Coordination and response
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What is homeostatis
The maintenance of a constant internal environment
What is a stimulus
A change in the environment
What are auxins
Plant growth hormones
What is a tropism
A plant's response to a directional stimulus
List different types of tropism
- Phototropism - plant's response to light
- Geotropism - plant's response to gravity
Describe the roots and shoots response to light
- Roots - negative phototropism
- Shoots - positive phototropism
What is a coleoptile
- Simple plants used to investigate tropism
- Cereal seedling
What is a clinostat?
Apparatus used to remove the effect gravity/light/water
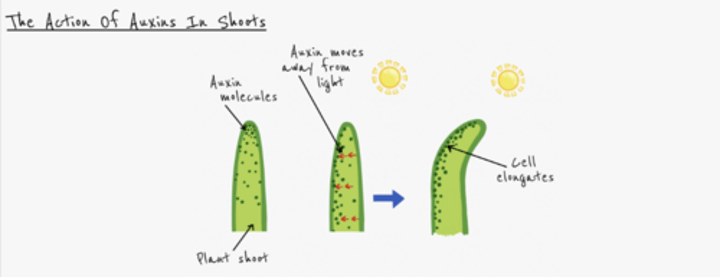
Describe how a stem may bend towards the light
- Auxins concentrate on the side furthest from the light
- Causes cell elongation
- Stem bends towards light
What are the sense organs in a human?
- Eye - receives light energy
- Ear - receives sound and kinetic energy
- Muscle - receives kinetic energy
- Tongue - receives chemical energy
- Nose - receives chemical energy
- Skin - receives kinetic and heat energy
What is the difference between hormonal and nervous responses?
- Nervous involves electrical impulses, hormonal involves chemicals carried in the blood
- Nervous response faster, hormonal slower
- Nervous response short-lived, hormonal long-lived
- Nervous response very localised, hormonal wide-spread
What is the CNS?
- Brain and spinal cord
- Linked to sense organs by nerves
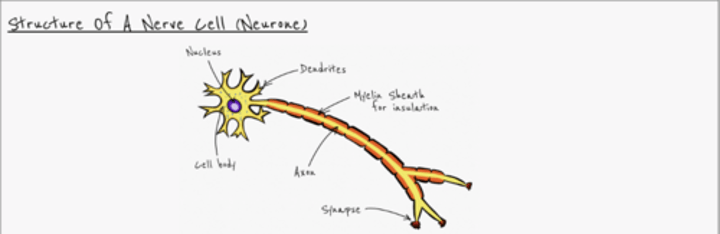
What is the structure of a Nerve Cell?
Nucleus
Cell body
Dendrites
Myelin Sheath for insulation
Axon
Synapse
What is the list of responses in a nervous response?
- Stimulus - receptor - sensory neurone - CNS - motor neurone - effector - response
- Involves electrical impulses and synapses
What is the list of responses in a reflex action?
- Stimulus - receptor - sensory neurone - relay neurone - motor neurone - effector - response
- Involves electrical impulses and synapses
- e.g. withdrawal of finger from hot object
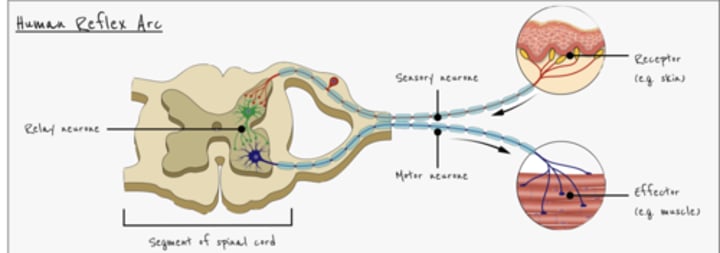
What is a synapse?
- formed when the dendrites of two neurones meet
How is a reflex action different to a regular response?
Reflex action is faster, involuntary, and involves relay neurone
What is an effector?
- Muscle (contracts) or a gland (secretes a hormone)
What is the role of the chornoid?
stops light being refracted inside the eye
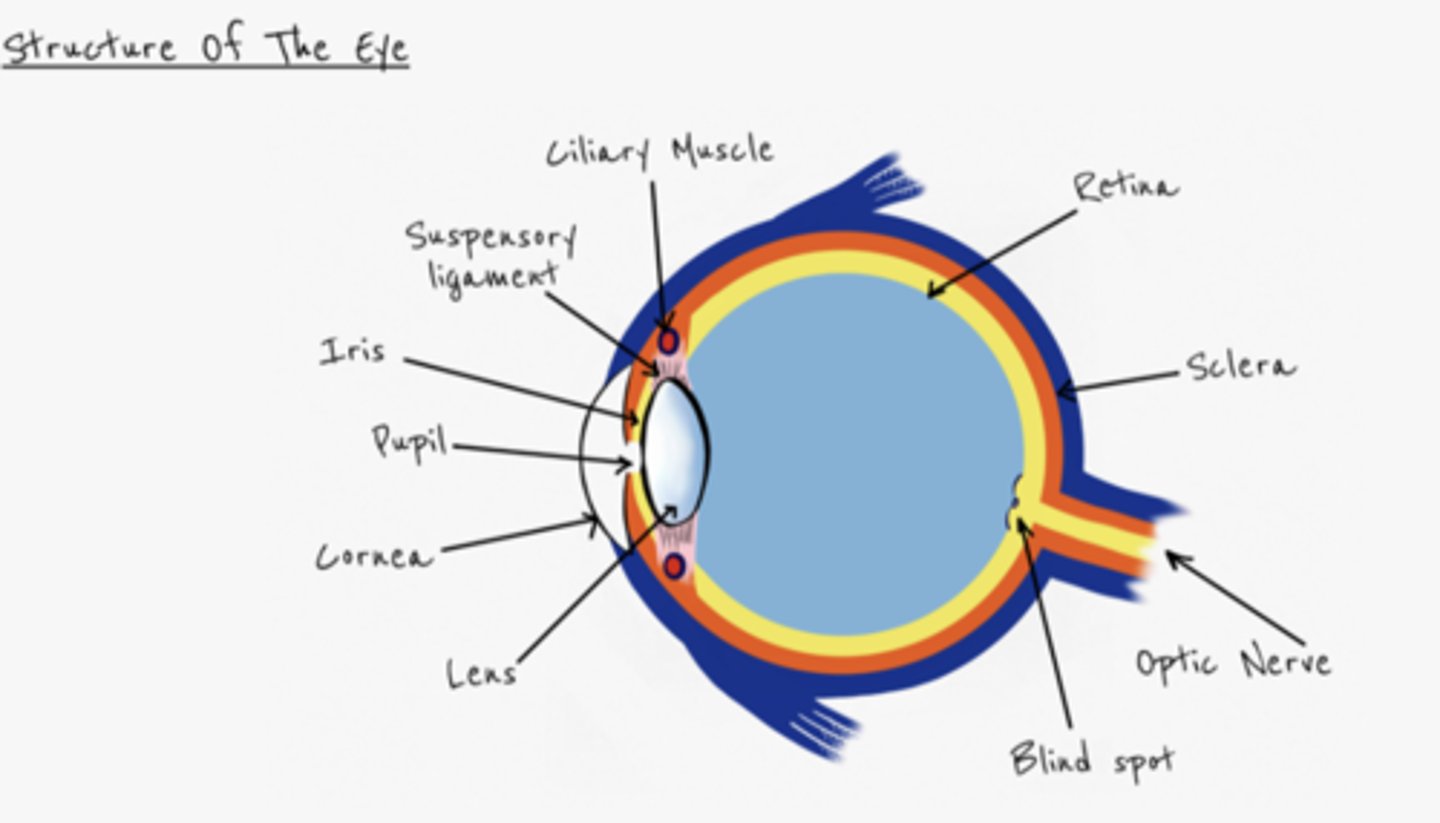
What's the role of the cornea?
refracts light
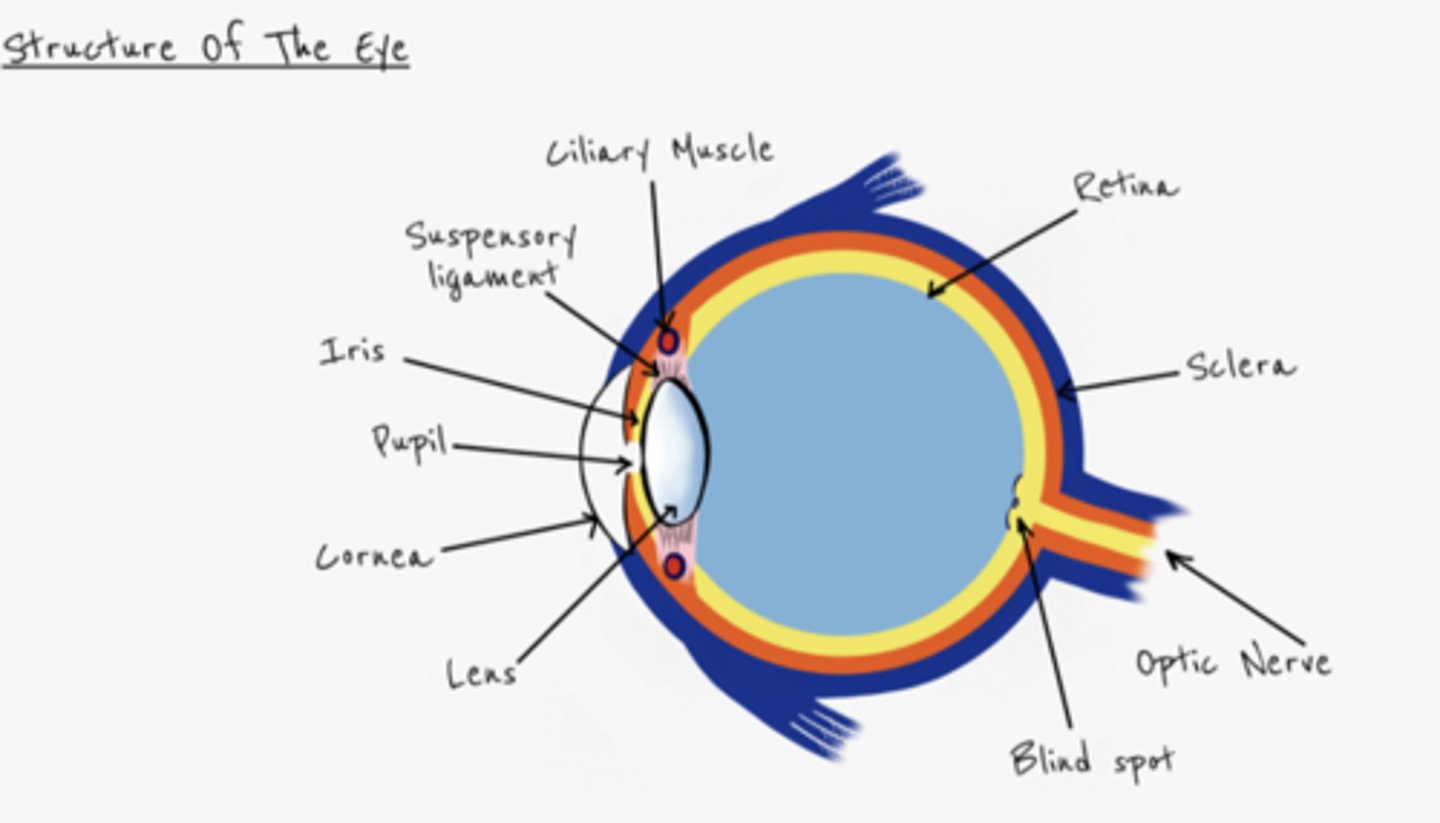
What's the role of the lens?
refracts light
What's the role of the conjuctiva?
Protects eye
What's the role of the sclera?
tough outer casing, protects the eye
What's the role of the retina?
contains photoreceptors (rods (dim light) and cones (detect colour)) which are sensitive to light
What's the role of the iris?
contains radial and circular muscles which control the size of the pupil
What's the role of the pupil?
allows light to enter the eye
What's the role of the suspensory ligament and cilicary muscles?
- control the shape of the lens
What's the role of the optic nerve?
- takes electrical impulses from the eye to the brain
What's the role of the blind spot?
where the the optic nerve enters the eye
What is accommodation?
- Changes that take place within the eye
- Enable us to focus on objects at different distances
How does the eye focus on a nearby object?
- Ciliary muscle contracts
- Suspensory ligaments slacken
- Lens fat
- Light refracted strongly
How does the eye focus on a faraway object?
- Ciliary muscle relax
- Suspensory ligaments taut
- Lens thin
- Light refracted less strongly
How does the pupil constrict in bright light and why is this necessary?
- Circular muscles contract
- Radial muscles relax
- Pupil constricts
- Protects the retina from the bright light
How does the pupil dilate in dim light and why is this necessary?
- Circular muscles relax
- Radial muscles contract
- Pupil dilates
- Allows more light to enter the eye
What is the role of the skin?
- Sense organ for pain, touch and pressure
- Tough outer layer
- Controls heat loss
- Barrier - prevents entry of pathogens
- Prevents water loss
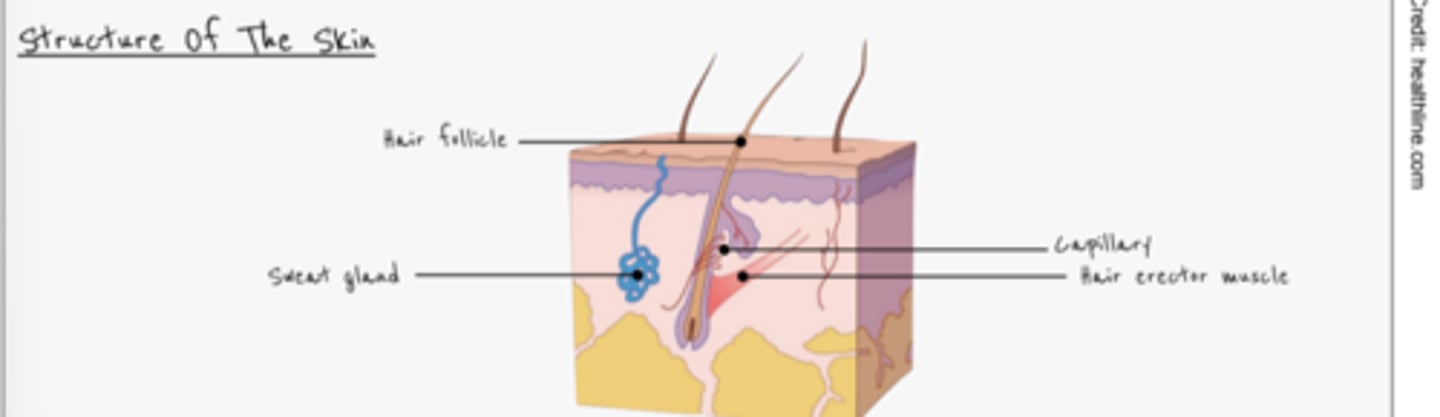
Explain what happens when your body temperature is too high
- Hair erector muscles relax
- Hairs lay flat
- Less insulating air trapped close to the body
- Vasodilation (arterioles dilate)
- Blood flows closer to skin surface
- More heat radiated
- Sweat evaporates and cools the body
Explain what happens when your body temperature is too low
- Hair erector muscles contract
- Hairs stand up
- More insulating air trapped close to the body
- Vasoconstriction (arterioles constrict)
- Less blood flows to surface of skin
- Less heat radiated
- Shiver - contraction of muscle releases heat
Where is adrenaline produced?
Adrenal gland
What is the effect of adrenaline on the body?
- Prepares the body for 'flight or fight'
- Pupils dilate - allows more light to enter the eye
- Hairs stand up on end - to appear more intimidating
- Breathing rate increases - to allow more oxygen into the body
- Heart rate increases - to deliver more oxygen around the body
- Blood diverted from gut to muscles
How is blood sugar level decreased?
- Pancreas secretes insulin
- Insulin converts soluble glucose into insoluble glycogen
Where is testosterone made and what is its function?
- Testes
- Stimulate secondary sexual characteristics e.g. voice deepening, sperm production, pubic hair
Where is oestrogen made and what is its function?
- Ovaries
- Stimulates secondary sexual characteristics e.g. hips widening, breast growth, pubic hair
- Repairs uterus lining
- Inhibits FSH production, stimulates LH production
Where is progesterone made and what is its function?
- Initially corpus luteum, later in pregnancy the placenta
- Maintains uterus lining
what is the synaptic cleft
a small gap between neurones
electricity cannot travel in air, so the impulses are converted temporarily into chemical signals
how do neurotransmitters work
1) the electrical impulse travels along the axon
2) vesicles fuse with the pre-synaptic membrane, the neurotransmitters fuse into the synaptic cleft
3) neurotransmitters diffuse- passive process along a concentration gradient- across synaptic cleft
4) neurotransmitters attach to receptors on the post synaptic membrane
5) triggers an impulse that travels along the post synaptic neurone
6) neurotransmitters destroyed to prevent continued stimulation of second neurone
how do drugs impact the nervous system?
binds to neurotransmitter receptors triggering impulses in different regions of the brain