A&P II Final Exam Nerd Notes
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
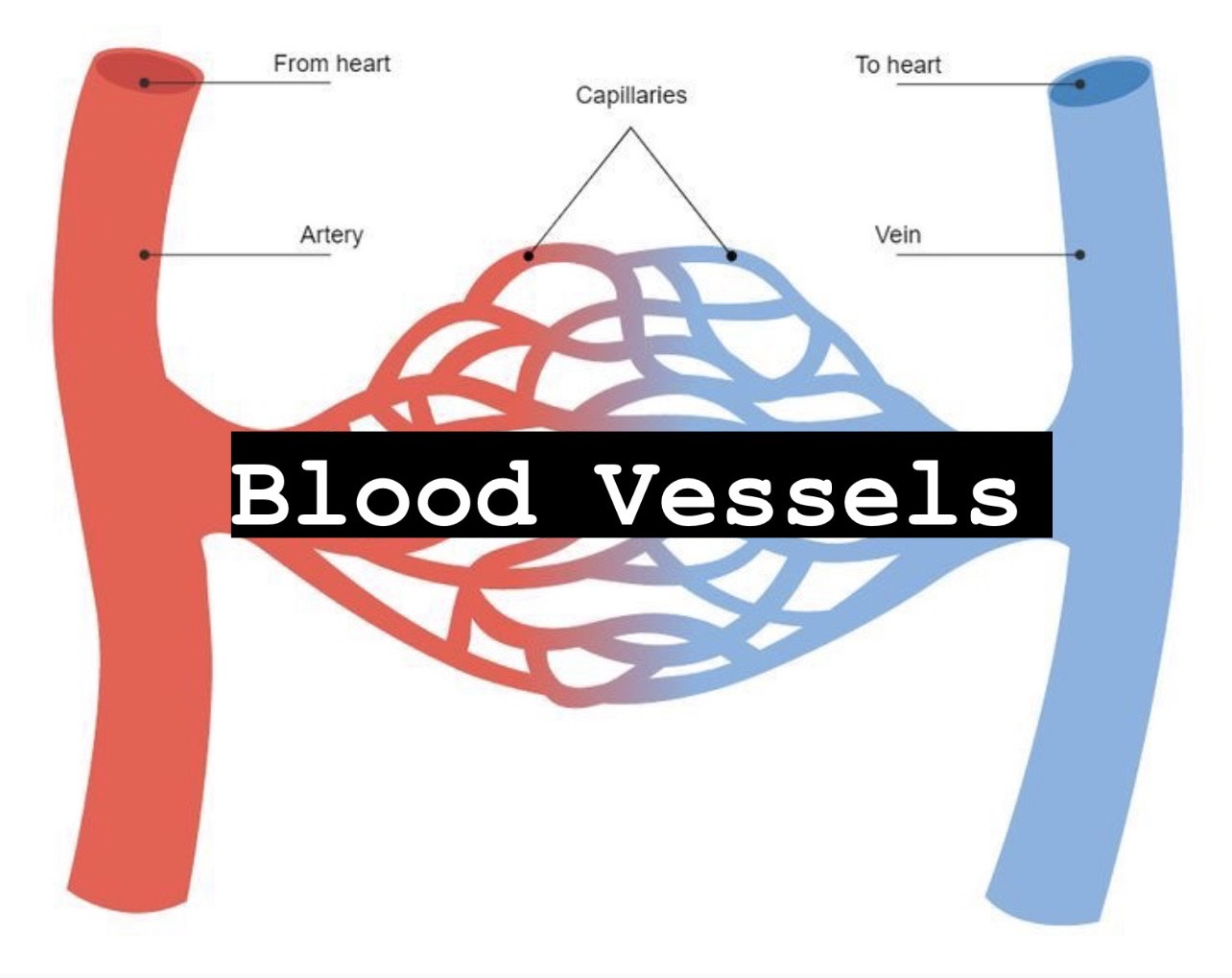
Endocrine, Blood, Blood Vessels
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
where is estrogen produced
estrogen and progesterone are produced in ovaries; estrogen is needed to drive the maturity of internal reproductive organs and outer secondary sexual characteristics

list the endocrine organs
pineal gland, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, thymus, adrenal glands, pancreas, gonads (ovary & testis)

how does increased thyroid hormone levels affect individuals
increases blood pressure due to stiffened arteries, increased cardiac output, and possibly heart palpitations

what is the difference between cushings and addisons
Cushing’ syndrome is often caused by tumors or the overuse of corticosteroids and display in a patient as “moon face” and “buffalo hump”
Addison’s disease involves deficits in both glucocorticoids and mineralocortioids that decrease plasma glucose resulting in weight loss and bronzing of skin; the common treatment is hormone replacement therapy

what does the adrenal cortex secrete? what does it control?
the adrenal cortex secretes several different hormones; the hormones mineralocorticoids (aldosterone) is the homeostatic control of salt & water balance

how does the RAAS system work?
the RAAS is important in clinical settings because it is a pathway designed to regulate blood pressure; when blood volume/pressure decreases kidney cells (juxtaglomerular) release renin from storage granules promoting angiotensin cascade causing vasoconstriction and release of aldosterone. This increases Na+ and water retention in kidney to increase blood volume/pressure

what is the difference between alpha & beta cells?
alpha cells produce the hormone glucagon to increase blood glucose level though the process of glycogenolysis (breaking) and gluconeogenesis (building) that occurs in the liver
beta cells secrete insulin when blood glucose levels are high; the mechanisms involved are promoting membrane transport, inhibiting glycogenolysis (breaking) and inhibiting gluconeogenesis (building)

the thyroid gland produces _________ hormones
water-soluble hormones include all amino acid-based excluding thyroid hormones
T4 (thyroxine) and T3 (triiodothyronine)

what do lipid-soluble hormones do?
lipid soluble hormones can enter the cell thus act on intracellular receptors that involve decreasing gene expression

list the primary functions of pituitary hormones
growth hormone: anabolic hormone that mobilized fats & spares glucose
thyroid- stimulating hormone : release thyroid hormones
adrenocorticotropic hormone: release glucocorticoids & androgens
follicle-stimulating hormone:
females: estrogen production & follicle maturation
males: sperm production
luteinizing hormone:
females: estrogen & progesterone production
males: testosterone production
prolactin: females promotes lactation

the role of insulin in the body is?
insulin not only is important for energy production inside the cell but also for storing glycogen and fat ( in adipose tissue)

list the factors that influence insulin release
elevated blood glucose levels: primary stimulus
rising blood levels of amino acids and fatty acids
release of acetylcholine by parasympathetic nerve fibers
hormones glucagon, epinephrine, growth hormone, thyroxine, glucocorticoids
somatostatin and sympathetic nervous system inhibit insulin release

describe estrogen and progesterone
the gonads and the adrenal cortex produce steroid sex hormones
estrogen and progesterone are produced in ovaries; estrogen is needed to drive the maturity of internal reproductive organs and outer secondary sexual characteristics
estrogen with progesterone ratio/levels are responsible for menstrual cycles, when both are at lowest point in the follicular phase (shedding of uterine line) begins

descirbe the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis
Hypothalamic hormones (tropic hormone) stimulate the release of anterior pituitary hormones (tropic hormone) which in turn stimulate the thyroid gland to release thyroid hormones

what is the processes of platelet formation
platelets begin with the hematopoietic stem cells, the one that is differentiated to develop lymphoid and myeloid cells, and differentiates into a megakaryocyte that has multiple developmental stages before resulting in formed platelets
what binds O2 in RBC and how many
the heme groups of hemoglobin are what bind oxygen, so hemoglobin can transport 4 oxygen molecules
list functions of blood
blood is used for the transport (delivery guy), regulation, and protection (preventative)
the blood delivers cell sustaining oxygen, nutrients, and hormones
the blood removes metabolic wastes, that would hinder cells of doing their jobs at high concentrations
list the layers of blood after centrifugation
when blood is centrifuged, there are 3 distinct layers, from top to bottom, they are: plasma, buffy coat, and erythrocytes
what are formed elements
formed elements include RBC (erythrocytes), WBC (leukocytes) and platelets
what do cells get from blood
the blood delivers cell sustaining oxygen, nutrients, and hormones
what is the function of fibrin
fibrin develops a matrix of trapped RBCs and platelets
what is a D antigen
Rh+ indicates presence of D antigen, 85% of Americans are this type
what is blood plasma made of?
blood plasma is 90% water and 10% dissolved solutes
out of all the numerous substances in plasma, the largest % is plasma proteins and of those albumin is the majority
albumin in plasma functions as a buffer keeping blood pH in homeostasis and also maintains the osmatic pressure of plasma
what type of biomolecule is hemoglobin
hemoglobin is a protein that has 2 alpha and 2 beta polypeptides, and 4 heme groups
a RBC contains 250 million hemoglobin proteins
what is the life span of RBCs
the life span of RBCs are 100-120 days
what is albumins function
albumin in plasma functions as a buffer keeping blood pH in homeostasis and also maintains the osmatic pressure of plasma
what are the stem cells that make lymphocytes
lymphoid stem cells produce lymphocytes
at what developmental age is Anti-A observed
Anti-A or Ant-B form in blood at about 2 months of age
what is the red bone marrow known for
the formation of blood is hematopoiesis and occurs in the red bone marrow
blood without A or B agglutinations is
type O blood has neither A nor B agglutinations
Type O blood is the universal donor
what is the difference between granulocytes and agranulocytes
WBCs constitute less than 1% of blood volume and are composed of granulocytes and agranulocytes
granulocytes are immune cells that contain granules of molecules that promote inflammation; these three are neutrophils 50-70%, eosinophils 2-4%, and basophils 0.5-1%
agranulocytes are cells without granulocytes and are found in blood at relative percentages of 25-45% lymphocytes and 3-8% monocytes
why don’t RBCs produce energy
RBCs are the only cells in our bodies that are absent of nucleus and organelles, so they do not respond to stimuli or produce energy
RBC formation is stimulated by __________
erythropoietin (EPO) is a hormone that stimulates formation of RBCs; the kidneys release this hormone in response to hypoxia (low oxygen in the blood)
what cells are granulocytes
(BEN) basophils, eosinophils, neutrophils
what does O2 loading mean
the lungs are important for oxygen loading and carbon dioxide unloading within RBC
what is platelet plug formation
platelet plug formation begins with platelets adhering to collagen fibers that trigger platelets to release chemicals that make local platelets stickier.
what is exercise hyperemia
though the short-term metabolic increase leads to general increased blood flow, long-term autoregulation includes developing new vessels (angiogenesis). This increase of vessels is commonly found in individuals that live at high-altitudes. This is the advantage of living and training >6 months in high-altitude locations
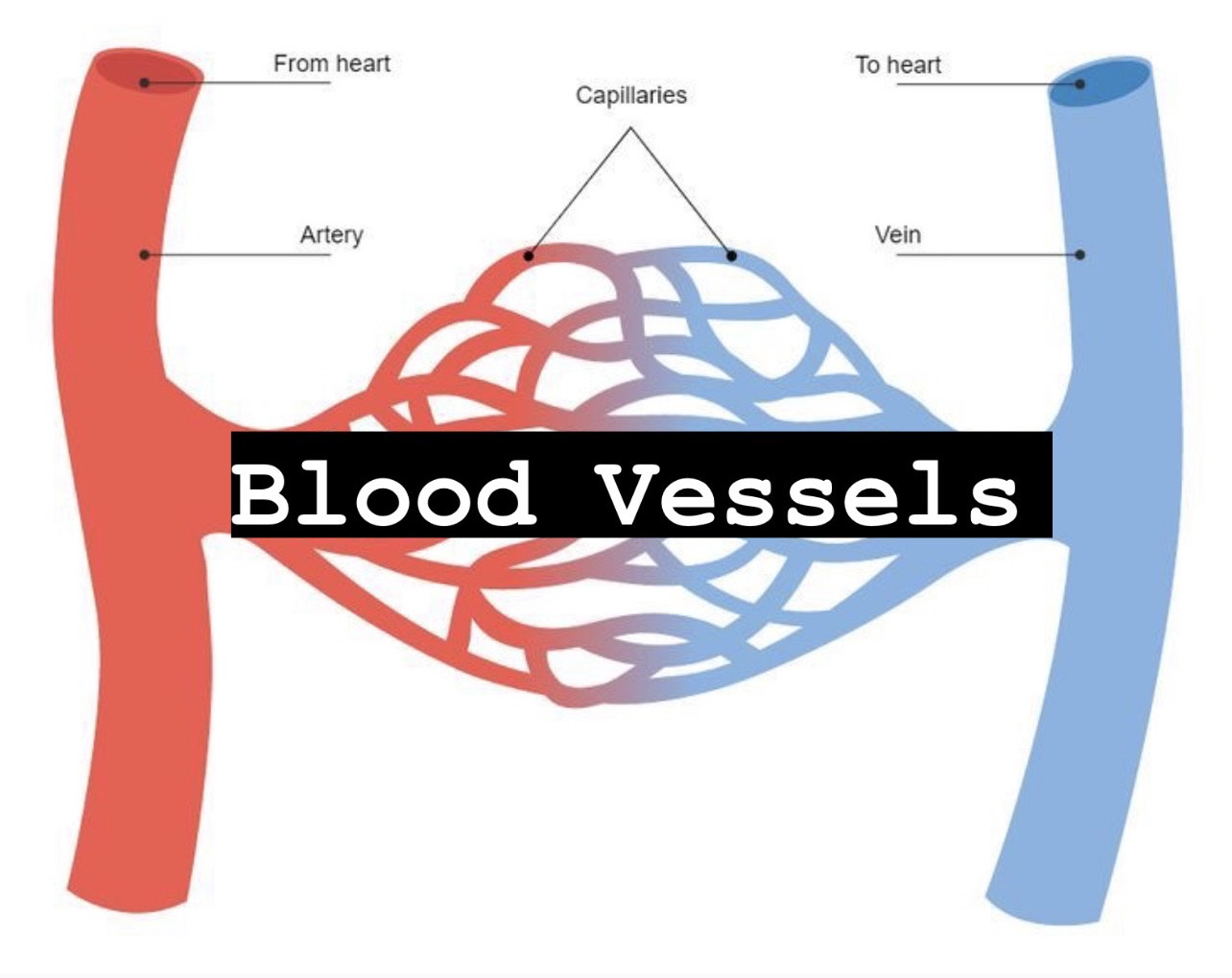
what is blood flow determined by
resistance to blood flow is multifactorial that includes: viscosity, blood vessel length, and blood vessel diameter
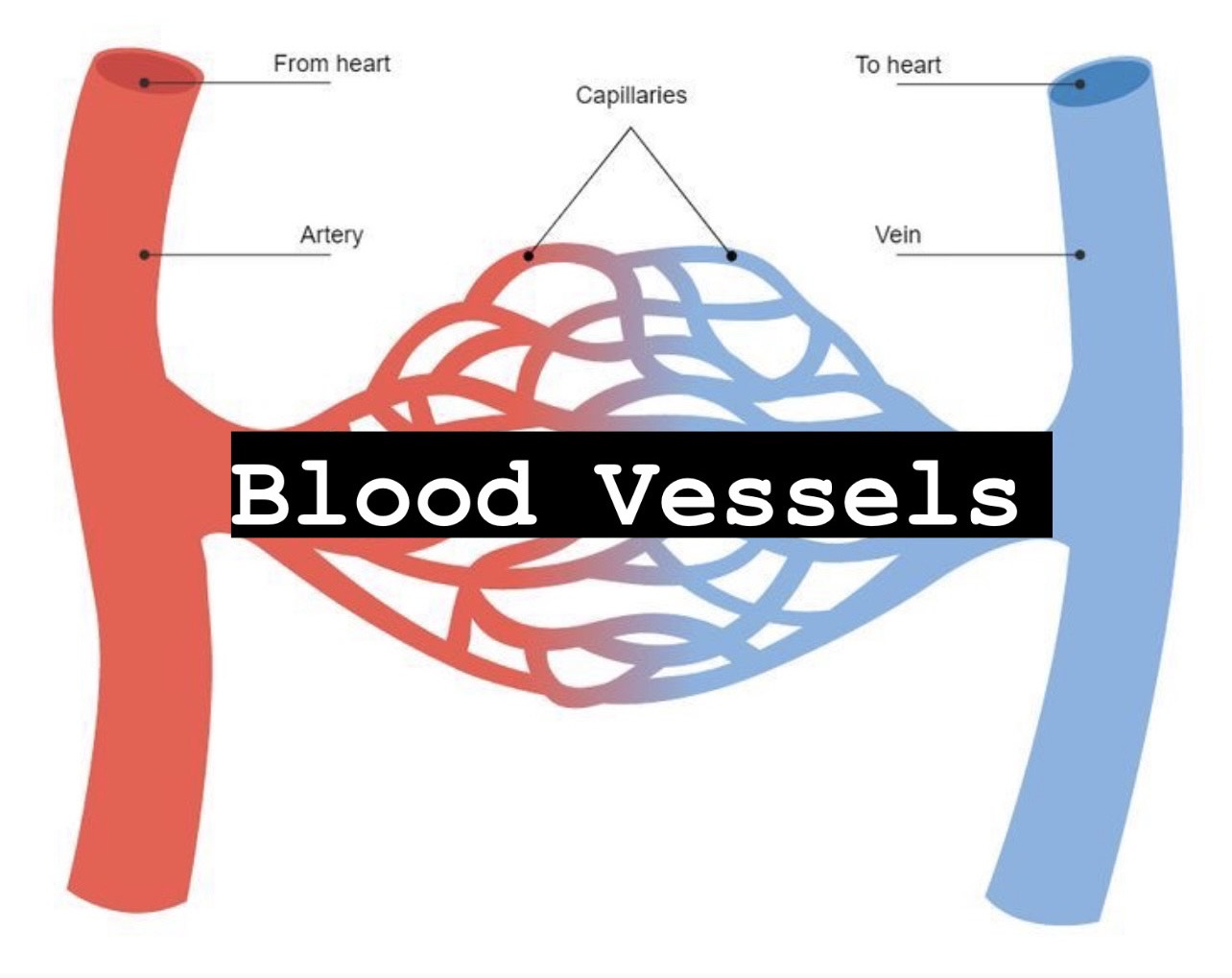
describe bulk flow and how it works
bulk flow of blood an diffusion are two different things; the molecules involved are plasma for bulk flow and both gases and ions
bulk flow is not a complete exchange of fresh plasma for old plasma, but an incomplete exchange for fresh plasma for old plasma
describe nitric oxide and its release
endothelial cells release nitric oxide into the blood stream that causes vasodilation
what are adaptation for persons in high altitudes
though the short-term metabolic increase leads to general increased blood flow, long-term autoregulation includes developing new vessels (angiogenesis). This increase of vessels is commonly found in individuals that live at high-altitudes. This is the advantage of living and training >6 months in high-altitude locations
list pressures in capillaries
there are three different capillary pressures that occur
arterial end +10 mmHg
mid capillary 0 mmHg
venous end -7 mmHg
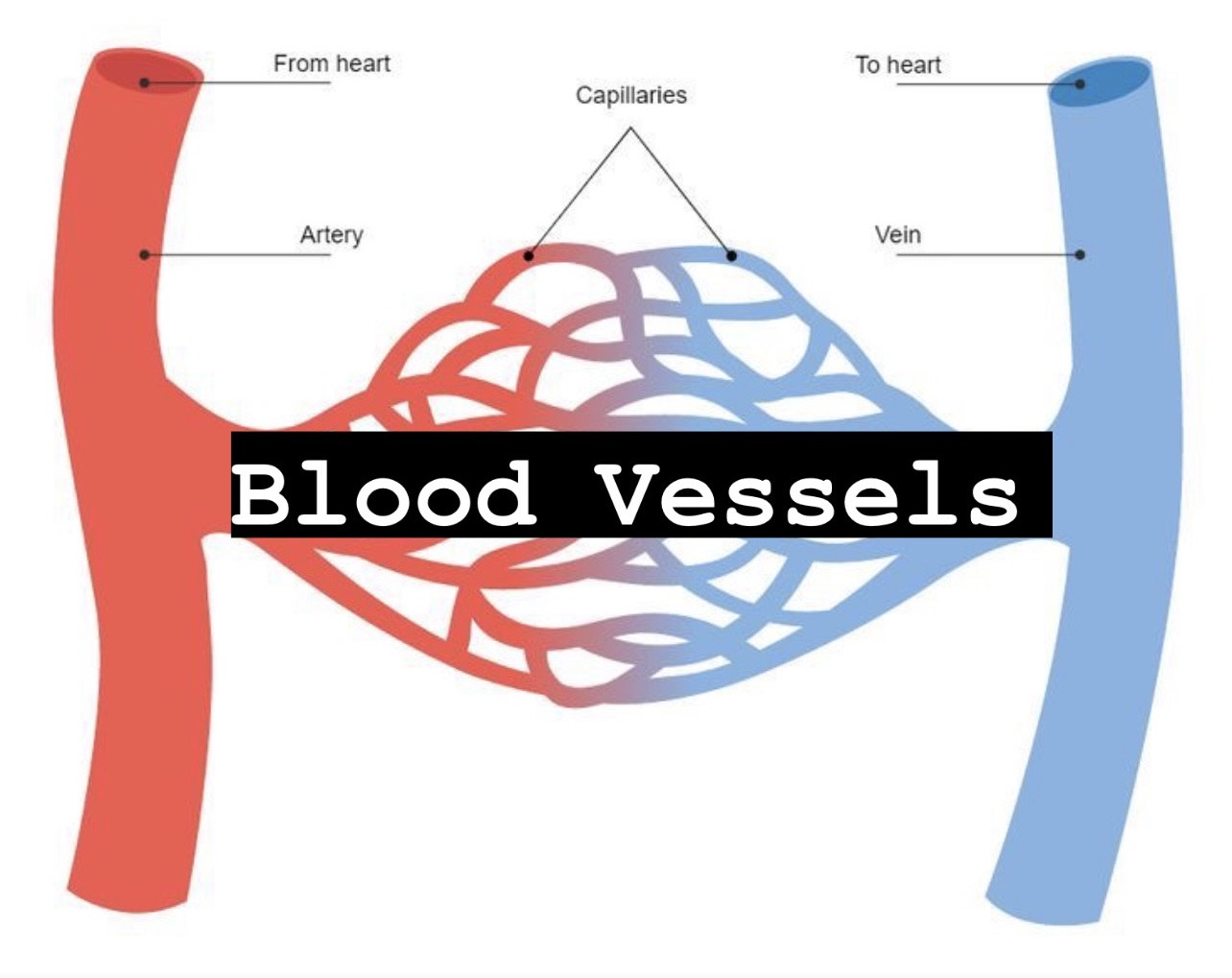
how does autonomic nervous system ANS respond in cold weather
the autonomic nervous system will constrict all vessels, except internal organs and brain, during extreme exposure to cold or profuse bleeding
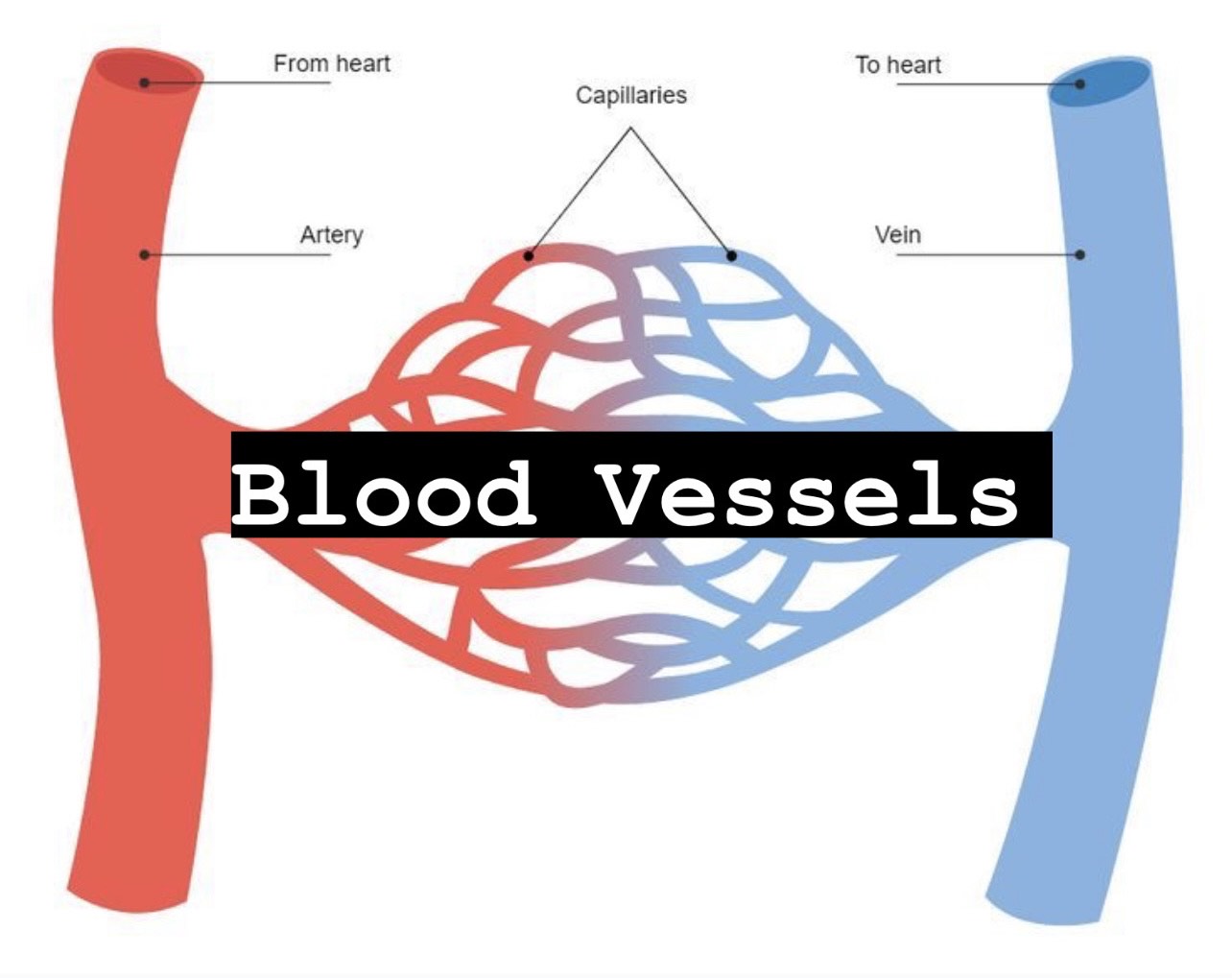
list hypertension risk factors
risk factors for hypertension include (internal) genetics and (external) diet, obesity, and stress