BSC2085 L 7
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
A joint that holds bones together and allows skeletal system flexibility.
Articulation
Joints joined by fibrous tissue, mostly synarthrotic (no movements). Types include sutures and syndesmoses.
Fibrous Joints
Type of fibrous joint that interlocks bones, primarily found in the skull.
Sutures
Type of fibrous joint where articulating bones are connected by short ligaments, such as the tibia and fibula.
Syndesmoses
Joints where articulating bones are connected by cartilage, mostly amphiarthrotic (slight movements). Types include symphyses and synchondroses.
Cartilaginous Joints
Type of cartilaginous joint where bones are connected by broad fibrocartilage discs (e.g., intervertebral discs).
Symphyses
Type of cartilaginous joint where bony portions are united by hyaline cartilage (e.g., 1st rib/sternum).
Synchondroses
Joints that allow free movement, with articulating bone ends separated by a joint cavity filled with synovial fluid.
Synovial Joints
enclose joint surface;
reinforced by ligaments; may contain bursae (fluid sacs); may contain fibrocartilage pads (articular discs)
Articular Capsule
Inner layer of smooth connective tissue that produces synovial fluid.
Synovial Membrane
A motor neuron and the muscle fibers it innervates.
Motor Unit
The area where a neuron's axon interacts with muscle cells.
Neuromuscular Junction
A neurotransmitter released at the neuromuscular junction that signals muscle contraction.
Acetylcholine (ACh)
The process where muscle fibers generate tension and shorten in response to stimulation.
Muscle Contraction
A type of muscle contraction where muscle length does not change while force is applied.
Isometric Contraction
A type of muscle contraction where muscle length changes, but the force remains the same.
Isotonic Contraction
Types of synovial joints:
plane
hinge
pivot
condyloid/ellipoidal
saddle
ball and socket
flat surface (intercarpal/tarsal joints & vertebrocostal joints of ribs 2-7)
plane
round end to concave surface
(elbow & interphalangeal joints)
hinge
round/conical bone to shallow
depression/foramen (atlas & axis)
Pivot
oval condyle to
ellipsoidal depression (radiocarpal joint &
metacarpophalangeal joints)
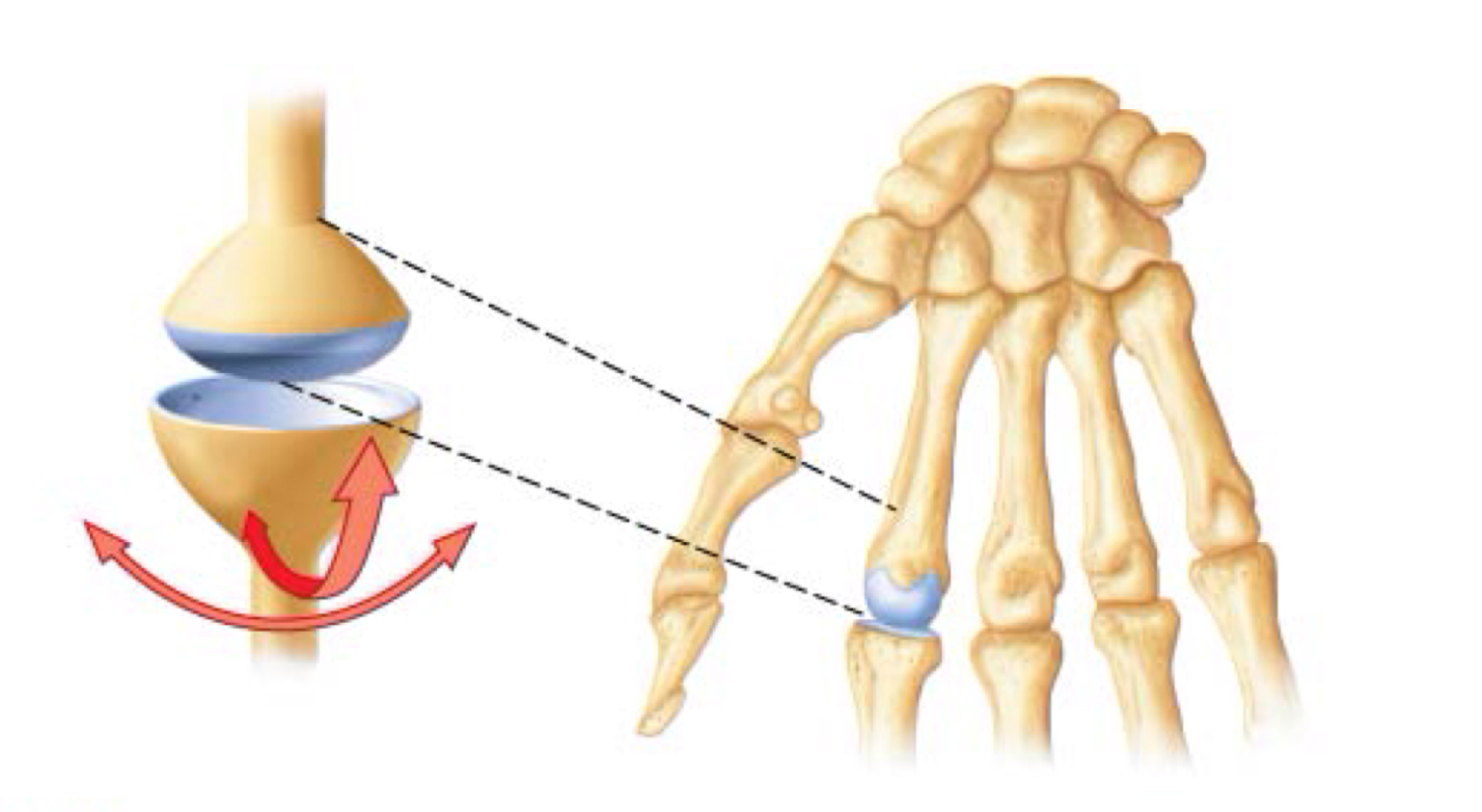
Condyloid/Ellipsoidal
saddle shaped, one convex, one
concave (metacarpal & trapezium of wrist)
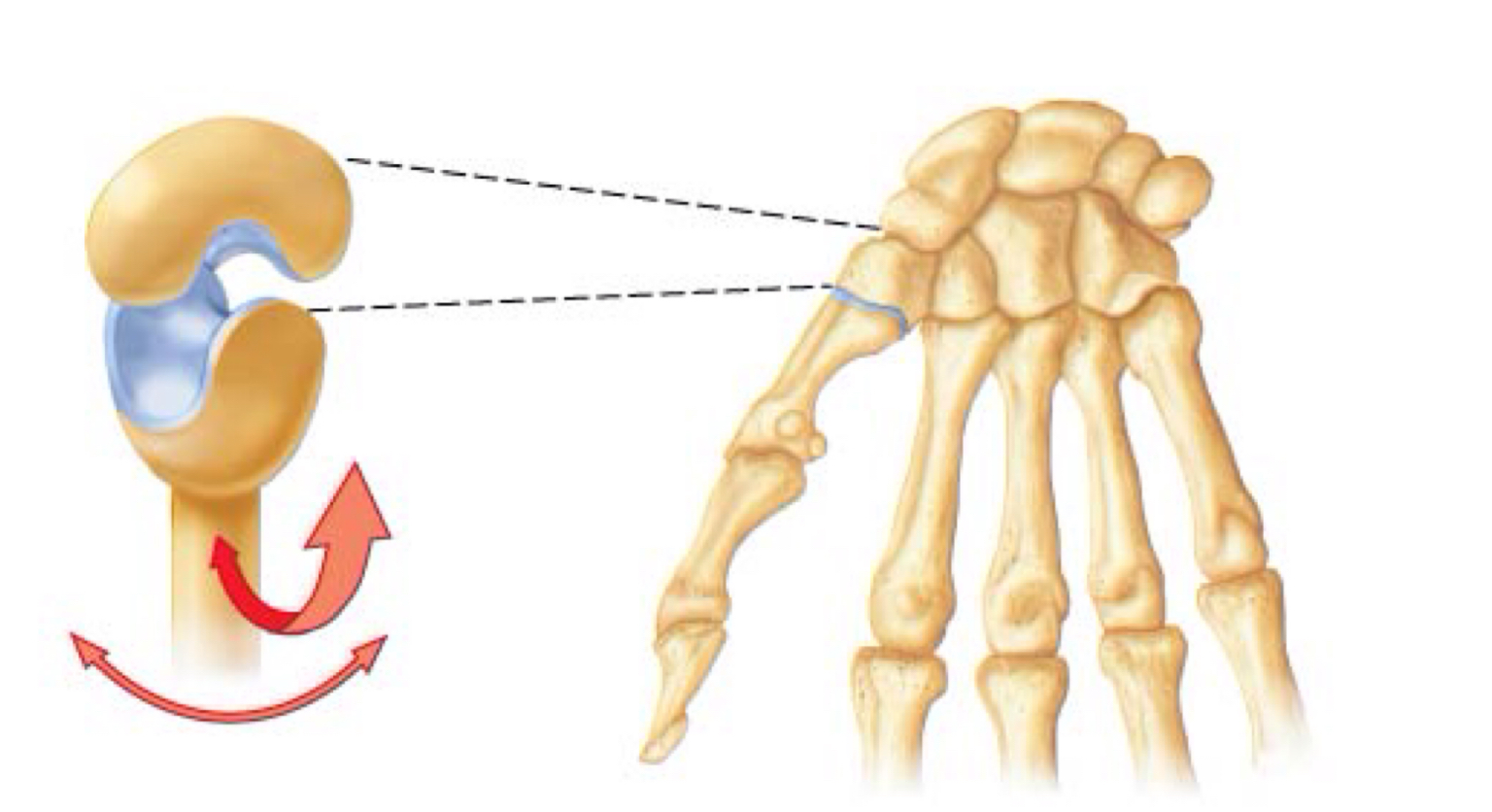
Saddle
ball-shaped head fits into
cuplike depression
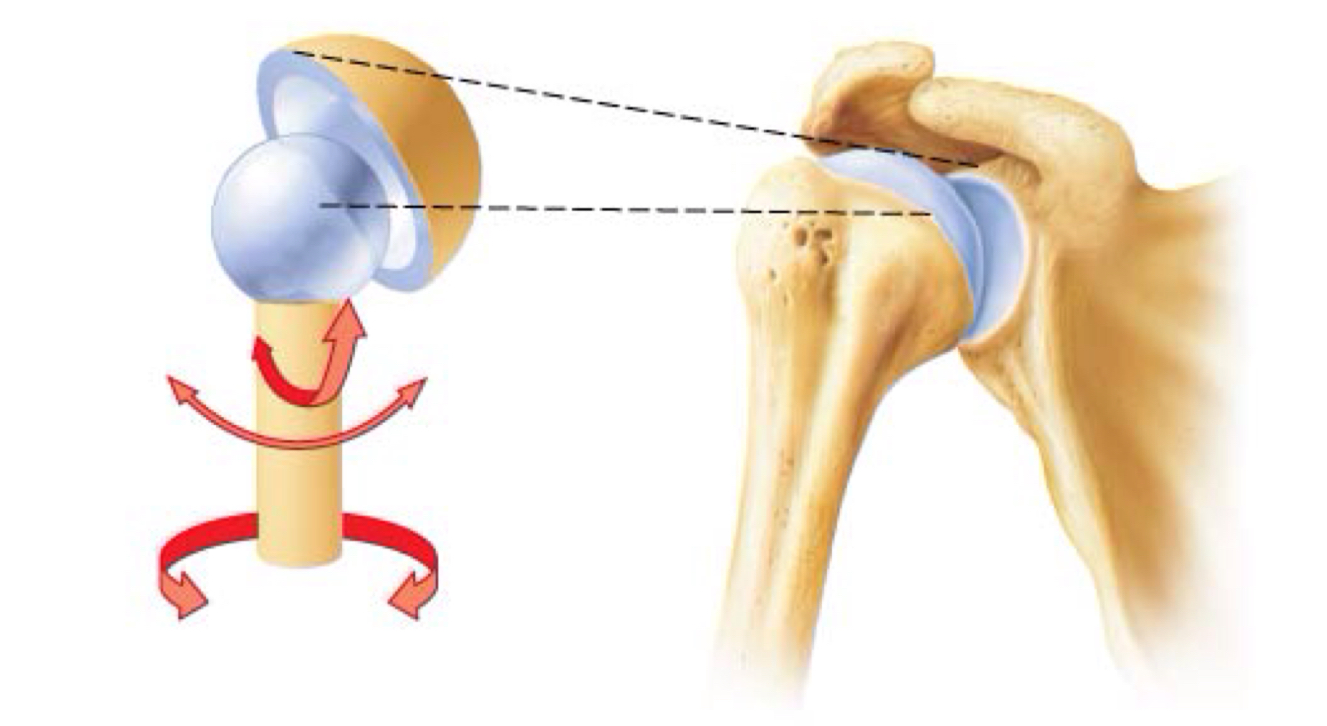
Ball and socket
decrease joint angle
Flexion
increase joint angle
Extension
increase joint angle over 180°
Hyperextension
limb away from midline
Abduction
limb towards midline
Adduction:
movement around longitudinal axis
Rotation
distal end moves in circle
Circumduction
palm from anterior to posterior
Pronation
palm from posterior to anterior
Supination
medial turn of sole
Inversion
lateral turn of sole
Eversion
ankle joint dorsal movement
Dorsiflexion:
ankle joint flex downward
Plantar flexion:
forms the thin filaments, anchored by
the Z disc
Actin
forms the thick filaments, anchored
by the M line
myosin
smallest functional contractile unit
of muscle. From Z disc of an I band to next Z disc
Sarcomere:
indention of the
sarcolemma (plasma membrane) forms a tubule
at A/I band junction
Transverse (T) tubule
•region of sarcomere containing thick filaments
A band
region of sarcomere containing only thin filaments
I band
muscle cell’s smooth
endoplasmic reticulum, used to store calcium
(Ca2+) ions
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
structure consisting of two terminal cisterns
of the sarcoplasmic reticulum and a transverse
tubule between them
Triad
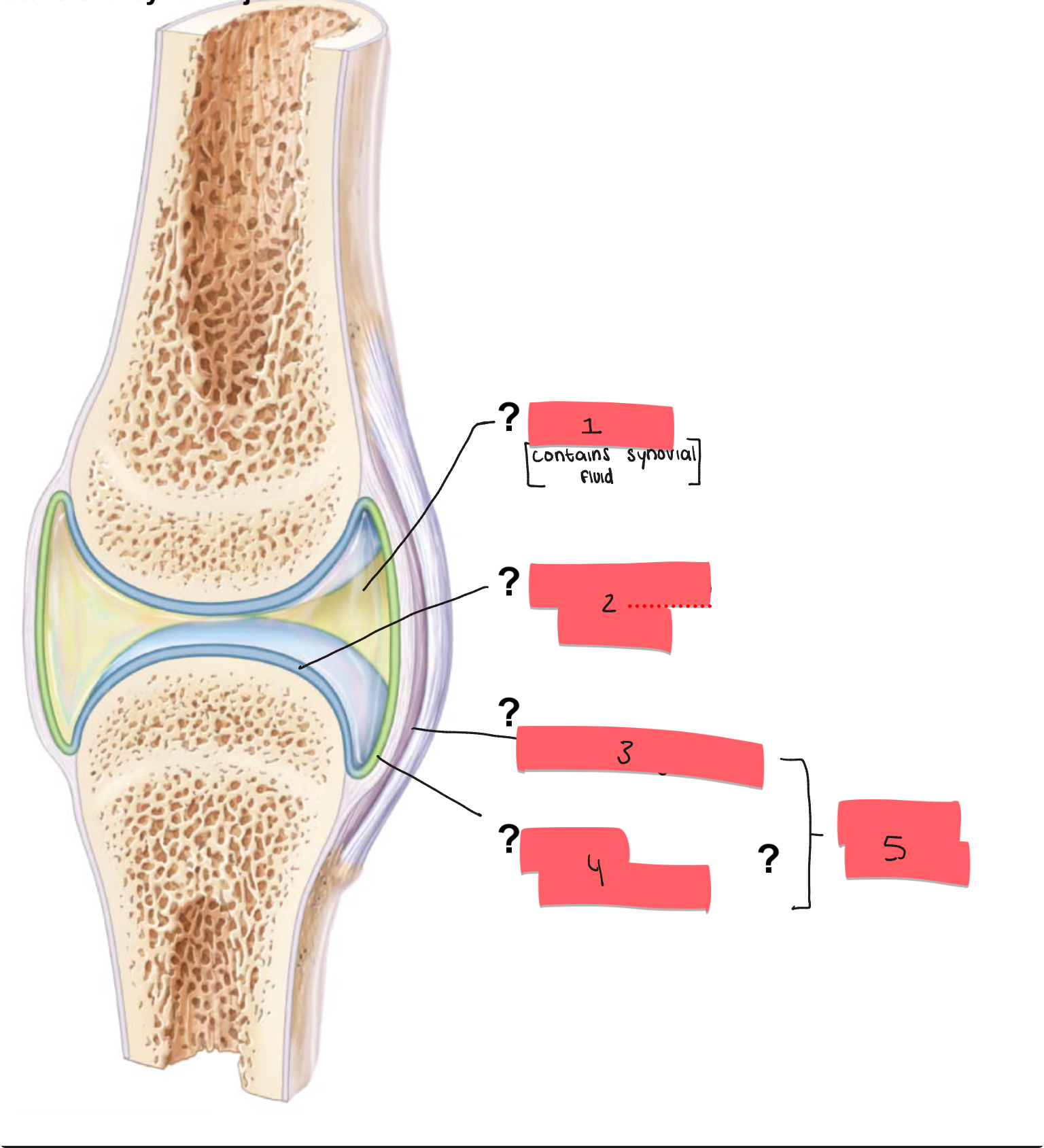
1?
joint cavity
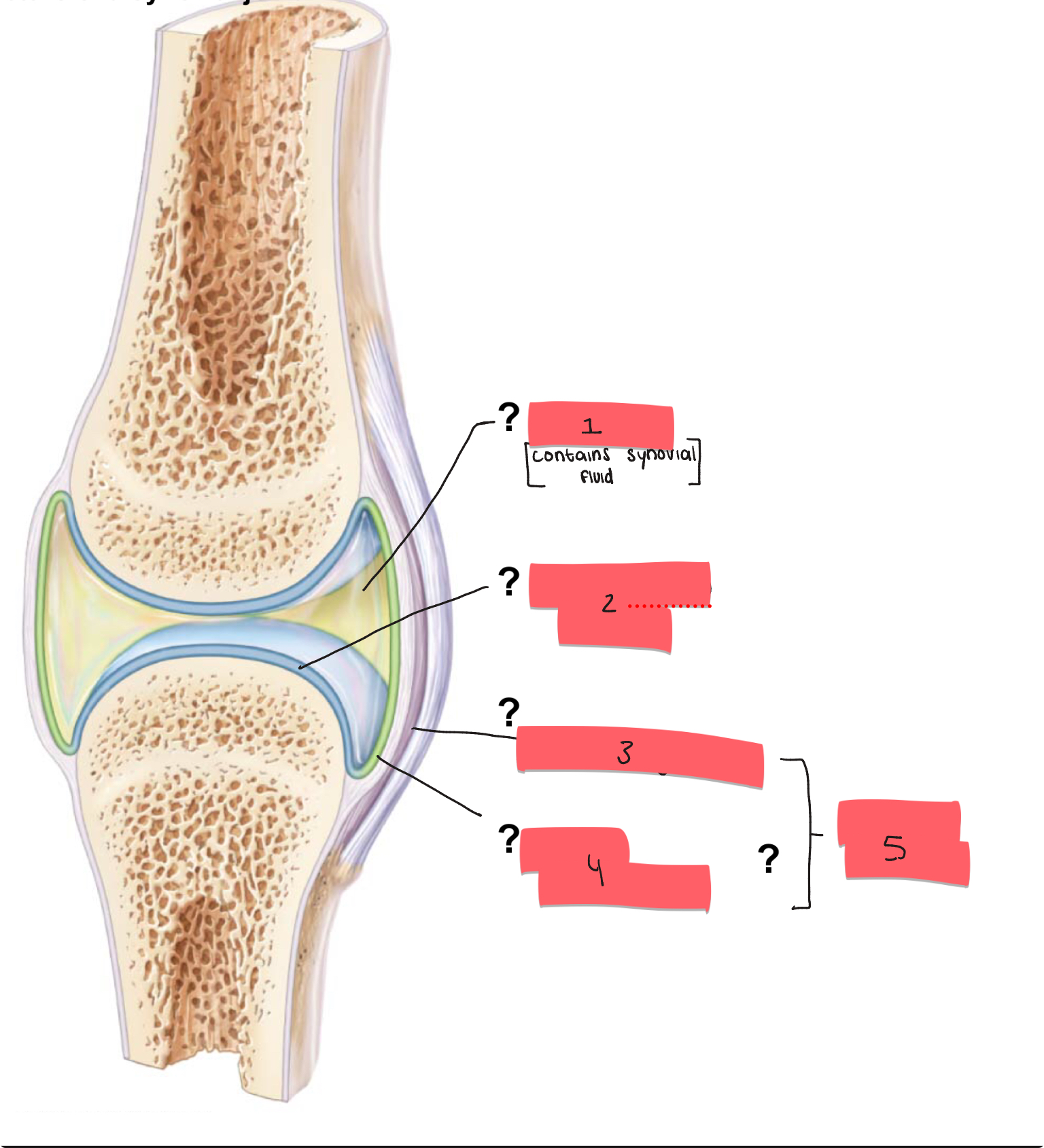
2
articular cartilage
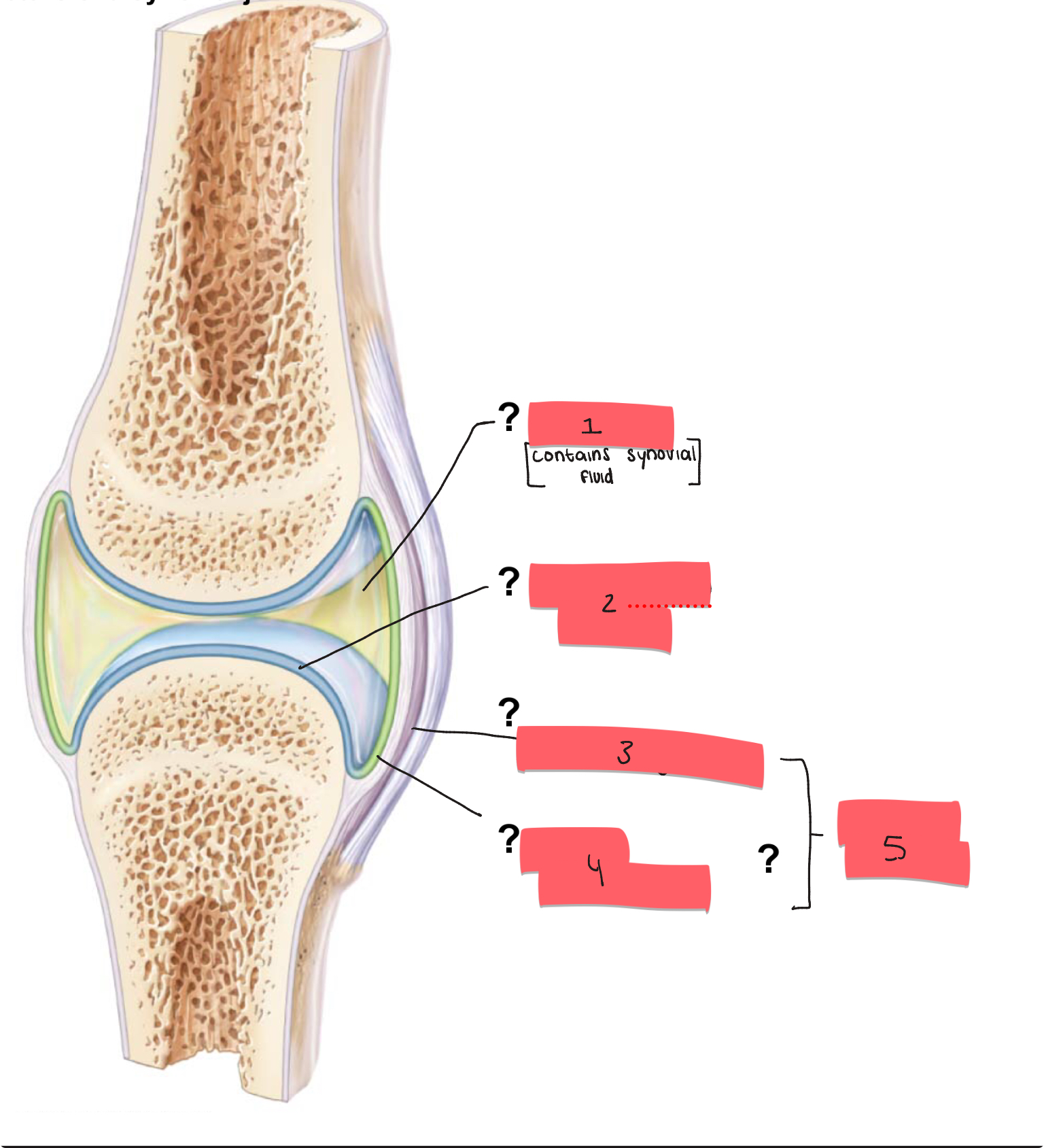
3
fibrous layer
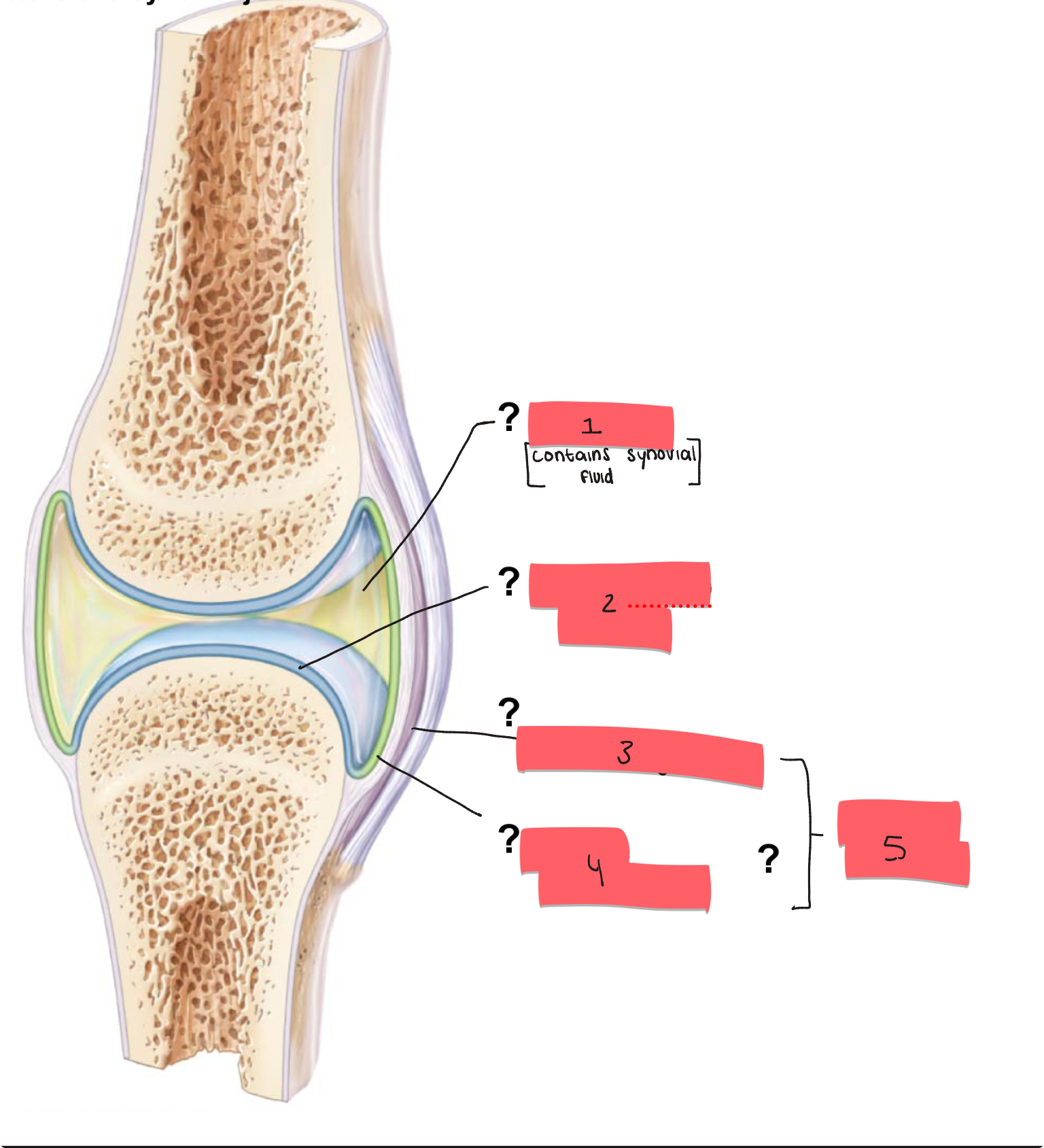
4
synovial membrane
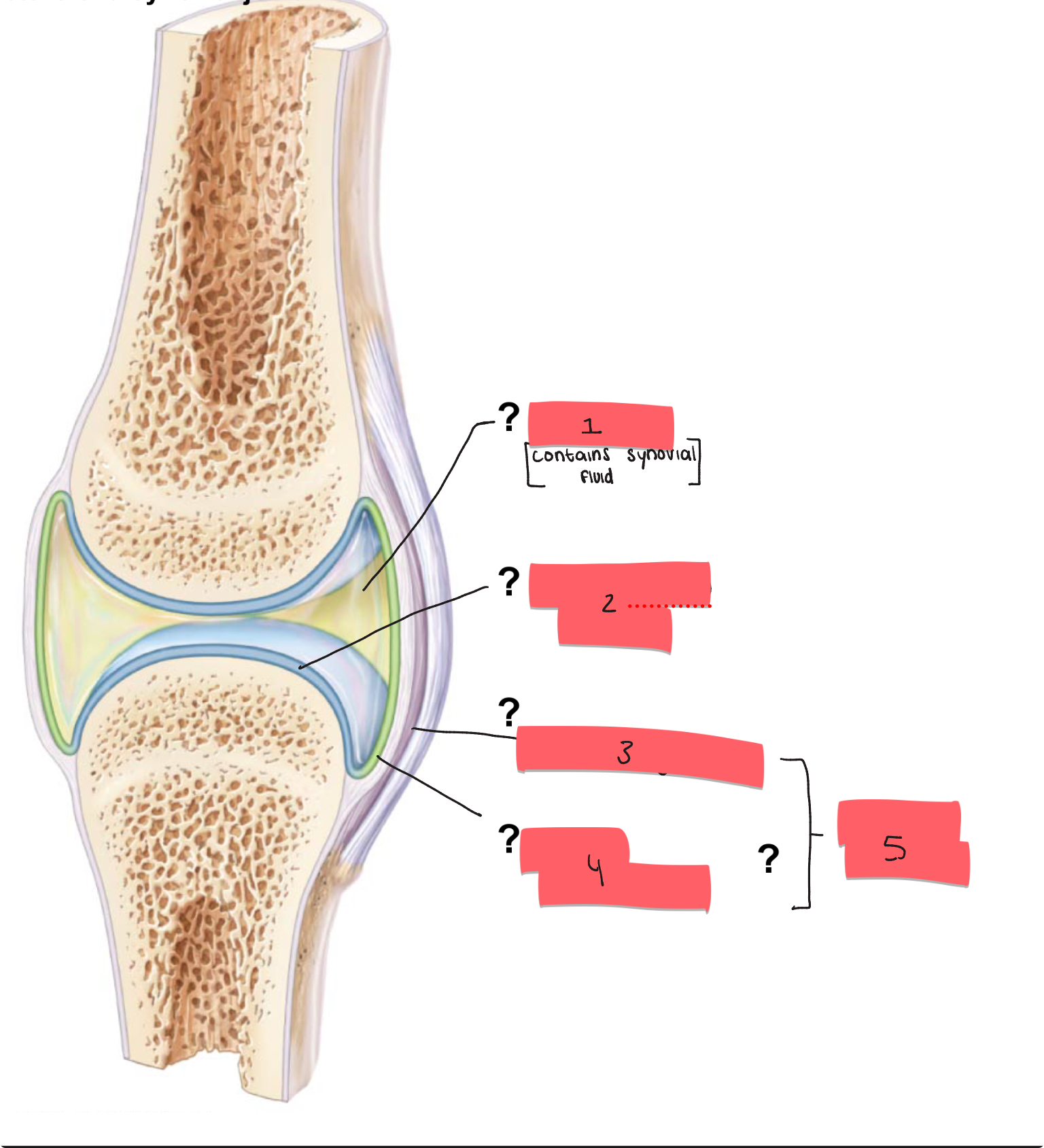
5
articular capsule
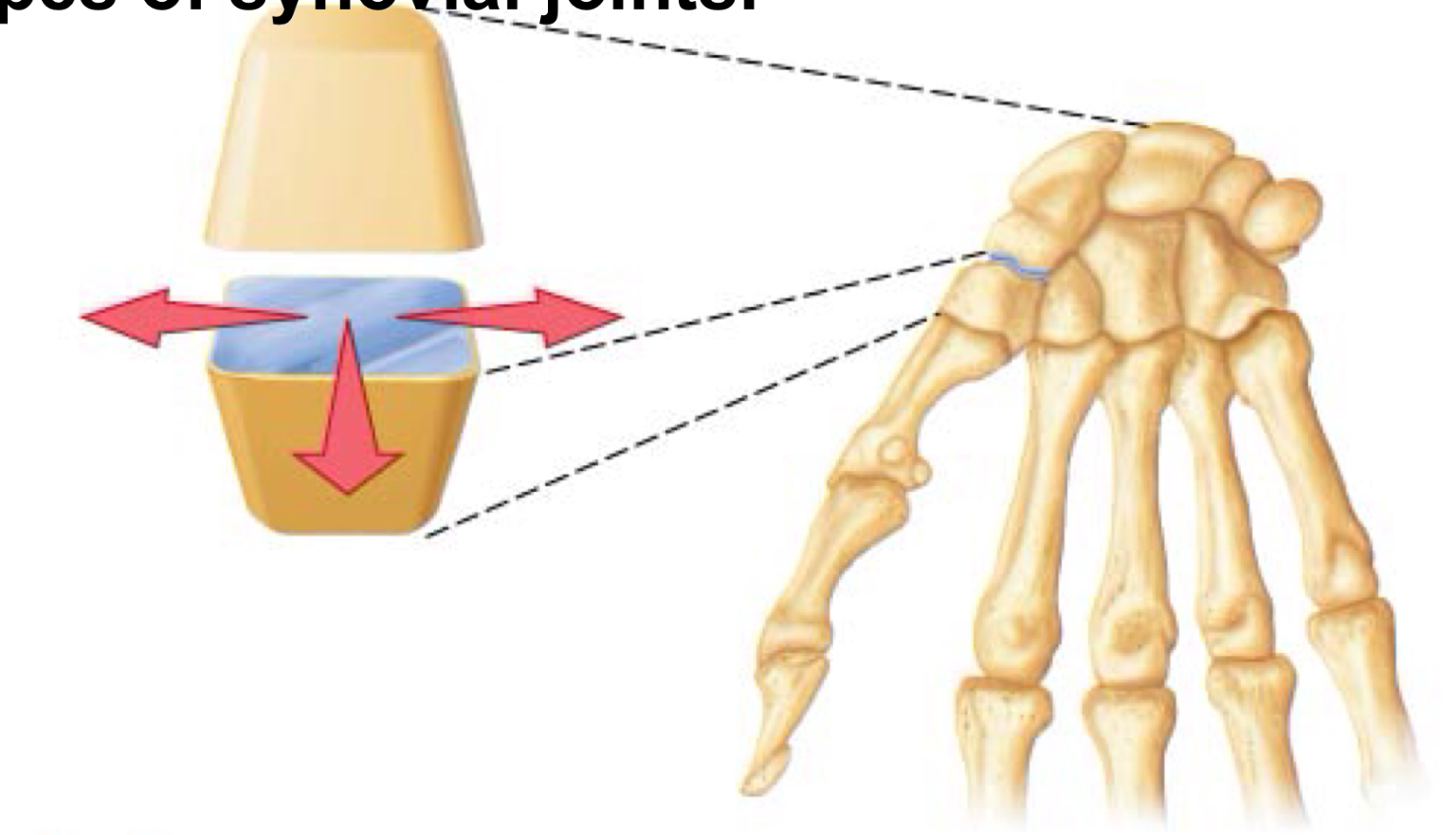
identify
plane joint
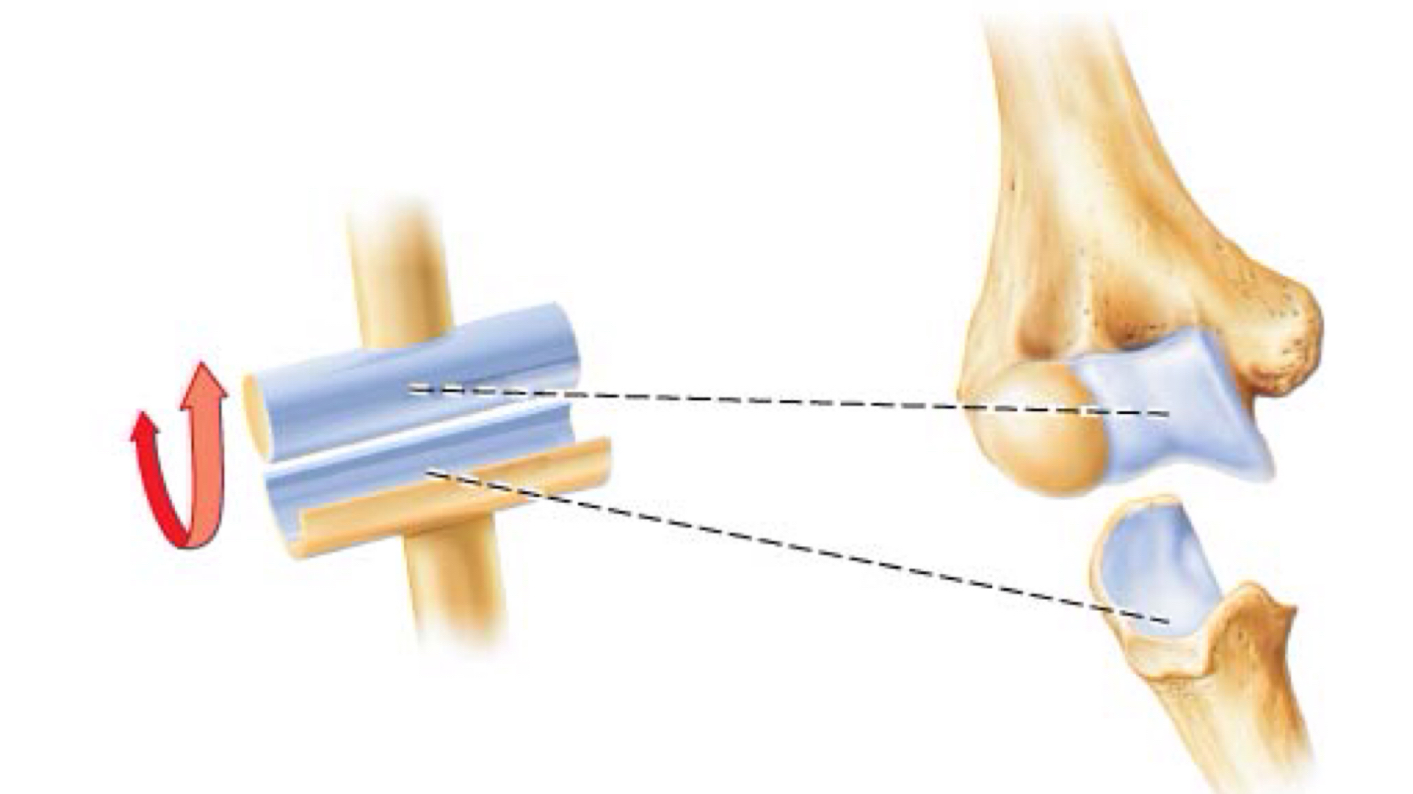
identify
hinge joint
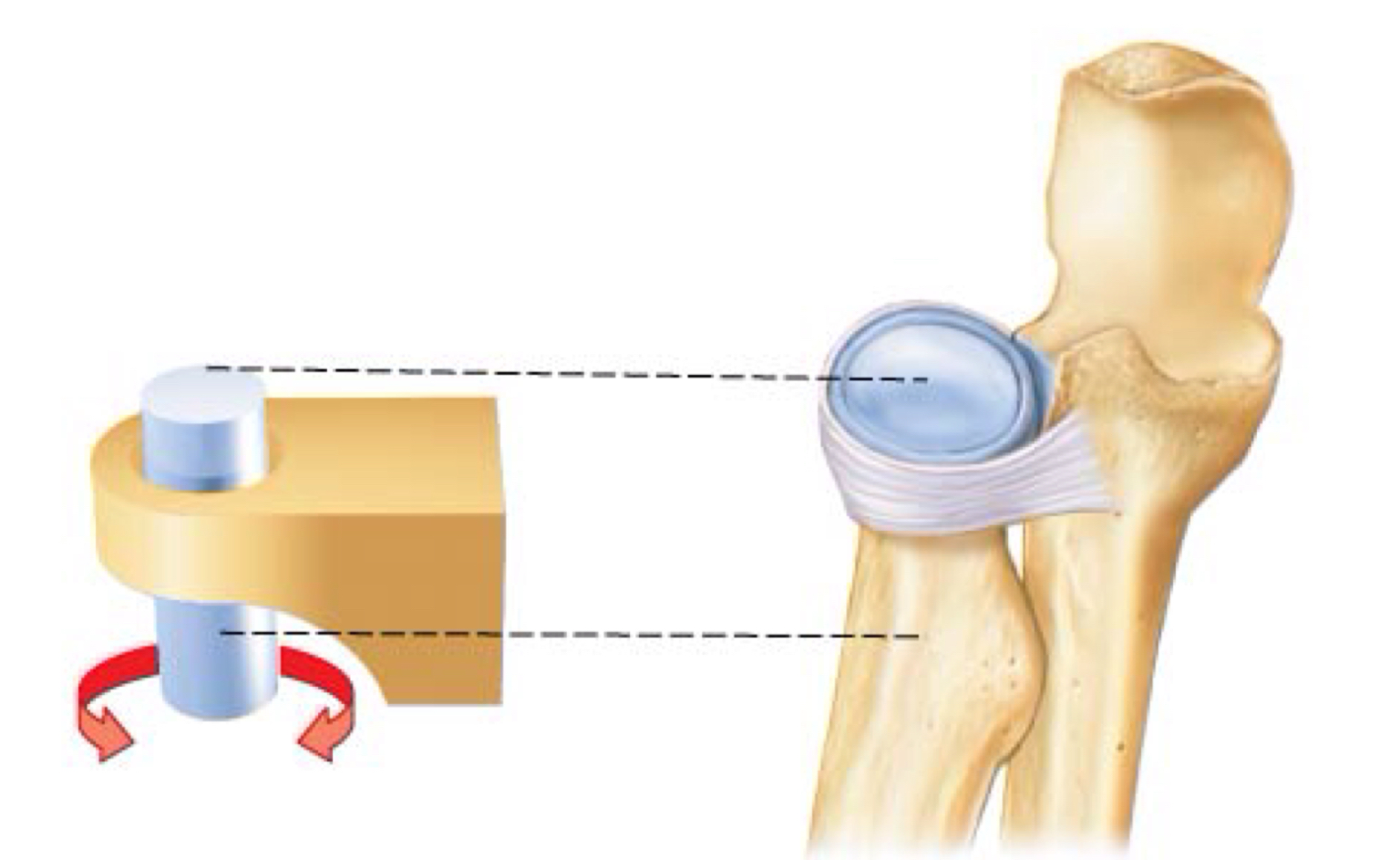
identify
pivot joint
identify
condylar joint
identify
saddle joint
identify
ball and socket joint
1
hyperextension
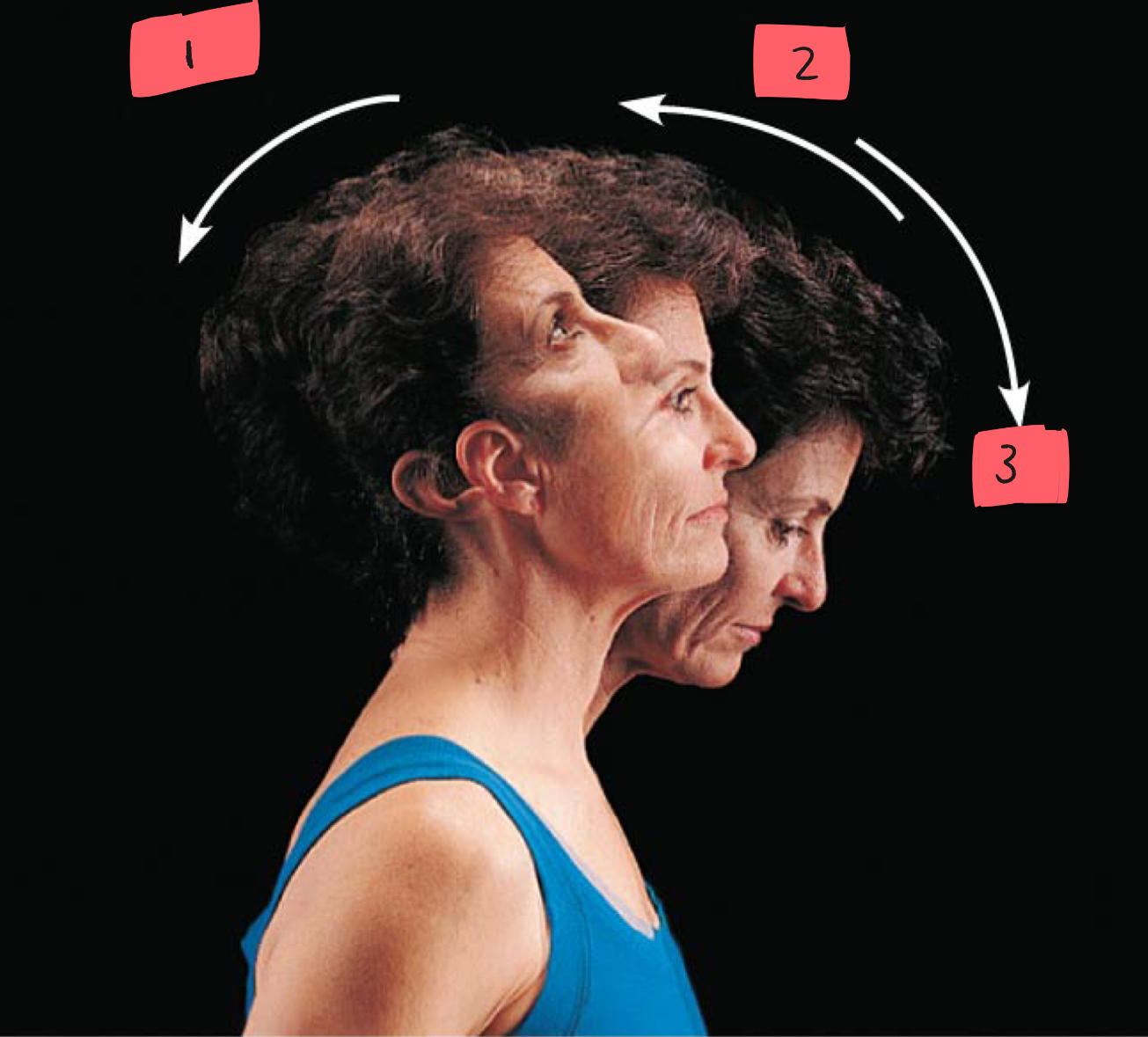
2
extension
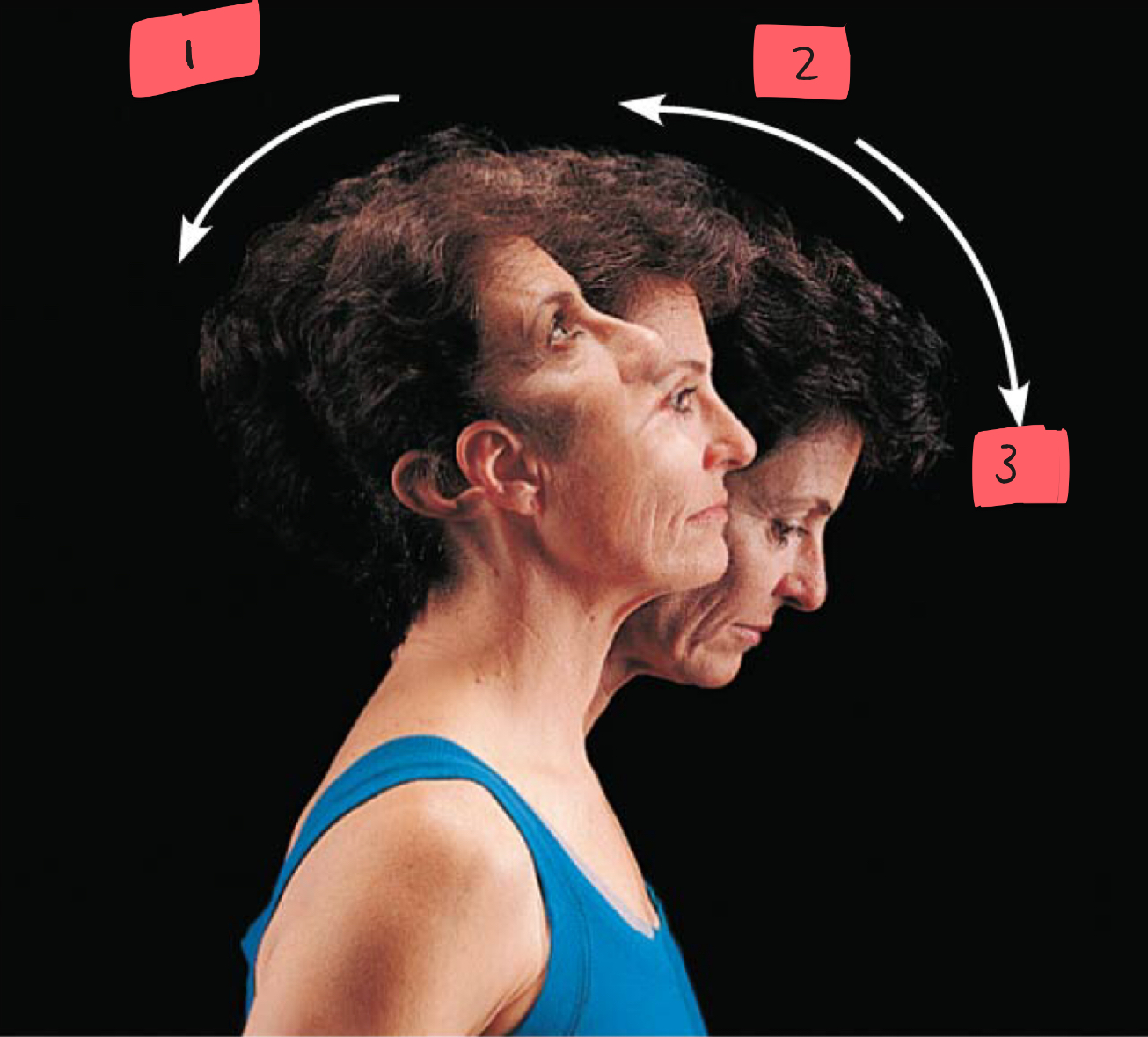
3
flexion
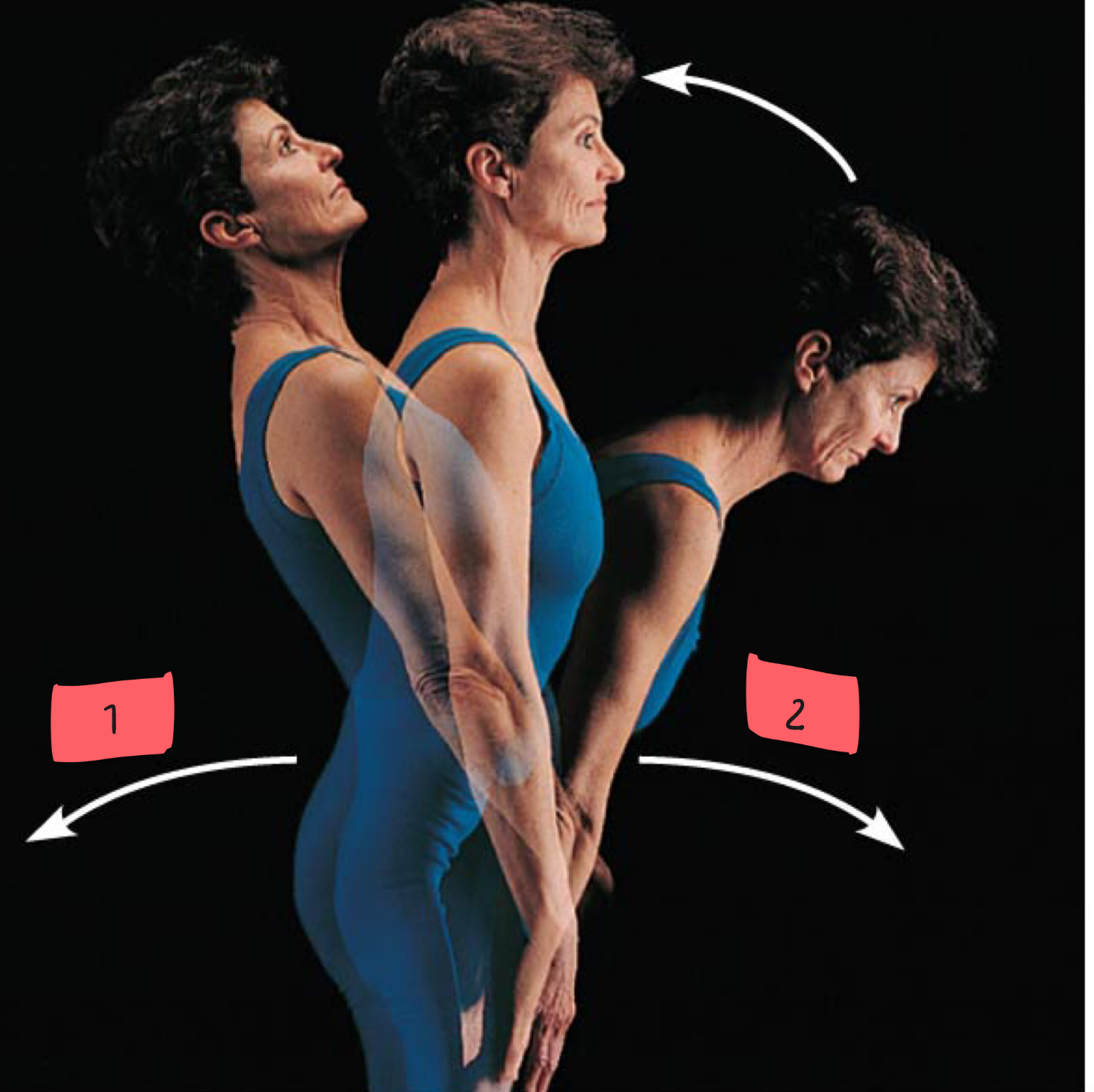

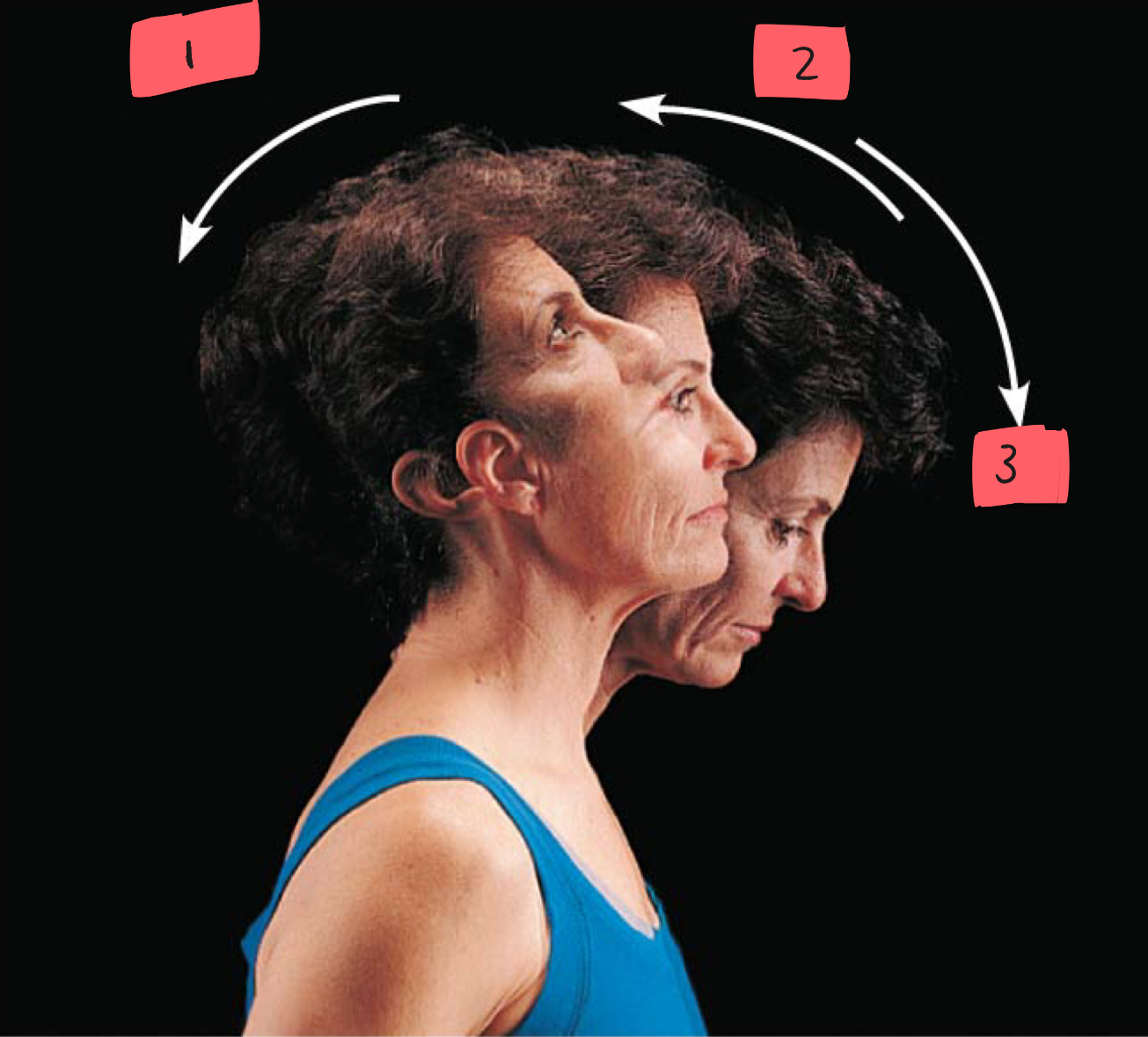
1
hyperextension
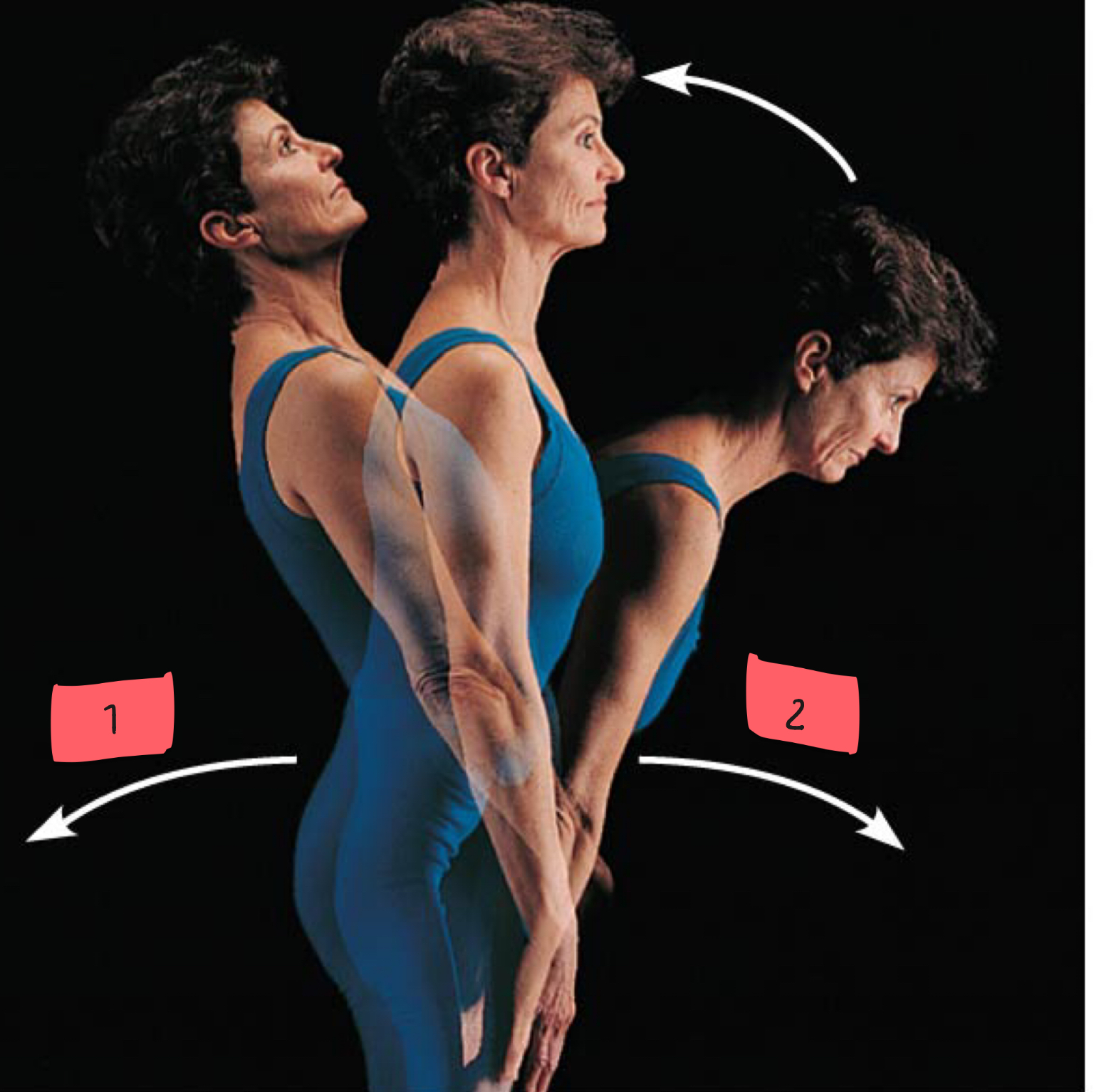

2
flexion
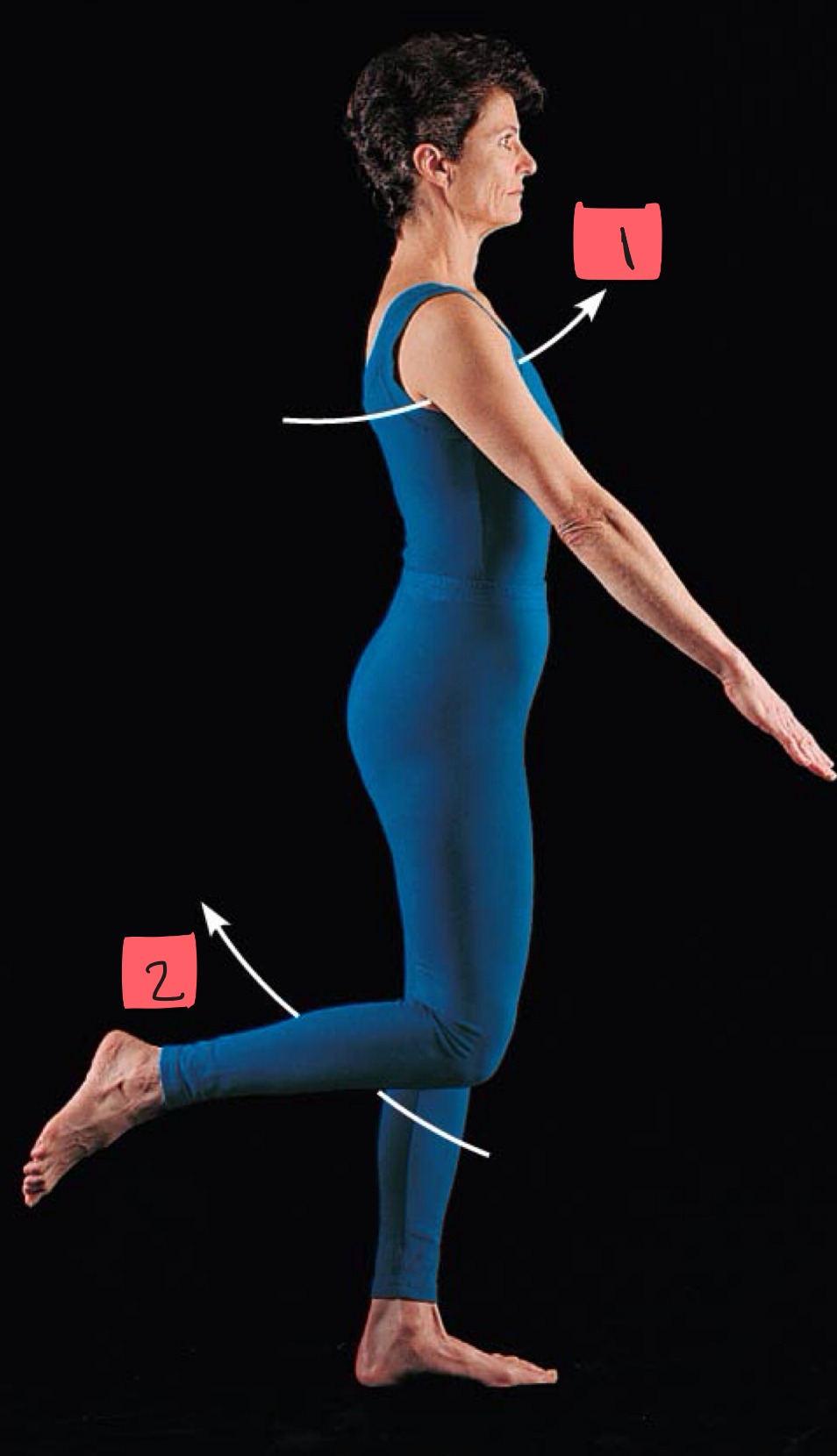

1
flexion
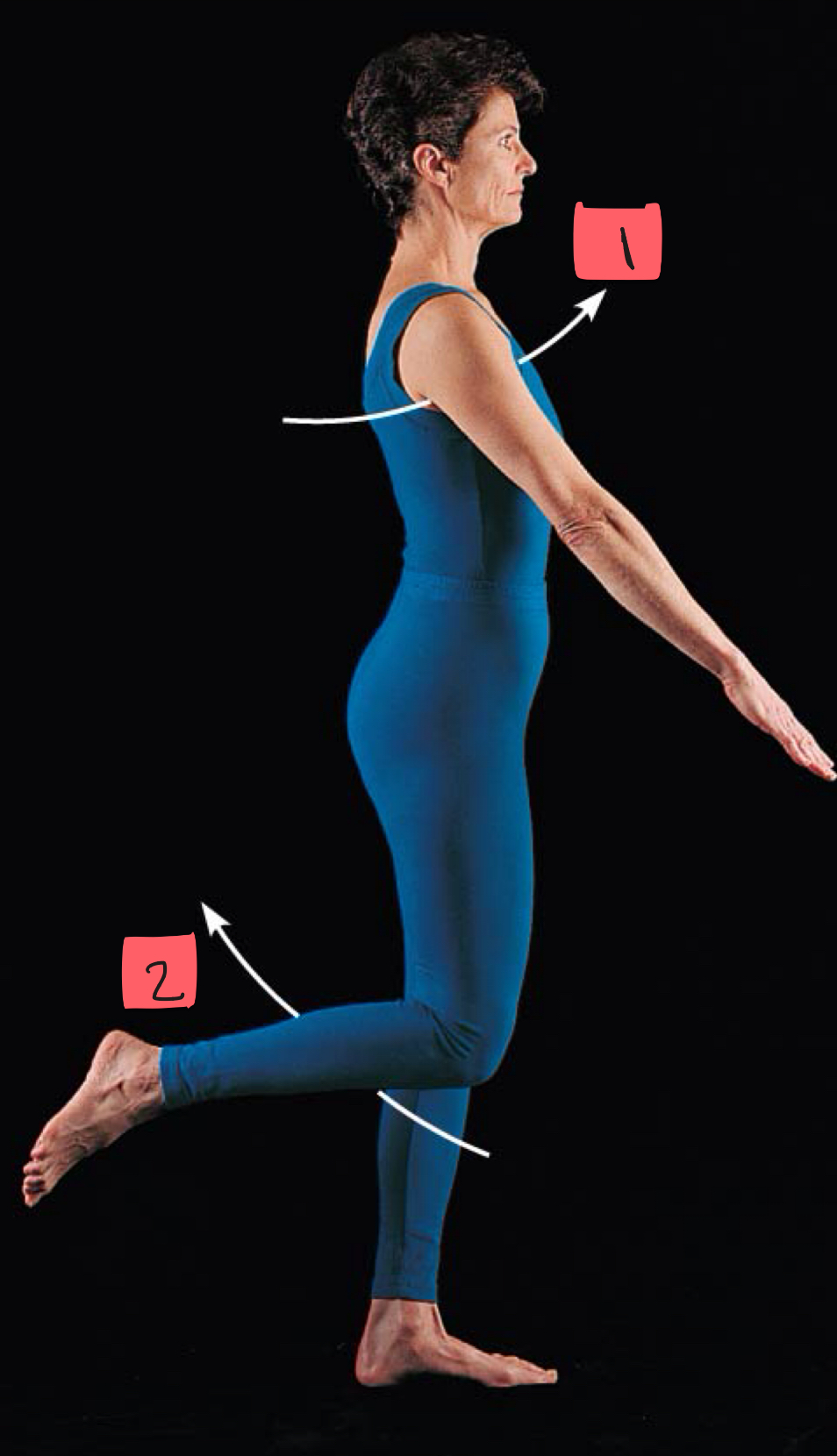

2
flexion

1
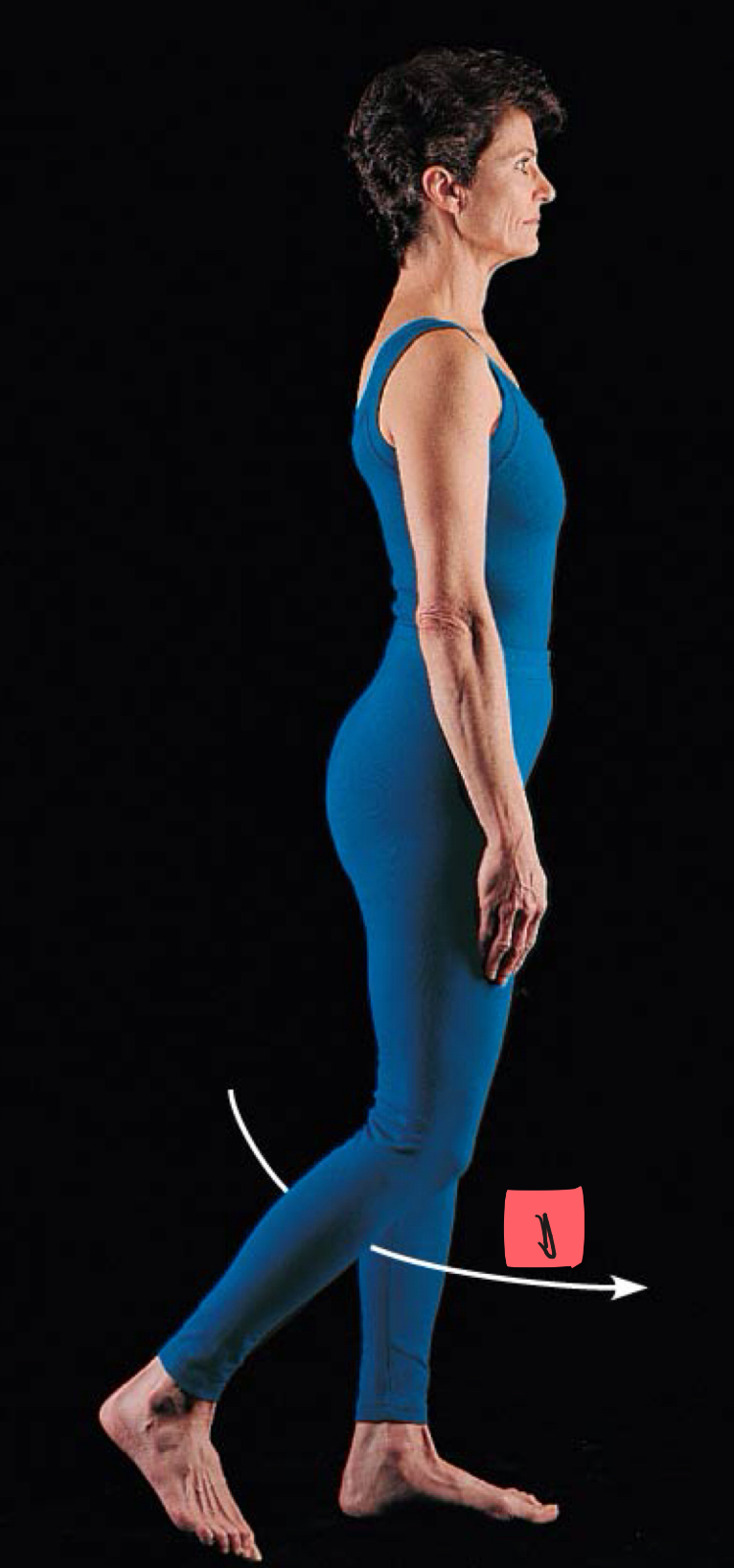
extension

1
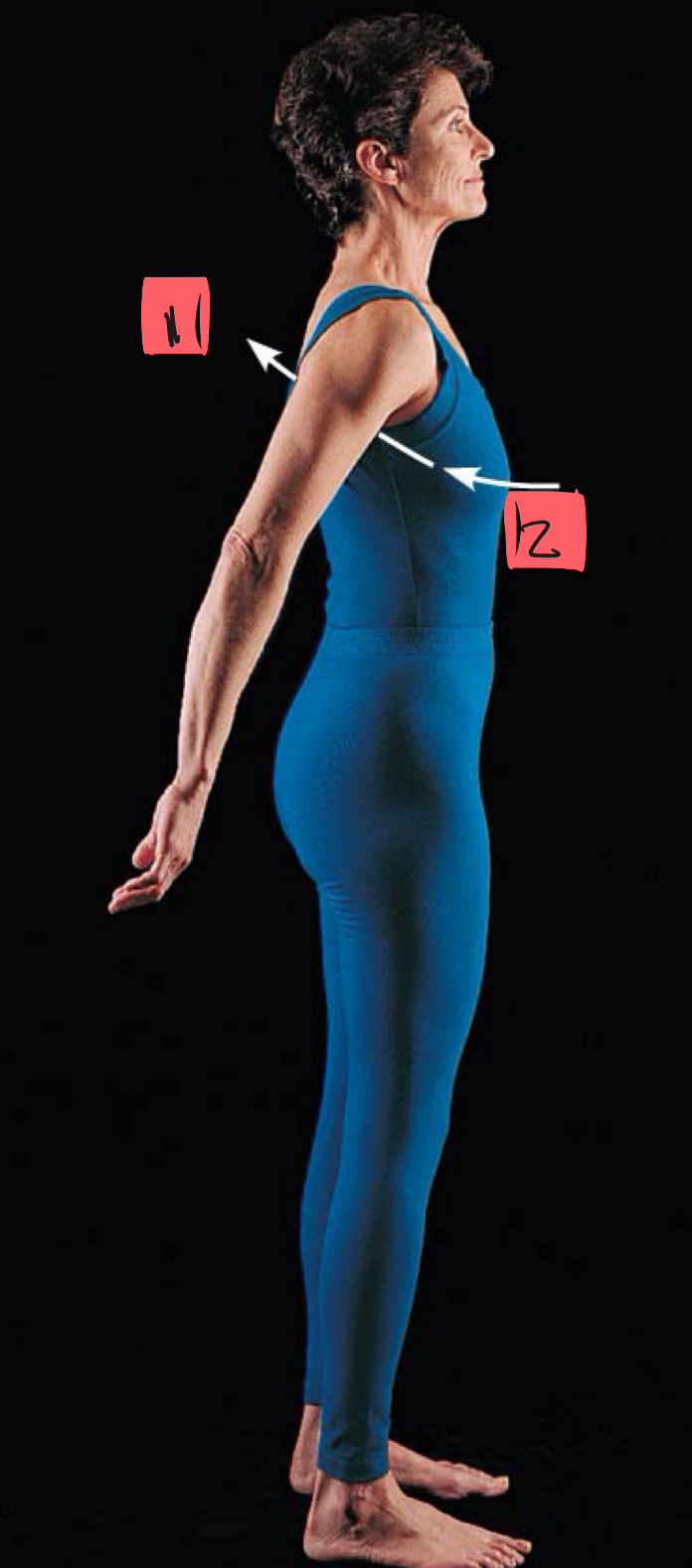
hyperextension
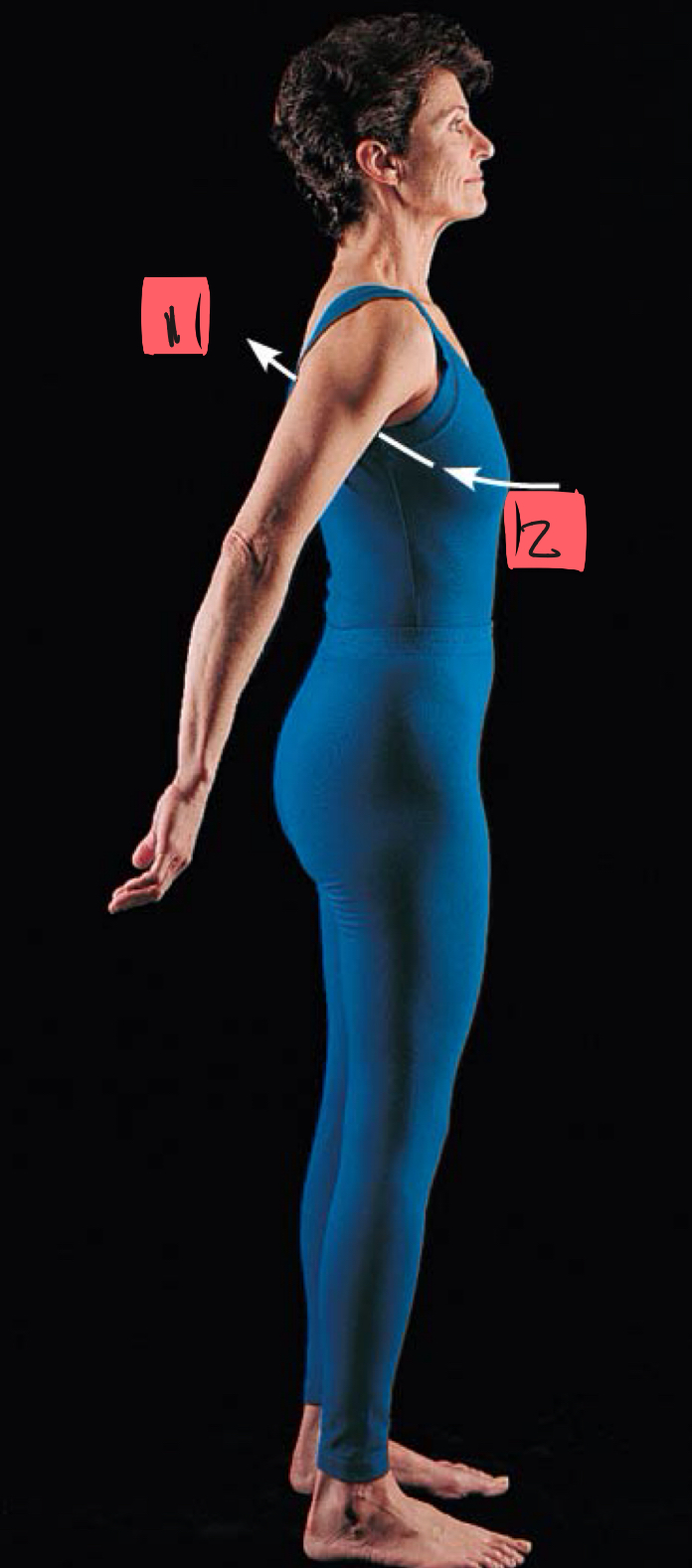

2
extension
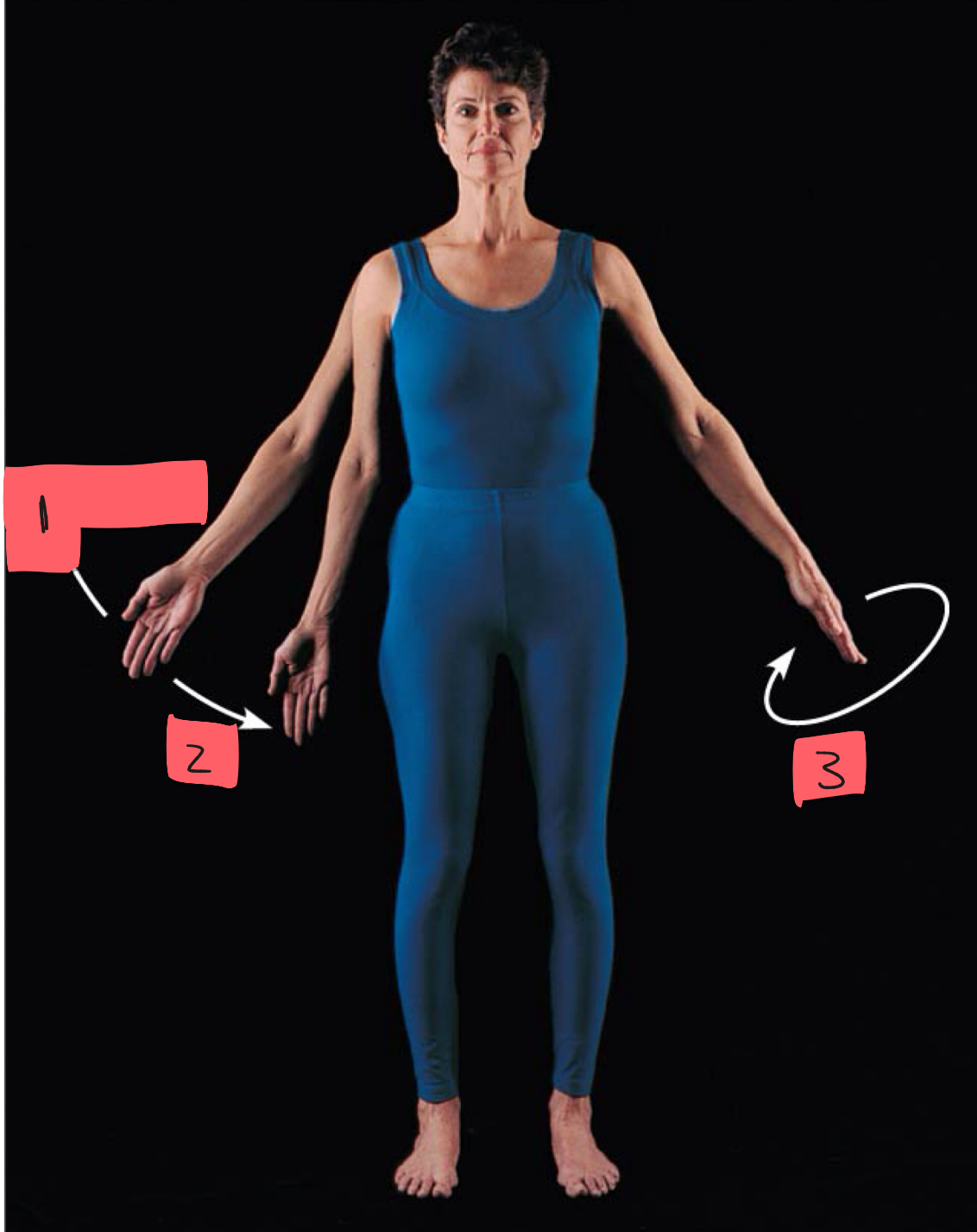
1
abduction
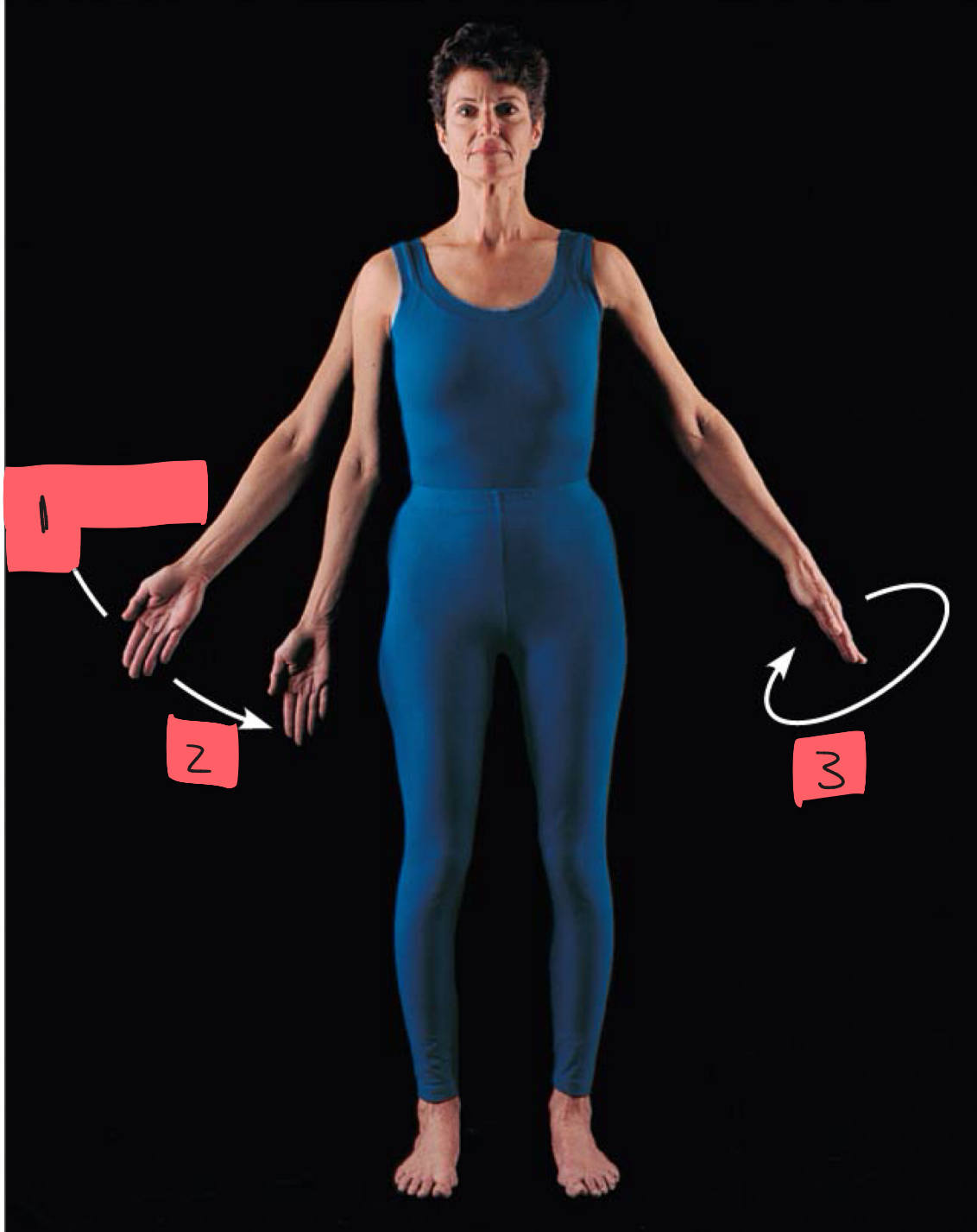
2
adduction
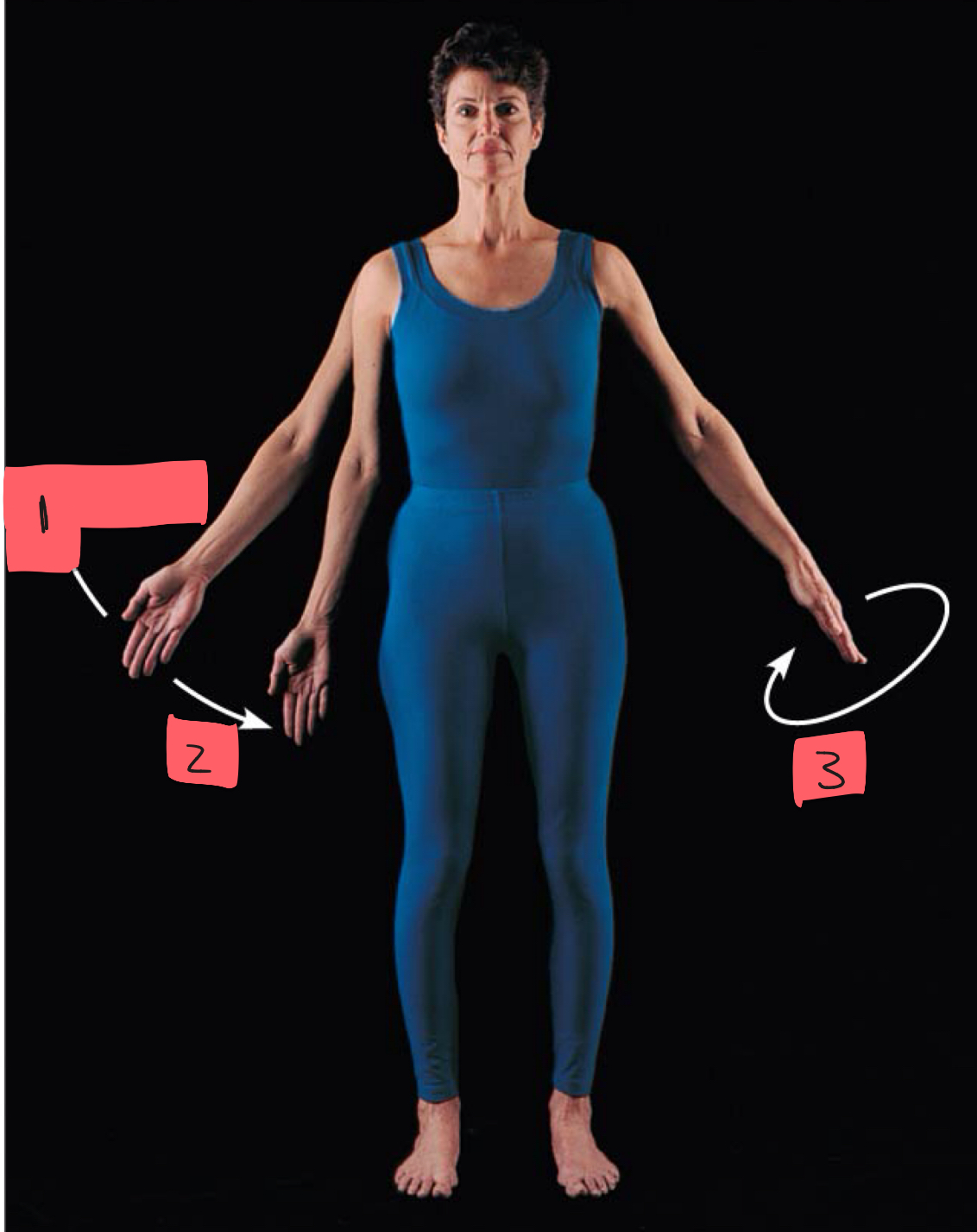
3
circumduction
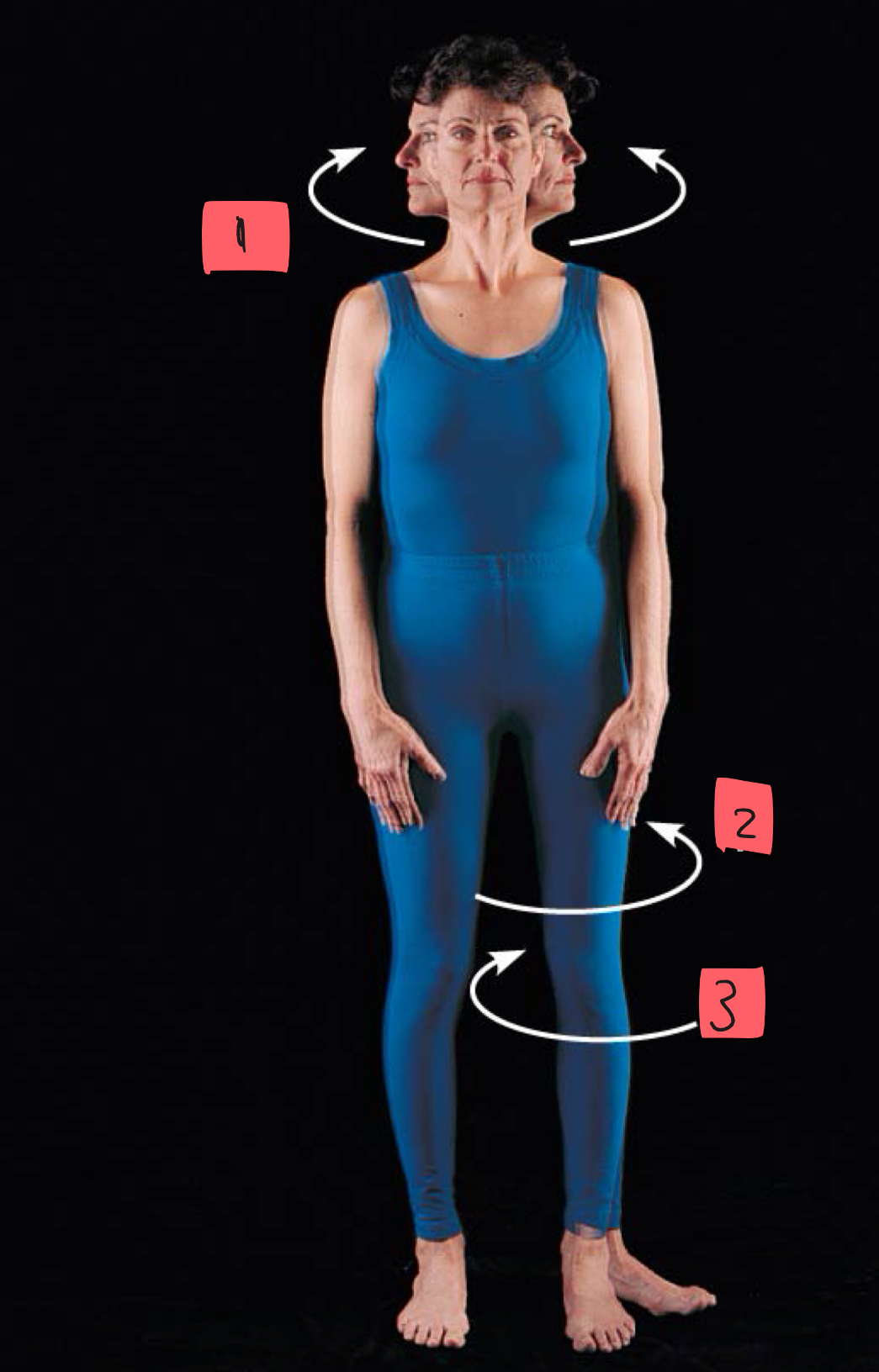

1
rotation
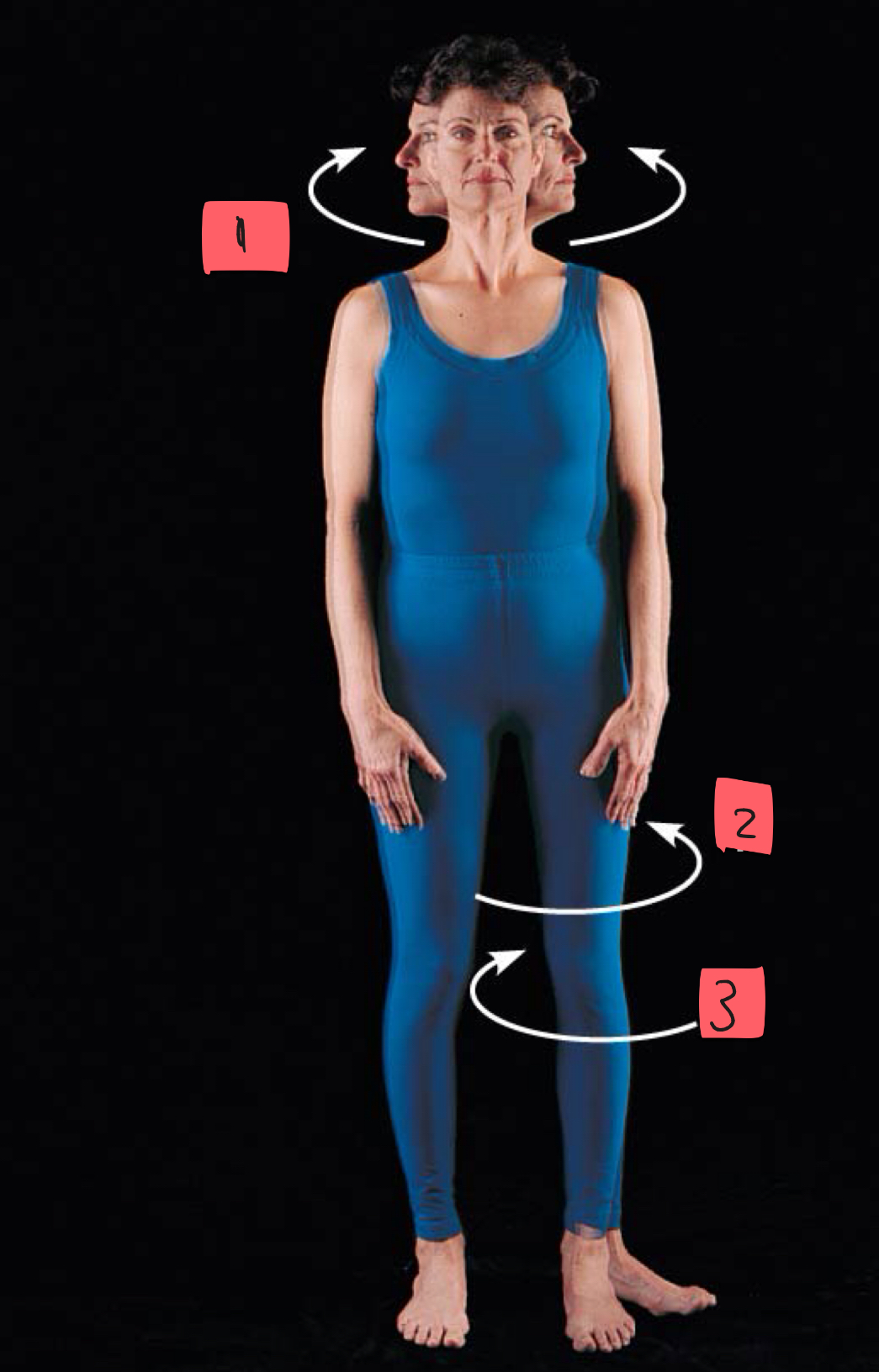

2
lateral rotation
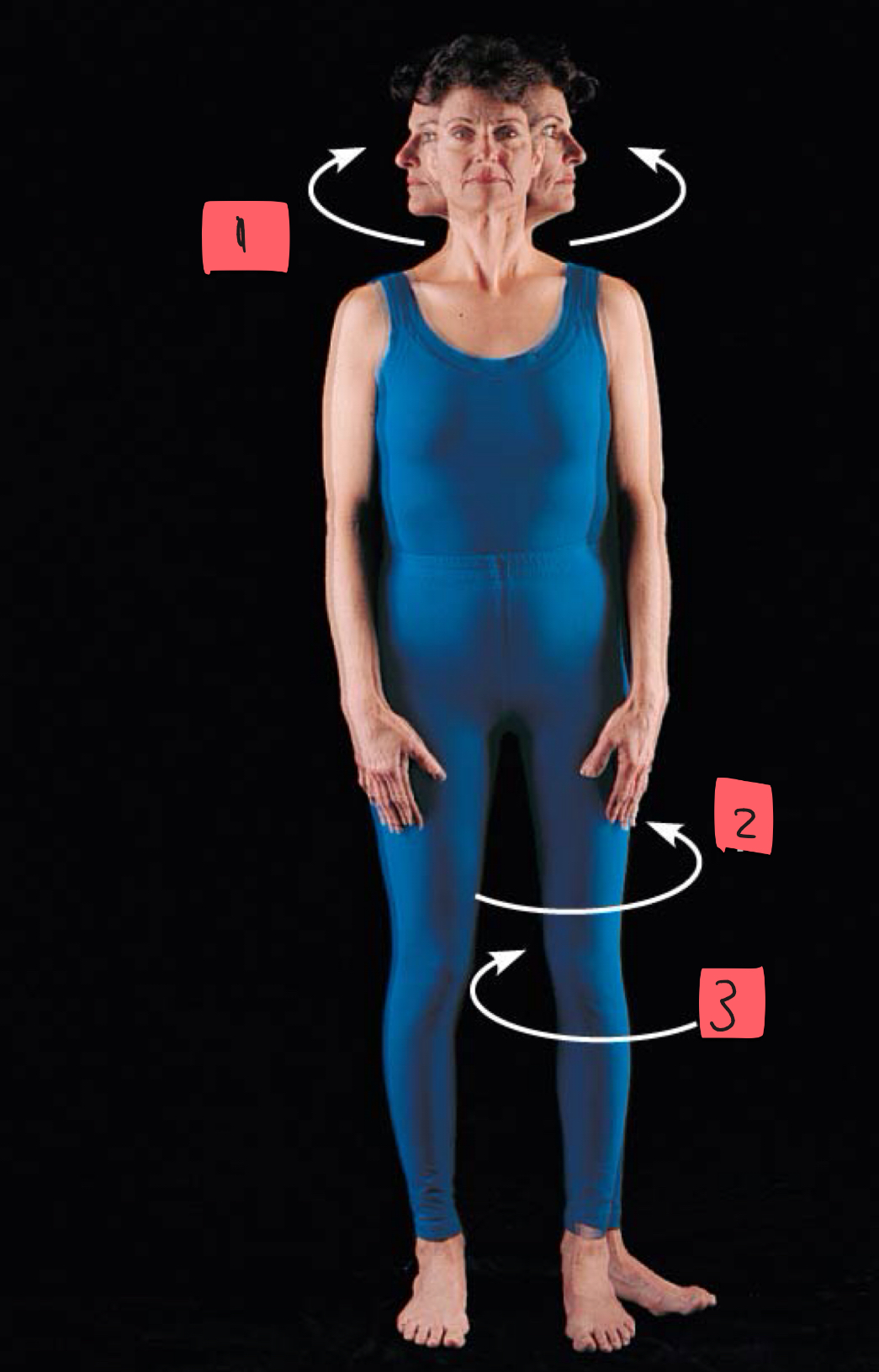

3
medial rotation
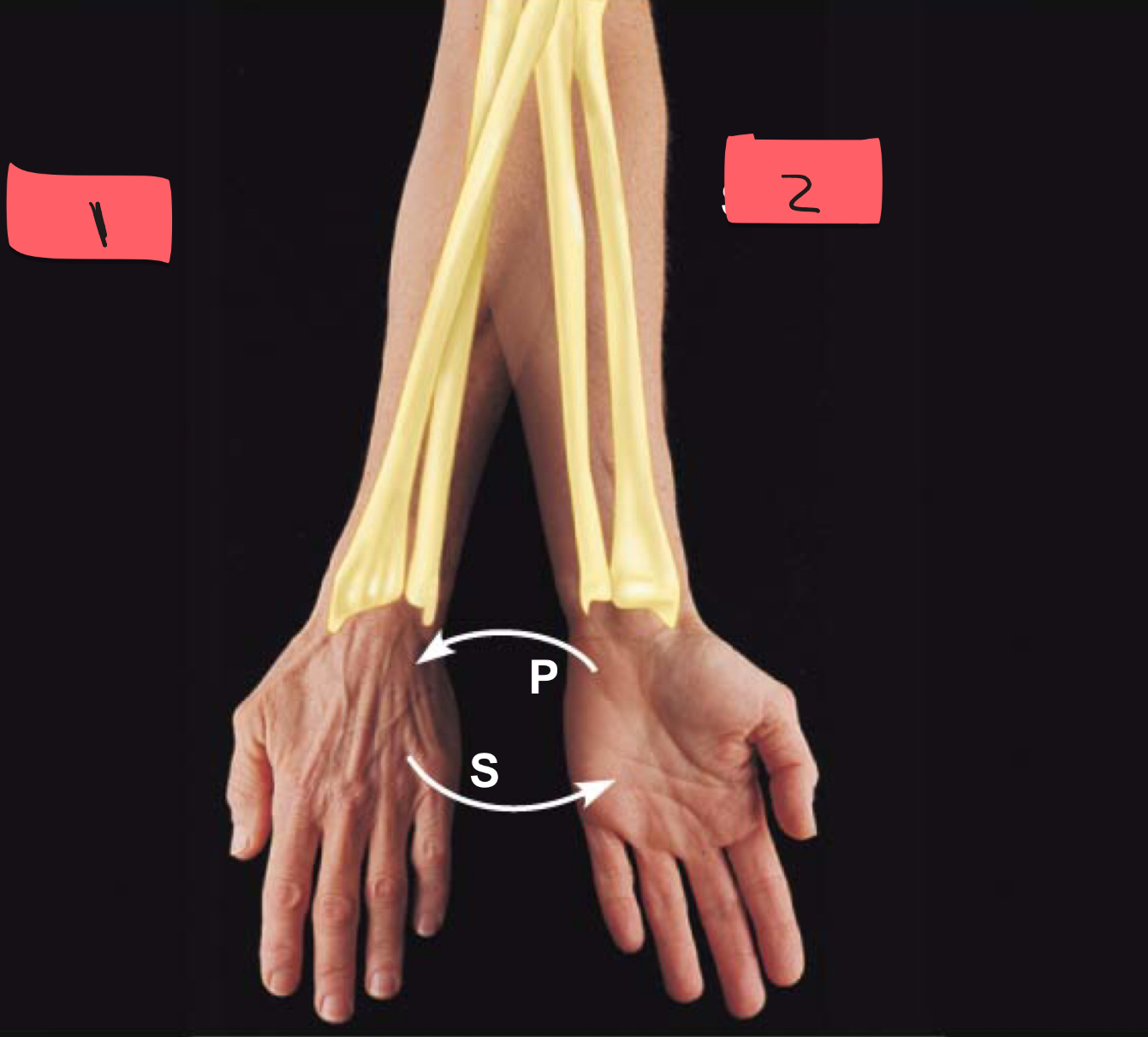
1
pronation
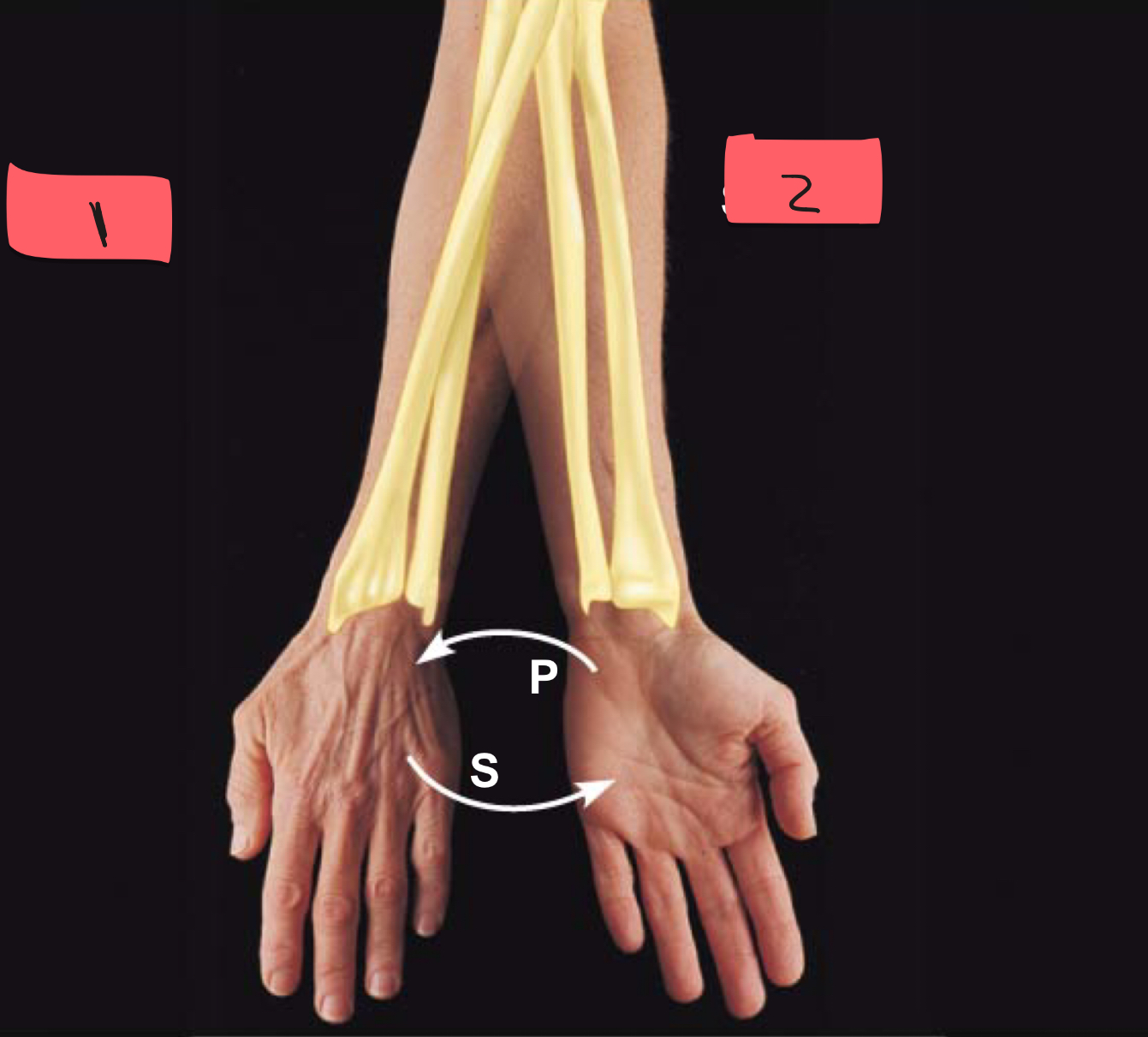
2
supination
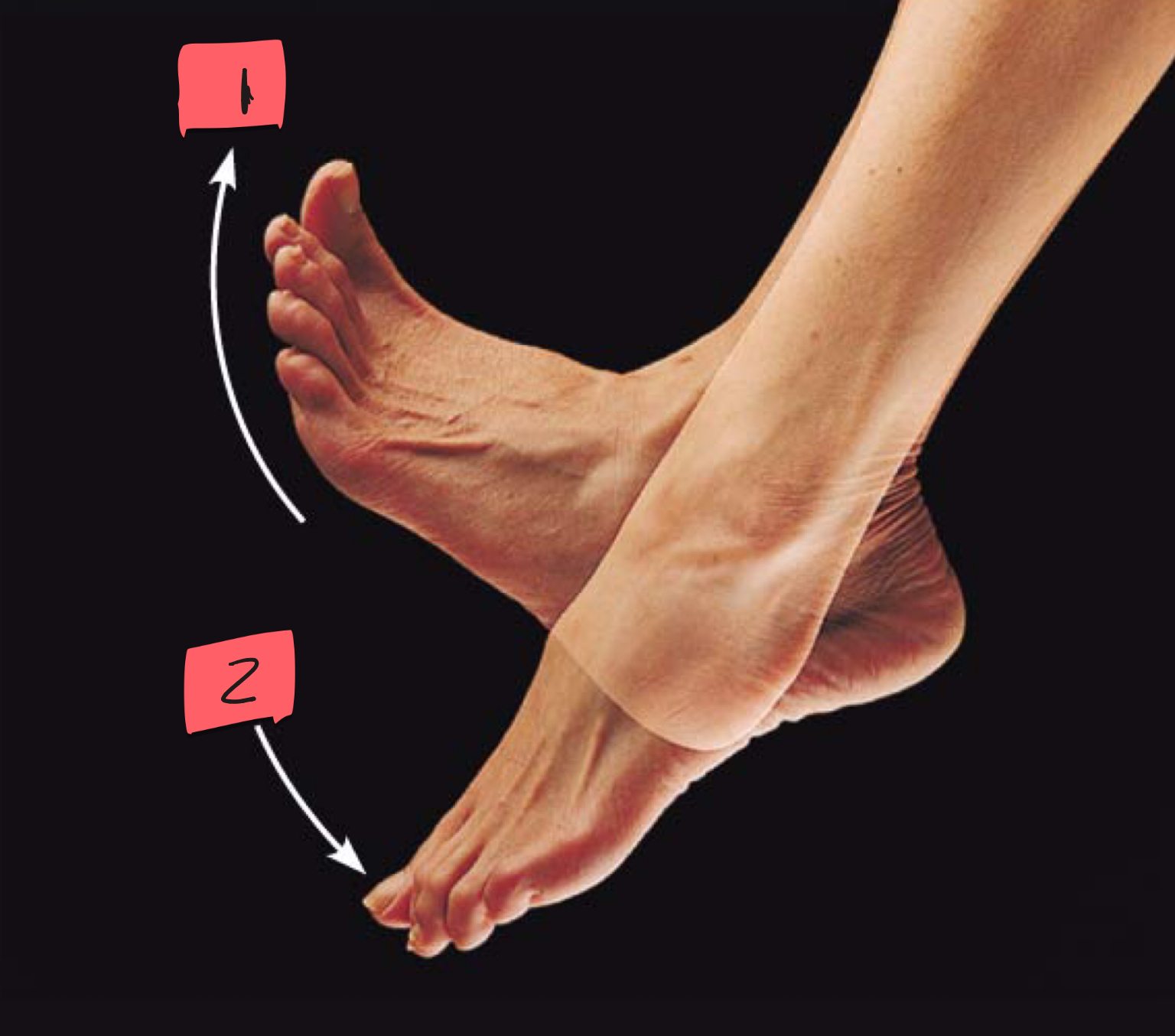
1
dorsiflexion
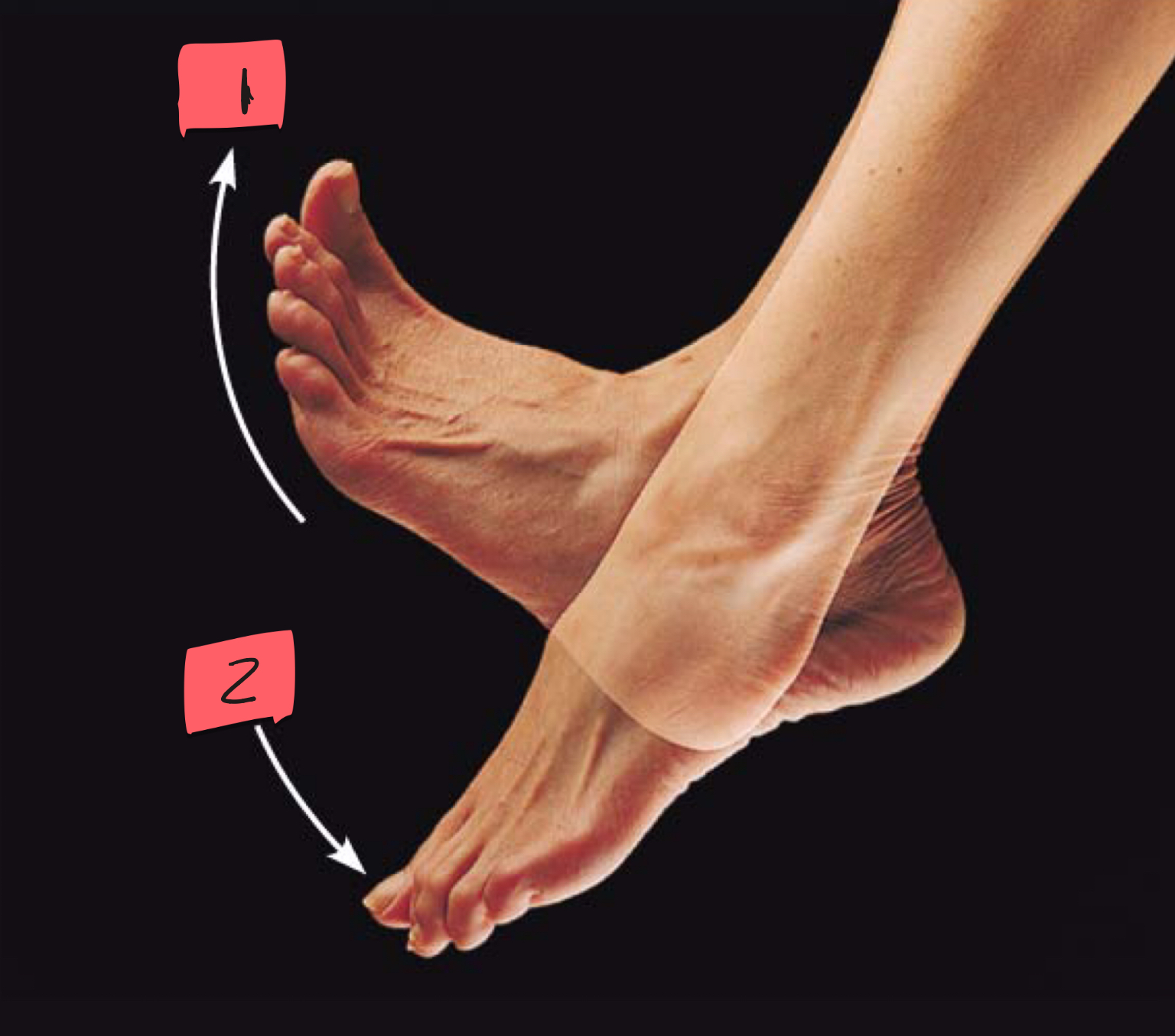
2
plantar flexion
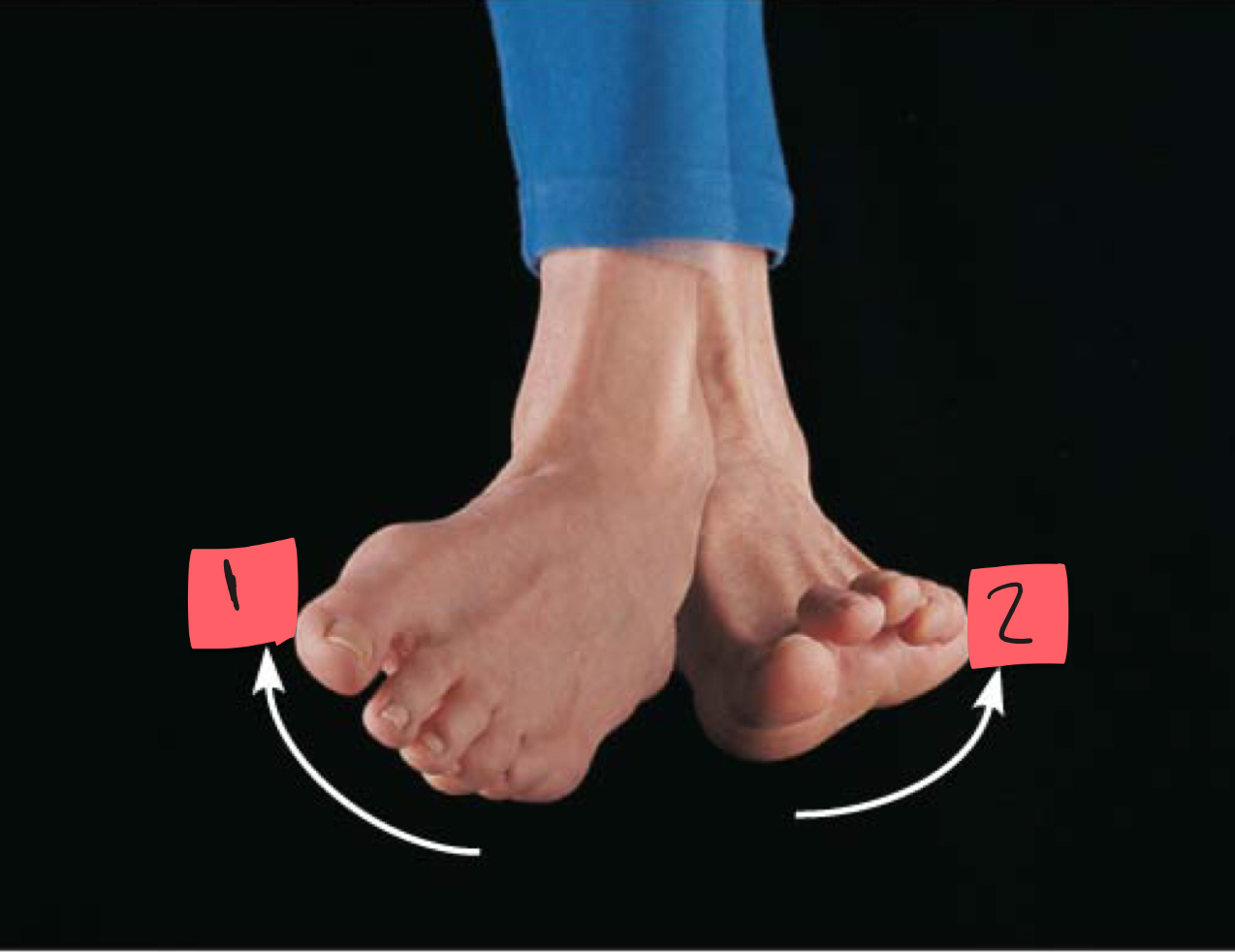
1
inversion
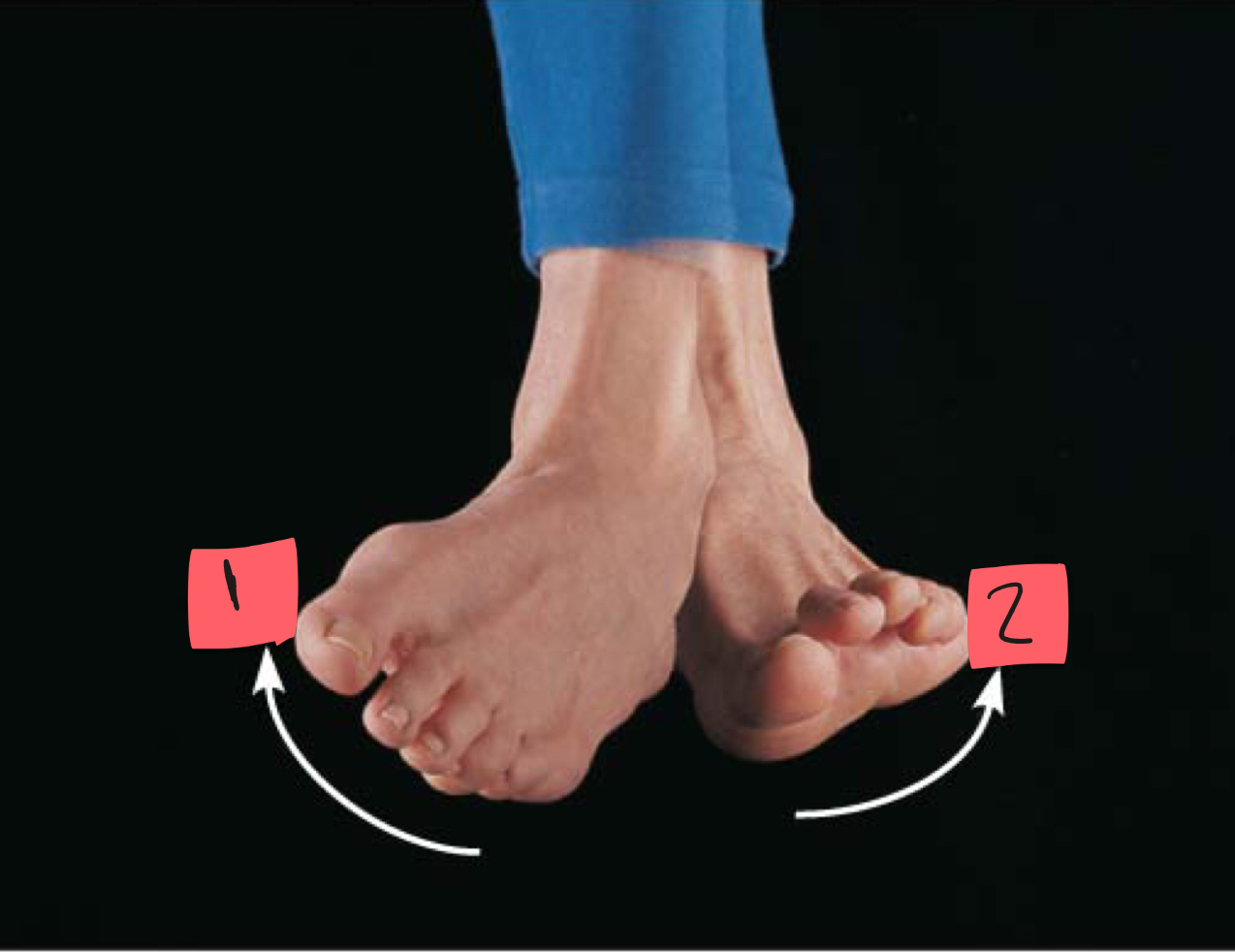
2
eversion
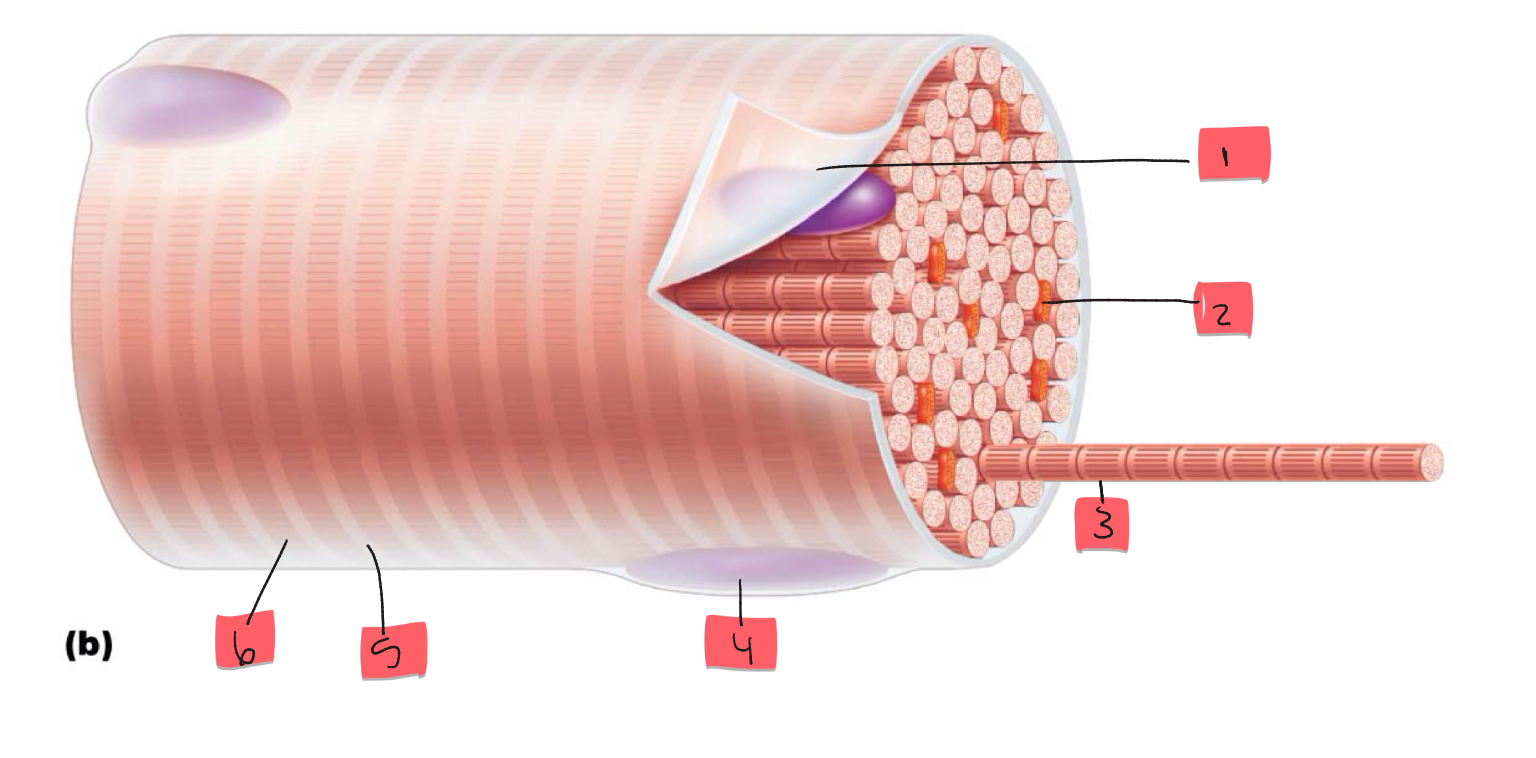
1
sarcolemma
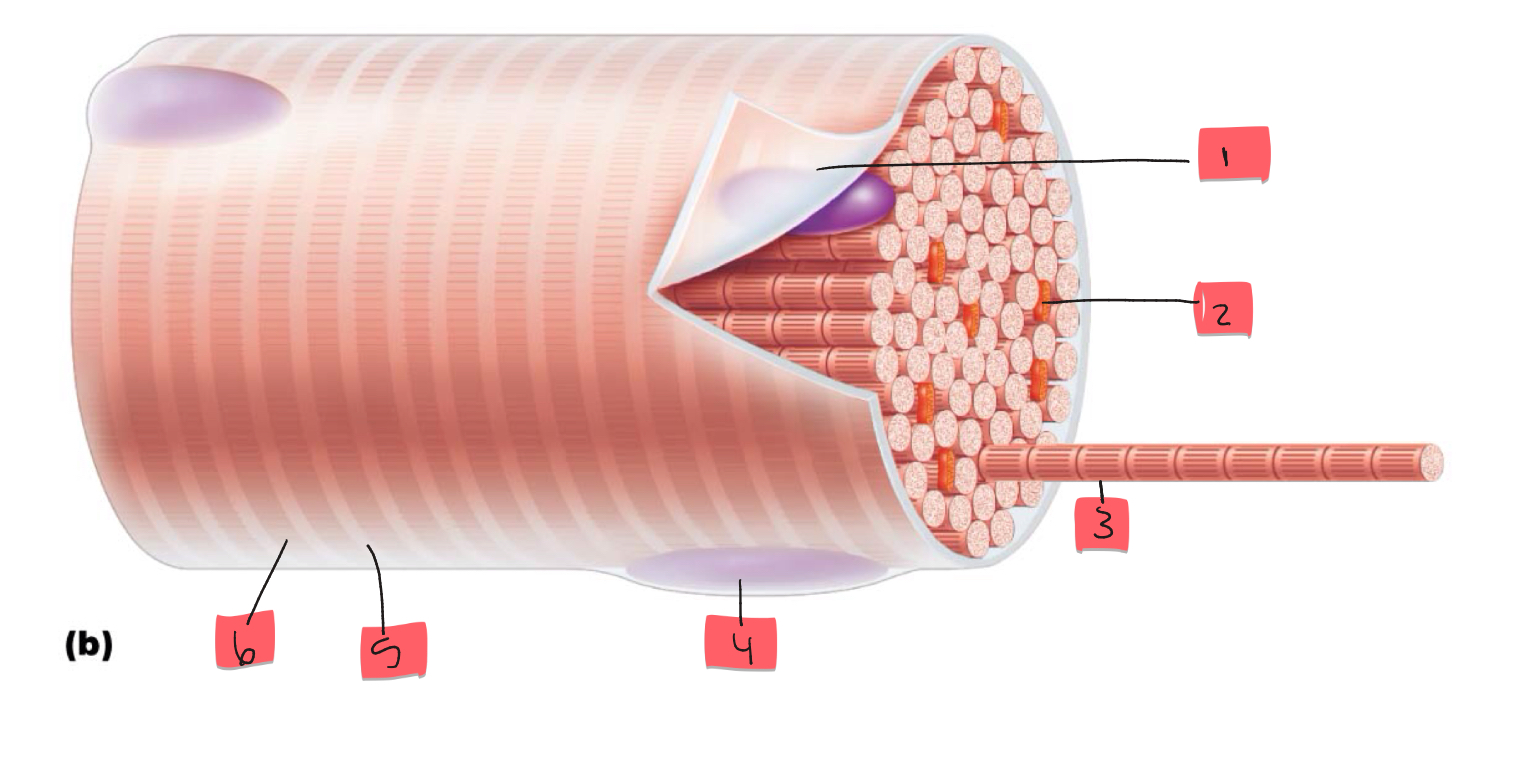
2
mitochondrion
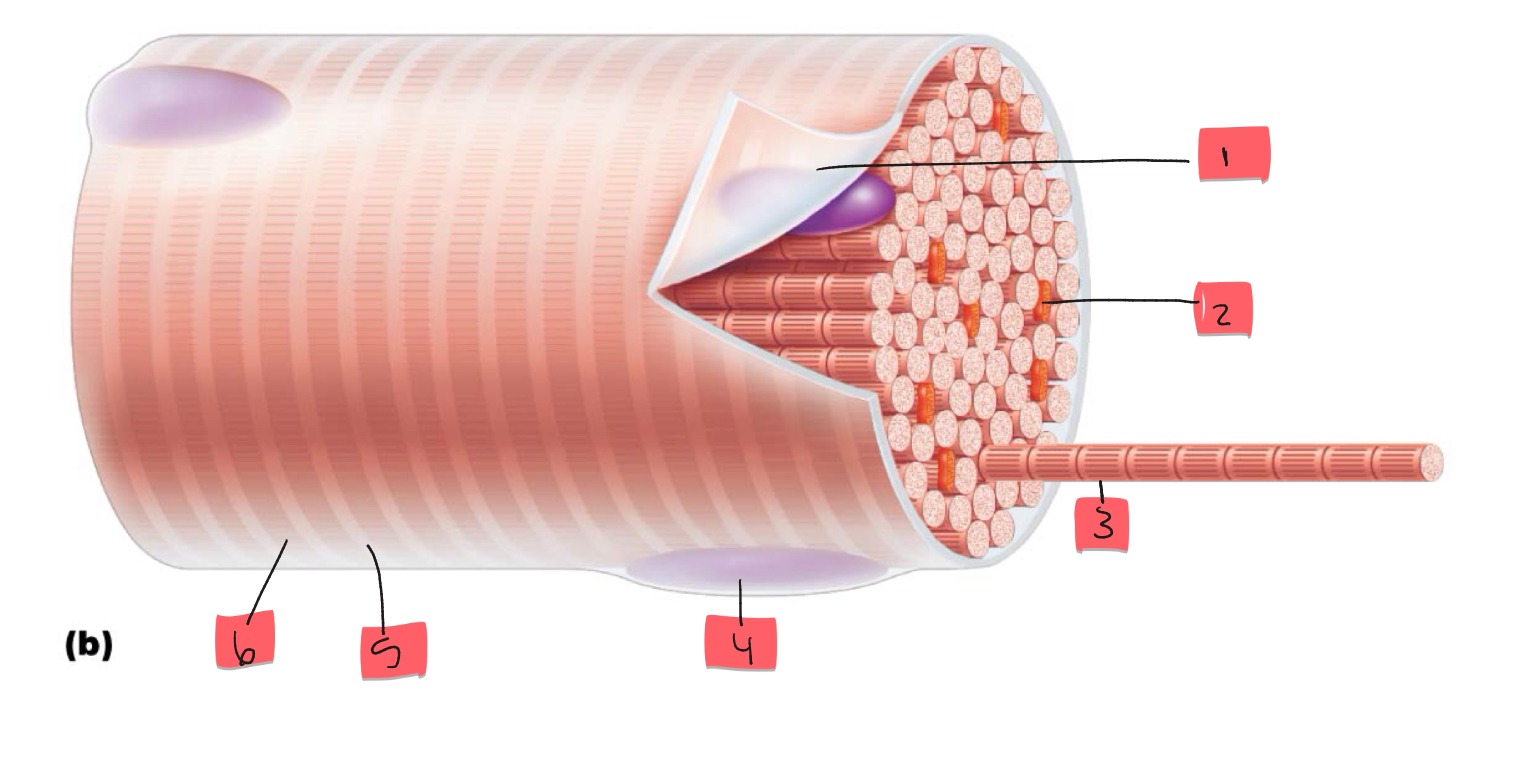
3
myofibril
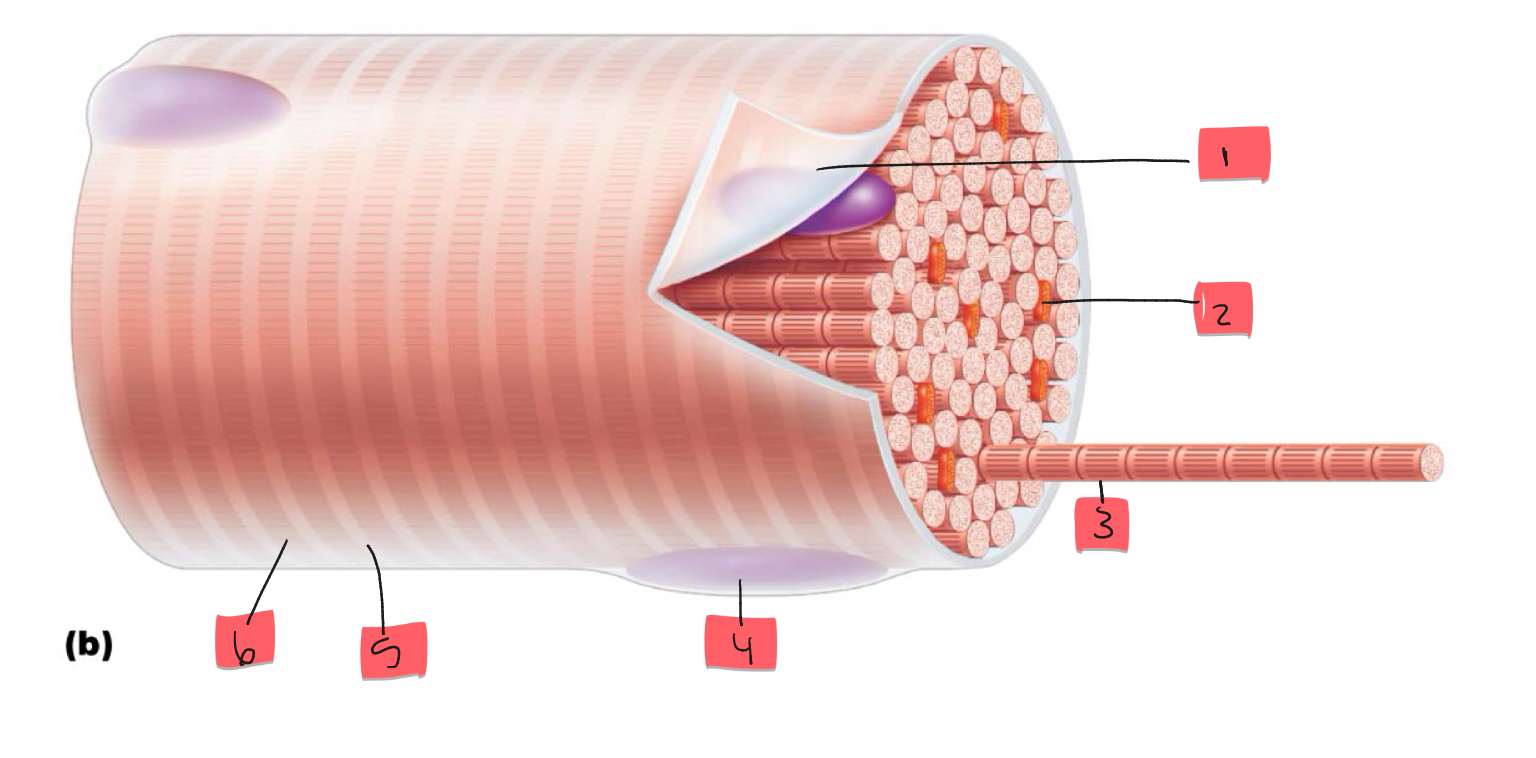
4
nucleus
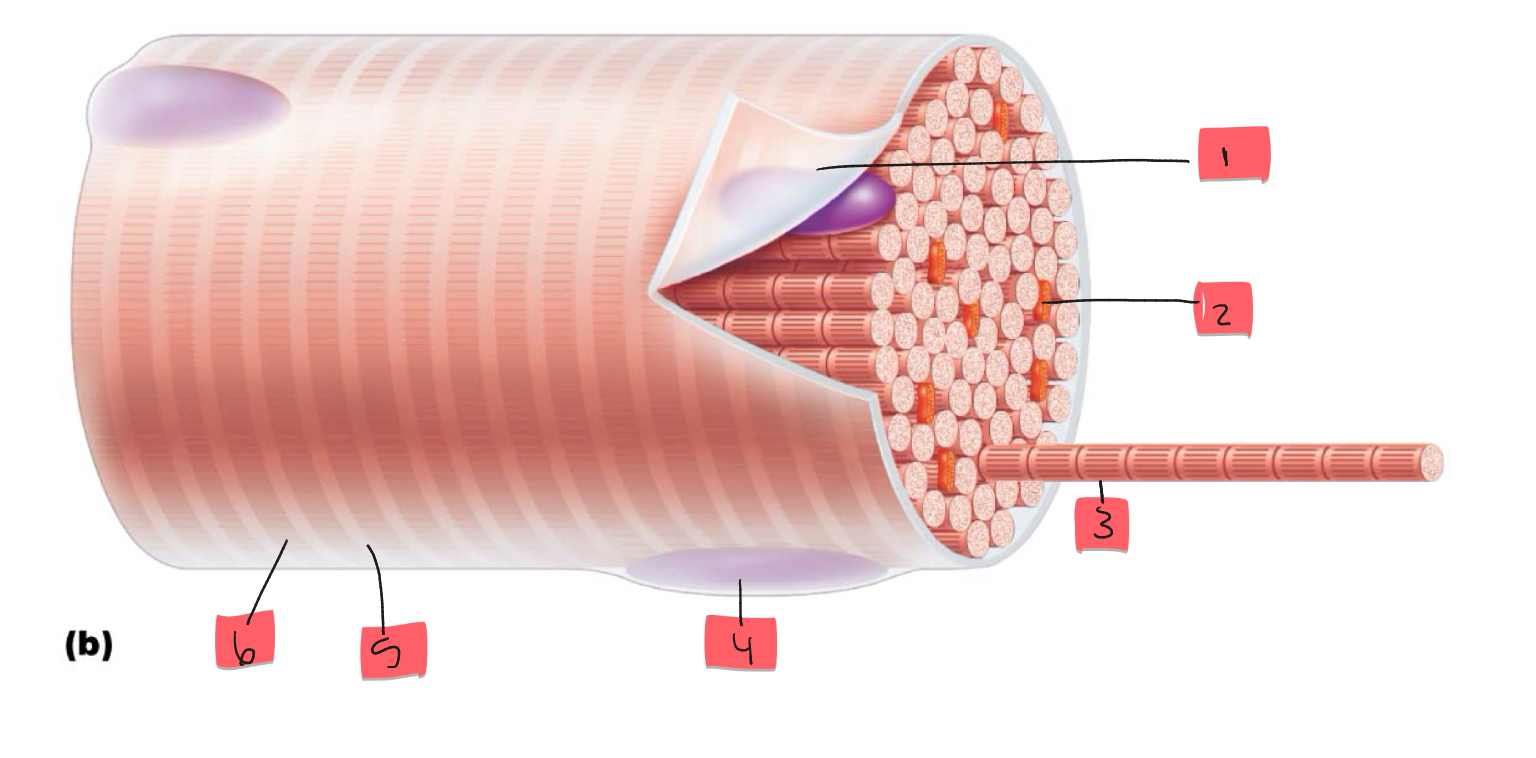
5
light I band
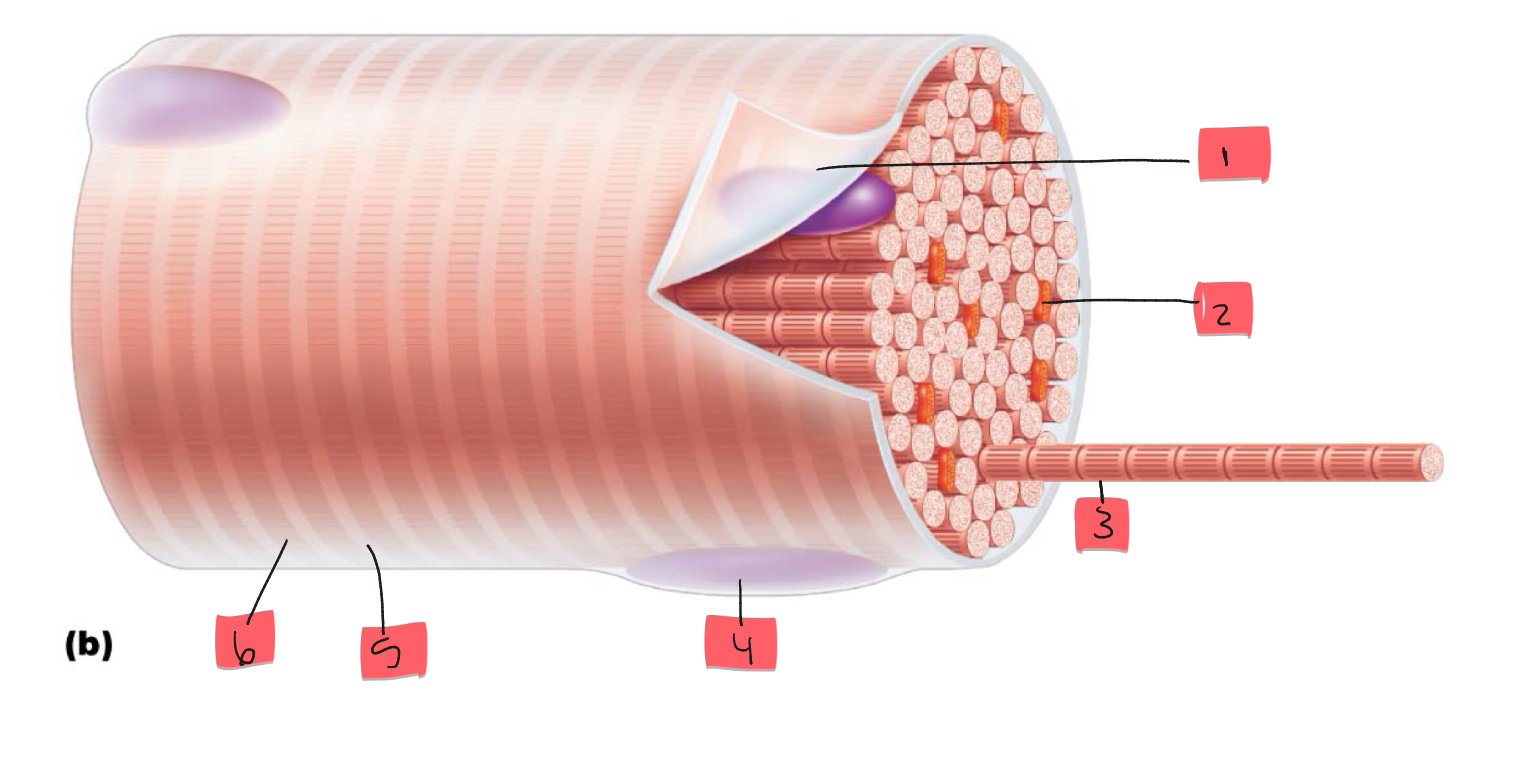
6
Dark A band
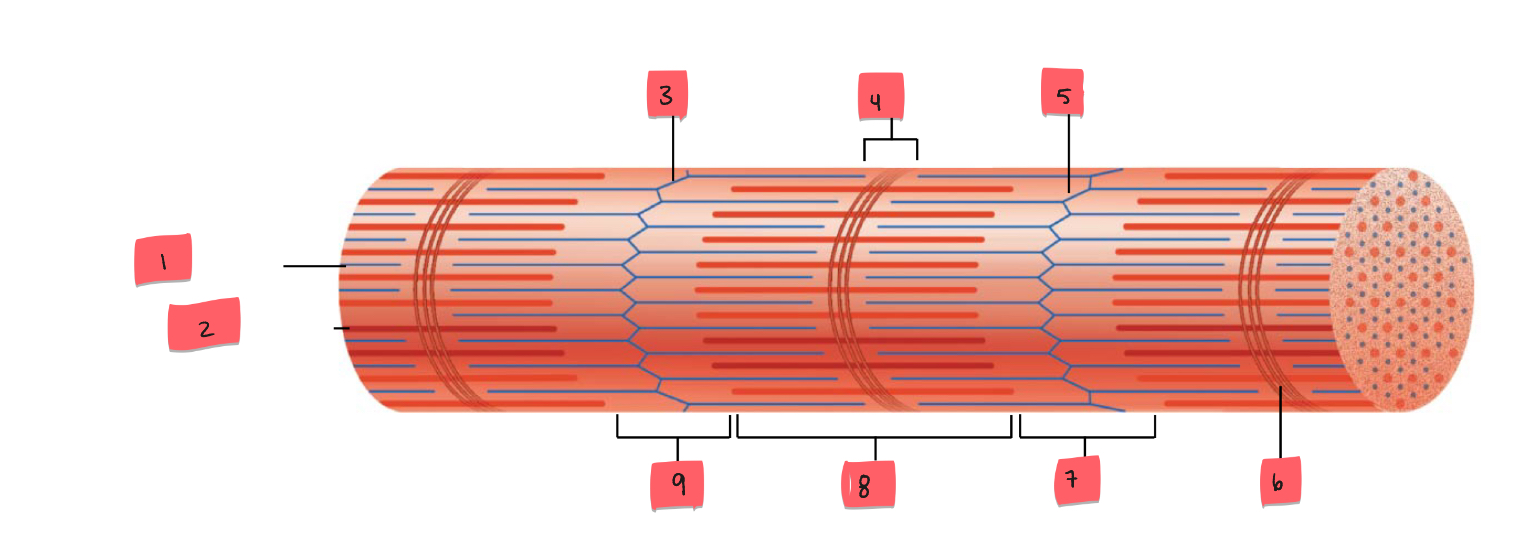
1
thin (actin) filament
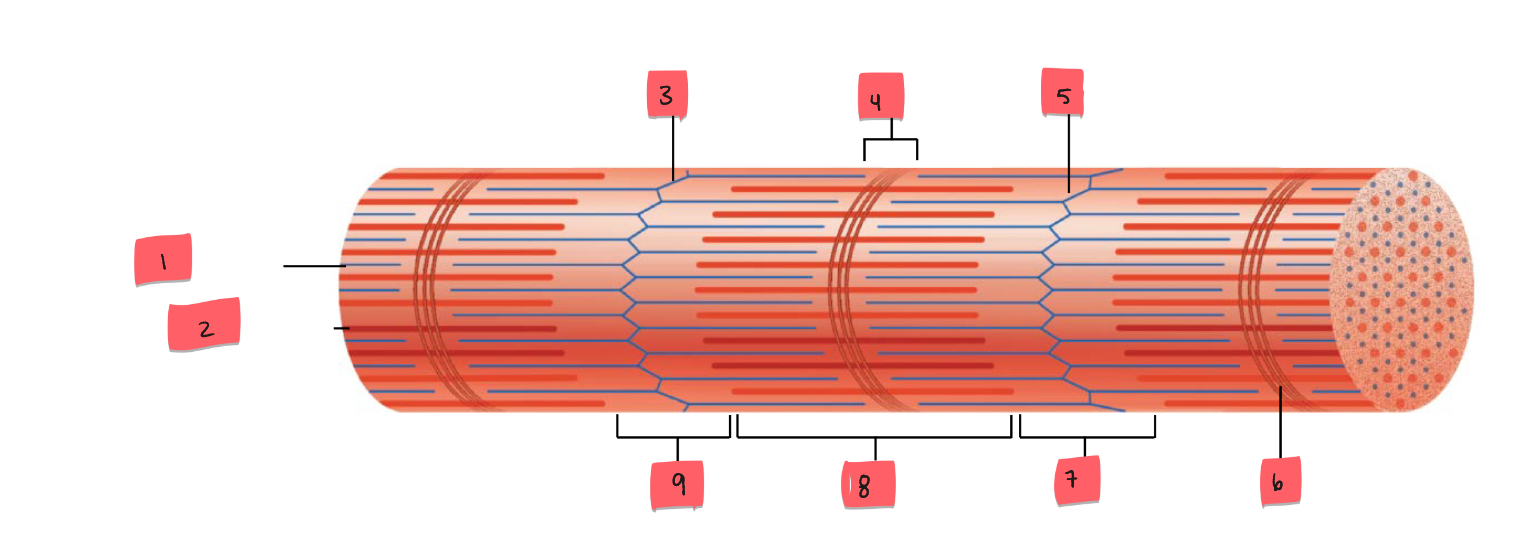
2
thick (myosin) filament
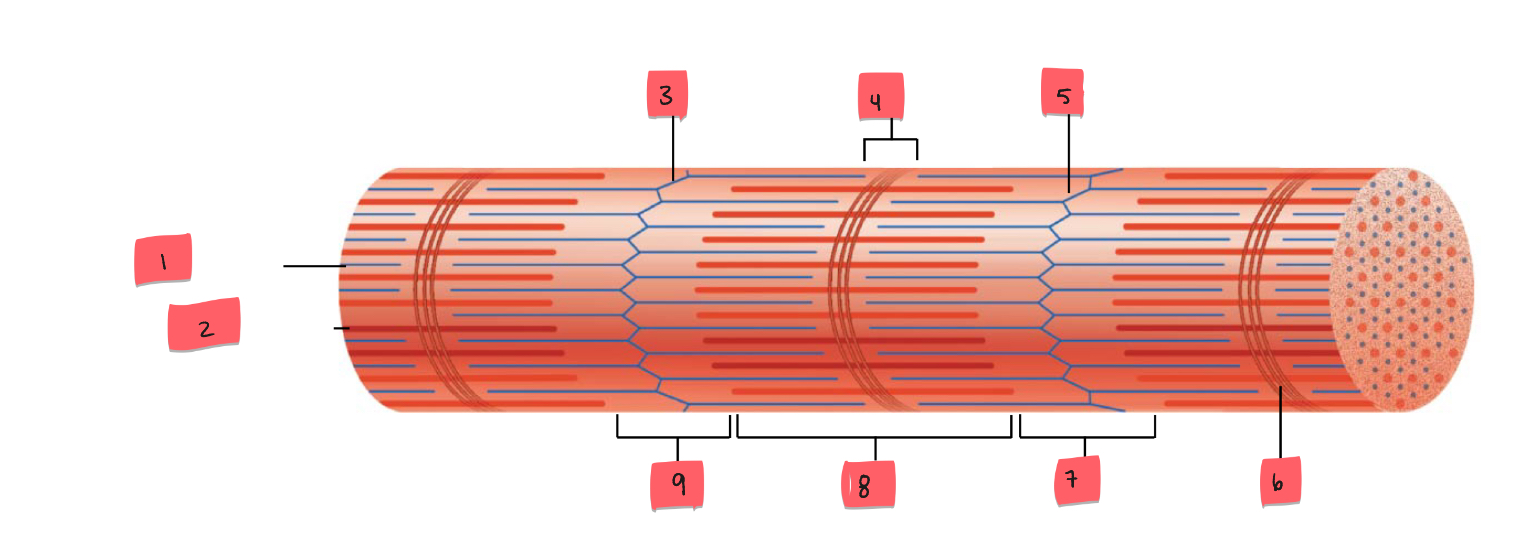
3
Z disc
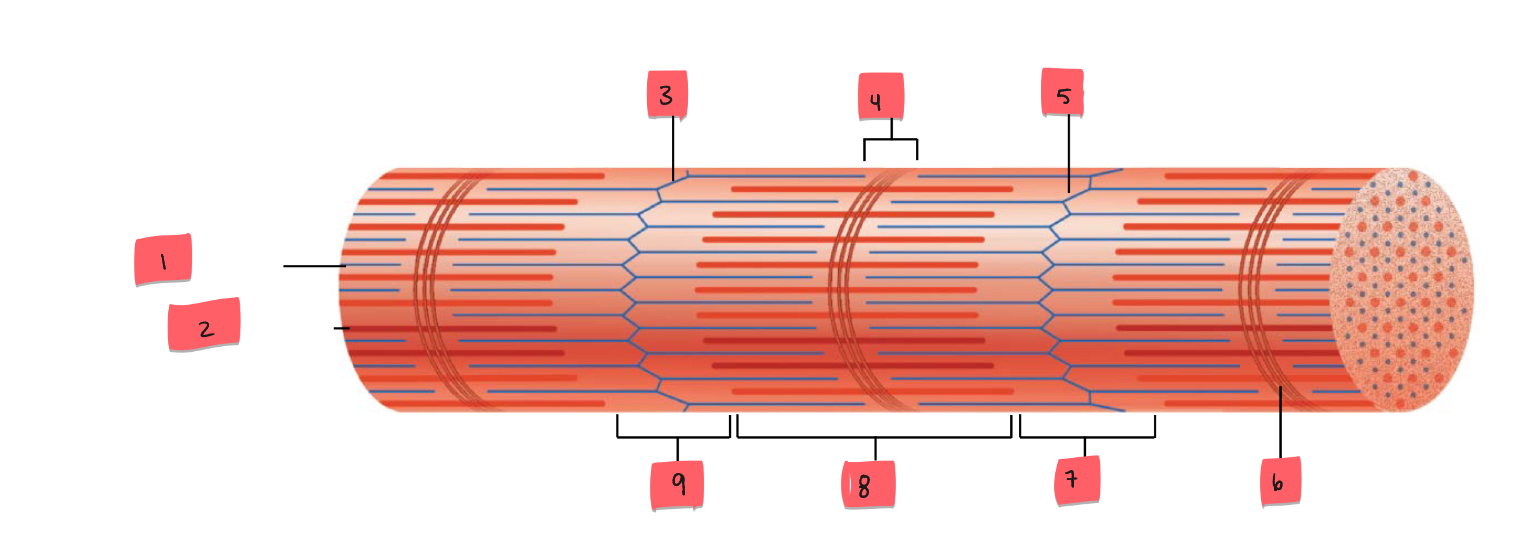
4
H zone
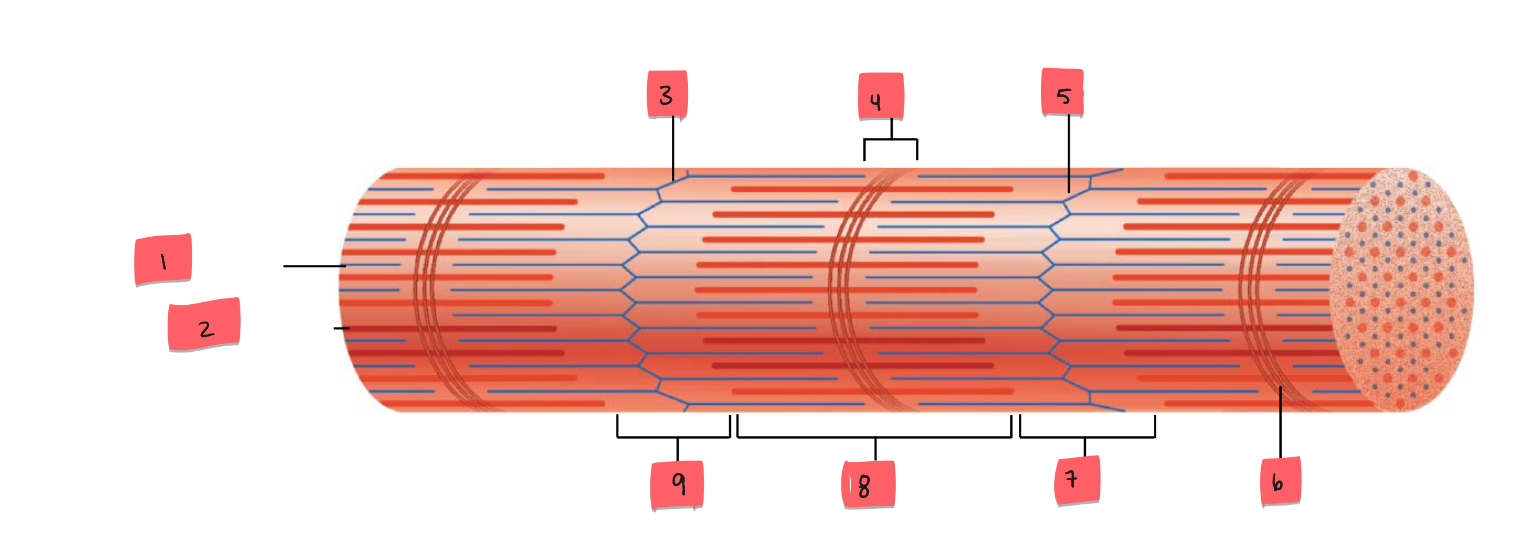
5
Z disc
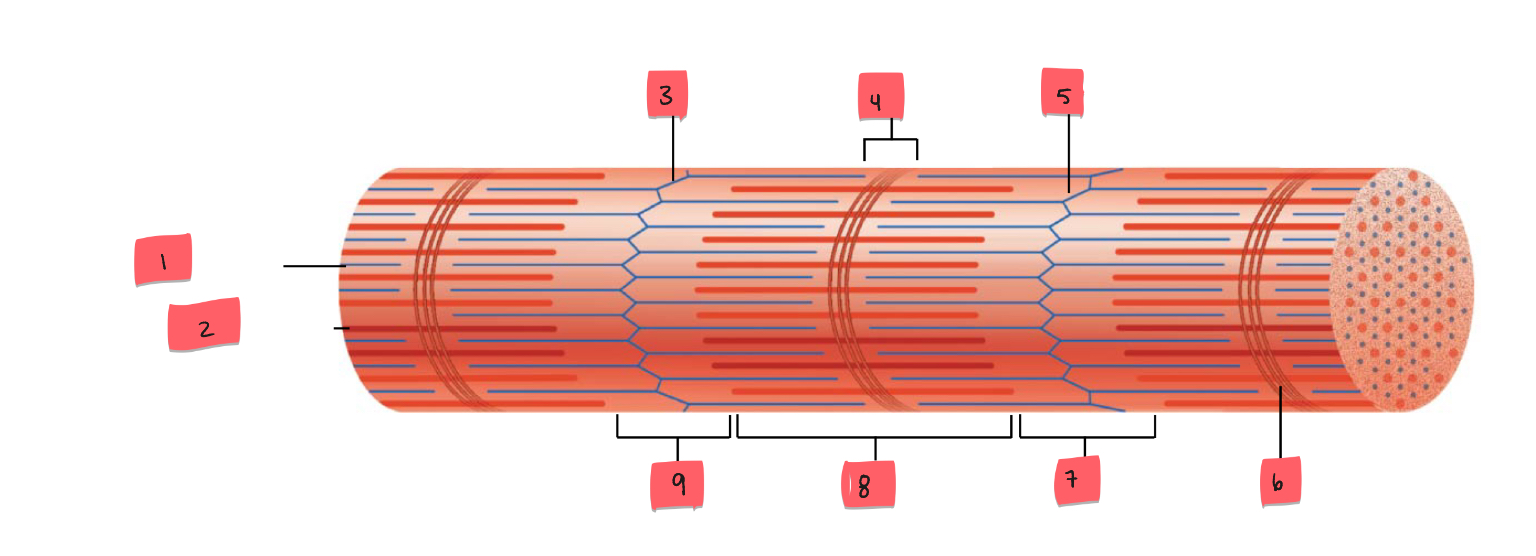
6
M line
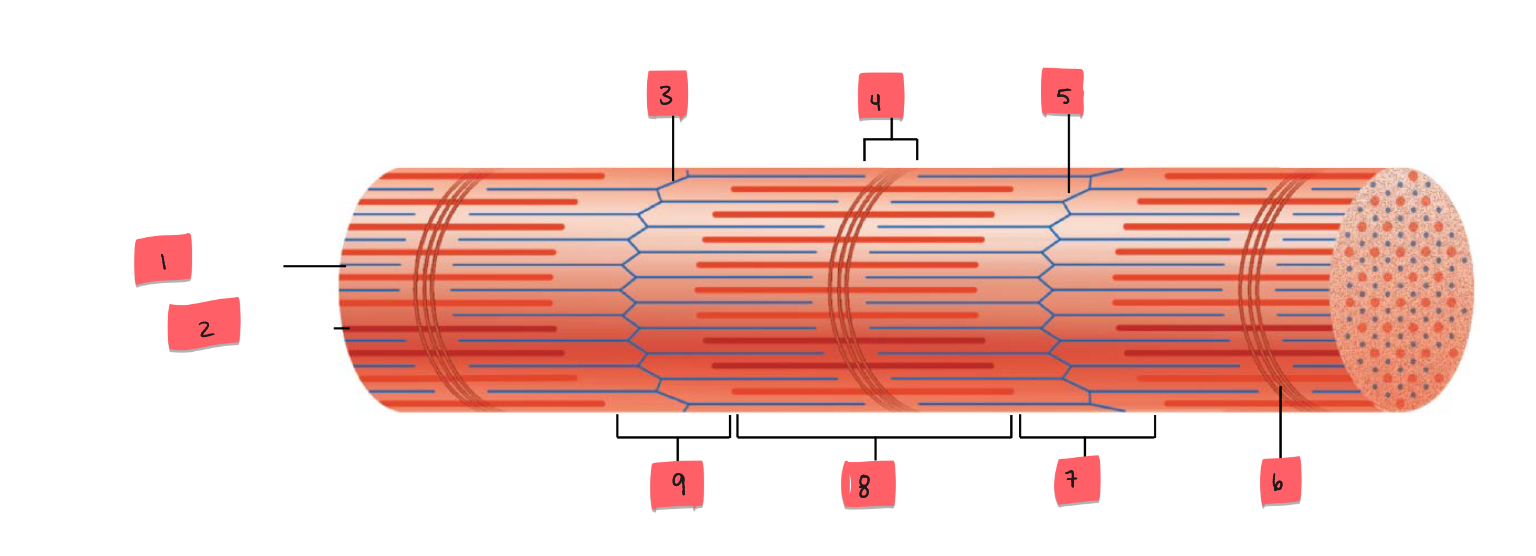
7
I band
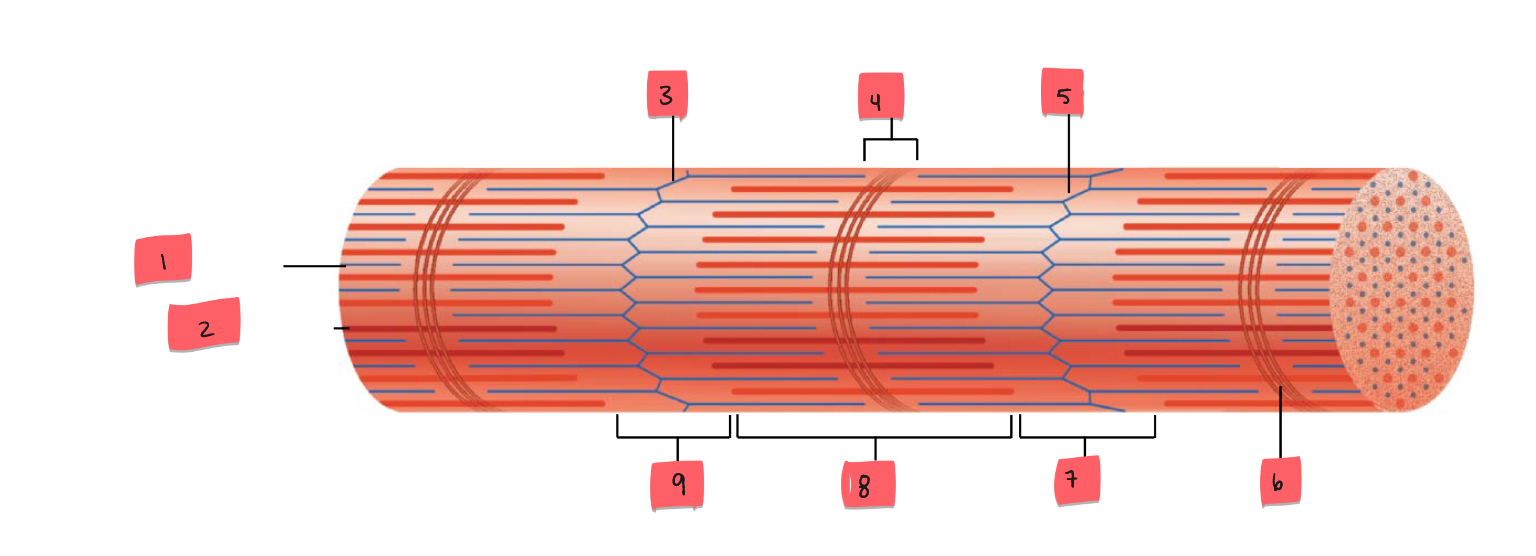
8
A band
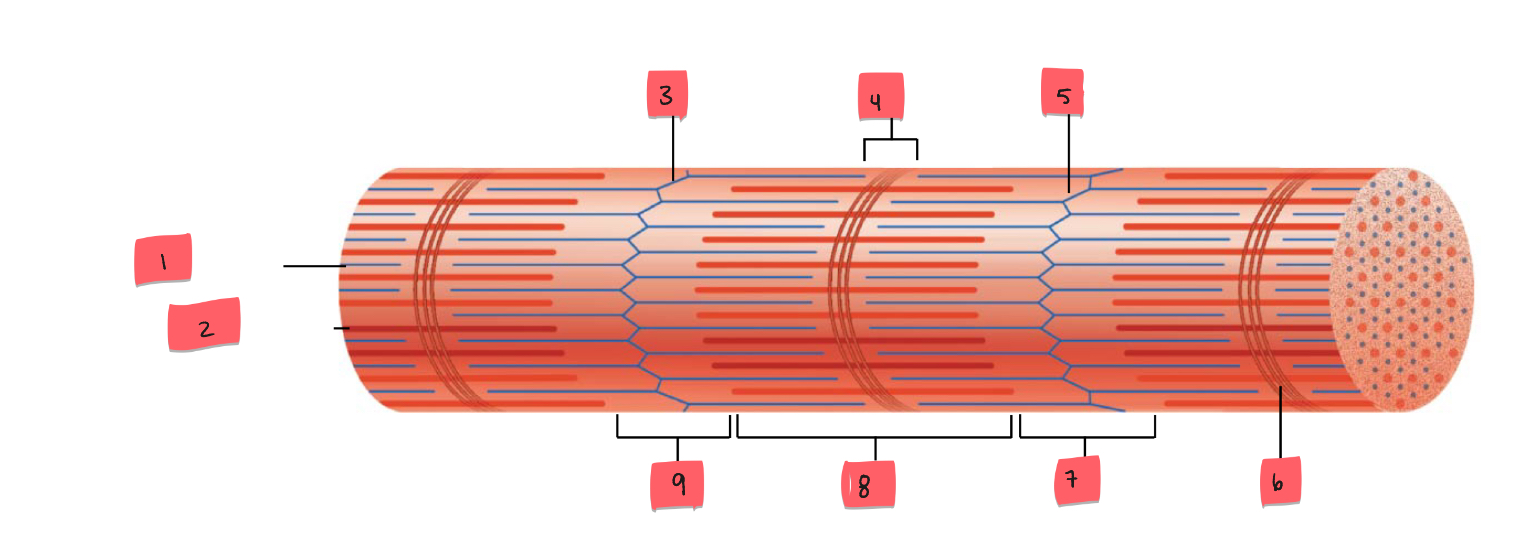
9
I band
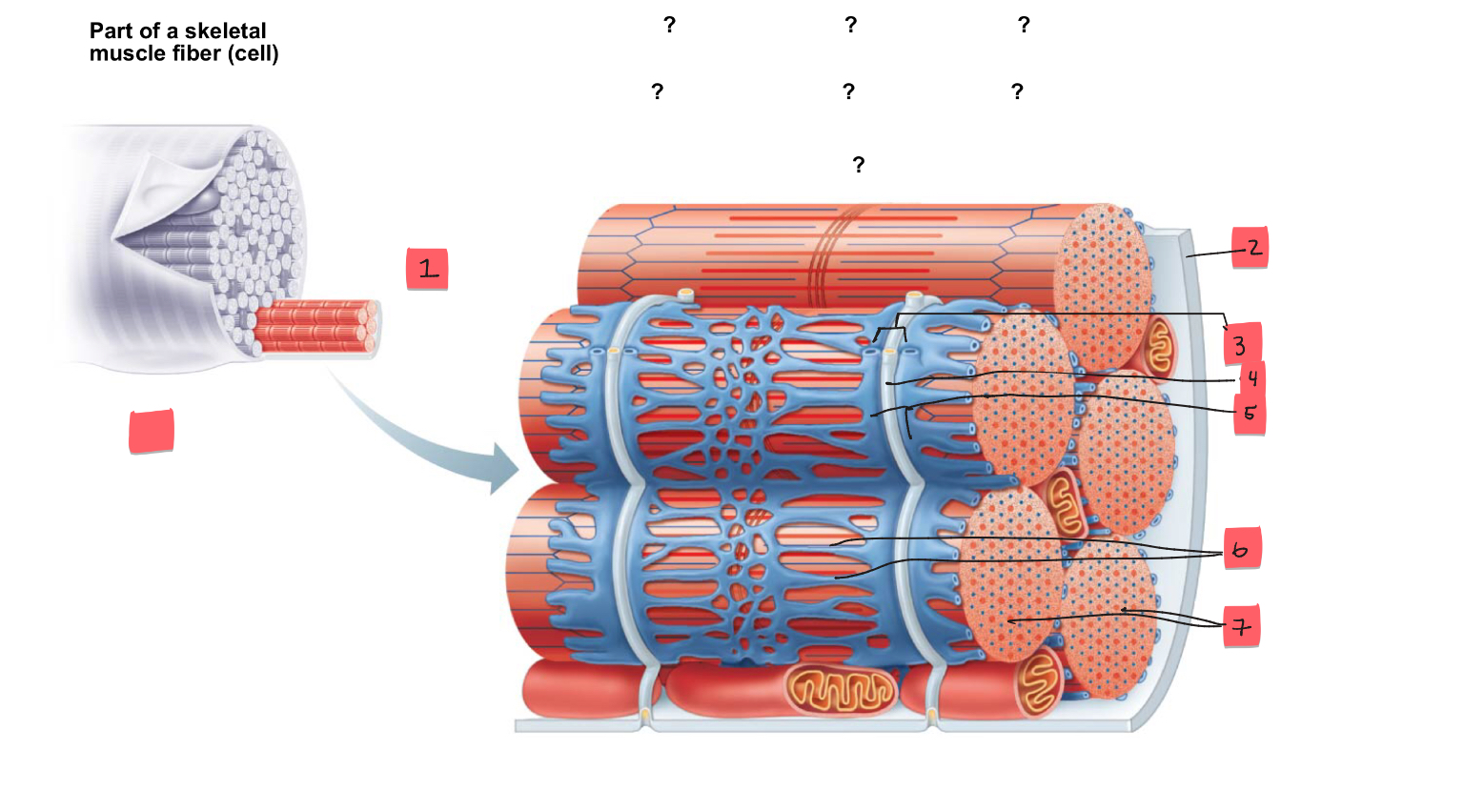
1
myofibril
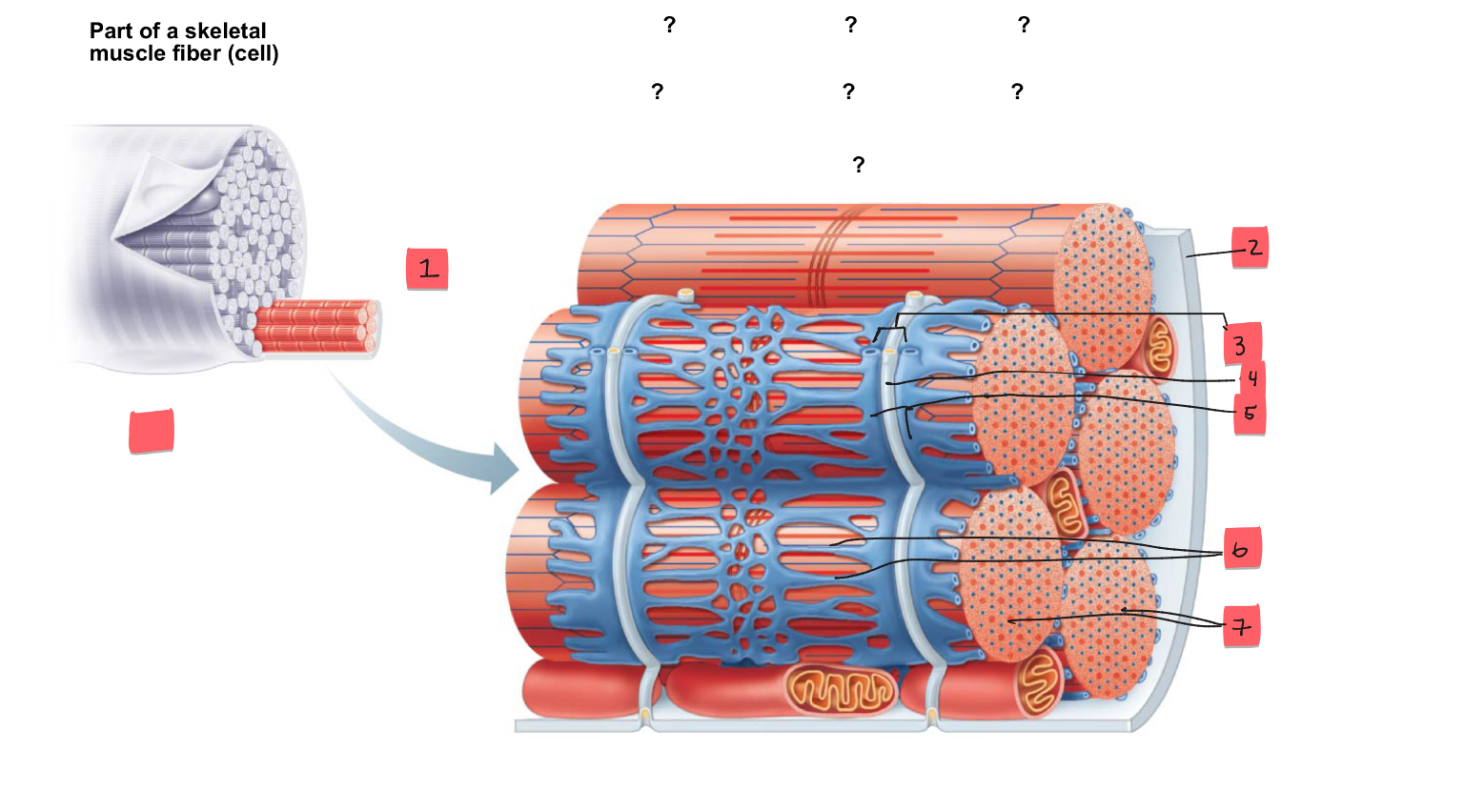
2
sarcolemma
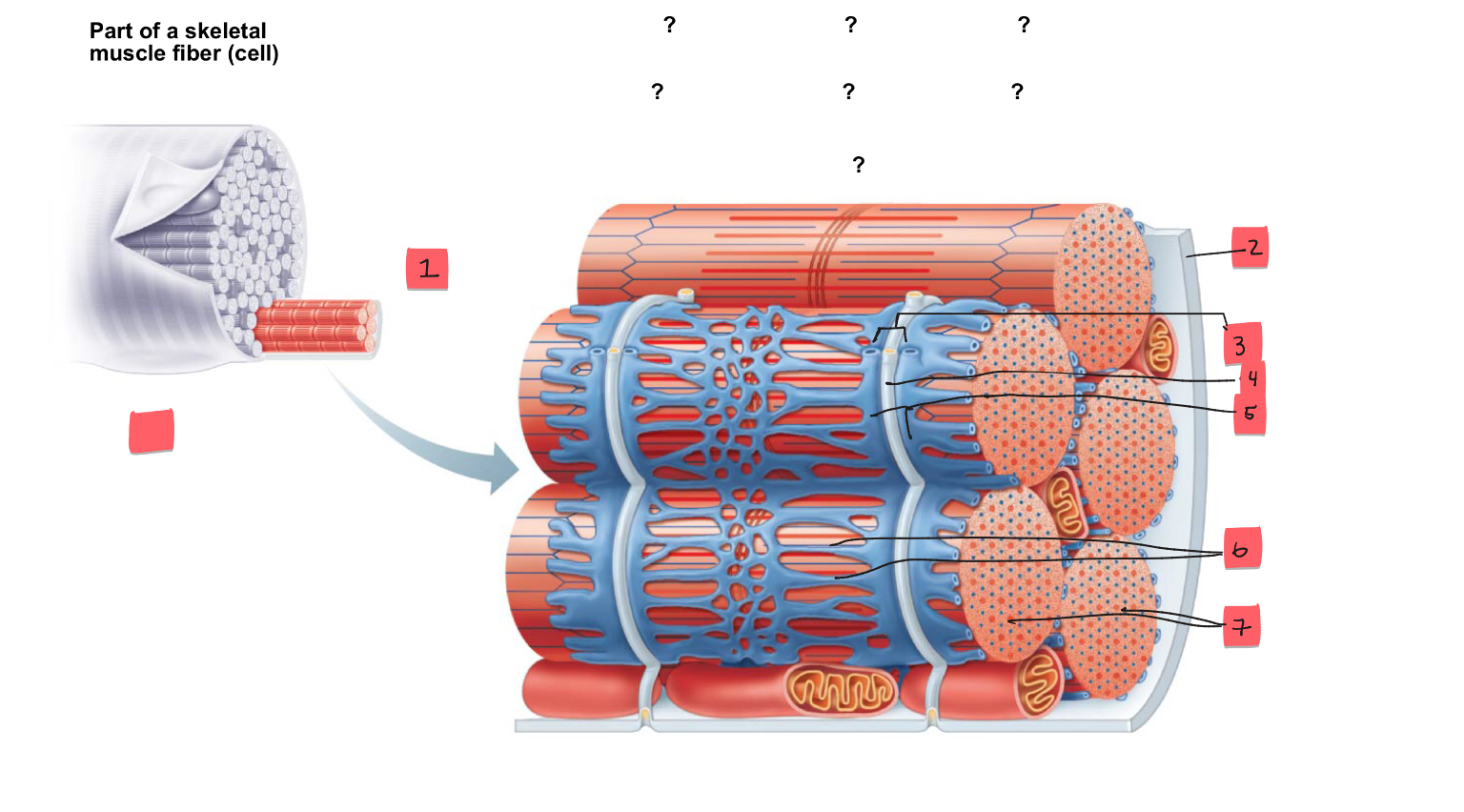
3
triad
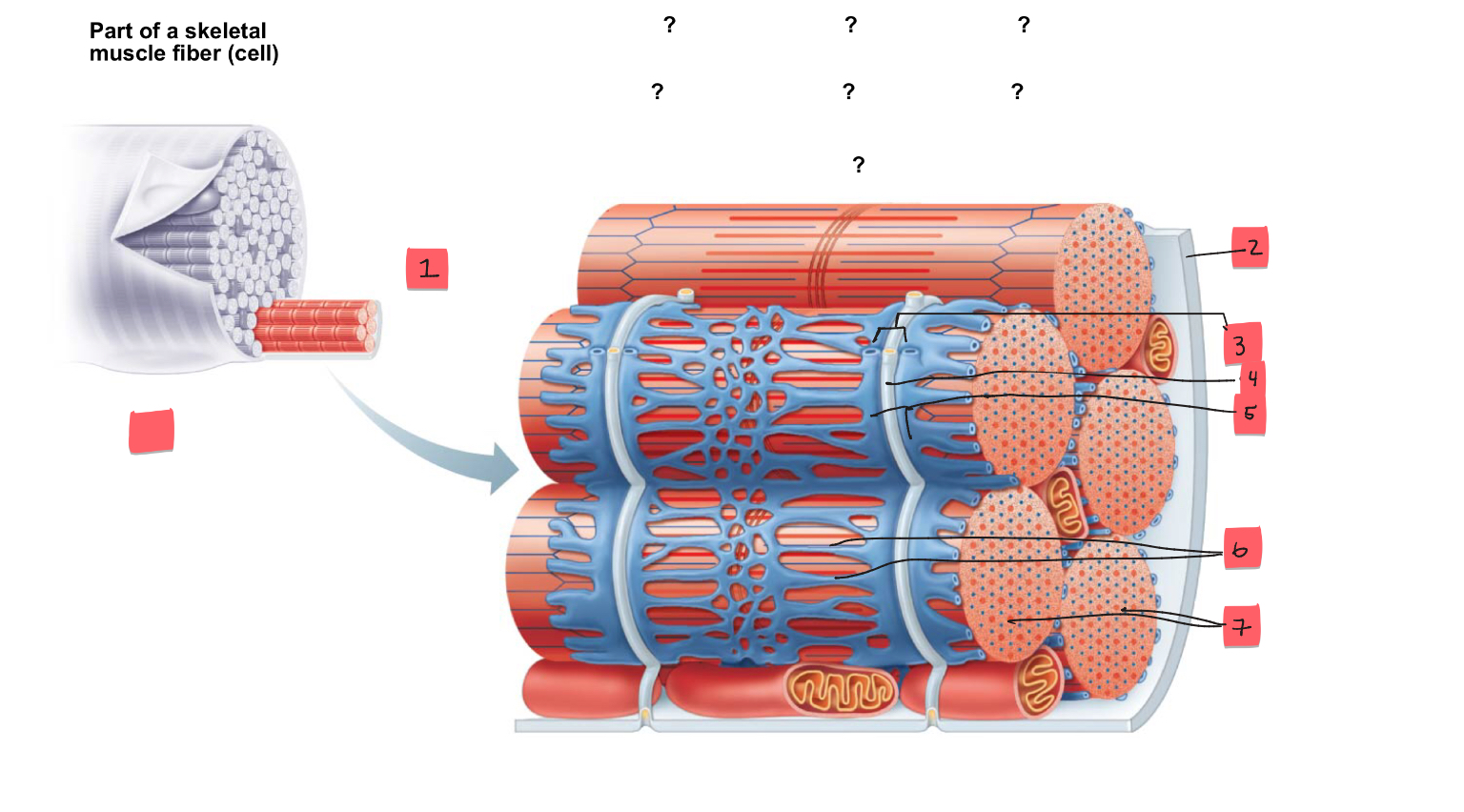
4
t tubule
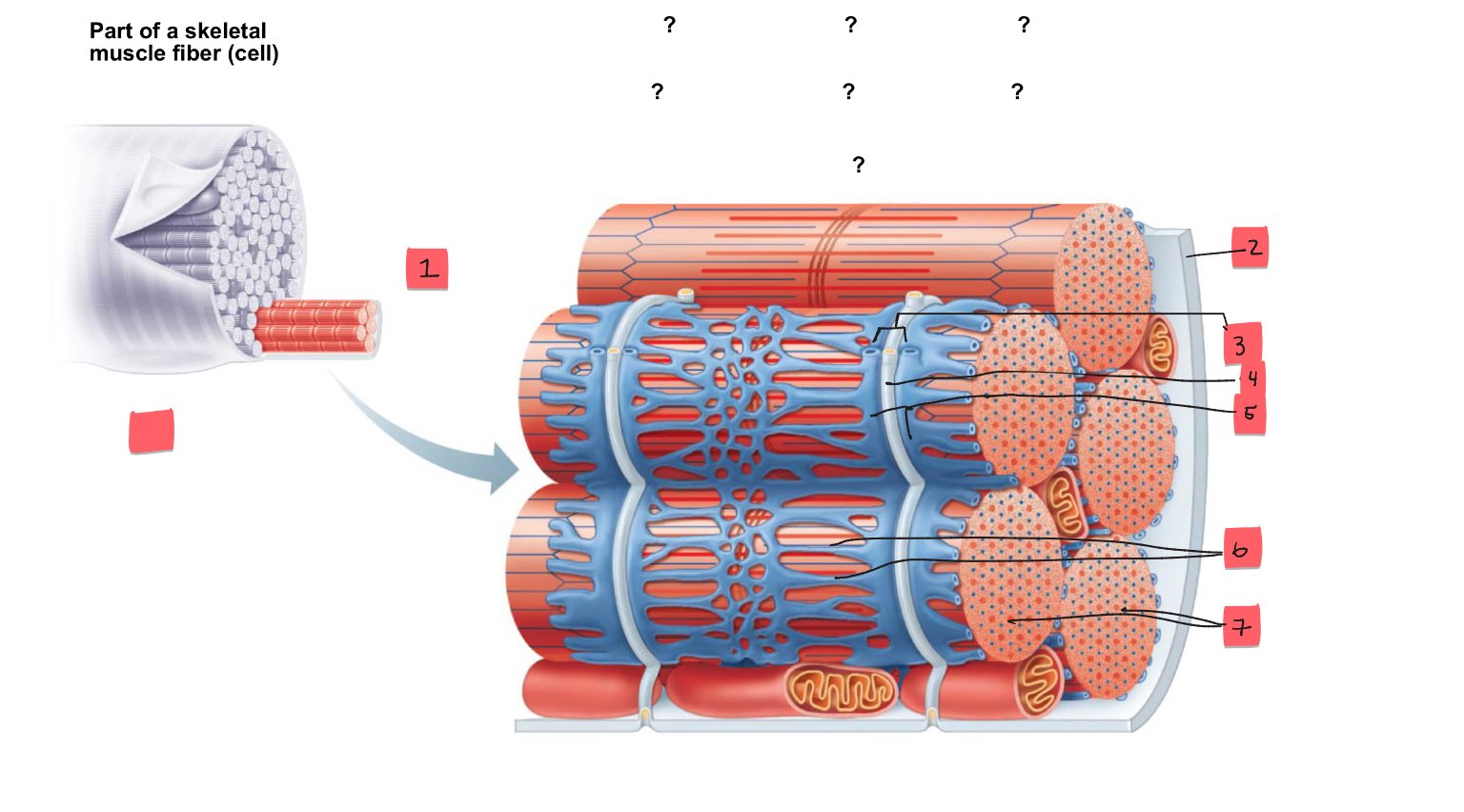
5
terminal cisterns of the SR (2)
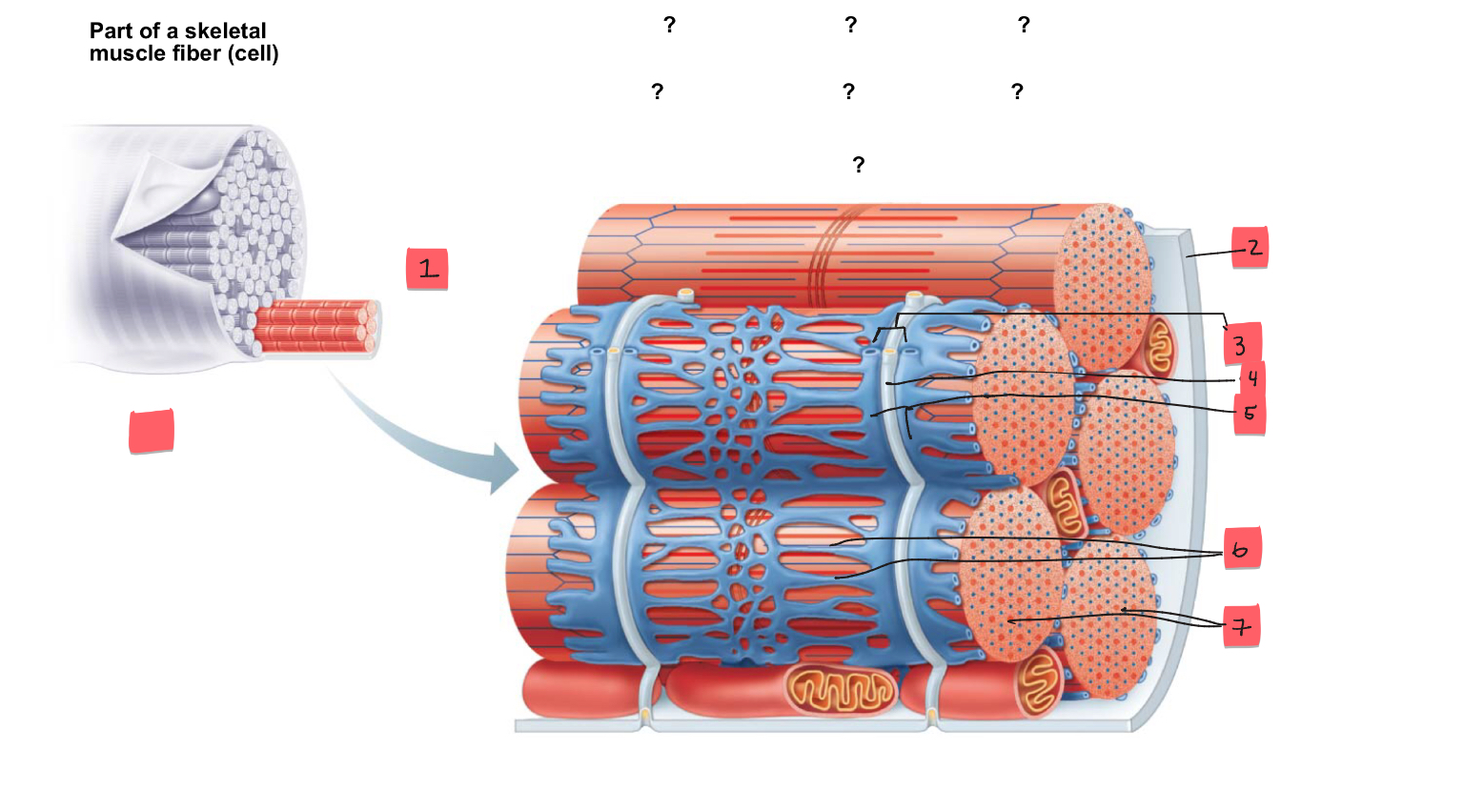
6
tubules of the SR
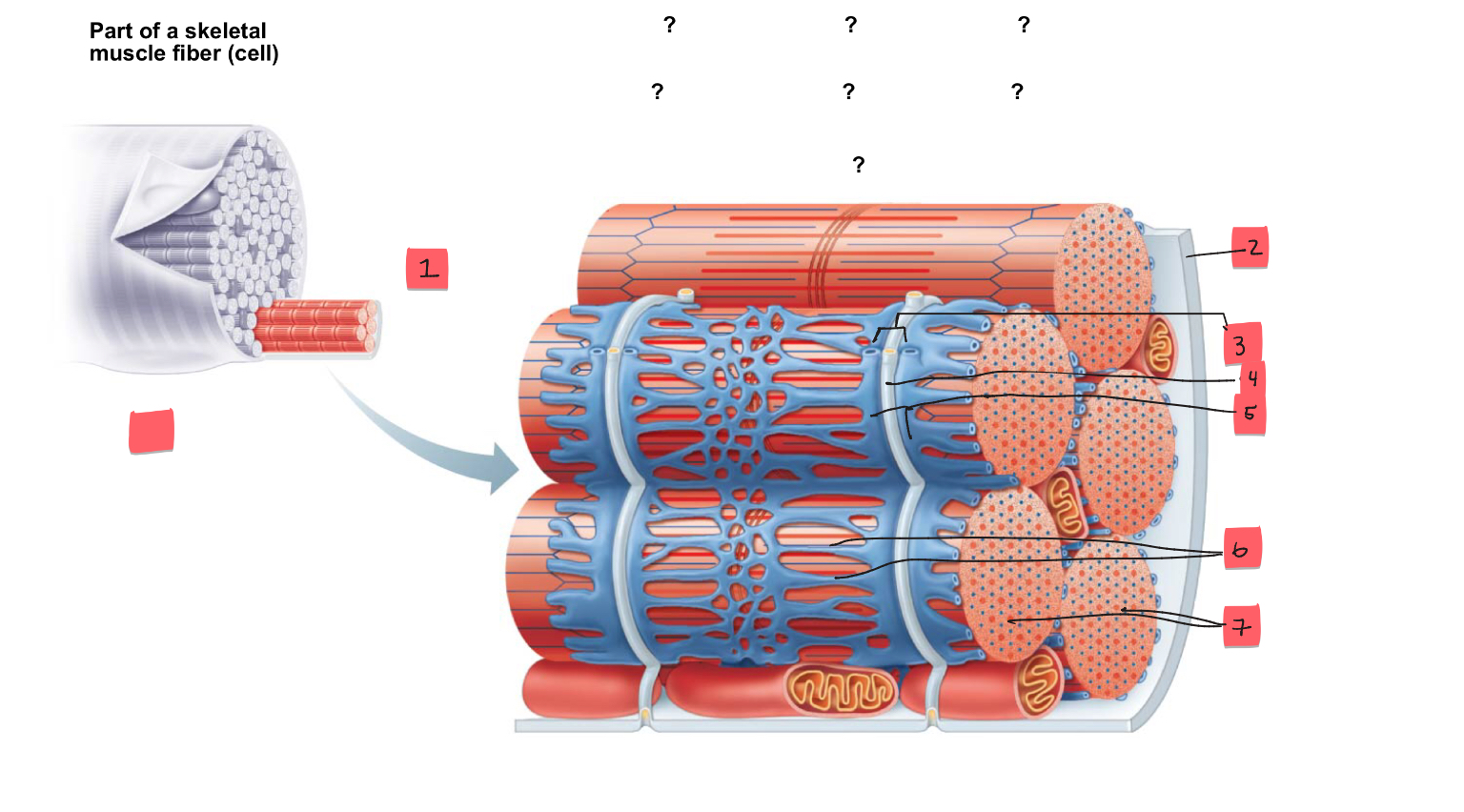
7
myofibrils
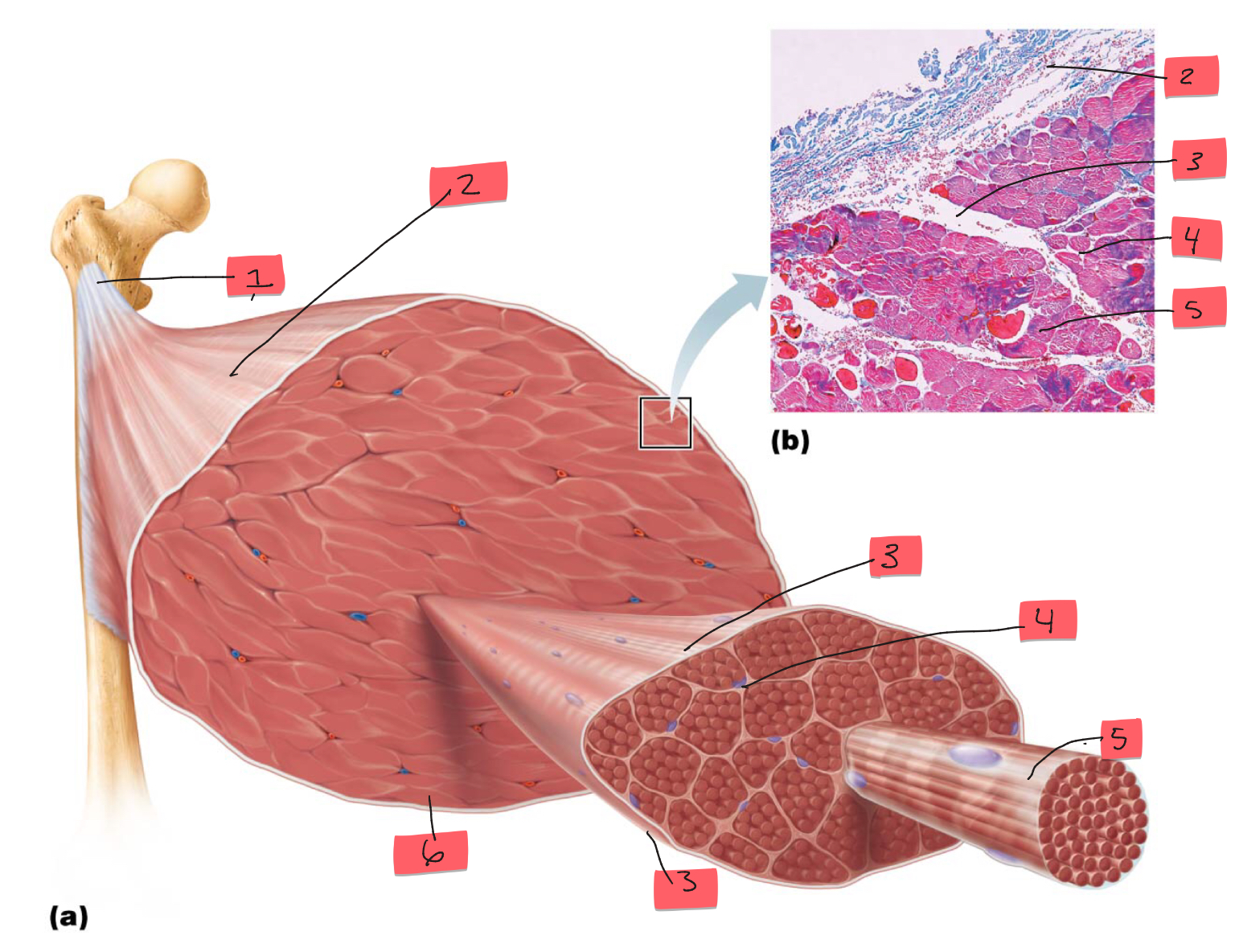
1
tendon