DNA structure and function
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Discovery of chromatic/chromosomes
Mid 1800’s → Fleming looked at plants under a microscope
saw distinct chromosomes at stages of cell division
Function was unclear in 1800’s
Isolating nucleic acids
1868→ Friedrich Miescher isolated nucleic acid from pus
Contained H, O, N and phosphorus
Later found that chromosomes contained nucleic acids and proteins
Chromosomal theory of inheritance
Late 1800’s→ Boveri and Sutton (1902)→ idea that chromosomes carry inherited info between parents and offspring
studied nematode worms and grasshoppers
Realised that egg cells have ½ chromosomes of an adult cell
Said that chromosomes are linear structures with genes at specific points along them
Genetic transformation
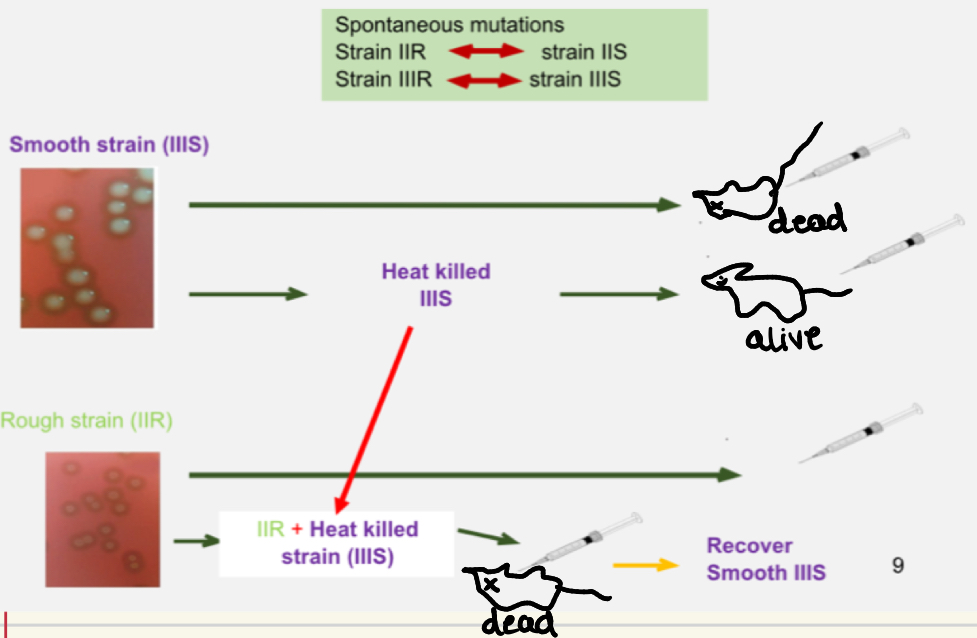
1928→ Griffith
streptococcus pheumoniae cause pneumonia
Found 2 strains in mice
Rough= Harmless to mouse, Smooth = deadly
What did Griffiths do with mice
Injected with rough = mice alive
Injected with smooth = mice dead
Injected with heat killed smooth = mice alive
Injected with heat killed S and live R = mice died, and live S recovered from mouse
Concluded that something in the heat killed S must’ve caused it.
A substance from the dead S was transferred to the live R, changing its genetic makeup.
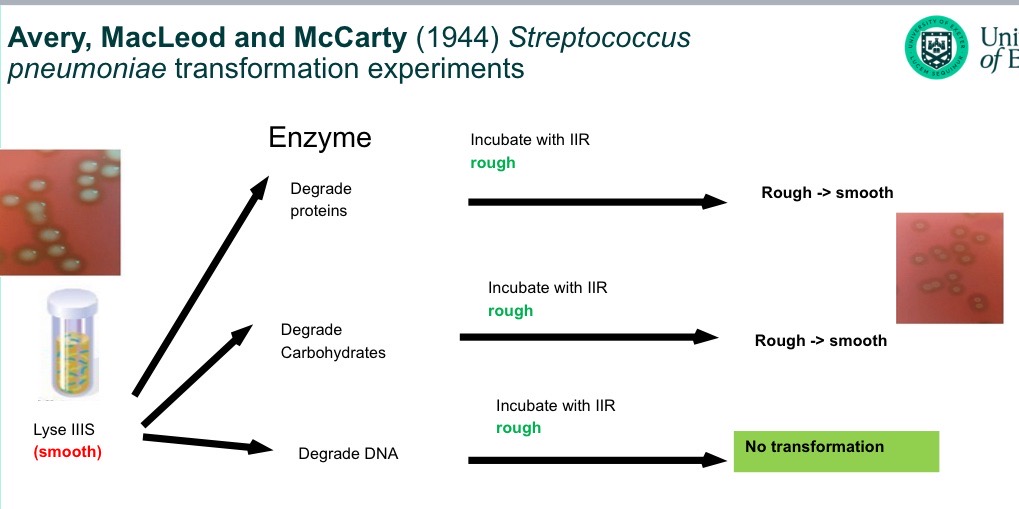
Further strep experiments
1944→ Avery, McLeod and McCarthy
transformation experiments
Degrade S proteins. Incubate with rough
Degrade S carbohydrates, incubate with R
Degrade S DNA, incubate with R
only the DNA one didn’t transform S to R
Must mean DNA plays a role in transformation.
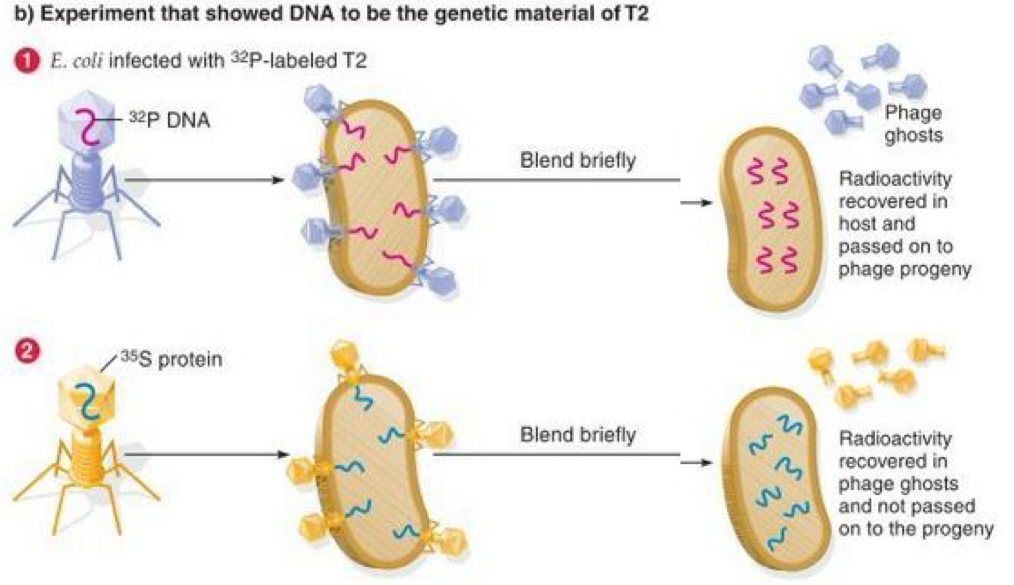
Bacteriophage experiments
1953→ Hershey and Chase
Bacteriophage (only DNA and proteins)
Grew phage in:
radioactive phosphorus (in DNA)
Sulphur (in proteins)
Only radioactive phosphorus was passed onto offspring
Strong evidence DNA carries genetic info
First DNA structure images found
1940-48→ Wilkins
first clear images of DNA with X-ray crystallography
Sperm isolated from squid, showed a long thin McClure (fuzzy DNA)
Double helix structure found
1953→ Crick and Watson
used info from Rosalind Franklin’s X-ray data
Found DNA contains repeating phosphate and deoxyribose groups
A&T and C&G always occurred in 1:1 ratio
Suggested a helical/corkscrew shape
Franklin and Goslings sister paper
High resolution image of Beta-DNA (hydrated)- lots more spots
Enabled calculation of basic DNA dimensions:
Probably helical
Phosphate groups on the outside
Two coxial molecules
Estimated diameter
Consistent with Crick and Watson estimates
Forms of DNA
A = dehydrated
B = hydrated, most common
Z = transient form found in living things
Basic DNA structure
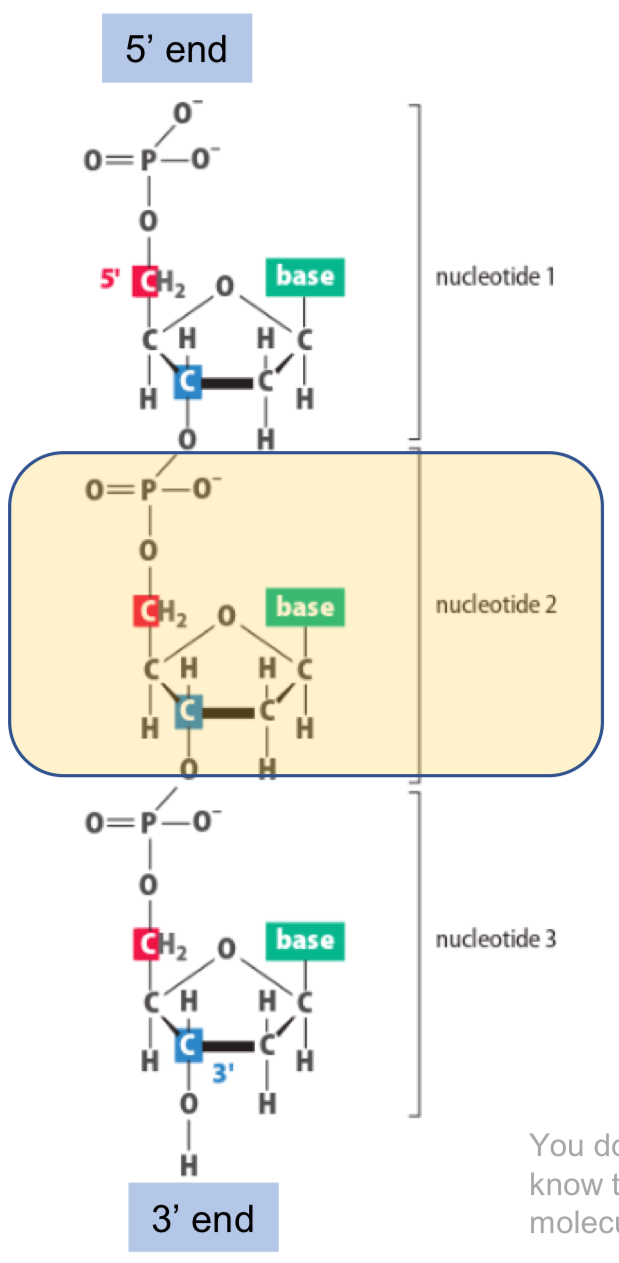
Deoxyribonucleic acid
nucleotide = sugar, phosphate and base
RNA = ribose sugar, DNA = deoxyribose sugar
5’ and 3’ end
5’ to 3’ = coding strand
3’ to 5’ = complementary
Bases
Purines = Adenine and Guanine
2 rings
Pyrimidines = Thymine and Cytosine (Uracil for T in RNA)
one ring (pyramid)
A&T = two H bonds
C&G = three H bonds
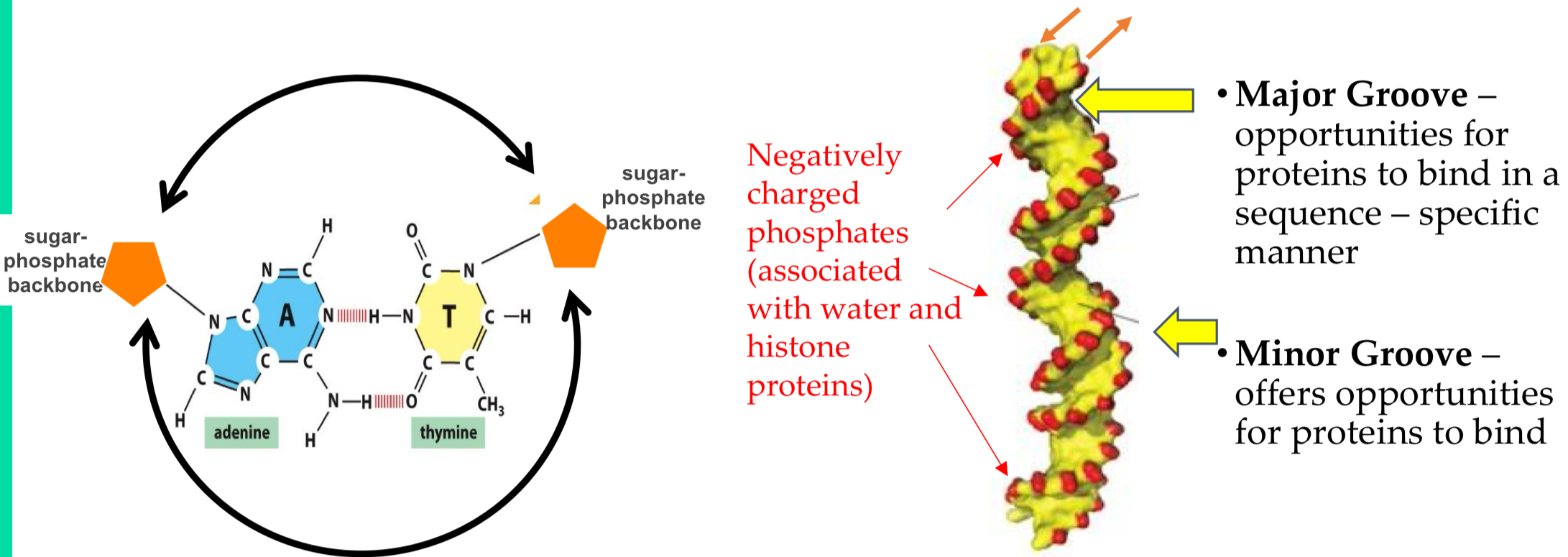
Antiparallel implications
Major groove = opportunities for proteins to bind to sequence in a specific manner
Minor groove = opportunities from proteins to bind
-ve charged phosphates associate with water and histone proteins
Base Paris are planar with hydrophobic stacking interactions between bases
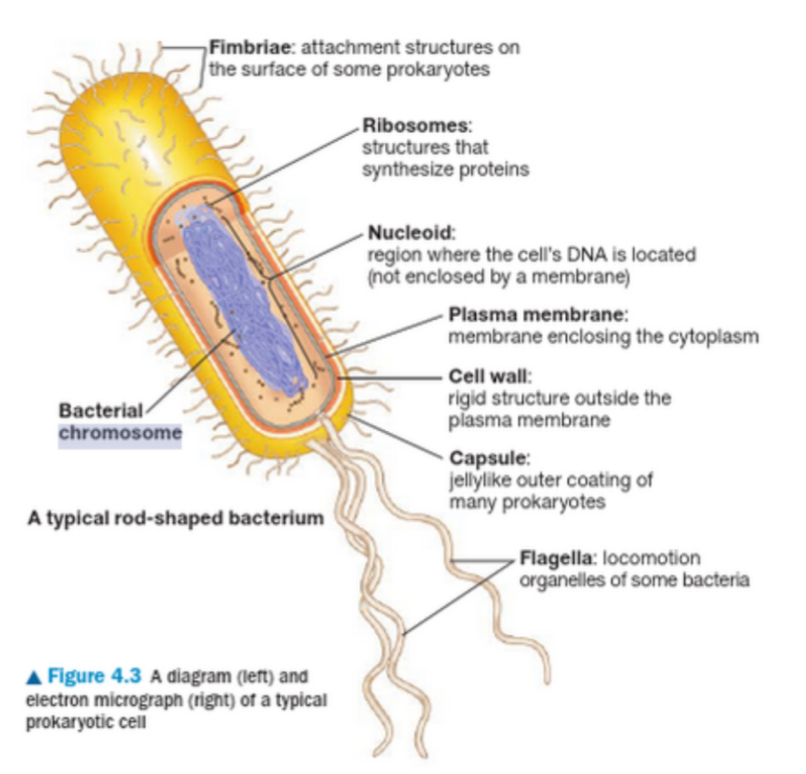
Prokaryote (bacterial)
no nucleus- single circular DNA= nucleoid
Small, about 5Mb
Have plasmids (tiny DNA circles as small as 1000bp) important in antibiotic resistance
Eukaryote
plants, animals, fungi, protists
Genome = all DNA in nucleus and other organelles e.g. mitochondria
Nucleus = linear chromosomes
Mitochondria and chloroplasts = circular DNA
Haploid human nuclear genome = 3Gb (3 billion bases)
Human mitochondrial genome = 15Kb (Kb 1000)
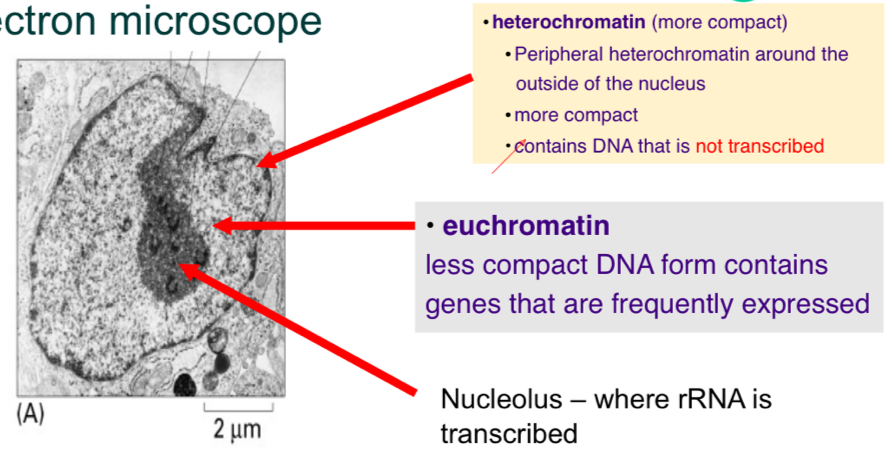
Hetero/euchromatin
Heterochromatin = more compact
Contains DNA that is not transcribed
Peripheral hetero = around outside of nucleus
Euchromatin
less compact DNA form
Genes that are frequently expressed
Chromosome arrangement
→ a very large DNA-protein complex
most human cells have 46 (22 pairs autosomal and 1 pair sex)
XY = male
XX = female
Gamete have 23 chromosomes
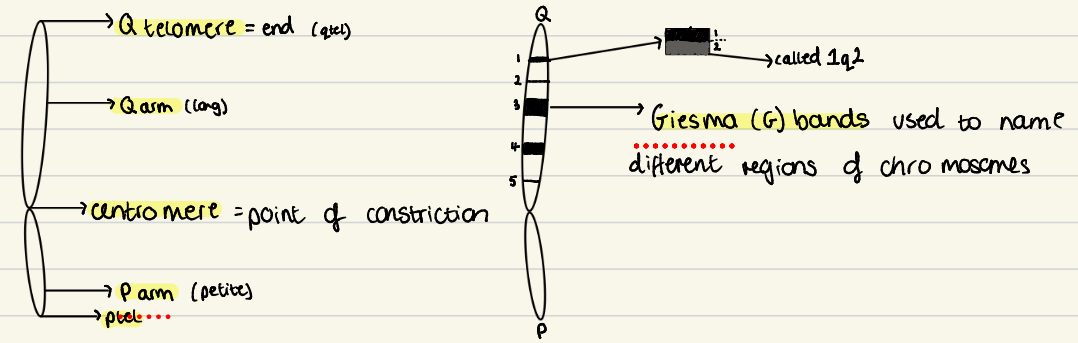
Q arm = long, P = small
Centromere = point of constriction
Q telomere = Q end, P telomere = P end
Geisma (G) bands used to name different regions of chromosomes
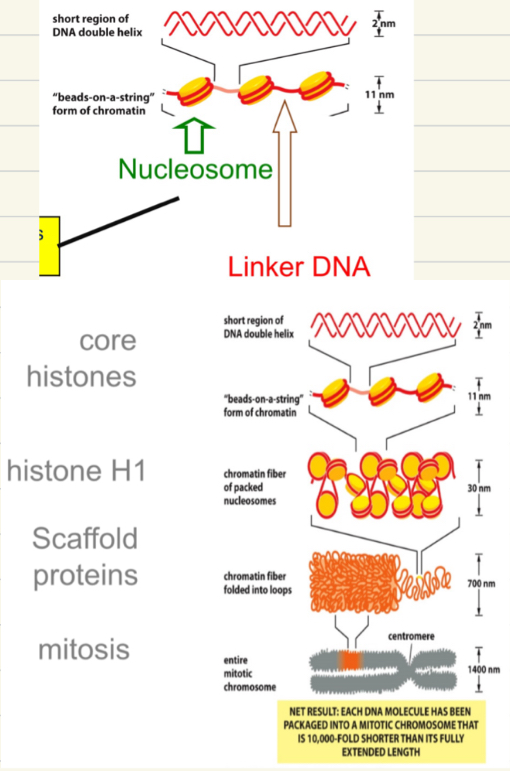
DNA packing
observed as ‘beads on a string’
DNA. Wraps 1.65 times around the 8 core histone to form nucleosomes
Histones are +ve charged DNA is -ve
Core Histones = H2A, H2B, H3, H4
H1 = brings nucleosome together to form a chromatin fibre
Chromatin further condensed by scaffold proteins
10,000 fold shorter than extended length