5. small animal med- diseases of the stomach
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
what are the general clinical signs suggestive of gastric disease?
1. vomiting is the principle sign
2. hematemesis
3. melena
4. ptyalism
5. abdominal distention/pain
6. retching/burping
in general, what diagnostic testing is used to work up a patient with suspected gastric disease?
1. survey abdominal rads
2. ultrasound
3. endoscopy
4. surgery (take full thickness biopsies)
how are abdominal radiographs beneficial for investigating gastric disease?
serial studies sometimes required, can use contrast to evaluate motility or foreign body
what does ultrasound evaluate in patients with gastric disease?
-evaluates stomach wall layers
-deep ulceration
-masses
-perforation
how can endoscopy help with diagnosis of gastric disease?
visualization of stomach mucosa
can take gastric mucosal biopsies
what are the general disease of the stomach?
acute gastritis
chronic gastritis
foreign body
gastric erosion and ulceration
bilious vomiting syndrome
what is acute gastritis?
sudden onset of vomiting (<2 weeks) due to mucosal insult or inflammation
± hematemesis, dysrexia
abdominal pain and fever uncommon

What are the ddx categories of acute gastritis?
primary vs secondary
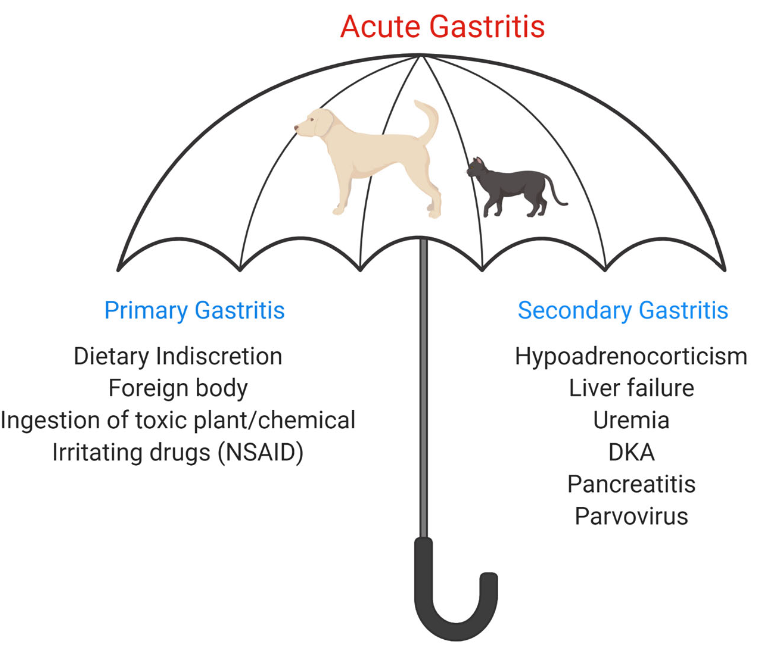
what are possible causes of primary acute gastritis?
-dietary indiscretion
-foreign body
-ingestion of toxic plant/chemical
-irritating drugs (NSAIDs)
what are possible causes of secondary acute gastritis?
-hypoadrenocorticism (addison's)
-liver failure
-uremia
-DKA
-pancreatitis
-parvovirus
HULPDP
how is acute gastritis diagnosed?
diagnostic plan depends on history and exam:
-at minimum abdominal radiographs +/- ultrasound (look for foreign material)
-rule out secondary GI disease (CBC/chem/UA/TT4)
± pancreatic lipase for acute pancreatitis, ± parvo test
how is acute, uncomplicated gastritis treated?
-tx of underlying condition
-no food for 24 hours, water in small amounts
-feed a highly digestible/low residue diet, small amounts, frequently (dogs GI low fat) then transition to normal diet over 5-7d
-use anti-emetic (maropitant) cautiously
-consider ondansetron for nausea
-consider SQ or IV fluids +/- electrolyte replacement if necessary
if a patient shows no improvement for treatment of acute uncomplicated gastritis, what should be done next?
if no improvement within 24-48 hours or if signs are recurrent, further testing and hospitalization should be offered
what should the diagnostic plan for chronic vomiting include?
-r/o secondary disease (CBC/chem/UA/TT4)
-r/o chronic pancreatitis (cPLI/fPLI)
-fecal flotation
-abdominal imaging to r/o pyloric outflow obstruction
-basal cortisol to screen for hypoadrenocorticism/addison's (dogs only)
-if normal, empirical deworming, elimination/hypoallergenic diet trial for tx of idiopathic gastritis
-No response to diet trial? endoscope with biopsy of stomach ± small intestine
what is chronic gastritis often seen in conjunction with?
chronic small intestinal disease (diarrhea, weight loss)
what are differentials for chronic gastritis/vomiting (primary GI)?
1. parasitic gastritis (Ollulanus tricuspis, physaloptera spp.)
2. idiopathic or allergic gastritis
3. gastric dysmotility/outflow obstruciton
which animals is ollulanus tricuspis seen in? how is it transmitted?
cats only
cat-to-cat transmission through ingestion of vomitus
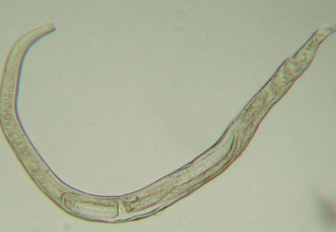
what gastric disease does ollulanus tricuspis cause in cats?
granulomatous gastritis
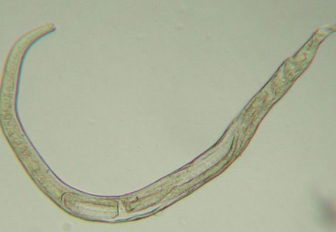
How is ollulanus tricuspis diagnosed in cats?
larvae detected in gastric juice or vomitus after centrifugation
find larvae or worms in histologic sections
CANNOT see on endoscopy (0.7mm -1.0mm in length)
how is ollulanus tricuspis treated?
fenbendazole 50mg/kg PO q24hrs x 5 days
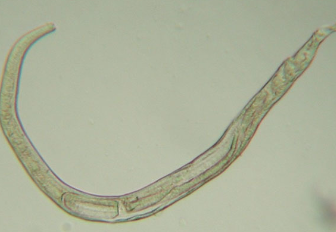
which animals does physalopteria spp. infect? how is it transmitted?
dogs and cats
animals become infected after ingestion of insect intermediate host or vertebrate prey
most common in Midwest
How is physaloptera spp. diagnosed?
manual removal during endoscopy
found in vomitus or on endsocpy (3-6 cm in length)
how are physalopteria spp. infections treated?
-manual removal during endoscopy
-pryantel pamoate 20mg/kg PO every 2 weeks for 3 treatments
empirical therapy with an anthelminthic is warranted in cases of unexplained gastritis
which animals is idiopathic or allergic gastritis more common in?
more common in cats (than dogs)
what is idiopathic/allergic gastritis?
lymphoplasmacytic (idiopathic) or allergic (eosinophilic) inflmmation
often associated with chronic small intestinal disease
how is idiopathic/allergic gastritis diagnosed?
endoscopic diagnosis preferred (look for mucosal inflammation)
how is idiopathic/allergic gastritis treated?
-elimination/hypoallergenic diet trial
-prednisone/prednisolone with gradual decrease to lowest effective dose (or budesonide)
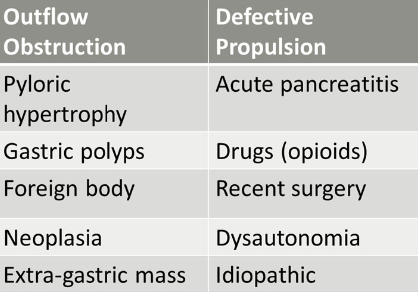
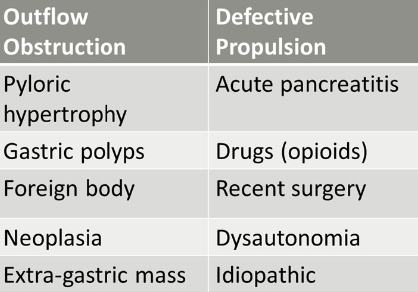
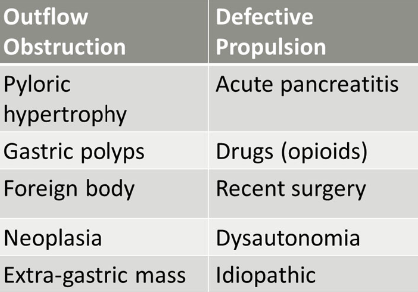
What are the general causes for delayed gastric emptying?
outflow obstruction
defective propulsion
what are causes of outflow obstruction causing delayed gastric emptying?
pyloric hypertrophy
gastric polyps
foreign body
neoplasia
extra-gastric mass

what are causes of defective propulsion causing delayed gastric emptying?
acute pancreatitis
drugs (opioids)
recent surgery
dysautonomia (rare)
idiopathic
when is delayed gastric emptying suspected?
suspected when pet vomits food >8hours after a meal
may see abdominal distention and bloat (without volvulus)
how is delayed gastric emptying diagnosed?
-abdominal rads to determine if gas or food bloat and evaluate for gastric/pyloric FB
-contrast rad study (evaluate stomach emptying over time, “beak” or “string” sign assoc with pyloric thickening)
-U/S to look for pyloric thickening
-endoscopy or full-thickness surgical biopsies
how is delayed gastric emptying treated?
-address outflow obstruction, if present
-address cause of defective propulsion, if present
-supportive care in acute cases (NG tube, aspirate stomach contents, trickle feed diet, oral cisapride or oral/CRI metoclopramide)
-critical patients IV eythromycin CRI
how do patients with pyloric hypertrophy present?
may be described as projectile vomiting that is often delayed (8-10 hours after eating)

what are the 2 types of pyloric hypertrophy?
1. muscular
2. mucosal
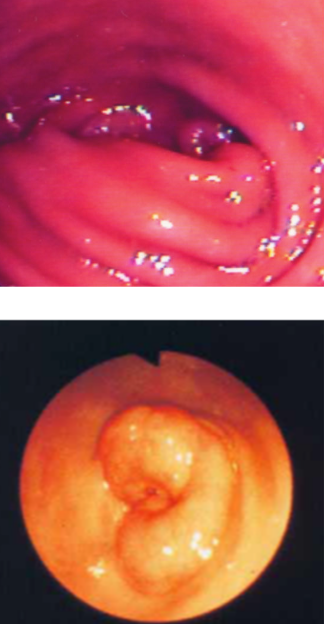
what is muscular pyloric hypertrophy?
hypertrophy of the pyloric sphincter
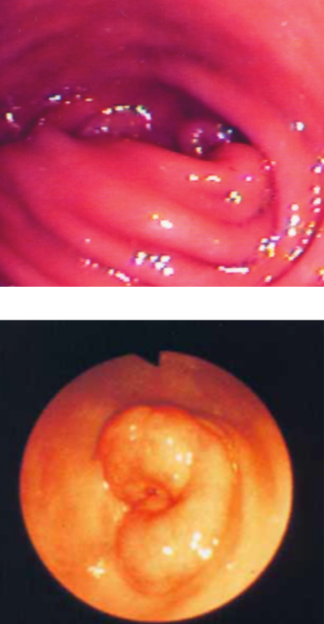
how do animals with muscular pyloric hypertrophy typically present?
vomiting shortly after weaning (true vomiting, not regurgitation)
young brachycephalic breeds overrepresented
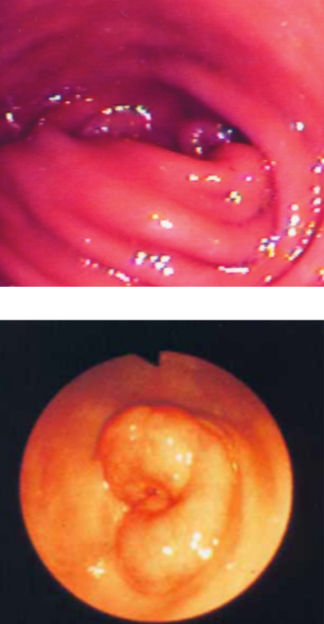
what is mucosal pyloric hypertrophy?
mucosal hypertrophy of the pylorus secondary to chronic inflammation and irritation
may be mistaken for neoplasia on U/S or endoscopy
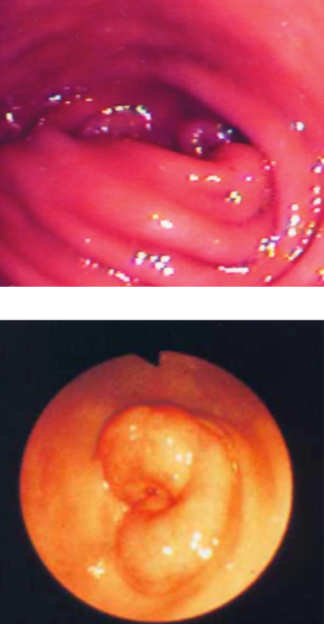
which animals most commonly get mucosal pyloric hypertrophy?
middle-to old-aged dogs, small, purebred (lhasa apso, shih tzu, mini poodle)
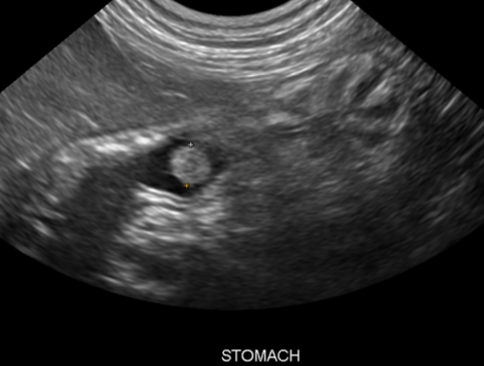
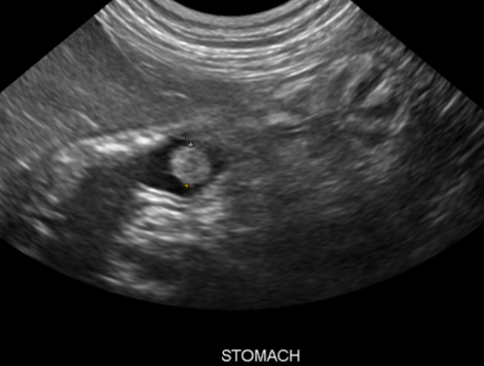
how is pyloric hypertrophy diagnosed?
abdominal ultrasound and/or radiographic barium contrast studies to document gastric rentention
how is pyloric hypertrophy treated?
-treat underlying cause of gastritis with mucosal hypertrophy
-often idiopathic/food-responsive gastritis
-anti-emetic to prevent vomiting
-feed highly digestible, low fat, caloric dense food
-may require surgery in severe cases
what surgical techniques are used to treat severe cases of pyloric hypertrophy?
-mucosal resection with mucosal hypertrophy
-pyloric opening techniques→ pyloromyotomy or gastroduodenostomy
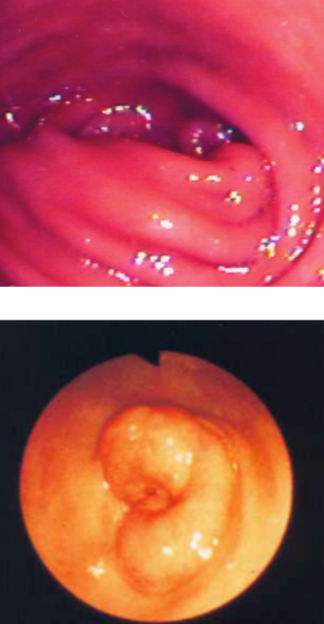
what are gastric polyps?
benign inflammatory masses in the stomach antrum, pylorus, and/or duodenum in cats (rarely dogs)
mostly in senior pets
what are clinical signs of gastric polyps?
-chronic vomiting and anorexia without weight loss
-can cause pyloric outflow obstruction
-ulceration of polyp can cause anemia, melena, hematemesis
What is the etiology of gastric polyps?
unknown etiology but often concurrent chronic gastritis
how are gastric polyps diagnosed?
-ultrasound (homogenous mucosal masses with normal wall layering)
-endoscopy (looks like cauliflower)
-histopathology to confirm
how are gastric polyps treated?
-need to remove polyps to relieve obstruction (endoscopic electrocautery or surgical removal)
-follow with a 4wk tapering course of prednisone
-consider hypoallergenic food for tx of chronic gastritis
what are clinical signs of gastric foreign bodies?
acute or chronic vomiting
- +/- hematemesis
- +/- dysrexia
- +/- diarrhea
look under the tongue of cats!
how are gastric foreign bodies diagnosed?
radiographs +/- ultrasound
serial radiographs may be needed if food in stomach
how are gastric foreign bodies treated?
-induce vomiting (unless caustic or sharp)
-endoscopic retrieval
-gastrotomy

which drugs are used to induce vomiting in dogs and cats?
dogs: apomorphine (0.05 mg/kg IV)
cats: dexmedetomidine (5-10 ug/kg IM)
what causes gastric erosion/ulceration?
almost always secondary to underlying disease or local irritation
rarely idiopathic in dogs and cats
What general categories of ddx cause gastric erosion/ulceration?
metabolic/endocrine, inflammatory, neoplastic, drug-induced, hypotension, idiopathic
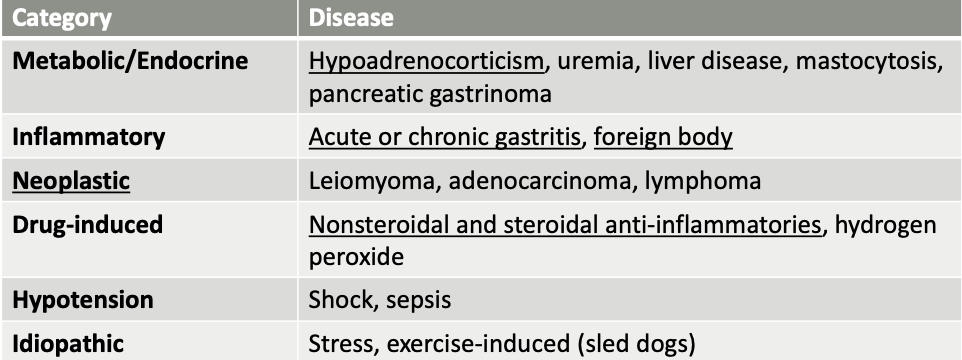
what are metabolic/endocrine causes of gastric erosion/ulceration?
hypoadrenocorticism (Addison’s)
uremia
liver disease
mastocytosis
pancreatic gastrinoma
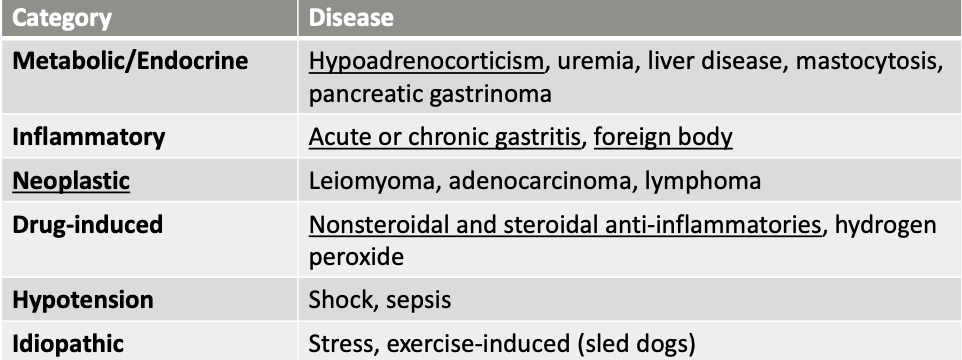
what are inflammatory causes of gastric erosion/ulceration?
acute or chronic gastritis
foreign body
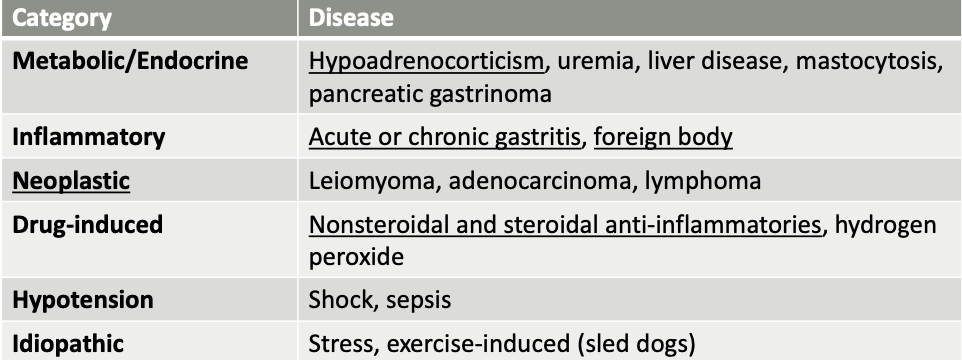
what are neoplastic causes of gastric erosion/ulceration?
leiomyoma
adenocarcinoma
lymphoma
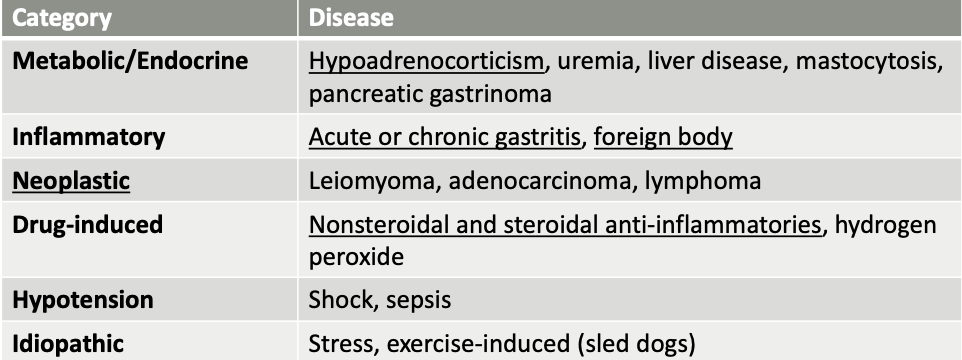
what are drug-induced causes of gastric erosion/ulceration?
Nonsteroidal and steroidal anti-inflammatories
hydrogen peroxide
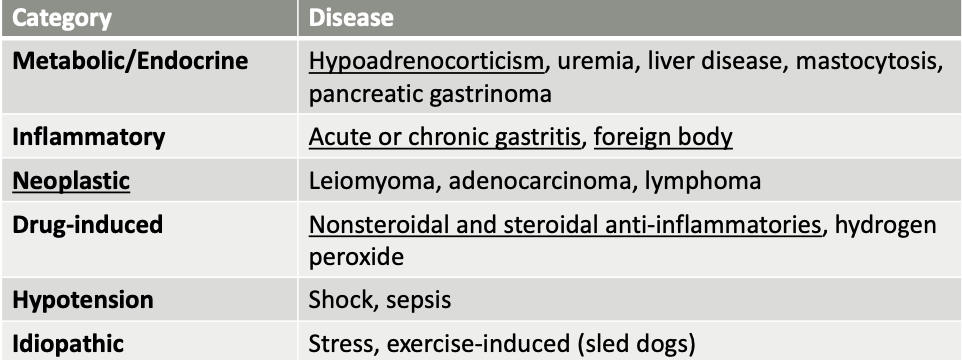
what hypotensive diseases can cause gastric erosion/ulceration?
shock, sepsis
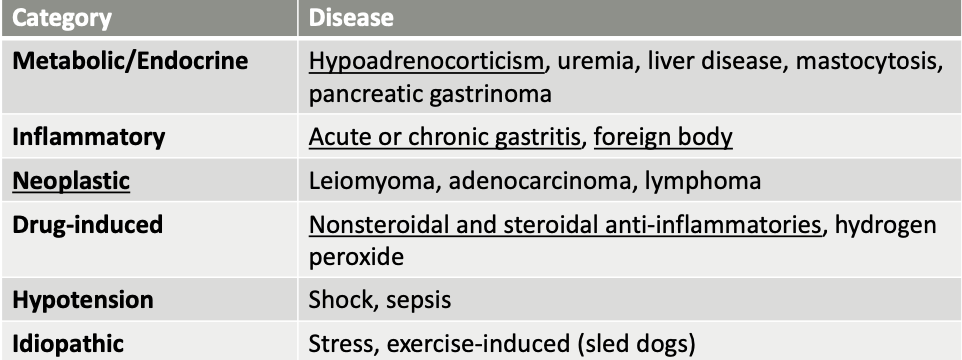
how common are idiopathic causes of gastric erosion/ulceration?
rare
seen in sled dogs from extreme exercise
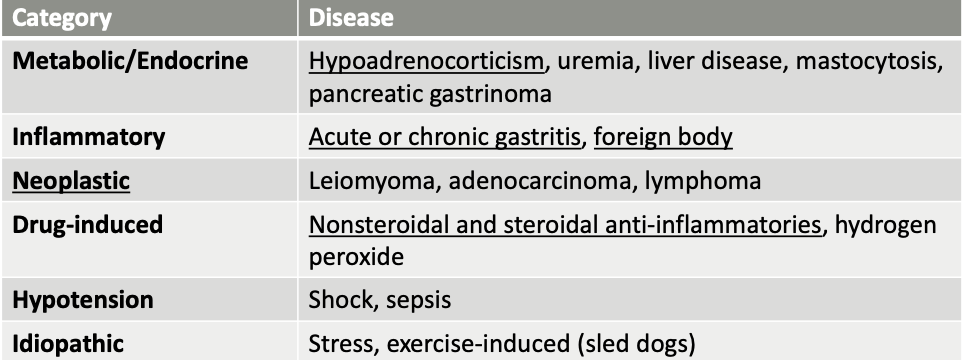
what clinical signs and lab findings should raise concern for gastric ulceration?
-hematemesis
-melena
-unexplained regenerative anemia
-iron deficiency anemia (chronic blood loss from GI tract)

how is gastric erosion/ulceration diagnosed?
-history (ask about steroids/NSAIDs, supplements - aspirin?)
-CBC/chem/UA
-abdominal imaging
-endoscopy
What type of anemia is seen with gastric ulceration and erosion?
chronic: microcytic, hypochromic non-regenerative anemia (iron deficiency anemia)
acute: regenerative anemia
how is gastric erosion/ulceration treated?
treat underlying etiology
suppress gastric acid secretion
-PPIs: omeprazole (oral) 1mg/kg BID or pantoprazole (IV)

can gastroprotectants be used as antiemetics?
no, gastroprotectants should NOT be used as antiemetics!
which animals is bilious vomiting syndrome seen in?
dogs only
young, mixed-breed, castrated male dogs
what is bilious vomiting syndrome?
early morning vomiting of bile without food
reflux of duodenal fluid into gastric lumen causing mucosal irritation
what is the treatment for bilious vomiting syndrome?
-late bedtime meal
-proton pump inhibitor
-prokinetic (metoclopramide, cisapride)