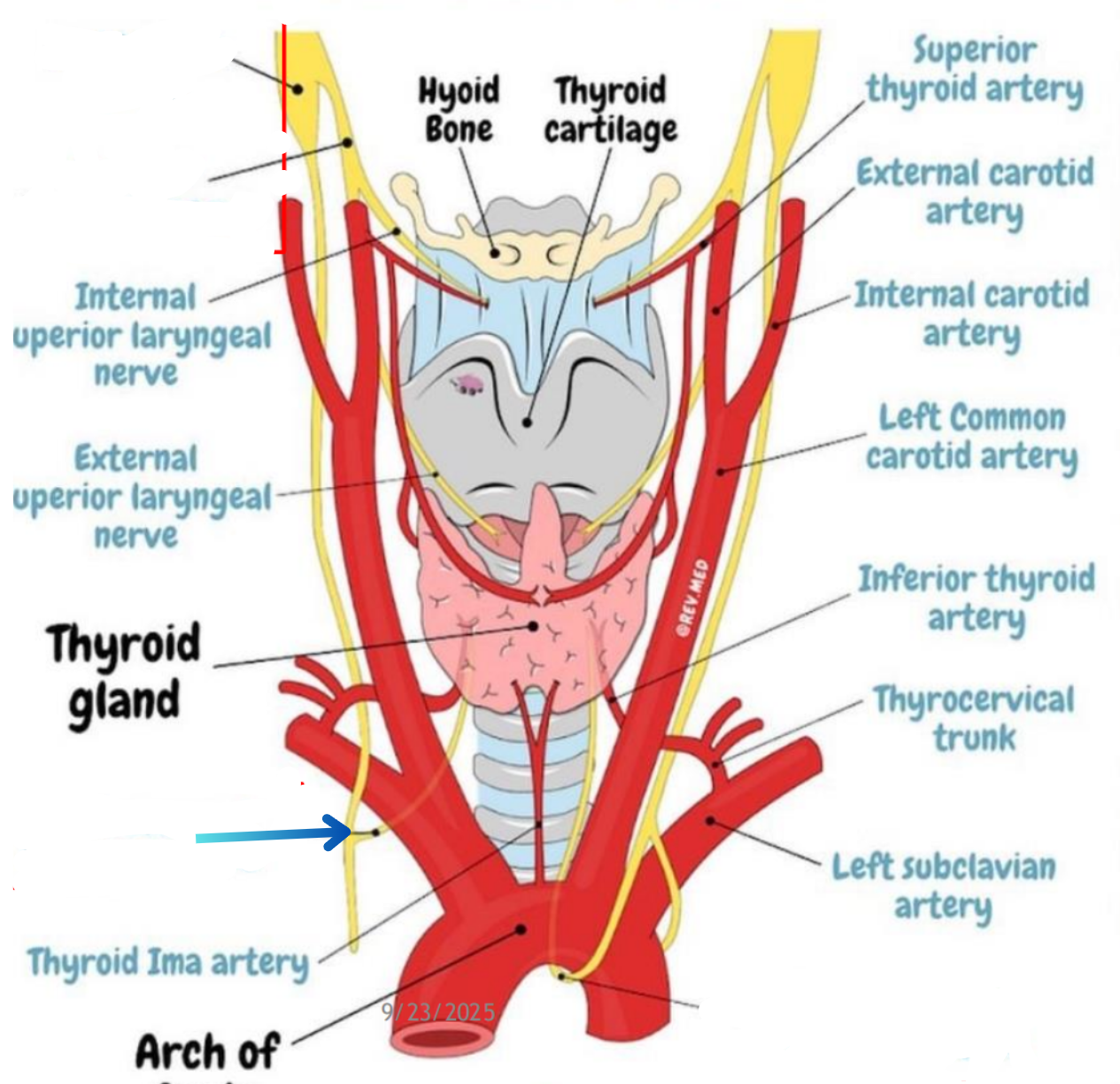
Right recurrent laryngeal neve
Left recurrent laryngeal nerve
Internal jugular vein
Inferior thyroid vein
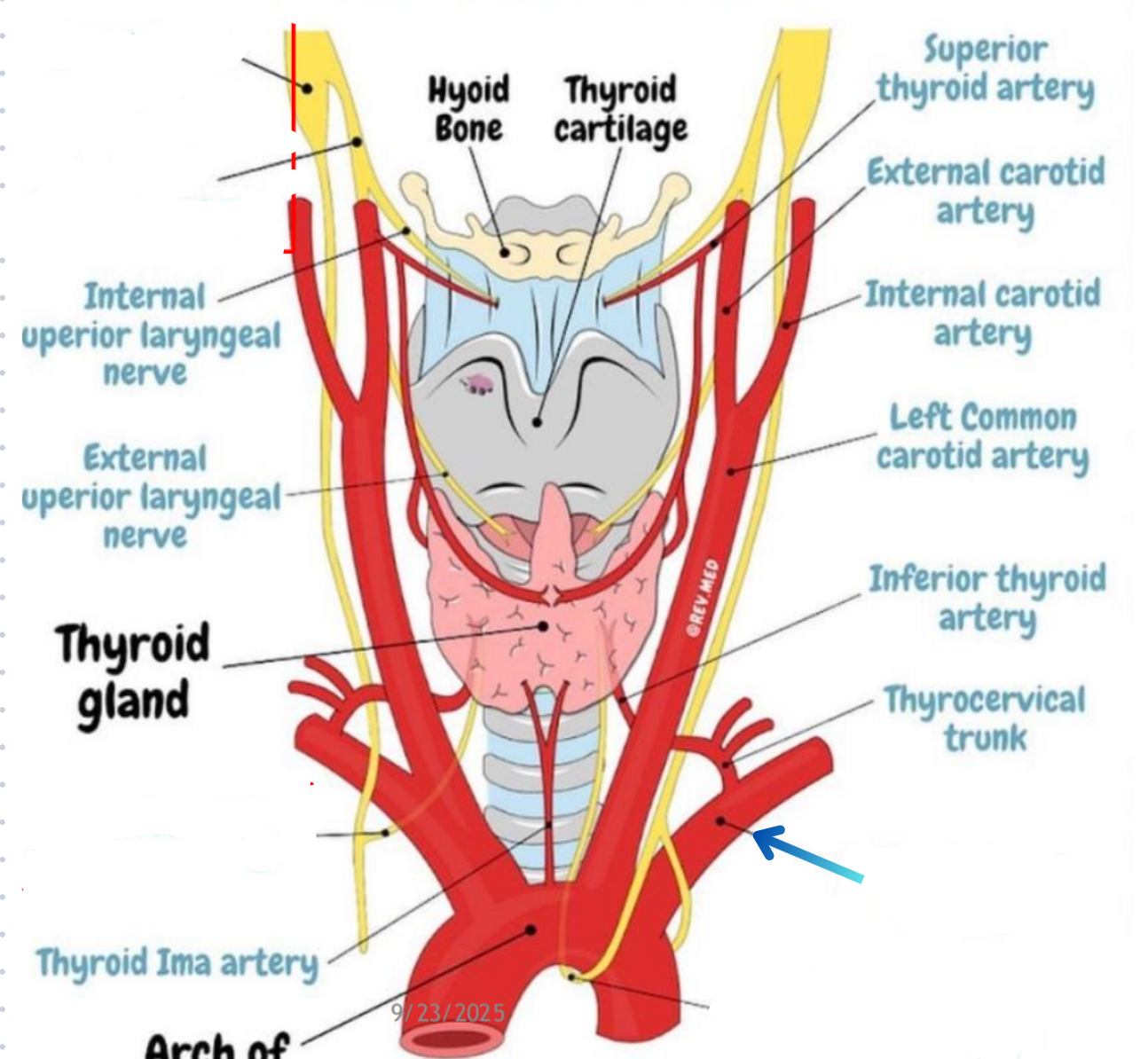
Superior thyroid artery
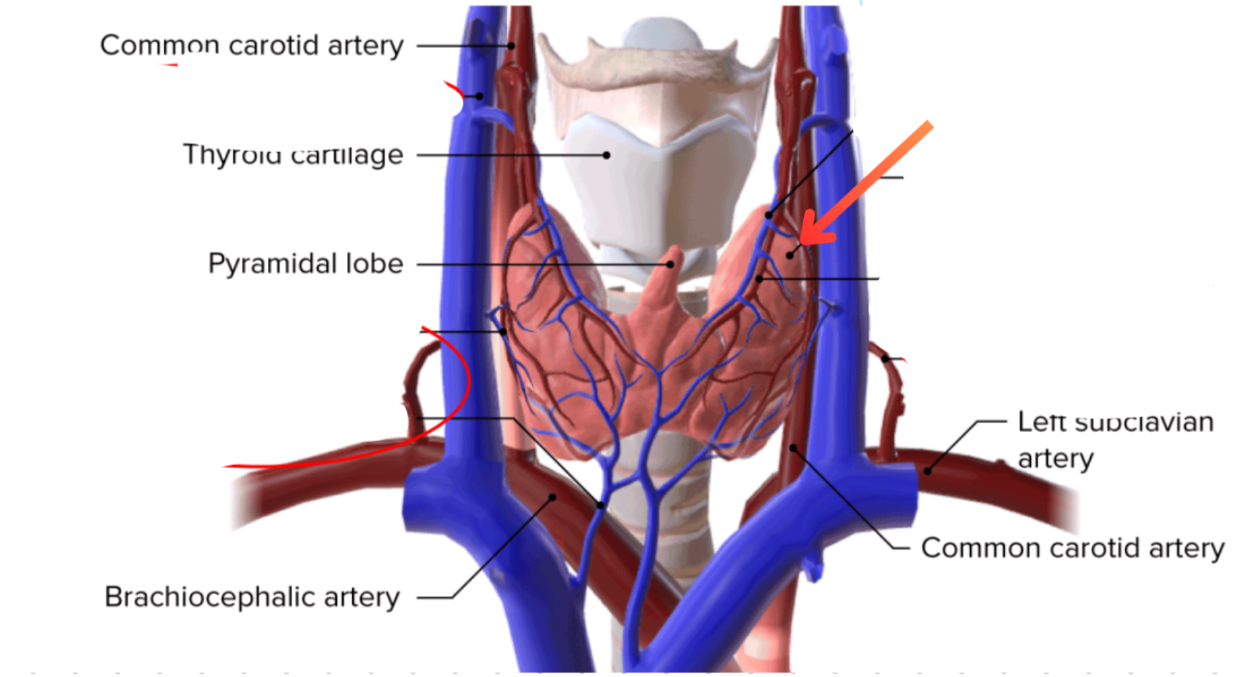
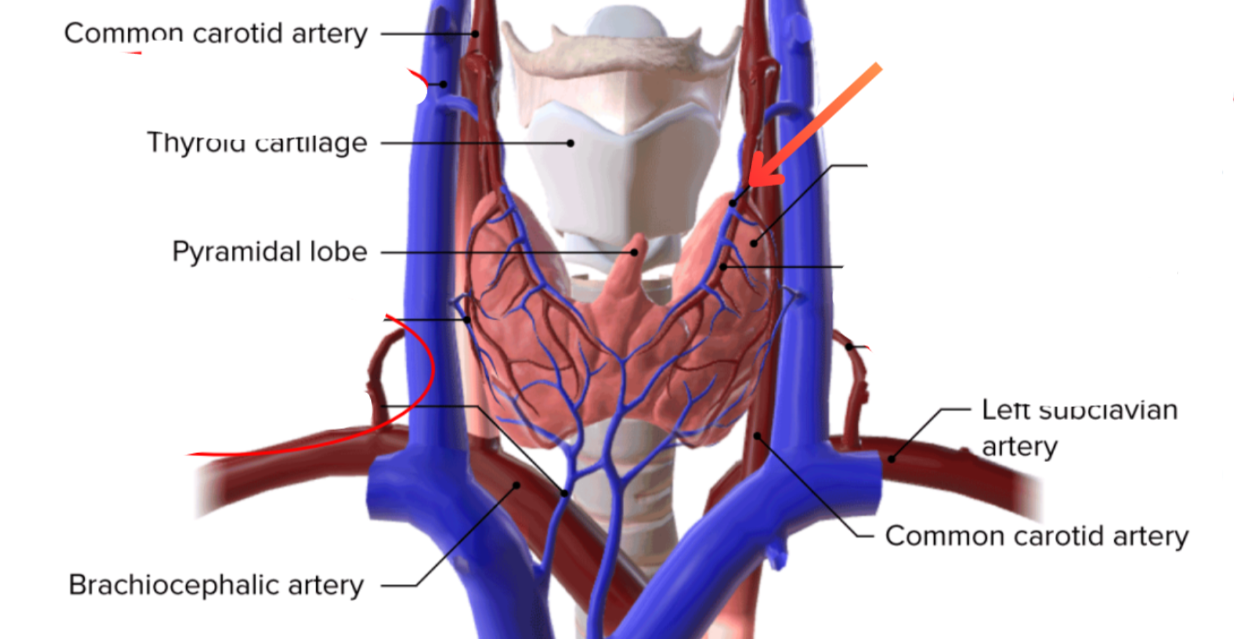
External carotid artery → Superior thyroid vein
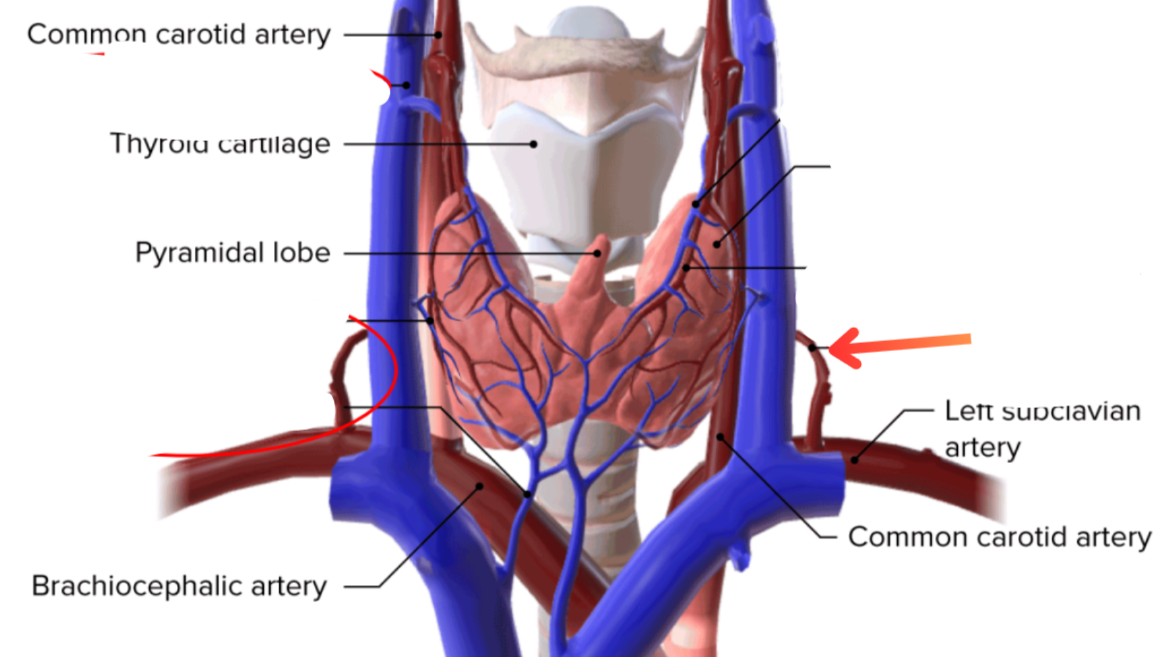
Subclavian artery → Inferior thyroid artery
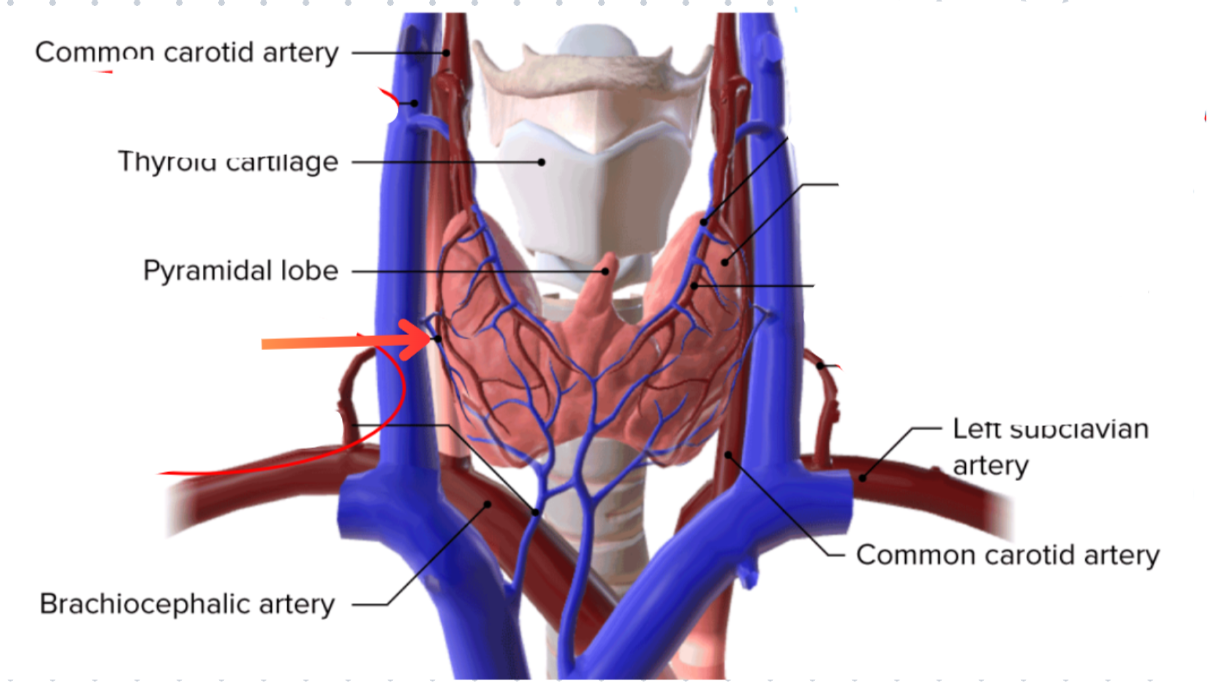
Middle thyroid vein
Path of blood from the superior and middle thyroid veins
Sup + Mid thyroid veins → Internal jugular vein → Braciocephalic vein
Characteristics of sailvary glands
Exocrine glands
Vary widely in size
Classified based on nature of the saliva they secrete
Function of salivary glands
Protect and lubricate oral mucosa
Release amylase that starts digestion of carbohydrates
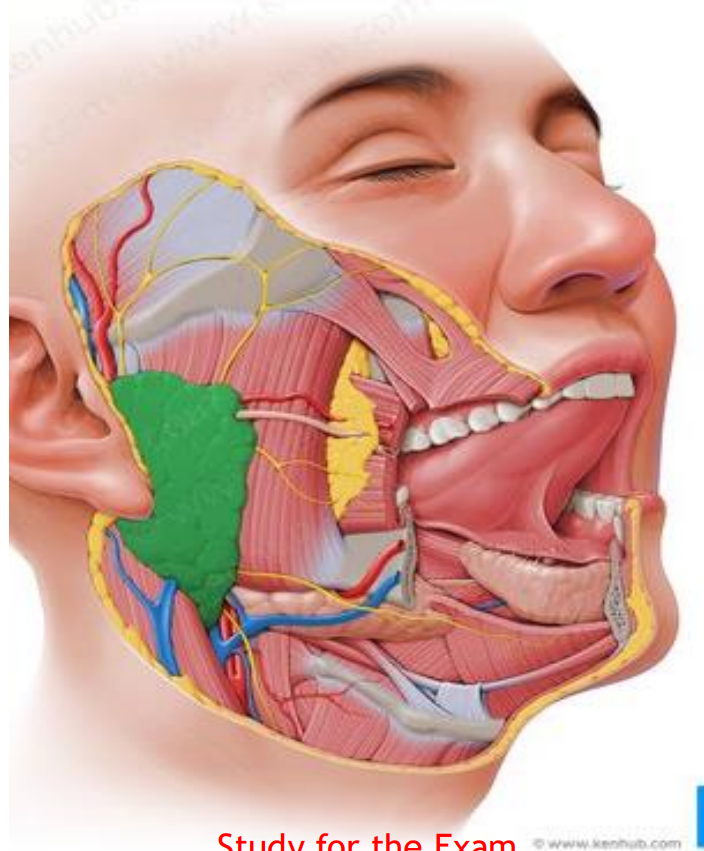
Parotid gland
Largest salivary gland
20% of saliva production
Associated with CN IX, C2 and C3
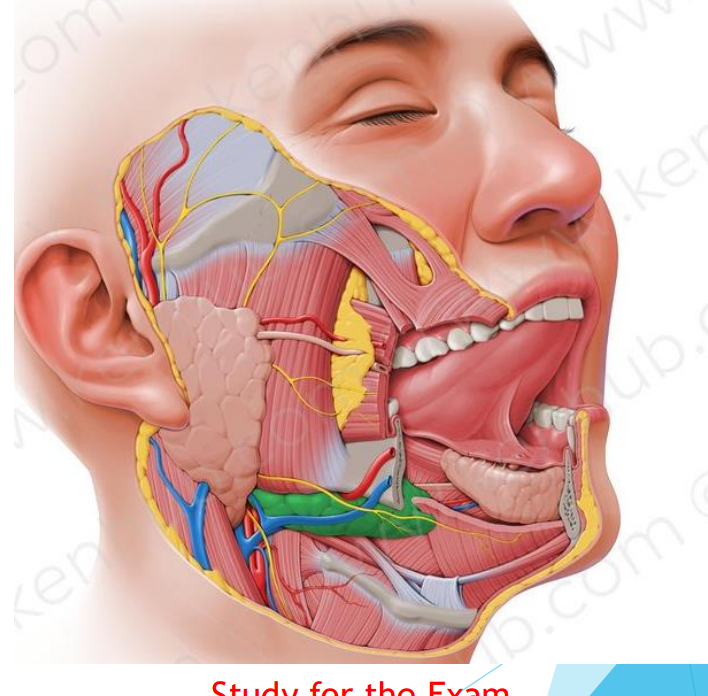
Submandibular gland
70% of saliva production
Associated with CN VII
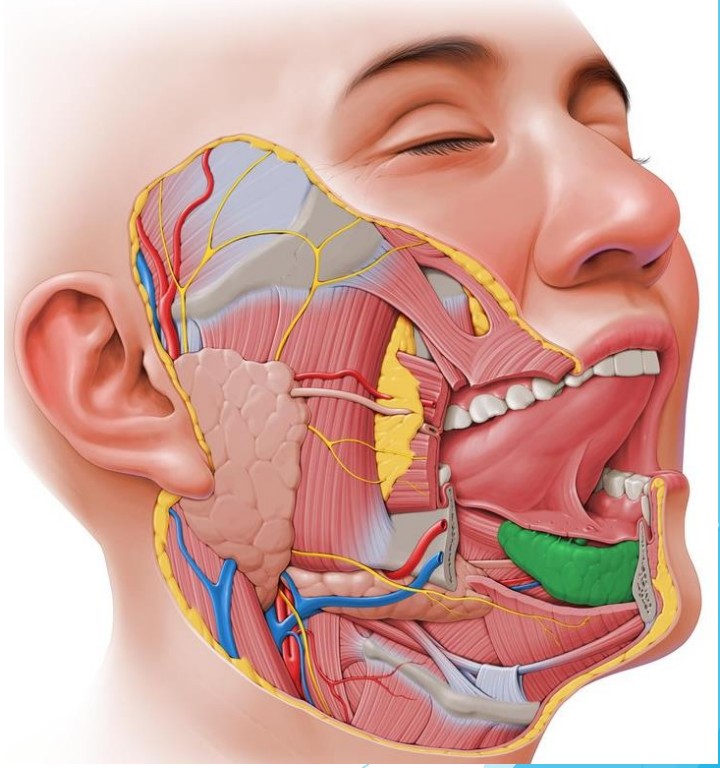
Sublingual gland
Smallest salivary gland
5% production of saliva
CN VII (Facial nerve)
Stensen’s duct
Parotid duct
Wharton’s duct
Submandibular duct
Bartholin’s ducts
Sublingual duct
Minor salivary glands
600-1000 of ‘em
>1% of saliva production
Located in oral cavity and muscles of the tongue
Ruch in mucin, antibacterial proteins, and secretory immunogloblin
Continuous, slow glands