Lab 1 & 2: Introduction to Lab Safety and Microscopy
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
Laboratory Safety
Key to reducing injury and illness in labs.
Proper Training
Essential for awareness of potential lab dangers.
Preventative Measures
Focus on preventing dangers rather than reacting.
Rules of Conduct
Guidelines students must follow in the lab.
Emergency Procedures
Instructions for handling emergencies in the lab.
Risk Assessment Statement
Document evaluating potential lab hazards.
Laboratory Safety Agreement
Form students must sign for lab participation.
High-Risk Release Form
Acknowledgment of risks in laboratory activities.
Pathogenic Microorganisms
Microbes that can cause disease in humans/animals.
Bio-safety Level 2
Safety level for handling moderate-risk pathogens.
Lab Coat Protocol
Wear lab coat upon entering, remove when leaving.
Closed-Toe Shoes
Required footwear to protect feet in lab.
Hand Washing
Mandatory before and after lab sessions.
Disinfecting Work Area
Clean lab counter before and after use.
No Eating or Drinking
Prohibited to prevent contamination in the lab.
Safety Glasses
Must be worn at all times in the lab.
Equipment Reporting
Report defects in lab equipment immediately.
Bacti-cinerator Use
Follow specific directions for safe operation.
Flammable Liquids
Keep away from heat sources in the lab.
Biohazard Disposal
Used cultures must be disposed of properly.
First-Aid Kit Location
Know where to find first-aid supplies in lab.
Glass Disposal Box
Designated container for discarded glassware.
Chemical Safety Shower
Emergency equipment for chemical exposure.
Contaminated Material Disposal
Follow protocol for disposing of hazardous waste.
Incident Report
Document detailing accidents or unusual events.
Risk Assessment Statement
Evaluation of potential hazards in lab activities.
High-Risk Release Form
Permission form for students with health risks.
Informed Choice
Decision-making based on understanding risks involved.
Opportunistic Pathogens
Microorganisms that cause disease in weakened hosts.
Standard Precautions
Guidelines to prevent transmission of infections.
Pathogenicity
Ability of an organism to cause disease.
Living Bacterial Cultures
Samples of bacteria used for laboratory exercises.
True Pathogens
Organisms that consistently cause disease in healthy hosts.
Environmental Cultures
Samples collected from surroundings for microbial analysis.
Body Specimen Samples
Biological materials collected for microbiological testing.
Escherichia coli
Common bacterium, often used in labs.
Staphylococcus aureus
Bacterium known for causing infections.
Bacillus subtilis
Bacterium used in laboratory studies.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Opportunistic pathogen, often found in hospitals.
Serratia marcescens
Bacterium associated with hospital-acquired infections.
Micrococcus luteus
Bacterium commonly found on skin.
Enterobacter aerogenes
Bacterium that can cause infections in humans.
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Skin bacterium, often non-pathogenic.
Proteus vulgaris
Bacterium associated with urinary tract infections.
Mycobacterium smegmatis
Non-pathogenic mycobacterium used in labs.
Citrobacter freundii
Bacterium that can cause infections in immunocompromised.
Laboratory Safety Rules
Guidelines for safe conduct in lab settings.
Lab Station Supplies
Items needed for conducting laboratory experiments.
Safety Violations
Non-compliance with established safety procedures.
Compound Light Microscope
Instrument for viewing small objects not visible to the naked eye.
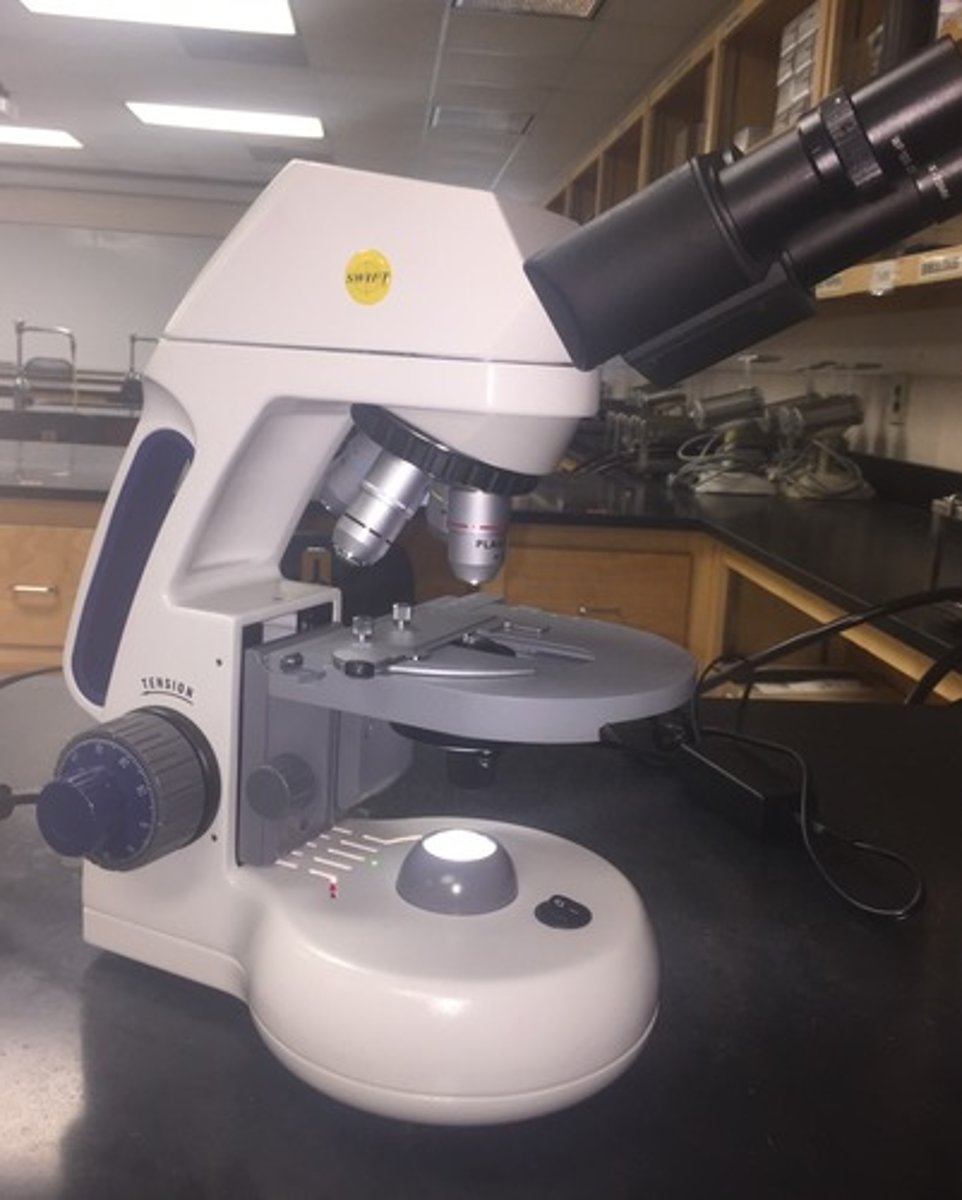

Microscopy
Science of investigating small objects using microscopes.
Ocular Lens
Lens closest to the eye; magnifies up to 10x.
Objective Lens
Lenses closer to the specimen; primary image formation.

Condenser
Lens below stage; focuses light on specimen.
Diaphragm
Controls light amount passing to the specimen.
Mechanical Stage
Platform for placing microscope slides.
Stage Clips
Holds microscope slides in place during viewing.
Illuminator
Light source for the microscope; mirror or bulb.
Coarse Adjustment Knob
Moves stage for initial focusing at low power.
Fine Adjustment Knob
Used for precise focusing of the image.
Base
Supports all parts of the microscope.
Total Magnification
Calculated by multiplying ocular and objective lens powers.
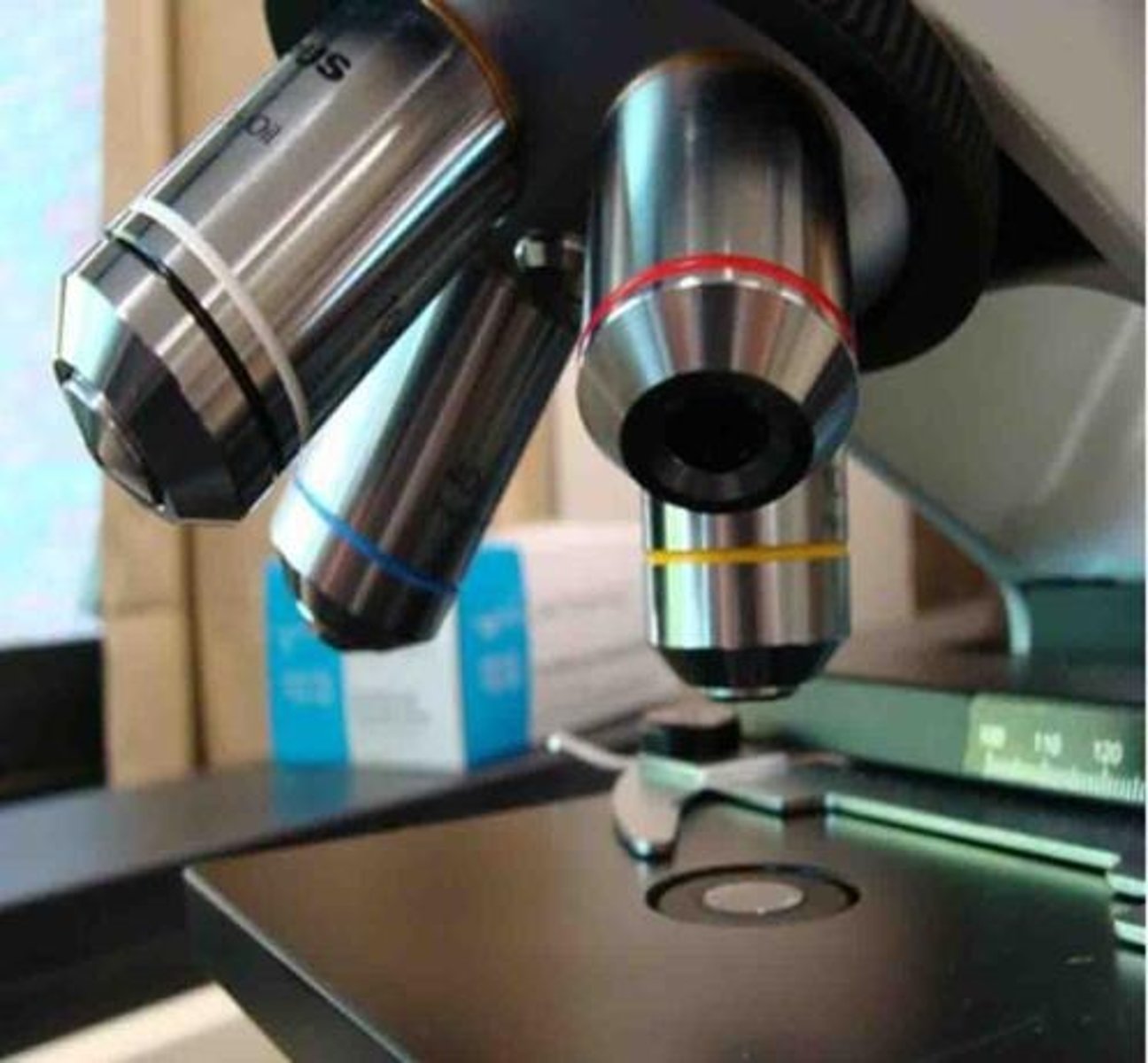
Scanning Power Objective Lens
Red band; magnifies objects 4x.
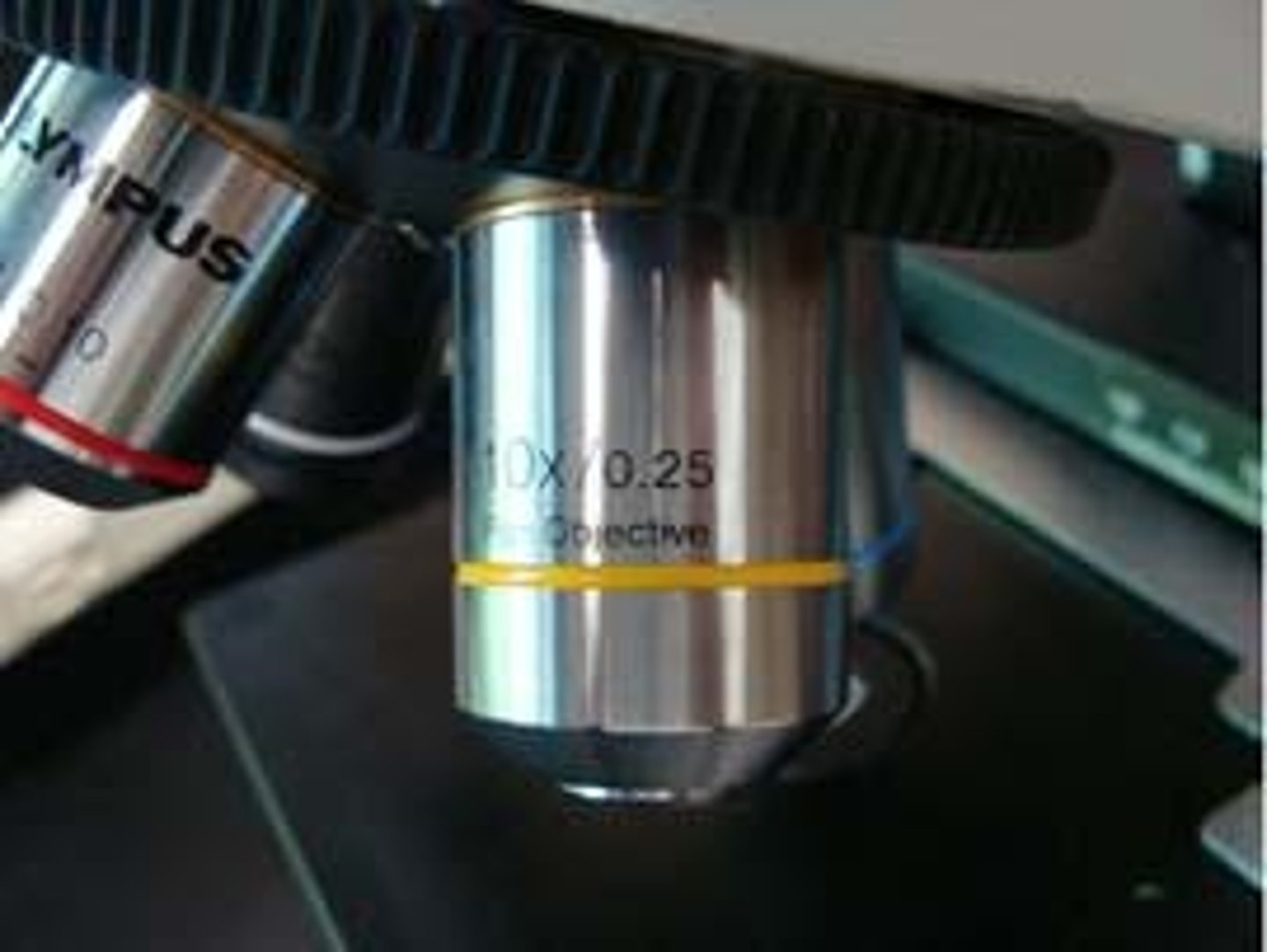
Low Power Objective Lens
Yellow band; magnifies objects 10x.
Parfocal
Lenses remain in focus when switching objectives.
Body
Tube connecting eyepiece to objective lenses.
Nosepiece
Rotating part holding all objective lenses.
Left Ocular Adjustment
Adjusts for vision differences between eyes.
Field of View
Lighted circle seen through ocular lenses.
Parfocal
Maintains focus when switching objectives.
High Dry Objective Lens
Magnifies objects 40x; blue banded.
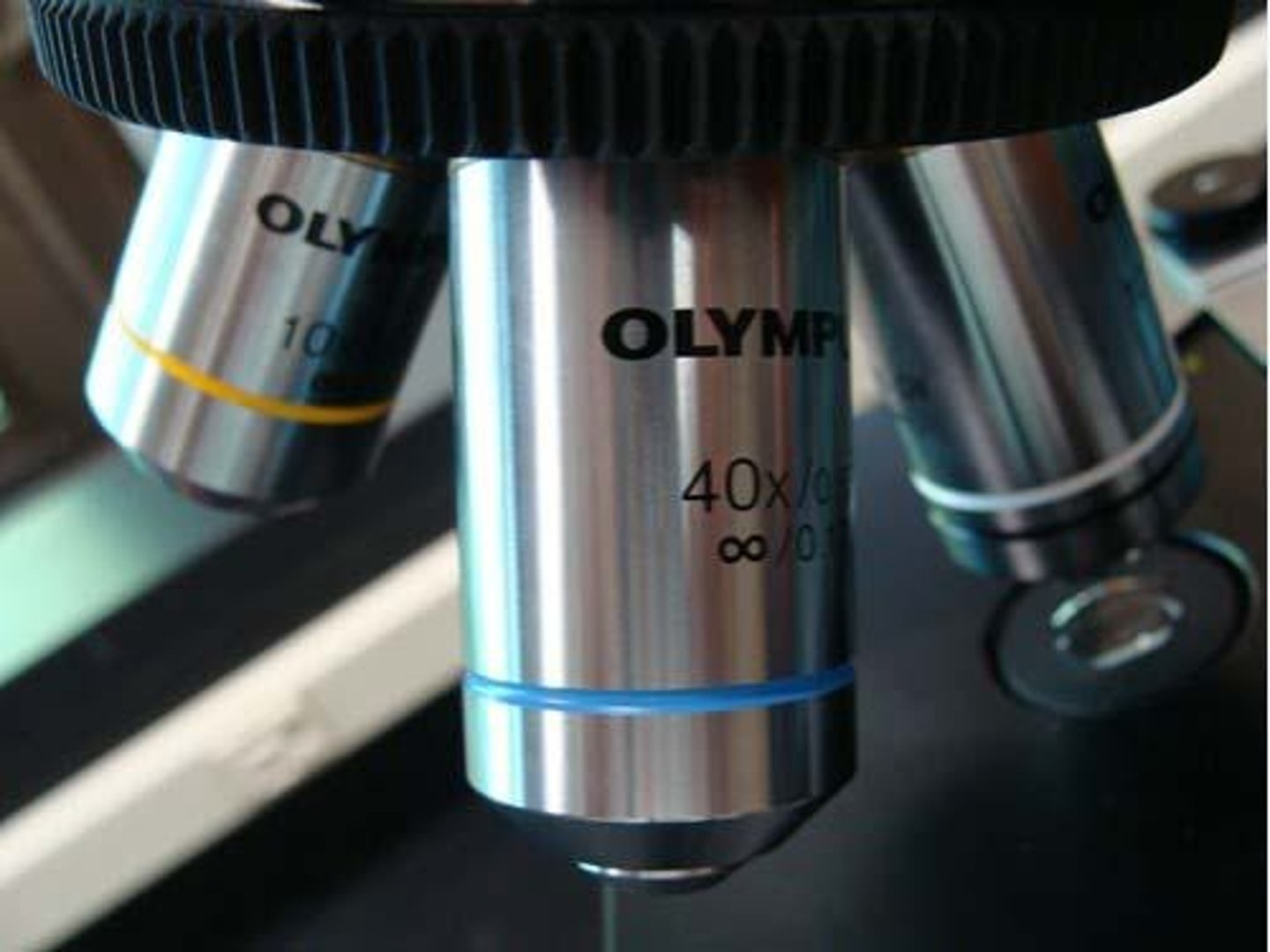

Total Magnification
Product of ocular and objective lens magnification.
Oil Immersion Lens
Highest magnification power at 100x.
Refractive Index
Measure of how light bends in materials.
Diaphragm
Controls light intensity reaching the specimen.
Rheostat
Adjusts light intensity for the microscope.
Condenser
Focuses light onto the specimen slide.
Coarse Adjustment Knob
Moves stage quickly for initial focusing.
Fine Adjustment Knob
Refines focus for clearer image details.
Mechanical Stage
Holds slides securely during observation.
Stage Clips
Secure slides on the mechanical stage.
Nosepiece
Rotates to switch between objective lenses.
Field of View
Visible area through the ocular lens.
Oil Application
One drop only for 100x magnification.
Cleaning Lenses
Use lens paper; dab, don't wipe.
Transporting Microscope
Hold base and arm; avoid scooting.
Light Bulb Care
Start with low light to prevent breakage.
Cleaning Slides
Use camp wipe for slides, not lenses.
Oily Stage Cleaning
Use kim-wipes to clean oily stages.
Objective Lens Order
Start with lowest magnification, then increase.
Image Centering
Adjust slide to center specimen in view.