UWORLD Rheumatology Step 2 CK
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Patients with diffuse sclerosis (SSc) frequently have extradermal organ involvement, especially the lungs. The most common pulmonary compilation in patients with SSC is ___.
Interstitial fibrosis
- leading cause of death
Pt has dysphagia, Raynaud phenomenon, expensive skin thickening => diffuse systemic sclerosis (SSc aka scleroderma)
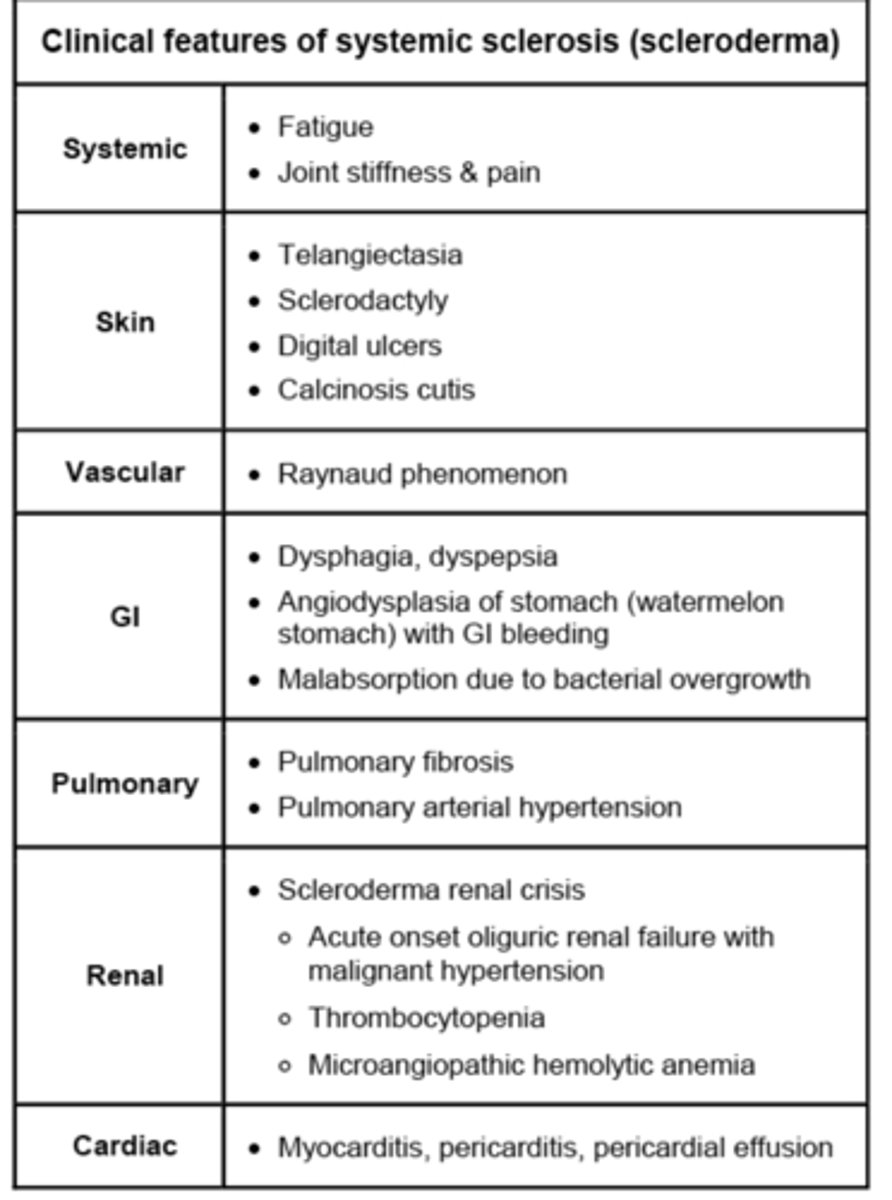
How is ankylosing spondylitis confirmed?
Plain film X-ray AP => fused SI joints and/or bamboo spine
Seronegative spondyloarthropathy progressive inflammatory back pain, common males, young pt presenting with progressive LBP and spinal stiffness > 3 mo., morning stiffness > 30 min, pain improves with exercise
* when AS is strongly suspected clinically and lumbar spine X-ray is negative or equivocal MRI is recommended highly sensitive and specific SI may be diagnostic
Pain: rapid onset, may be severe
A "popping" sensation at the time of injury
Significant swelling (effusion/hemarthrosis)
Joint instability
Dx?
ACL injury
- anterior laxity of tibia relative to femur (anterior drawer test)
- Dx: MRI
- Tx: RIC, +/1 sx
Rapid deceleration or direction changes, pivoting on LE w/ foot planted
Rupture of popliteal cyst (Baker cyst) associated with which condition?
OA of the knee
- > posterior knee pain, swelling, calf resembling DVT
- > older adults
___ common in young female athletes with chronic overuse rather than acute trauma to the knee. Pain over the anterior knee that is reproduced by extending the knee and comprising the patella.
Patellofemoral pain
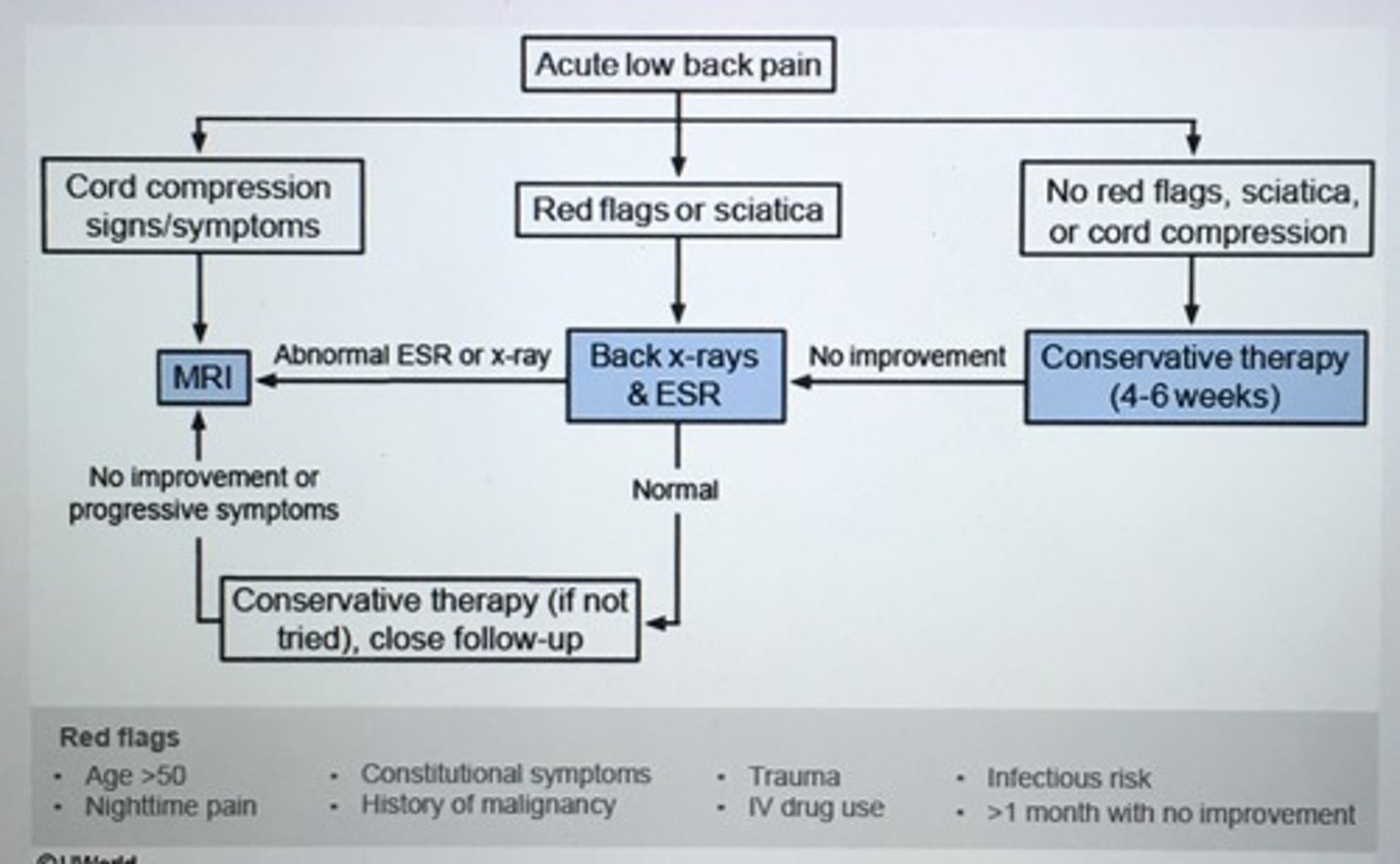
In patient with acute 'mechanical' back pain w/o significant neurological deficit what is the approach to tx?
Conservative approach period 4-6 weeks
- early mobilization
- muscle relaxants
- NSAIDs
* Bed rest and PT has not been shown to be helpful
** Pain persists after 4-6 weeks of conservative tx or progressive neuro deficit evolves get MRI or CT w/ w/o contrast myelography
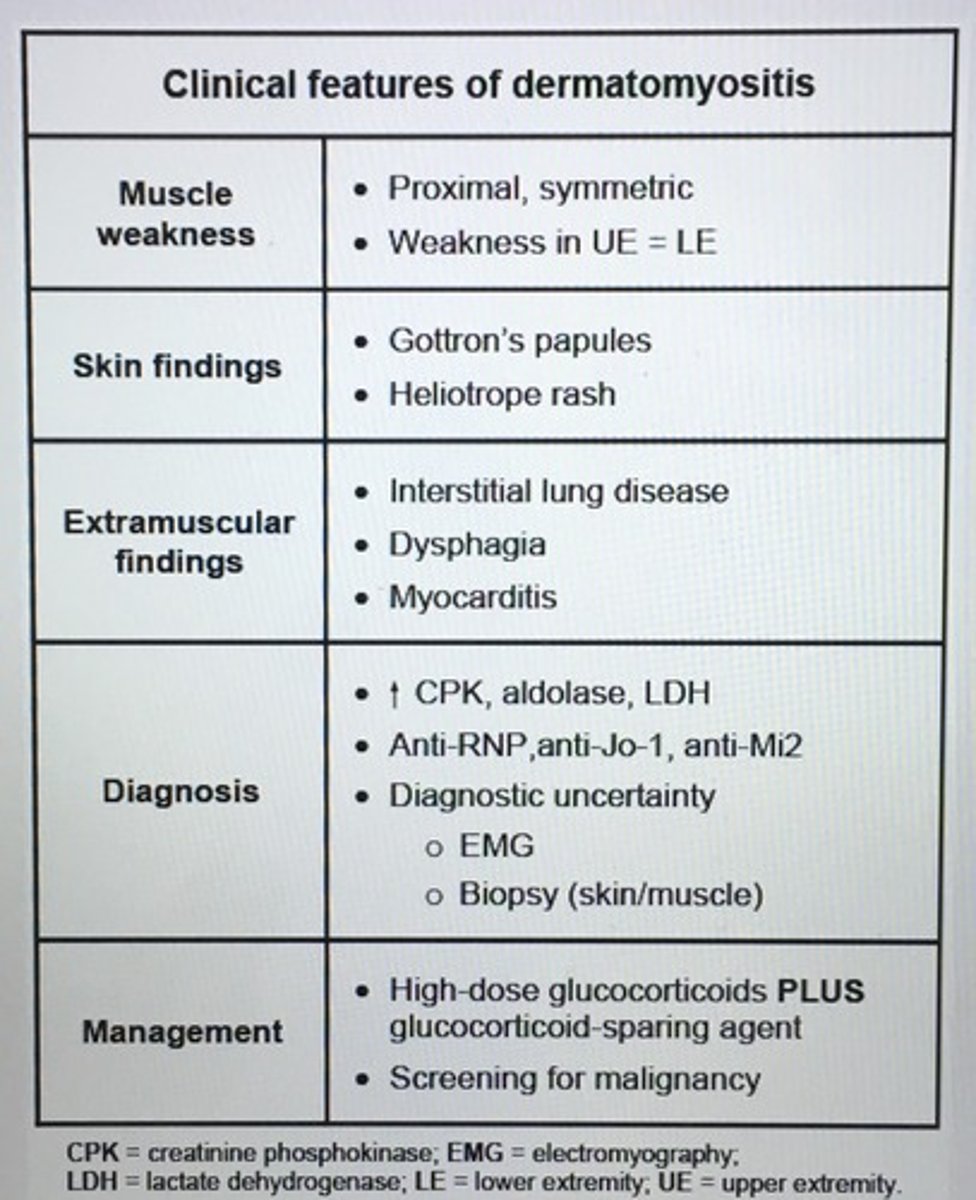
Fluctuating muscle weakness
- ocular (ptosis, diplopia)
- bulbar (dysphagia, dyasthria)
- facial, neck & limb muscles
Myasthenia gravis
- Acetylcholine receptor in the postsynaptic membrane
Proximal muscle weakness
Autonomic dysfunction (dry mouth)
CN involvement (ptosis)
Diminished or absent DTR
Lambert-Eaton syndrome
- diminished or absent DTR
Symmetrical & proximal muscle weakness
Interstitial lung dz, esophageal dysmotility, Raynauds
Polyarthritis
Skin findings
Can be due to a paraneoplastic syndrome in malignancy
Dermatomyositis, polymyositis
- muscle fiber injury
- Gottron's papules, heliotrope rash in dermatomyositis
- confirm dx muscle biopsy
What accounts for the majority of cases of avascular necrosis of bone (osteonecrosis)?
Chronic corticosteroid use
Chronic excessive ingestion alcohol
Antiphospholipid syndrome
- Pt presents with slow progressive anterior hip pain with limitation of ROM, MRI is the most sensitive test
What is required in SLE patient with new onset of lupus nephritis?
Renal biopsy
- immunosuppressive tx can be given once lupus nephritis is classified
Arthritis must be present for at least ___ weeks in order to dx RA.
6 weeks
Pt presents with one week of pain in multiple joints, MCP and PIP, and wrist. Pt has contact with children. Resolves in 2 mo. Dx.
Viral arthritis
- Parvovirus
- acute, morning stiffness > 30 min, lack of joint swelling, absence systemic symptoms
___ induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head usually presents as progressive hip or groin pain w/o restriction of ROM and normal X-ray on early stages.
Corticosteroid
- MRI gold standard for dx
- other causes: alcoholism, hemoglobinopathies
Screening for osteoporosis.
DEXA screening for osteoporosis in all women age > 65 years
Reactive arthritis findings.
Urethritis
Conjunctivitis
Mucocutaneous lesions
Enthesitis (Achilles tendon pain)
Asymmetric oligoarthritis
Seronegative spondyloarthropathy resulting from enteric or GU infection
tx: NSAIDs
Pts with ___ complain of shoulder pain aggravated by activities such as reaching or lifting the arm over the head.
Rotator cuff tendonitis
- impingement
- Neer test (passive motion of the arm above the head) = pain and guarding confirms impingement
- Lidocaine into shoulder -> improved ROM and relief = rotator cuff tendonitis
MRI - definitive dx
Pseudogout is a form of acute arthritis induced by the release of ___ crystals from sites of chrondrocalcinosis (calcification of articular cartilage) into the joint space.
Calcium pyrophosphate dehydrate (CPPD)
- rhomboid, positive birefringent crystals dx
___ result from excessive fluid production by an inflamed synovium as occurs in cases of RA, OA, and cartilage tears.
Baker cyst
- sometimes hurst and relate their contents into the calf -> appear similar to DVT
Ankylosing spondylitis involved primarily the ___ of the axial skeleton.
Apophyseal (facet) joints
- measure inflammatory markers (ESR, C-reactve protein)
- HLA-B27 typing
- Imaging spine
- Pain improved w/ exercise, hip/buttock pain, anterior uveitis, enthesitis (tendon insertion of bone inflammation)
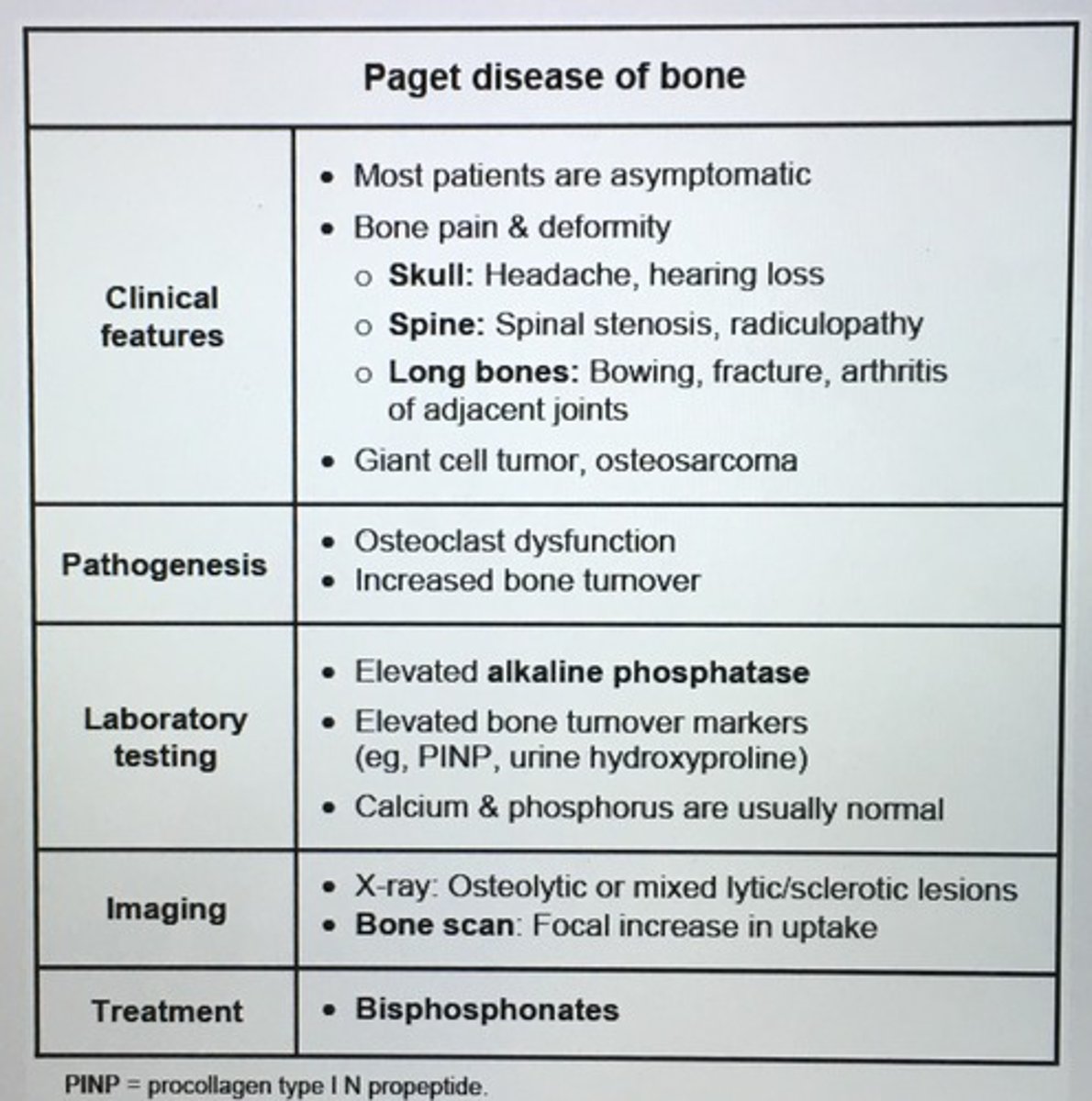
The single most common cause of asx isolated elevation of alkaline phosphatase in an elderly pt is ___.
Paget's disease of bone (osteitis deforming)
- defective osteoid formation at sites of high bone turnover hypertrophy of bone
- skull, clavicles, pelvis, and long bones
- pathological fractures, pain, osteosarcoma, and neuro sxs
___ are the most common findings on cervical radiography in pts with cervical spondylosis.
Osteophytes - bone spurs
= 10% of people older 50
- limited neck rotation and lateral bending due to OA and secondary muscle spasm
Over 60, back pain radiates buttocks and thighs, numbness and paresthesias, sx worse during walking and lumbar extension, flexion alleviates the sx. Pedal pulses normal. Dx confirmed with MRI.
Lumbar spinal stenosis
- enlarged osteophytes at the facet joints and hypertrophy of the ligament flavum
__ disease of the vertebrae typically presents as pain that is chronic, dull, worse at night, and changes little with activity. Pain non-radiating.
Metastatic disease
Tx Sarcoidosis
Systemic glucocorticoids if symptomatic
- hilar adenopathy w/ or w/o reticulonodular infiltrates, bx of noncaseating granulomas
- INC ACE
Pt has keratoconjuncitivits and xerostomia. Dental caries with difficulty swallowing. Enlargement of glands and firmness with lymphocytic infiltration of the salivary glands. Dx.
antibodies to Ro/SSA and or SSB(La)
Antimitochondrial
Primary biliary cirrhosis
Pt suffering for ankylosing spondylitis for 2 decades or longer are at an INC risk of ___.
Vertebral fracture due to DEC bone mineral density
- osteopenia/osteoporosis cause by inflammation that results in INC osteoclast activity
Acute mono arthritis, hot, swollen, DEC ROM, fever, elevated ESR and CRP.
Septic arthritis
- blood cx
- synovial fluid analysis: leukocytosis (>50,000), gram stain, cx
Initial tx septic arthritis
Gram + cocci: Vanco
Gram - cocci: 3rd gen Cephalosporin
Negative microscopy: Vanco + 3rd gen cephalosporin if immunocompromised
Risk factors septic arthritis
Abnormal joint: OA, RA, prosthetic joint, gout
Age > 80
DM
IV drug abuse, alcoholism
Intra-articular glucocorticoid injections
Paget disease of bone (osteitis deformans) associated with which levels?
Calcium
Serum Phosphate
Alkaline phosphatase
Urinary hydroxyproline
Calcium Normal
Phosphate Normal
Alkaline phosphatase INC
Hydroxyproline INC (along with INC deoxypyridinonline, N-telopeptide, C-telopeptide)
Fatigue, widespread pain, cognitive/mood disturbances. Dx. Initial tx.
Fibromyalgia
- Amitriptyline
- aerobic exercise, good sleep hygiene
- Duloxetine, milnacipran, pregabalin alternative tx
__ multi-systemic inflammatory condition characterized by recurrent oral and genital ulcers, skin lesions, seen most commonly in Turkish, Asian, and Middle eastern population.
Behcet's syndrome
Dx: Bx
Tx: Steroids

Fall outstretched hand, shoulder pain nd weakness when lifting arm above the head is suggestive of ___ pathology. Lidocaine injection does not help. Dx. Imaging?
Rotator cuff tear
- MRI visualize soft tissue structures
Tenderness & swelling tibial tubercle, preadolescent/adolescent athletes, recent growth spurt, INC pain with sports relived by rest.
Osgood-Schlatter disease
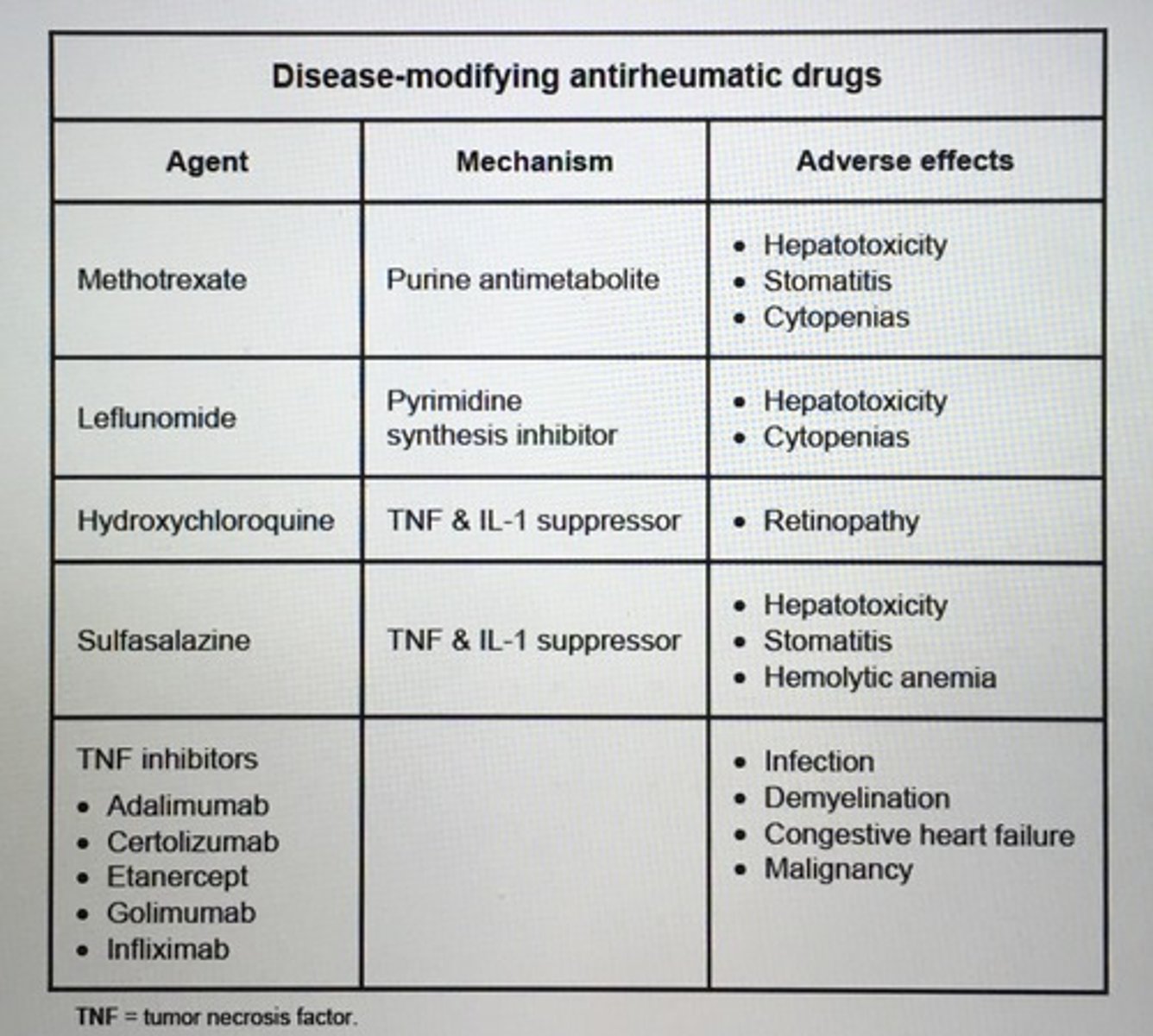
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs
Methotrexate: INC oral ulcers, acute rise in serum transaminases
folic acid supplementation recommended pts on MTX
Felty syndrome
Seen in pts with severe, long standing > 10 years RA characterized by neutropenia and splenomegaly
Pathogenesis carpal tunnel syndrome
Occurs 30% hypothyroidism
- deposition of mucopolysshacharide protein complexes w/in the perineum and the endoneurium of the median nerve
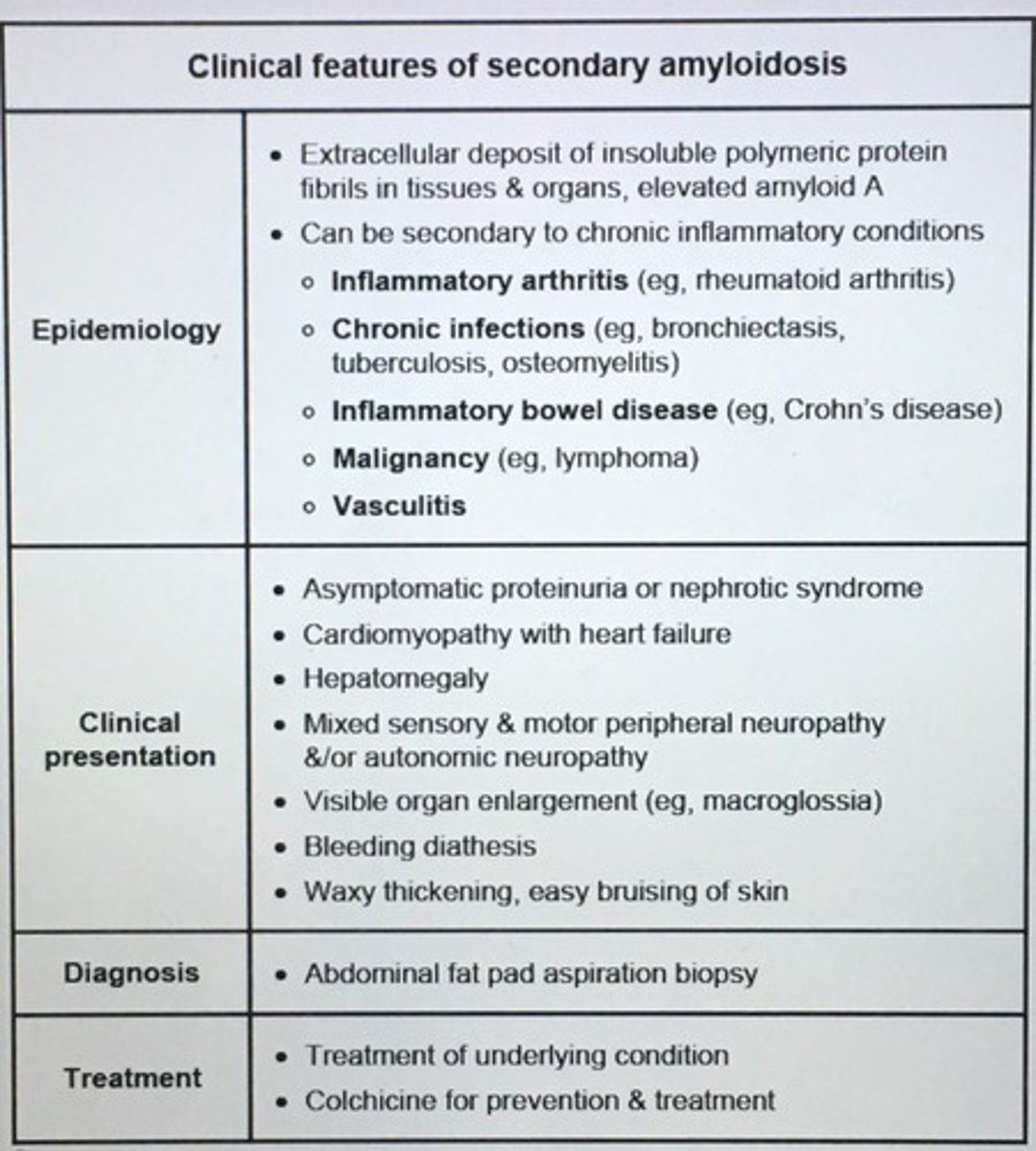
Clinical features of secondary amyloidosis.
Symmetrical proximal muscle weakness, difficulty climbing stairs, getting up from a chair, carrying heavy groceries. Elevated muscle enzymes (CK, aldolase, LDH, aspartate aminotransferase). EMG abnormal.
Polymyositis
- anti-Jo-1
- Bx: endomysial mononuclear infiltration patchy necrosis
- associated with malignancy as a paraneoplastic syndrome
- tx: corticosteroids (prednisone) and glucocorticoid-sparing agents (methotrexate, azathioprine)
Age > 50. Aching and morning stiffness > pain in shoulder, hips, neck, torso. No muscle tenderness. Elevated ESR >40. Sxs improve with corticosteroids.
Polymyalgia rheumatica
- morning stiffness > 1 month pain in shoulder and hip girdles
- low dose prednisone
- associated with temporal arteritis
___ is a complication of giant cell or temporal arteritis.
Aortic aneurysm
- serial chest x-ray followup
Gout is a common complication of ___ disorders due to excessive turnover of purines and resulting INC uric acid production.
Myeloproliferative disorders
- polycythemia vera
RA presents with progressive and symmetrical joint involvement. Common sites include MCP + PIP fingers, MTP toes, and wrist. RA most commonly affects the __ spine.
Cervical spine in the axial skeleton and can cause -> spinal subluxation and spinal cord compression
Lateral epicondylitis is degeneration of the ___ tendon near the lateral epicondyle.
Extensor carpi radialis brevis
Complications of ankylosing spondylitis.
AR
Osteoperosis/vertebral fractures
Cauda equina
Chondrocalcinosis on imaging. Inflammatory effusion. Acute mono or oligoarticular arthritis. Peripheral joints (knee common).
Pseudogout (acute calcium pyrophosphate crystal arthritis)
- calcification of articular cartilage
- intra-articular glucocorticoids
- NSAIDs
- Colchicine
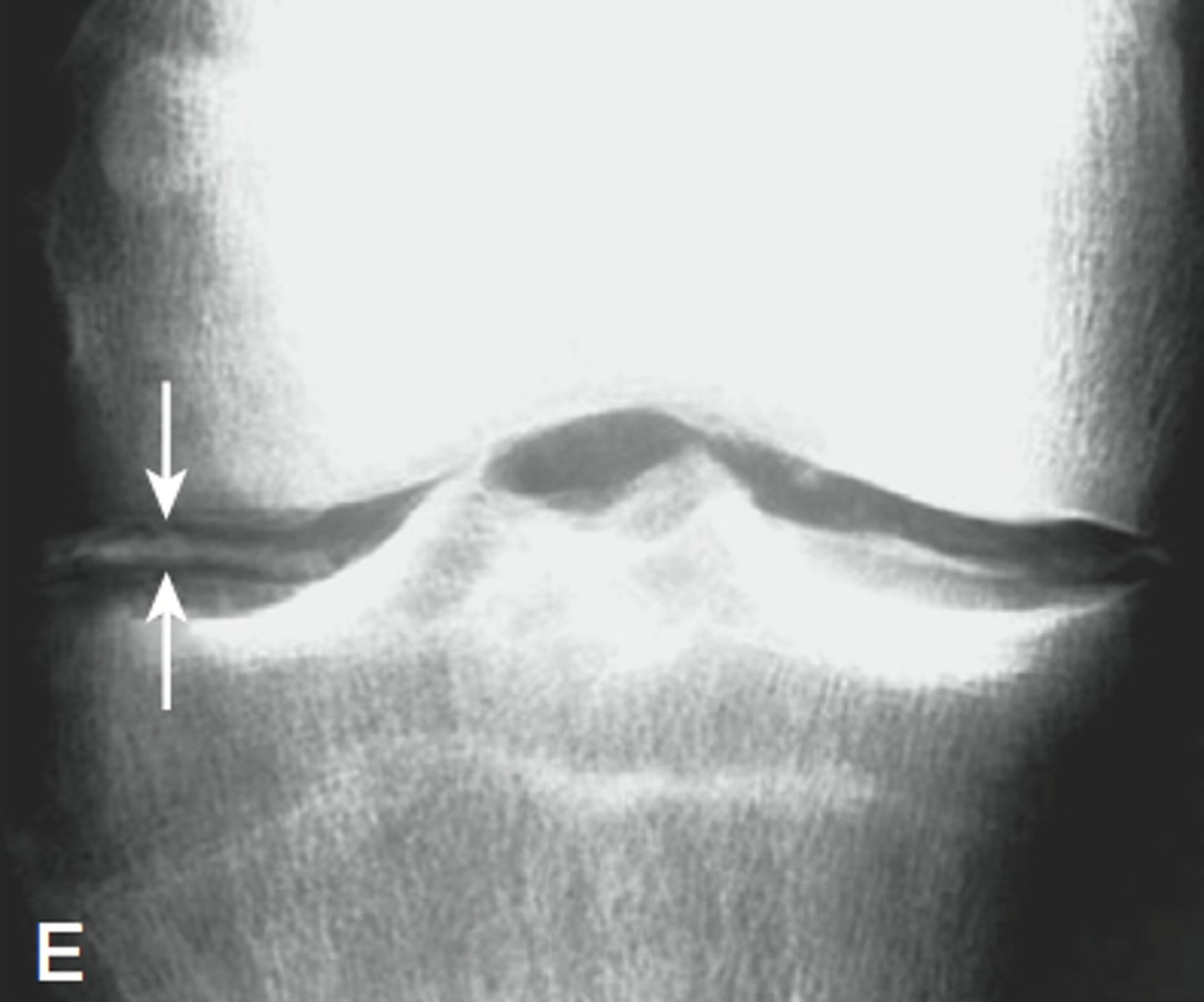
> 50, obesity, prior joint injury, chronic insidious onset, minimal/no morning stiffness, knees/hips, DIP joints, cervical/lumbar spine, hard, bony enlargement of joints. Crepitus with movement. Dx.
Osteoarthritis
- X-rays show narrowed joint space, osteophytes, subchondral sclerosis
Associated diseases with pseudogout.
Hemochromatosis
Hyperparathyroidism
Hypothyroidism
Hypercalcemia
___ many occur in association with inflammatory arthritis. Ankylosing spondylitis and __ are both associated with HLA-B27 and may occur in association with one another. Positive P-ANCA absence vasculitis.
IBD
- UC
- bloody diarrhea, anemia, and negative stool cultures, skin (erythema nodosum, pyoderma gangrenosum), episcleritis, arthritis, and cholangitis
Erythema nodosum (EN) is a condition of painful, red, or violaceous SQ nodules common on the anterior lower legs. Which test should be ordered next to r/o more serious disease?
CXR
- sarcoidosis patients with EN 25% or TB
Clinical features of dermatomyositis
Malignancies: ovarian, lung, pancreatic, stomach, colorectal, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma
DIP joint, asymmetric oligoarthritis, symmetric polyarthritis, arthritis mutilans, dactylitis, nail pitting, onycholysis, swelling hands or feet with pitting edema.
Psoriatic arthritis
- arthritis precedes skin disease
- NSAIDs, methotrexate, anti-tumor necrosis factor
Tx pyoderma gangrenosum.
Systemic corticosteroids
Skin biopsy r/o other causes
SE long term cyclophosphamide.
Bladder carcinoma, acute hemorrhagic cystitis, sterility, myelosuppression
hemorrhagic cystitis and bladder cancer are caused by acrolein, bladder-toxin metabolite of cyclophosphamide
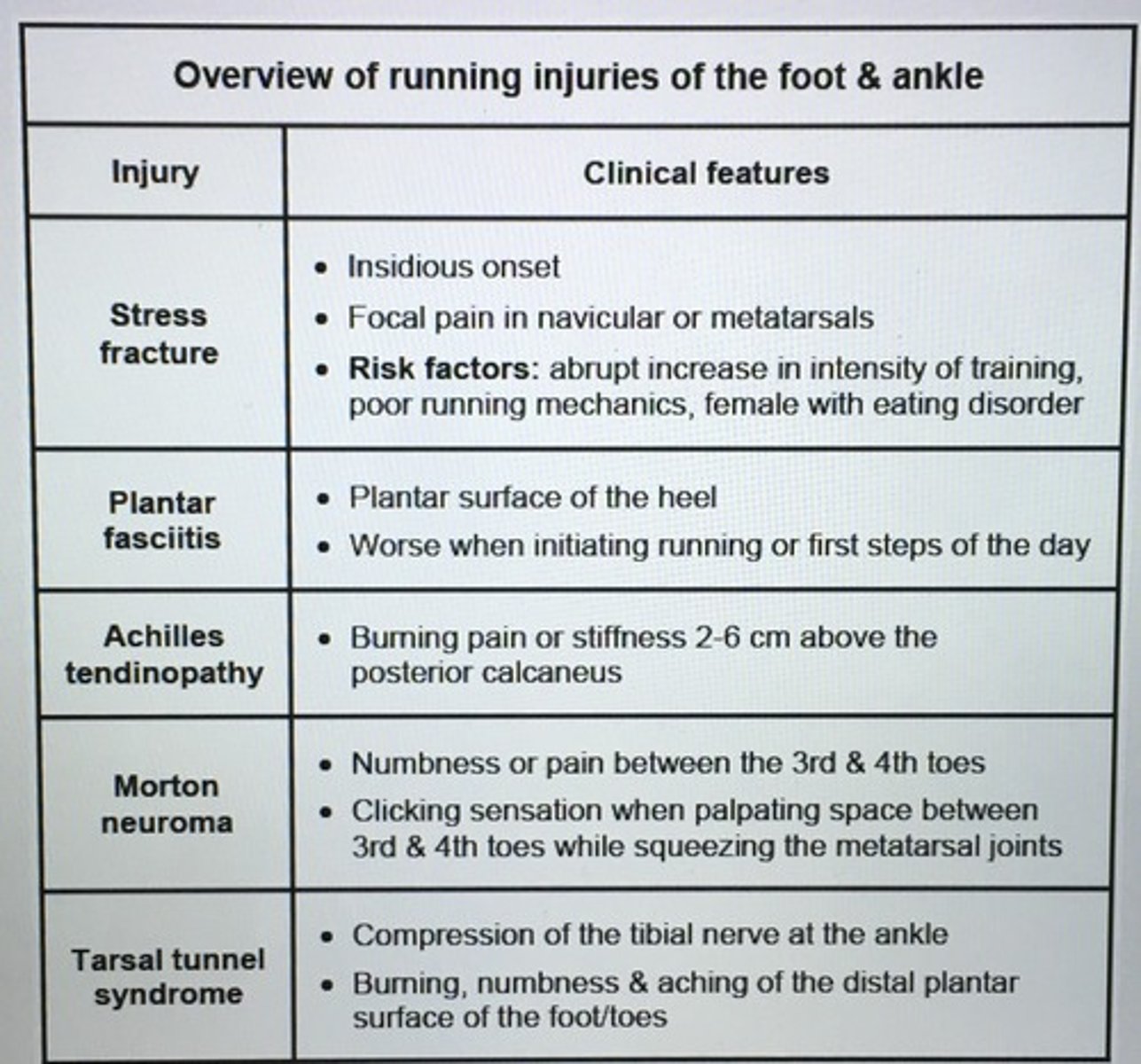
Overview of running injuries of the foot and ankle.
Paget disease of bone clinical features. Labs. Imaging. Tx.
Triggers for gout.
Alcohol use
Surgery/trauma
Dehydration
Certain meds (diuretics, low dose aspirin, cyclosporine)
High protein (meat, seafood), fructose, sweetened beverages
Which factors decrease risk of gout.
Dairy product intake
Vitamin C > 1500
Coffee intake > 6 cups/day
SE hydroxychloroquine
Retinopathy
- baseline ophthalmology evaluation annual reassessment after 5 years
TNF & IL-1 suppressor
SE Methotrexate
Hepatotoxicity
Stomatitis
Cytopenias
Purine antimotabolite
SE sulfasalizine
Hepatotoxicity
Stomatitis
Hemolytic anemia
TNF & IL-1 suppressor
Tenderness to gentle percussion over the spinous process of IVDU.
Vertebral osteomyelitis
Staph aureus
ESR > 100
MRI dx
IV abx
Rheumatoid arthritis algorithm
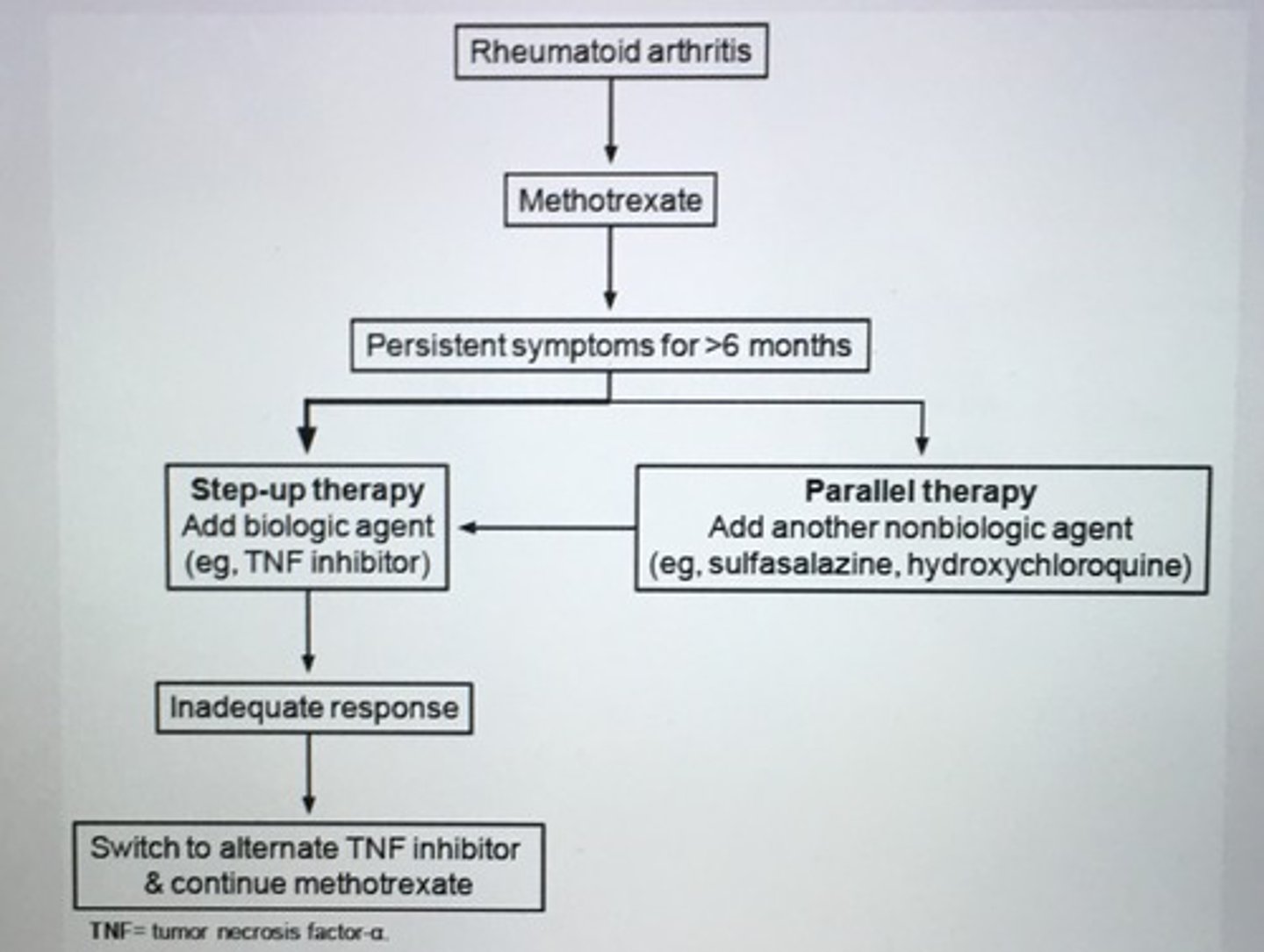
Disease modifying anti rheumatic drugs
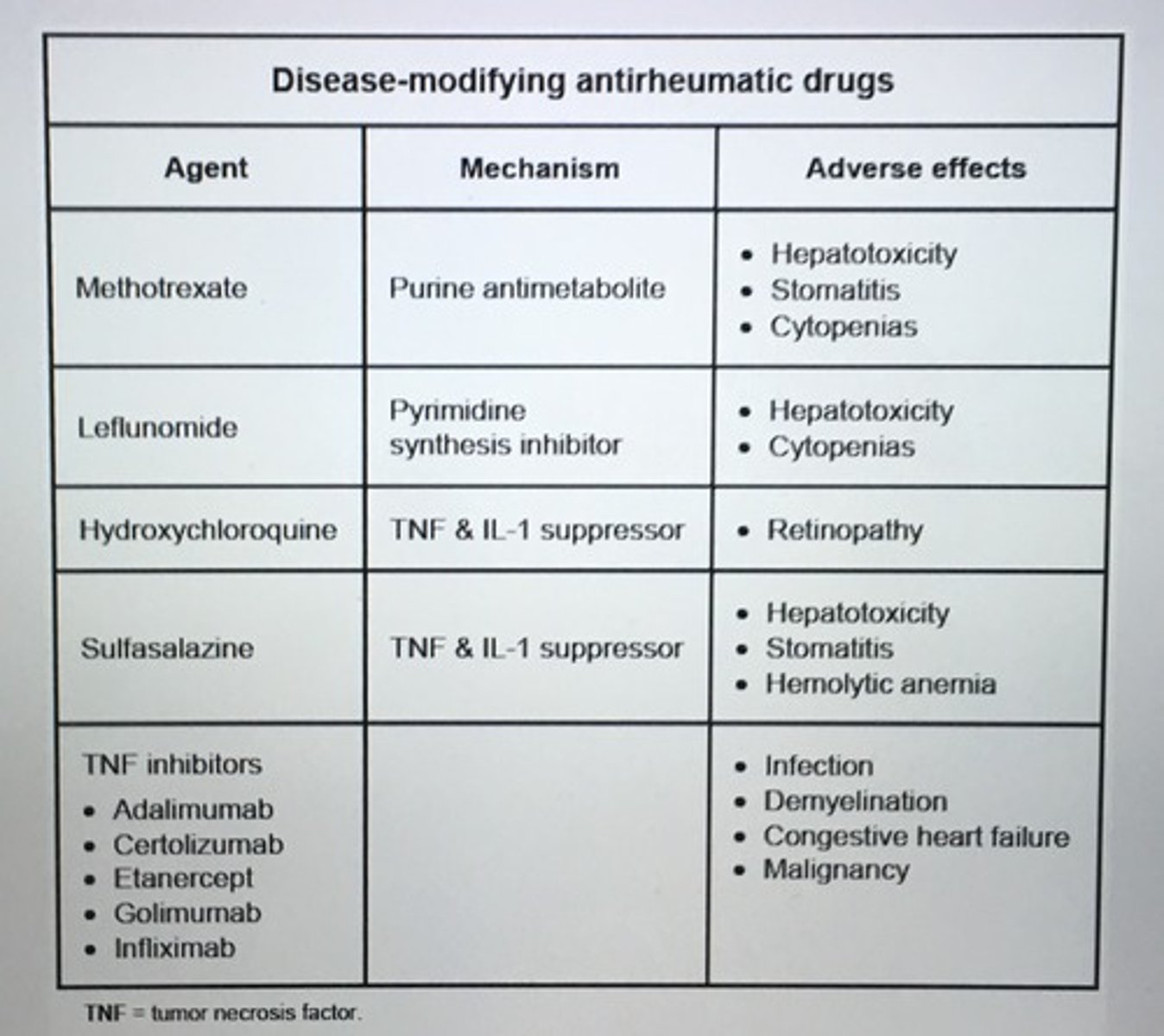
Before starting methotrexate test patients for?
Hep B, Hep C, TB
Majority of LBP is due to MSK cause but the following red flags suggest systemic disorder, herniated disc, or bony abnormalities may be presents:
- Age > 50
- Hx previous cancer
- Constitutional sxs (fever, unexplained weight loss)
- Nighttime pain causing sleep difficulty
- No response to previous therapy
- Neuro sxs
Most common ocular manifestation of giant cell arteritis.
Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy
Amaurosis fugax: transient vision field defect progressing to monocular blindness
GCA with vision loss: give high dose IV glucocorticoids (methylprednisolone) for 3 days followed by oral high dose glucocorticoids
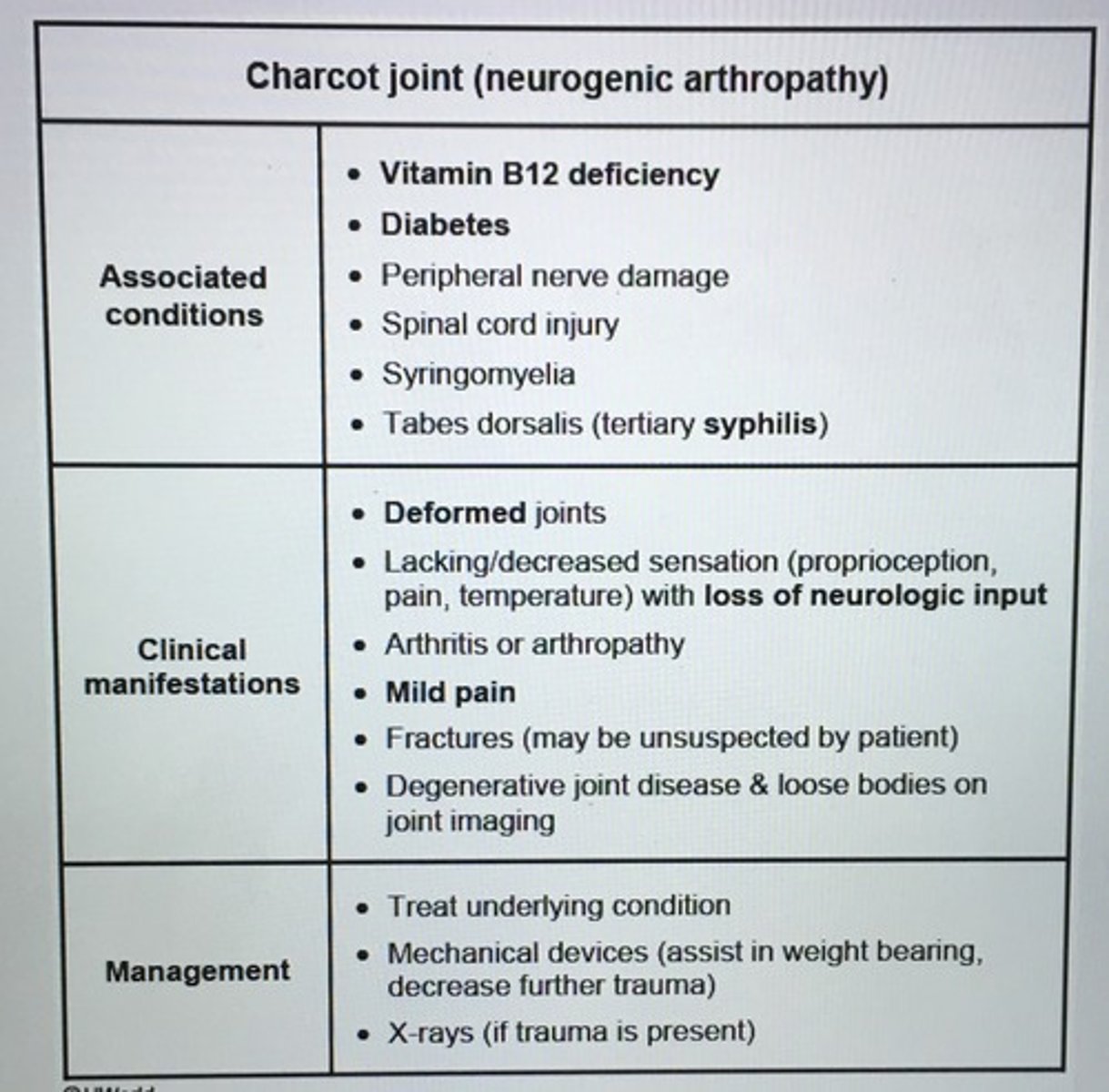
Charcot joint (neuropathic arthropathy) Clinical findings and tx.
Pathophysiology Paget disease of bone.
INC bone turnover 2/2 osteoclast dysfunction leads to bone breakdown and compensatory increase bone formation
Complications of Paget disease of bone.
Benign giant cell tumors
Osteosarcoma