Understanding Employee Motivation in Organizations
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
What is the definition of motivation in the context of industrial psychology?
Motivation is defined as the internal force that drives a worker to action, as well as the external factors that encourage that action.
What are the four key individual differences that influence employee motivation?
1. Personality 2. Self-esteem 3. Instinct Motivation Tendency 4. Need for achievement
What does the acronym OCEAN stand for in relation to personality?
OCEAN refers to the five major dimensions of personality: Openness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, and Neuroticism.
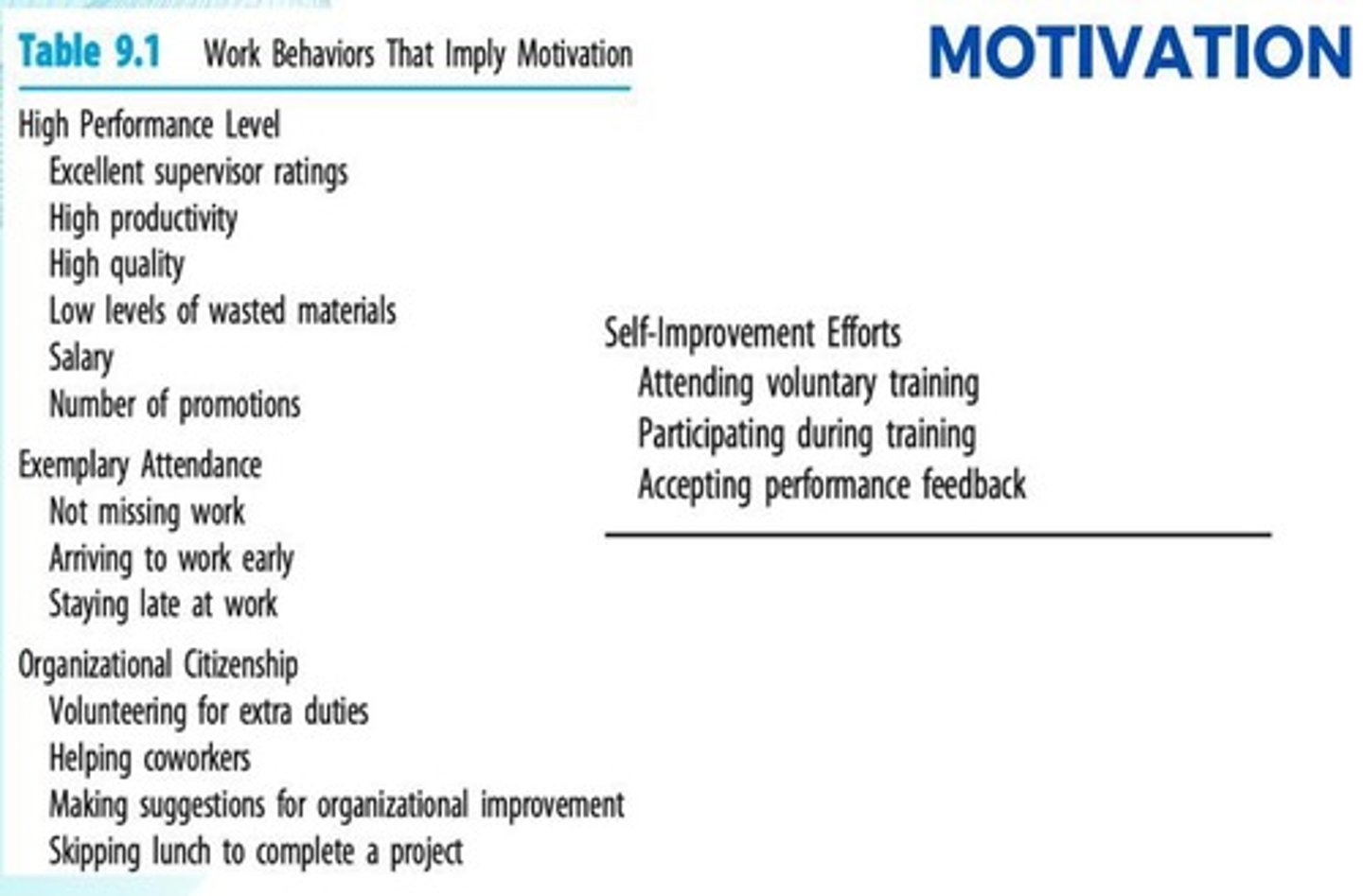
What are Organizational Citizenship Behaviors (OCBs)?
Behaviors that are not part of an employee's job but contribute to making the organization a better place to work.
How does self-esteem influence employee motivation?
Employees will be motivated to perform at levels consistent with their levels of self-esteem.
What is chronic self-esteem?
Chronic self-esteem is a long-term sense of confidence that does not change over time.
What is situational self-esteem?
Situational self-esteem refers to the ability to feel confident based on a specific situation or task, also known as 'self-efficacy'.
What is socially influenced self-esteem?
Socially influenced self-esteem depends on whether social norms are met and does not work independently.
What are the conditions under which employees will be highly motivated according to various theories?
Employees will be highly motivated if: 1. They have a motivating personality. 2. Their expectations are met. 3. The job aligns with their values. 4. They have achievable goals. 5. They receive feedback on goal attainment. 6. The organization rewards them fairly.
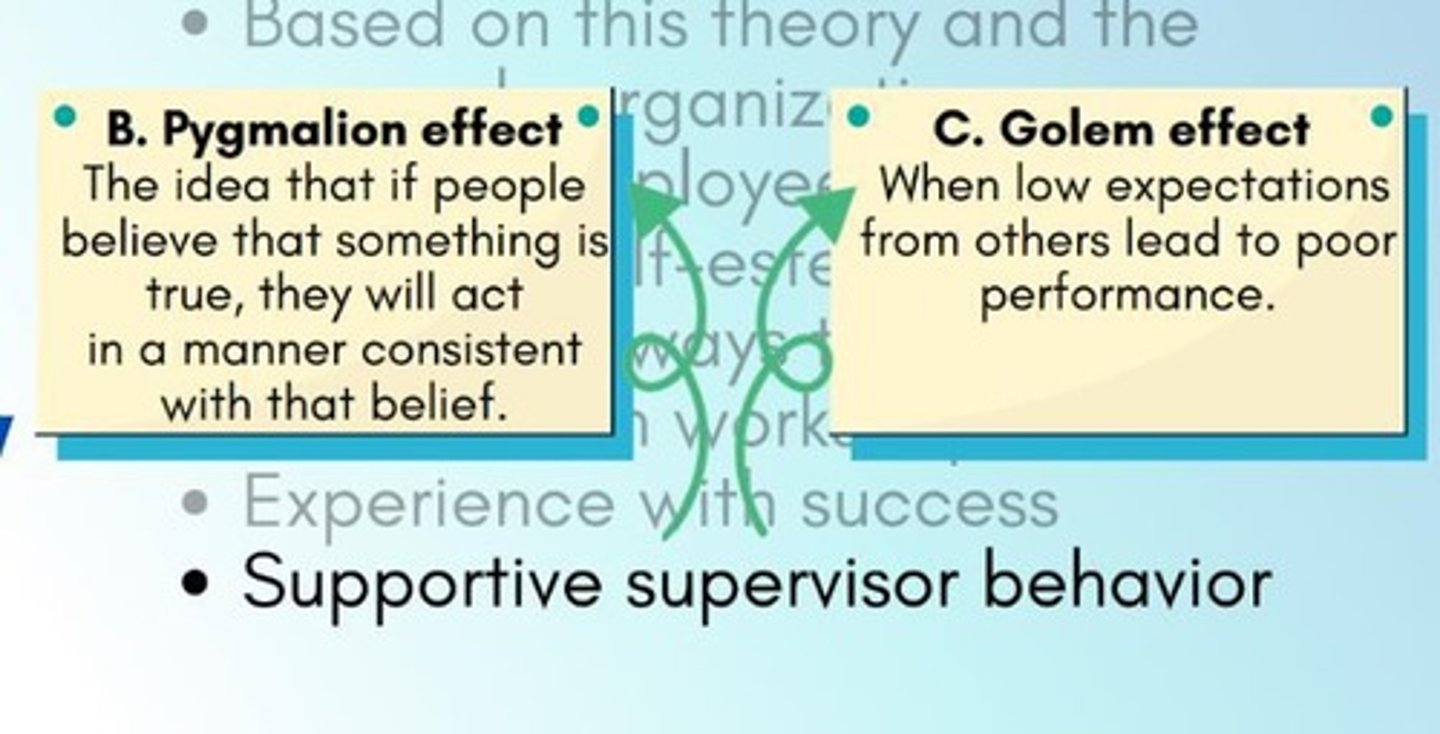
What is the Golem Effect?
The Golem Effect refers to the phenomenon where negative expectations from others can lead to decreased performance.
What is intrinsic motivation?
Intrinsic motivation is the drive to perform well because individuals genuinely enjoy the tasks or appreciate the challenge, independent of external rewards.
What is extrinsic motivation?
Extrinsic motivation arises from nonpersonal factors such as pay, coworkers, and opportunities for advancement.
What is the Work Preference Inventory (WPI)?
The Work Preference Inventory is a tool that measures an individual's orientation toward intrinsic versus extrinsic motivation.
Who developed the theory regarding the need for achievement, affiliation, and power?
The theory was developed by David McClelland in 1961.

What is the relationship between intrinsic motivation tendency and performance?
A high intrinsic motivation tendency is associated with high performance and productivity.
What are the three main ways organizations can improve employee self-esteem?
1. Self-esteem workshops 2. Experience with success 3. Supportive supervisor behavior.
What is the basic premise of consistency theory in relation to self-esteem?
Consistency theory posits that employees will be motivated to perform at levels consistent with their self-esteem.
How does job satisfaction relate to motivation?
Job satisfaction is subjective and enters when employees are motivated.
What role do coworkers play in employee motivation?
Employees are influenced by the motivation levels of their coworkers.
What does it mean for an employee's expectations to be met in the workplace?
It means that the employee's anticipated outcomes from the job align with their actual experiences.
What is the significance of achievable goals in employee motivation?
Achievable goals help ensure that employees feel capable of success, which can enhance their motivation.
What are the three needs according to trait theory that motivate individuals?
Need for achievement, need for affiliation, and need for power.
What does the need for achievement refer to?
The extent to which a person desires to be successful.
What characterizes individuals with a high need for affiliation?
They desire to be around other people and prefer teamwork.
What does the need for power indicate in trait theory?
The extent to which a person desires to be in control of others.
What is the self-fulfilling prophecy?
The phenomenon where expectations from others affect an individual's behavior, leading to outcomes that confirm those expectations.
What is the Galatea Effect?
The self-expectation that leads individuals to produce more positive outcomes based on their own beliefs.
What is the Pygmalion Effect?
The phenomenon where positive expectations from others lead to improved performance.
What is self-regulation in the context of behavior?
A person's ability to select, set, and modify goals to adapt to changing conditions.
What are the four steps in the self-regulation process?
1. Choose goals and set levels for each goal. 2. Plan how to accomplish those goals. 3. Take action toward accomplishing the goals. 4. Evaluate progress and adjust goals as necessary.
What is a realistic job preview?
An accurate representation of what a job will be like, provided to potential employees before or during employment.
What can happen if job expectations do not match reality?
It can hurt motivation and satisfaction.
What does job characteristics theory propose?
Certain characteristics of a job will make it more or less satisfying, depending on the worker's needs.
What are the key characteristics that make a job motivating according to job characteristics theory?
Skill variety, task identity, task significance, and autonomy.
How does skill variety contribute to job motivation?
It involves using various skills for the job, enhancing engagement and satisfaction.
What is task identity?
Knowing the identifiable tasks one is capable of completing from start to finish.
What does task significance refer to?
The meaningful impact of the task, not just for oneself but for others as well.
What role does autonomy play in job motivation?
It provides employees with control over how they perform their tasks.
What is an example of self-regulation in a simple task?
An employee sets a goal to write a 100-page report in 2 weeks, breaks it down into daily tasks, monitors progress, and adjusts as necessary.
What might an employee do if they are not meeting their progress goals?
They could change the goal, change their behavior, or increase their effort.
What is the importance of monitoring progress in self-regulation?
It allows individuals to evaluate their performance and make necessary adjustments to achieve their goals.
How can supportive supervisors affect employee motivation?
By providing the right praises and support, which can enhance self-esteem and motivation.
What is the impact of procrastination on self-regulation?
Self-regulation in work helps avoid procrastination, leading to better goal attainment.
What factors influence employee motivation toward a goal?
Motivation often depends on how well the job matches what employees want, value, and expect.
What is the psychological contract in the workplace?
It refers to the expectations employees have in mind about their job, which may not be formally documented.
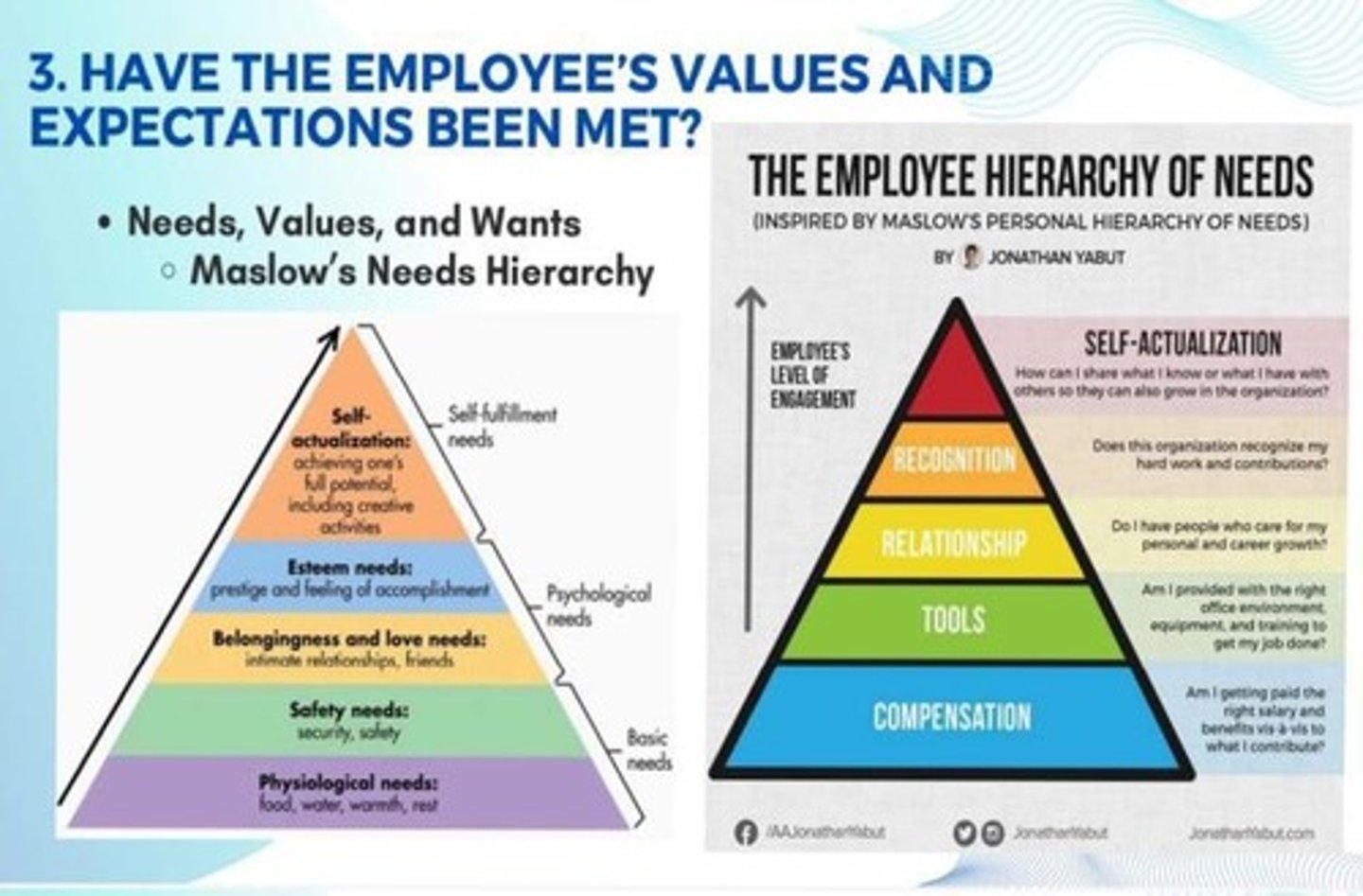
What are the three theories that focus on employees' needs and values?
Maslow's Needs Hierarchy, ERG Theory, and Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory.
What are hygiene factors in Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory?
Job-related elements that prevent dissatisfaction but do not motivate, such as compensation and safety.
What are motivators in Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory?
Elements of a job that concern the actual duties performed by the employee and lead to true motivation.
What is the relationship between hygiene factors and motivation?
Adequate hygiene factors prevent dissatisfaction, but only motivators create true motivation.
What is the SMART criteria for goal setting?
Goals should be Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
Why are measurable goals important?
They allow tracking of progress and success, making the path to achievement clearer.
What does ERG Theory stand for?
Existence, Relatedness, and Growth, which are three levels of needs.
What happens when higher-level needs are blocked according to ERG Theory?
People may focus more on lower-level needs, such as pay or security.
What is the importance of setting achievable goals?
Goals should be challenging yet realistic to avoid discouragement or unethical behavior.
What is the significance of time-bound goals?
They work best when there is a set time frame for completion, helping prioritize tasks.
What does research say about employee participation in goal setting?
Participation does not significantly improve performance but increases commitment to achieving the goal.
What is the impact of delayed feedback on performance?
It weakens the connection between the action and its consequence, reducing its impact on performance.
What is the role of feedback in employee motivation?
Feedback helps employees understand their progress and adjust their efforts toward achieving goals.
How does a mismatch between an employee's needs and job offerings affect motivation?
It can lead to low levels of motivation and job satisfaction.
What is the effect of micromanagement on employee motivation?
It can reduce motivation by limiting employees' freedom and autonomy.
How can goal setting increase employee motivation?
By providing clear targets, such as improving attendance or boosting sales.
What are the levels of satisfaction in ERG Theory?
Existence, Relatedness, and Growth.
What is the relationship between goals and employee success?
Goals must be perceived as possible to motivate employees toward success.
What is the significance of aligning goals with employee responsibilities?
Relevant goals associated with the employee's job enhance motivation and satisfaction.
What does Herzberg's theory suggest about job satisfaction?
It posits that job satisfaction is influenced by both hygiene factors and motivators.
What is the principle of contingency of consequences in employee motivation?
Rewards or punishments must be directly connected to specific behaviors to effectively influence and shape future actions.
How does the timing of incentives affect their effectiveness?
Incentives are most effective when given immediately after the behavior.
What is the Premack Principle in the context of motivation?
The idea that more preferred activities can be used to reinforce less preferred activities.
What types of rewards can be used to motivate employees?
Supervisors should use a variety of incentives, including financial, non-financial, and social rewards.
What is the significance of feedback in the goal-setting process?
Feedback should be provided to employees on their progress, making it specific to their behavior to increase effectiveness.
What is the reinforcement hierarchy?
A rank-ordered list of reinforcers for an individual, from most preferred to least preferred.
How do financial rewards motivate employee performance?
They can be part of an employee's compensation package or used as bonuses for achieving specific goals.
What is performance pay?
A system where employees are paid based on their individual production.
What is merit pay?
An incentive plan where employees receive pay bonuses based on performance appraisal scores.
What is the role of individual-based versus group-based incentives?
Individual incentives reward personal performance, while group-based incentives reward collective performance.
How should feedback be delivered to employees for it to be effective?
Feedback should be positive and informational rather than negative and controlling.
What is the relationship between effort and outcome in Vroom's theory of motivation?
Expectancy is the perceived relationship between the amount of effort an employee puts in and the resulting outcome.
What is the impact of recognizing performance on employee motivation?
Recognizing performance can enhance motivation by reinforcing positive behaviors.
What are incentive insecurities?
Concerns or doubts employees may have regarding the effectiveness or fairness of incentive programs.
How does the preference for certain activities affect reinforcement?
If an employee prefers an activity, it is more likely to reinforce their behavior, reducing the likelihood of less preferred activities.
What is the importance of clear communication regarding rewards?
It is essential for employees to understand what specific behaviors led to their rewards.
How can supervisors ensure that incentives are effective?
By being trained to use a variety of incentives tailored to different employee motivations.
What are the consequences of not providing timely feedback to employees?
Lack of timely feedback can diminish the effectiveness of goal setting and motivation.
What is the relationship between motivation and expectancy?
Higher motivation correlates with a stronger belief in one's ability to achieve desired outcomes.
What types of behaviors can incentives target?
Incentives can target behaviors such as good attendance, high performance, accident avoidance, referrals, or employee retention.
What is the effect of punished or ignored behaviors according to operant conditioning?
Punished or ignored behaviors are likely to decrease or disappear.
What is instrumentality in the context of performance evaluation?
The extent to which the outcome of a worker's performance, if noticed, results in a particular consequence.
What are group incentive plans designed to do?
Motivate a team, department, or entire organization by tying rewards to collective performance rather than individual output.
What is profit sharing?
A system that provides employees with a percentage of profits above a certain amount.
What does valence refer to in motivation theory?
The extent to which an employee values a particular consequence or reward.
What is gain sharing?
A group incentive system where employees receive a bonus based on improvements in group productivity.
How can punishment be used to change employee performance?
By punishing undesired behaviors instead of rewarding desired ones, such as suspending employees for low performance.
What are stock options in the context of group incentives?
A method where employees are given the option to buy stock in the future at the price when the options were granted.
What is the expectancy theory proposed by Victor Vroom?
A theory suggesting that if veteran employees are positive about their jobs, new employees are likely to mirror that positivity.
What is equity theory in job satisfaction?
A theory stating that employees will be satisfied if their ratio of effort to reward is similar to that of other employees.
What are inputs in equity theory?
Elements that employees put into their jobs, such as effort, time, experience, and loyalty.
What are outputs in equity theory?
What employees get from their jobs, including salary, benefits, and promotions.
What is the input/output ratio?
The comparison of how much employees believe they put into their jobs versus what they believe they receive.
What is organizational justice?
A theory that suggests employees who perceive fair treatment are more likely to be satisfied and motivated.
What are the three types of justice in organizational justice?
Distributive Justice (outcome fairness), Procedural Justice (process fairness), and Interactional Justice (treatment respect).