Chemical Kinetics: Temperature, Activation Energy, and Mechanisms
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Temperature
Measure of average kinetic energy of molecules.
Reaction Rate
Speed at which reactants convert to products.
Collision Model
Reactions require molecular collisions to occur.
Activation Energy (Ea)
Minimum energy needed for a reaction to proceed.
Transition State
High-energy state during a chemical reaction.
Activated Complex
Species present at the transition state.
Reaction Coordinate Diagram
Visual representation of energy changes in reactions.
Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution
Distribution of molecular kinetic energies at a temperature.
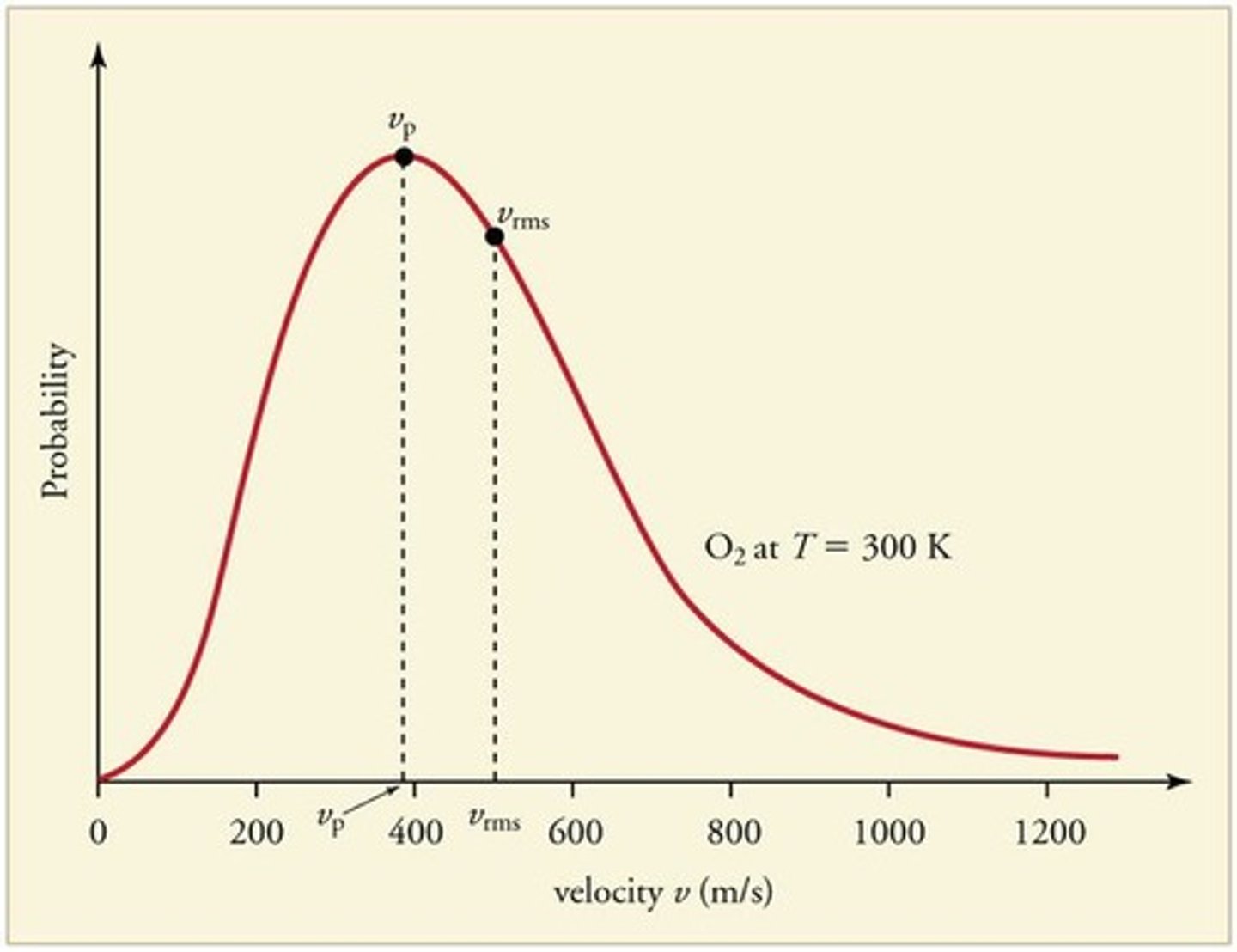
Frequency Factor (A)
Likelihood of effective collisions in a reaction.
Arrhenius Equation
Mathematical relationship between rate constant and activation energy.
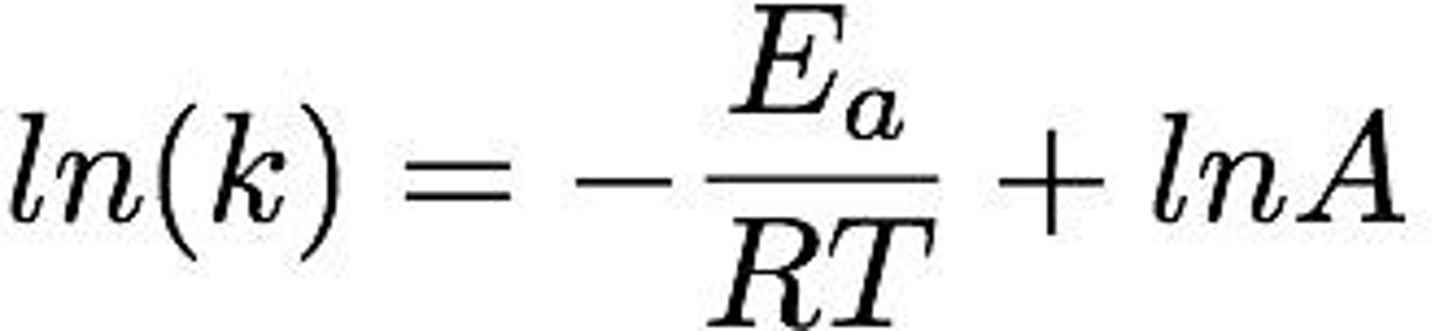
Natural Logarithm
Logarithm to the base e, used in Arrhenius Equation.
Elementary Reaction
Single step in a reaction mechanism.
Molecularity
Number of molecules involved in a reaction step.
Rate Law
Expression relating reaction rate to reactant concentrations.
Rate-Determining Step
Slowest step in a multistep reaction mechanism.
Catalyst
Substance that increases reaction rate by lowering activation energy.
Enzyme
Biological catalyst that speeds up biochemical reactions.
Induced Fit Mechanism
Model where substrate binding changes enzyme shape.
Kinetic Energy
Energy of motion, related to temperature.
Energy Barrier
Energy threshold that must be overcome for reaction.
Reaction Mechanism
Sequence of steps converting reactants to products.
Intermediate
Species formed during the reaction but not in products.
Temperature Increase Effect
Higher temperature increases reaction rate and energy distribution.
Slope of ln k vs. 1/T
Used to calculate activation energy from experimental data.
Dotted Line in Distribution
Represents activation energy in Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution.
Broadening of Distribution
Wider range of energies at higher temperatures.
Collision Orientation
Correct alignment needed for effective molecular collisions.
Energy Changes
Variations in energy throughout a chemical process.
Chemical Reaction
Process where reactants transform into products.
Fast Step
Step in a reaction mechanism that occurs quickly.
Slow Step
Step in a reaction mechanism that limits overall rate.
Reactants and Products
Substances consumed and formed in a chemical reaction.