Drainage Basin
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Tributaries
river or stream flowing into a larger river or lake
Drainage basin
area drained by a river and its tributaries.it’s an open system – it receives water and other external influences and discharges water and material out of the system
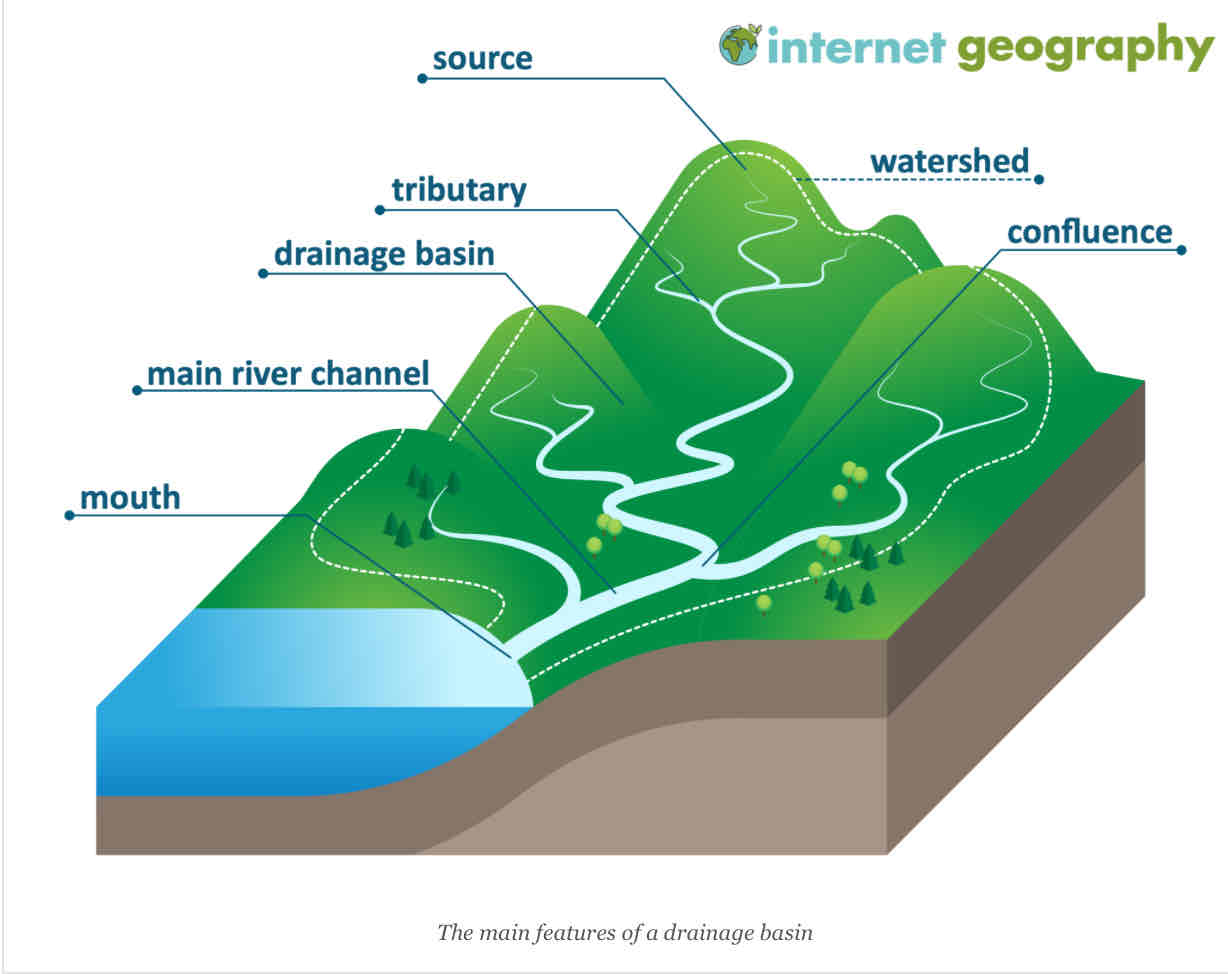
Source
The origin/ starting point of the river
Confluence
When a smaller river flows through and joins the bigger river
River system / Channel network
comprises a main river and all its contributing tributaries.
Watershed
the edge of a drainage basin. It’s a raised piece of land that separates one drainage basin from another.
Mouth
Where the river ends
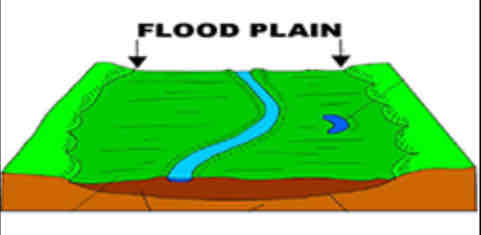
Floodplain
an area of low-lying ground adjacent to a river, formed mainly of river sediments and subject to flooding.
Open system
They allow for movement of energy and matter across its boundaries
Inputs
Precipitation, snow, rainfall, frost, hail and dew & irrigation water/use of desalinated water
Output
Evaporation
Infiltration (flow)
Water on the ground enters the soil
The infiltration capacity is the maximum rate at which rain can be absorbed by soil in a given condition
Overland Flow (surface runoff) (flow)
Unconfined flow of water above ground / occurs when precipitation exceeds infiltration rate
Percolation (Flow)
When water goes into the ground
Storages
Vegetation
Aquifers
Soil
Cryosphere
Vegetation
the water that is caught and stored by vegetation
Interception: Water retained by the plant /Precipitation that does not reach the soil, blocked by leaves.
Aquifers (permeable rocks that store groundwater inside)
Percolation
Process of underground water moving slowly through the ground
Water table
The upper surface of the infiltrated zone
Soil
Field capacity
Amount of water held in the soil
Wilting points
Minimum soil moisture content. Leading to permanent wilting
cryosphere (snow and ice environment)
The snow, glacier, permafrost, and frozen ground are significant storage and sources of freshwater
Transpiration
water evaporates into atmosphere through plants
Pool
a part of the river often characterized by slow-moving water
Base flow
the part of a river's discharge that is provided by groundwater seeping into the bed of a river. It is a relatively constant flow although it increases slightly following a wet period.
Aquifers
rock and sediment that stores groundwater