Unit 11: Across the Lifespan
1/196
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
197 Terms
How does pregnancy affect minute ventilation?
Progesterone is a respiratory stimulant, it increases minute ventilation by up to 50%
-Vt increases by 40%
-RR increases by 10%
How does pregnancy affect the mother's ABG?
Progesterone = RR stimulant
- it ↑ minute ventilation up to 50% (tv > RR rate)
→ mom's PaCO2 falls = respiratory alkalosis
Renal compensation eliminates bicarb to normalize blood pH
A small ↓ in physiologic shunt explains the mild ↑ in PaO2
WHICH then ↑s the driving pressure of O2 across placenta = IMPROVES fetal gas exchange
Arterial pH = no change (or slight ↑)
-PaO2 = ↑ (104-108)- d/t HYPERVENT & slight ↓ in physiologic shunt
-PaCO2 = ↓ (28-32)
-HCO3 = ↓ (20)
How does pregnancy affect the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve?
Right shift (↑ P50) → facilitates O2 unloading to the fetus
How does pregnancy affect the lung volumes + capacities?
↓ FRC 2/2 ↓ ERV + RV
↑ O2 consumption + ↓ FRC hastens onset of hypoxemia.
Failure to reverse hypoxemia → brain death of the mother + fetus
How does CO change during pregnancy + delivery?
Compared to pre-labor:
1st stage labor: CO ↑ 20%
2nd stage labor: CO ↑ 50%
3rd stage labor: CO ↑ 80%
-returns to pre-labor values in 24-48 hrs
-returns to pre-preg values in ~2 wks
-twins cause CO to ↑ 20% above a single fetus pregnancy

How do BP + SVR change during pregnancy?
↑ BV + ↓ SVR = net effect on MAP
Progesterone causes ↑ NO → vasodilation + ↓ response to angiotensin + NE

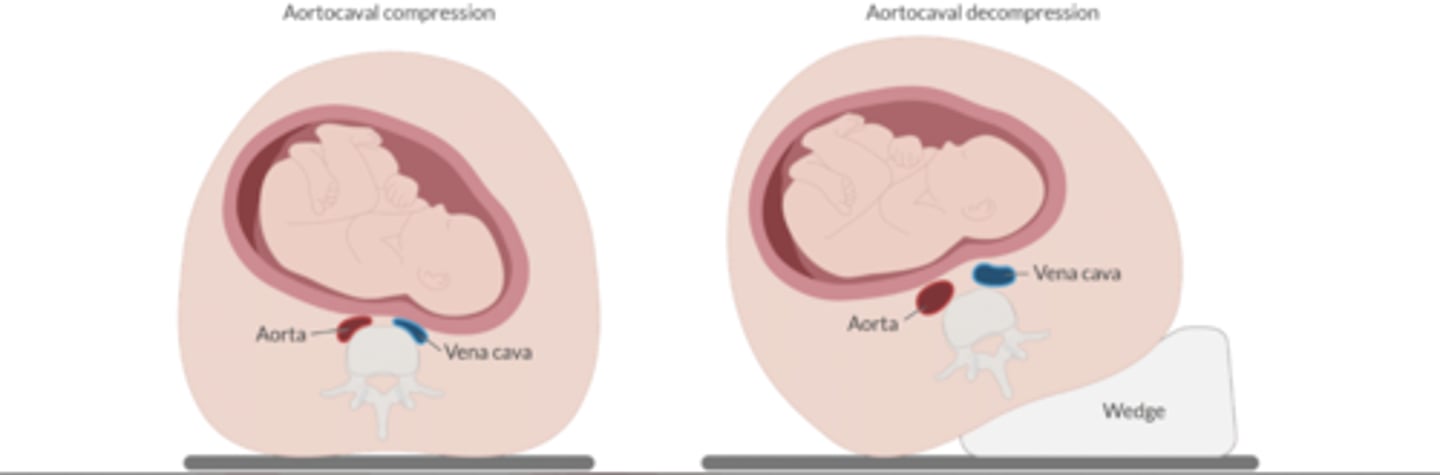
Who is at risk for aortocaval compression? How do you treat it?
Pregnant women
In supine, a gravid uterus compresses both the vena cava + the aorta. This ↓ venous return + arterial flow to the uterus + LE. ↓ CO compromises fetal perfusion + cause the mother to lose consciousness.
Tx: LUD: elevate mother's right torso 15º
How does the intravascular fluid volume change during pregnancy?
↑ 35%
-plasma volume ↑ 45%
-Erythrocyte volume ↑ 20%
What hematologic changes accompany pregnancy?
↑ clotting factors: 1, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12
Anticoagulants:
-Protein S ↓
-no △ Protein C
↑ fibrin breakdown
↓ 11 + 13 antifibrinolytic system
How does MAC △ during pregnancy?
↓ by 30-40%
probably 2/2 ↑ progesterone
How does pregnancy affect gastric pH + volume?
↑ V + ↓ pH
2/2 ↑ gastrin
How does pregnancy affect gastric emptying?
Before onset of labor: no change
After onset of labor: slowed
How does pregnancy affect uterine BF?
Non-pregnant: 100mL/min
Term: up to 700mL/min or 10% CO
-some texts say up to 800-900 mL/min
What conditions can reduce UBF
Uterine BF is NOT auto regulated.
Therefore, it is dependent on MAP, CO, + uterine vascular resistance
1. ↓ perfusion: maternal hypoTN
-sympathectomy
-hemorrhage
-aortocaval compression
2. ↑ resistance
-uterine contraction
-HTN conditions that ↑ UVR
Uterine BF equation
UBF = (uterine a. P - uterine v. P) / uterine vascular resistance
Discuss the use of phenylephrine + ephedrine in the laboring patient.
Classic: neo ↑ UVR + ↓ placental perfusion
More recent: Neo is as efficacious as ephedrine in maintaining placental perfusion + fetal pH in healthy mothers.
-mothers who received neo had higher fetal pH (less fetal acidosis)
Which law determines which drugs will pass through the placenta?
Fick's principle
Characteristics that factor transfer:
-Low molecular weight
-High lipid solubility
-Nonionized
-Nonpolar

Fick's equation
Rate of diffusion =
(Diffusion coefficient x SA x [ ] gradient b/t mom/fetus) / membrane thickness
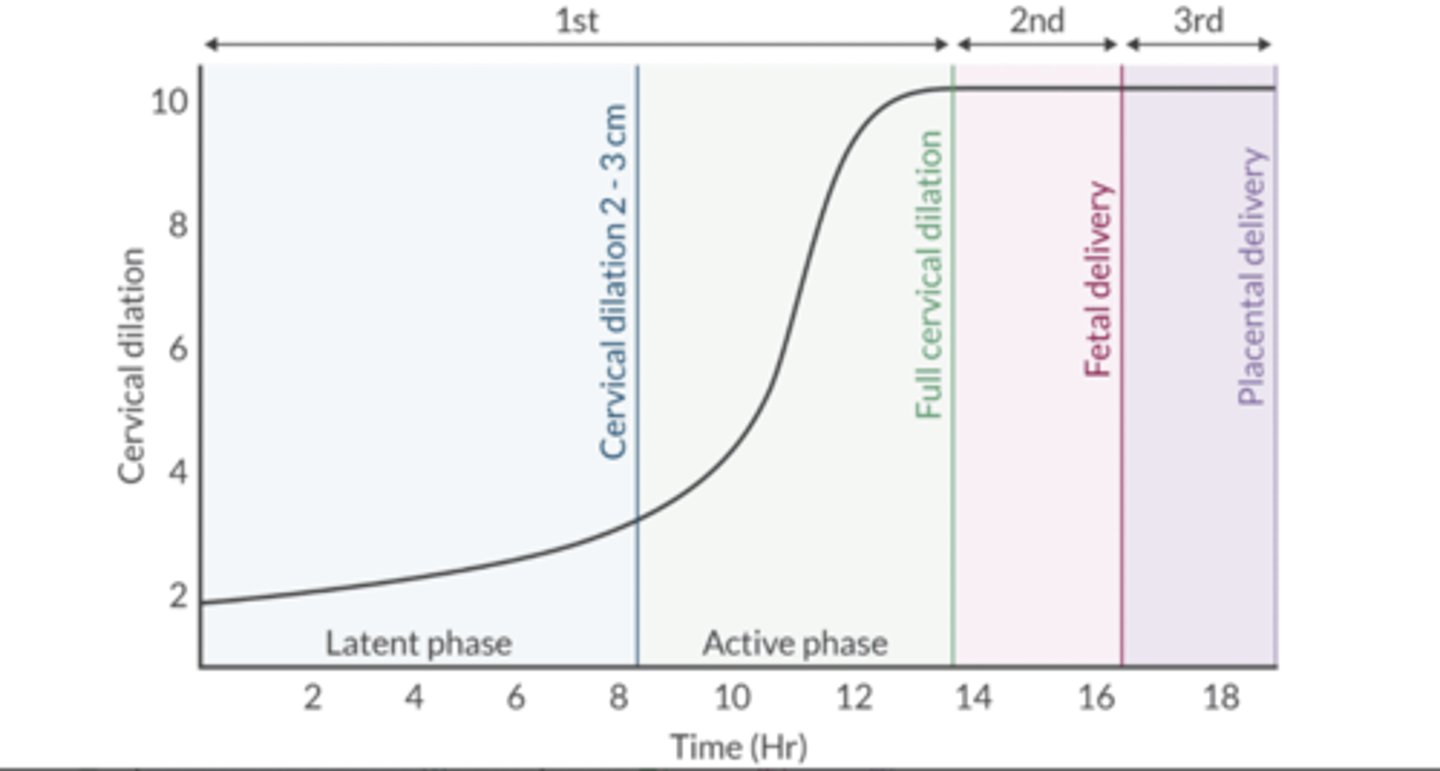
Define the 3 stages of labor.
Stage 1: Beginning of regular contractions to full cervical dilation (10 cm)
Stage 2: Full cervical dilation to delivery of the fetus
Stage 3: Delivery of the placenta
How does uncontrolled labor pain affect the mother and fetus?
1. ↑ maternal catecholamines → HTN → ↓ UBF
2. Maternal hyperventilation → L shift of oxyhgb curve → ↓ deliver of O2 to fetus
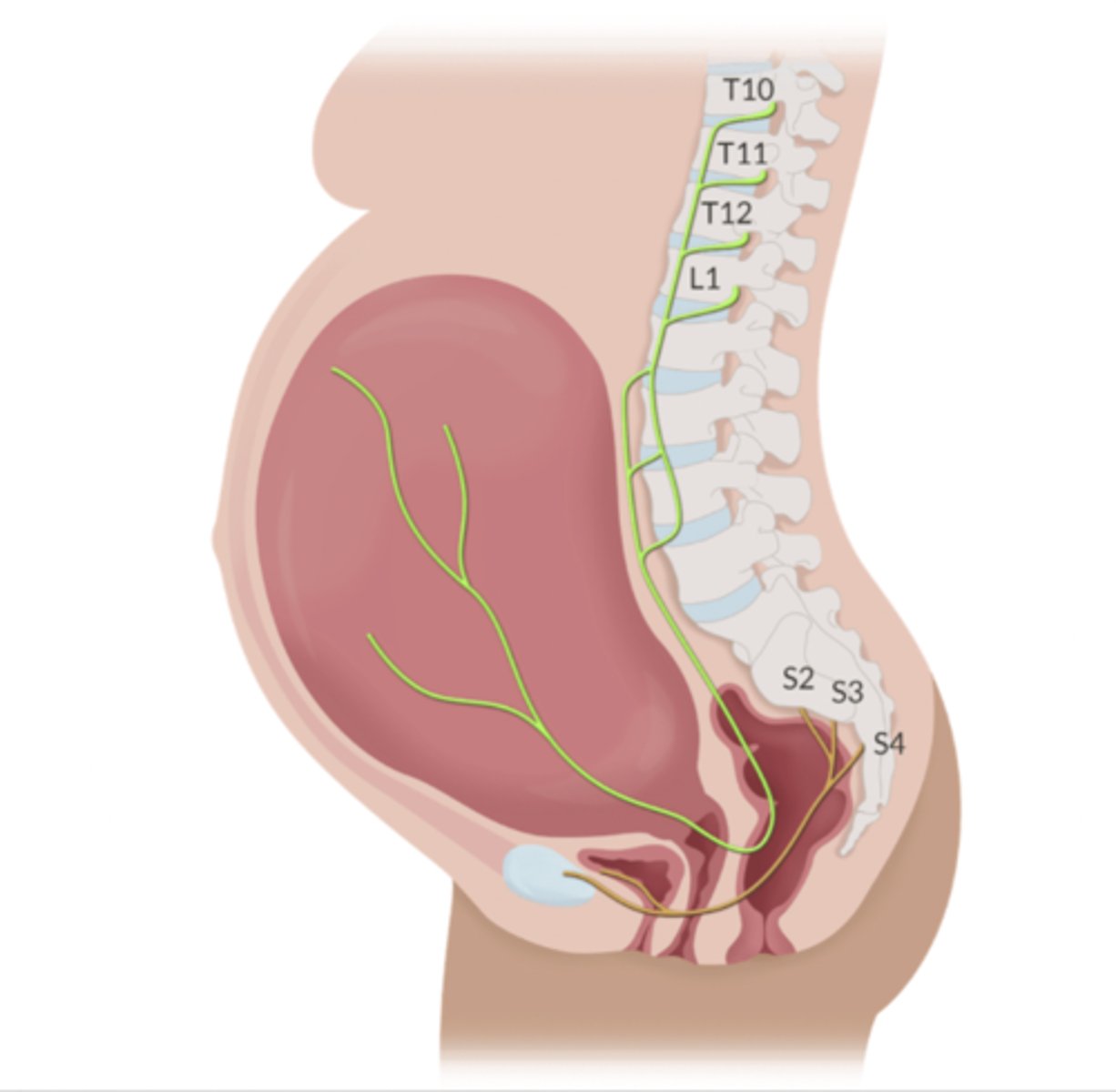
Compare + contrast the pain that results from the first + second stage of labor.
First stage:
-Pain begins in the lower uterine segment + cervix
-T10-L1 posterior n roots
Second stage:
-Adds pain impulses from vagina, perineum, + pelvic floor
-S2-S4 posterior n roots
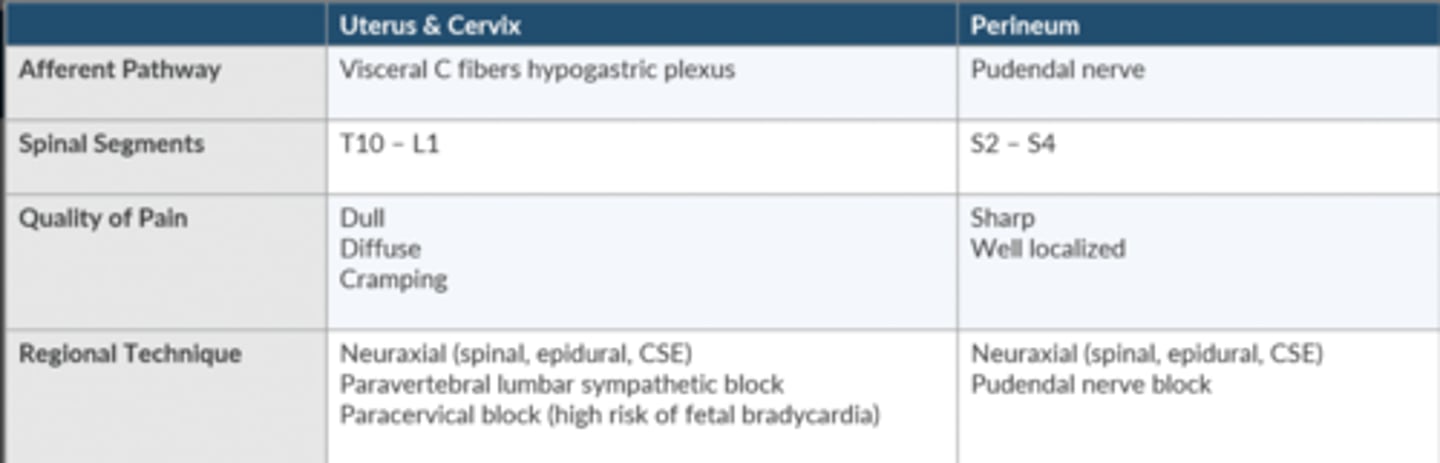
Compare + contrast the regional anesthetic techniques that can be used for 1st + 2nd stage labor pain.
Neuraxial techniques
T10-L1 level for stage 1
Extend to S2-S4 for stage 2
Describe the "needle through the needle" technique for CSE.
Epidural space ID w/epidural needle
Spinal needle is placed through epidural needle.
LA is injected into the intrathecal space
Epidural catheter is threaded through the epidural needle
Compare + contrast bupivicaine + ropivicaine for labor
Both long duration amides
Bupi:
-racemic mixture
-minimal tachyphylaxis
-low placental transfer
-↑ sensory blockade
-↑ cv tax w/R-enantiomer
-cv tox before seizures
-0.75% CI via epidural 2/2 risk of toxicity w/IV injection
Ropiv:
-S-enantiomer of bupi + sub of propyl group
-↓ risk cv tox v bupi
-↓ potency v bupi
-↓ motor block v bupi
Discuss the use of 2-chloroprocaine for labor.
-Useful for emergency C/S when epidural is already in place (very fast onset)
-Metabolized by pseudocholinesterase in the plasma - minimal placental transfer
-Antagonizes opioid receptors (mu & kappa) and ↓ the efficacy of epidural morphine
-Risk of arachnoiditis when used for spinal 2/2 preservatives
-Solutions w/o methylparaben + metabisulfite do not cause neurotoxicity
Discuss the consequences of an epidural that is placed in the subdural space.
w/in 10-25 min after the epidural is dosed, the pt will experience symptoms of an excessive cephalad spread of LA.
Subdural space is a potential space that holds a very low volume.
What is the treatment for a total spinal?
May result from:
-epidural dose injected into the subarachnoid space
-epidural dose injected into the subdural space
-a single shot spinal after a failed epidural
Treatment:
-vasopressors
-IVF
-LUD
-Elevate the legs
-intubation if LOC
Discuss the fetal heart rate
Surrogate measure of overall fetal wellbeing.
Provides indirect method to assess fetal hypoxia + acidosis
Fetus responds to stress w/peripheral vasoconstriction, HTN, + baroreceptor mediated ↓ HR
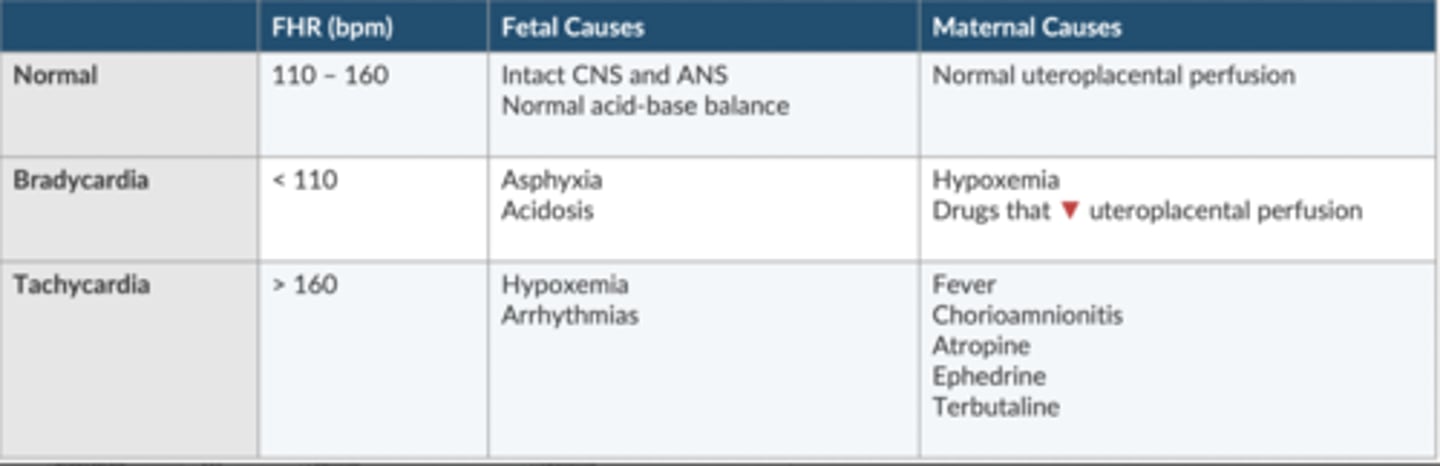
Which type of fetal decelerations are unremarkable? Which cause concern?
Unremarkable: early decel
Concern: late + variable decels
VEAL: CHOP
Variable: cord compression
Early: Head compression
Accelerations: OK, or give O2
Later: Placental insufficiency
Define premature delivery.
Before 37 weeks gestation or less than 259 days from the last menstrual cycle.
Leading cause of perinatal M+M
-↑ risk for newborns <1500g
↑ incidence w/multip + PROM
List potential complications from premature delivery.
Respiratory distress syndrome
Intraventricular hemorrhage
NEC
Hypoglycemia
Hypocalcemia
Hyperbilirubinemia
Discuss the use of steroids agents in the prevention of premature delivery.
Betamethasone hastens fetal lung maturity
-effect w.in 18 hrs
-peak benefit at 48 hrs
seldom given after 33 weeks gestation
Discuss the use of tocolytic agents in the prevention of premature delivery.
-stop labor ~24-48 hrs.
-provide bridge that allows the corticosteroids time to work.
ABX prophylaxis for chorioamnionitis
seldom given after 33 weeks gestation
What are the side effects of β2 agonists when used for tocolysis?
Terbutaline, Ritodrine
-Hypokalemia 2/2 intracellular shift
-cross placenta + may ↑ FHR
-↑BG 2/2 glycogenesis in the liver
-newborn of. a hyperglycemic mother is at risk of post-delivery hypoglycemia.
--mothers glucose is gone
--insulin in neonatal circulation remains
What are the side effects of hypermagnesemia?
Apnea
HypoTN
Skeletal m weakness (synergism w/NDNMB)
CNS depression
↓ responsiveness to ephedrine + phenylephrine
What is the treatment fro hypermagnesemia?
Supportive measures
Diuretics to facilitate excretion
IV Ca to antagonize Mg
How can oxytocin be administered?
synthesized in the supraoptic + paraventricular (primary) nuclei of the hypothalamus.
Released from the posterior pituitary gland
IV (diluted in IVF)
OB can inject directly into the uterus
What are the potential side effects of oxytocin?
Water retention
Hyponatremia
HypoTN
Reflec tachycardia
Coronary vasoconstriction
How can methergine be administered?
-It can be given 0.2 mg IM (not IV)
-IV administration can cause significant vasoconstriction, hypertension, and cerebral hemorrhage
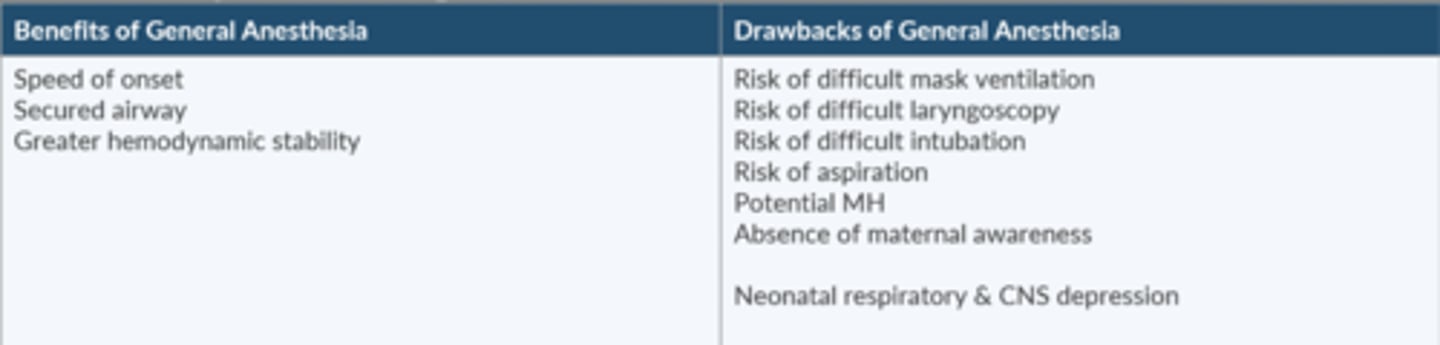
What are the pros + cons of GA for C-section?
Mortality is 17x higher
Failure to successfully manage the a.w. is the most common cause of maternal death
Pros
-speed of onset
-secured a.w.
-↑ HD stability
Cons
-risk diff MV/DL/intubation
-risk of aspiration
-potential MH
-absence of maternal awareness
-neonatal respiratory + CNS depression
Describe aspiration prophylaxis for the pt scheduled for a C-section.
Sodium citrate to neutralize gastric acid
-w/in 15-30 min of induction
H2 antagonist (ranitidine) to ↓ gastric acid secretion
Gastrokinetic agent (metoclopramide) to hasten gastric emptying + ↑ LES tone
-1 hour before induction
When is the pregnant pt who present for non-OB Sx at risk for aspiration?
~18-20 weeks gestation = "full-stomach"
RSI + aspiration prophylaxis
-maybe earlier if pt has GERD
-also in immediate postpartum period
What is the risk of NSAIDs when used in the pregnant patient?
Avoid in the 1st trimester
may close the ductus arteriosus
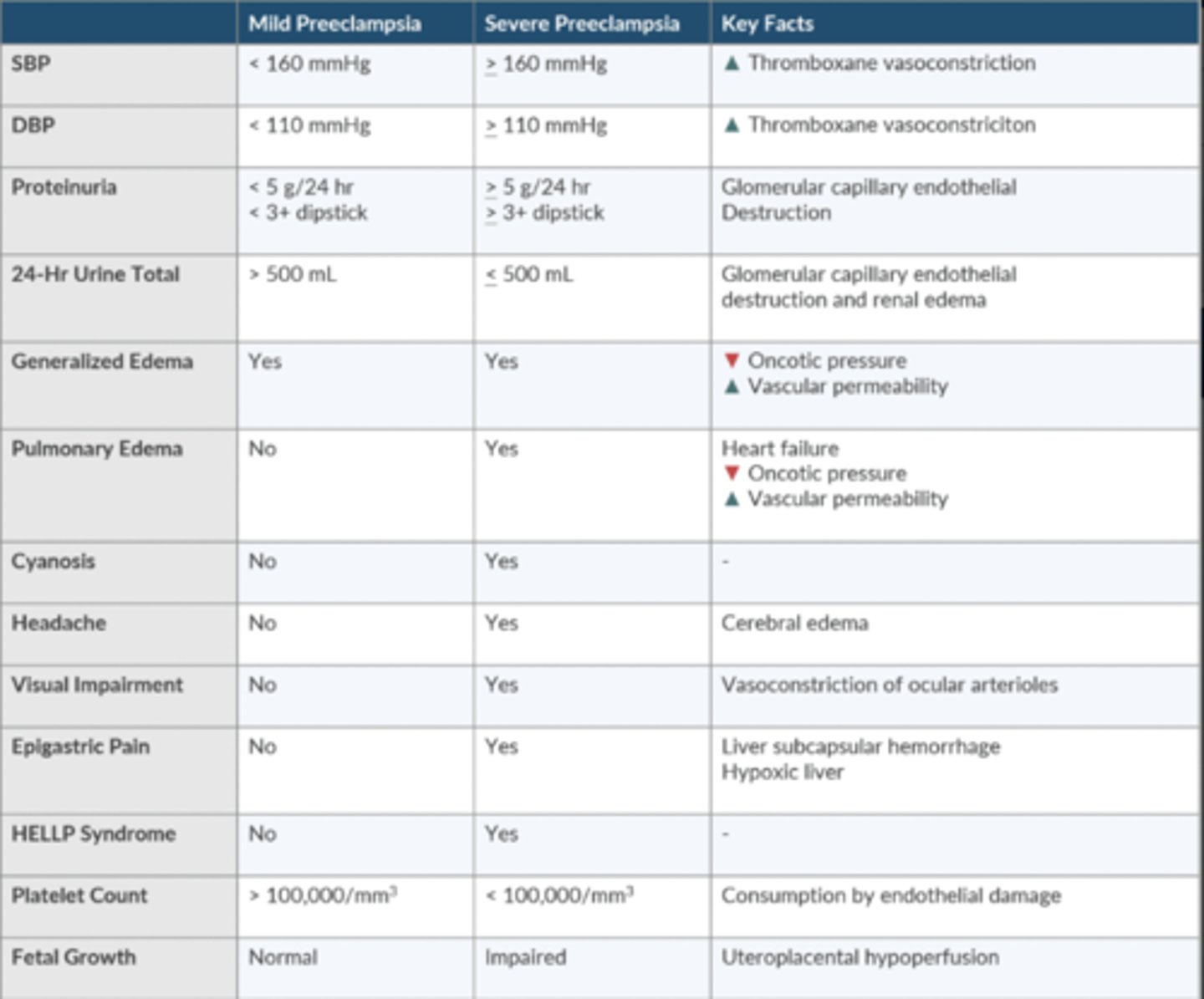
Compare + contrast the diagnostic criteria for gestational HTN, preeclampsia, and eclampsia.
Gestational
-after 20 weeks
-mild
-no proteinuria
-no seizures
Preeclampsia
-after 20 weeks
-mild/severe
-proteinuria
-no seizures
Eclampsia
-after 20 weeks
-severe
-proteinuria
-seizures
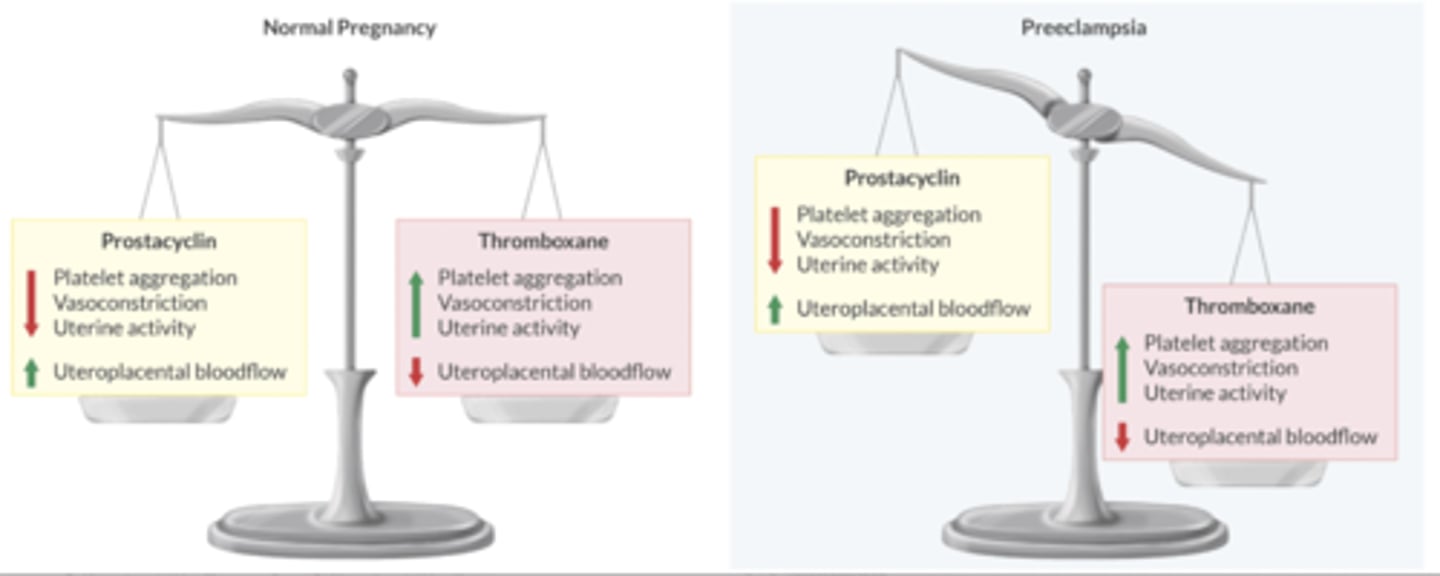
Discuss the balance of prostacyclin + thromboxane in the pt w/preeclampsia.
Healthy placenta produces thromboxane + prostacyclin in equal amounts.
Preeclamptic pt produces up to 7x more thromboxane than prostacyclin
↑ Thromboxane favors:
-vasoconstriction
-Plt aggregation
-↓ placental BF
Compare + contrast mild + severe preeclampsia.
Discuss the use of Mg for preeclampsia
Seizure prophylaxis:
-Load 4g over 10 min
-Infusion 1-2g/hr
Mg Tox Tx: 10mL of 10% Ca gluconate IV
Detail the anesthetic management for the pt w/preeclampsia.
-Fluid management is balanced b/t a volume contracted Pt + a "leaky" vasculature from endothelial dysfxn
-Neuraxial anesthesia assists w/BP control + provides better uteroplacental perfusion
-Check Plt before placing neuraxial (>100,000)
-2/2 a.w. swelling, these pts have a higher incidence of diff intubation
-exaggerated response to sympathomimetics + methergine
-If Mg therapy, ↑ sensitivity to NMB
-Mg relaxes the uterus + ↑ risk of postpartum bleeding
What is HELLP syndrome? What is the definitive treatment?
Hemolysis
Elevated liver enzymes
Low Platelet count
Developing in 5-10% of those w/preeclampsia.
Experience epigastric pain + upper abd tenderness
Definitive Tx is delivery of fetus
Discuss the anesthetic considerations for maternal cocaine abuse.
Ester-type local that inhibits NE reuptake in pre-synaptic cleft w/ NE ↑ SNS tone.
-CV risks: ↑HR, dysthymia, MI
-Acute intox ↑ MAC
-Chronic use ↓ MAC
-OB risks: spont abortion, premature labor, placental abruption, low APGAR scores
-HTN is probably best treated w/casodilators
-BB can → HF if SVR is sig elevated
-HypoTN may not respond to ephedrine in chronic abusers (d/t catecholamine depletion)
-Chronic abuse is associated w/thrombocytopenia
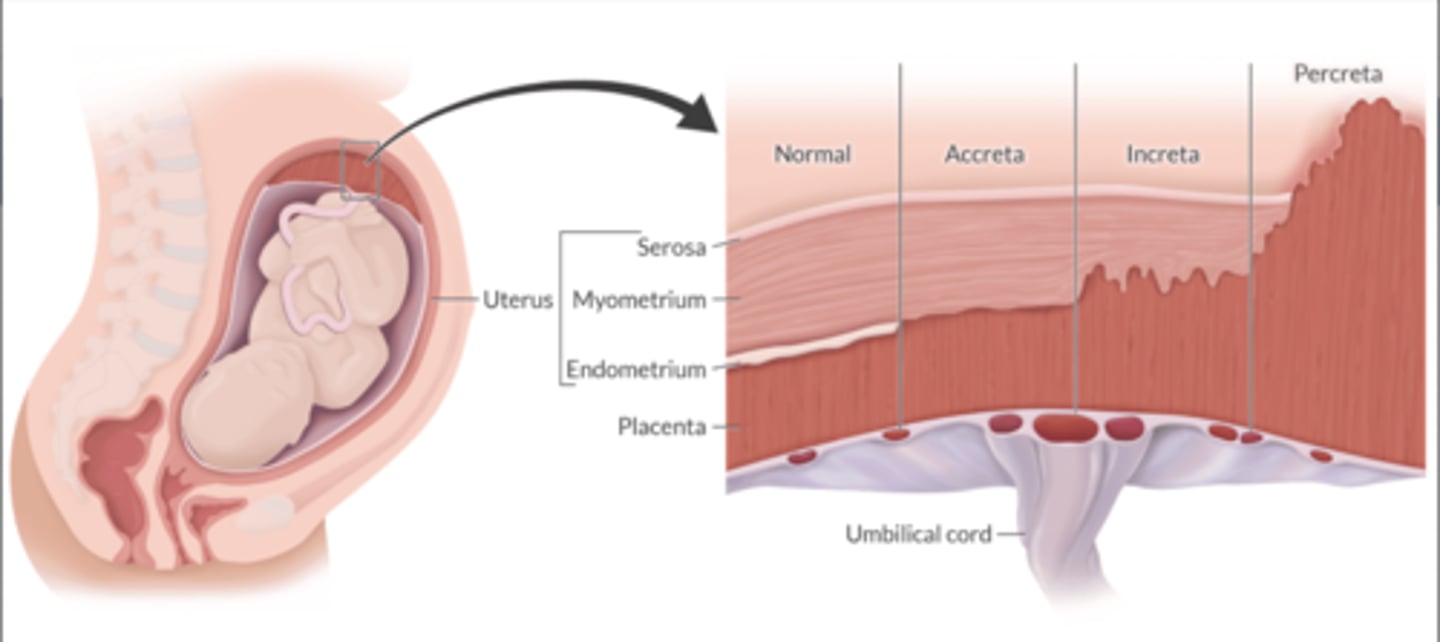
What is the difference b/t placenta accrete, intreat, and percreta? What is the major risk that these complications present?
Normal implantation: decider of endometrium.
A: attaches to the surface of the myometrium
I: invades the myometrium
P: extends beyond the uterus
Uterine contractility is usually impaired
Potential for tremendous blood loss.
Neuraxial is safe, GA is preferred
What is placenta previa? How does it present?
Placenta attaches to the lower uterine segment
-partially or completely covers the cervical os
-associated w/painless vaginal bleeding
-Potential for hemorrhage
What conditions ↑ the risk of placenta previa?
Previous C-sections
Hx of multiple births
What are the risk factors for placental abruption? How does it present?
Partial or complete separation of the placenta from the uterine wall prior to delivery. Results in hemorrhage + fetal hypoxia.
Risk Factors:
-PIH
-Preeclampsia
-Chronic HTN
-Cocaine use
-Smoking
-Excessive alcohol use
Presents w/painful vaginal bleeding. Pain may be so severe to cause breakthrough pain when an epidural is in place.
What is the most common cause of postpartum hemorrhage? What are the risk factors?
Uterine atony
Risk Factors:
-Multiparity
-Multiple gestations
-Polyhydramnios
-Prolonged oxytocin infusion prior to Sx
A Pt suffers from retained placental fragments. What IV medication can you give to help with the extraction?
IV nitroglycerine
-uterine relaxation
What are the treatment options for uterine atony?
-Uterine massage
-Oxytocin
-Ergot alkaloids
-Intrauterine ballon
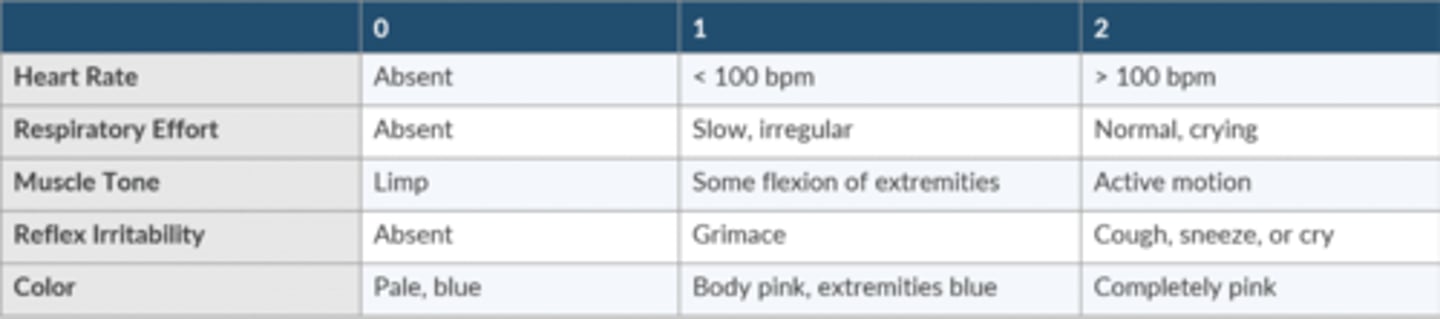
What does the APGAR score mean?
-Used to assess the newborn and guide resuscitation efforts
-Parameters are evaluated at 1 and 5 minutes after delivery
-May be predictive of neurologic outcome
-Normal → 8-10
-Moderate distress → 4-7
-Impending demise → 0-3
Know how to calculate the APGAR score.
HR
absent = 0
<100 = 1
>100 = 2
Respiratory Effort
Absent = 0
Slow, irregular = 1
Normal, crying = 2
Muscle tone
Limp = 0
Some flexion of extremities = 1
Active motion = 2
Reflex irritability
Absent = 0
Grimace = 1
Cough, sneeze, or cry = 2
Color
Pale, blue = 0
Body pink, extremities blue = 1
Completely pink = 2
What is the best indicator of ventilation during neonatal resuscitation?
Resolution of bradycardia
How do you dose epinephrine + fluids during neonatal resuscitation?
1:10,000
10-30mcg/kg IV
0.05-0.1mg/kg intratracheal
Volume expander
PRBC, NS, LR
10mL/kg over 5-10 minutes
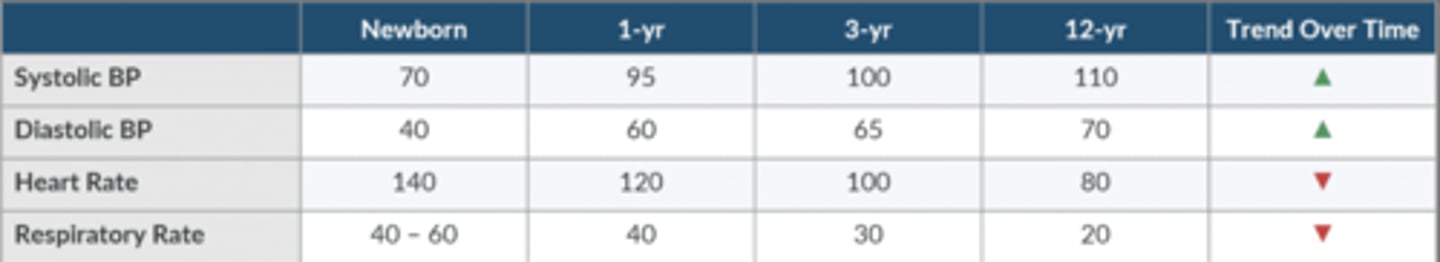
What are the normal vital signs for a newborn? How do they trend as the child ages?
SBP 70
DBP 40
HR 140
RR 40-60
Why is the neonate's minute ventilation higher than the adult?
O2 consumption + CO2 production are 2x the adult's
It is metabolically more efficient to ↑ RR that to ↑ Vt
What is the primary determinant of BP in the neonate?
Heart rate
BP = HR x SV x SVR
Describe the autonomic influence on the newborn's heart.
immature at birth (SNS > PSNS) laryngoscopy/suctioning can → Bradycardia
-admin atropine to mitigate
BaroR reflex is poorly developed.
Contrast the breathing pattern in adults + infants.
Adult: mouth or nose
Infant: preferential nose up to 5 mo
-most infants convert to oral if nasal is obstructed
-bilat choanal atresia may req emergency a.w. management if infant is unable to mouth breathe
Contrast the relative size of the tongue in adults + infants
Adult: small r/t oral volume
Infant: large r/t oral volume
-tongue closer to soft palate + more likely to obstruct upper a.w.
-more difficult to displace during laryngoscopy
Contrast the relative neck length in adults + infants.
Adult: longer
Infant: short
-more acute angle required to visualize glottis
Contrast the epiglottis shape in adults + infants.
Adult: C shape, floppier, shorter
Infant: U shape, stiffer, longer
-stiff epiglottis makes it more difficult to displace during DL
Contrast the VC position in adults + infants.
Adult: perpendicular to trachea
Infant: anterior slant
-visualization + passage of ETT may be more difficult
-ETT may get stuck in the anterior commissure
Contrast the laryngeal position in adults + infants.
Adult: C5-C6
Infant: C3-C4
-larynx more superior/cephalad/rostral, but NOT anterior.
-only more "anterior" during neck flexion
-Same position as the adult ~5-6 y/o
Contrast the narrowest point of the a.w. in adults + infants.
Adult: glottis (VC)
Infant: cricoid or glottis
-resistance to ETT beyond the VC is likely the cricoid ring
-cricoid tissue is prone to inflammation + edema formation → stridor or obstruction
-Pouiseuille's law - small △ in radio can sig ↑ resistance to airflow
Contrast the orientation of the R mainstem bronchus in adults + infants.
Adult: more vertical
Infant: less vertical
-up to 3 y/o, both bronchi 55º
-adult: R 25º, L 45º
Contrast the optimal intubation position for adults + infants.
Adult: sniffing
Infant: head on bed w/shoulder roll
-infant has lg occiput
-sniffing position will place glottic opening in a more anterior position
Contrast the O2 consumption, Alveolar ventilation, RR, Vt in neonates + adults.
neonatal SA is 1/3 of the adult + O2 consumption is 2x the adult. neonate must ↑ alveolar ventilation to sustain normal gas tensions.
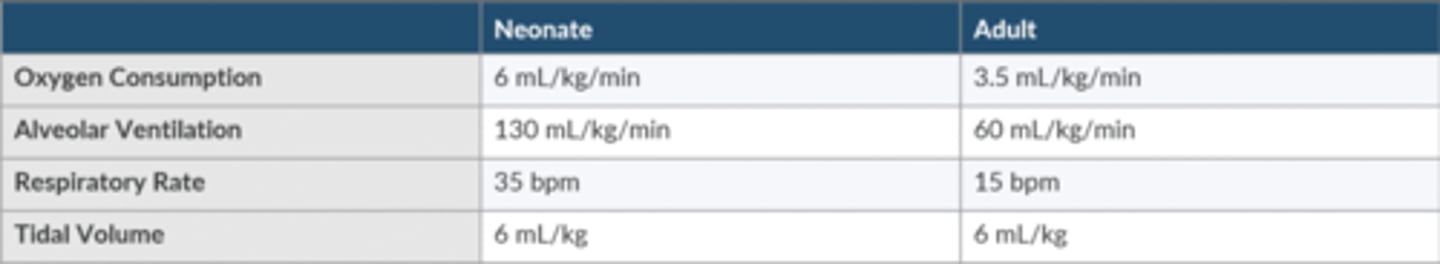
Why do neonates desaturate faster than adults?
Neonates have a/an:
-Increased oxygen consumption to support metabolic demand
-Increased alveolar ventilation to increase oxygen supply
-Slightly decreased FRC reflects a reduced oxygen reserve
-The net result is that the neonate has an increased ratio of alveolar ventilation relative to the size of its FRC.
Why is an inhalation induction faster with a neonate than with an adult?
↑ ratio of alveolar ventilation r/t the size of FRC
Faster turnover of FRC
What is the difference b/t fast + slow twitch m fibers? How does this r/t neonatal pulmonary mechanics?
Diaphragm + intercostal m are composed of 2 types of m fibers:
Type 1: slow-twitch
-built for endurance - resistant to fatigue
Type 2: fast-twitch
-built for short bursts of heavy work - tire easily
Smaller # of Type 1/endurance fibers in the diaphragm ↑ neonate's risk for respiratory fatigue + failure
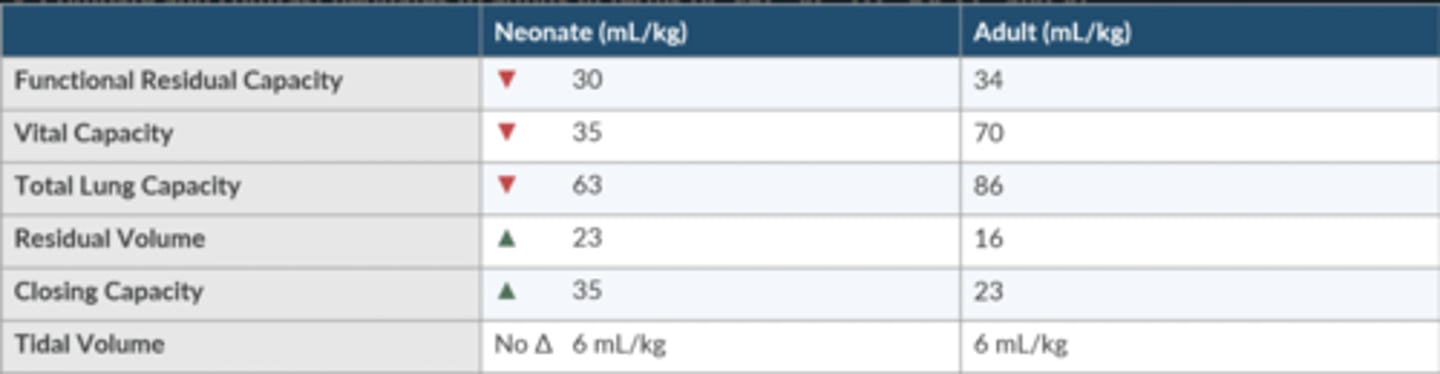
Compare + contrast neonates to adults in terms of FRC, VC, TLC, RV, CC, and Vt.
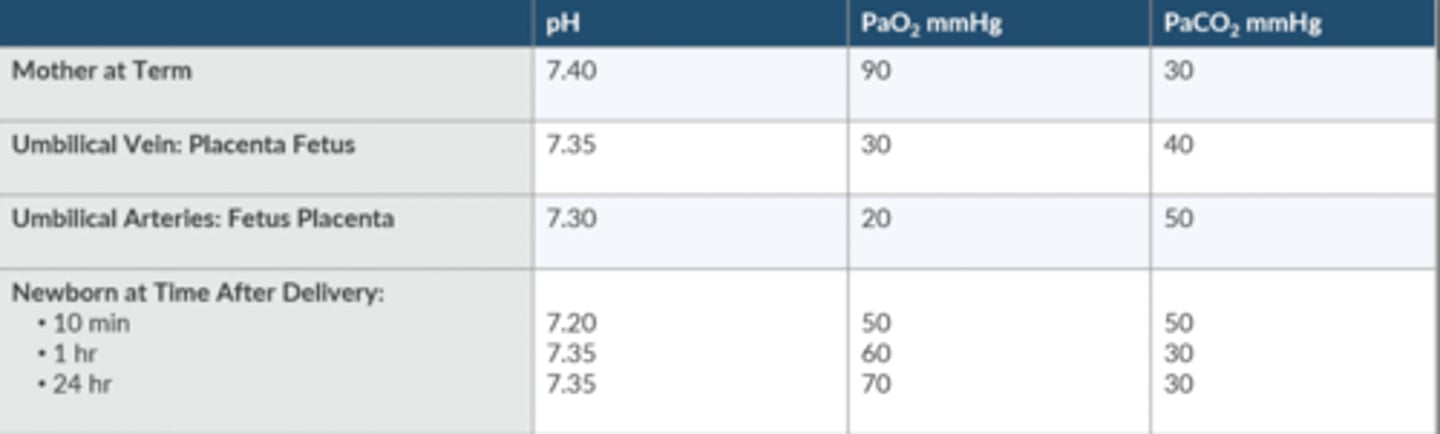
How does the newborn's ABG change from delivery to the 1st 24 hours of life?
How does hypoxemia affect ventilation in the newborn?
Respiratory control doesn't mature until 42-44 weeks.
-before maturation: hypoxemia depresses ventilation
-after maturation: hypoxemia stimulates ventilation
What is the P50 of fetal hgb? Why is this important?
19 mmHg
Oxyhgb curve shifts L (L = love)
benefits fetus by creating O2 partial P gradient across the uteroplacental membrane that facilitates passage of O2 from the mother to the fetus.
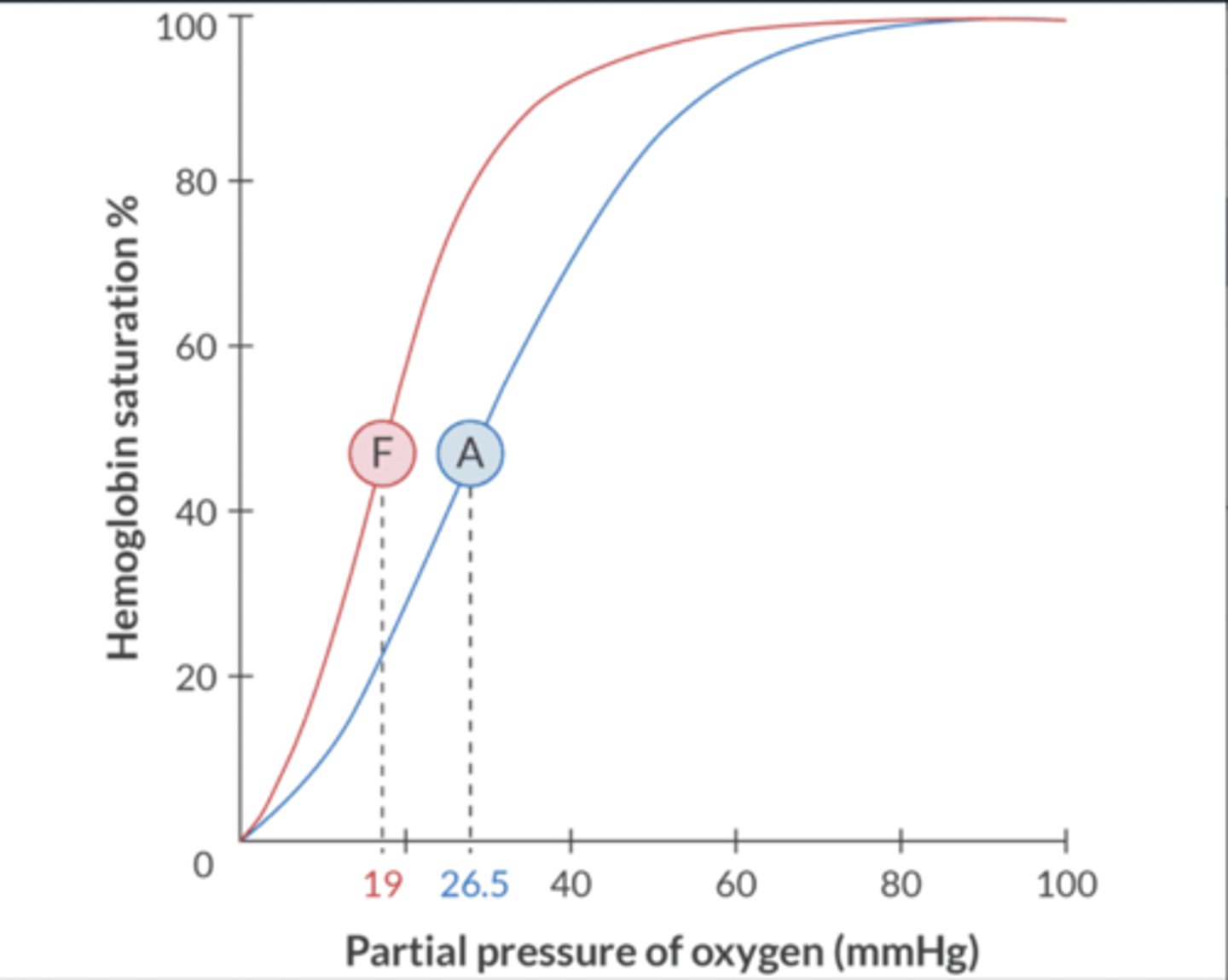
Why does Hgb F have a higher affinity for O2?
Adult Hgb (HgbA) consists of 2 ⍺ + 2 β chains
Hgb F consists of 2 ⍺ + 2 gamma chains
2,3 DPG causes a R shift in oxyhgb curve, but only β chains have a binding site for 2,3 DPG
Hgb F does not bing 2,3 DPG
-shifts curve L (L = love)
What are the indications for the FFP transfusion in the neonate?
Emergency reversal of warfarin
Correction of coagulopathic bleeding w/↑ PT > 1.5 or ↑ PTT
Correction of coagulopathic bleeding if > 1 BV has been replaced + coagulation studies are not easily obtained.
What is the dose for FFP transfusion in the neonate?
10-20 mL/kg
When is Plt transfusion indicated in the neonate? What it the dose?
to maintain Plt > 50,000
5 mL/kg if from apheresis
1pk/10kg if pooled concentrate
Describe the physiologic changes that occur as a result of a massive transfusion.
Alkalosis: 2/2 citrate metabolism to bicarbonate in the liver
Hypothermia: 2/2 cold blood
Hyperglycemia: 2/2 dextrose additive to stored blood
Hypocalcemia: 2/2 binding of Ca by citrate
Hyperkalemia: 2/2 administration of older blood
What is normal H/H at birth, 3 months, + 6-12 months?
Newborn: 14-20/45-65
3 months: 10-14/31-41
6-12 months: 11-15/33-42
Adult F: 12-16/37-47
Adult M: 14-18/42-50
What is the estimated blood volume in the premature neonate, term neonate, infant, child >1 y/o?
Premie: 90-100 mL/kg
Term: 80-90 mL/kg
Infant: 75-80 mL/kg
>1 y/o: 70-75 mL/kg
A 3-kg neonate requires emergency exploratory laparotomy for necrotizing enterocolitis. Her pre-op Hct is 50%. What is the maximum allowable blood loss to maintain a Hct of 40%?
EBV x [(Hct start - Hct target) / Hct start]
3kg x 90 mL/kg = 270
50% - 40% = 10%
270 x [10/50]
= 54
When do GFR + renal tubular fxn achieve full maturation?
Normal GFR 8-24 months
-before maturation, poor job conserving water → intolerant of fluid restriction
-unable to excrete lg volumes of water → do not do well with fluid overload
Normal tubular fxn 2 yrs
-1st few days: obligate Na loser
-then better to retain than excrete
-tendency to lose glucose to urine
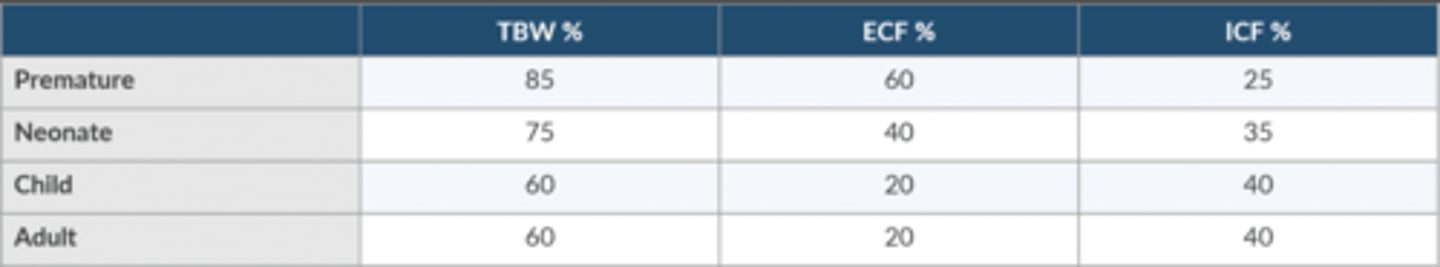
Compare + contrast the distribution of body water in the premie, neonate, child, and adult.
Premie
TBW 85
ECF 60
ICF 25
Neonate
TBW 75
ECF 40
ICF 35
Child
TBW 60
ECF 20
ICF 40
Adult
TBW 60
ECF 20
ICF 40
What signs suggest dehydration in the neonate?
-Sunken anterior fontanel
-Weight loss (a 10% reduction the first week is normal)
-Irritability or lethargy
-Dry mucus membranes
-Absence of tears
-Decreased skin turgor
-Increased hematocrit in the absence of transfusion
Describe the 4:2:1 rule of fluid management.
-Step 1: 0-10 kg → Begin with 4 mL/kg/hr
-Step 2: 10-20 kg → Add 2 mL/kg/hr to the previous total
-Step 3: > 20 kg → Add 1 mL/kg/hr to the previous total
-If the patient is > 20 kg → patient's weight in kg + 40
How should the NPO fluid deficit be replaced?
Multiply hourly maintenance rate by # of hours NPO time.
Replace over 3 hours
1st hr: 50%
2nd + 3rd hr: 25%
How should 3rd space losses be replaced?
Minimal surgical trauma: 3-4 mL/kg/hr
Moderate surgical trauma 5-6 mL/kg/hr
Major surgical trauma: 7-10 mL/kg/hr
Generally, 1st hour of anesthesia is not included
What ratio should be used to replace blood loss w/crystalloid, colloid, and blood?
Crystalloid: 3:1
Colloid: 1:1
Blood: 1:1
Which pediatric populations should receive an IVF that contains glucose?
Generally not recommended.
Reserved for @ risk of developing hypoglycemia:
-prematurity
-< 48 hrs of age
-small for gestational age
-newborns of diabetic mothers
-children w/DM who received insulin on day of Sx
-children who receive glucose-based parental nutrition
What is the CO in the newborn? How does this affect pharmacokinetics?
200mL/kg/min
Drugs are delivered + removed from the rest of the body faster than in an adult
Discuss plasma protein binding in the neonate.
-Before 6 months of age there are lower [ ] of albumin and alpha-1 acid glycoprotein
-Highly protein bound drugs will display higher free drug levels, which ↑ the risk of toxicity.