Lecture 36 & 37: Parasitic Protozoa of Phylum Apicomplexa
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What is the difference between monoxenous and heteroxenous?
M: 1 host life cycle
H: 2 host lifecycles
What are there three classifications of coccidia?
intestinal, tissues, blood
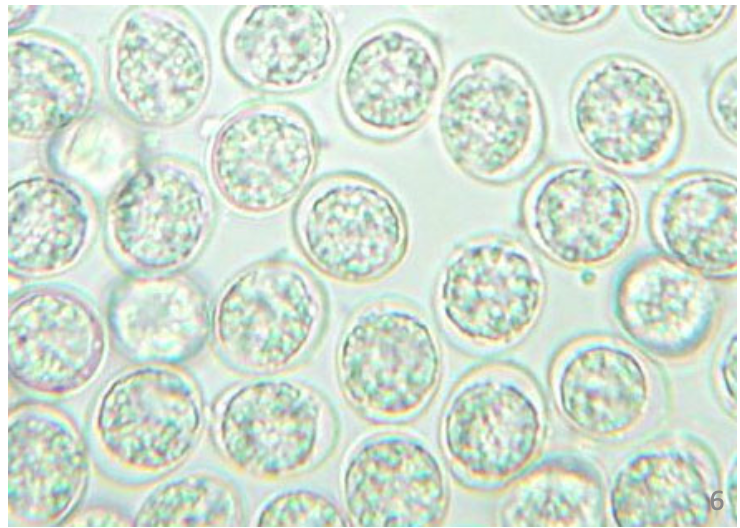
coccidia
What are cryptosporidium spp. associated with?
waterborne outbreaks
What is unique about cryptosporidium spp. metabolism?
pathways are more similar to bacteria than other apicomplexa
lack Krebs cycle → cannot synthesize fatty acids
lack plastid bodies for manufacturing food
unresponsive to anti-coccidal drugs
Oocysts of all cryptosporidium spp. are passed in feces, immediately _________, and morphologically indistinguishable.
infective
True or false: cryptosporidium spp. are able to survive in the environment and water treatment by chlorination.
true
Describe the life cycle of cryptosporidium spp.
Direct lifecycle
sexual and asexual replication in small intestinal epithelium
oocysts passed in feces following 3-5 day incubation
immediately infection
host infection via fecal-oral route and ingestion of oocysts
asymptomatic or symptomatic
What are the clinical signs of cryptospordidium spp. infections?
voluminous watery diarrhea
mucous present, rarely blood/leukocytes
abdominal discomfort, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, fatigue, fever
self-limiting if immunocompetent
What species is cryptosporidium most associated with?
dairy calves
How does cryptosporidium cause malnutrition and reduced growth?
blunting of brush border, loss of microvilli, villous atrophy in SI
What is an important part of supportive care for cryptosporidium infections since there are no consistently effective pharmaceutical products?
restoring electrolyte balance from diarrhea
What species of intestinal coccidia infects domestic livestock through ingestion of sporulated oocysts?
eimeria sp.
Where do eimeria sp. replicate?
asexual replication in small intestine
sexual replication in large intestine
What is the diarrhea caused by eimeria sp. associated with?
destruction of enterocytes by developing oocysts
What is disease of coccidiosis associated with?
onset of sexual replication in host tissues, mechanical disruption of mucosal cell by gametes

Eimeria oocysts
Coccidiosis is a function of:
age, nutrition, stress, sex, season, gestational status, inherent pathogenicity
How is coccidia treated?
environmental hygiene and chemoprophylaxis
What stage of replication do chemoprophylactic drugs target?
asexual
What is the function of coccidiostatic drugs?
arrest development of specific stages of the lifecycle (parasites remain alive in the tissues)
What type of drugs used to treat coccidia allow the parasite to resume development and completion of lifecycle if withdrawn?
coccidiostatic drugs
True or false: anticoccidial drugs may have static and cidal properties depending on the dose of the drug and length of parasite exposure to the drug.
true
How does coccidiostatic drug decoquinate function?
feed additive
acts on the sporozoite stage
parasite penetrates host cell, further development is arrested
no activity against adult parasites
How does coccidiostatic drug amprolium function?
drinking water additive
ats on 1st generation schziont in the intestinal cell wall
prevents differentiation into metrozoites
suppress sexual stages and sporulation of oocysts
What are drugs with coccidiocidal activity and what do they act on?
diclazuril, ponazuril, totazuril; act on apicoplast organelle involved in biosynthesis of fatty acids and AA metabolism
What class of drugs have coccidiocidal activity and coccidiostatic and what do they act on?
sulfonamides (ex. Albon); active against folic acid pathway and interfere with folate biosynthesis
What is a clinical drawback from using sulfonamides?
significant negative effects on gut microbiota

cystiosospora (intestinal coccidia)
What cystoisospora sp. infect dogs vs cats?
Dogs: C. canis and C. ohioensis
Cats: C. felis and C. rivolta