1. Slide Flaschcards
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key concepts from the lecture notes on electric charges, conductors/insulators, charging methods, and basic atomic structure.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Electric charge
A property of matter due to protons and electrons that leads to electric forces; measured in Coulombs.
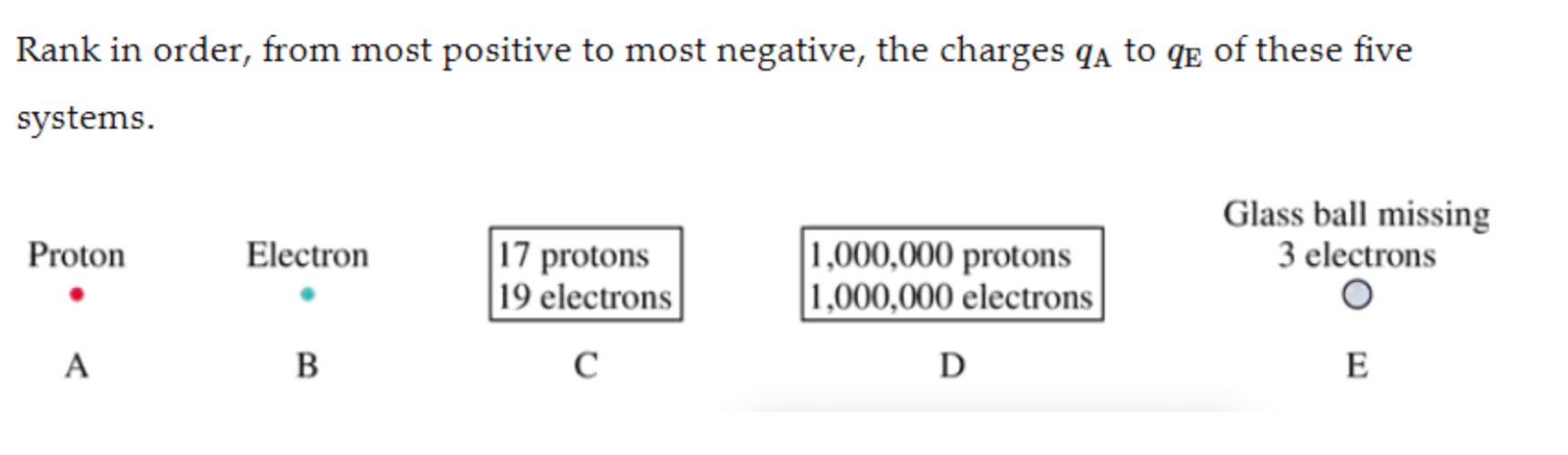
qE, qA, Qd, Qb, Qc
Measurement of electric charges
A rod attracts a positively charged hanging ball. The rod is
Negatively Charged
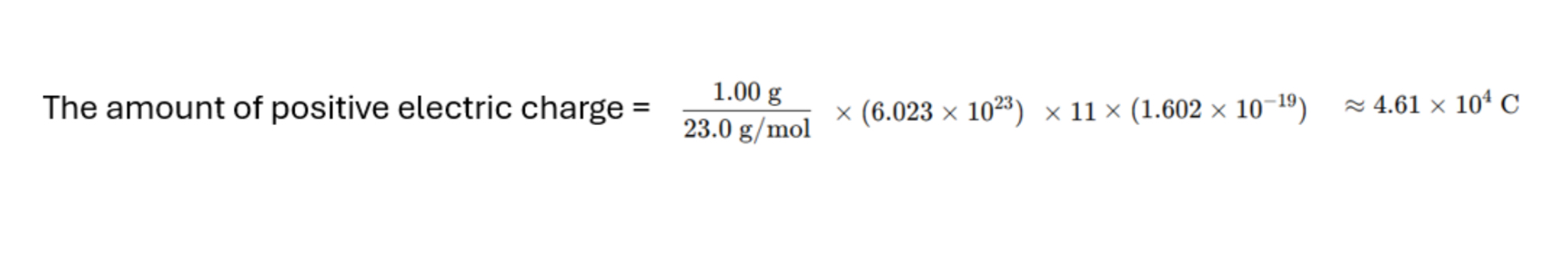
The amount of positive electric charge approx. = 4.61 × 10^4 C
Find the amount of positive electric charge in 1 gm of sodium (23Na)
atoms. (Note: The nucleus of a sodium atom contains 11 protons, and each mole contains 6.023 × 10²3 atoms)
Proton
Positively charged subatomic particle located in the atomic nucleus.
Electron
Negatively charged subatomic particle that orbits the nucleus.
Coulomb (C)
SI unit of electric charge; 1 C ≈ 6.24×10^18 elementary charges.
Elementary charge (e)
Fundamental unit of electric charge; magnitude of proton’s charge, e ≈ 1.6×10^-19 C.
q (or Q)
Net electric charge of an object; q = (Np − Ne) × e.
Charge quantization
Net charge of macroscopic objects is an integer multiple of the elementary charge e.
Neutral
Having no net electric charge (q = 0).
Positive charge
Charge carried by protons; attracts negative charges.
Negative charge
Charge carried by electrons; the sign is negative.
Conductor
Material through which electric charge moves easily (e.g., metals).
Insulator
Material in which electric charge is largely immobile (e.g., plastic, rubber).
Frictional charging (triboelectric effect)
Charging by rubbing; transfer of electrons between materials due to friction.
Charging by touching (conductive charging)
Charging a conductor by direct contact, allowing charge to flow onto/off the object.
Grounding
Connecting to Earth to redistribute or remove excess charge.
Ionization
Process of removing or adding electrons to atoms, creating ions.
Atom
Basic unit of matter consisting of a nucleus and surrounding electrons.
Nucleus
Central positively charged core of an atom containing protons (and neutrons).
Fundamental unit of charge
Symbolized by e; the smallest unit of electric charge (~1.6×10^-19 C).
Conservation of charge
Charge is neither created nor destroyed; total charge in a closed system remains constant.
Like charges repel
Two positive or two negative charges push away from each other.
Opposite charges attract
A positive and a negative charge attract each other.
Charge distribution on an isolated conductor
Excess charge resides on the surface; the interior field of a conductor at rest is zero.