To show the reaction between ethanol and Fehling’s reagent
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
Procedure
➢ The ethanal is placed in a test tube in a warm water bath
➢ Using a dropper, Fehling’s reagent is added to the ethanal
Result: The blue colour of Fehling’s reagent turns into a brick red precipitate
Note: When repeated with propanone in place of ethanal, no colour change is observed
What is Fehling’s reagent and why does it have a blue colour?
• Fehling’s reagent is an equal mixture of Fehling’s A and Fehling’s B
• The blue colour is caused by the presence of copper (II) (Cu+2) ions in the solution
Write the half reactions that occur when Fehling’s solution is added to ethanal
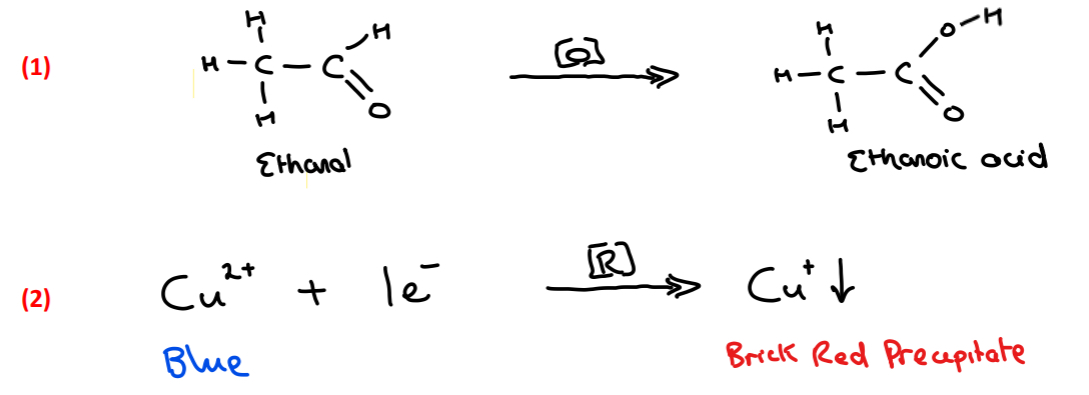
Explain the colour change that occurs when Fehling’s reagent is reacted with ethanal
• Fehling’s solution contains Cu 2+ ions causing a blue colour
• When reacted with ethanal Cu 2+ are reduced (gain 1 e–) to Cu+ ions
• Cu+ ions have a red colour and are not soluble so a brick red precipitate forms