APUSH AMSCO Chapter 2 Vocab: The Thirteen Colonies and the British Empire, 1607-154
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Cecil Calvert, Lord Baltimore
proprietor of Maryland, implemented Act of Toleration for religious freedom (limited to Christians)
Act of Toleration
first colonial statute (Maryland) granting religious freedom (to all Christians). But statute called for death of anyone who denied divinity of Jesus
Roger Williams
respected Puritan minister, but was banished from Massachusetts Bay by Puritans because he believed an individual's conscious was beyond the control of church/civil authority. went to Narragansett Bay and established settlement of Providence 1636
Providence
est 1636 by Roger Williams. recognized rights of Native Americans (paid them fairly for use of their land). Religious freedom (Catholics, Quakers, Jews could worship freely). Founded one of first Baptist churches of America
Anne Hutchinson
also questioned doctrines of Puritan authorities. Believed in antinomianism. Banished from Bay Colony by Puritans. Established Portsmouth 1638, not far from Roger Williams' Providence settlement. Was killed in a Native American uprising a few year slater on Long Island
antinomianism
idea that faith alone, not deeds, necessary for salvation
Rhode Island
1644, Roger Williams granted charter from Parliament to join Providence and Portsmouth into a single colony. Became a colony that tolerated diverse beliefs, served as a refuge for many.
Halfway Covenant
1660s, a generation had passed since founding of first Puritan colonies in New England. To be a full member of Puritan church, had to have felt a "profound religious experience" known as a conversion. But no native-born generation had these experiences. This covenant offered by some clergy offered partial church membership to people even if they haven't felt a conversion. Was an attempt to maintain church's influence and membership. Rejected by many ministers
Quakers
believed in equality of men and women, nonviolence, resistance to military service. Believed religious authority found within each person's soul, not Bible or other outside source. Were persecuted and jailed for their beliefs in England
William Penn
Quaker, proprietor of Pennsylvania, enacted liberal ideas in government, wanted to provide a religious refuge for Quakers/other persecuted people
Holy Experiment
Penn wanted to make a colony that would be a religious refuge for Quakers and other persecuted people
Charter of Liberties (1701)
a written constitution for early Pennsylvania under Penn that guaranteed freedom of worship for all and unrestricted immigration
rice plantation
as tobacco fell, rice and indigo became most profitable crops. this plantation system used most in South Carolina, worked enslaved Africans. Resembled economy and culture of West Indies
tobacco farms
farming in North Carolina. small and self-sufficient. less reliant on slaves
John Cabot
English explorer who explored Americas more than a century before England actually started colonizing
Jamestown
first permanent English colony in America, established 1607 by the Virginia Company. Struggled at first. (starvation) Took a while for them to prosper, even after the introduction of tobacco.
Later developed into Virginia
Puritans
dissenters of Protestant Reformation in England, believed that the Church of England could be reformed. wanted to purify church of Roman leftovers. Unlike Separatists, did not want to leave church completely. Seeked religious freedom so got charter for Massachusetts Bay Company (1629)
Separatists
Dissenters of Protestant Reformation in England, wanted to leave the church completely and organize a completely separate church independent of royal control. Left England in search of religious freedom. Eventually came to Americas and established Plymouth in MA
Pilgrims
Separatists known as this because of their travels in search of a haven for their religion (first went to Holland for religious freedom, but then set sail for Virginia)
Mayflower
ship of 100 passengers heading for Virginia. Less than half were Separatists, most were just there with economic motives rather than religious
Plymouth colony
accidental colony (separatists intended to go to Jamestown, made landfall too far north), along Massachusetts. Good relations with Native Americans, first Thanksgiving and stuff
Massachusetts Bay Colony
Puritans went here, seeking religious freedom. Led by John Winthrop. Established 1630, founded Boston
John Winthrop
led Puritans to Massachusetts Bay Colony, was governor for 20 years
Great Migration
movement started by civil war in England in 1630s drove out 15 thousand more settlers to MA Bay Colony
Virginia
Chesapeake colony chartered by Virginia Company in 1606, started with Jamestown as a corporate colony. Became a royal colony officially in 1624
Thomas Hooker
led large group of Boston Puritans into fertile Connecticut River Valley, founded colony of Hartford in 1636. Hartford drew up first written constitution in American history, The Fundamental Orders of Connecticut. Established rep government that was parliament-style
John Davenport
started second settlement in Connecticut Valley 1637, called New Haven
Connecticut
1665, New Haven joined with more democratic Hartford settlement to make colony. Royal charter for this colony granted limited degree of self-government, including electing a governor
New Hampshire
last colony to be founded in New England, originally part of Massachusetts Bay but was split off by King Charles II who hoped to increase royal control over the colonies, 1679. Was a royal colony subject to authority of an appointed governor
The Carolinas
Charles II granted a huge tract of land between VA and Spanish FL to 8 nobles who helped him regain the throne in 1663 (during Restoration). 1729 - 2 royal colonies, SC and NC, made from original grant
New York
easily took control (without a fight) of this from the Dutch (originally called New Amsterdam) because King Charles II wanted to close the gap between New England and the Chesapeake Colonies. Dutch in the colony treated well though
New Jersey
split off of New York in 1664 because NY was too big to administer. Following a bunch of chaos with changing of land titles between various groups of Quakers who bought/sold their proprietary repeatedly, British crown settled matters and made this area a single, united royal colony
Pennsylvania
established by William Penn, 1681, recognized all religious freedoms. was a refuge for those who were prosecuted
Delaware
3 lower counties that broke off of Pennsylvania, granted own assembly (but didn't get own governor separate from PA governor until American Revolution)
Georgia
last colony chartered, mainly as a buffer between Spanish Florida and prospering South Carolina. Originally established by philanthropists, but they gave up on the poorly prospering colony. Became royal colony in 1752. Copied SC's plantation system
James Oglethorpe
one of the philanthropists who helped establish Georgia for England's jailed debtors who wanted a new life (and found Savannah in 1733), was colony's first governor
Wampanoags
tribe in southern New England, resisted English encroachment on their land
Metacom
chief of the Wampanoags, known to colonists as King Phillip. United many tribes in southern New England against English settlers. Was eventually killed by colonists
King Philip's War
King Philip united a bunch of southern New England tribes in retaliation to English encroachment on native land. Was bloody and viscous war, many towns/villages burned and thousands of people died. In the end, colonies defeated Native Americans and killed King Phillip. Ended most American Indian resistance in New England
Mayflower Compact
Pilgrims drew up and signed a document that pledged they would make decisions based on will of majority, representative government in New England
Virginia House of Burgesses
12 years after founding of Jamestown, VA's colonists organized first every representative assembly in America
Sir William Berkeley
royal governor of VA. Used dictorial powers to govern on behalf of large planters, failed to protect small farmer's on VA's western frontier from Native American attacks
Bacon's Rebellion
poor farmer organized a rebellion against Berkeley's government (VA) in 1676. Led raids/massacres against American Indian Villages on VA Frontier. Burned Jamestown to the ground after defeating governor's forces. But short-lived; rebellion died with Bacon, who died of dysentery
Fundamental Orders of Connecticut (1639)
first written constitution in American history, established parliamentary-style representative government (Hartford colony, 1636)
New England Confederation
1640s. New England colonies face constant threat of attack from Native Americans, Dutch, and French. But England in the midst of a civil war so colonies had to fend for themselves. 1643, 4 New England colonies formed a military alliance (lasted to 1684, when English crown restored and colonial rivalries picked up again)
Frame of Government (1682)
Pennsylvania, guaranteed representative assembly elected by landowners
corporate colonies
operated by joint-stock companies (at least during colonies' early years); ex - Jamestown
royal colonies
under direct authority/rule of king; ex - Virginia after 1624
proprietary colonies
under authority of individuals granted charters of ownership by king; ex - Pennsylvania/Maryland
chesapeake colonies
Virginia and Maryland, the "tidewater" colonies
"low country"
Carolinas (and eventually Georgia)
"back country"
land from the foothills of the Appalachian to the western frontier of European settlement
joint-stock company
A company that sells stock/shares (investors), expect to make a profit
Virginia Company
joint stock company of England, chartered by King James I and founded first permanent English settlement in the Americas, Jamestown
mercantilism
economic policy of minimizing imports and maximizing exports. colonies were expected to contribute to the accumulation of wealth for their mother country (colonies provide raw materials to parent country for the growth and profit of parent country's industries)
Navigation Acts
a series of acts (1650-1673) that implemented the mercantilist policy and forbade colonial trade with other countries and intended to increase the crown's surveillance on colonial economic activities
Dominion of New England
King James II combined various New England colonies (NY, NJ, etc) into a single larger administrative unit in an attempt to increase royal control over colonies (also got rid of the representative assemblies). Was shortlived because King James II was overthrown back in England in a matter of years
Sir Edmund Andros
King James II sent this person to serve as governor of the Dominion of New England. was instantly unpopular because he levied taxes, limited town meetings, revoked land titles
Glorious Revolution of 1688
uprising that overthrew the unpopular King James II (disliked because kept trying to assert his royal powers). Replaced him with William and Mary
indentured servants
Virginia Company's first attempt at meeting the labor demands of the colonies; British immigrants who were under contract with a master/landowner who paid for their passage to the Americas and worked for a specified amount of time (5-7 years). Provided temporary laborers
headright system
Virginia's attempts to attract immigrants by offering land. 50 acres were offered to each immigrant who paid for their own passage, or to any plantation owner who paid for another immigrant's passage
slavery
West Africans brought to the Americas, originally like indentured servants. Soon slavery laws evolved and they were slaves for life, and passed on their slave status to their kids. Worked rice/indigo plantations in the south
triangular trade
3-part trade route from New England to West Africa to the West Indies and back. Traded rum for slaves in West Africa, slaves for sugarcane in the West Indies, and sold sugar for making rum
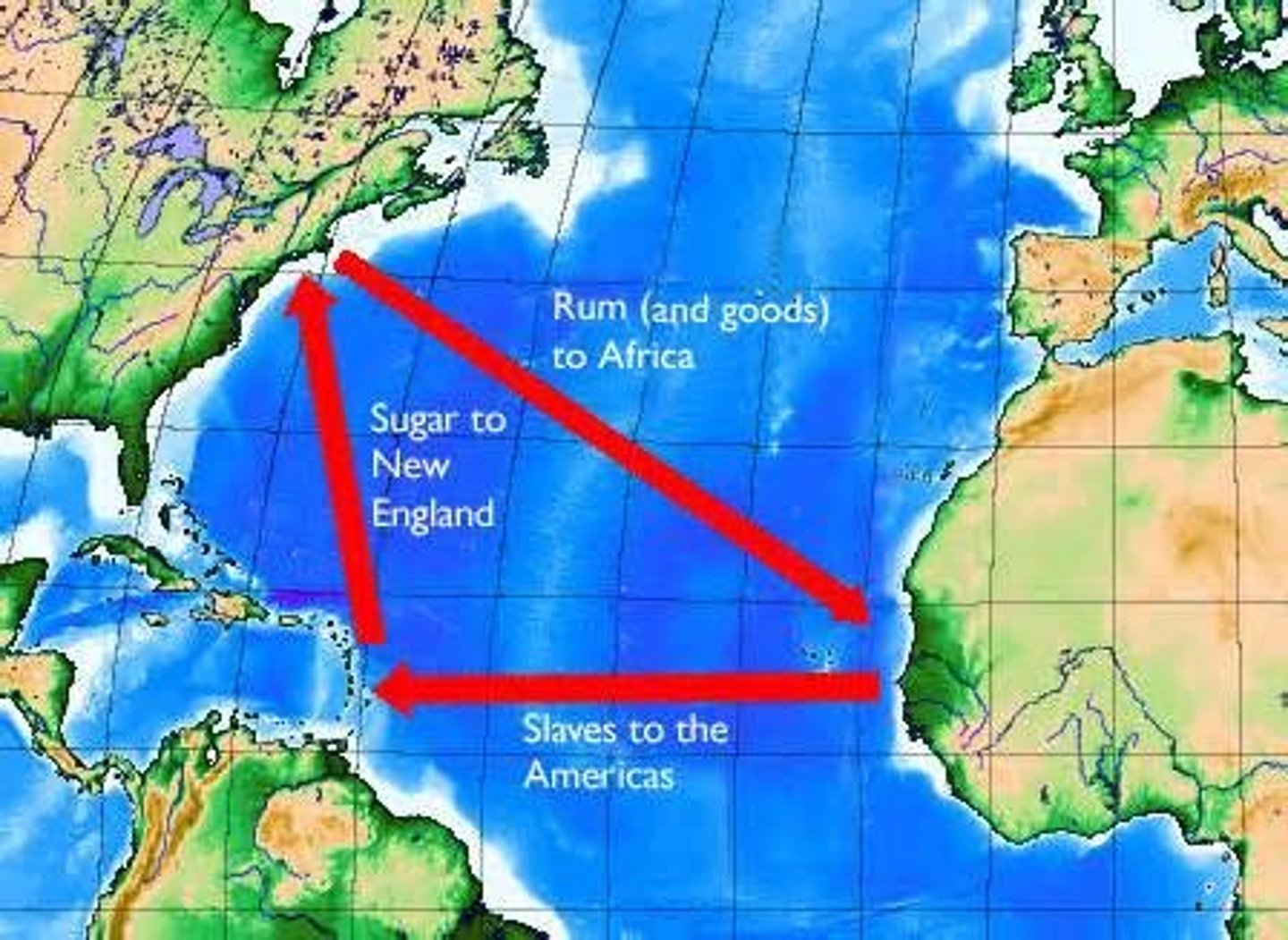
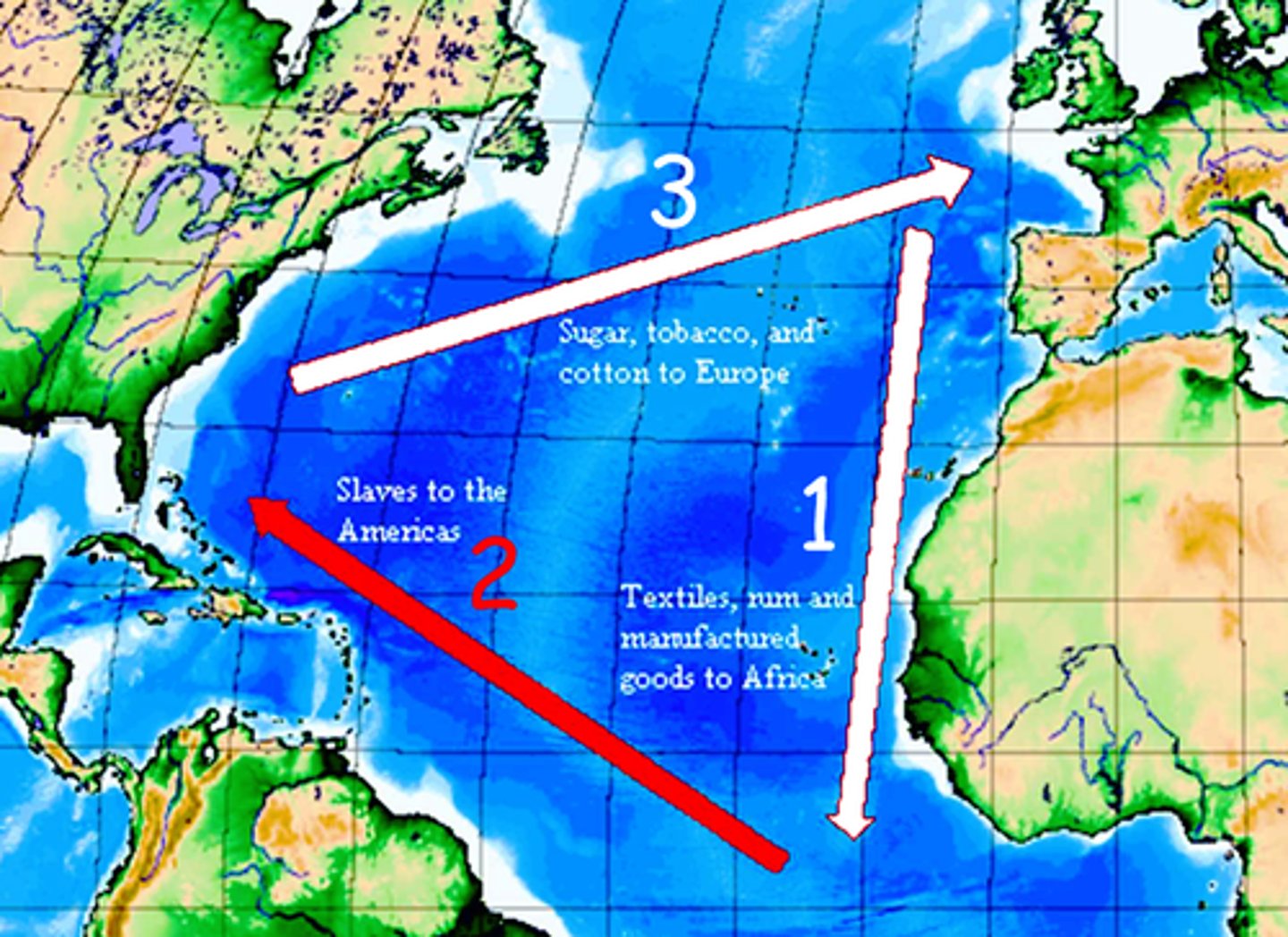
Middle Passage
A voyage that brought enslaved Africans across the Atlantic Ocean to North America and the West Indies
capitalism
-Colonization brought wealth to European imperial powers which resulted in political and economic innovations.
-Economic innovations like joint stock companies emerged and capitalism began to replace feudalism (gold and silver increased wealth of European countries, led to banking/capitalism)