Carbonyl, carboxylic acids and esters
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Conditions for aldehyde oxidation:
60°
____ are easily oxidised but ____ are not
aldehydes
ketones
Aldehydes and ketones can be reduced to alcohols by ____
sodium tertahydridoborate (III) NaBH4 and heat and H20
equation for reaction between a ketone and NaBH4
CH3COCH2CH3 + 2[H]→ CH3CH(OH)CH2CH3
Aldehydes and ketones contain a ____ bond
polar C=O
Where is the partial positive and negative charge?
+ CARBON
- Oxygen
What part of ketones or aldehydes can be attached by nucleophiles?
partially positive carbon
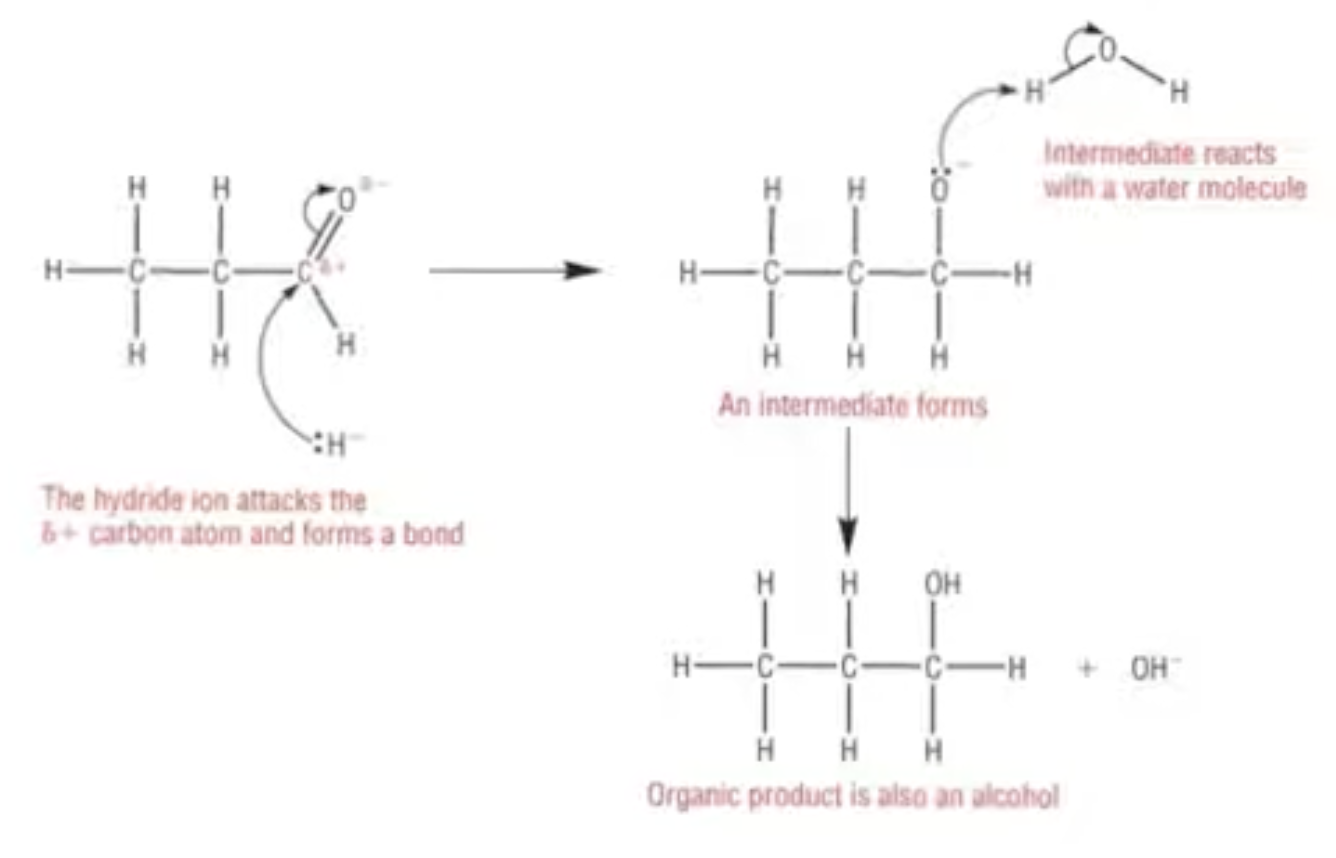
Mechanism for nucleophilic addition on aldehyde and ketones with :H- ion:
Hydride ion, from NaBH4:
Ketones/aldehydes reaction with hydrogen cyanide + what forms?
hydroxynitride
cn-
how is reaction carried out?
in alkaline solution containing potassium cyanide. alkaline solution is needed to generate nucleophile :CN-
How can presence of C=O can be detected?
2,4-dinitrophenylhrazine (2,4-DNP)
How to make bradys reagent and what colour is it?
4-DNP is dissolved in methanol + sulphuric acid
pale orange solution
What forms if a carbonyl group is present if Brady’s reagent is added?
orange ppt
ppt can be used further to identify original aldehyde?
filtering, purifying and drying, measuring melting temperature
What is the other name of Tollen’s reagent?
silver nitrate in aq ammonia
What happens when reacted with aldehyde?
colourless solution of silver complex is reduced to metallic silver when it oxidises an aldehyde.
Silver mirror
equations for tollens reagent
Ag+ (s) + e- —> Ag (s)
R-C(H)=O +[O]—> R-C(OH)=O
Why do shorter chain carboxylic acids dissolve readily in water?
form hydrogen bonds with water
Solubility of carboxylic acids ____ as chain length ____ because ____
decreases
increases
chain is hydrophobic
Why is -OH group in carboxylic acids more acidic than -OH group in alcohols?
C=O group pulls electrons away from -OH group, making hydrogen atom more partially positive and therefore easier to remove
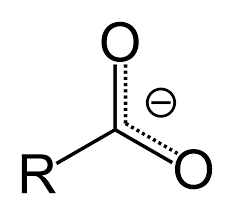
what forms when H is removed from carboxylic acid group?
charge and double bond character is shared evenly across both oxygen atoms
equation of carboxylic acid reaction with alkali:
CH3COOH (aq) + NaOH (aq) —> CH3COO-Na+ (aq) + H2O
equation of carboxylic acid and metal oxide:
2CH3COOH(aq) + CaO (s) —> (CH3COO-)2Ca2+ + H2O
equation of carboxylic acid and metal carbonate:
2CH3COOH(aq) + CaCO3 (aq) —> (CH3COO-)2Ca2+ +CO2 + H2O
What is used to differentiate between carboxylic acids and phenols?
Metal carbonates as carboxylic are acidic enough
Hydrolysis definition:
reaction were water breaks chemical compound into compounds. H and OH in water molecules become incorporated into 2 compounds
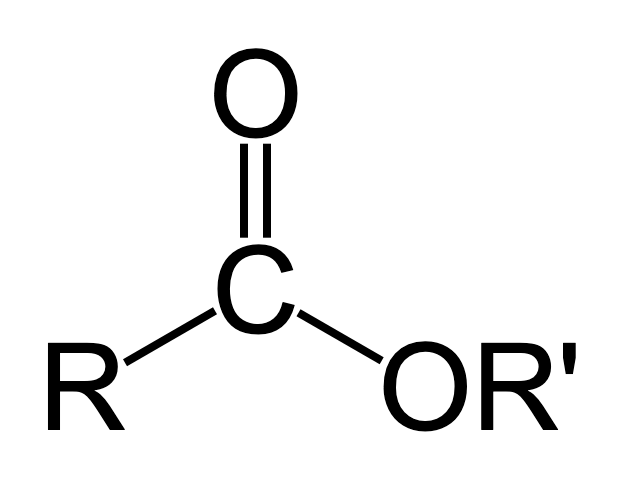
ester display formula
acyl chloride display formula
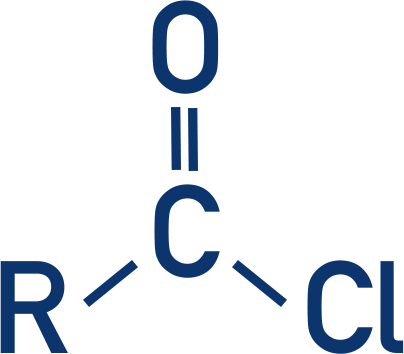
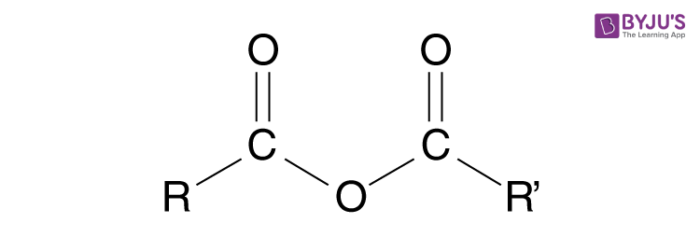
acid anhydride display formula
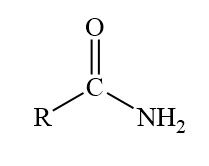
amide display formula
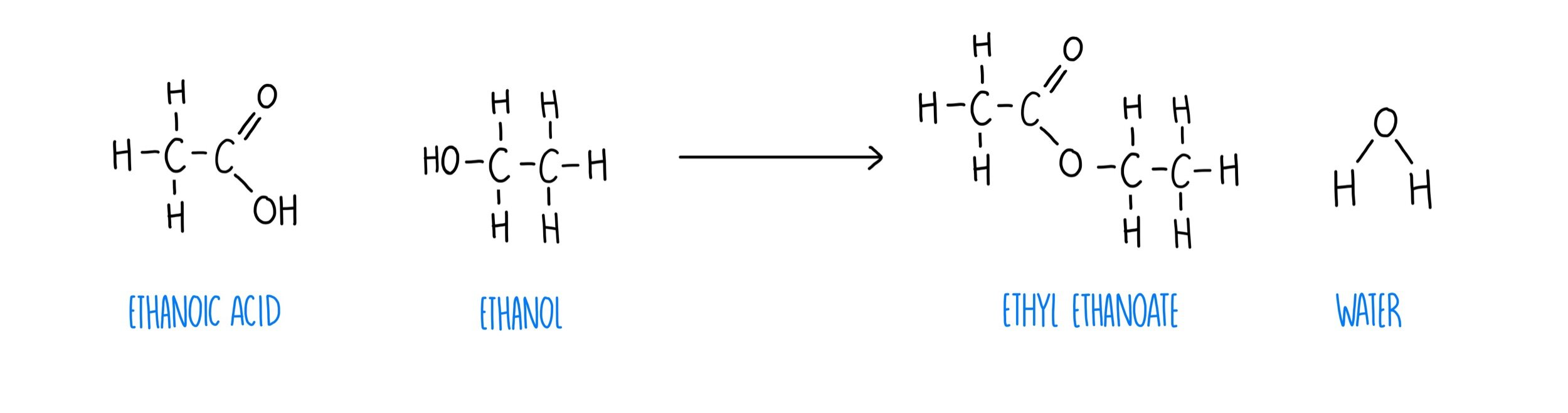
carboxylic acids react with alcohols to make an ___ + conditions needed
ester
heat + acid catalyst
alcohol and carboxylic acid to ester
how are esters named?
1st part: ____thyl derived from alcohol
2nd part: ____oate derived from acid
Hydrolysis is the opposite of _____
esterification
How to carry out acid hydrolysis?
ester+ water+ warm + sulphuric acid catalyst
reaction doesn’t go to competition
CH3COOCH2CH3 + H2O —>< CH3COOH + CH3CH2OH
What is alkaline hydrolysis?
1st reaction goes to completion, rather than reaching equilibrium
Forms a carboxylate salt
CH3CH2COOCH3 + NaOH —> CH3CH2COO-Na+ + CH3OH
carboxylate salt can be made in carboxylic using dilute acid
CH3CH2COO- + H+ —> CH3CH2COOH
Acyl chloride group
COCl
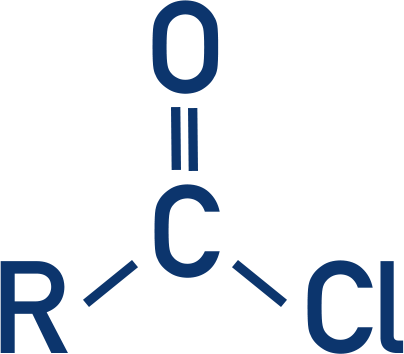
What suffix is used for things with acyl chloride group?
-oyl chloride
How are acyl chlorides formed?
carboxylic acids + thionyl chloride (SOCl2)
equation for formation of acyl chloride
CH3CH2COOH + SOCl2 —> CH3CH2COCl +SO2 + HCl
What are the partial charges of acyl chlorides?
carbon atom of C=O group is partially pos and O and Cl are partially neg
what is leaving group of acyl chlorides and why?
Cl because C-Cl bond isn’t very strong
what are acyl chlorides susceptible to?
nucleophilic attack, in addition-elimination reaction
general equation of substitution of chlorine atom by nucleophile:
ROCl + Nu- —> RCONu + Cl-
How does acyl chloride react with water?
vigorous
equation for acyl chloride with water
CH3COCl —H20—> CH3COOH + HCl
acyl chlorides reaction with alcohols?
react rapidly
produce ester and misty fumes of hydrogen chloride
e.g. of reaction of acyl chlorides and alcohol
CH3COCl —CH3OH—> CH3CH(O)OCH3 + HCl
ethanoyl chloride —> methyl ethanoate + hydrogen chloride
acyl chlorides reaction with phenol
reactive enough to react with acyl chlorides
CH3COCl + HO(C6H5) —> CH3COO(C6H5) + HCl
ethanoyl chloride + phenol —> phenyl ethanoate + hydrogen chloride
acyl chlorides reaction with ammonia
nitrogen atom in ammonia has lone pair, used for nucleophilic attack on C=O group. Produces amide and hydrogen chloride
equation of acyl chloride and ammonia
CH3COCl —NH3—> CH3CONH2 + HCl
what further reaction occurs when hydrogen chloride reacts with excess ammonia
HCl + NH3 —> NH4Cl
overall reaction:
CH3COCl —2NH3—> CH3CONH2 + NH4Cl
ethanoyl chloride —> ethylamide + ammonium chloride
amide vs amine
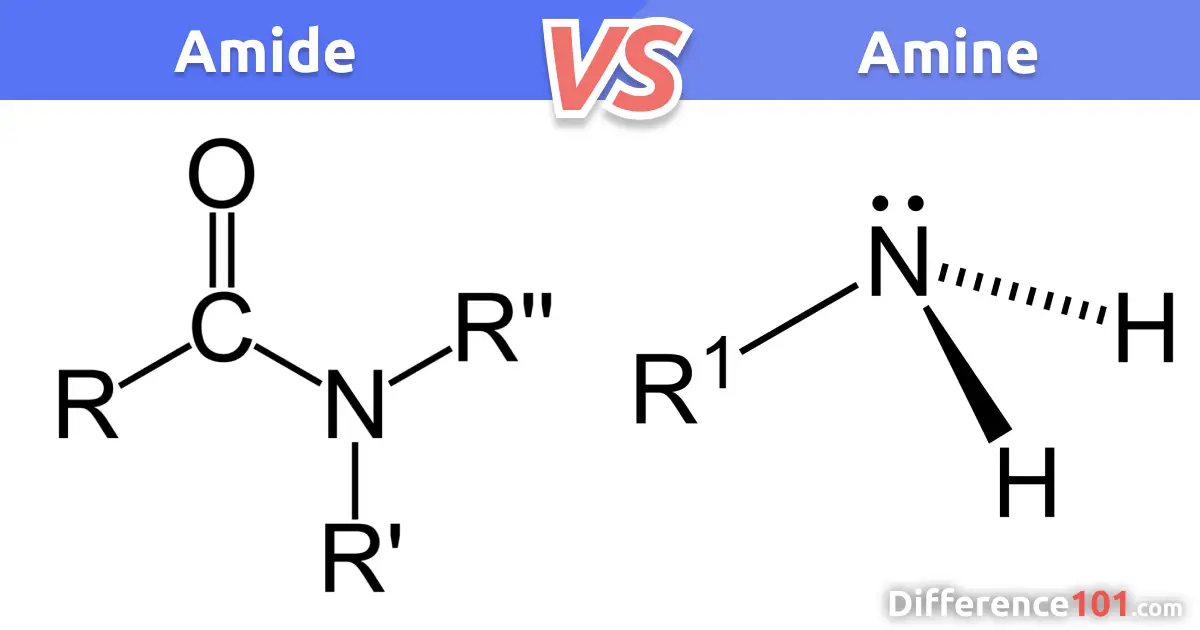
reaction of amines and acyl chloride
react same way as with ammonia
product is substituted amide (N-substituted amide)
equation of amines and acyl chloride
CH3CH2COCl + :NH2(CH3) —> CH3CH2C(O):NHCH3 + HCl
propanoyl chloride + methylamine —> N-methylpropanamide + hydrogen chloride
if secondary amine is used then product contains two substituted alkyl groups equation:
CH3CH2COCl + :NH(CH3)CH3 —> CH3CH2C(O):N(CH3)CH3 + HCl
N,N-dimethylprioanamide
What happens if tertiary amine?
reaction does not happen

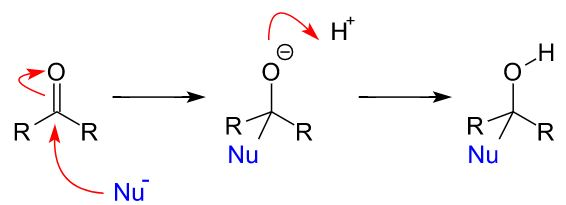
General Mechanism of aldehyde with nucleophile:
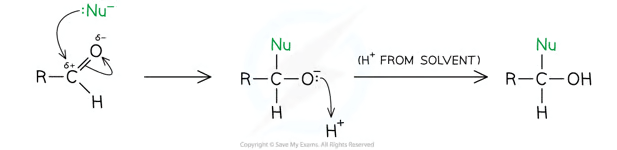
General Mechanism of a ketone:

Addition of HCN to carbonyl compounds + name:
The products of the reaction are hydroxynitriles
The nitrile group is the priority functional group so it is attached to carbon 1 and results in the suffix -nitrile
The hydroxyl group is not the priority functional group so the hydroxyl group is named using the hydroxy- prefix, rather than the -ol suffix
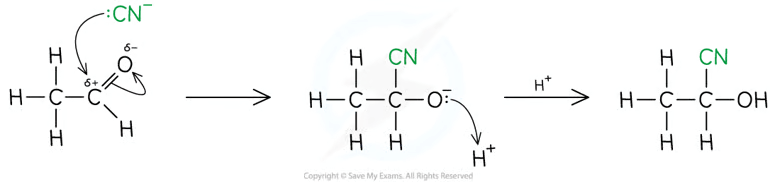
Reduction of Carbonyls:
There are a large number of reducing agents which will reduce both an aldehyde and a ketone to an alcohol
Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced to secondary alcohols
Possibly the most common reducing agent for this is sodium tetrahydridoborate, NaBH4
You may also see this named as sodium borohydride in some sources
In an aqueous solution, NaBH4 generates the hydride ion nucleophile, :H-
The hydride ion will reduce a carbonyl group in an aldehyde or a ketone, but is not strong enough to reduce a C=C double bond
This is because it is attracted to the C in the C=O bond, but is repelled by the high electron density of the C=C bond
When this reaction takes place, it is an example of a nucleophilic addition reaction
Carboxylic acid to a primary alcohol:
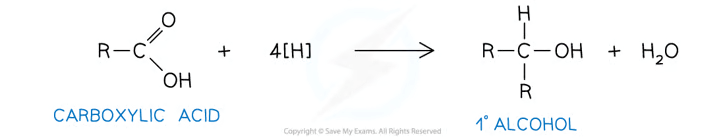
Aldehyde to a primary alcohol:

Ketone to a secondary alcohol:

__________ is a reagent which detects the presence of carbonyl compounds
2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (also known as 2,4-DNP)
The carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones undergoes a ________ reaction with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine
condensation
The product formed when 2,4-DNPH is added to a solution that contains an aldehyde or ketone is a ______ which can be purified by recrystallisation
deep-orange precipitate
The _______ of the formed precipitate can then be measured and compared to literature values to find out which specific aldehyde or ketone had reacted with 2,4-DNPH
melting point
Tollens' reagent contains the silver(I) complex ion ____
[Ag(NH3)2]+
Tollens' reagent forming
aqueous ammonia is added to a solution of silver nitrate
If gently warmed with Tollens' reagent, an ______ will become oxidised
aldehyde
how are esters made?
condensation reaction between a carboxylic acid and alcohol with concentrated H2SO4 as catalyst
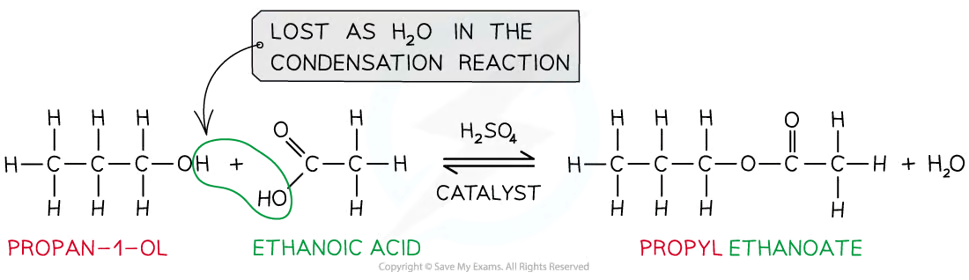
what is another way of esterification?
Esterification can also take place by reacting acid anhydrides with alcohols at room temperature
The acid anhydrides are more reactive than carboxylic acids
The reaction is not reversible and a higher yield is achieved.

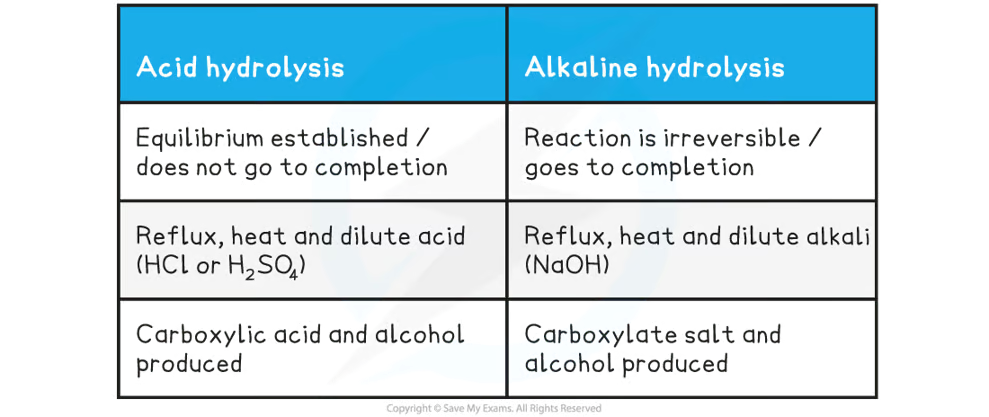
Esters can be _____ to reform the carboxylic acid and alcohol by either dilute acid or dilute alkali and heat
hydrolysed
When an ester is heated under reflux with dilute acid (eg. sulfuric acid) what occurs + why?
an equilibrium mixture is established as the reaction is reversible
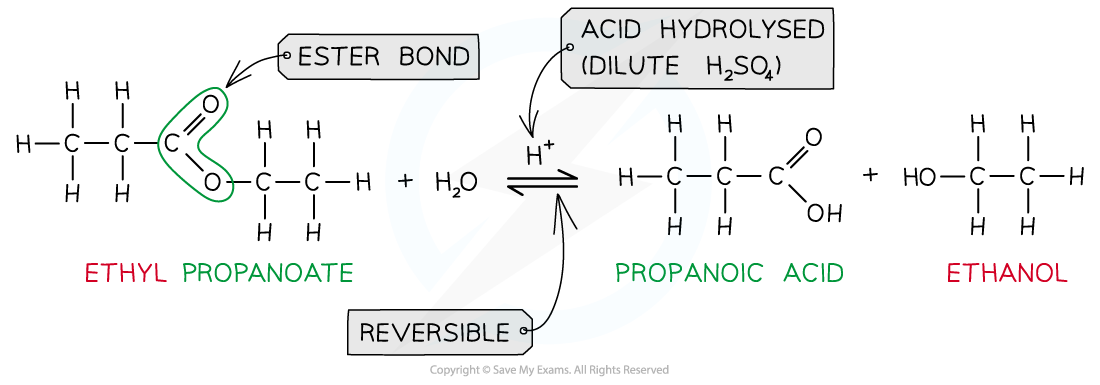
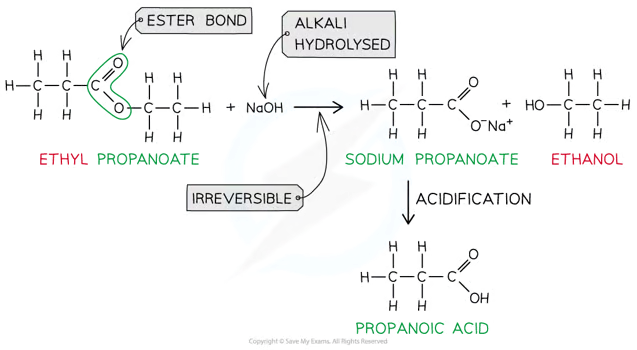
heating the ester under reflux with dilute alkali (eg. sodium hydroxide) is an _____ reaction as the ester is fully hydrolysed and what forms?
irreversible
sodium carboxylate salt which needs further acidification to turn into a carboxylic acid
hydrolysis of acyl chlorides
formation of a carboxylic acid and HCl
addition-elimination reaction:
A water molecule adds across the C=O bond
A hydrochloric acid (HCl) molecule is eliminated

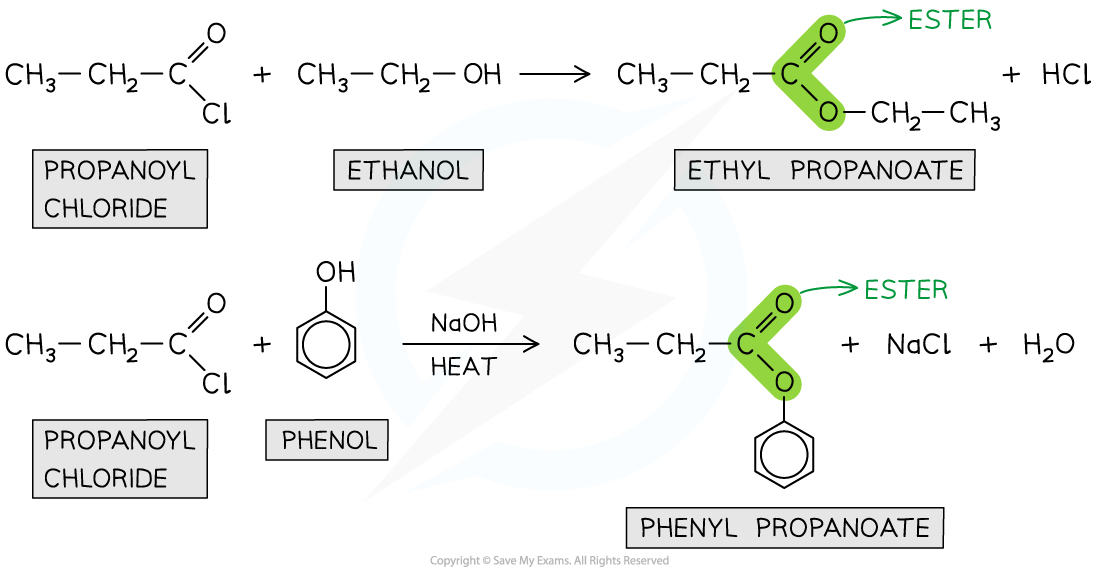
Formation of esters from Acyl chlorides
react with alcohols and phenols to form esters
reaction with phenols requires heat and a base
Esters can also be formed from the reaction of carboxylic acids with phenol and alcohols however, this is a slower reaction as carboxylic acids are less reactive and the reaction does not go to completion (so less product is formed)
The esterification of acyl chlorides is also an addition-elimination reaction
The alcohol or phenol adds across the C=O bond
A HCl molecule is eliminate
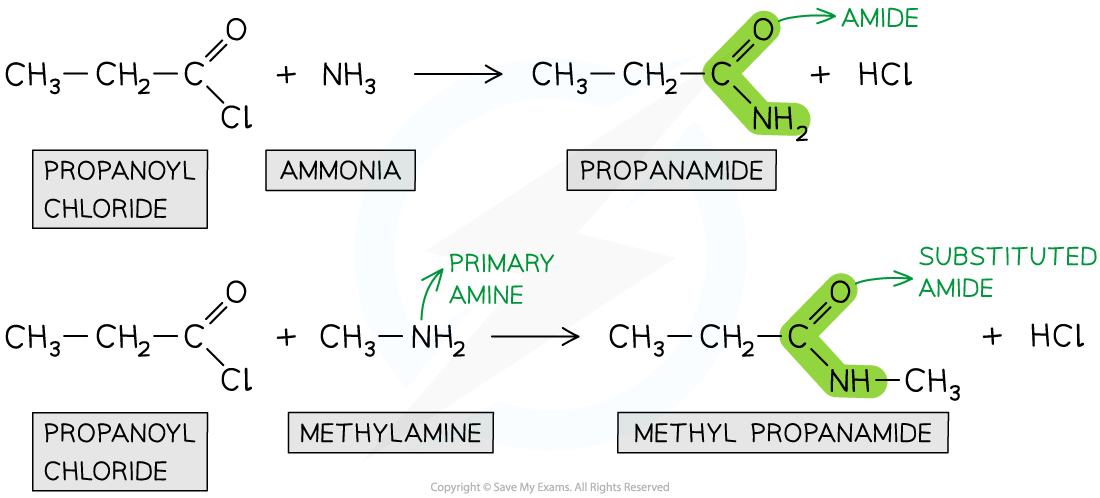
Formation of amides
Acyl chlorides can form amides from their condensation reaction with amines and ammonia
The nitrogen atom in ammonia and amines has a lone pair of electrons which can be used to attack the carbonyl carbon atom in the acyl chlorides
The product is a primary amide (when reacted with ammonia) or secondary amide (when reacted with primary amines)
This is also an example of an addition-elimination reaction as
The amine or ammonia molecule adds across the C=O bond
A HCl molecule is eliminated
how to make ester into carboxylic acid hydrolysis?
heat + reflux + dilute acid
CN —> COOH
aqueous acid e.g. HCl(aq)/H2SO4(aq)