1.1 Research in Psychology
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Psychology
scientific study of behavior and mental processes
behavior vs. mental processes
behavior is observable, external
mental processes are not observable, internal
4 Goals of Psychology
Description – describe behaviors by observations
Explanation – explain behaviors
Prediction – predict when a behavior will happen
Change – change inappropriate behavior
Empirical Evidence
info gathered through observation or experimentation
Falsifiability
can be proven wrong
Replication
reproducing a study to see if you get the same results
Clever Hans Effect
an animal/person senses what someone wants them to do, even though they are not deliberately being given signals
aka observer-expectancy effect
artifacts
the study results that were caused/changed by an accidental factor
Confirmation Bias
The tendency to see things that confirm what one already believe and ignore things that challenge it
ex. only remembering when your horoscope was right and forgetting times it was wrong
Hindsight Bias
The tendency to believe, after learning the outcome, that you knew it all along
ex. saying you knew a team would win after the game
Overconfidence
We tend to think we know more than we do.
82% of U.S. drivers consider themselves to be in the top 30% of their group in terms of safety.
Quantitative Research
uses numbers
approach is nomothetic
has variables
uses experiments, measurements
+ generalizable
-narrow
Nomothetic Approach
meant to find universal laws
Experimental Studies
independent and dependent variables (2 total)
cause and effect inferences
quantitative
Independent Variable
the variable manipulated by the researcher
Dependent Variable
the variable expected to change due to the independent variable
Cause and Effect Inferences
determining if an association really has a cause-and-effect relationship
if DV changes when the IV is changed
Correlational Studies
2 variables that aren’t manipulated (no IV / DV)
connection between variables exists
no cause and effect variables because unknown directionality or confounding variables
quantitative
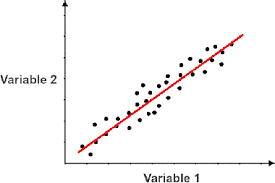
positive correlation
when one variable increases so does the other
ex. shoe size goes up as hight does
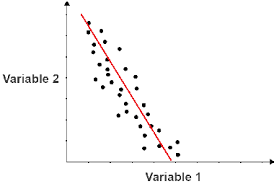
negative correlation
when one variable increases the other decreases
ex. The lower the temp the more layers you wear
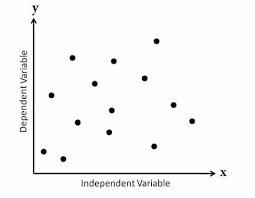
no correlation
no clear connection between variables
directionality
which variable had the impact on the other
confounding variables
unpredicted variable is changing the DV instead of the IV
Descriptive Studies
2+ variables
observe variables separately
basically compiling data
Qualitative Research
involves texts
approach is ideographic
no variables
methods: interview, observations, case studies
+more depth
-not generalizable
Idiographic Approach
meant to learn about an individual or specific group
Case Study
in depth investigation of an individual or specific group
Sample
the group taking part in a research study
Sampling
process of finding and recruiting individuals for a study
credibility
degree the results can be trusted to reflect reality
bias
causes results of study to not reflect reality
generalizability
extent results can be applied beyond the sample and its setting
construst
mental process
can’t be directly observed
operationalization
expressing a construct in observable terms
measurable behavior