Midterm Exam Practice Questions Ch. 1 - Ch. 6
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
The FASB provides a fair-value reporting option for investments. Which of the following investments generally requires the use of the equity method of accounting?
available for securities
held to maturity
20-50% ownership in investments
more than 50% ownership
variable interests
20-50% ownership in investments
A necessary condition to use the equity method of reporting for an equity investment is that the investor company must
have the ability to exercise significant influence over the operating and financial policies of the investee
own at least 30% of the investee’s voting stock
possess a controlling interest in the investee’s voting stock
not have the ability to exercise significant influence over the operating and financial policies of the investee
have the ability to exercise significant influence over the operating and financial policies of the investee
All of the following would require use of the equity method for investments except:
material intra-entity transactions.
investor participation in the policy-making process of the investee
valuation at fair value
technological dependency
interchange of managerial personnel
valuation at fair value
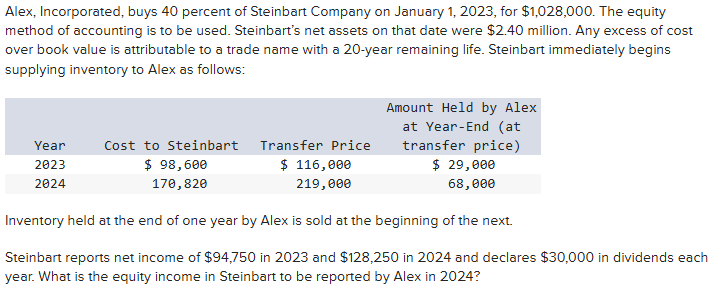
$38,896
$43,656
$52,056
$58,956
$43,656
A company has been using the fair-value method to account for its investment. The company now has the ability to significantly influence the investee and the equity method has been deemed appropriate. Which of the following statements is true?
A cumulative effect change in accounting principle must occur.
A prospective change in accounting principle must occur.
A retrospective change in accounting principle must occur.
The investor will not receive future dividends from the investee.
Future dividends will continue to be recorded as revenue.
A prospective change in accounting principle must occur.
A permanent decline in the investee’s market value is recorded as a:
reduction of the Equity in Subsidiary Income account.
an Extraordinary Loss on the Investor’s Income Statement.
reduction in the Investment Account.
increase to the Investment Account.
no entry is made for market value declines.
reduction in the Investment Account
Which of the following is a not a reason for a business combination to take place?
Cost savings through elimination of duplicate facilities.
Quick entry for new and existing products into domestic and foreign markets.
Diversification of business risk.
Vertical integration.
Increase in stock price of the acquired company.
Increase in stock price of the acquired company
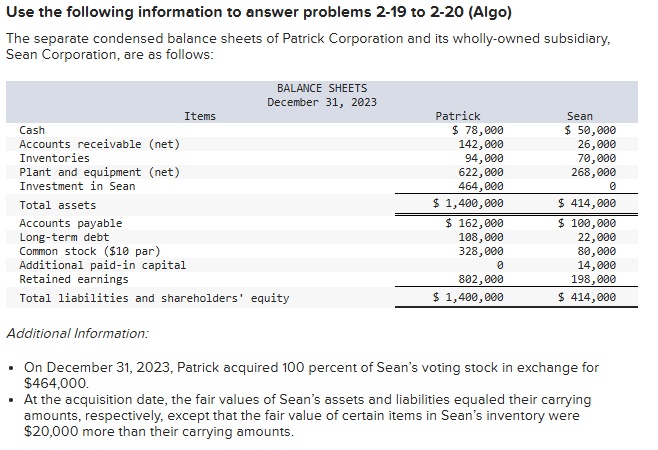
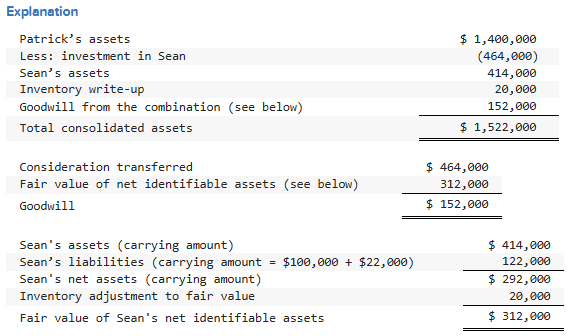
In the December 31, 2023, consolidated balance sheet of Patrick and its subsidiary, what amount of total assets should be reported?
$1,380,000
$1,400,000
$1,522,000
$1,986,000
$1,522,000
What is the primary difference between: (i) accounting for a business combination when the subsidiary is dissolved; and (ii) accounting for a business combination when the subsidiary retains its incorporation?
If the subsidiary is dissolved, it will not be operated as a separate division.
If the subsidiary is dissolved, assets and liabilities are consolidated at their book values.
If the subsidiary retains its incorporation, there will be no goodwill associated with the acquisition.
If the subsidiary retains its incorporation, assets and liabilities are consolidated at their book values.
If the subsidiary retains its incorporation, the consolidation is not formally recorded in the accounting records of the acquiring company.
If the subsidiary retains its incorporation, the consolidation is not formally recorded in the accounting records of the acquiring company.
Acquired in-process research and development is considered as
a definite-lived asset subject to amortization.
a definite-lived asset subject to testing for impairment.
an indefinite-lived asset subject to amortization.
an indefinite-lived asset subject to testing for impairment.
a research and development expense at the date of acquisition.
an indefinite-lived asset subject to testing for impairment.
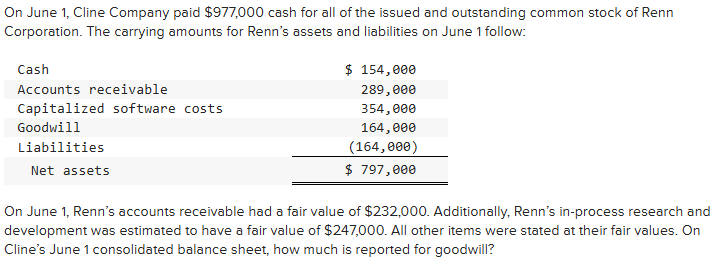
$154,000
$67,000
$354,000
$97,000
$154,000

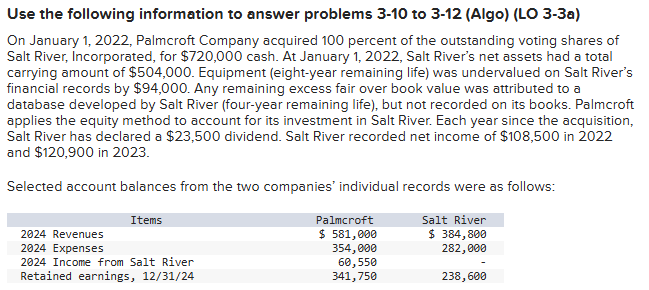
What is considered net income for Palmcroft and Salt River for 2024?
$227,000
$287,550
$312,550
$322,550
$287,550
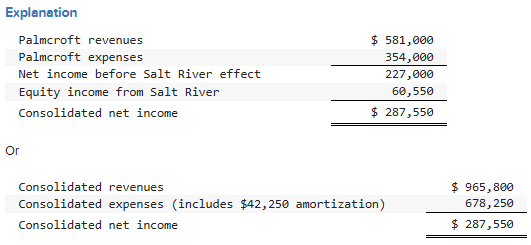
Which one of the following accounts would not appear in the consolidated financial statements at the end of the first fiscal period of the combination?
Goodwill
Equipment
Retained Earnings
Common Stock
Equity in Subsidiary Earnings
Equity in Subsidiary Earnings
Under the partial equity method, the parent recognizes income when,
dividends are received from the investee
dividends are declared by the investee
the related expense has been incurred
the related contract is signed by the subsidiary
it is earned by the subsidiary
it is earned by the subsidiary
According to GAAP regarding amortization of goodwill, which of the following statements is true?
Goodwill recognized in consolidation must be amortized over 20 years.
Goodwill recognized in consolidation must be expensed in the period of acquisition.
Goodwill recognized in consolidation will not be amortized but subject to an annual test for impairment.
Goodwill recognized in consolidation can never be written off.
Goodwill recognized in consolidation must be amortized over 40 years.
Goodwill recognized in consolidation will not be amortized but subject to an annual test for impairment.
According to the FASB ASC regarding the testing procedures for Goodwill Impairment, the proper procedure for conducting impairment testing is:
Goodwill recognized in consolidation may be amortized uniformly and only tested if the amortization method originally chosen is changed.
Goodwill recognized in consolidation must only be impairment tested prior to disposal of the consolidated unit to eliminate the impairment of goodwill from the gain or loss on the sale of that specific entity.
Goodwill recognized in consolidation may be impairment tested in a two-step approach, first by quantitative assessment of the possible impairment of the fair value of the unit relative to the book value, and then a qualitative assessment as to why the impairment, if any, occurred for disclosure.
Goodwill recognized in consolidation may be impairment tested in a two-step approach, first by qualitative assessment of the possibility of impairment of the unit fair value relative to the book value, and then quantitative assessments as to how much impairment, if any, occurred for disclosure.
Goodwill recognized in consolidation may be impairment tested in a two-step approach, first by qualitative assessment of the possibility of impairment of the unit fair value relative to the book value, and then quantitative assessments as to how much impairment, if any, occurred for asset write-down.
Goodwill recognized in consolidation may be impairment tested in a two-step approach, first by qualitative assessment of the possibility of impairment of the unit fair value relative to the book value, and then quantitative assessments as to how much impairment, if any, occurred for asset write-down.
With respect to identifiable intangible assets other than goodwill, which of the following is true?
If the value of the identified asset meets a de minimis exception, the entity may elect to treat it as goodwill.
An identifiable intangible asset with an indefinite useful life must be assessed for impairment once every three years.
If the average fair value of the asset is less than the average carrying amount of the asset with respect to, and determined for, the preceding three-year period, the asset is considered impaired and the entity may recognize a loss.
A quantitative evaluation of value is required each year regardless of circumstances.
If a qualitative assessment of the asset performed by an entity indicates impairment is likely, a quantitative assessment must be performed to determine whether there has been a loss in fair value.
If a qualitative assessment of the asset performed by an entity indicates impairment is likely, a quantitative assessment must be performed to determine whether there has been a loss in fair value.
Which of the following is false regarding contingent consideration in business combinations?
Contingent consideration payable in cash is reported under liabilities.
Contingent consideration payable in stock shares is reported under stockholders' equity.
Contingent consideration is recorded because of its substantial probability of eventual payment.
The contingent consideration fair value is recognized as part of the acquisition regardless of whether eventual payment is based on future performance of the target firm or future stock price of the acquirer.
Contingent consideration is reflected in the acquirer's balance sheet at the present value of the potential expected future payment.
Contingent consideration is recorded because of its substantial probability of eventual payment.
On January 1, 2023, Chamberlain Corporation pays $650,800 for a 60 percent ownership in Neville. Annual excess fair-value amortization of $18,300 results from the acquisition. On December 31, 2024, Neville reports revenues of $485,000 and expenses of $312,000 and Chamberlain reports revenues of $785,000 and expenses of $449,000. The parent figures contain no income from the subsidiary. What is consolidated net income attributable to Chamberlain Corporation?
$447,120
$490,700
$485,000
$428,820
$428,820
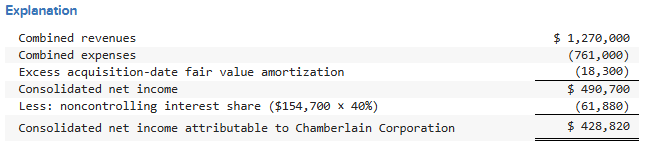
For business combinations involving less than 100 percent ownership, the acquirer recognizes and measures all of the following at the acquisition date except
identifiable assets acquired, at fair value.
liabilities assumed, at book value.
non-controlling interest, at fair value.
goodwill, or a gain from bargain purchase.
intangible assets acquired, at fair value.
liabilities assumed, at book value.
When Valley Company acquired 80% of the common stock of Coleman Corporation, Coleman owned land with a book value of $75,000 and a fair value of $125,000.
What is the total amount of excess land allocation at the acquisition date?
$0
$40,000
$50,000
$60,000
$75,000
$50,000
FV - BV = excess allocation
⬇
$125,000 - $75,000 = $50,000
Dodd Company acquired 75% of the common stock of Wallace Corporation for $1,800,000. The fair value of Wallace's identifiable net assets was $2,100,000, and the book value was $1,900,000. The noncontrolling interest shares of Wallace are not actively traded.
What is the total amount of goodwill recognized at the date of the acquisition?
$0
$100,000
$200,000
$300,000
$700,000
$300,000
Acquisition-date FV of Wallace Corp. - FV of Wallace’s Identifiable Net Assets = Goodwill
⬇
($1,800,000 / 75%) - $2,100,00 = ?
⬇
$2,400,000 - $2,100,000 = $300,000
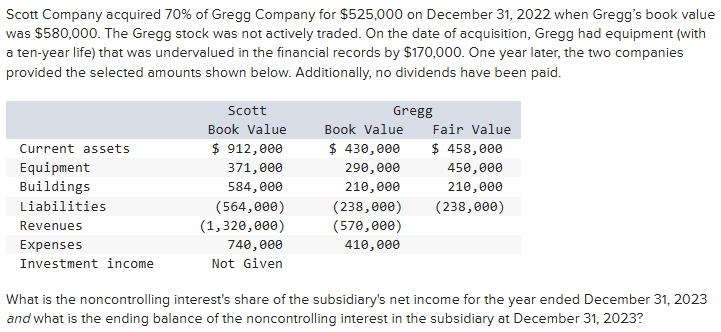
$48,000 and $262,800
$48,000 and $273,000
$42,900 and $267,900
$42,900 and $262,800
$48,000 and $267,900
$42,900 and $267,900
[Subsidiary's Income ($570,000 − $410,000) × 30% = $48,000] − [Excess Equipment Amortization for 2023 ($170,000 ÷ 10) × 30% = $5,100] = $42,900
[Noncontrolling Interest at Acquisition (Fair Value $750,000 × 30%) = $225,000] + [Noncontrolling Interest 2023 Income $42,900] = $267,900
When a subsidiary is acquired sometime after the first day of the fiscal year, which of the following statements is true?
Income from subsidiary is not recognized until there is an entire year of consolidated operations.
Income from subsidiary is recognized from date of acquisition to year-end.
Excess cost over acquisition value is recognized at the beginning of the fiscal year.
No goodwill can be recognized.
Income from subsidiary is recognized for the entire year.
Income from subsidiary is recognized from date of acquisition to year-end.
Which of the following statements is false regarding multiple acquisitions of a subsidiary's existing common stock?
The parent recognizes a larger percent of subsidiary income.
A step acquisition resulting in control may result in a parent recognizing a gain on revaluation.
The book value of the subsidiary will increase.
The parent's percent ownership in subsidiary will increase.
Noncontrolling interest in subsidiary's net income will decrease.
The book value of the subsidiary will increase.
Jax Company used the acquisition method when it acquired its investment in Saxton Company. Jax now sells some of its shares of Saxton such that neither control nor significant influence exists. Which of the following statements is true?
The difference between selling price and acquisition value is recorded as a realized gain or loss.
The difference between selling price and acquisition value is recorded as an unrealized gain or loss.
The difference between selling price and carrying value is recorded as a realized gain or loss.
The difference between selling price and carrying value is recorded as an unrealized gain or loss.
The difference between selling price and carrying value is recorded as an adjustment to retained earnings.
The difference between selling price and carrying value is recorded as a realized gain or loss.
On October 6, 2024, Ronan Corporation sold land to Bane Company, its wholly owned subsidiary. The land cost $72,400 and was sold to Bane for $96,000. For consolidated financial statement reporting purposes, when must the gain on the sale of the land be recognized?
Proportionately over a designated period of years
When Bane sells the land to a third party
No gain may be recognized.
As Bane uses the land
When Bane begins using the land productively
When Bane sells the land to a third party
Charleston Incorporated acquired 75% of Savannah Manufacturing on January 4, 2023. During 2023, Charleston sold Savannah $460,000 of goods, which had cost $380,000. Savannah still owned 20% of the goods at the end of the year. In 2024, Charleston sold goods with a cost of $520,000 to Savannah for $700,000, and Savannah still owned 15% of the goods at year-end. What amount of intra-entity gross profit should be deferred in 2024?
$27,000
$20,250
$16,000
$12,000
$0
$27,000
($700,000 − $520,000) × 15% = $27,000
Poole Company acquired 100% of Mullen Incorporated on January 3, 2024. During 2024, Poole sold goods to Mullen for $2,500,000 that cost Poole $1,850,000. Mullen still owned 30% of the goods at the end of the year. Cost of goods sold was $11,200,000 for Poole and $6,600,000 for Mullen. What was consolidated cost of goods sold?
$15,105,000
$15,300,000
$15,495,000
$17,800,000
$17,995,000
$15,495,000
Explanation:
Intra-Entity Gross Profit ($2,500,000 − $1,850,000) $650,000 × Intra-Entity Transfer Remaining in Ending Inventory (30%) = $195,000
Consolidated Cost of Goods Sold = Parent’s Cost of Goods Sold ($11,200,000) + Subsidiary’s Cost of Goods Sold ($6,600,000) − Cost of Goods Sold in Intra-Entity Transfer ($2,500,000) + Intra-Entity Gross Profit Deferred ($195,000) = $15,495,000
Walsh Company sells inventory to its subsidiary, Fisher Company, at a profit during 2023. With respect to one-third of the inventory sold to Fisher, Walsh accounts for it using the equity method of accounting.
In the consolidation worksheet for 2024, which of the following accounts would be credited to eliminate unrecognized intra-entity gross profit with regard to the 2023 intra-entity transfers?
Retained earnings
Cost of goods sold
Inventory
Investment in Fisher Company
Sales
Cost of Goods Sold
Prescott Incorporated owned 80% of the voting common stock of Hutchins Corporation. During 2024, Hutchins made several sales of inventory to Prescott. The total selling price was $190,000 and the cost was $105,000. At the end of the year, 30% of the goods were still in Prescott’s inventory. Hutchins’s reported net income was $320,000. Assuming there are no excess amortizations associated with the consolidation, and no other intra-entity asset transfers, what was the net income attributable to the noncontrolling interest in Hutchins?
$47,000
$58,900
$64,000
$69,100
$90,900
$58,900
Explanation:
Subsidiary’s Net Income ($320,000) − Intra-Entity Gross Profit Deferred [($190,000 − $105,000) × 30% = $25,500] = $294,500 × Noncontrolling Interest (20%) = $58,900 Net Income Attributable to the Noncontrolling Interest
Stark Company, a 90% owned subsidiary of Parker, Incorporated, sold land to Parker on May 1, 2023, for $80,000. The land originally cost Stark $85,000. Stark reported net income of $200,000, $180,000, and $220,000 for 2023, 2024, and 2025, respectively. Parker sold the land purchased from Stark for $92,000 in 2025. Both companies use the equity method of accounting.
Which of the following will be included in a consolidation entry for 2024?
Debit Retained Earnings for $5,000.
Credit Retained Earnings for $5,000.
Debit Investment in Subsidiary for $5,000.
Credit Investment in Subsidiary for $5,000.
Credit Land for $5,000.
Credit Retained Earnings for $5,000.
Explanation:
Subsidiary’s Land Transfer Value $80,000 − Subsidiary’s Land Book Value $85,000 = $5,000 Loss on Intra-Entity Transfer of Land
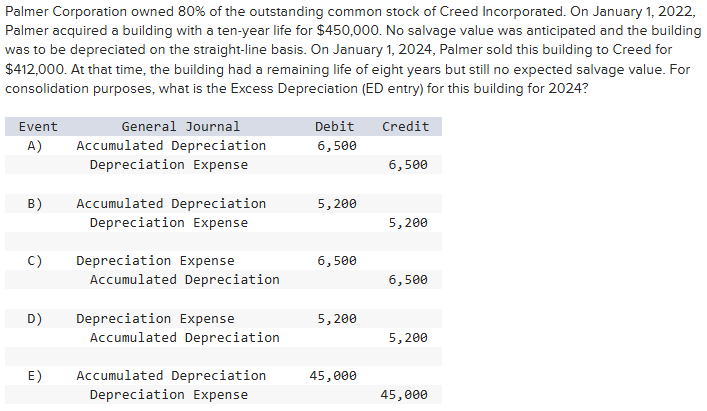
Option A
Option B
Option C
Option D
Option E
Option A
Explanation:
Transfer Cost $412,000 ÷ 8 years = $51,500 Annual Depreciation by Creed
Palmer Depreciation: (Cost ($450,000) − salvage value ($0)) divided by useful life (10 years) = $45,000
Depreciation expense should be decreased by $6,500.
All of the following are examples of variable interests except
guarantees of debt
stock options
lease residual value guarantees
participation
assets purchase options
stock options
Which of the following statements regarding consolidation of a Variable Interest Entity with its primary beneficiary is true?
The consolidation of a Variable Interest Entity with its primary beneficiary requires the business enterprise to follow a separate process than the one required for consolidations based on voting interests.
All intra-entity transactions between the primary beneficiary and the Variable Interest Entity are included in the consolidation.
Only intra-entity transactions between the primary beneficiary and the Variable Interest Entity resulting from intra-entity transfers are eliminated in the consolidation.
Variable Interest Entities with controlling interests must include one hundred percent of the primary beneficiary’s net income in a consolidation.
The allocation of the Variable Interest Entity’s net income is based on an analysis of the underlying contractual arrangements between the primary beneficiary and other holders of variable interests.
The allocation of the Variable Interest Entity’s net income is based on an analysis of the underlying contractual arrangements between the primary beneficiary and other holders of variable interests.
Which of the following statements is false regarding the assignment of a gain or loss when an affiliate’s debt instrument is acquired on the open market?
Subsidiary net income is not affected by a gain on the debt transaction.
Subsidiary net income is not affected by a loss on the debt transaction.
Parent Company net income is not affected by a gain on the debt transaction.
Parent Company net income is not affected by a loss on the debt transaction.
Consolidated net income is not affected by a gain or loss on the debt transaction.
Consolidated net income is not affected by a gain or loss on the debt transaction.
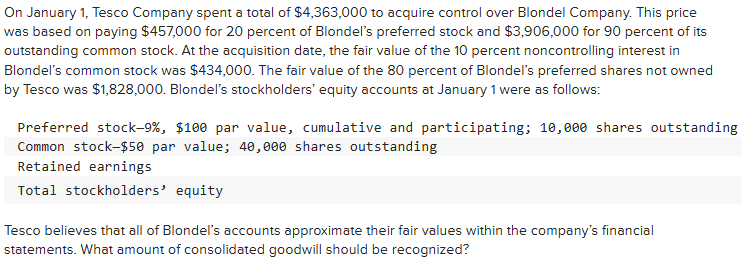
$435,000.
$892,000.
$321,500.
$457,000.
$435,000
Explanation:

Where do intra-entity transfers of inventory appear in a consolidated statement of cash flows?
They do not appear in the consolidated statement of cash flows.
Supplemental schedule of noncash investing and financing activities.
Cash flows from operating activities.
Cash flows from investing activities.
Cash flows from financing activities.
They do not appear in the consolidated statement of cash flows.
How would consolidated earnings per share be calculated if the subsidiary has no convertible securities or warrants?
Parent's earnings per share plus subsidiary's earnings per share.
Parent's net income divided by parent's number of shares outstanding.
Consolidated net income divided by parent's number of shares outstanding.
Average of parent's earnings per share and subsidiary's earnings per share.
Consolidated income divided by total number of shares outstanding for the parent and subsidiary.
Consolidated net income divided by parent's number of shares outstanding.
A subsidiary issues new shares of common stock at an amount below book value. Outsiders buy all of these shares. Which of the following statements is true?
The parent's additional paid-in capital will be increased.
The parent's investment in subsidiary will be increased.
The parent's retained earnings will be increased.
The parent's additional paid-in capital will be decreased.
The parent's retained earnings will be decreased.
The parent's additional paid-in capital will be decreased