Biotechnology Midterm 2
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
DNA → RNA → protein
genetic code → characteristic
What is the expanded central dogma of molecular biology?
DNA (+epigenomics) → RNA → protein (environmental factors)
What is bioinformatics?
scientific discipline created from the interaction of biology, mathematics, and computer science that utilizes a body of tools and algorithms needed to handle large and complex biological information
What drives omics?
DNA sequencing technology
What is the basis of roche sequencing?
One DNA molecule per bead then amplify in microreactors in emulsion then crosslink to glass side
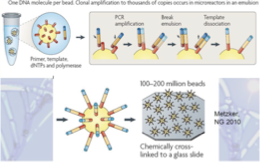
What are 3 major databanks?
NCBI (US), DDBJ (Japan), ENA/EBI (Europe)
What is the basis of Illumina SBS sequencing?
DNA fragments → connector connection to flowcell → bind to primer (Bridge) → PCR amplification → dissociation of bridging → sequencing by fluorescence
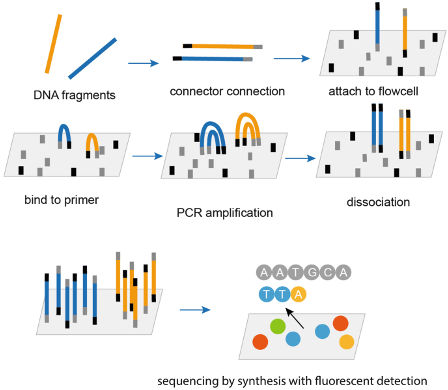
What is the basis of Helicos (SMS) sequencing
Synthesize → wash → image → cleave → repeat with next base
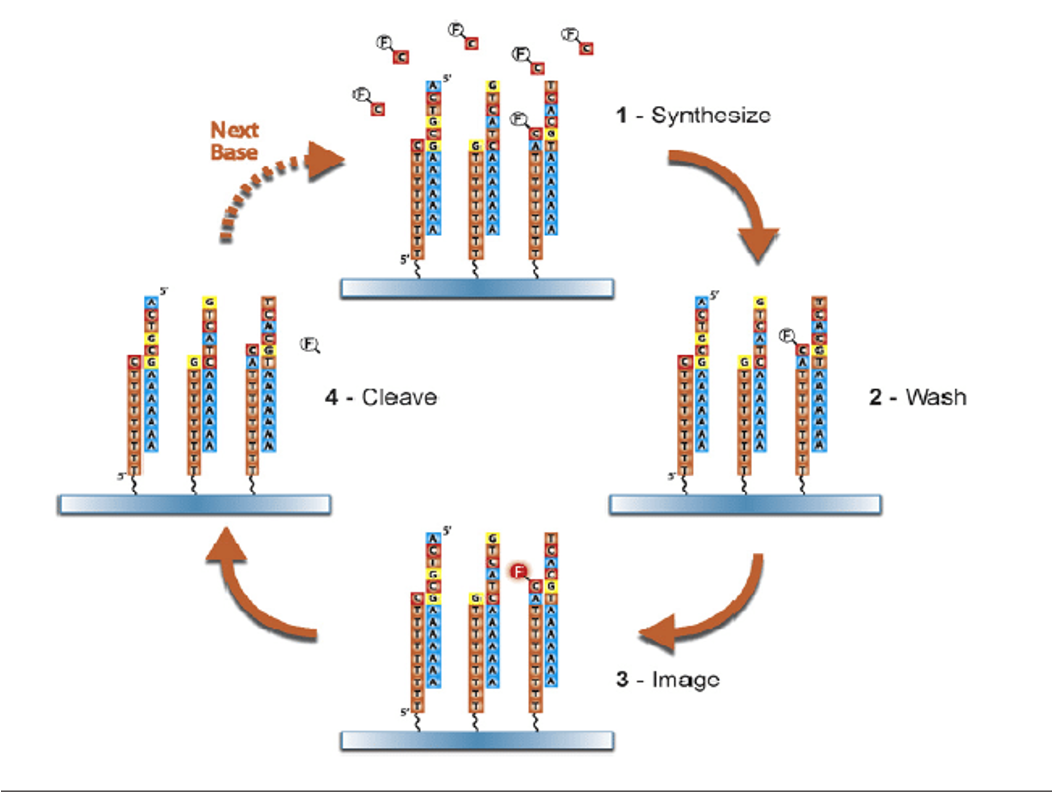
What is the basis of PacBio SMS sequencing?
prepared DNA sample → nanowell (single molecule becomes circle and goes through DNA polymerase to make double strand) → fluorescent nucleotides as DNA polymerase goes around → fluorescent intensity over time→ sequence
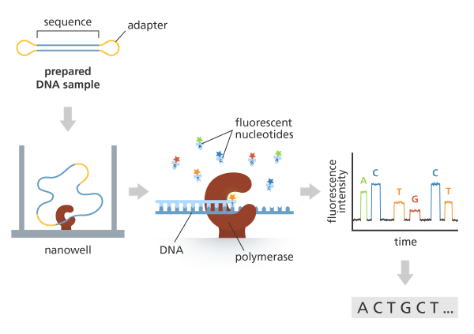
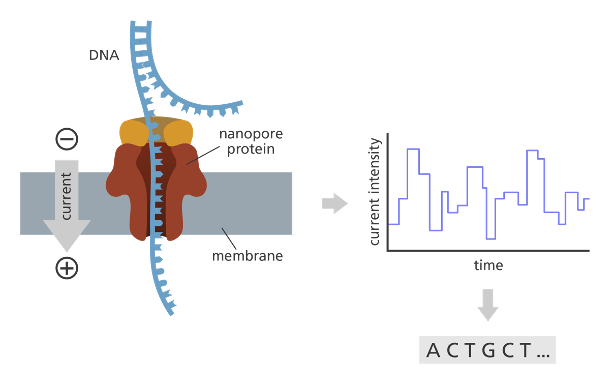
What is the basis of Oxford Nanopore SMS sequencing?
DNA into nanopore protein with current → current intensity over time → sequence
What does genomics look at?
DNA sequence
What does transcriptomics look at?
RNA levels/expression levels
What does proteomics look at?
protein expression
what does metablomics look at?
Global metabolite analysis
What is the GTEx portal?
genotype-tissue expression portal
What is the 1000 genomes project?
collection of de-identified human genomic sequence variation data to provide a comprehensive resourse on human genetic variation
What is the International Genome Sample Resource?
1000 genomes project data plus sequence data from:
human genome diversity project (HGDP)
simons genome diversity project (SGDP)
gambian genome variation project (GGVP)
What is the NCI’s genomics data commons (GDC)?
cancer genomic databank maintained by the NCI
What are the FAIR data principles?
Findable
Accessible
Interoperable
Reusable
What is the US and European Privacy laws called?
US- HIPAA
EU- GDPR
What are the responsibilities in accordance to data ethics and privacy
protect sensitive human genomic data
informed consent and data ownership
balancing open science with responsible stewardship
What are the 3 best practices for bioinformatics?
document code and parameters, share workflows and data openly, embrace community standards
Define plant biotechnology
improvement to crop plants through selective breeding and hybridization with greater variety of genetic information in a more precise and controlled manner
What are fertilizers?
compounds to promote growth, usually applied either by soil (root uptake) or leaves, can be organic or inorganic, have caused many problems
What is the purpose of fertilizers?
increase crop yield
What is the problem with algal blooms?
pollute lakes near areas of agriculture
Define algal blooms
relatively rapid increase in the population of usually phytoplankton algae in an aquatic system
What are the results of algal blooms?
death of fish and disruption of whole lake ecosystem
How do insects hurt crops?
leave larvae which damages the plant
Define pesticide
any substance that kills organisms that we consider undesirable
what are the 4 ideal pesticide qualities?
kill only target species
have no effect on non-target species
avoid development of resistance
breakdown to harmless compounds after a short time
What are the problems with DDT?
expensive, toxic to both harmful and beneficial species, run-off problems, affects food pyramid
How does DDT affect the food chain?
concentrates in fish and fish-eating birds, interferes with calcium metabolism causing thinning in the eggs laid by birds which causes the eggs to break before incubation is done which leads to decrease in population
in plant biotechnology, what are living cells used to make?
pharmaceuticals, foods, beverages
In plant biotech, what are organisms such as bacteria used for?
protect the environment
In plant biotech, what is DNA science used for?
production of products diagnostics and research
Why would we want to modify an organism?
better crop yield, herbicide or disease resistance nutrition or pharmaceuticals, vaccine delivery