FNH 160 Exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/187
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:29 AM on 4/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
188 Terms
1
New cards
What is the endocrine system?
Endocrine system is a **communication** system as it communicate with various tissue in body to regulates **homeostasis** through secretion of **hormones** that act on target cells
2
New cards
Endocrine vs Nervous System
\
**Endocrine**
Endocrine glands release hormones that interact with target cells
Slower acting
Longer duration (required for growth)
More dispersed (but still specific)
\
\
**Nervous**
Neurons send electrical signals to other neurons or effector cells (glands/muscles)
Rapid, precise responses
Brief in duration (required for movement)
Target tissues are muscles and glands
**Endocrine**
Endocrine glands release hormones that interact with target cells
Slower acting
Longer duration (required for growth)
More dispersed (but still specific)
\
\
**Nervous**
Neurons send electrical signals to other neurons or effector cells (glands/muscles)
Rapid, precise responses
Brief in duration (required for movement)
Target tissues are muscles and glands
3
New cards
What are the principles of Endocrinology
Endocrine system consists of **ductless endocrine glands scattered throughout body**
\
→ General mechanism:
Glands secrete hormones that travel through bloodstream to target cells; target cells contain receptors for binding with a specific hormone; hormone binding regulates or directs a particular function/response
\
**Glands** are **epithelial tissue** specialized at secreting products from cells; either exocrine (excrete through ducts) or endocrine (secrete chemicals, especially hormones, into bloodstream)
\
→ General mechanism:
Glands secrete hormones that travel through bloodstream to target cells; target cells contain receptors for binding with a specific hormone; hormone binding regulates or directs a particular function/response
\
**Glands** are **epithelial tissue** specialized at secreting products from cells; either exocrine (excrete through ducts) or endocrine (secrete chemicals, especially hormones, into bloodstream)
4
New cards
Overall Functions of the Endocrine System:
**1. Regulate nutrient metabolism, H2O, and electrolyte balance**
**2. Adaptations to stress**
**3. Promote growth and development**
**4. Control reproduction**
**5. Regulate red blood cell production**
**6. Along with the autonomic nervous system, control and integrate digestion and absorption of food**
**2. Adaptations to stress**
**3. Promote growth and development**
**4. Control reproduction**
**5. Regulate red blood cell production**
**6. Along with the autonomic nervous system, control and integrate digestion and absorption of food**
5
New cards
Regulation of Endocrine Signals
**Recap:** Glands secrete hormones that travel through bloodstream to target cells; target cells contain receptors for binding with a specific hormone; hormone binding regulates or directs a particular function/response
\
Endocrine signals are regulated by **[ ] of hormone in plasma** and **receptiveness of target cells to hormones**
→ Increase/decrease in \[ \] of hormones = more/less response
\
→ Increase/decrease in receptors on target cells = more/less hormones bind thus more/less response
\
Endocrine signals are regulated by **[ ] of hormone in plasma** and **receptiveness of target cells to hormones**
→ Increase/decrease in \[ \] of hormones = more/less response
\
→ Increase/decrease in receptors on target cells = more/less hormones bind thus more/less response
6
New cards
**So how do we exactly regulate these two processes?**
1. Control amount of hormone being secreted **(main mechanism in controlling ES)** by:
→ Negative feedback
→ Neuroendocrine
→ Diurnal
\
2. Hormones that are then secreted and bound to target cells; these cells can be more/less responsive to hormones by producing more/less receptors **(main mechanism in controlling ES)**
\
3. Secreted hormones are after inactivated/metabolized and excreted through urine (amount of hormones secreted are usually similar to amount of hormones being excreted **Ex.** we use this for pregnancy test)
\
→ Wen having a kidney/renal issue, these chould affect your excretion of hormones
7
New cards
Regulation of Hormone Secretion
**→** __**Negative-Feedback Control**__ **(Ex. Thyroid hormone) -** Anterior pituitary secretes thyroid-stimulating hormone which stimulates thyroid gland to release more/less thyroid hormones which then glas beghins to increase/decrease release of thyroid hormone into bloodstream to turn back to normal until hormone inhibits anterior pituitary to end the process
\
**→** __**Neuroendocrine Reflexes**__ **-** Through the nervous system, we mentioned how autonomic NS connects to adrenal medulla (some sympathetic fibers synapse with other neurons while some synapse to adrenal medulla) which stimular to release epinephrine, a hormone, into bloodstream. Thus NS play a role in directly controlling section of certain hormones
\n
**→** __**Diurnal (day and night) Rhythms (Circadian (throughout the day) Rhythms)**__ **-** Certain hormones are regulated through a natural pattern of release which revolves around a daily cycle.
\
**Ex 1.** Plama cortisol lvls rise few after one sleeps until it peaks as soon as they are awake and decreases throughout the day until it reaches the lowest at night an repeats
\
**Ex 1.** Melatonin pills asists people to sleep during the night
\
**Ex 1.** Female reproductivce hormones are about monthly circles where hormones increase/decrease
\
**→** __**Neuroendocrine Reflexes**__ **-** Through the nervous system, we mentioned how autonomic NS connects to adrenal medulla (some sympathetic fibers synapse with other neurons while some synapse to adrenal medulla) which stimular to release epinephrine, a hormone, into bloodstream. Thus NS play a role in directly controlling section of certain hormones
\n
**→** __**Diurnal (day and night) Rhythms (Circadian (throughout the day) Rhythms)**__ **-** Certain hormones are regulated through a natural pattern of release which revolves around a daily cycle.
\
**Ex 1.** Plama cortisol lvls rise few after one sleeps until it peaks as soon as they are awake and decreases throughout the day until it reaches the lowest at night an repeats
\
**Ex 1.** Melatonin pills asists people to sleep during the night
\
**Ex 1.** Female reproductivce hormones are about monthly circles where hormones increase/decrease
8
New cards
How are target cells influenced?
Hormones only influence target cells that express a specific receptor for that specific hormone
\
Target-cell receptors for a particular hormone can be **altered (↑/↓)** as a physiological control mechanism
\
→ To **increase** response to a hormone - Increase (upregulate) expression of receptors
→ To **decrease** response to a hormone - Decrease (downregulate) expression of receptors
\
**Thus receptors on target cells are always in flux however this causes a problem!!**
\
**Ex.** When there’s an insulin responsive, there will be receptors for insulin. Blood glucose lvls increase thus insulin secreted by glands, travels through bloodstream until it binds to target cells receptors to command cell to take up glucose thus glucose lvls decrease. However, when there’s an insulin resistance (type 2 diabetes), there will be less insulin receptors/less functional receports. Thus, as glucose lvls increase and insulin is secreted, it won’t binds to receptors and blood glucose remain high and elevated.
\
Target-cell receptors for a particular hormone can be **altered (↑/↓)** as a physiological control mechanism
\
→ To **increase** response to a hormone - Increase (upregulate) expression of receptors
→ To **decrease** response to a hormone - Decrease (downregulate) expression of receptors
\
**Thus receptors on target cells are always in flux however this causes a problem!!**
\
**Ex.** When there’s an insulin responsive, there will be receptors for insulin. Blood glucose lvls increase thus insulin secreted by glands, travels through bloodstream until it binds to target cells receptors to command cell to take up glucose thus glucose lvls decrease. However, when there’s an insulin resistance (type 2 diabetes), there will be less insulin receptors/less functional receports. Thus, as glucose lvls increase and insulin is secreted, it won’t binds to receptors and blood glucose remain high and elevated.
9
New cards
What results in endocrine disorders
Disorders of the endocrine system typically result from abnormal secretion**:**:
\
**→ Hypersecretion -** too much hormone secreted into the blood
**→ Hyposecretion -** too little hormone secreted into the blood
→ Target cell reduced sensitivity to the hormone (**Ex.** insulin resistence)
\
These can occur as a result of genetics, autoimmune disorders, tumors, lifestyle/diet, medications and more
\
**→ Hypersecretion -** too much hormone secreted into the blood
**→ Hyposecretion -** too little hormone secreted into the blood
→ Target cell reduced sensitivity to the hormone (**Ex.** insulin resistence)
\
These can occur as a result of genetics, autoimmune disorders, tumors, lifestyle/diet, medications and more
10
New cards
What are the hormones classes in endocrine system?
Two main categories of hormones\*\*: Hydrophilic\*\* and **Lipophilic**
Distinctions influence **hormone synthesis +storage** and **secretion**, **transport**, and **effects at target cells**
\
**Hydrophilic**
Soluble in water
**Ex**. Epinephrine, insulin, glucagon (proteins)
\
__**hormone synthesis +storage**__
Synthesized in rough ER & processed in golgi
Stored in cell
\
__**secretion**__
Released via exocytosis upon stimulation
\
__**transport**__
Dissolve in plasma
\
__**effects at target cells**__
When interacting with target cells, they bind to **surface membrane receptors**, produce effects through a second-messenger system
**Two major pathways**
→ cAMP (cyclic adenosine monophosphate)
→ Calcium
\
\
\
**Lipophilic**
Soluble in lipid or fats
**Ex** **1** steroids (testosterone, estrogen, cortisol) (lipids)
**2** thyroid hormone
\
__**hormone synthesis +storage**__
Synthesized in smooth ER
No storage (diffuse out plasma membrane to enter blood)
\
__**secretion**__
Rate of secretion controlled by rate of synthesis
\
__**transport**__
Some bound to plasma proteins (eg. albumin)
Some free and bound forms in equilibrium
Only "unbound forms" are biologically active and bind to target cells
\
__**effects at target cells**__
When interacting with target cells, they diffuse across membrane and bind to **intracellular receptors**
Activate specific genes to cause synthesis of new proteins and enzymes
Distinctions influence **hormone synthesis +storage** and **secretion**, **transport**, and **effects at target cells**
\
**Hydrophilic**
Soluble in water
**Ex**. Epinephrine, insulin, glucagon (proteins)
\
__**hormone synthesis +storage**__
Synthesized in rough ER & processed in golgi
Stored in cell
\
__**secretion**__
Released via exocytosis upon stimulation
\
__**transport**__
Dissolve in plasma
\
__**effects at target cells**__
When interacting with target cells, they bind to **surface membrane receptors**, produce effects through a second-messenger system
**Two major pathways**
→ cAMP (cyclic adenosine monophosphate)
→ Calcium
\
\
\
**Lipophilic**
Soluble in lipid or fats
**Ex** **1** steroids (testosterone, estrogen, cortisol) (lipids)
**2** thyroid hormone
\
__**hormone synthesis +storage**__
Synthesized in smooth ER
No storage (diffuse out plasma membrane to enter blood)
\
__**secretion**__
Rate of secretion controlled by rate of synthesis
\
__**transport**__
Some bound to plasma proteins (eg. albumin)
Some free and bound forms in equilibrium
Only "unbound forms" are biologically active and bind to target cells
\
__**effects at target cells**__
When interacting with target cells, they diffuse across membrane and bind to **intracellular receptors**
Activate specific genes to cause synthesis of new proteins and enzymes
11
New cards
**Mechanism of Action of Hydrophilic Hormones via Activation of Cyclic AMP Second-Messenger System**
Hormone (first messenger) binds to surface cell receptor, which causes a change in receptor, releasing GDP to bind to GTP. This causes a change in a protein which then activtates a different protein to convert ATP → **cAMP** which turns on kinase (protein) which phosphorylate a target protein
12
New cards
Mechanism of Action of Hydrophilic Hormones via Concurrent Activation of the Ca 2+ Second- Messenger Pathway and the DAG Pathway
Hormone (first messenger) binds to surface cell receptor, which causes a change in receptor, releasing GDP to bind to GTP. This causes a change in a protein which then activtate phospholipase to cleaves one phopholipids in cell membrane to release inositol triphosphate (IP3) to command cell to release **Ca 2+** from its stores into cell which binds to calmodulin thus both activate kinase (portein) to which then phosphorylate a target protein
13
New cards
Amplification of the Initial Signal by a Second-Messenger Pathway
When we have a second messenger, we can amplify the message. This is due to single hormone binding to a single receptor, this receptor activates multiple cycles to which this activates multiple cAMP, thus actviating multiple kinase (protein) and phosphorylate many diff target proteins
\
→ This signifies how a message is being **amplified** thus reason why hormones lvls are kept very low as little amount of hormone can cause a large impact to the body
\
→ This signifies how a message is being **amplified** thus reason why hormones lvls are kept very low as little amount of hormone can cause a large impact to the body
14
New cards
Activation of Genes by Lipophilic Hormones
Hormones enter the target cell through simple diffusion then bind to intermolecular receptor, many specifically bind to a hormone response element on DNA whichinduces transcription of mRNA to produce new proteins
15
New cards
What is the pituitary gland, what does it consist of, and how does it work along with the hypothalamus?
The pituitary (hypophysis) is a small gland located at base of brain; connected to hypothalamus by a thin connecting stalk
\
Pituitary gland consists of two distinct lobes:
**1. Posterior pituitary gland**
→ Nervous tissue **(neurohypophysis)**
→ Doesn’t make hormones but hold hormones produced in hypothalamus then secreted by anterior pituitary
\
**2. Anterior pituitary gland**
→ Glandular epithelial tissue **(adenohypophysis)**
→ Release of hormones from both glands is controlled by hypothalamus
\
Pituitary gland consists of two distinct lobes:
**1. Posterior pituitary gland**
→ Nervous tissue **(neurohypophysis)**
→ Doesn’t make hormones but hold hormones produced in hypothalamus then secreted by anterior pituitary
\
**2. Anterior pituitary gland**
→ Glandular epithelial tissue **(adenohypophysis)**
→ Release of hormones from both glands is controlled by hypothalamus
16
New cards
\
What is the function of the hypothalamus in relation to the posterior pituitary gland?
What is the function of the hypothalamus in relation to the posterior pituitary gland?
In hypothalamus, neurons (cells) reproduce 2 hormones which is send down their axon (through the stock) and into posterior pituitary. They remain at the terminal neurons until neuron is stimulated to which hormones are then secreted into bloodstream thus hypothalamus is what produces hormones whereas posterior pituitary is the terminal
\
Hormone #1 - **Vasopressin (ADH)**
This target kidneys to conserve water during urine formation and arterioles (blood vessels) to constrict (close) thus both processes increase blood pressure
\
Hormone #2 - **Oxytocin**
Stimulates uterine contraction during childbirth and milk ejection during breastfeeding
\
Hormone #1 - **Vasopressin (ADH)**
This target kidneys to conserve water during urine formation and arterioles (blood vessels) to constrict (close) thus both processes increase blood pressure
\
Hormone #2 - **Oxytocin**
Stimulates uterine contraction during childbirth and milk ejection during breastfeeding
17
New cards
When osmoreceptors in the blood send signals to the hypothalamus to indicate that the blood is too concentrated, which of the following would occur?
Stimulation of neurons in the hypothalamus lead to secretion of vasopressin from the posterior pituitary
18
New cards
In childbirth, oxytocin is released from the _____ to the ____
Posterior pituitary, systemic blood
19
New cards
What does anterior pituitary secrete?
Synthesizes and secretes **six** hormones; most are **tropic** hormones
**→ Tropic hormones:** regulate hormone secretion by other endocrine glands
\
1\. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
→ Stimulates thyroid to secrete thyroid hormone
\
2\. Adreno-cortico-tropic hormone (ACTH)
→ Stimulates adrenal cortex to secrete cortisol
\
3\. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
→ In females, stimulates growth & development of ovarian follicles and secretion of estrogen
→ In males, required for sperm production
\
4\. Luteinizing hormone (LH)
→ In females, responsible for ovulation and luteinization
→ In males, stimulates testosterone secretion
\
5\. Growth hormone (GH)
→ Stimulates release of somato-medins from liver
→ Regulates growth & metabolism
\
6\. Prolactin (PRL)
→ \*\*Not a tropic hormone
→ Enhances breast development and milk production in females
**→ Tropic hormones:** regulate hormone secretion by other endocrine glands
\
1\. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
→ Stimulates thyroid to secrete thyroid hormone
\
2\. Adreno-cortico-tropic hormone (ACTH)
→ Stimulates adrenal cortex to secrete cortisol
\
3\. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
→ In females, stimulates growth & development of ovarian follicles and secretion of estrogen
→ In males, required for sperm production
\
4\. Luteinizing hormone (LH)
→ In females, responsible for ovulation and luteinization
→ In males, stimulates testosterone secretion
\
5\. Growth hormone (GH)
→ Stimulates release of somato-medins from liver
→ Regulates growth & metabolism
\
6\. Prolactin (PRL)
→ \*\*Not a tropic hormone
→ Enhances breast development and milk production in females
20
New cards
Regulation of Anterior Pituitary Hormone Secretion
Although anterior pituitary produces its own hormones, it’s **regulated by hypothalamus**
\
Two main factors regulate anterior pituitary hormone secretion:
1\. **Hypothalamic hypophysiotropic** hormones (hormones released by hypothalamus that act on pituitary):
→ Releasing and inhibiting hormones released from hypothalamus
\
2\. Feedback by target-gland hormones
\
\
\
**1.** Hypophysiotropic hormones (releasing/inhibiting hormones) produced by neurons in hypothalamus enter hypothalamic capillaries instead going down the stock into anterior pituitary
\
**2.** These hypothalamic capillaries rejoin to form the hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system (a blood vessel that connects two organs) branches into capillaries of anterior
\
**4.** Hypophysiotropic hormones, which leave blood then across anterior, stimulate (releasing hormones) or inhibit (inhibiting hormones) release of anterior pituitary hormones
\
**5.** When stimulated by appropriate hypothalamic releasing hormone, anterior pituitary secretes a given hormone into these capillaries
\
**6.** Anterior pituhary rejoin to form a vein, through which anterior pituitary hormones leave for ultimate distribution throughout the body by the circulation
\
\
\
**Example:** Regulation of cortisol in stress response
When stressed, stress response activates hypothalamus which then releases **corticotropin-releasing hormone**. This hormone travels to portal system and into anterior pituitary to stimulate anterior pituitary to release **adrenocorticotropic hormone.** These hormones enter bloodstream and enter adrenal cortex which will stimulate cortisol. Cortisol undergoes general circulation and acts on target cells to produce changes to help resist stress
\
**Key point #1:** Hypothalamus controls secretion from anterior pituitary and anterior pituitary controls section from gland
\
**Key point #2:** Secretion of cortisol then begins to act as a negative feedback to inhibit hypothalamus and anterior pituitary
\
\
**Example:** Regulation of thyroid hormone secretion
Hypothalamus secretes **thyrotropin-releasing hormone** which travels through portal system into anterior pituitary which will then secrete **thyrotropin-stimulating hormone** to which travels into bloodstream and into **thyroid** which will secrete **thyroid hormones.** Thyroid hormones then create negative feedback to inhibit hypothalamus and anterior pituitary
\
Two main factors regulate anterior pituitary hormone secretion:
1\. **Hypothalamic hypophysiotropic** hormones (hormones released by hypothalamus that act on pituitary):
→ Releasing and inhibiting hormones released from hypothalamus
\
2\. Feedback by target-gland hormones
\
\
\
**1.** Hypophysiotropic hormones (releasing/inhibiting hormones) produced by neurons in hypothalamus enter hypothalamic capillaries instead going down the stock into anterior pituitary
\
**2.** These hypothalamic capillaries rejoin to form the hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system (a blood vessel that connects two organs) branches into capillaries of anterior
\
**4.** Hypophysiotropic hormones, which leave blood then across anterior, stimulate (releasing hormones) or inhibit (inhibiting hormones) release of anterior pituitary hormones
\
**5.** When stimulated by appropriate hypothalamic releasing hormone, anterior pituitary secretes a given hormone into these capillaries
\
**6.** Anterior pituhary rejoin to form a vein, through which anterior pituitary hormones leave for ultimate distribution throughout the body by the circulation
\
\
\
**Example:** Regulation of cortisol in stress response
When stressed, stress response activates hypothalamus which then releases **corticotropin-releasing hormone**. This hormone travels to portal system and into anterior pituitary to stimulate anterior pituitary to release **adrenocorticotropic hormone.** These hormones enter bloodstream and enter adrenal cortex which will stimulate cortisol. Cortisol undergoes general circulation and acts on target cells to produce changes to help resist stress
\
**Key point #1:** Hypothalamus controls secretion from anterior pituitary and anterior pituitary controls section from gland
\
**Key point #2:** Secretion of cortisol then begins to act as a negative feedback to inhibit hypothalamus and anterior pituitary
\
\
**Example:** Regulation of thyroid hormone secretion
Hypothalamus secretes **thyrotropin-releasing hormone** which travels through portal system into anterior pituitary which will then secrete **thyrotropin-stimulating hormone** to which travels into bloodstream and into **thyroid** which will secrete **thyroid hormones.** Thyroid hormones then create negative feedback to inhibit hypothalamus and anterior pituitary
21
New cards
Why is the hypothalamus considered the main link between the nervous and endocrine systems?
→ Hypothalamus receives inputs (ex. stress) from nervous system and connects with endocrine system through pituitary glands
22
New cards
If the thyroid gland was not functioning and we had **hyposecretion** from thyroid gland, but the anterior pituitary gland functioning, what would you expect to see?
→ High TSH and low thyroid hormones
23
New cards
Vasopressin and oxytocin are peptide (water-soluble) hormones. They most likely exert effects on cells by**:**
→ Binding to receptors and turning on secondary messenger pathways
24
New cards
What is the Pineal gland
Pineal gland secretes **melatonin**
\
Melatonin helps keep body’s circadian rhythms in synchrony
with light–dark cycle and promotes sleep
\
It also:
→ Influences reproductive activity, including onset of puberty
→ Enhances immunity
→ Slows aging
→ Acts as antioxidant (stelading elections) to remove free radicals
\
Melatonin helps keep body’s circadian rhythms in synchrony
with light–dark cycle and promotes sleep
\
It also:
→ Influences reproductive activity, including onset of puberty
→ Enhances immunity
→ Slows aging
→ Acts as antioxidant (stelading elections) to remove free radicals
25
New cards
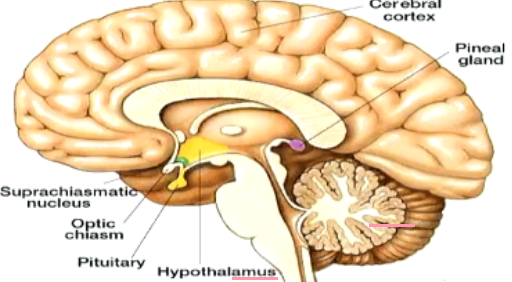
What is the SCN
The way pineal gland is connected to day-night cycle is through **SCN** which is a body’s master biological clock
\
Self-induced cyclic variations in **clock protein** concentrations within SCN induce cyclic changes in neural discharge from SCN to which then allows for pineal gland to know if it’s day or night to secrete melatonin into body
\
→ Cycle takes about a day
→ Drives body’s circadian rhythms
\
\
**Clock Proteins & Circadian Rhythms**
**The entire cycle takes about 24 hours**
\
1\. Clock proteins are synthesized and begin to accumulate (build up) in cytosol
\
2\. As day wears on, these clock proteins reach a critical mass and are transported into nucleus where they block genetic process responsible for their own production
\
4\. Lvl of clock proteins gradually dwindles as they degrade within nucleus. This also removes their inhibitory influence from the clock-protein genetic machinery
\
5\. No longer blocked, these genes once again rev up production of more clock proteins as cycle repeats itself
\
Self-induced cyclic variations in **clock protein** concentrations within SCN induce cyclic changes in neural discharge from SCN to which then allows for pineal gland to know if it’s day or night to secrete melatonin into body
\
→ Cycle takes about a day
→ Drives body’s circadian rhythms
\
\
**Clock Proteins & Circadian Rhythms**
**The entire cycle takes about 24 hours**
\
1\. Clock proteins are synthesized and begin to accumulate (build up) in cytosol
\
2\. As day wears on, these clock proteins reach a critical mass and are transported into nucleus where they block genetic process responsible for their own production
\
4\. Lvl of clock proteins gradually dwindles as they degrade within nucleus. This also removes their inhibitory influence from the clock-protein genetic machinery
\
5\. No longer blocked, these genes once again rev up production of more clock proteins as cycle repeats itself
26
New cards
How is the biological clock synchronized with enviromentntal cues?
The body’s biological rhythms are synchronized with activity levels driven by surrounding environment
\
Main environmental cue = **Daily changes in light intensity**
\
→ Specialized photoreceptors in retina pick up light signals from external environment and transmit them directly to SCN which then talks to pineal gland to let it know that light has appeared thus end production of melatonin
\
**Environmental Factors Influencing Circadian Rhythms**
1\. Light –including blue light from electronic devices
2\. Shift work and travel
3\. Caffeine and other stimulants
\
**Why is this important?**
**When we disturb our cardigan rhythms, we are more likely to develop chronic diseases**
\
Main environmental cue = **Daily changes in light intensity**
\
→ Specialized photoreceptors in retina pick up light signals from external environment and transmit them directly to SCN which then talks to pineal gland to let it know that light has appeared thus end production of melatonin
\
**Environmental Factors Influencing Circadian Rhythms**
1\. Light –including blue light from electronic devices
2\. Shift work and travel
3\. Caffeine and other stimulants
\
**Why is this important?**
**When we disturb our cardigan rhythms, we are more likely to develop chronic diseases**
27
New cards
Healthy Sleep Habits
→ Consistent sleep schedule
→ Limit exposure to bright light & electronic devices before bedtime
→ Avoid caffeine in the afternoon or evening
→ Healthy diet
→ Exercise regularly
→ Limit exposure to bright light & electronic devices before bedtime
→ Avoid caffeine in the afternoon or evening
→ Healthy diet
→ Exercise regularly
28
New cards
What factors influence growth?
Factors influencing growth include**:**
→ Genetic determination of an individual’s maximum growth capacity
→ An adequate diet to achieve max growth
→ Freedom from chronic disease and stressful environmental conditions
→ Normal levels of growth-influencing hormones
→ Genetic determination of an individual’s maximum growth capacity
→ An adequate diet to achieve max growth
→ Freedom from chronic disease and stressful environmental conditions
→ Normal levels of growth-influencing hormones
29
New cards
The growth spurt in adolescence (puberty) is largely stimulated by:
→ Increased secretion of androgens (sex hormones) whereas postnatal growth spurt is largely stimulated by growth hormones
30
New cards
Growth Hormone (GH)
It’s secreted from anterior pituitary and has effects on growth and fuel metabolism
\
GH works both directly on cells and indirectly via action of **somatomedins**
\
GH enters liver and stimulate release of somatomedins which are peptide hormones which also influences growth (not like insulin but similar)
→ Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) – main
→ Insulin-like growth factor-2 (IGF-2) – main during fetal development
\
GH works both directly on cells and indirectly via action of **somatomedins**
\
GH enters liver and stimulate release of somatomedins which are peptide hormones which also influences growth (not like insulin but similar)
→ Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) – main
→ Insulin-like growth factor-2 (IGF-2) – main during fetal development
31
New cards
How does Growth hormone and IGF-1 (somatomedins) work?
Growth hormone and IGF-1 (somatomedins) pormote growth by:
\
→Increasing # of cells (**hyperplasia**) → Through increasing cell division and preventing cell death
\
→Increasing the size of cells (**hypertrophy**) → Through increasing protein synthesis
\
→Stimulate growth of long bones to provide height (found in legs and arms)
\
→Increasing # of cells (**hyperplasia**) → Through increasing cell division and preventing cell death
\
→Increasing the size of cells (**hypertrophy**) → Through increasing protein synthesis
\
→Stimulate growth of long bones to provide height (found in legs and arms)
32
New cards
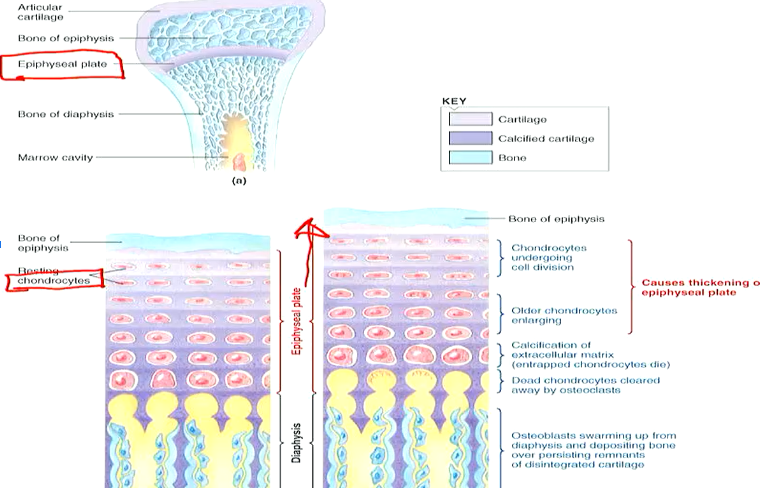
How is growth hormone connected to bone?
GH (largely through IGF-1) promotes bone growth through
→ Promoting increase of chondrocytes (cartilage forming cells)
→ Stimulating activity of osteoblasts (bone building cells)
\
Under stimulation of GH, bones grow in length at the epiphyseal plate through adolescence
\
At end of adolescence, epiphyseal plates close (plate filled with bone) so that bones cannot lengthen
→ Promoting increase of chondrocytes (cartilage forming cells)
→ Stimulating activity of osteoblasts (bone building cells)
\
Under stimulation of GH, bones grow in length at the epiphyseal plate through adolescence
\
At end of adolescence, epiphyseal plates close (plate filled with bone) so that bones cannot lengthen
33
New cards
Growth in long bones occurs through a process known as:
**→ Endochondral-ossification (within chondrocytes/cartilage-forming bone)**
34
New cards
What is the Physiological Actions of GH & IGF
Actions accomplished by GH (alone or via IGF)
\
→ Increased cartilage and bone growth
→ Promotion of hypertrophy and hyperplasia of tissues (cells grow by #’s and/or size)
→ (both promote growth)
\
→ Sparing/saving of amino acids and increased protein synthesis for growth
→ Sparing/saving blood glucose
→ Increased lipolysis (breakdown of stored fat) and use of fatty acid **(basically burn fat but save protein and glucose)**
→ (these three shift metabolism)
\
→ Increased cartilage and bone growth
→ Promotion of hypertrophy and hyperplasia of tissues (cells grow by #’s and/or size)
→ (both promote growth)
\
→ Sparing/saving of amino acids and increased protein synthesis for growth
→ Sparing/saving blood glucose
→ Increased lipolysis (breakdown of stored fat) and use of fatty acid **(basically burn fat but save protein and glucose)**
→ (these three shift metabolism)
35
New cards
Factors That Influence GH Secretions
Secretion of GH is greater during periods of increased growth
\
Factors that influence GH secretion**:**
**→ Diurnal rhythm -** GH release is greatest during deep sleep
\
**→ Exercise -** Promotes release of GH, which may aid muscle growth after exercise
\
**→ Stress & low blood glucose levels -** Promote release of GH to shift metabolism towards glucose sparing
\
Factors that influence GH secretion**:**
**→ Diurnal rhythm -** GH release is greatest during deep sleep
\
**→ Exercise -** Promotes release of GH, which may aid muscle growth after exercise
\
**→ Stress & low blood glucose levels -** Promote release of GH to shift metabolism towards glucose sparing
36
New cards
Regulation of Growth Hormone Secretion
**1.** Hypothalamus is normally stimulated to release GH at night during deep sleep and can also be stimulated to release more GH in response to exercise, stress, or low glucose levels
\
**2.** In response to stimulation, hypothalamus secretes **(gas pedal)** GHRH (growth hormone releasing hormone) and stops secreting **(brake pedal)** GHIH (growth hormone inhibiting hormone) \n
**4.** GHRH stimulates the anterior pituitary to release GH
\
**5.** GH stimulates release of IGF-1 from liver
\
**6.** GH & IGF1 have effects on growth and metabolism
\
**7.** IGF1 exerts negative feedback on the anterior pituitary and hypothalamus
\
**2.** In response to stimulation, hypothalamus secretes **(gas pedal)** GHRH (growth hormone releasing hormone) and stops secreting **(brake pedal)** GHIH (growth hormone inhibiting hormone) \n
**4.** GHRH stimulates the anterior pituitary to release GH
\
**5.** GH stimulates release of IGF-1 from liver
\
**6.** GH & IGF1 have effects on growth and metabolism
\
**7.** IGF1 exerts negative feedback on the anterior pituitary and hypothalamus
37
New cards
**Examples of the Effect of Abnormalities in Growth Hormone Secretion on Growth**
\
Describe three potential causes of growth hormone insufficiency. (Hint: Consider how growth hormone secretion is regulated, where it is secreted from, and other potential causes of hormone insufficiency from lecture 11)
\
What might be the effects of excess growth hormone in childhood? How would this differ from growth hormone excess in adulthood?
\
Describe three potential causes of growth hormone insufficiency. (Hint: Consider how growth hormone secretion is regulated, where it is secreted from, and other potential causes of hormone insufficiency from lecture 11)
\
What might be the effects of excess growth hormone in childhood? How would this differ from growth hormone excess in adulthood?
**→ Defect in hypothalamus (not enough GHRH)**
**→ Defect in anterior pituitary (not secreting enough GHRH)**
**→ Defective receptors for GH in target tissues (not likely but could occur)**
\
**→Childhood - Increase in height as long bones still grow (↑GH → ↑height)**
**→ Adulthood - Long bones close thus no more growth except for hand/head/face (acromegaly)**
**→ Defect in anterior pituitary (not secreting enough GHRH)**
**→ Defective receptors for GH in target tissues (not likely but could occur)**
\
**→Childhood - Increase in height as long bones still grow (↑GH → ↑height)**
**→ Adulthood - Long bones close thus no more growth except for hand/head/face (acromegaly)**
38
New cards
what causes growth hormones excess?
Most often caused by tumour of GH-producing cells in anterior pituitary
\
Symptoms depend on age of individual when abnormal secretion begins
**→ Childhood - Gigantism:** tallness, with large head, hands & feet
**→ Adulthood - Acromegaly:** large hands and feet, prominent forehead & chin
\
Symptoms depend on age of individual when abnormal secretion begins
**→ Childhood - Gigantism:** tallness, with large head, hands & feet
**→ Adulthood - Acromegaly:** large hands and feet, prominent forehead & chin
39
New cards
What would be expected effects of growth hormone deficiency in adulthood?
Decreased body muscle
40
New cards
What is the thyroid gland
Thyroid gland is located on the neck and is made up of follicles cells which surround colloid (extracellular matrix)
41
New cards
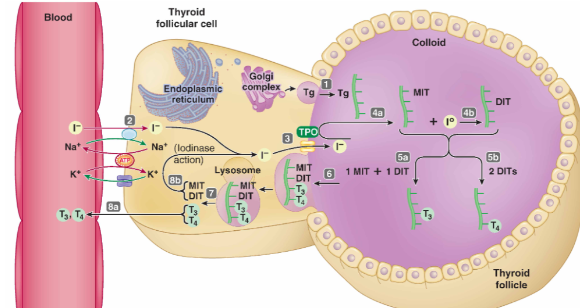
**Synthesis, Secretion and Transport of the Thyroid Hormone**
Thyroid hormone synthesis requires **iodine** (essential mineral obtained from diet)
\
**1.** Idioine is taken up from bloodstream and into follicular cells of thyroid by Na+/I co-transport through **secondary active transport**
\
**2.** A protein if then formed called **thyroglobulin (Tg)** in the colloid
\
**3.** Iodide is then secreted into colloid
\
**4.** Attachment of iodine to Tg generates MIT (mono-iodothyronine), DIT (di-iodothyronine), **T3 (tri-iodothyronine)** and **T4 (tetraiodothyronine)**
\
**5.** When thyroid hormones required, thyroglobulin-containing colloid is taken into follicular cells by phagocytosis and these cells will release T3 and T4 from thyroglobulin through **simple diffusion (they are lipophilic)**
\
**6.** In plasma, thyroid hormones bind to proteins called **thyroxine-binding globulin TBG**
\
**7.** Most of T4 is converted to T3 (more active form of thyroid hormone)
\
**8.** Free/unbounded hormone binds to target cell receptors
\
**1.** Idioine is taken up from bloodstream and into follicular cells of thyroid by Na+/I co-transport through **secondary active transport**
\
**2.** A protein if then formed called **thyroglobulin (Tg)** in the colloid
\
**3.** Iodide is then secreted into colloid
\
**4.** Attachment of iodine to Tg generates MIT (mono-iodothyronine), DIT (di-iodothyronine), **T3 (tri-iodothyronine)** and **T4 (tetraiodothyronine)**
\
**5.** When thyroid hormones required, thyroglobulin-containing colloid is taken into follicular cells by phagocytosis and these cells will release T3 and T4 from thyroglobulin through **simple diffusion (they are lipophilic)**
\
**6.** In plasma, thyroid hormones bind to proteins called **thyroxine-binding globulin TBG**
\
**7.** Most of T4 is converted to T3 (more active form of thyroid hormone)
\
**8.** Free/unbounded hormone binds to target cell receptors
42
New cards
Regulation of Thyroid Hormone Secretion
Hypothalamus releases thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) which enters anterior pituitary and secretes thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH will stimulate thyroid gland to release thyroid hormone (by taking a chunk of the colloids to release T3 and T4). Thyroid hormones then act as negative feedback on hypothalamus and anterior pituitary
43
New cards
Main Actions of Thyroid Hormone
Thyroid hormone mainly determines **basal metabolic rate (metabolism required to keep us alive)** and heat production
\
→ It also has **sympathomimetic** effects **-** enhances effect of sympathetic system (target-cell responsiveness to epinephrine & norepinephrine)
\
**—>** It also has **cardiovascular** effects - enhance heart rate and force of contraction
\
Essential for **normal growth** and development (enhances secretion and effects of GH), especially of CNS
**Ex.** Someone who’s pregnant with low thyroid hormone will be passed to the infant and impair its growth and infants with low thyroid hormones will lead severe low brain development
\
→ It also has **sympathomimetic** effects **-** enhances effect of sympathetic system (target-cell responsiveness to epinephrine & norepinephrine)
\
**—>** It also has **cardiovascular** effects - enhance heart rate and force of contraction
\
Essential for **normal growth** and development (enhances secretion and effects of GH), especially of CNS
**Ex.** Someone who’s pregnant with low thyroid hormone will be passed to the infant and impair its growth and infants with low thyroid hormones will lead severe low brain development
44
New cards
Abnormalities of Thyroid Function
**Hypothyroidism** (↓T3/T4)
→ Primary failure of thyroid gland (**ex.** thyroid does not make sufficient hormone)
→ Secondary to a deficiency of TRH, TSH, or both
→ Inadequate dietary supply of iodine
\
**Hyperthyroidism** (↑T3/T4)
→ Most common cause is **Graves’ disease** (autoimmune disease where body erroneously produces thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins (TSI))
→ Primary failure of thyroid gland (**ex.** thyroid does not make sufficient hormone)
→ Secondary to a deficiency of TRH, TSH, or both
→ Inadequate dietary supply of iodine
\
**Hyperthyroidism** (↑T3/T4)
→ Most common cause is **Graves’ disease** (autoimmune disease where body erroneously produces thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins (TSI))
45
New cards
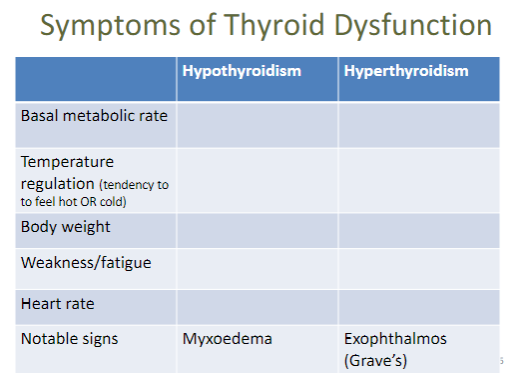
Symptoms of Thyroid Dysfunction
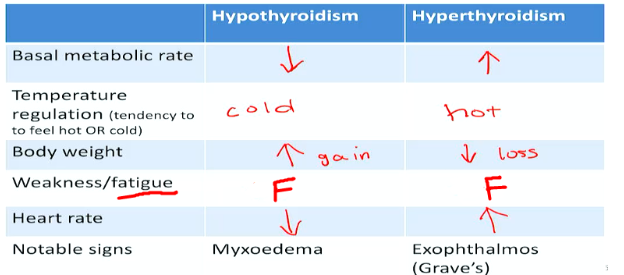
46
New cards
Thyroid Gland Overstimulation
A goiter is an enlarged thyroid gland
\
Occurs with excess TSH levels as TSH not only tells thyroid gland to make more thyroid hormone but also stimulates thyroid growth
\
Can occur in both hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism
\
→ Classic sign of severe iodine deficiency
\
Occurs with excess TSH levels as TSH not only tells thyroid gland to make more thyroid hormone but also stimulates thyroid growth
\
Can occur in both hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism
\
→ Classic sign of severe iodine deficiency
47
New cards
What are the hormones released by adrenal cortex?
steroid hormones:
**Mineral-o-corticoids** (**aldosterone**) - Influence mineral balance (Na+and K+)
\
**Gluc-o-corticoids** (**cortisol**) - Major role in glucose metabolism and stress response
\
**Sex hormones** (Most abundant is androgen **DHEA**) - Identical to those produced by reproductive organs
**Mineral-o-corticoids** (**aldosterone**) - Influence mineral balance (Na+and K+)
\
**Gluc-o-corticoids** (**cortisol**) - Major role in glucose metabolism and stress response
\
**Sex hormones** (Most abundant is androgen **DHEA**) - Identical to those produced by reproductive organs
48
New cards
What does Mineralocorticoids: Aldosterone hormone do, and how increase/ decrease amount of this hormone effect the body?
Hormone acts on kidney to promote Na+ retention (hold Na+), which increases water lvl thus increases blood volume and blood pressure
\
Aldosterone is **essential for life**; without it, a person would die from circulatory shock within two days
\
**→ Hyper-secretion -** Increase in Na+ retention thus increase blood volume + pressure
\
**→ Hypo-secretion -** Decrease in Na+ in body thus decrease blood volume +pressure
\
Aldosterone is **essential for life**; without it, a person would die from circulatory shock within two days
\
**→ Hyper-secretion -** Increase in Na+ retention thus increase blood volume + pressure
\
**→ Hypo-secretion -** Decrease in Na+ in body thus decrease blood volume +pressure
49
New cards
What does Glucocorticoids: Cortisol hormone do, and how increase/ decrease amount of this hormone effect the body?
METABOLIC ROLE:
→ Hormone mainly **increases blood glucose** but also\*\*:\*\*
→ Stimulates **protein breakdown**, especially in muscle (use for energy)
→ Increases **lipolysis** (breakdown of fat)
\
**Overall, increases availabilities of fuels that body can use for energy**
\
ADDITIONAL ROLES:
→ Key role in adaptation to stress (increases blood glucose to prepare body for flight/fight or fasting)
→ At pharma-cological levels, cortisol causes anti-inflammatory and anti-immune effects
\
Useful in inflammatory disorders
Long-term use can result in unwanted side effects
\
\
**→ Hypo-secretion -** **hypoglycemia** (↓ blood glouse), low energy, weight loss, poor response to stress
\
**→ Hyper-secretion - Crushing syndrome**
(1) Increase release of cortisol thus increase negative feedback loops processes thus inhibition of CRH and ACTH thus reduction in cortisol production (2) lower immunity over time thus increase in obtaining infections (3) increase of fat breakdown which becomes stored in abdomen (stomach) (4) increase in protein breakdown for energy thus decrease in muscle mass and ability to repair tissue
→ Hormone mainly **increases blood glucose** but also\*\*:\*\*
→ Stimulates **protein breakdown**, especially in muscle (use for energy)
→ Increases **lipolysis** (breakdown of fat)
\
**Overall, increases availabilities of fuels that body can use for energy**
\
ADDITIONAL ROLES:
→ Key role in adaptation to stress (increases blood glucose to prepare body for flight/fight or fasting)
→ At pharma-cological levels, cortisol causes anti-inflammatory and anti-immune effects
\
Useful in inflammatory disorders
Long-term use can result in unwanted side effects
\
\
**→ Hypo-secretion -** **hypoglycemia** (↓ blood glouse), low energy, weight loss, poor response to stress
\
**→ Hyper-secretion - Crushing syndrome**
(1) Increase release of cortisol thus increase negative feedback loops processes thus inhibition of CRH and ACTH thus reduction in cortisol production (2) lower immunity over time thus increase in obtaining infections (3) increase of fat breakdown which becomes stored in abdomen (stomach) (4) increase in protein breakdown for energy thus decrease in muscle mass and ability to repair tissue
50
New cards
Difference between metabolic effects of growth hormone and cortisol is that GH:
→ Spares proteins
51
New cards
Glucocorticoids (eg. Prednisone) are prescribed for reducing inflammation in disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis. Side effects of long-term glucocorticoid use could include:
→ Downregulation/inhibition of the CRH-ACTH system and reduced endogenous cortisol synthesis
→Reduced immunity and increased susceptibility to infections
→ Fat deposition in abdomen
→Reduced immunity and increased susceptibility to infections
→ Fat deposition in abdomen
52
New cards
Control of Cortisol Secretion
Cortisol is secreted by **HPA** axis (hypothalamus, pituitary and adrenal)
\
**→ Diurnal rhythms:** Cortisol secretion increases when sleeping reaching a peak in morning, then decrease during day, reaching their lowest at bedtime
\
**→ Stress:** Increases cortisol secretion to metabolically prepare body for dealing with stress
\
Upon stimulation hypothalamus by diurnal rhythm and stress, it releases CRH. This stimulates anterior pituitary to release ACTH, which stimulates release of cortisol from adrenal cortex (increasing blood glucose, protein and fats). Then, cortisol acts on hypothalamus and anterior pituitary in a negative feedback loop
\
**→ Diurnal rhythms:** Cortisol secretion increases when sleeping reaching a peak in morning, then decrease during day, reaching their lowest at bedtime
\
**→ Stress:** Increases cortisol secretion to metabolically prepare body for dealing with stress
\
Upon stimulation hypothalamus by diurnal rhythm and stress, it releases CRH. This stimulates anterior pituitary to release ACTH, which stimulates release of cortisol from adrenal cortex (increasing blood glucose, protein and fats). Then, cortisol acts on hypothalamus and anterior pituitary in a negative feedback loop
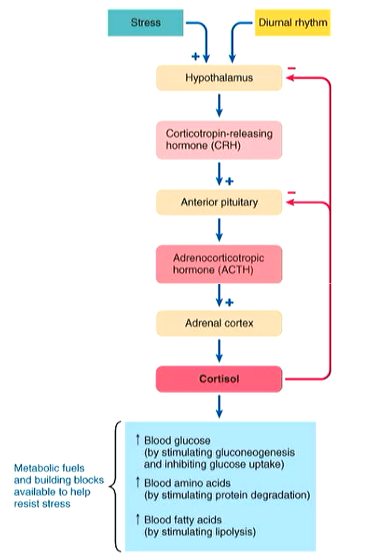
53
New cards
What does Adrenal Sex Hormones: DHEA hormone do, and how increase/ decrease amount of this hormone effect the body?
Adrenal cortex secretes both male and female sex hormones in **both** sexes
\
Hormone: Dehydroepiandrosterone (**DHEA**) which is androgen (male hormone)
\
→ Effects in males are overpowered by testicular testosterone in males thus this hormone doesn’t affect males
→ Effect in females:
1. Growth of pubic and axillary (armpits) hair
2. Enhancement of pubertal growth spurt
3. Development and maintenance of female sex drive
\
\
**→ Hypo-secretion -** low sex drive in females and little-to-no pubic and anxillary hair
\
**→ Hyper-secretion -** **Adrenogenital syndrome**
When someone is unable to form cortisol, brain sends signals/stimulating adrenal cortex to form cortisol yet this simply makes sex hormones which cause brain to take this signal as issue with the ovaries or testes and turn them off and no longer become able to produce sex hormones (become sterol)
\
Symptoms in females
→ Hirsutism (facial hair growth)
→ Deepening of voice, more muscular arms and legs
→ Breasts become smaller and menstruation may cease
\
Hormone: Dehydroepiandrosterone (**DHEA**) which is androgen (male hormone)
\
→ Effects in males are overpowered by testicular testosterone in males thus this hormone doesn’t affect males
→ Effect in females:
1. Growth of pubic and axillary (armpits) hair
2. Enhancement of pubertal growth spurt
3. Development and maintenance of female sex drive
\
\
**→ Hypo-secretion -** low sex drive in females and little-to-no pubic and anxillary hair
\
**→ Hyper-secretion -** **Adrenogenital syndrome**
When someone is unable to form cortisol, brain sends signals/stimulating adrenal cortex to form cortisol yet this simply makes sex hormones which cause brain to take this signal as issue with the ovaries or testes and turn them off and no longer become able to produce sex hormones (become sterol)
\
Symptoms in females
→ Hirsutism (facial hair growth)
→ Deepening of voice, more muscular arms and legs
→ Breasts become smaller and menstruation may cease
54
New cards
What does the adrenal medulla secrete?
Adrenal medulla secretes catecholamines (epinephrine (80%) and norepinephrine (20%))
55
New cards
What are the Adrenergic Receptors?
**Alpha (α) receptors (⍺1):** **Excitatory, constrictio**n - Constriction (↑) of blood vessels, constricts radial muscles of eye (leads to dilation of pupils)
\
**Alpha (α) receptors (⍺2): Inhibitory -** ↓Sympathetic nerve activity and digestive function
\
**Beta (β) receptors (β1): Excitatory (heart)** - (↑) Heart rate and force of contraction
\
**Beta (β) receptors (β2): Relaxation** - Dilate bronchioles, bladder, smooth muscle on digestive organs, release energy stores
\
**Alpha (α) receptors (⍺2): Inhibitory -** ↓Sympathetic nerve activity and digestive function
\
**Beta (β) receptors (β1): Excitatory (heart)** - (↑) Heart rate and force of contraction
\
**Beta (β) receptors (β2): Relaxation** - Dilate bronchioles, bladder, smooth muscle on digestive organs, release energy stores

56
New cards
Sympathetic Stimulation of the Adrenal Medulla
Catecholamine secretion by adrenal medulla is controlled entirely by **sympathetic input**
\
**Fear or stressors** activate sympathetic system and stimulate release of adrenomedullary catecholamines
\
**Epinephrine**, in turn, also affects CNS to promote a state of **arousal** and increased **CNS alertness**
\
→ This permits “quick thinking” that helps a person cope with an impending emergency
\
**Fear or stressors** activate sympathetic system and stimulate release of adrenomedullary catecholamines
\
**Epinephrine**, in turn, also affects CNS to promote a state of **arousal** and increased **CNS alertness**
\
→ This permits “quick thinking” that helps a person cope with an impending emergency
57
New cards
Epinephrine secretion would cause stimulation of ___ receptors on the heart and ___ heart rate
Beta 1, increase
58
New cards
What is stress?
→ Stress is a nonspecific response of body to any factor that overwhelms threatens body’s ability to maintain homeostasis
\
→ The **stressor** can be physical, chemical, physiological, infectious, or psychological/emotional, social
\
→ The **stressor** can be physical, chemical, physiological, infectious, or psychological/emotional, social
59
New cards
A General Reaction/body process to Stress
**A General Reaction to Stress**
1\. Activation of **sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight)** and secrete epinephrine (FAST process)
→ Prepares body for **fight-or-flight** response
\
2\. Secretion of **cortisol** via the **HPA** axis (SLOWER process)
→ Helps body cope by mobilizing metabolic resources (fuel/energy and high alertness)
\
3\. **Decreased insulin** secretion
→ Elevation of blood glucose and fatty acids
\
4\. Increased secretion of **vasopressin** and **aldosterone** as when body understress, it can’t distinguish if body is bleeding thus both are secreted
→ Maintenance of blood volume and blood pressure
1\. Activation of **sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight)** and secrete epinephrine (FAST process)
→ Prepares body for **fight-or-flight** response
\
2\. Secretion of **cortisol** via the **HPA** axis (SLOWER process)
→ Helps body cope by mobilizing metabolic resources (fuel/energy and high alertness)
\
3\. **Decreased insulin** secretion
→ Elevation of blood glucose and fatty acids
\
4\. Increased secretion of **vasopressin** and **aldosterone** as when body understress, it can’t distinguish if body is bleeding thus both are secreted
→ Maintenance of blood volume and blood pressure
60
New cards
Role of the Hypothalamus in Stress
The hypothalamus receives input from the periphery and central nervous system
\
Upon receiving input about a stressor the hypothalamus:
→ activates the sympathetic nervous system
→ secretes CRH to stimulate ACTH and cortisol release
→ triggers the release of vasopressin
\
Upon receiving input about a stressor the hypothalamus:
→ activates the sympathetic nervous system
→ secretes CRH to stimulate ACTH and cortisol release
→ triggers the release of vasopressin
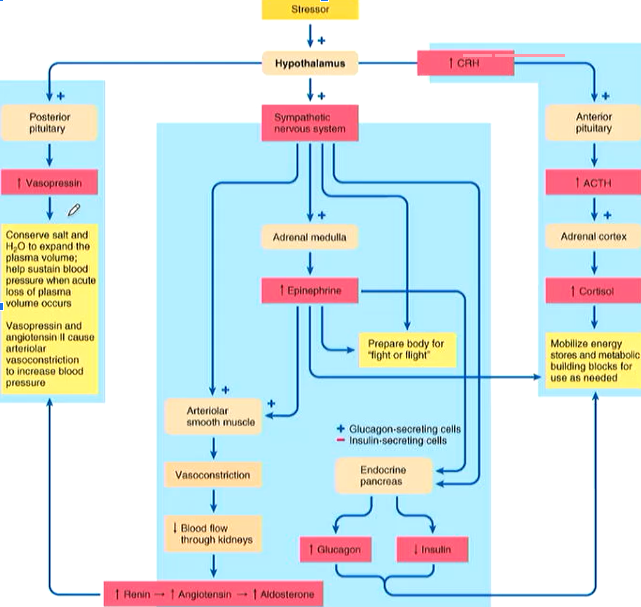
61
New cards
What is chronic stress? and how to reduce stress?
Stress that is persistent, lasting, or does not resolve is called **chronic stress**
→ this is where cortisol is elevated, sympathetic system always turned on, blood pressure is elevated
\
Chronic stress can lead to muscle tension, hypertension (high blood pressure), heart disease, impaired immune defences, weight gain, fatigue (as body can’t be in this process for long)
\
**To reduce stress:**
1\. Exercise regularly
2\. Ensure adequate sleep & nutrition
3\. Build a social support network
4\. Practice mindfulness
→ this is where cortisol is elevated, sympathetic system always turned on, blood pressure is elevated
\
Chronic stress can lead to muscle tension, hypertension (high blood pressure), heart disease, impaired immune defences, weight gain, fatigue (as body can’t be in this process for long)
\
**To reduce stress:**
1\. Exercise regularly
2\. Ensure adequate sleep & nutrition
3\. Build a social support network
4\. Practice mindfulness
62
New cards
What are energy providing nutrients
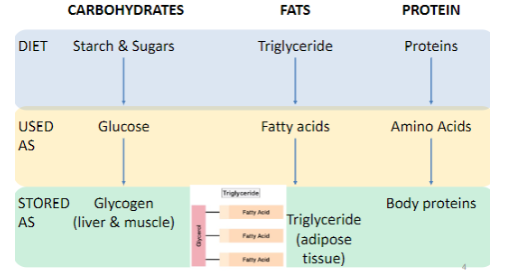
63
New cards
What is fuel metabolism
Metabolism are all chemical rxn’s that occur within cells
→ Includes rxn’s involving **catabolism** (breakdown), **anabolism** (synthesis), and **transformation** of **proteins, carbohydrates, and fats**
→ Includes rxn’s involving **catabolism** (breakdown), **anabolism** (synthesis), and **transformation** of **proteins, carbohydrates, and fats**
64
New cards
What is catabolism and anabolism?
**Catabolism** - breakdown or degradation of large, organic molecules within cells in two lvls:
\
→ Molecules broken down into subunits during __digestion__, this is called **hydrolysis** (ex: protein to amino acids)
→ Sybunits are then __absorbed__ and broken down further through **oxidation** to provide cells with **energy (ATP)**
\
→ We rely mostly on carbs and fats for energy but rarely proteins
→ Since protein only molecules that contains nitrogen atoms, this must be removed through urination
\
\
\
**Anabolism** - subunits are used to create large molecules using ATP to:
→ make materials used by cells (proteins, enzymes etc.)
→ store excess materials when not used
\
→ Molecules broken down into subunits during __digestion__, this is called **hydrolysis** (ex: protein to amino acids)
→ Sybunits are then __absorbed__ and broken down further through **oxidation** to provide cells with **energy (ATP)**
\
→ We rely mostly on carbs and fats for energy but rarely proteins
→ Since protein only molecules that contains nitrogen atoms, this must be removed through urination
\
\
\
**Anabolism** - subunits are used to create large molecules using ATP to:
→ make materials used by cells (proteins, enzymes etc.)
→ store excess materials when not used
65
New cards
What are Interconversions among Organic Molecules and where does it occur and why are they important?
→ These interconversions / transformations occur in liver
→ Glucose and amino acids can convert to fats while amino acid can be used to make glucose
→ These allow us to gain most of our nutrients that we need but **essential nutrients** can't OR can't be made enough in body thus must come from diet (ex. iodine, vitamin D)
→ Glucose and amino acids can convert to fats while amino acid can be used to make glucose
→ These allow us to gain most of our nutrients that we need but **essential nutrients** can't OR can't be made enough in body thus must come from diet (ex. iodine, vitamin D)
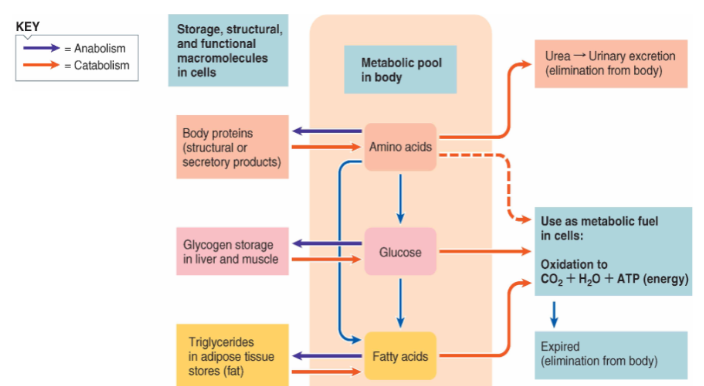
66
New cards
What are the states that the body fluctuates between?
Body fluctuates from **absorptive** (fed) and **post**-**absorptive** (fasted) states
→ **absorptive** (fed): fuel consumed and stored for later use
→ **post**-**absorptive** (fasted): stored fuel used and broken down to provide body energy
\
**Glucose in blood must be maintained within narrow ranged as it's essential for brain and red blood cells**
→ **absorptive** (fed): fuel consumed and stored for later use
→ **post**-**absorptive** (fasted): stored fuel used and broken down to provide body energy
\
**Glucose in blood must be maintained within narrow ranged as it's essential for brain and red blood cells**
67
New cards
**Regulation of Fuel Metabolism**
**Insulin** and **glucagon**: key hormones that regulate fuel metabolism and maintains blood glucose homeostasis
\
→ both produced and released by endocrine pancreas
\
\
\
**Insulin** - Hormone of absorptive state; it ↓blood glucose and promote **anabolism** and storage of fuel nutrients
\
**Glucagon** - Hormone of post-absorptive state; it ↑blood glucose and promote **catabolism** and fuel nutrients
\
\
\
There are also these hormones that can affect fuel metabolism
→Similar to glucagon hormone, growth hormone, ↑blood glucose and ↑fat breakdown but spares proteins
\
→ Cortisol hormone ↑blood glucose and ↑fat breakdown but ↑protein breakdown
\
→ both produced and released by endocrine pancreas
\
\
\
**Insulin** - Hormone of absorptive state; it ↓blood glucose and promote **anabolism** and storage of fuel nutrients
\
**Glucagon** - Hormone of post-absorptive state; it ↑blood glucose and promote **catabolism** and fuel nutrients
\
\
\
There are also these hormones that can affect fuel metabolism
→Similar to glucagon hormone, growth hormone, ↑blood glucose and ↑fat breakdown but spares proteins
\
→ Cortisol hormone ↑blood glucose and ↑fat breakdown but ↑protein breakdown
68
New cards
What is Absorptive (Fed) State process, action, and key hormone?
**Process -** increase lvl of glucose, fats and amino acids in blood
**Action -** ↓blood glucose and excess fuel must be stored stored (anabolism)
\
**key hormones: Insulin**
→ **↑glucose** in absorptive state simulates **beta-cells** in **pancreas** to **secrete insulin**
→ Insulin will tell cells to take up glucose, fats and amino acids and store fuel for later use (anabolism)**:**
\
(glucose → glycogen) (fatty aids → triglyceride) (amino acids → proteins)
**Action -** ↓blood glucose and excess fuel must be stored stored (anabolism)
\
**key hormones: Insulin**
→ **↑glucose** in absorptive state simulates **beta-cells** in **pancreas** to **secrete insulin**
→ Insulin will tell cells to take up glucose, fats and amino acids and store fuel for later use (anabolism)**:**
\
(glucose → glycogen) (fatty aids → triglyceride) (amino acids → proteins)
69
New cards
**Regulation of Insulin**
1\. Negative feedback loop when homeostasis of glucose achieved (primary control)
\
2\. Feedforward loop: as food travels through **guts**, it send signals to pancreas to release insulin in preparation thus glucose lvls increase and negative feedback occurs
\
3\. Increase in **amino acids** in blood causes for stimulation of insulin and as glucose lvls increase, negative feedback occurs
\
4\. Sympathetic NS (epinephrine) decreases insulin
\
2\. Feedforward loop: as food travels through **guts**, it send signals to pancreas to release insulin in preparation thus glucose lvls increase and negative feedback occurs
\
3\. Increase in **amino acids** in blood causes for stimulation of insulin and as glucose lvls increase, negative feedback occurs
\
4\. Sympathetic NS (epinephrine) decreases insulin
70
New cards
What is Post-absorptive (Fasted) State process, action, and key hormone?
**Process -** ↓blood glucose, fats and amino acids in blood
**Action - ↑**blood glucose and fuel stores broken down to provide energy for cells
\
**key hormones: Glucagon**
→ **↓glucose** in post-absorptive state stimulates **alpha-cells** in pancreas to **secrete glucagon**
→ Glucagon will use energy stores and break:
\
(glycogen → glucose ) (triglyceride → fatty aids) (proteins → amino acids)
**Action - ↑**blood glucose and fuel stores broken down to provide energy for cells
\
**key hormones: Glucagon**
→ **↓glucose** in post-absorptive state stimulates **alpha-cells** in pancreas to **secrete glucagon**
→ Glucagon will use energy stores and break:
\
(glycogen → glucose ) (triglyceride → fatty aids) (proteins → amino acids)
71
New cards
Complementary Actions of Glucagon and Insulin (just explain general process in a block-to-block formate
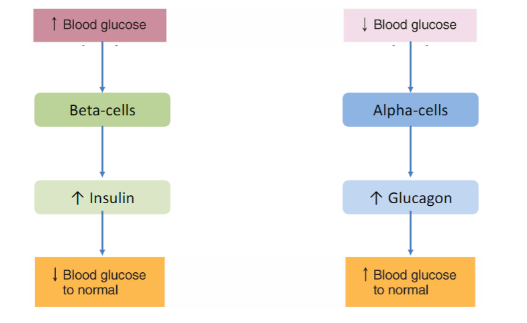
72
New cards
Dysregulation of Insulin: Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes are most common disorders which are caused by elevated blood glucose lvls
**→ Type 1 -** lack of insulin secretion (**hypo-secretion**)
**→ Type 2 -** normal/ increased insulin but reduced sensitivity of insulin target cells
\
**Without the aid of insulin, glucose is not taken up by cells. This leads to:**
→ Cells unable to use glucose
→ High levels of glucose in blood (hyperglycemia)
→ Excess glucose is excreted in urine leading to excess urination and dehydration
→ Dehydration decreases blood volume and influence all cells of body (most relevant to nervous and renal systems)
→ Over time, excess blood glucose can also damage proteins and nerves
\
**The effects of long-term uncontrolled diabetes:**
→ Cardiovascular issues (Heart disease)
→ Kidney damage
→ Vision problems
→ Peripheral neuropathy (tingling in extremities, can require amputation in severe cases)
**→ Type 1 -** lack of insulin secretion (**hypo-secretion**)
**→ Type 2 -** normal/ increased insulin but reduced sensitivity of insulin target cells
\
**Without the aid of insulin, glucose is not taken up by cells. This leads to:**
→ Cells unable to use glucose
→ High levels of glucose in blood (hyperglycemia)
→ Excess glucose is excreted in urine leading to excess urination and dehydration
→ Dehydration decreases blood volume and influence all cells of body (most relevant to nervous and renal systems)
→ Over time, excess blood glucose can also damage proteins and nerves
\
**The effects of long-term uncontrolled diabetes:**
→ Cardiovascular issues (Heart disease)
→ Kidney damage
→ Vision problems
→ Peripheral neuropathy (tingling in extremities, can require amputation in severe cases)
73
New cards
Glucose Counter-Regulatory Hormones
→ Glucagon, epinephrine, growth hormone and cortisol increase blood glucose
→ Only insulin decreases glucose
→ Only insulin decreases glucose
74
New cards
Food Intake
Desire to eat ("appetite") is controlled by appetite regulating hormone
\
**Short term regulation** occurs in response to eating/not eating
→ Empty stomach releases **ghrelin** to **stimulate appetite** in brain
→ Small intestine releases **gut hormones** to **suppress appetite** in brian
\
**Long term regulation**
→ Pancreas releases **insulin** to **suppress appetite** when glucose increases
→ Adipose tissue releases **leptin** to **suppress appetite** (leptin lvl is proportional to amount of adipose) thus as fat stores decrease, less leptin is released thus stimulate appetite and vise versa
→ In obesity, Leptin levels are high but target tissues (including neurons) become resistant to leptin’s effects
\
**Short term regulation** occurs in response to eating/not eating
→ Empty stomach releases **ghrelin** to **stimulate appetite** in brain
→ Small intestine releases **gut hormones** to **suppress appetite** in brian
\
**Long term regulation**
→ Pancreas releases **insulin** to **suppress appetite** when glucose increases
→ Adipose tissue releases **leptin** to **suppress appetite** (leptin lvl is proportional to amount of adipose) thus as fat stores decrease, less leptin is released thus stimulate appetite and vise versa
→ In obesity, Leptin levels are high but target tissues (including neurons) become resistant to leptin’s effects
75
New cards
Psychosocial and Environmental Influences on Food Intake
→ Habits (eating at set times)
→ Social situations (going out for dinner)
→ Availability of food (”That candy looks good”)
→ Pleasure/reward systems associated with eating
→ Stress
→ Social situations (going out for dinner)
→ Availability of food (”That candy looks good”)
→ Pleasure/reward systems associated with eating
→ Stress
76
New cards
What are some function of the bone?
**Functions**
→ Support and protection for soft tissue and organs
→ Assists in movement
→ Storage reservoir for calcium and other minerals
→ Bone marrow: source of all blood cells
→ Support and protection for soft tissue and organs
→ Assists in movement
→ Storage reservoir for calcium and other minerals
→ Bone marrow: source of all blood cells
77
New cards
What are types of bones?
**Types**
→ Femur bone (long)
→ Flat bone (sternum)
→ Irregular bone (vertebra)
→ Short bone (fingers and toes)
→ Femur bone (long)
→ Flat bone (sternum)
→ Irregular bone (vertebra)
→ Short bone (fingers and toes)
78
New cards
What is the bone anatomy?
The bone contains 2 parts**:**
\
**→ Epiphysis (short section) -** made up contains spongy bone (contains red bone marrow)
Spongy bone has more free space to support bone (strong) without being heavy
\
**→ Diaphysis (long section) -** made up of compact bone (contains medullary cavity which contains red bone marrow which isn't associated with making RBC's)
\
Compact bone is more compact to support bone (heavy and hard). They are arranged into ring structure called **osteon** (funtional unit of the bone) and within it, there's a central canal (blood supply) and each of these rings act as **osteocytes** (bone cells) within matrix of Ca+
\
**→ Epiphysis (short section) -** made up contains spongy bone (contains red bone marrow)
Spongy bone has more free space to support bone (strong) without being heavy
\
**→ Diaphysis (long section) -** made up of compact bone (contains medullary cavity which contains red bone marrow which isn't associated with making RBC's)
\
Compact bone is more compact to support bone (heavy and hard). They are arranged into ring structure called **osteon** (funtional unit of the bone) and within it, there's a central canal (blood supply) and each of these rings act as **osteocytes** (bone cells) within matrix of Ca+
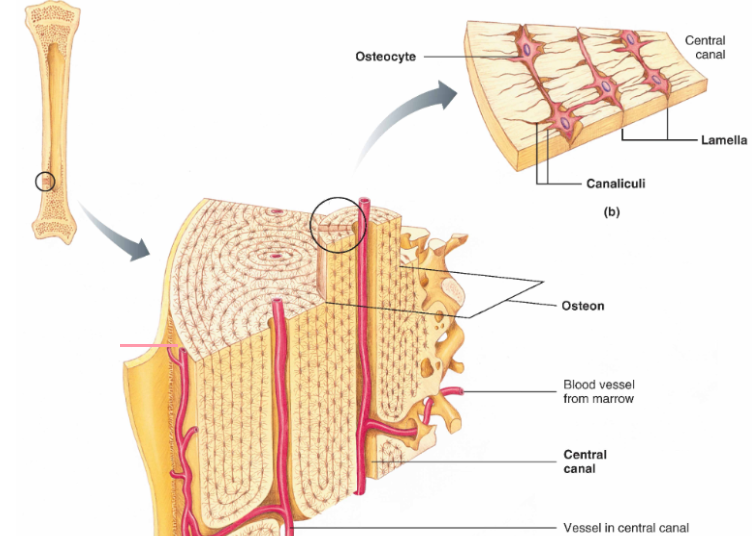
79
New cards
How are bones living and dynamic
Bone are living tissues composed of cells; these cells are embedded into hard matrix composed of collagen and **calcium-phosphate**
\
**→** Bones have blood and nerve supply and are connective tissue (few cells embedded into matrixs thus bone are connective)
\
**→** Bones have blood and nerve supply and are connective tissue (few cells embedded into matrixs thus bone are connective)
80
New cards
How does bone grow?
Bone building (deposition) and dissolving (resorption) occurs throughout life
\
Adults bone building deposition is = bone resorption but later on, bone dissolving becomes greater thus leading to net bone loss
\
Children bone deposition is greater than bone resorption thus leading to **bone growth**
**→** bone growth is driven by (1) GH hormone (2) IGF-1 hormone (3) sex hormones
**→** bone growth is stimulated by mechanical stress (certain exercises)
\
Bones are build and resorbed through process called **remodeling** which occurs throughout life span so we can rebuild small fractures and releases Ca+, P and other minerals from bone
\
Adults bone building deposition is = bone resorption but later on, bone dissolving becomes greater thus leading to net bone loss
\
Children bone deposition is greater than bone resorption thus leading to **bone growth**
**→** bone growth is driven by (1) GH hormone (2) IGF-1 hormone (3) sex hormones
**→** bone growth is stimulated by mechanical stress (certain exercises)
\
Bones are build and resorbed through process called **remodeling** which occurs throughout life span so we can rebuild small fractures and releases Ca+, P and other minerals from bone
81
New cards
What are bone cells?
**→ Osteo**__**b**__**lasts** bone cell secrete bone matrix to __b__uild new bone
**→ Osteo**__**c**__**lasts** bone cell breaks bone to release __c__alcium
**→ Osteocytes** mature bone cells embedded in calcium matrix
**→ Osteo**__**c**__**lasts** bone cell breaks bone to release __c__alcium
**→ Osteocytes** mature bone cells embedded in calcium matrix
82
New cards
Body Ca 2+
90% Ca2+ found in bones
10% Ca2+ found in other tissues
90% in cells 10% in extracellular (50% bound to protein and 50% are free which we want to maintain)
\
**→** Extracellular Ca2+ is important for\*\*:\*\*
1\. neuromuscular excitability
2\. release of neurotransmitters
3\. contraction of cardiac and smooth muscle
4\. clotting blood
\
**→** Intracellular Ca2+ is important for\*\*:\*\*
1\. secondary messenger
\
Ca2+ must be kept at a small range or it will disturb neuromuscular excitability
**→ Hyper-calcaemia -** reduce ability to excite or contract muscles
**→ Hypo-calcaemia -** overexcitability of nerves and muscles; if svere increase, this will cause fatal spastic contractions of respiratory muscles (can't breath)
10% Ca2+ found in other tissues
90% in cells 10% in extracellular (50% bound to protein and 50% are free which we want to maintain)
\
**→** Extracellular Ca2+ is important for\*\*:\*\*
1\. neuromuscular excitability
2\. release of neurotransmitters
3\. contraction of cardiac and smooth muscle
4\. clotting blood
\
**→** Intracellular Ca2+ is important for\*\*:\*\*
1\. secondary messenger
\
Ca2+ must be kept at a small range or it will disturb neuromuscular excitability
**→ Hyper-calcaemia -** reduce ability to excite or contract muscles
**→ Hypo-calcaemia -** overexcitability of nerves and muscles; if svere increase, this will cause fatal spastic contractions of respiratory muscles (can't breath)
83
New cards
**Control of Ca 2+ Levels**
Control of Ca2+ occurs at three locations**:**
1\. Resorption of Ca+ from **bone → rapid maintenance of homeostasis**
2\. Absorption of dietary Ca2+ by **intestine**
3\. Excretion of Ca2+ in urine by **kidneys**
( both: long term maintainece of Ca2+ balance)
\
Regulation of Ca2+ occurs by three hormones**:**
1\. Parathyroid PTH
2\. Vitamin D
3\. Calcitonin
1\. Resorption of Ca+ from **bone → rapid maintenance of homeostasis**
2\. Absorption of dietary Ca2+ by **intestine**
3\. Excretion of Ca2+ in urine by **kidneys**
( both: long term maintainece of Ca2+ balance)
\
Regulation of Ca2+ occurs by three hormones**:**
1\. Parathyroid PTH
2\. Vitamin D
3\. Calcitonin
84
New cards
What is Parathyroid Hormone
→ **Primary Regulator of Ca2+**
→ Hormone secreted by parathyroid gland
→ Essential for life as it prevents fatal consequence of hypo-calcaemia
→ When Ca2+ decreases, PTH increases Ca2+ in free plasma by it affecting **bone**, **kidneys** and **intestine** (indirectly)
→ Controls activation of vitamin D
\
**Side Note:** PTH is small and since they are located in thyroid, people that get surgery on them, accidentally remove parathyroid glands thus people often died thus now surgeons are careful to not remove any to preserve its function
→ Hormone secreted by parathyroid gland
→ Essential for life as it prevents fatal consequence of hypo-calcaemia
→ When Ca2+ decreases, PTH increases Ca2+ in free plasma by it affecting **bone**, **kidneys** and **intestine** (indirectly)
→ Controls activation of vitamin D
\
**Side Note:** PTH is small and since they are located in thyroid, people that get surgery on them, accidentally remove parathyroid glands thus people often died thus now surgeons are careful to not remove any to preserve its function
85
New cards
PTH - effect on bone
As Ca2+ decreases, parathyroid gland secretes PTH which goes to bone to either have a fast or slow exchange
\
**→ Fast exchange -** PTH tells bone to move Ca from fluid into blood
\
1\. PTH first activates membrane-bound calcium pumps in the plasma membranes of osteocytes and osteoblasts
2\. Pumps promote movement of calcium from the bone fluid into these cells
3\. Calcium is then transferred into the plasma of the central canal
\
**Slow exchange -** If Ca+ balance is not restored by quick exchange, PTH stimulates osteoclasts cell to break bone to release calcium into blood
\
**→ Fast exchange -** PTH tells bone to move Ca from fluid into blood
\
1\. PTH first activates membrane-bound calcium pumps in the plasma membranes of osteocytes and osteoblasts
2\. Pumps promote movement of calcium from the bone fluid into these cells
3\. Calcium is then transferred into the plasma of the central canal
\
**Slow exchange -** If Ca+ balance is not restored by quick exchange, PTH stimulates osteoclasts cell to break bone to release calcium into blood
86
New cards
PTH - effect on kidneys
As Ca2+ decreases, parathyroid gland secretes PTH which goes to kidneys to keep Ca2+ and promote release of PO43- during urine
\
→ (Ca and PO4 3 forms complex thus to be able to use Ca, we must release PO4)
→ PTH enhances activation of vitamin D in kidneys
\
→ (Ca and PO4 3 forms complex thus to be able to use Ca, we must release PO4)
→ PTH enhances activation of vitamin D in kidneys
87
New cards
PTH - effect on intestine
→ PTH has no direct effect on intestine
→ Indirectly increases absorption of Ca2+ and PO43- from small intestine by helping activate vitamin D
→ Indirectly increases absorption of Ca2+ and PO43- from small intestine by helping activate vitamin D
88
New cards
Activation of Vitamin D
Must be activated in **liver** and **kidneys** (stimulated by PTH) to function
\
→ Main function is stimulating Ca2+ and PO43- absorption from intestine
→ Without it, most Ca2+ will be absorbed by intestine and released as body feces
→ It enhances effect of PTH on bone
\
→ Main function is stimulating Ca2+ and PO43- absorption from intestine
→ Without it, most Ca2+ will be absorbed by intestine and released as body feces
→ It enhances effect of PTH on bone
89
New cards
What are Calcitonin
Hormone produced by C-cells of thyroid gland
\
→ Secreted when Ca2+ in plasma increases
→ Negative feedback to bring Ca2+ lvl down
→ Decreased Ca2+ by inhibiting activity of bone osteoclasts
→ Important only during **hyper-calcaemia**
\
→ Secreted when Ca2+ in plasma increases
→ Negative feedback to bring Ca2+ lvl down
→ Decreased Ca2+ by inhibiting activity of bone osteoclasts
→ Important only during **hyper-calcaemia**
90
New cards
What would you expect to see in PTH hypersecretion? (Hyperparathyroidism)?
→ Hypercalcaemia and hypophosphatemia
91
New cards
What would be the main clinical presentations of PTH hypersecretion? (Hyperparathyroidism)?
→ Weakened bone and muscle weakness (from reduced excitability) (Ca2+ released from bone)
92
New cards
What would you expect to see in PTH hyposecretion? (Hypoparathyroidism)?
→ Hypocalcaemia and hyperphosphataemia
93
New cards
What would be the main clinical presentation of PTH hyposecretion? (Hypoparathyroidism)?
→ Only muscle spasms (from overexcitability) (bone isn’t affected)
94
New cards
what indicates Vitamin D Deficiency and how does it occur in childhood and adulthood?
Deficiency in Vitamin D indicated a decrease in calcium
\
→ Children - Rickets
→ Adults - Osteomalacia
(both: unpermineralized (soft) bone)
\
→ Children - Rickets
→ Adults - Osteomalacia
(both: unpermineralized (soft) bone)
95
New cards
how does muscle system achieve homeostasis in body?
Muscle system helps in movement to:
\
→ Flee from danger
→ To obtain nutrient + H2O
→ Breathing is achieved by muscles in the respiratory sys
→ Pumping blood is achieved my heart contracting its muscles
→ Digestion process is achieved by it moving through digestion muscle tracts
→ When cold, body shivers to generate heat
\
→ Flee from danger
→ To obtain nutrient + H2O
→ Breathing is achieved by muscles in the respiratory sys
→ Pumping blood is achieved my heart contracting its muscles
→ Digestion process is achieved by it moving through digestion muscle tracts
→ When cold, body shivers to generate heat
96
New cards
The key characteristic that differentiates muscle from other tissues is
→ Ability to contact (shorten); by shortening, movement is generated through body
97
New cards
What are the types of muscle tissue?
→ Muscle comprises largest group of tissues in body
\
Three types of muscle\*\*:\*\*
1\. **Skeletal muscl**e attach to bone to generate movement of the body
2\. **Cardiac muscle** found only in heart
3\. **Smooth muscl**e appears throughout body systems as components of hollow organs and tubes
\
→ Striated muscle contain dark and light bands; this is due to contraction in cardiac and skeletal muscles are arranged in patterns
\
**Note:** respiratory muscles are skeletal muscle thus **voluntarily**
\
Three types of muscle\*\*:\*\*
1\. **Skeletal muscl**e attach to bone to generate movement of the body
2\. **Cardiac muscle** found only in heart
3\. **Smooth muscl**e appears throughout body systems as components of hollow organs and tubes
\
→ Striated muscle contain dark and light bands; this is due to contraction in cardiac and skeletal muscles are arranged in patterns
\
**Note:** respiratory muscles are skeletal muscle thus **voluntarily**
98
New cards
What is skeletal muscle and what is it composed of?
Skeletal muscle is covered in connective tissue which extends to the ends and attach to a bone; this connection is called **tendon**
\
Looking closely to our muscle, we see little bundles and each bundle is an individual **muscle fiber** (1 single cell) which contains many **myofibril** which is the active part of the muscle thus it’s the thing that contracts
\
Myofibril is made up on a **sarcomere** which is the functional part of muscle which is smallest part that contracts
\
Looking closely to our muscle, we see little bundles and each bundle is an individual **muscle fiber** (1 single cell) which contains many **myofibril** which is the active part of the muscle thus it’s the thing that contracts
\
Myofibril is made up on a **sarcomere** which is the functional part of muscle which is smallest part that contracts
99
New cards
What are muscle fibers, how is it fromed, and the components of a muscle fiber?
A muscle consists of a # of **muscle fibers** (muscle cells) lying parallel to one another and held together by connective tissue
\
Muscle fibres are formed by #’s of myofibril diffusing together to create a single long cell thus it’s **multinucleated** (cell that has mutiple nuclei) thus muscle fibers are elongated, cylindrically shaped and usually extend entire length of muscle
\
Unique components of muscle fibres include:
→ **Sarcolemma -** plasma membrane of muscle fibre
→ **Sarcoplasmic reticulum -** specialized endoplasmic reticulum of muscle cells (plays key role in Ca 2+ entry for muscle contraction)
→ **Myofibrils -** contractile organelles
\
Muscle fibres are formed by #’s of myofibril diffusing together to create a single long cell thus it’s **multinucleated** (cell that has mutiple nuclei) thus muscle fibers are elongated, cylindrically shaped and usually extend entire length of muscle
\
Unique components of muscle fibres include:
→ **Sarcolemma -** plasma membrane of muscle fibre
→ **Sarcoplasmic reticulum -** specialized endoplasmic reticulum of muscle cells (plays key role in Ca 2+ entry for muscle contraction)
→ **Myofibrils -** contractile organelles
100
New cards
What are myofibrils and what does it consist of?
**Myofibrils** are the contractile elements of muscles
\
They consist of repeated **sarcomeres**, or contractile units that are made of a regular arrangement of thick and thin filaments
→ **Thick filaments** - myosin (protein)
→ **Thin filaments** - actin (protein)
\
Viewed microscopically, a myofibril displays alternating dark bands (the A bands) and light bands (the I bands), giving appearance of striations
\
They consist of repeated **sarcomeres**, or contractile units that are made of a regular arrangement of thick and thin filaments
→ **Thick filaments** - myosin (protein)
→ **Thin filaments** - actin (protein)
\
Viewed microscopically, a myofibril displays alternating dark bands (the A bands) and light bands (the I bands), giving appearance of striations