intro (pangea and everything to do with it)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
dinosaur as a ruling species
causes other species tend to be much smaller and nocturnal to survive
non-avian dinosaur
these are the ones that went extinct
avian dinosaur
= bird
not extinct
Theropod descendants
Original therapods could not fly
Only gliding or short bursts of flying
archaeopteryx
considered a dino and a bird
dino
bony tail
teeth
bird
wings
feathers
conceived earlier as a transitional form or a missing link
probably couldn't fly
feathers does not mean that they can fly
dinosaur grey areas
non-avian and avian
ex.
archaeopteryx
microraptor
4-winged din bird
feathered
not sure if fly or gliding
amboteryx
dino bat
had feathers but membranes as well which is similar to bats
Some had the capability to swim but also could be on land
ex. Spinosaurus
Semi aquatic
Feet that could paddle
Retracted nostrils
Nostrils are not at the tip of the nose
Dense bones for buoyancy
Broad tail that acts like a rudder
Most hunting was in the rivers
fossil location
found on every continent
'Cause only lived on land
In their time, the world was not made into the continents that it is right now
not just dinosaurs
earth’s layers
from outermost to inner most:
crust
mantle
outer core
liquid
inner core
solid
due to extreme pressure
as you go inward
Fe, Mg, Ni will inc. and Si, Al will dec.
more metallic, pressure, temp., and density
as you go outward
Si, Al will inc and Fe, Mg, Ni will dec.
more silicate minerals
each is diff. in mechanical behav. and phase
crust
solid, rigid and brittle (cuz cool)
types
continental
thick
Si, Al
low density
mainly granite
oceanic
thin
rich in Fe and Mg
higher density
mostly basalt
mantle
solid
ductile plastic
plate move cuz heat allows the mantle to be malleable
uppermost mantle
rigid and brittle solid
at the base of crust
divided into:
asthenosphere
ductile solid
deep mantle
less ductile solid
lithosphere
uppermost mantle + crust
lithosphere plates
moves during plate tectonics
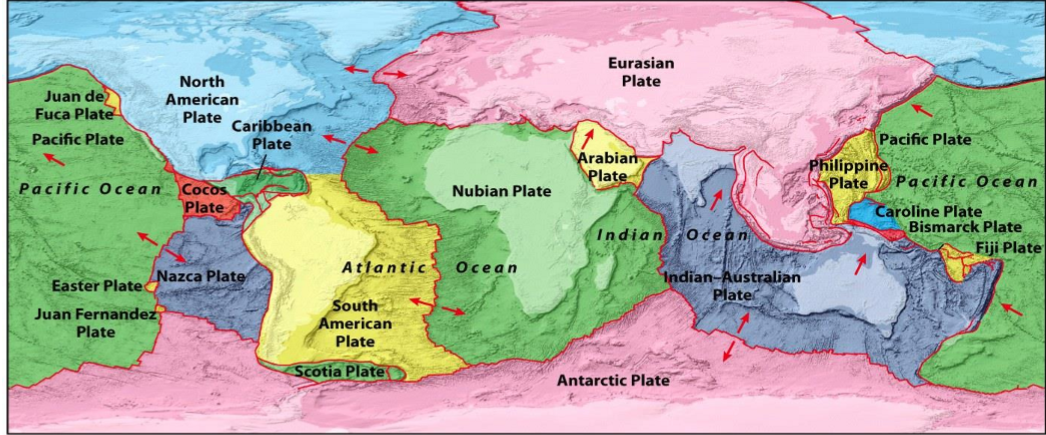
plate tectonics
Red Arrows
Away from each other = divergent
ex. Between the South American plate and the nubian plate
Forms a mid ocean Ridge
Well cause the land continents on them to be further apart millions of years from now
Towards each other = convergent
ex. between juan de fuca and north american
juan de fuca was a larger plate that was recycled under the North American one because of subduction
ex. Between the Indian Australian plate and the Eurasian plate
forms mountains
arrows moving past each other = transform
single arrows = overall movement of a plate
plates move ~ 0 to 10 cm
Locations on the boundaries with subduction are more likely to experience hazards like earthquakes and volcanoes
tectonic theory
lithospheric plates move and interact in response to forces in the earth
during subduction
the subducting plate loses structural integerity
plate boundaries
where 2 plates meet
types
divergent
convergent
transform
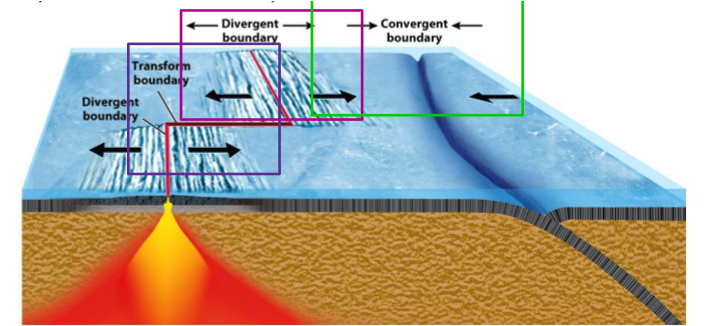
divergent boundary
move away from each other
mostly on the seafloor
causes seafloor spreading
hot rock rises up, melts and fills in the gaps between existing crust
rock that moves away from the ridge will be older
ex.
Iceland
mid ocean ridge
a long row of subsea volcanoes
wraps all around the world
ongoing process
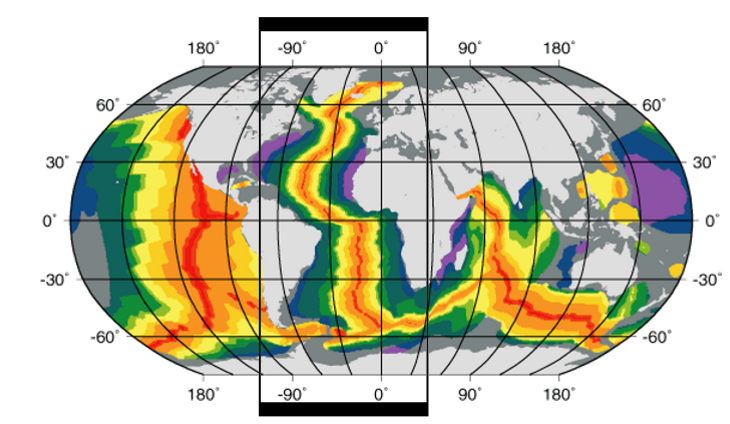
convergent boundaries
move towards each other
types
ocean-continent
ocean-ocean
ocean-continent convergent boundary
ocean always subducts under continental
forms deep trench
leading edge of continental crust get composed and deformed = mountains and volcanoes
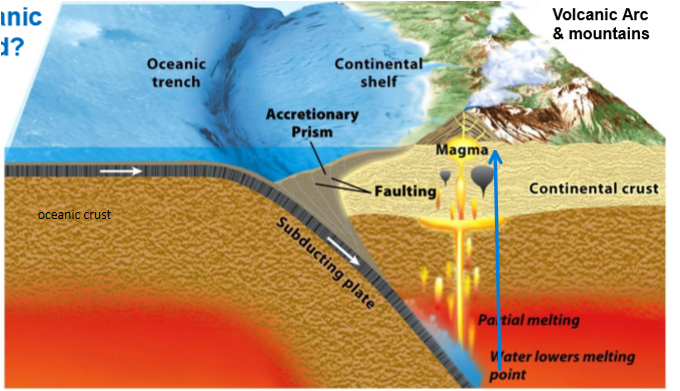
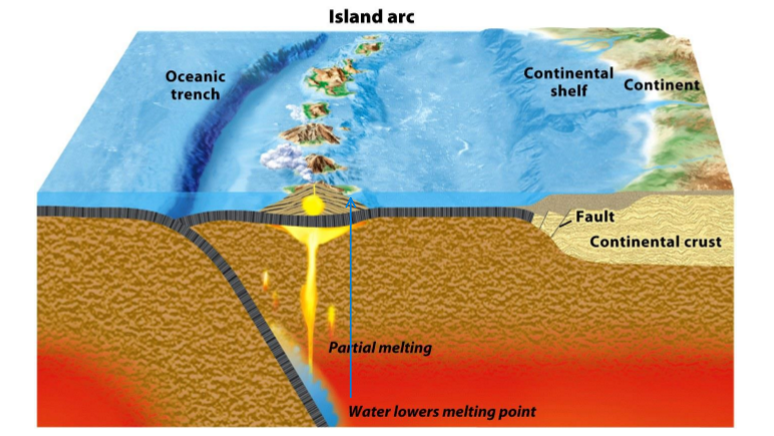
ocean-ocean convergent boundary
they collide with each other
subducting plate will be older, colder, and denser
the non-subducting plate will have volcanic islands
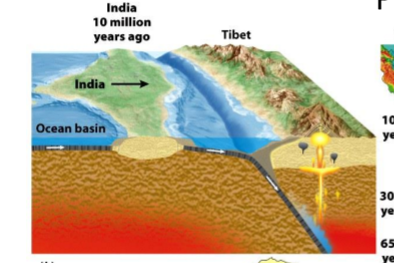
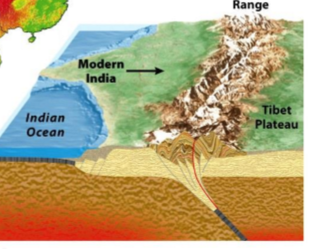
continent-continent convergent boundary
results in large mountains
sequence
oceanic-cont
oceanic subduction
cont.-cont. eventually
subduction stops
collides into large mountains
ex.
himalayans
indian and eurasion plates converge
transform boundary
grind past each other
crust is not created or destroyed
forms along divergent boundaries
relives the stress it causes
connects in diff. ways
connects spreading ridge + subduction zone = divergent and convergent
ex. Q charlotte fault
connects 2 plates moves in the same direction
ex. Nootka fault
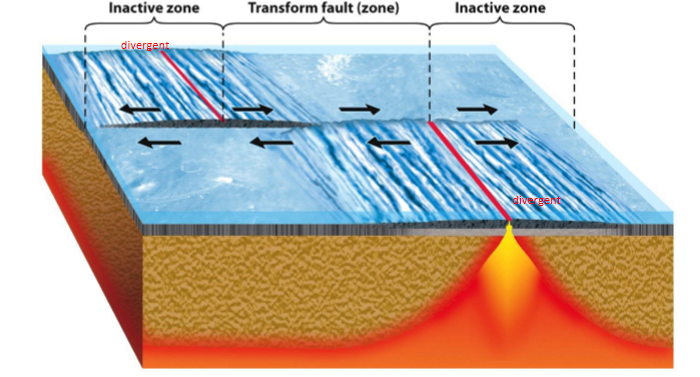
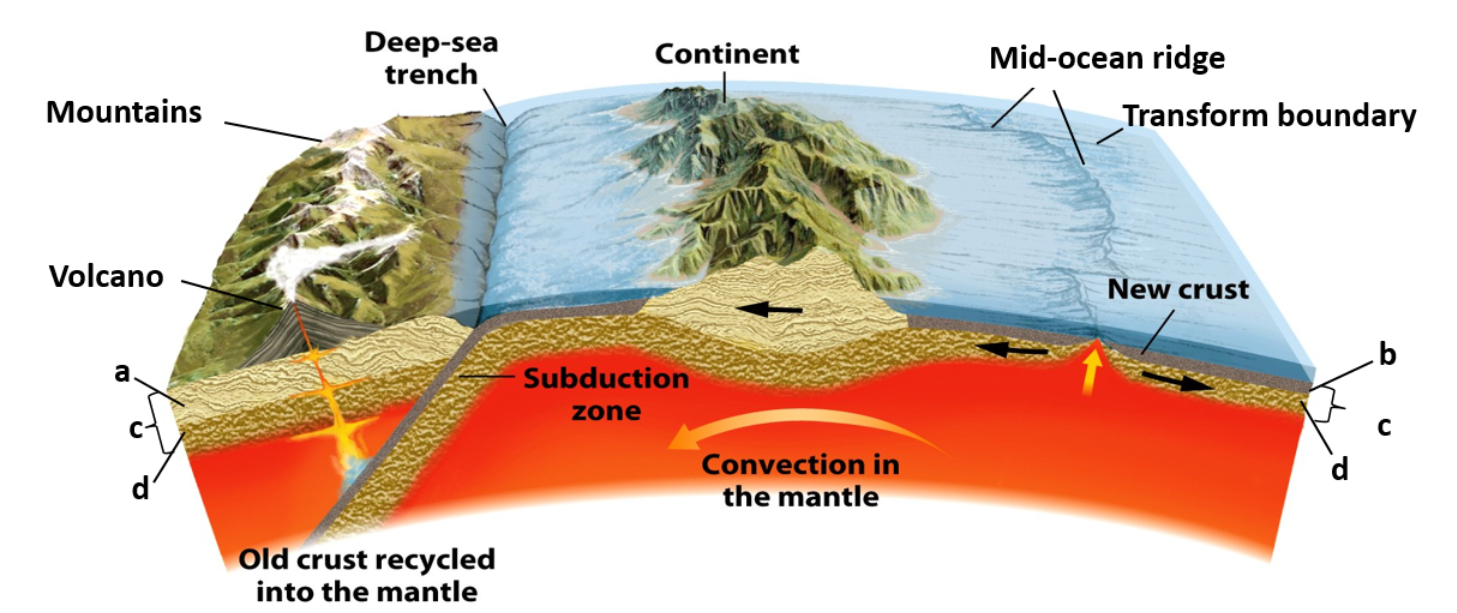
diagram of layers
a = continental crust
b = oceanic crust
c = lithosphere
d = rigid uppermost mantle
all of the above layers are involved in plate motion
convection
occurs in the mantle
sequence
bottom most water is heated
expands and becomes less dense
rises
that heat from the water is lost at the surface
causes it to contract
becomes more dense and sinks back to the bottom
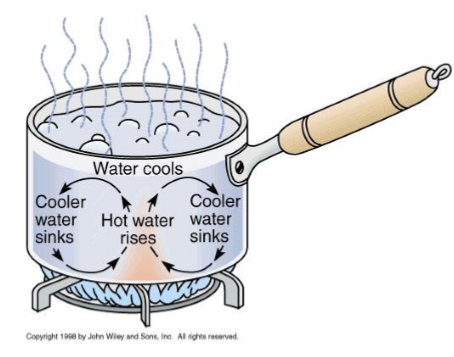
plate movement
through heat
plate makeup
oceanic lithosphere is high density and asthenosphere is weak
lithosphere moves along the mantle
plate movement cause
plates get pulled down into trenches
gravity pushes the plates down the slope from the Ridge to the trench
There are probably other forces as well
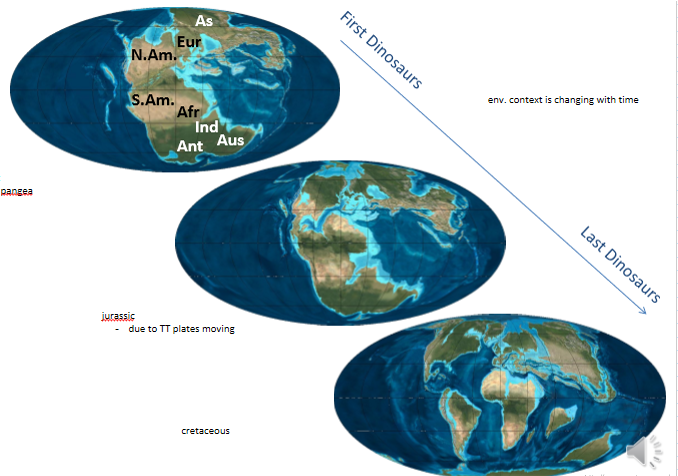
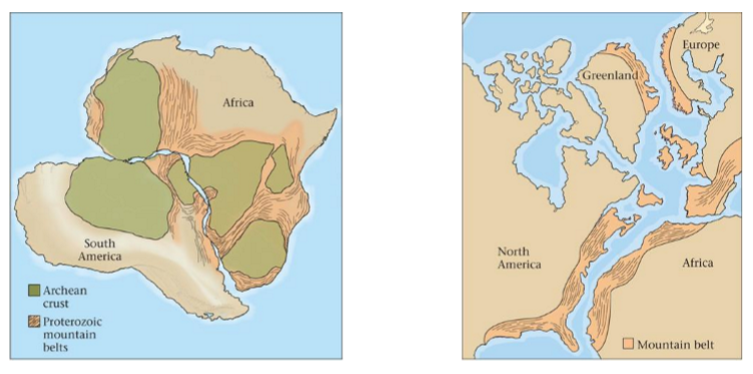
proof for pangea
By matching fossils and rocks of the same age and type from different continents we can see where they might have been connected
Alfred Wagner
It is not possible for these organisms to have crossed the ocean
So the land masses must have been 1 supercontinent
Ancient mountain belts have been split across divergent boundaries
from pangea to now
Late Permian
260 million years ago
Just before dinosaurs
One supercontinent
The South Pole has ice sheets all over
Glacial till
Ice moves across the surface of the earth and picks up rocks
Late triassic
220 million years ago
The time of the first dinosaurs
Pangea starts shifting north
The ice sheet on the South Pole has melted
Allows animals to migrate, although mountains are still blocking some passages
Early Jurassic
200 million years ago
Pangea starts breaking up
Lots of flooding because of less ice sheets and mountains building
Middle Jurassic
170 million years ago
Pangea breaks up even more
Sea levels rise enough to create inland seas
Late Jurassic and early Cretaceous
120 million years ago
Pangea breaks into two smaller supercontinents
Laurasia and gondwana
India starts moving N at 15 cm each year
Will collide with Asia 40 million years later
Middle Cretaceous
105,000,000 years ago
Gondwana breaks apart forming into Africa and South America
Australia is still stuck to Antarctica
High sea levels
Late Cretaceous
90 million years ago
Extreme flooding
Africa, Europe, India become flooded and the western interior seaway forms over North America
Cretaceous paleogene boundary
65.5 million years ago
End of the dinosaurs
Continents are almost at their modern position
Sea levels begin to drop