Sensation and Perceptions
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Sensation
is the process by which we receive information from the environment
stimuli
A stimulus is a detectable
input from the environment
Sensory receptors do what?
nerve
endings) recieve stimuli
Perception
the process of organizing and interpreting sensory information, enabling us to
recognize meaningful objects and events.
Transduction
Transduction is the process of
converting the energy of a stimulus
into neural activity. The stimulus is
recoded as a neural pattern.
AKA: Transduction=translation
Transduction Process
receive sensory stimulation, often using specialized receptor cells.
transform that stimulation into neural impulses.
deliver the neural information to our brain.
Absolute Threshold
the minimum stimulation necessary to detect a
particular light, sound, pressure, taste, or odor 50
percent of the time.
Difference Threshold
the minimum stimulation necessary to detect a
difference in a particular light, sound, pressure,
taste, or odor 50 percent of the time.
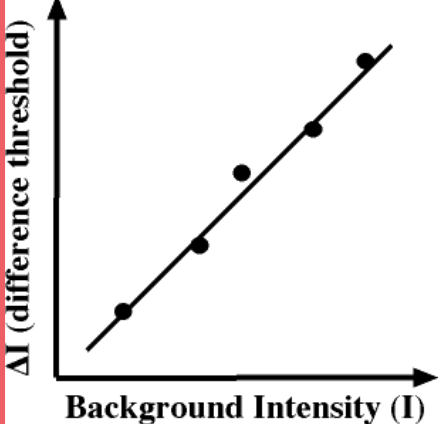
Weber‘s Law
that the just-
noticeable difference (JND) between
two stimuli are in a constant proportion of
the original stimulus intensity.
In simple terms, the bigger the original
stimulus, the bigger the change needed
to be for you to notice it
Signal Detection Theory
a theory predicting how and when we detect the presence of a faint stimulus (signal) amid background stimulation (noise). Assumes there is no single absolute threshold and that detection depends partly on a person’s experience expectations, motivation, and alertness
Priming
the activation, often unconsciously, of certain associations, thus predisposing
one’s perception, memory, or response.
selective attention
the focusing of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus
Inattentional blindness
not noticing stimuli when focused on others
Change blindness
a form of inattentional blindness; not noticing a change in the environment due to selective attention
BOTTOM-UP
information flowing from the
sensory receptors to the brain
TOP-DOWN
Stimuli processed by one’s
experiences and predictions
Schema
A cognitive framework, based on previous
knowledge and experiences, that helps
humans organize and interpret incoming
information.
Perceptual Set
Psychological sets that rely on familiar ways of
perceiving stimuli