Interest Rates, Bond & Stock Valuation, Pension Funds, and Financial Risks
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
What is the Required Rate of Return (r)?
The interest rate that an investor should receive given a certain risk level (e.g., default, liquidity).
How is the Required Rate of Return (r) used?
It is used to find the fair present value (PV) of a security.
What does it mean if the current market price (P) is less than the fair price (Pᵖ)?
The security is undervalued, so you should buy this security.
What does it mean if the current market price (P) is greater than the fair price (Pᵖ)?
The security is overvalued, so you should sell this security.
What does it mean if the current market price (P) equals the fair price (Pᵖ)?
The security is fairly priced given its risk levels.
What is the formula for calculating the fair present value of a bond?
PV = sum of all expected cash flows discounted at the bond's required rate of return.
What is the Expected Rate of Return (E(r))?
The interest rate an investment expects to earn given the security's current market price and expected cash flows.
What does it indicate if E(r) is greater than or equal to r?
The projected cash flows are sufficient to compensate for the risk, so you should buy this security.
What does it indicate if E(r) is less than r?
The projected cash flows are insufficient to compensate for the risk, so you should sell this security.
What is the Realized Rate of Return (̅r)?
The interest rate that was actually earned on an investment; an ex-post measure.
What does it mean if ̅r is greater than r?
The investor earned more than needed to cover the risk.
What does it mean if ̅r is less than r?
The investor earned less than the interest rate required to compensate for risk.
What are the two sources of cash flows from a bond?
Periodic coupon payments and the face (par) value repaid at maturity.
What happens to the bond's market value if the required rate of return is lower than the coupon rate?
The bond is traded at a premium.
What happens to the bond's market value if the required rate of return equals the coupon rate?
The bond is traded at par.
What happens to the bond's market value if the required rate of return is higher than the coupon rate?
The bond is traded at a discount.
What is the market value of a bond if the required rate of return is 8% and the coupon rate is 10%?
The market value is $1,152.47.
What is the market value of a bond if the required rate of return is 10%?
The market value is $1,000.
What is the market value of a bond if the required rate of return is 12%?
The market value is $874.50.
What is the formula to calculate the fair present value of a bond?
PV = PMT/(1+r)^n + FV/(1+r)^n, where PMT is the coupon payment, FV is the face value, and r is the required rate of return.
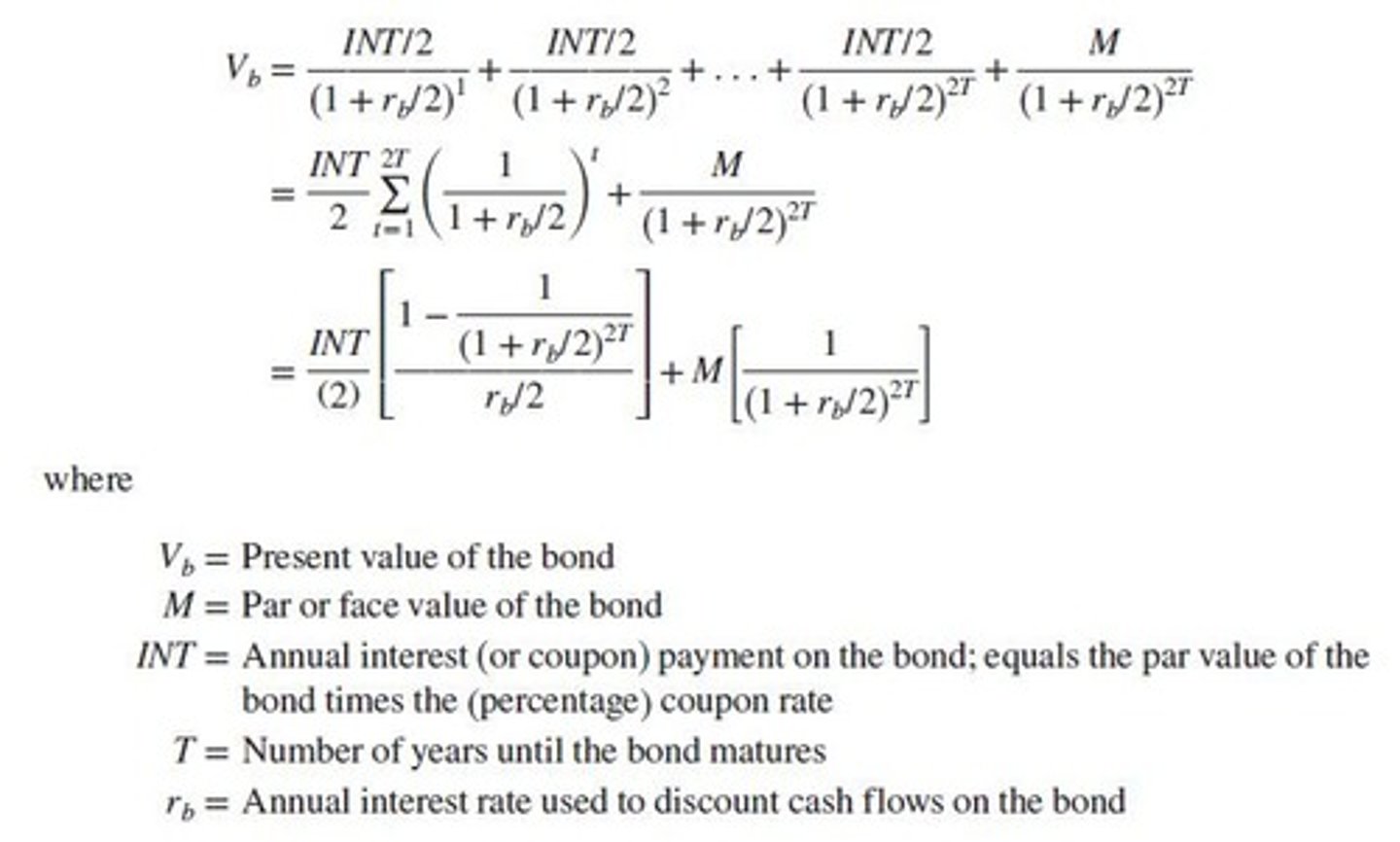
What are the four measures of interest rates discussed?
Required Rate of Return, Expected Rate of Return, Realized Rate of Return, and Fair Present Value.

What happens to the current market price if there is a large unexpected negative event?
The security becomes undervalued, demand decreases, and the price drops.
What happens to the current market price if there is a large unexpected positive event?
The security becomes overvalued, demand increases, and the price rises.
What is the relationship between the current market price and fair present value in an efficient market?
The current market price equals the fair present value.
What is the significance of the coupon rate in bond valuation?
If the coupon rate is higher than the required rate of return, the bond trades at a premium.
What is the formula for the present value of a bond?
Vb = ∑ (C / (1 + r)^t) + (F / (1 + r)^T), where C = coupon payment, r = required rate of return, F = face value, T = time to maturity.

What does a negative present value indicate in bond valuation?
It indicates a cash outflow, such as an investment in the bond.
What is a premium bond?
A bond that trades for more than its face value, typically because its coupon rate is higher than the market rate.
What is a par bond?
A bond that trades at its face value, typically when its coupon rate equals the market rate.
What is a discount bond?
A bond that trades for less than its face value, typically because its coupon rate is lower than the market rate.
What is yield to maturity (YTM)?
YTM is the expected rate of return if the bondholder buys at the current market price and holds it until maturity.
What is the assumption regarding coupon payments in YTM calculations?
All coupon payments can be reinvested at the same rate as the yield to maturity.
What is the formula for the present value of a stock?
Fair price of stock = PV of all expected current and future dividends.
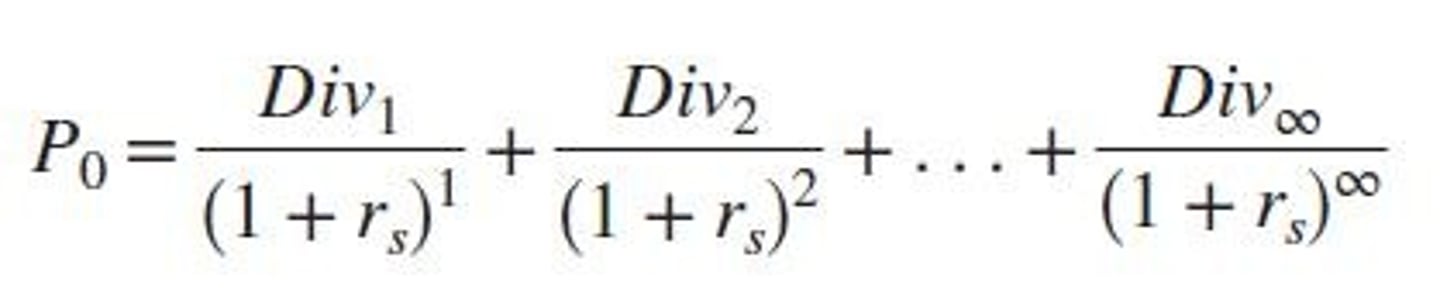
What are the three assumptions regarding future dividends in stock valuation?
1) Zero growth in dividends, 2) Constant growth rate in dividends, 3) Nonconstant growth in dividends.
What is the formula for calculating the fair value of a stock with zero growth in dividends?
P0 = D / r, where D is the dividend and r is the required rate of return.
How do you calculate the fair present value of a stock with constant growth in dividends?
P0 = D1 / (r - g), where D1 is the expected dividend next year, r is the required rate of return, and g is the growth rate.
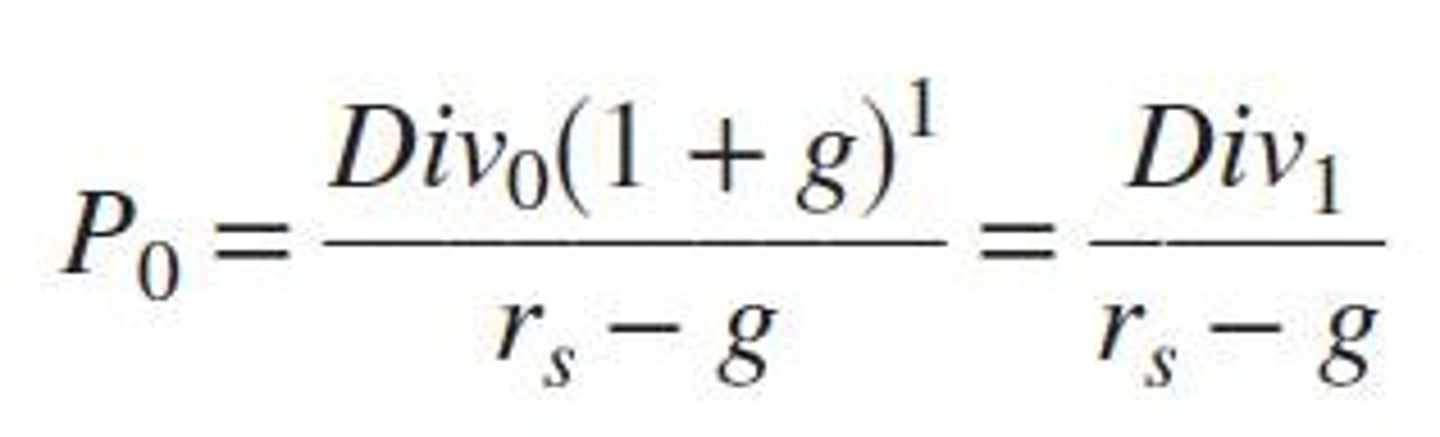
What is the realized rate of return on a stock investment?
It is the total return earned on an investment, including dividends and capital gains.
What is the expected rate of return on a stock investment?
It is the anticipated return based on the current market price, expected future selling price, and dividends.
What is the relationship between coupon rate and required rate of return for premium bonds?
When the coupon rate is greater than the required rate of return, the bond trades at a premium.
What happens to the bond price when the coupon rate is equal to the required return?
The bond price equals its face value (par bond).
What is the effect of a lower coupon rate compared to the market rate on bond pricing?
The bond will trade at a discount, meaning its price will be less than its face value.
What is the significance of the face value of a bond?
The face value is the amount paid back to the bondholder at maturity.
What does the term 'm' represent in bond valuation formulas?
The number of times per year that interest is paid.
In equity valuation, what is the role of retained earnings?
Retained earnings are reinvested to support future earnings and dividend growth.
What is the expected return on a stock if the current price is $32, expected future price is $45, and annual dividends are $1.5?
Expected return can be calculated using the formula: E(rs) = (D + (P3 - P0)) / P0.
What is the formula for calculating the present value of future cash flows?
PV = CF / (1 + r)^t, where CF is cash flow, r is the discount rate, and t is the time period.
What is the impact of market efficiency on stock pricing?
In efficient markets, stock prices reflect the present value of expected future dividends.
What is the formula for the present value of a bond that pays multiple coupons per year?
Vb = ∑ (C/m) / (1 + r/m)^(mt) + F / (1 + r/m)^(mT), where m is the number of coupon payments per year.
What is the relationship between dividend growth and stock value?
Higher dividend growth leads to higher stock value.
What is the effect of a bond trading at a premium on its yield to maturity?
When a bond trades at a premium, the coupon rate is greater than the yield to maturity.
What is the significance of the required rate of return in stock valuation?
It is used to discount future cash flows to determine the fair value of the stock.
What was the dividend paid by JPM at the end of last year?
$3.50
What is the constant growth rate of dividends for JPM?
2% per year
What is the required rate of return on JPM stock?
10%
What is the fair present value of JPM stock?
$44.63
What was the dividend paid by Bank of America (BOA) at the end of last year?
$4.80
What is the constant growth rate of dividends for BOA?
1.75% per year
What is the current selling price of BOA stock?
$52 per share
What is the expected rate of return on BOA stock?
11.14%
What is the first step in finding the present value of a stock with supernormal growth?
Find the present value of the dividends during the period of supernormal growth.
What is the second step in the three-step process for supernormal growth?
Find the price of the stock at the end of the supernormal growth period using the constant growth model.
What is the third step in the process for valuing a stock with supernormal growth?
Add the present value of dividends during supernormal growth to the present value of the stock price at the end of that period.
What is the expected supernormal growth rate for Home Depot (HD) stock over the next five years?
10%
What is the constant growth rate expected for HD stock after the supernormal growth period?
4%
What was the dividend paid by HD last year?
$4
What is the required rate of return on HD stock?
15%
What are pension funds similar to?
Life insurance companies and mutual funds.
What is a unique feature of pension funds?
They are exempt from current taxation.
What percentage of financial assets did U.S. households have invested in pension funds in 2021?
20%
When was the first pension fund established in the U.S.?
1759
What are the two main sectors in pension funds?
Public Pension Funds and Private Pension Funds.
What is a defined benefit pension fund?
A retirement plan where the employer guarantees a specific benefit amount based on a formula.
What is a defined contribution pension fund?
A retirement plan where the employer does not pre-commit to providing a specified retirement income.
What is the flat benefit formula in defined benefit pension funds?
Pays a flat dollar amount for each year of employment.
What is the career average formula in defined benefit pension funds?
Based on a percentage of the employee's average salary over their entire years of employment.
What is the final pay formula in defined benefit pension funds?
Based on a percentage of the average salary during the last few years of employment times years of service.
What retirement benefit does an employee with 20 years of service at AT&T receive if they retire now under a flat benefit formula?
$40,000
What retirement benefit does the same employee receive if they retire in 5 years?
$50,000
What retirement benefit does the same employee receive if they retire in 10 years?
$60,000
What is the final pay formula for retirement benefits?
An employee receives an annual benefit payment of 2.5% of her average salary during her last five years of service times her total years employed.
What are the three types of defined benefit pension funds?
1. Final Pay Plans, 2. Career Average Plans, 3. Cash Balance Plans.
Which defined benefit formula typically produces the largest retirement benefit increase?
Final Pay Plans.
What is a key characteristic of defined benefit plans?
The employer must set aside sufficient funds to ensure future payments.
What is the main difference between defined benefit (DB) and defined contribution (DC) plans?
DB plans promise a specific benefit at retirement, while DC plans depend on contributions and investment performance.
What is a fully funded pension plan?
A plan that has sufficient funds to meet all future payment obligations.
What are fixed-income funds in defined contribution plans?
Funds that often guarantee a minimum rate of return, like bond funds.
What are variable-income funds in defined contribution plans?
Funds with no guaranteed return, where all investment gains and losses pass through to participants.
What is a benefit of defined contribution plans?
Employees have the potential for higher returns based on investment performance.
What is a downside of defined contribution plans?
Employees bear the investment risk and may face losses.
What are private pension funds?
Retirement plans created by private employers and administered by financial institutions.
What is the primary reason defined contribution plans dominate the private pension market?
They do not require employers to guarantee retirement benefits.
What is the risk-bearing difference between DB and DC plans?
In DB plans, the employer bears the investment risk; in DC plans, employees bear the risk.
What are 401(k) and 403(b) plans?
Employer-sponsored plans allowing both employer and employee contributions.
What is the tax treatment of contributions to 401(k) and 403(b) plans?
Contributions are pre-tax, reducing taxable income, and grow tax-deferred until withdrawal.
What is a Roth IRA?
An individual retirement account where contributions are made after-tax, allowing tax-free growth.
What is the contribution limit for a traditional IRA for individuals under 50?
$7,000.
What are insured pension funds?
Pension funds managed by life insurance companies, where contributions are pooled into the insurer's general account.
What are noninsured pension funds?
Pension funds managed by financial institutions other than life insurance companies, with separate trust accounts.
What is the expected return difference between insured and noninsured pension funds?
Insured funds have lower, stable returns; noninsured funds have higher, volatile returns.
What happens to contributions in an insured pension fund?
Contributions become the legal property of the insurance company.