BPK 326 - Abdomen & Pelvis Theory and OIAI Combined
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
Abdominal cavity rostral border
Diaphragm
Abdominal cavity inferior border
Opening of the top of the pelvis
Linea Alba
Creates the divisions of the left & right halves of the rectus abdominous
Flank = ?
Lateral surface of abdomen & pelvis
Abdominal wall layers from superficial to deep
Skin - Camper's Fascia - Scarpa fascia - Superficial investing fascia -External Oblique - Intermediate Investing Fascia - Internal Oblique - Deep Investing Fascia - Transverse Abdominus - Transverse fascia - Parietal Peritoneum
What is the relative postition of the Rectus abdominus?
Deep to the aponeurosis which is deep to skin
Posterior border of the abdomen
Quadratus lumborum
What runs through the inguinal canal
Spermatic cord
Structures that the inguinal ligament pins down
The femoral nerve, artery & vein
Inguinal Hernia
When a loop of intestine is pushed through the inguinal canal
Rectus sheath
Consists of the aponeurosis of EOs, IOs, & TA
RUQ Contains
Right lobe of liver
Gallbladder
Stomach : pylorus
Duodenum
Pancreas : head
Right adrenal gland
Right kidney
Right colic flexure
Ascending colon
Transverse colon
LUQ contains
Liver (left lobe)
Spleen
Stomach
Jejunum & proximal ileum
Pancreas : body and tail
Left kidney
Left adrenal gland
Left colic flexure
Transverse colon
Descending colon : superior part
RLQ contains
Cecum
Appendix
Most of ileum
Ascending colon : inferior part
Right ovary
Right uterine tube
Right ureter
Right spermatic cord
Uterus (if enlarged)
Urinary bladder (if very full)
LLQ Contains
Sigmoid colon
Descending colon : inferior part
Left ovary
Left uterine tube
Left ureter
Left spermatic cord
Uterus, (if enlarged )
Urinary bladder (if very full)
Peritonium
Is a double-walled lining the abdominal pelvic cavity and contains serous fluid.
3 Interior Divisions of the Abdomen
Retroperitoneal, Intraperitoneal, Infraperitoneal
Retroperitonal organs
Adrenal gland
Pancreas (except the tail)
Ureters
Colon (ascending and descending)
Kidneys
Esophagus
Rectum
Duodenum (second, third, and fourth parts)
Abdominal aorta
Inferior vena cava
Intraperitoneal organs
Liver
Gallbladder
Spleen
Stomach
Jejunum
Ilium
Transverse & sigmoid colon
Cecum (sometimes partially intraperitoneal)
Appendix
First part of the duodenum
Tail of the pancreas
Extraperitoneal organs
Bladder
Lower rectum
Male reproductive organs
2 Specializations of the Peritoneum
Mesentary & Omentum
Function of the Omentum
Protection
Allow the migration of immune cells into the peritoneal cavity.
Forms adhesions to physically wall off areas of inflammation
Source of tissue for wound repair
Esophagus structure
Has skeletal muscle, proximately and smooth muscle distally
Isn't uniform in width
Fundus
General term for the round part of any organ
Within stomach: often full of air
Cardia
Proximal part of the stomach
Pylorum
Distal part of stomach
Divided into pyloric antrum, pyloric canal & pyloric sphincter.
Movement of food through the stomach
Cardia >> body >> pyloric antrum >> pyloric canal >> pyloric sphincter >> duodenum
Greater Omentum
Extends from the greater curvature of the stomach
Hangs in a fold covering the small intestine
Attaches to the transverse colon
Lesser Omentum
Extends from the lesser curvature of the stomach
Attaches to both the liver and the duodenum
Haustra
Folds of the large intestine
Tenia Coli
Long ligament that helps to propel waste through the large intestine
Right Colic Flexure is known also as
The Hepatic Colonic Flexure
Diverticuli
Pouches in the wall of the colon. Tend to increase with aging.
Diverticulitis
Inflammation of the diverticula
Liver structure
2 lobes, right & left, separated by the Falciform Ligament. Ligament also tethers liver to the abdominal wall.
From inferior surface: caudate (anterior) & quadrate (posterior)
Gallbladder location
Inferior surface of the right lobe of the liver
Hepatic Triad
Hepatic portal vein, hepatic artery & bile duct
Hepatic portal vein
Oxygen poor but nutrient rich blood from digestive track to the liver
The flow of Bile
- Produced continuously in liver
- Gathered by left & right hepatic ducts which combine to form the Common Hepatic Duct (CHD)
- Bile travels via the CHD & drains into the Bile Duct (formed by both the CHD & the cystic duct)
- Then travels through the Hepatopancreatic Ampulla (formed by common bile & pancreatic ducts)
- Lastly enters the duodenum through the major duodenal papilla
- When sphincter at the duodenum is closed, bile Passively fills the Cystic duct thus filling the gallbladder
* Cystic duct has bidirectional flow
Function of the Minor Duodenal Papilla
An accessory pancreatic duct for emptying pancreatic secretions
Cholelithiasis?
Aka Gallstones
Splenomegaly?
Enlarged spleen
Functions of Spleen
Largest immunological organ
Produces antibodies, recycles RBCs, phagocytosis
Contains big reservoir of monocytes
Organs the Spleen is in Contact with
Splenic flexure of large intestine
Left kidney
Stomach
Spleen Rupture
Due to its superficial position
Most commonly caused by blunt, abdominal trauma (car, crash, high-speed collision)
Distictive feature of the superior border of the spleen
Has notches
High variability
Spleen is made of:
A tough fibrous capsule
Soft pulpy inside
Capsule doesn't need to break for rupture to occur
Spleen Blood Supply
Splenic artery (branch of the celiac trunk)
Abdominal Aorta Location & Bifurcation
Abdominal aorta travels anterior & left to IVC & splits into L & R common iliac arteries
3 Branches of the Abdominal Aorta
- Celiac Trunk : Splits into the Common Hepatic Artery (supplies the duodenum), Splenic Artery (supplies pancreas) & Left Gastric Artery (distal esophagus)
- Superior Mesenteric Artery
- L & R Renal Arteries
- Inferior mesenteric artery is inferior to all 3
Superior Mesenteric Artery
Supplies digestive tract from lower duodenum to 2/3 of the transverse colon, & pancreas
Splenic flexure is the division from the supply of the superior to the inferior mesenteric arteries
Inferior Mesenteric Artery
Supplies the descending and sigmoid colon, & part of the rectum
Urinary tract consists of:
Ureters
Bladder
Urethra
Kidneys
Kidney blood flow
Receives 25% of cardiac output
Supplied to by branches of abdominal aorta, which enter the kidney with the ureter at the renal hilum
Vein enters anterior to artery & ureter is inferior to both
Kidney's Function
Regulates pH, osmolarity & blood pressure
Facilitates removal of toxins
Adrenal/Suprarenal Glands Produce?
- Adrenal Cortex (superficial) makes cortisol, androgens & aldosterone
- Adrenal Medulla (interior) makes epinephrine & norepinephrine
Site of filtration?
Renal cortex
Renal cortex contains:
Renal corpuscles
Distil & proximal renal tubules
Smallest functional unit of the Kidney
Nephron
Renal Medulla is made of
Renal columns & pyramids
Pyramids have base & apex
Apex = Renal Papilla
What do renal columns contain
Urinary tubules
Blood vessels
Connective tissues that help maintain kidney structure & make sure the cortex adheres to the medulla
Urine production & flow
Produced in nephron >> go into papilla >> minor calyces >> major calyces > renal pelvis >> ureter >> bladder >> urethra
Renal & Ureteric Calculi
AKA Kidney stones
Stones larger than lumen of ureter cause pain
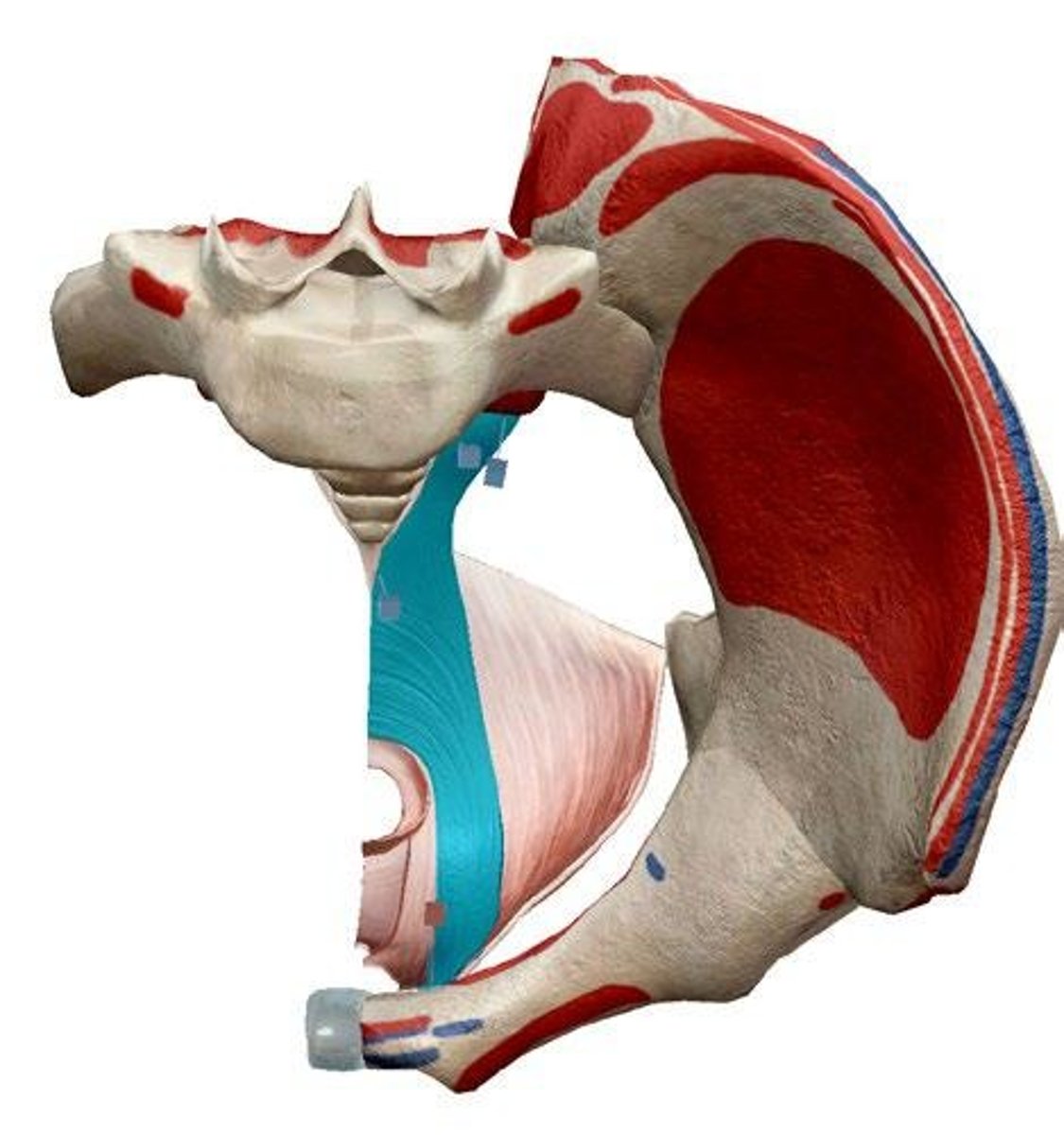
Roles of Pelvic Floor Muscles
Create a muscular floor to support the pelvis organs
Crucial to continence (bladder & bowel control) & sexual function
3 groups of Pelvic Diaphragm Muscles
Pelvic Diaphragm (proper)
The Urogénital Diaphragm
The Sphincters & Erectile muscles of the urogenital tract
Significant muscle of the Pelvic Diaphragm Proper
Levator Ani Group
3 Muscles within Levator Ani Group
Puborectalis
Pubococcygeus
Iliococcygeus
Medial 2 are immediately adjacent to vaginal canal & are vulnerable during delivery.
Pelvic Floor Injury
Common in vaginal delivery
Puborectalis & Pubococcygeus are most common muscles damaged
Uterus
Contains developing fetus during gestation
50-200g to ~1kg
Fundus is connected to ovaries via Fallopian tubes
Cervix is connected to vagina
Complications of Pregnancy & their Cause
Complication: Shortness of breath, heartburn, reduced stomach capacity, impaired intestinal transit & constipation
Cause: expanding uterus compresses adjacent organs, compromising function.
Broad Ligament
A sheet-like fold of peritoneum
Extends from the sides of the uterus to lateral wall & floor of pelvis. Holds uterus in position.
Round Ligament
True ligament
Extends from lateral aspect of uterus to the external labia (labium majorum)
Round Ligament Pain
Pain in pelvis & labia due to baby kicking or uterus being weighed down
Uterine Prolapse
Uterus collapses into vagina or outside the vagina
Happens when ligaments or pelvic Floor muscles are damaged
Fallopian Tubes Divisions
Intramural (medial)
Isthmus
Ampulla
Infundibulum (to lateral)
Ectopic Pregnancy's Most Common Form
Tubal pregnancy. Results in death of embryo & potentially the mom.
If it occurs in right uterine tube, can be misdiagnosed as appendicitis.
Tubal Ligation
A surgical method of birth control
Released ova simply degenerate & are absorbed
Vagina
AKA birth canal
A fibro-muscular tube
7-10cm
Facilitates childbirth, menstruation, sexual intercourse & pleasure
Cervix
Clinically important
Dilates during labour to admit baby into vagina
Checked routinely for changes indicative of cervical cancer via Pap smear
Cervical Os is the small & round opening
Appearance changes with progression of HPV & cancer
Vulva
Collective term for the external female genitalia
Tumescence =
Erection
Penis consists of mainly
Erectile bodies (tissues that have vascular spaces that can become engorged with blood)
Corpora Cavernosa (corpus caversonum when singular)
Primary erectile bodies of the penis
Big
Dorsal
Has large vascular sinuses
Make up the largest proportion of the penis
Crura are the base
Corpus Spongiosum
Ventral
Contains the urethra
Has large vascular sinuses
Continuous with the glans
Has less tunical covering relative to the corpus covernosum
Bulb is the base
Prepuce
The foreskin
Covers majority of the glans
Attaches to fascia overlying the body of the penis
Circumcision
+ = reduces risk of urinary tract infection, STIs
- = infection, permanent disfiguration, impaired sexual pleasure or function
Urethra
Extends from the internal urethral orifice of the bladder to the external urethral orifice of the glans
Prostatic Urethra
A division of the urethra where prostatic fluid enters
Contains the Urethral Crest where the Prostatic Ducts open bilaterally
Contains the Seminal Colliculus where Ejaculatory Ducts open bilaterally
Affected by Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
A non-cancerous increase in prostate size
Sx:
Waking up in night to pee
Urinary hesitancy
Intermittent Urinary flow
Bulbourethral Glands / Cowper's Glands
Located bilaterally along the spongy urethra near the base of penis
Eject lubricating fluid into the urethra
2 Openings that Increase Size of Urethra
Ampulla (proximally)
Navicular Fossa (distally)
Vas Deferens Ligation
Commonly called Vasectomy
The surgical form of birth control in males
Flow of Sperm (Production to Secretion)
Produced in testes, mature in epididymis.
Travel through vas deference, which merges with ejaculatory duct.
Ejaculatory duct has sperm & seminal vesicle secretions & goes through the prostate which inserts its secretions. After taking secretions from bulbourethral gland it then becomes the urethra.
External obliques
Origin: Ribs 5-12, sternum; Insertion: Iliac crest, inguinal ligament, linea alba, pubic tubercle; Action: Bilaterally: anterior flexion of the trunk and compression of the abdomen; Unilaterally: lateral flexion of the trunk and rotation to the opposite side.
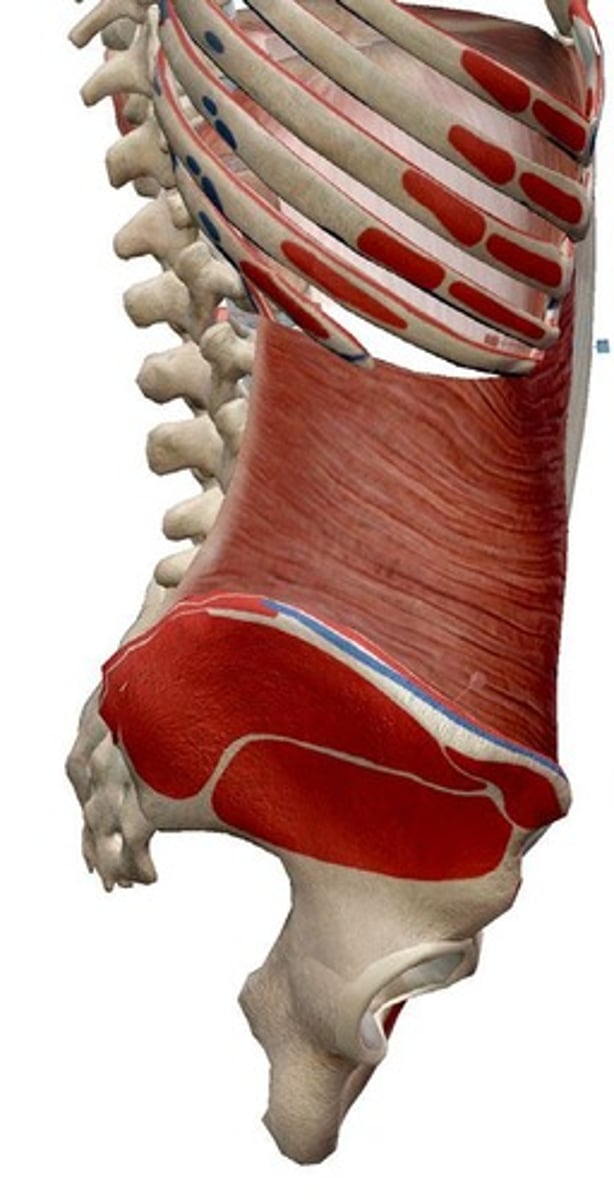
Internal obliques
Origin: Iliac crest, Inguinal ligament, thoracolumbar fascia; Insertion: Ribs 10-12, pectineal line, linea alba and abdominal aponeurosis (fuses with external oblique to become the rectus sheath); Action: Bilaterally: anterior flexion of the trunk and compression of the abdomen; Unilaterally: lateral flexion of the trunk and rotation to the same side.
Transverse abdominis
Origin: Iliac crest, thoracolumbar fascia, Costal cartilage of ribs 7-12; Insertion: Abdominal aponeurosis (and other midline structures); Action: Compression and tension of abdominal wall.
Rectus abdominis
Origin: Pubic crest, tubercle and symphysis; Insertion: Costal cartilages 5-7, Xiphoid process; Action: Flexion of the trunk.
Quadratus lumborum
Origin: Iliac crest; Insertion: Transverse processes L1-L5; rib 12; Action: Bilaterally: Extension of the trunk - but likely primarily contributes to stability of lumbar spine; Unilaterally: lateral flexion.
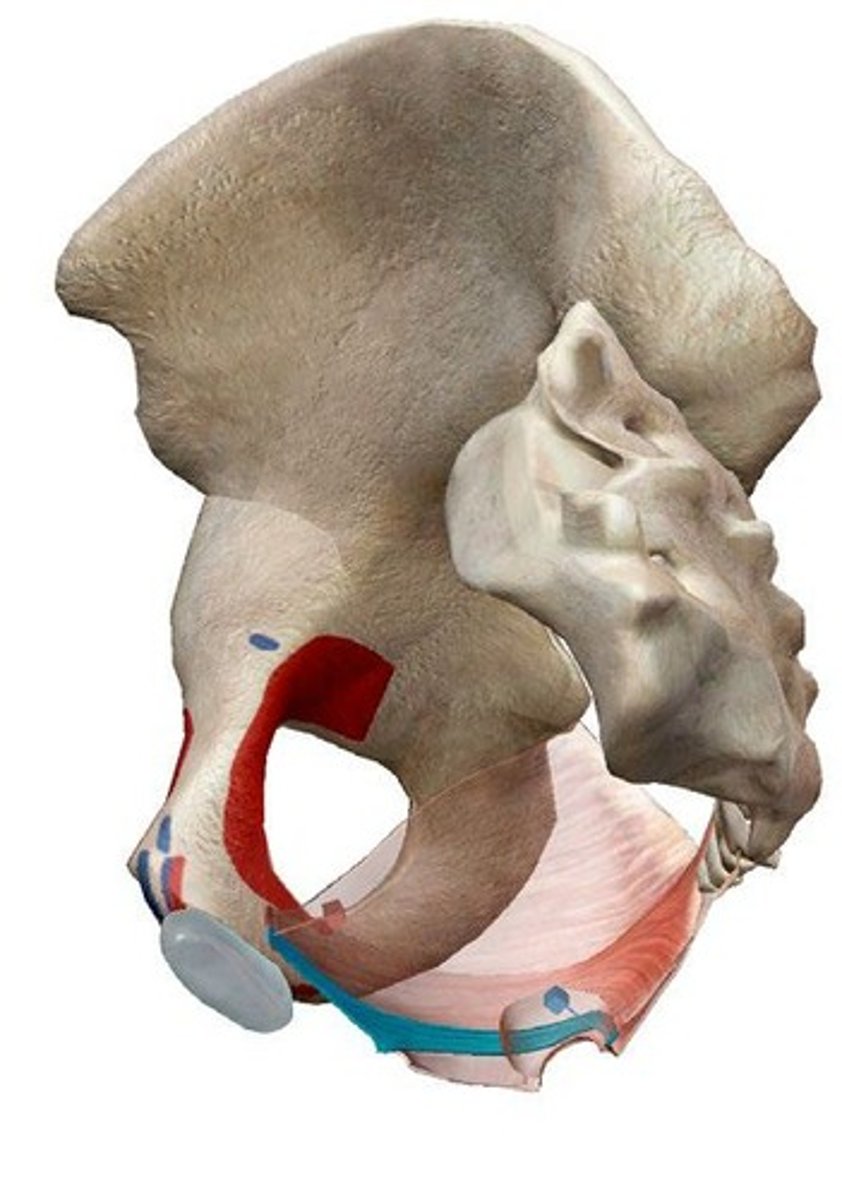
Puborectalis
Origin: anteriorly, from the pubic symphysis; posteriorly, encircling the anorectal junction; Action: inhibits defecation.
Pubococcygeus
Origin: pubic bone (lateral to the origin of puborectalis); Insertion: Coccyx; Action: Control urine flow; contract during orgasm. (pubo)