IB Exercise Science Unit 1 Exam
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Anterior
Front
Posterior
Back
Superior
Upward
Inferior
Downward
Medial
Towards the midline
Lateral
Away from the midline
Proximal
Above
Distal
Below
Plantar
Top of Foot
Dorsum
Bottom of foot
Agonist (Prime Mover)
The muscle responsible for the main action
Antagonist (Opposite force)
The muscle that opposes the agonist’s action
Agonist: Flexion
Antagonist: Extension
Agonist: Abduction
Antagonist: Adduction
Agonist: External Rotation
Antagonist: Internal Rotation
Agonist: Supination
Antagonist: Pronation
Agonist: Protraction
Antagonist: Retraction
Agonist: Dorsiflexion
Antagonist: Plantar Flexion
Agonist: Inversion
Antagonist: Eversion
Agonist: Elevation
Antagonist: Depression
Shoulder Abduction (Ag/Anta)
Deltoid/ Latissimus Dorsi
Shoulder Adduction (Ag/ Anta)
Latissimus Dorsi/ Deltoid
Elbow Flexion (Ag/ Anta)
Bicep Brachii/ Tricep Brachii
Elbow Extension (Ag/ Anta)
Tricep Brachii/ Biceps Brachii
Hip Abduction (Ag/ Anta)
Gluteus med & min/ Adductor magnus
Hip Adduction (Ag/ Anta)
Adductor magnus/ Gluteus med & min
Hip Flexion (Ag/ Anta)
Iliacus/ Gluteus max
Hip Extension (Ag/ Anta)
Gluteus max/ Iliacus
Knee Flexion (Ag/ Anta)
Hamstrings/ Quadriceps
Knee Extension (Ag/ Anta)
Quadriceps/ Hamstrings
Plantar Flexion (Ag/ Anta)
Gastrocnemius + Soleus/ Tibialis anterior
Dorsiflexion (Ag/ Anta)
Tibialis anterior/ Gastrocnemius + Soleus
Fibrous
Immovable connections formed by dense fibrous tissue
Ex: Skull (Jaw)
Cartilaginous
Slightly movable joints w/ cartilage connections
Ex: Rib cage and in between Vertebrae
Synovial
Freely movable joints w/ synovial fluid lubrication
Ex: Shoulder, Knee, and Elbow
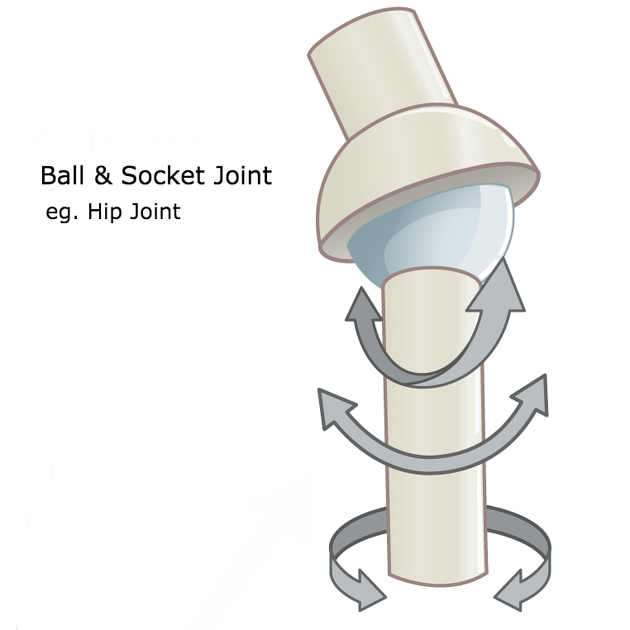
Ball and Socket Joint
Sphere-shaped head of one bone fits into a rounded cavity on the other bone
Ex: Shoulder, hip
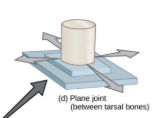
Gliding Joint
Usually flat or slightly curved bone
Ex: Wrist, Ankle
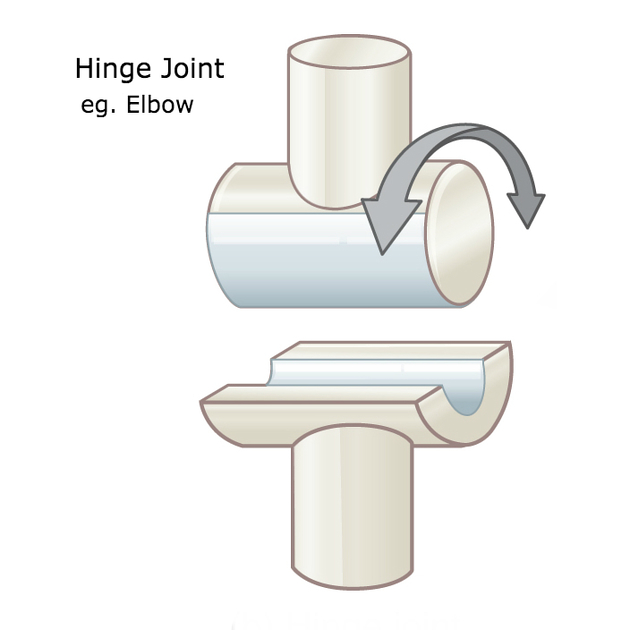
Hinge Joint
A convex surface fits into concave surface
Ex: Knee, Elbow
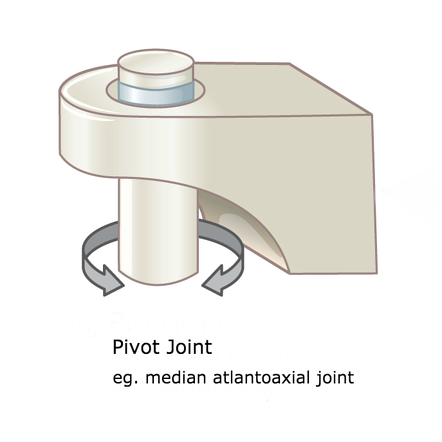
Pivot Joint
The rounded surface of one bone rolls around in a ring formed by bone and ligament
Ex: Neck and Forearm
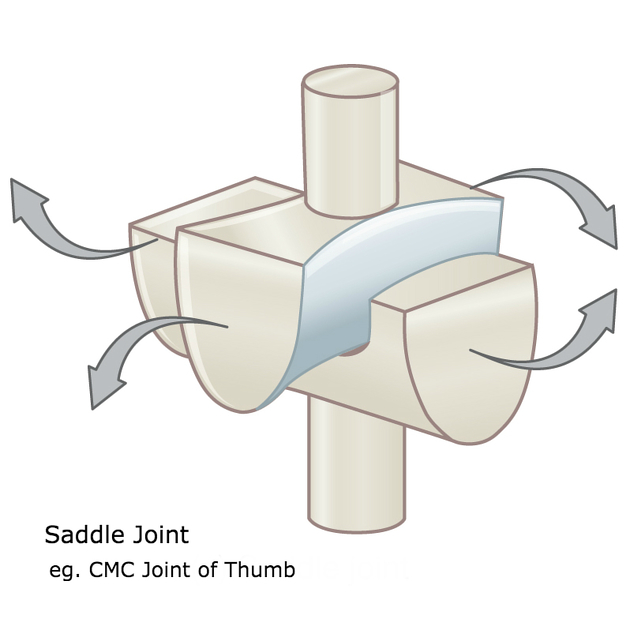
Saddle Joint
A saddle-shaped bone fits against another bone shaped like the legs of rider sitting in the saddle
Ex: Thumb joint
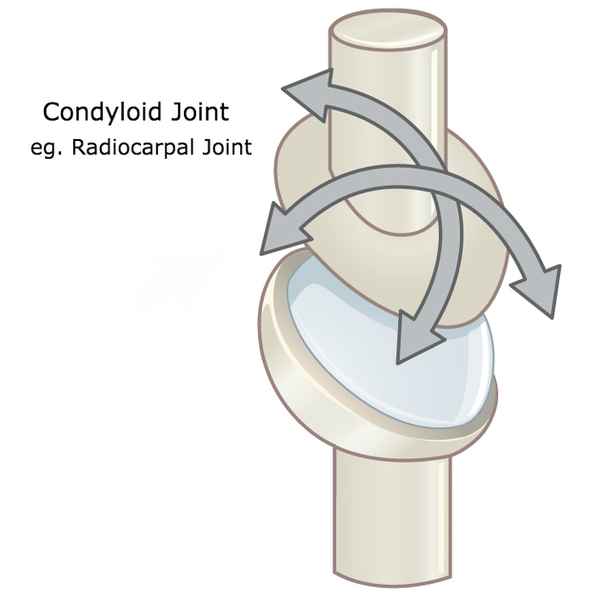
Condyloid Joint
Sphere-shaped head of one bone fits into a rounded cavity on the other bone
Ex: Knuckles
Ligaments (Stabilized Joints)
Connect bone to bone
Tendons (Enables Movement)
Connect Muscle to Bone
Flat Bone
Ex: Frontal Bone, Scapula, Sternum, Ribcage
Irregular Bone
Ex: Vertebrate, Maxilla, Mandible

Short Bone
Ex: Carpals, Tarsals
Sesamoid Bone
Ex: Patella
Long Bone
Ex: Femur, Humorous, Radius, Ulna, Tibia, Fibula, Phalanges

Pectoral Girdle
Helps articulate the limb bones to the main axial skeleton Scapula and Clavicle
Pelvic Girdle
Helps articulate the limb bones to the main axial skeleton Sacrum and Coccyx
Cervical Region of Vertebral Column (C1-C7)
Supports skull and neck
Thoracic Region of Vertebral Column (T1-T12)
Articulates w/ the ribs
Lumbar Region of Vertebral Column (L1-L5)
Carries majority of body weight
True Ribs (1-7)
Directly attach to sternum
False Ribs (8-10)
Indirect attachment
Floating Ribs (2)
Do not attach anteriorly
Protect abdominal organs
Attachment point for muscles and diaphragm
Axial Skeleton
Vertebral Column
Skull
Ribcage
Appendicular Skeleton
Limbs (Arms and Legs)
Supporting structures - Girdles (pectoral and pelvic)
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Involuntary movement
Line blood vessels, hollow organs and joints
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Involuntary movement
Heart beat
Skeletal Muscle Tissues
Voluntary movement
Muscle tendons attach to bone
Origin (Proximal)
The point where the muscle attached to the more stationary bone
Insertion (Distal)
The point where the muscle attached to the more moveable bone
Insertion (distal)
The point where the muscle attached to the most moved part of the bone
Myoglobin
Protein found in heart and skeletal muscles (vertebrae)
Slow-Twitch Muscle fibre
Have very slow contraction speed, primarily responsible for sustained low intensity activities
Fast-Twitch Muscle Fibre
Skeletal muscles cells responsible for rapid, powerful movements, fatigue rapidly due to their reliance on anaerobic metabolism
Type 1 (Slow Twitch)
best for endurance activities and rely on aerobic metabolism
small muscle fiber
Type 2a (Fast-Twitch Oxidative)
fibres are versatile because they use both aerobic and anaerobic metabolism
medium muscle fiber
Type 2b (Fast-Twitch Glycolytic)
fibres produce high force for short durations
large muscle fiber
Musculoskeletal System 5 Functions
to support body and stay upright
to allow movement (posture control (voluntary))
to protect body’s vital organs
to store minerals
generates 85% of body heat (involuntary (shivering))
Functions of Axial System
Human Nervous System
DOMS
Human Nervous System
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and Spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous Systems (PNS)
Nerves extending from spinal column to limbs
Motor pathways
Somatic Nervous System
Voluntary
Autonomic nervous system
Involuntary
D.O.M.S.
Delayed. Onset. Muscle. Soreness.
Occurs 24-72 hours after training
Occurs due to eccentric loading of the muscle
Duce to muscle damage and inflammation
During a dumbbell bicep curl, when the athlete is lowering the weight from the fully contracted position back to the starting position, what type of contraction occurs in the biceps brachii?
eccentric contraction - the muscle lengthens
An individual is performing a push-up and pauses midway, holding their body in a fixed position. What type of contraction occurs in the pectoralis major during this hold?
isometric contraction - generating force but no length change
When performing a bench press, which type of contraction occurs in the triceps brachii as the athlete pushes the bar up from their chest?
concentric contraction - the muscle shortens
In a wall sit exercise, the person maintains a seated position with their back against a wall and knees bent at a 90 degree angle. What type of muscle contraction occurs in the quadriceps during this static hold?
isometric contraction - generates force but no change in length
While performing a deadlift, what type of contraction occurs in the hamstrings and gluteus maximus as the person slowly lowers the bar back to the floor?
eccentric contraction - the muscle lengthens
During a pull-up, what type of contraction occurs in the latissimus dorsi as the athlete lifts their body toward the bar?
concentric contraction - muscle shortens