The Psychodynamic Approach
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
36 flashcards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What is the assumption of the Psychodynamic approach?
experiences in early childhood play a key role in determining an individual's mental/emotional state and outcomes in later life
there are vast swathes of the mind that are inaccessible to conscious awareness e.g Freud used the metaphor of an iceberg to explain the different levels of consciousness
What are the three levels in the mind?
Conscious mind, preconscious and unconscious
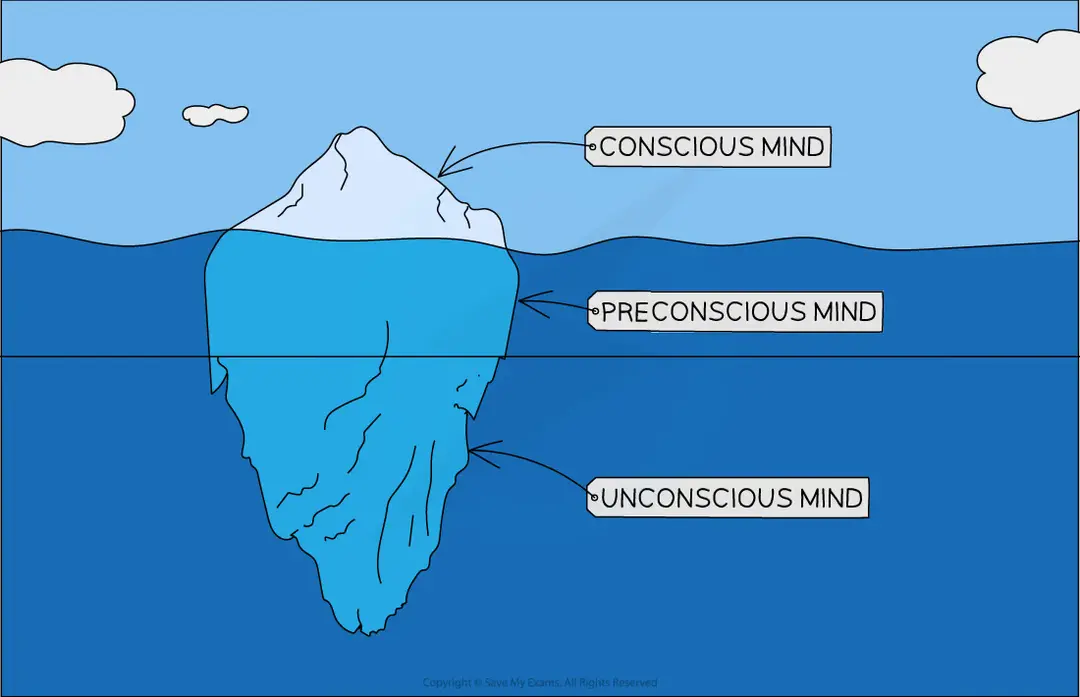
What is the conscious mind?
The part of the mind that the individual is aware of, which is used to form conscious thoughts (the tip of the iceberg)
What is the preconscious?
The part of the mind that sits just below the surface of the conscious mind, where dreams and 'Freudian slips' lurk
Freudian slips reveal secret feelings e.g. 'I loathe my husband' (when the intended phrase was 'I love my husband') - what is said appears to be accidental but it expresses the person's true, repressed feelings
Dreams reveal secret fears/desires e.g. dreams of flying = the wish to break free from limitations, to be free; dreams of being naked in public = anxiety about others accepting you
What is the unconscious mind?
The hidden depths and mass of the iceberg; the part of the mind that holds information and feelings that the individual may be unaware of e.g. secret fears or desires, repressed memories or emotions, the effects of trauma
Psychodynamic therapists suggest that psychoanalysis is a necessary way to confront the 'nasty' or frightening parts of the unconscious mind and to confront trauma
What is the structure of the personality components?
The Id, the superego and the ego
they work together within the personality of each individual
What is the Id?
According to Freud, the Id is present from birth (Freud described babies as being 'bundles of id')
The id is the instinctive part of our personality and operates according to the pleasure principle
It consists of pure erotic energy and primal urges (termed 'drives' by Freud)
The id seeks only self-indulgent pleasure and instant gratification
Rather like a spoilt child e.g. 'I want it 'now!'
The Id is important in early life to ensure survival, which is why an infant will cry until their needs are met
What is the super ego?
The Superego represents an internalised sense of right and wrong, the conscience/morality/ethics/judgemental aspect of the self
Moral standards are specifically learned via one's same-sex parent and the specific type of discipline instilled in one's childhood
(develops at around age 5)
What is the ego?
The Ego, according to Freud, develops around the age of two
The Ego operates according to the reality principle, rather like a sensible adult
The Ego is the reality principle, acting as the mediator between the Id and the Superego and balancing the demands of each at all times e.g.
The id must sometimes be 'tamed' as its wild impulses could lead to trouble
The Superego must sometimes be ignored if it is likely to lead to punitive self-blame or excessive
e.g anxiety disorders occur from an over developed super ego
What is the healthy psyche?
When all the components are balanced.
What is the neurotic psyche?
When the superego is more dominant.
What is the psychotic psyche?
When the Id is more dominant.
What is Freuds method?
Psychoanalysis which is a form of therapy to access the unconscious mind e.g dream analysis and free association
What are the five psychosexual stages during development?
Oral stage (0-1)
Anal stage (1-3)
Phallic stage (3-6)
Latency stage (6-12)
Genital stage (puberty onwards)
What is the oral stage description?
Focus of pleasure is on the mouth- mothers breast is the object of desire.
What is the oral stage fixation (consequences of unresolved conflict)?
Oral fixation: smoking, biting nails, sarcastic, critical
What is the anal stage description?
The focus of pleasure is on the anus, the child gains pleasure from withholding and expelling faeces. Toilet training is the major demand. Ego begins to develop- children become aware of the demands others are placing in them.
What are the fixations of the anal stage?
Anal retentive- perfectionist and obsessive
Anal expulsive- thoughtless and messy
What is the phallic stage description?
Focus of pleasure is on the genital area, child experiences the Oedipus (males) or electra (females) complex
What is the phallic stage fixation?
Phallic personality: narcissistic, reckless, possibly homosexual
What is the eodipus complex?
In the pahillic stage, Freud claimed boys develop incestous feelings towards their mother and a hatred towards their father (oedipus complex)
Leads them to repress their feelings towards their mother and identify with their father taking on his gender and moral values
What is the electra complex?
Girls in the phallic stage experience penis envy- experience desire for father and hate for mother
Although Freud was less clear on the process in girls, they are thought to give up their desire for their father ver time and replace this with a desire for a baby
What is the description of the latency stage?
Development of other activities means less concentration on sexual areas, earlier conflicts are repressed.
What if the genital stage description?
Primary source of pleasure is how the pursuit hetero relationships. Fixation and conflict may present this with the consequence that sexual perversions may develop.
What is the fixation of the genital stage?
Difficulty forming heterosexual relationships.
In order to deal with conflicts and problems in life, what did Freud state?
That the ego employs a range of defence mechanisms.
What are defence mechanisms?
Unconscious strategies used by the ego to manage anxiety caused by conflict between the parts of the personality.
What are the three defence mechanisms?
Repression, denial and displacement.
What is repression?
Forcing a distressing memory from the conscious mind to the unconscious.
What is denial?
Refusing to believe something because it is too acknowledge the reality.
What is displacement?
Transferring feelings from true source of distressing emotion onto a substitute target.
What are all the psychosexual stages meant for except the latency?
each stage marks a different conflict that the child much resolve in order to get to the next stage
What are the defence mechanism in the long term?
seen as psychologically unhealthy and undesirable
Evaluation of the psychodynamic approach: Androcentric
A weakness of Freud’s approach is that it considered androcentric. His views on women and female sexuality were less developed than his views on male sexuality. Freud seemed to ignore female sexuality and how it may differ from male sexuality. It has been argued that his treatments were therefore not effective for female patients.
Evaluation of the psychodynamic approach: Lack of scientific evidence
Critics also claim that there is no scientific evidence for Freud’s theory and that it is not scientific or falsifiable. Opponents claim that as the unconscious cannot be tested, Freud could interpret behaviour in any way to fit his theory.
seen as pseudoscientific- not a real science
However, Fisher and Greenberg summarised about 2,500 studies and concluded that experimental studies of psychoanalysis ‘compare well with studies relevant to any other major area of psychology’. They found support for the existence of unconscious motivation in human behaviour as well as defence mechanisms including repression, denial and displacement
Evaluation of the psychodynamic approach: Reductionism/ Holism
Psychodynamic approach suggests that much of our behaviour is determined by unconscious conflict (Reductionist), Freud believed that there was no such thing as an accident.
However, few psychologists accept this view as it leaves no room for individual differences and free will beyond early childhood (looking at people holistically)
This suggests that Freud’s views are too simplistic and extreme to generalise to a large population.