exam 3
1/142
Earn XP
Description and Tags
good luck vro last exam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
143 Terms
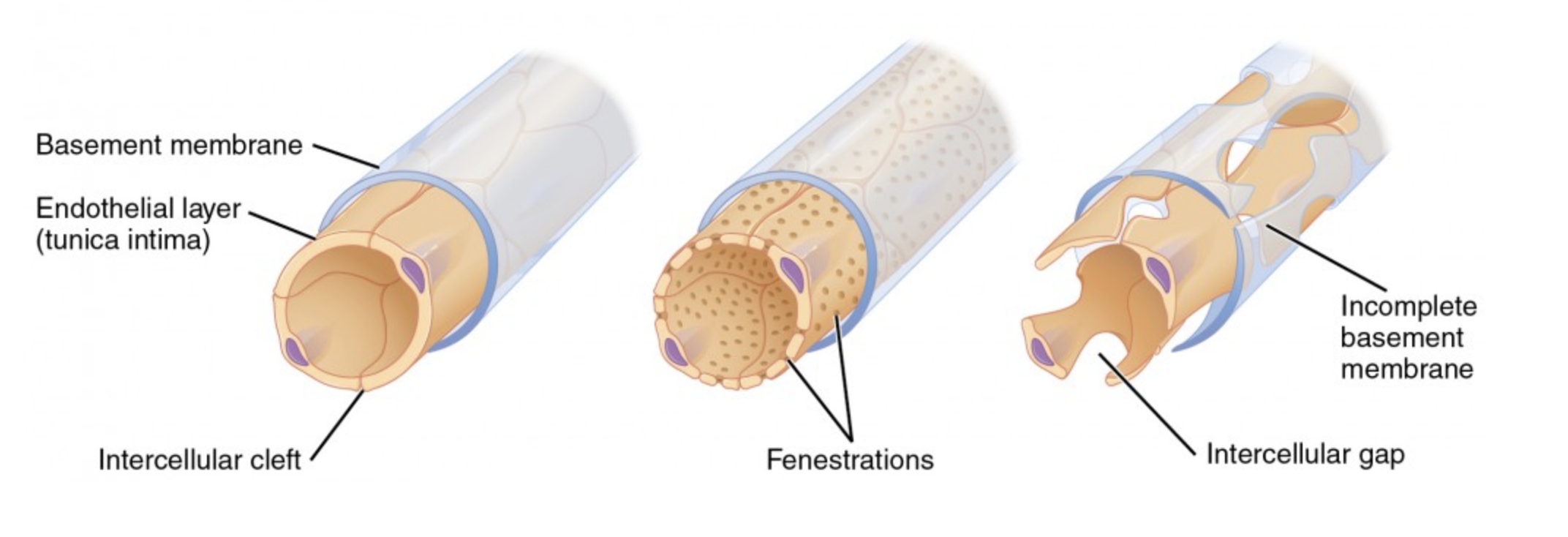
what are the 3 types of capillaries + their function
continuous (controlled exchange of cells), fenestrated (rapid exchange of cells), sinusoidal (passage of cells)

what are the 3 types of arteries + their functions
elastic arteries (conduct blood away from heart), muscular arteries (carry blood to specific organs), arterioles (control capillary blood flow)
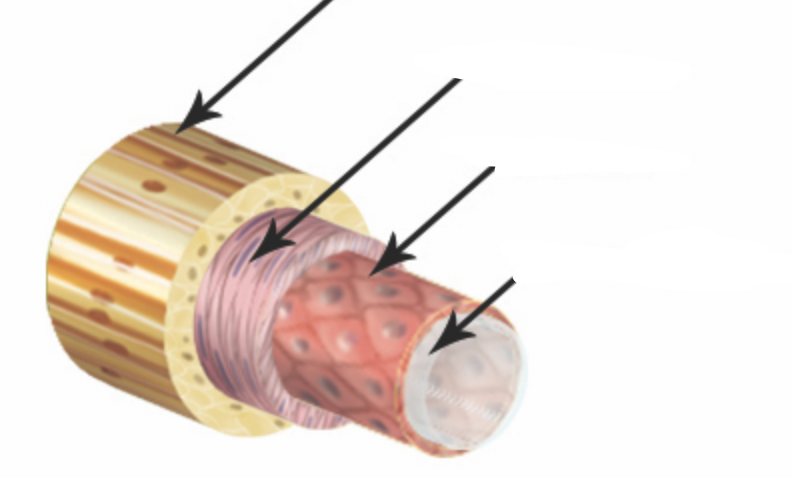
what are the layers of the blood vessels?
tunica intima, tunica media, tunica externa
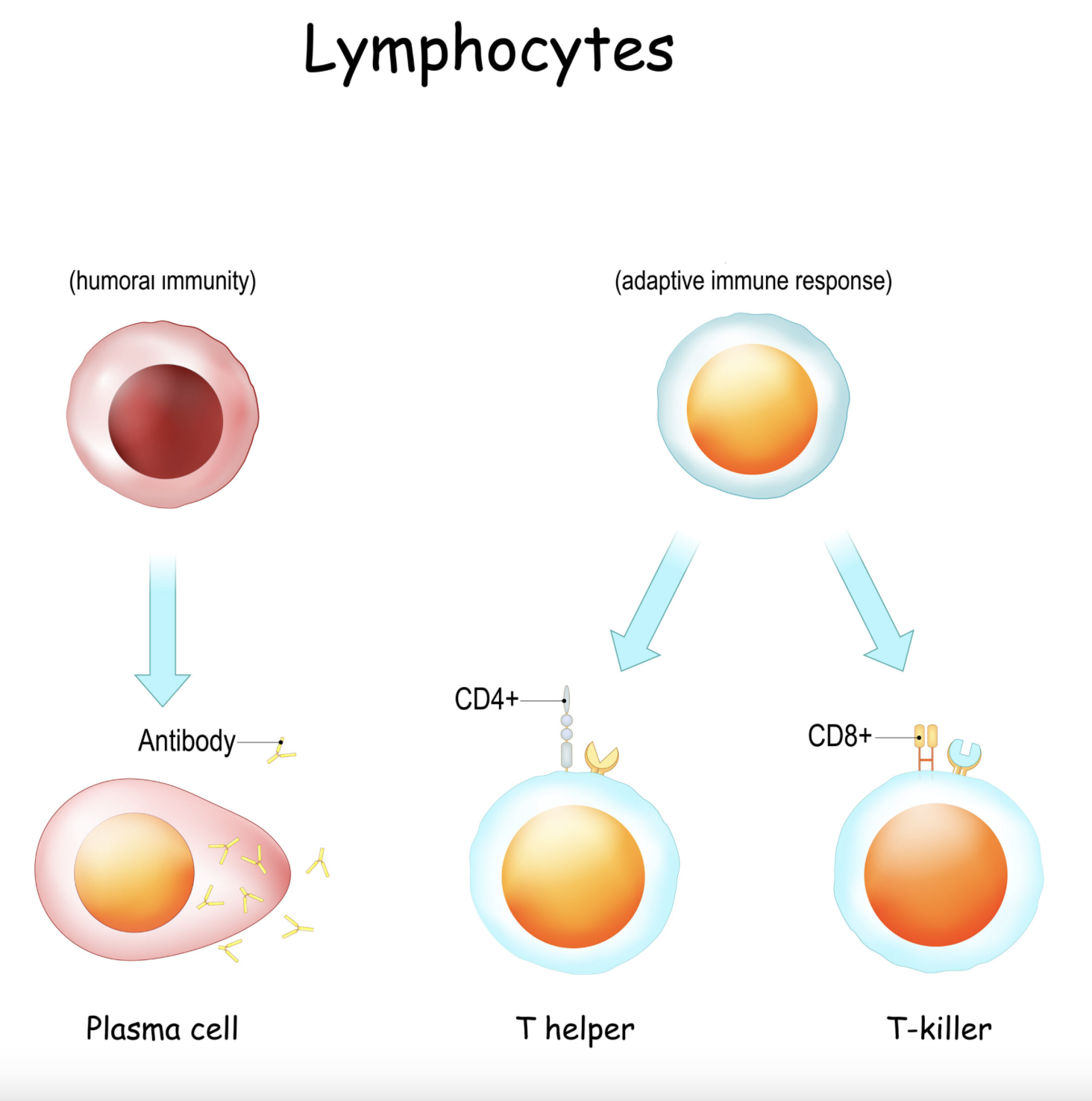
function of the lymphocytes and how do they differ?
T cells and B cells both protect against antigens; B cells build antibodies while T cells target infected cells directly
What are the different types of lymphatic vessels + their associated functions?
lymphatic capillaries (begin lymph flow), collecting vessels (transport lymph to lymph nodes), lymph nodes (filter lymph), lymphatic trunks (drain large body regions), lymphatic ducts (return lymph to circulation)
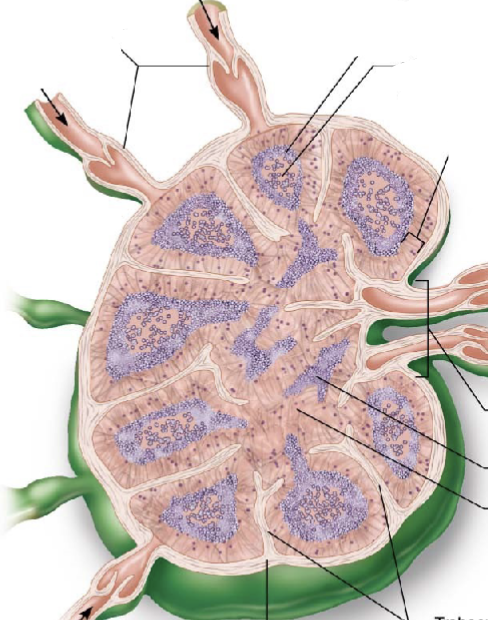
regions of the lymph nodes?
cortex (contains B cells); medulla (contain B cells, T cells, and plasma cells)
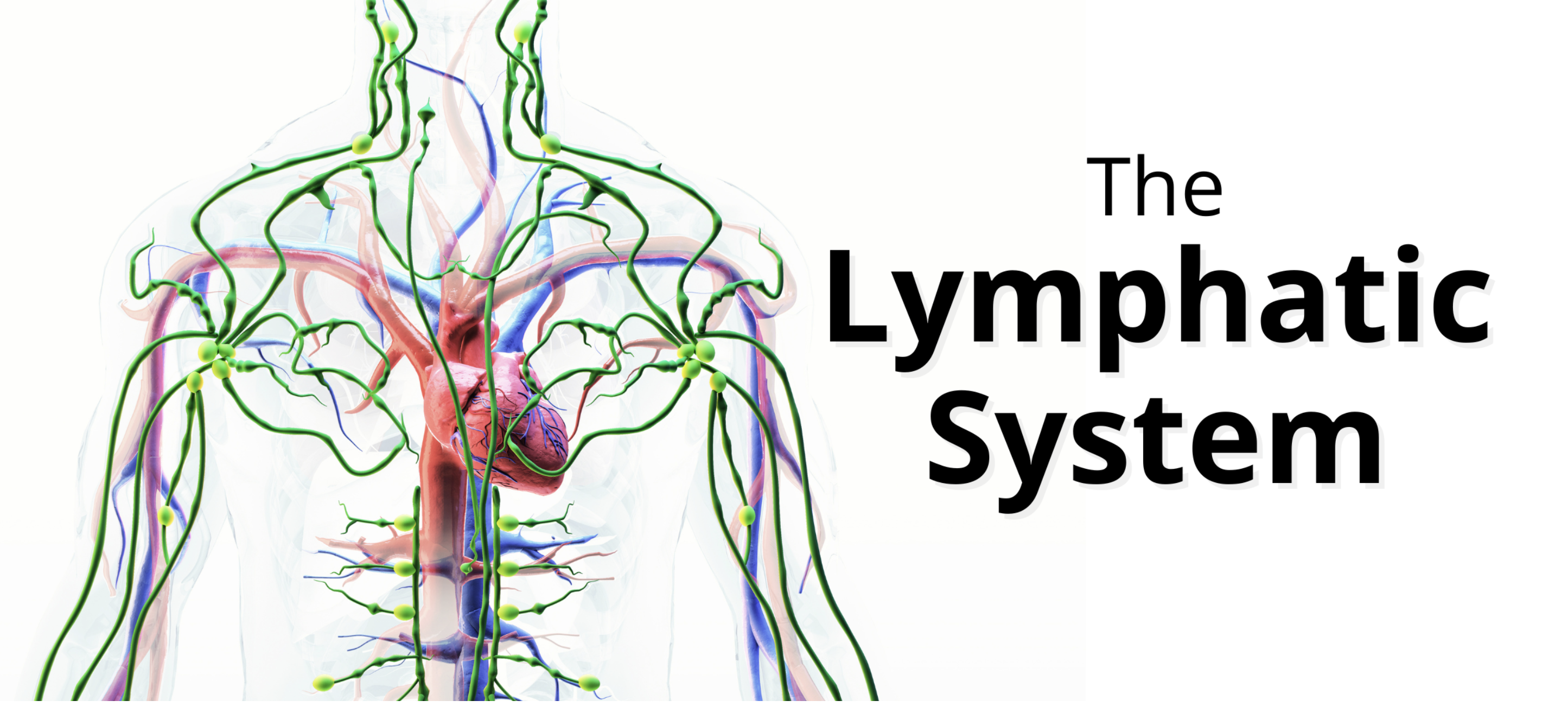
what are the functions of the lymphatic system?
fluid balance (lymphatic vessels and ducts), immunity (nodes and spleen), fat absorption (small intestine)
how is lymph returned to the circulatory system?
lymph flows through lymphatic vessels (capillaries, collecting vessels, lymphatic trunks and ducts), propelled by external forces (skeletal/respiratory pump), drains into thoracic or right lymphatic duct, enters the subclavian veins to become venous blood
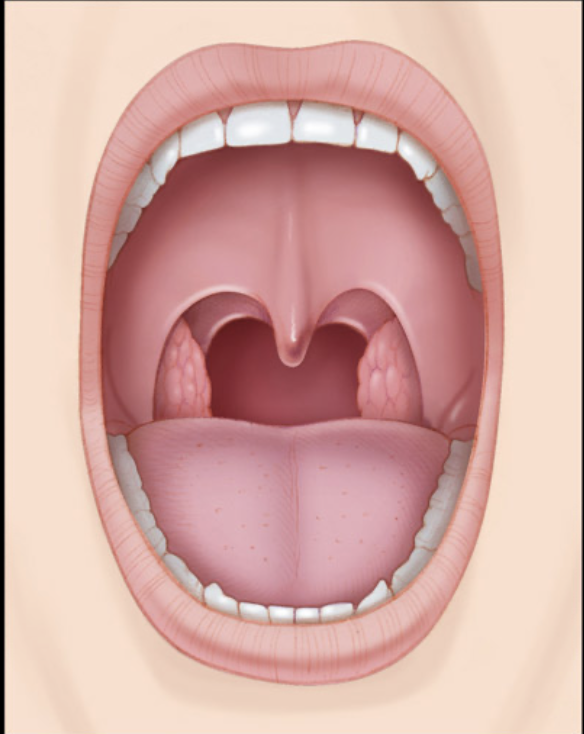
different types of tonsils and their locations?
palatine (sides of oropharynx), pharyngeal (roof of nasopharynx), lingual (base of tongue)
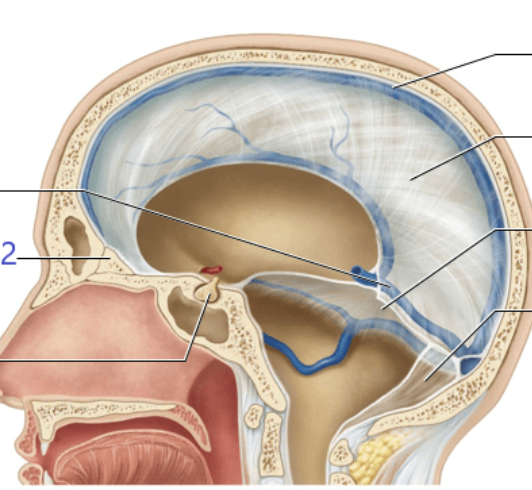
types of dural septa found in brain and the cerebellum?
falx cerebri (between cerebral hemispheres), tentorium celebrelli (between cerebrum and cerebellum), falx cerebelli (between cerebellum hemispheres), diaphragma sellae (pituitary gland)
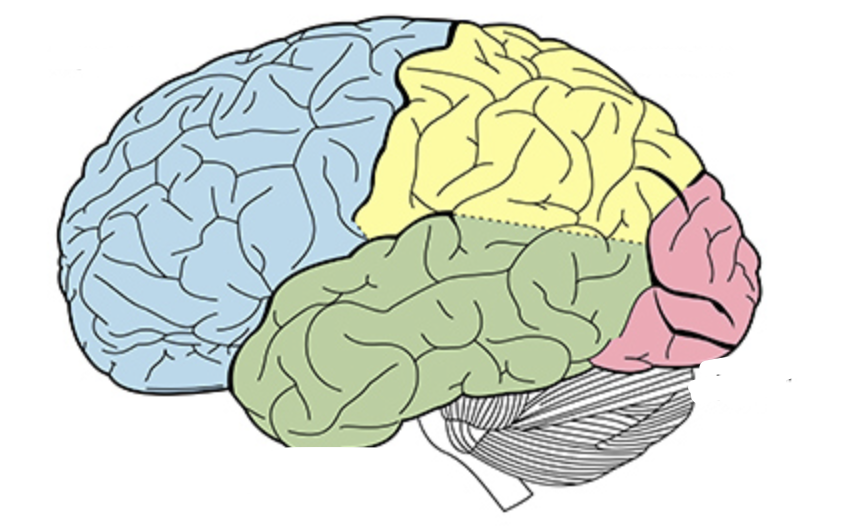
what are the lobes of the brain; and their general functions?
frontal lobe (motor control), parietal (sensory processing), temporal (memory), occipital (visual interpretation)
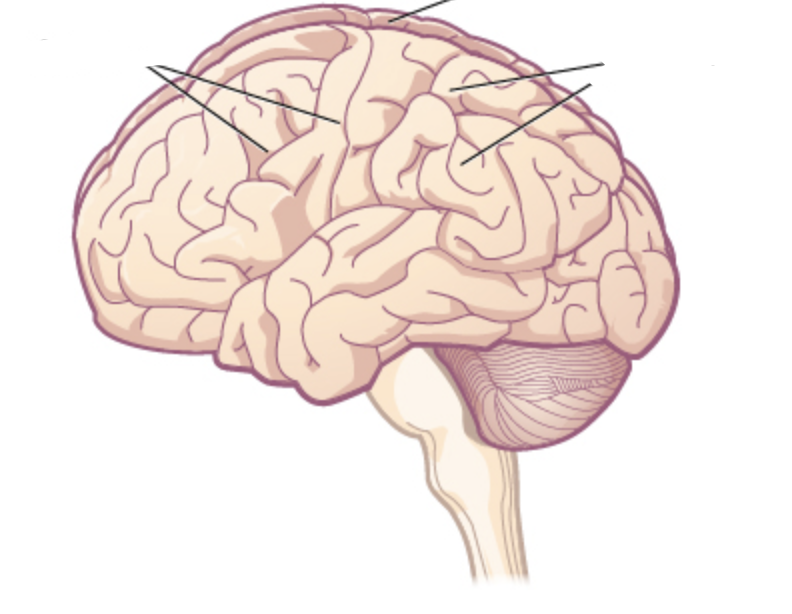
what are the markings of the cerebral hemisphere?
gyri (hills), sulci (grooves)

different layers of meninges and their organization?
dura mater (periosteal and meningeal layer), arachnoid mater, pia mater (adheres to surface of brain + spinal cord)
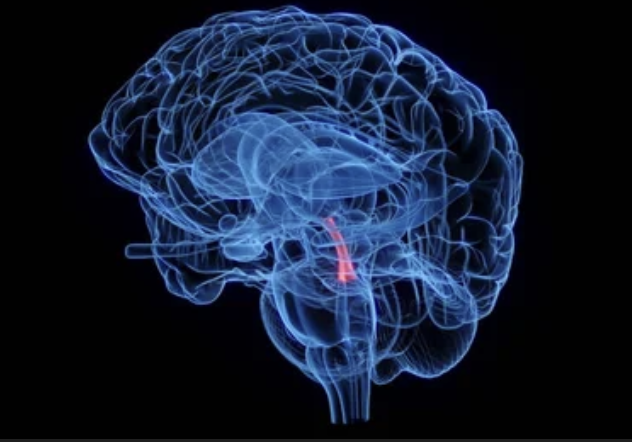
functions of the cerebral spinal fluid?
mechanical protection, chemical stability (homeostasis), circulation and transport
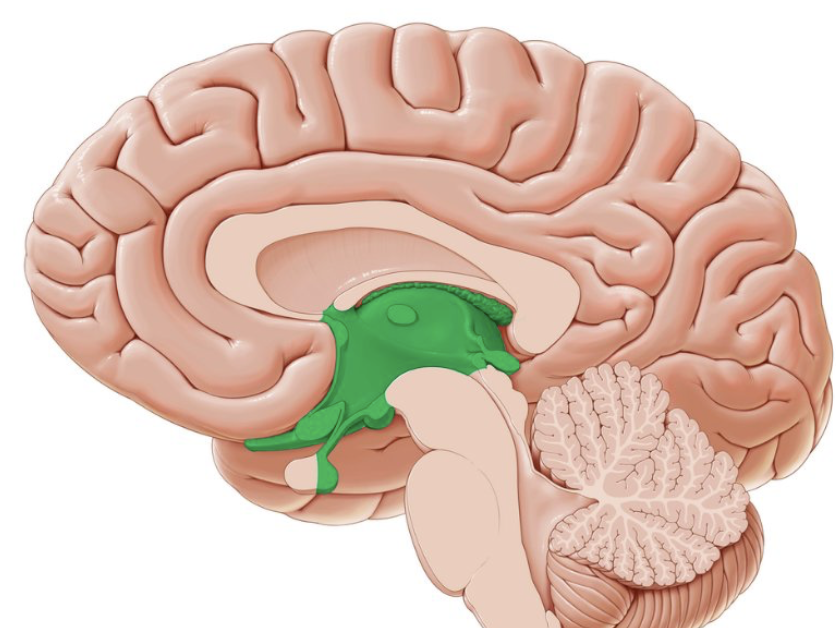
different parts of the diencephalon and their functions?
thalamus (sensory relay), hypothalamus (homeostasis), epithalamus (melatonin production)
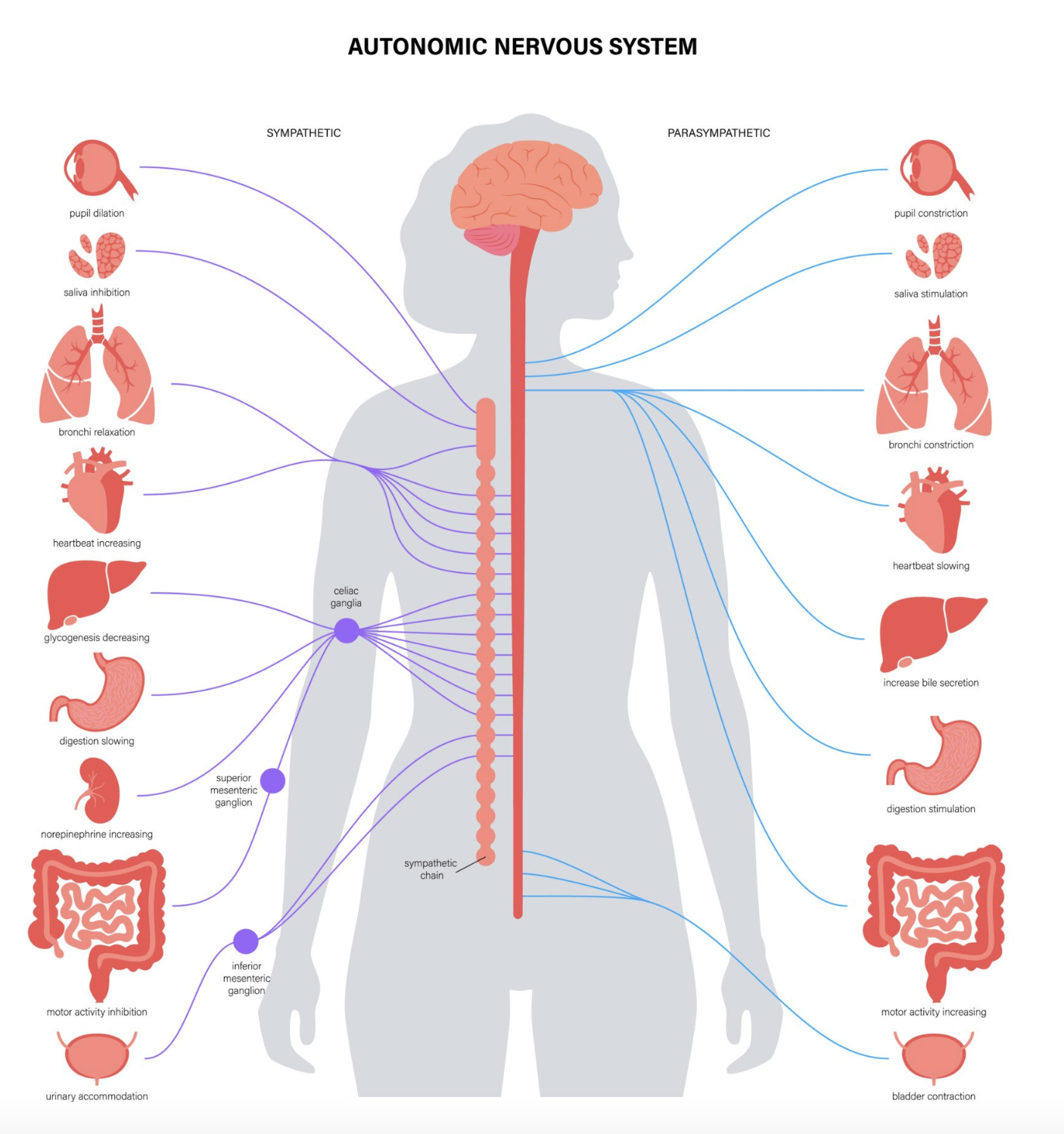
functions of the autonomic nervous system + the divisions
sympathetic (fight or flight), parasympathetic (rest and digest)
functions of the glial cells within the central nervous system (CNS)?
astrocytes (form blood brain barrier), oligodendrocytes (produce myelin sheath), microglia (immune), ependymal (lines ventricles of brain)
function of the glial cells within the peripheral nervous system? (PNS)
Schwann (production of myelin), satellite (support neuron bodies)
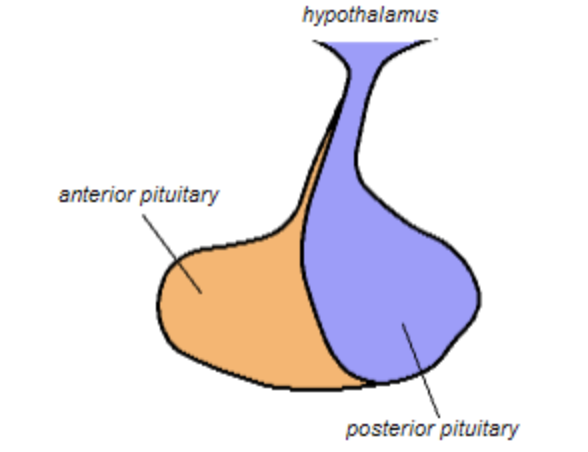
how does the hypothalamus communicate w/ the anterior pituitary gland and what structures are involved with that communication?
hypothalamus releases regulatory hormones through the hypophyseal portal system (median eminence - portal veins - anterior pituitary)
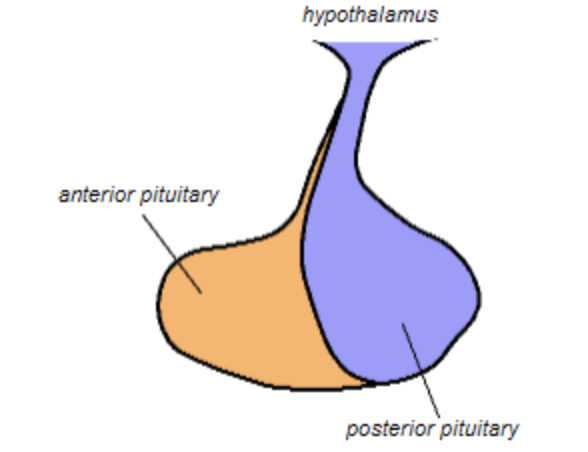
how does the hypothalamus communicate w/ the posterior pituitary gland and what structures are involved with that communication?
hypothalamic neurons synthesize hormones and they are transported down to axons of posterior pituitary gland (through hypothalamo - hypophyseal tract)
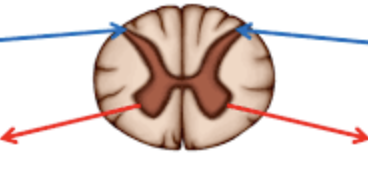
what kind of neurons do the spinal cord roots contain?
dorsal (sensory afferent); ventral (motor efferent)
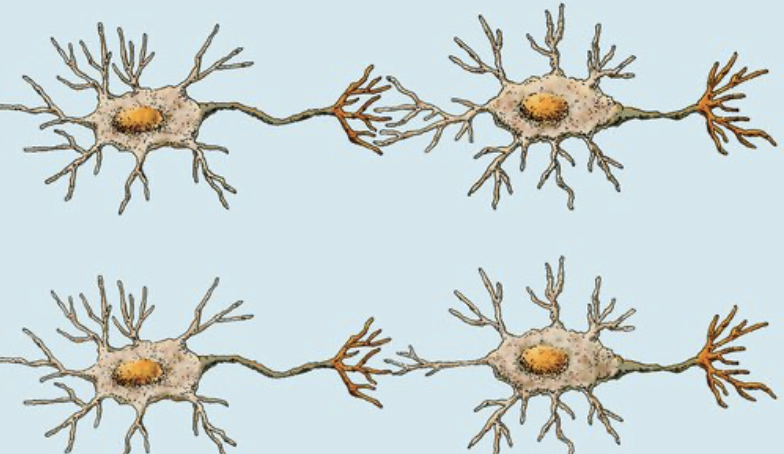
what are the components that make up the neuron + the function of those components?
cell body (soma; maintenance of neuron’s metabolism), dendrites (signal receive), axon (transmits action potentials)
what are the special characteristics of the neurons?
excitability, high metabolic rate, polarization
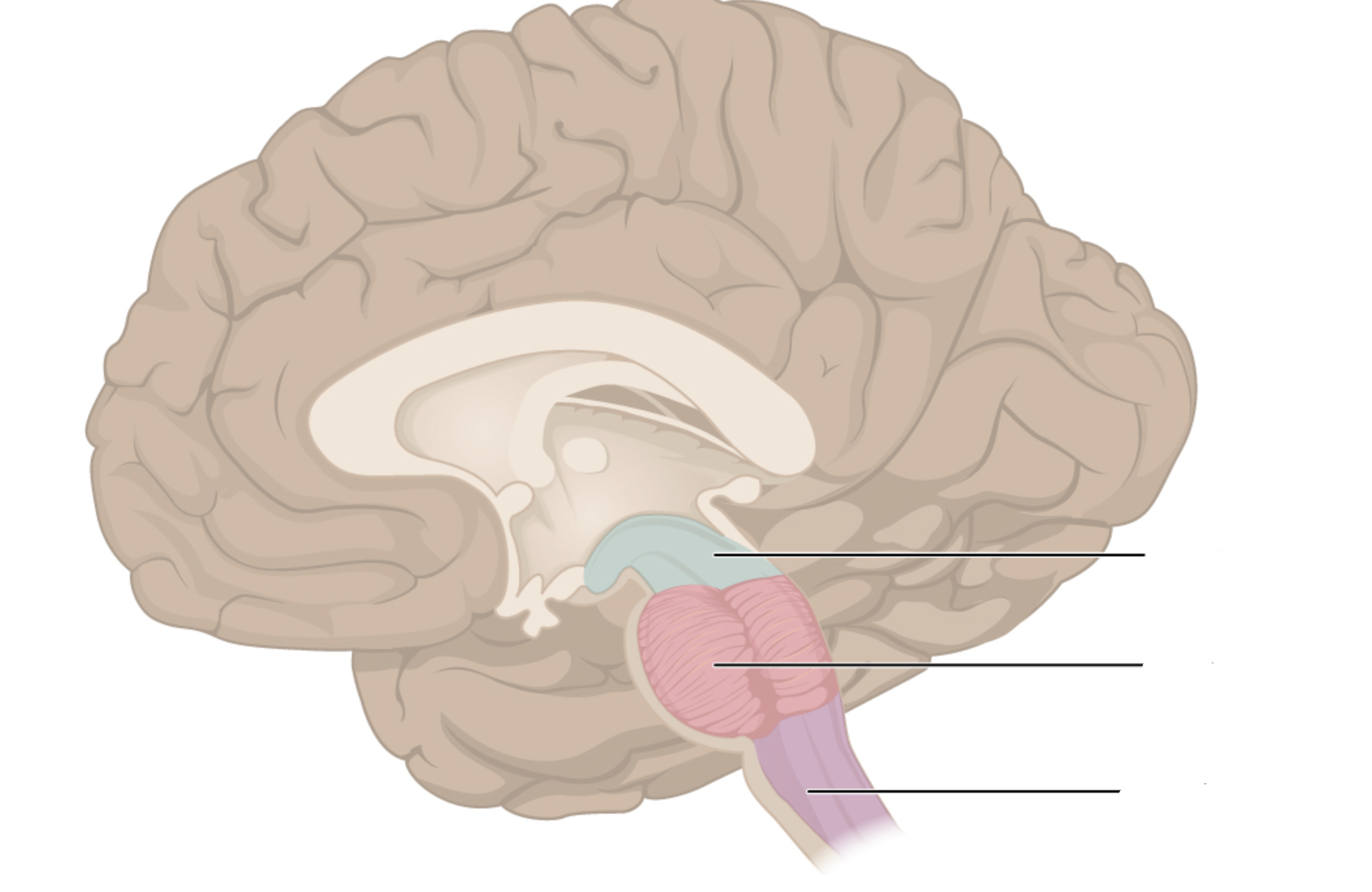
components of the brain stem + their functions?
midbrain (mesencephalon; visual auditory reflexes), pons (relays signals between cerebrum and cerebellum), medulla oblongata (heart rate; blood pressure)
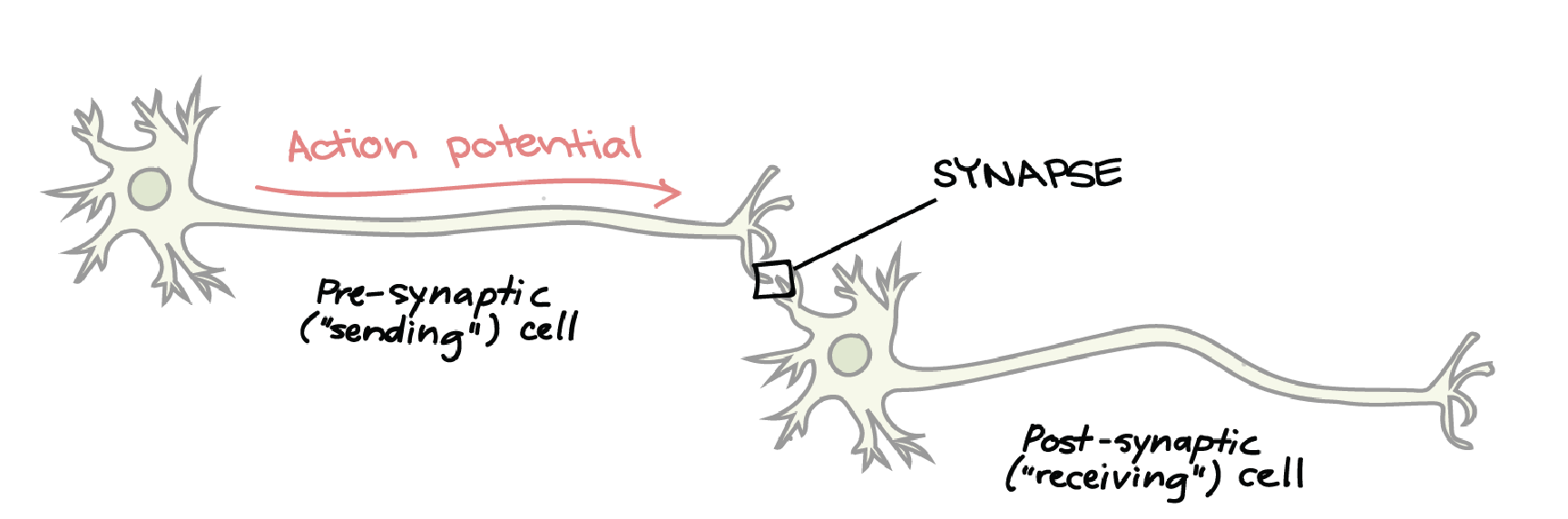
different components of the axondendritic chemical synapse?
presynaptic axon terminal (conducts impulses towards synapse); postsynaptic axon terminal (transmits electrical signal away from synapse)
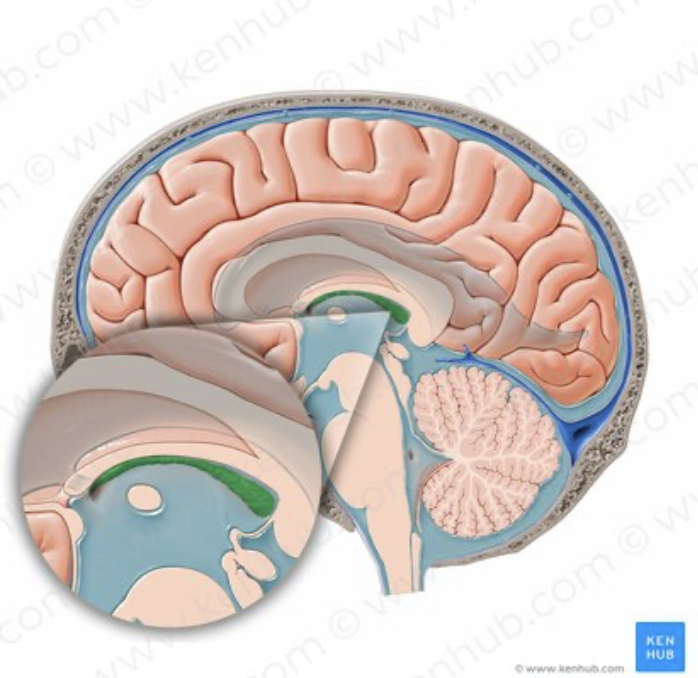
how is cerebral spinal fluid produced?
produced by the choroid plexus; through plasma filtration and active ion transport
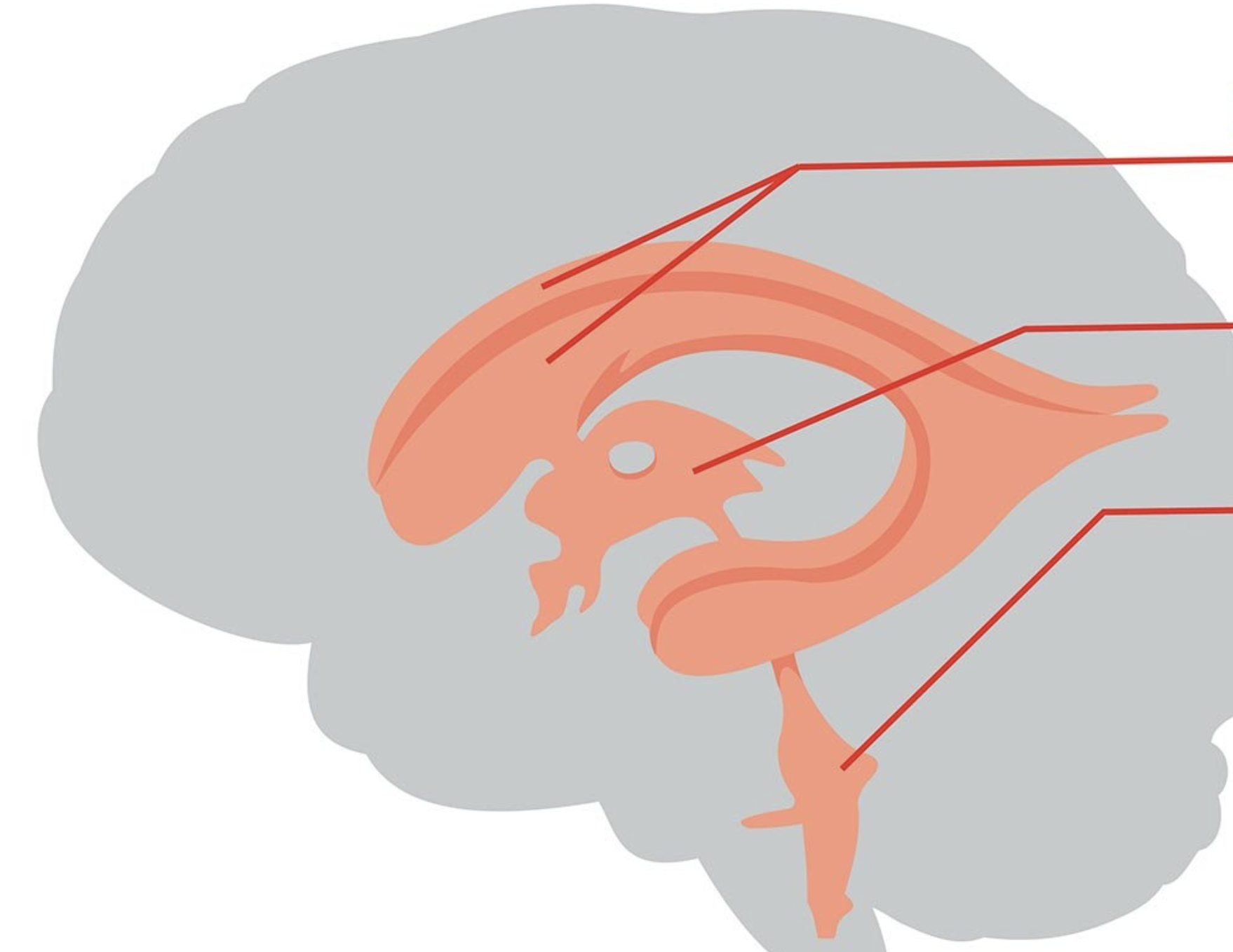
what ventricles do the cerebral spinal fluid flow through?
lateral ventricle, third ventricle, fourth ventricle, subarachnoid space
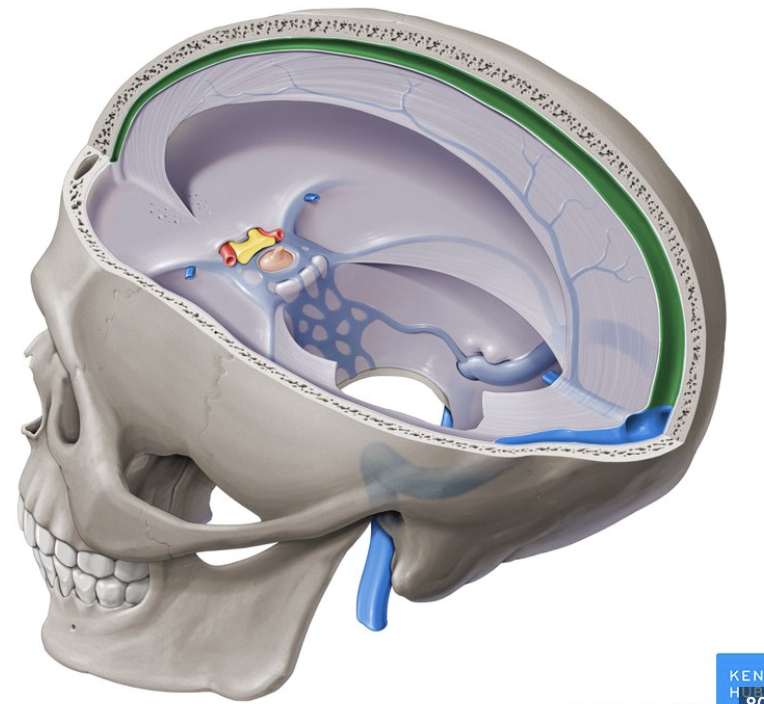
how does cerebral spinal fluid exit the brain?
enters the subarachnoid space, gets absorbed by the granulations within the superior sagittal sinus, enters the venous blood shortly thereafter
how do you classify receptors via stimuli?
mechanoreceptors (mechanical forces), thermoreceptors (temperature changes), photoreceptors (light), chemoreceptors (chemicals), nocicreceptors (pain/tissue damage)
how do you classify receptors via location?
mechanoreceptor (skin), thermoreceptor (skin), nocicreceptor (skin external damage), photoreceptor (eyes detect light), chemoreceptor (taste buds; olfactory receptors)

what molecules stimulate the basic taste sensations
sweet (sugar; sweeteners), sour (acid ions), salty (sodium), bitter (alkaloids), umami (amino acids primarily from meat)
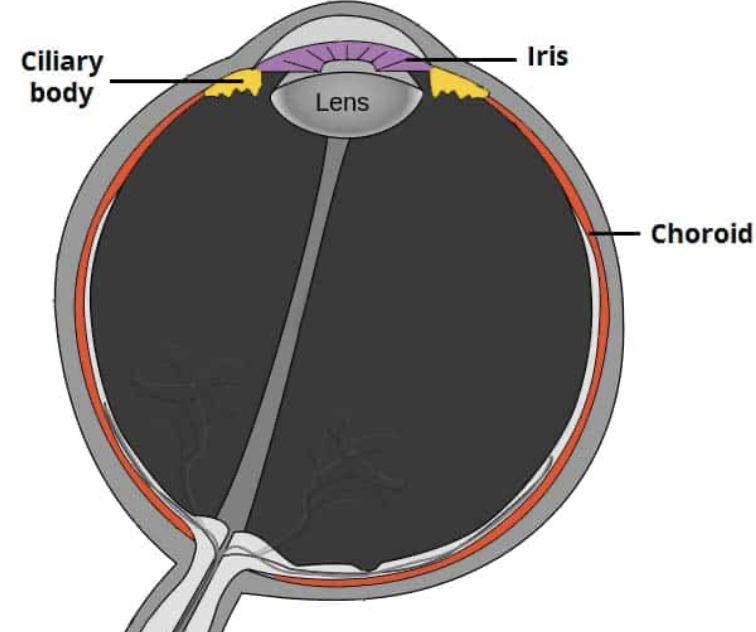
vascular layer of the eye (components + functions)
choroid (provides nutrients + oxygen to the retina), ciliary muscles (adjust lens shape), iris (light regulation)

how do amino acid based hormones differ from steroid based hormones?
amino is water soluble while steroid is lipid soluble; aminos receptor locations are the cell membrane while steroids is located in the nucleus/cytoplasm
what hormones from the pituitary gland are considered tropic hormones?
TSH (thyroid stimulating), ACTH, FSH (follicle stimulating), LH (luteinizing)
endocrine glands location?
pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal and pineal glands
main difference between a negative and positive feed back mechanism?
negative reduces or reverses a stimulus while a positive amplifies it; the goal of negative is to achieve homeostasis while positive aims at rapid completion
capillaries are the body’s smallest vessels, containing of _____ with a sparse basal lamina (basal thin layer)
endothelium
sympathetic vasomotor nerve fibers innervate the tunica media; what two actions stimulate the narrowing of the vessel and the widening of the vessel?
vasoconstriction narrows the vessel; vasodilation widens the vessel
system of tiny blood vessels that are located within larger blood vessels
vasa vasorum
thick wall mainly with large, low resistance lumen; located within all tunicas particularly within the tunica media
elastic arteries
elastic arteries give rise to this particular artery; also called distributing arteries because they deliver blood to body organs
muscular arteries
smallest of the arteries; participate in vasoconstriction which narrows the vessel and vasodilation which widens the vessel
arterioles
spider shaped stem cells that assist with the stabilization of capillary walls, controls permeability, and plays a role in vessel repair
pericytes
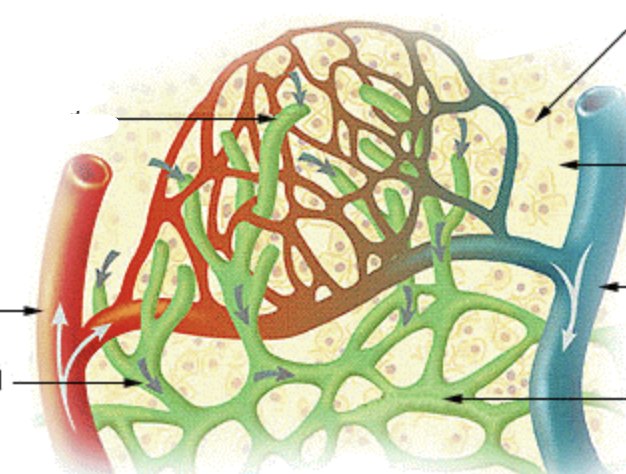
flow of blood through bed from arteriole to venule
microcirculation
branch off the arteriole that further branches into 10-20 capillaries that form the capillary bed
metarteriole
capillaries drain into post capillary?
venules
channel that directly connects arteriole w/ venule
vascular shunt
cuff of smooth muscle surrounding each true capillary that branches off metarteriole
pre capillary sphincter
consists of endothelium and a few pericytes; very porous
venules
prevent backflow of blood; most abundant within the veins of limbs
venous valves
flattened veins with extremely thin walls thus being composed of mostly endothelium
venous sinuses
interconnections of blood vessels are known as what?
vascular anastomoses
provides alternate pathways to ensure continuous flow; even if one artery is blocked
arterial anastomoses
shunts in capillaries
arteriovenous anastomoses
high abundance that occluded veins rarely block blood flow
venous anastomoses
blind-ended vessels that weave between tissue cells and blood capillaries; absent from bones teeth and bone marrow
lymphatic capillaries
specialized lymph capillaries present in intestinal mucosa
lacteals
drains into the right upper arm and right side of the head and thorax
right lymphatic duct
this type of duct trains into the rest of the body
thoracic duct
phagocytize foreign substances and help activate T cells
macrophages
capture antigens and deliver them to lymph nodes; also help with the activation of T cells
dendritic cells
areas where T and B cells mature (bone marrow and thymus for example)
primary lymphoid organs
where mature lymphocytes first encounter their antigen and become activated
secondary lymphoid organs
clusters of lymphoid follicles in wall of distal portion of small intestine
Peyer’s patches
contais a large abundance of lymphoid follicles; destroys bacteria preventing them form breaching intestinal wall, jimmy gaffigan got this particular body part removed
appendix
bilobed lymphoid organs that are found within the inferior neck
thymus
information gathered by sensory receptors about internal and external changes
sensory input
processing and interpretation of sensory input
integration
activation of effector organs (muscles/glands) and produces a response
motor output
brain and spinal cord of spinal dorsal body cavity; integration and control center
central nervous system
portion of nervous system outside of the CNS; contains mainly of nerves that extend from the brain to the spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
type of sensory fibers that convey impulses from PNS to CNS
afferent sensory fibers
convey impulses from visceral organs to CNS (type of sensory fiber)
visceral sensory fibers
transmits impulses from CNS to effector organs
motor (efferent) division
conduct impulses from CNS to skeletal muscle; a voluntary nervous system that deals with conscious control of skeletal muscles
somatic nervous system
contain visceral motor of nerve fibers; regulates smooth muscle and cardiac muscle among others. Considered an involuntary nervous system. has two subdivisions known as the sympathetic and parasympathetic
autonomic nervous system
small cells that surround and wrap delicate neurons
neuroglia (glial cells)
excitable cells that transmit electrical signals
neurons
most abundant, versatile, and highly branched of glial cells. Cling to neurons synaptic endings, and capillaries
astrocytes
small ovoid cells with thorny processes that touch and monitor neurons; can transform to phagocytize microorganisms and neuronal debris
microglial cells
line the central cavities of the brain and spinal column
ependymal cells
branched cells; process wrap CNS nerve fibers; forming insulating myelin sheaths in thicker nerve fibers
oligodendrocytes
clusters of neuron cell bodies in CNS and PNS
CNS: nuclei, PNS: ganglia
gaps between adjacent Schwann cells; sites where axon collaterals can emerge
myelin sheath gaps
thin fibers not wrapped in myelin; surrounded by Schwann cells but no coiling
nonmyelinated fibers
three or more processes (1 axon, other dendrites)
multipolar
two processes (one axon and one dendrite)
bipolar
one T-like process (two axons) also known as pseudo _____
unipolar
associated with sensory receptor
peripheral distal process
enters the cns
proximal (central) process
transmits impulses from sensory receptors toward CNS, almost all are unipolar, located within ganglia in PNS
sensory
carry impulses from CNS to effectors, multipolar, most cell bodies located within the CNS
motor
also known as association neurons, lie between the motor and sensory neurons
interneurons
neurons functionally connected by ________, junctions that mediate information transfer
synapses
neuron conducting impulses towards synapse (sends information)
presynaptic neuron
neuron transmitting electrical signal away from synapse (receives information)
postsynaptic neuron
the axon terminal of presynaptic neuron contains ____ that is filled with neurotransmitter
synaptic vesicles
receptor region on post synaptic neuron’s membrane: receives neurotransmitter; usually on dendrite or cell body. these two parts are separated by fluid filled _______
synaptic cleft
what two components make up the CNS?
brain and spinal cord
evolutional development of rostral (anterior) portion of CNS; resulted In increased number of neurons
cephalization