titrations
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
quantitative analysis
many teachers find _____________ a tough topic to teach
titration
simply a technique used by analytical chemists to determine the concentration of an unknown solution by reacting it with a solution of accurately known concentration
titration
this is an analytical technique most commonly used to calculate the concentration of an unknown substance with a known
analyte
the unknown substance in a titration
titrant
the known substance in a titration
quantitative
titration is a quantitative/qualitative chemical analysis
a solution is added to a sample to be analyzed
the basic principle of titration
titrant
this contains a known concentration of a chemical which reacts with the substance to be determined
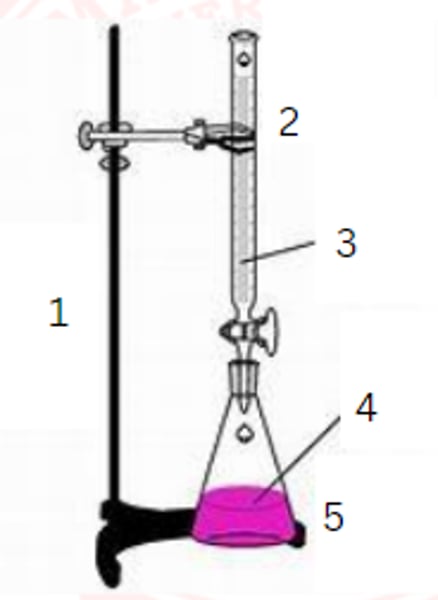
ring stand
1
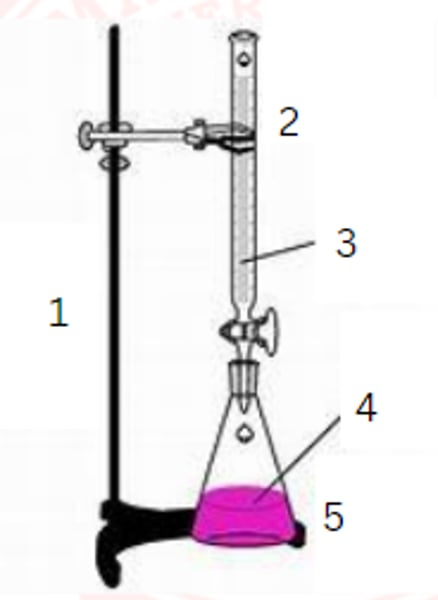
burette
2
standardized solution
3
sample
4
erlenmeyer flask
5
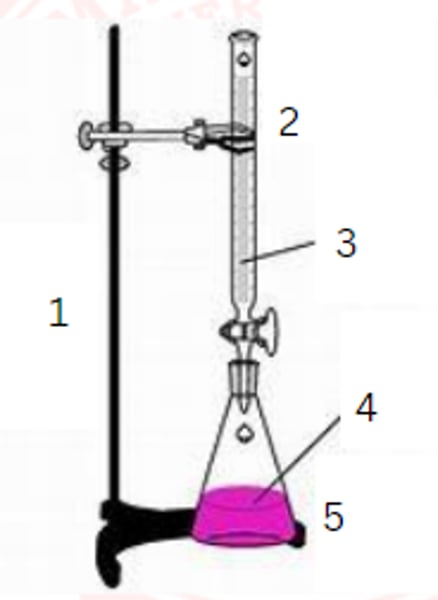
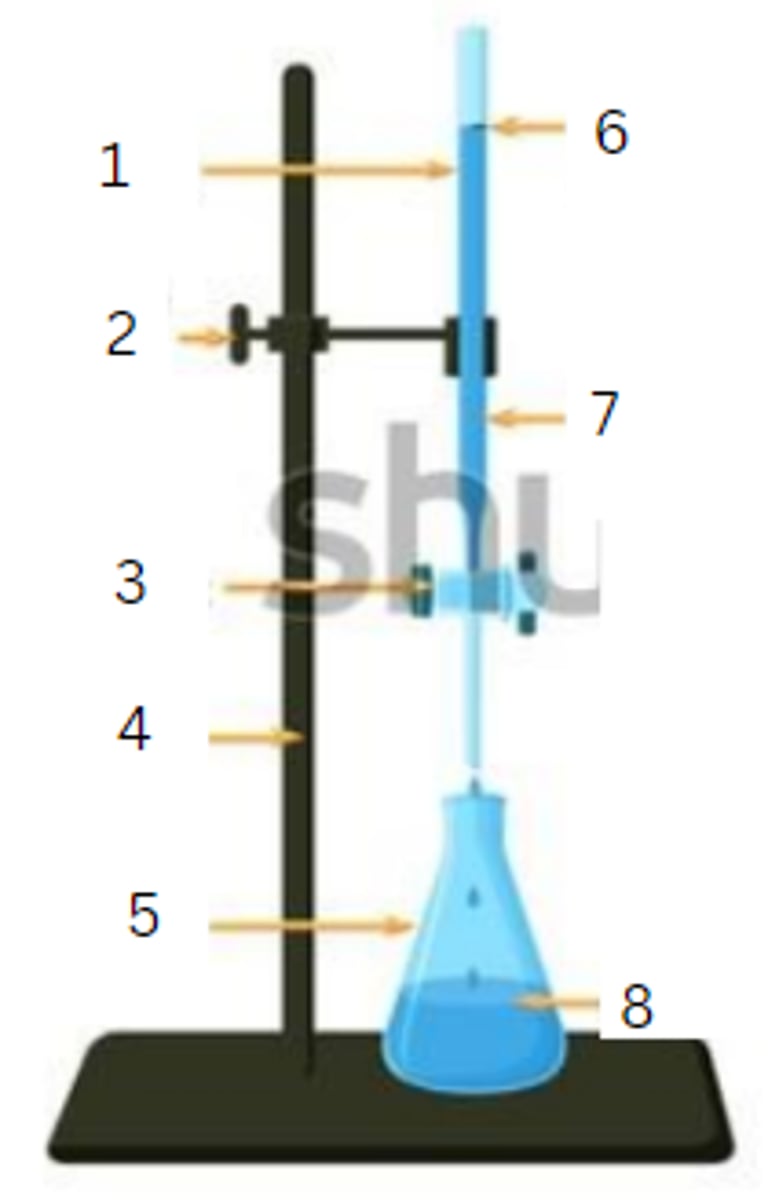
burette
1
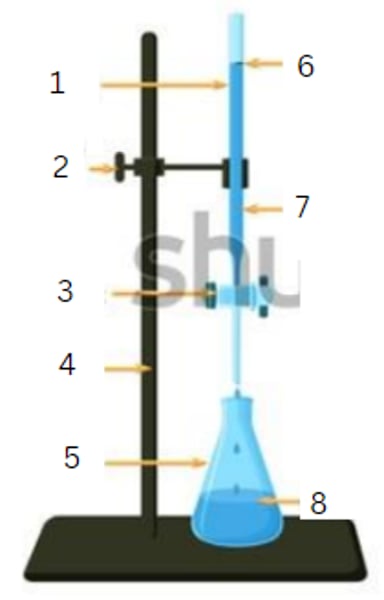
burette clamp
2
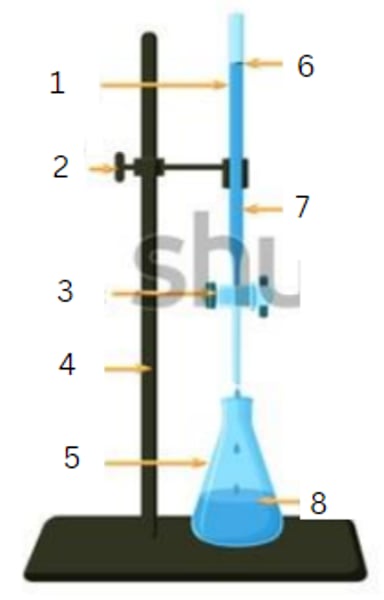
stopcock
3
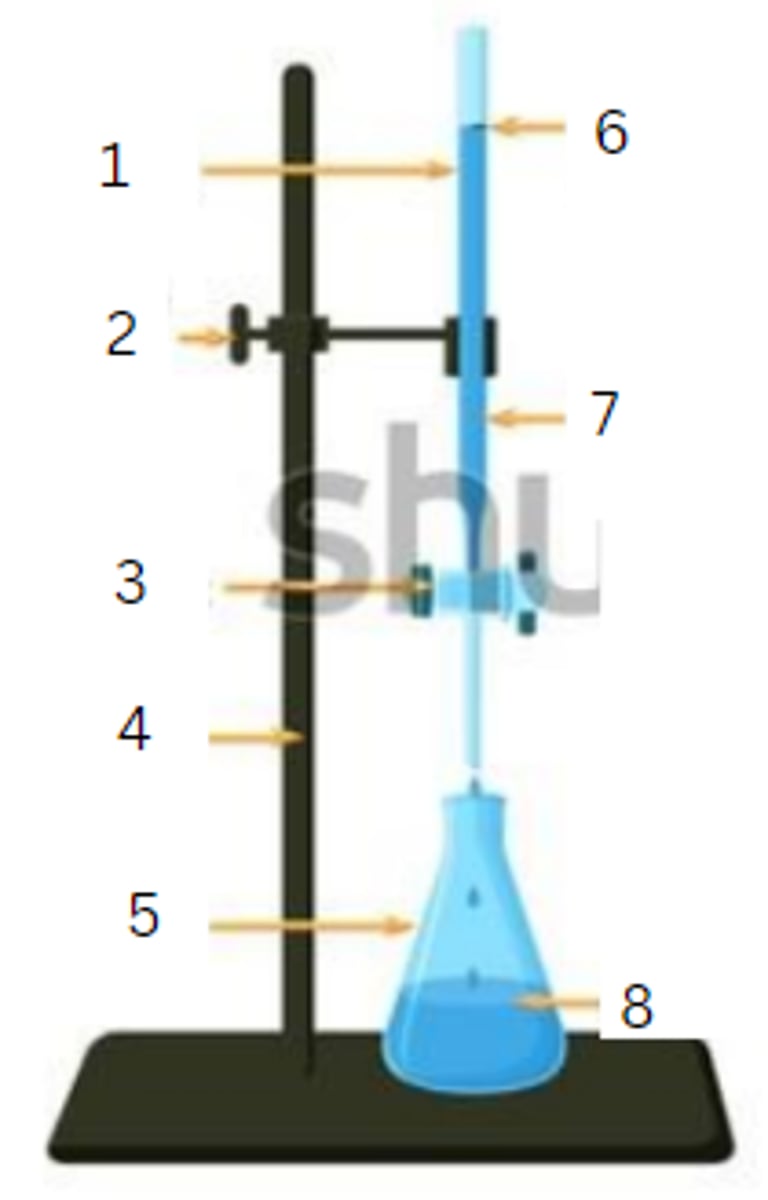
stand
4
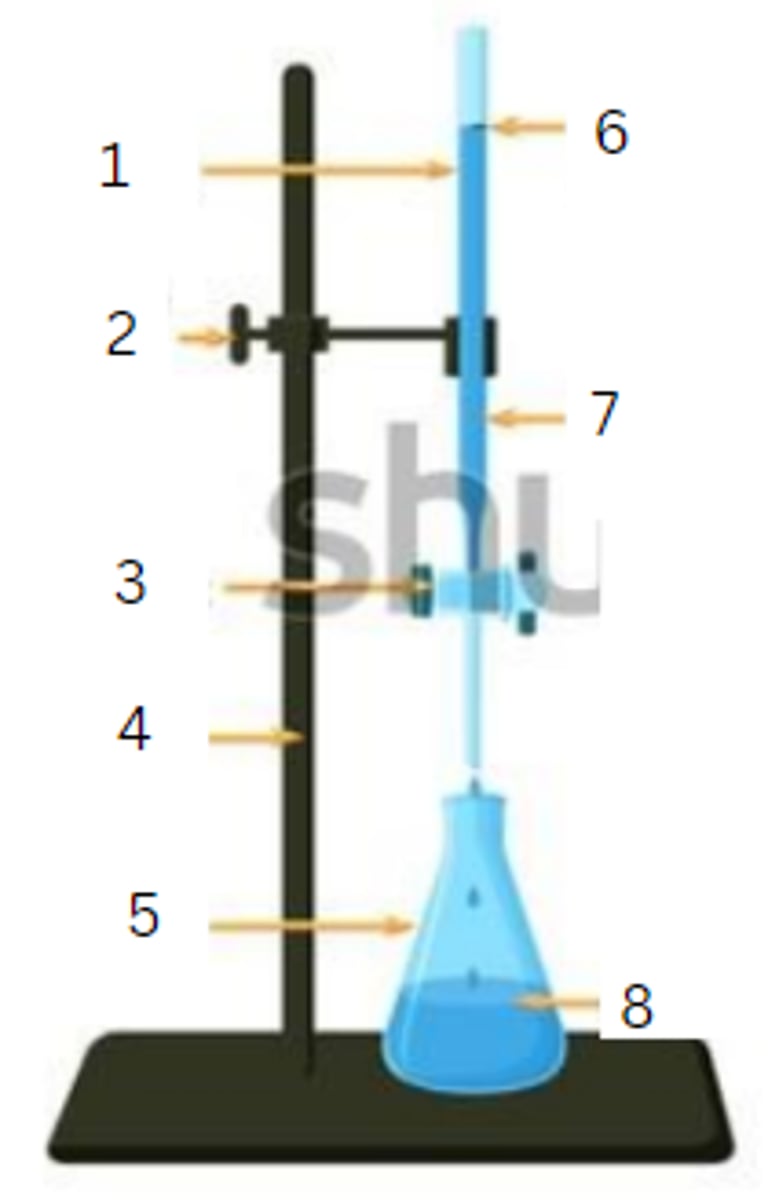
flask
5
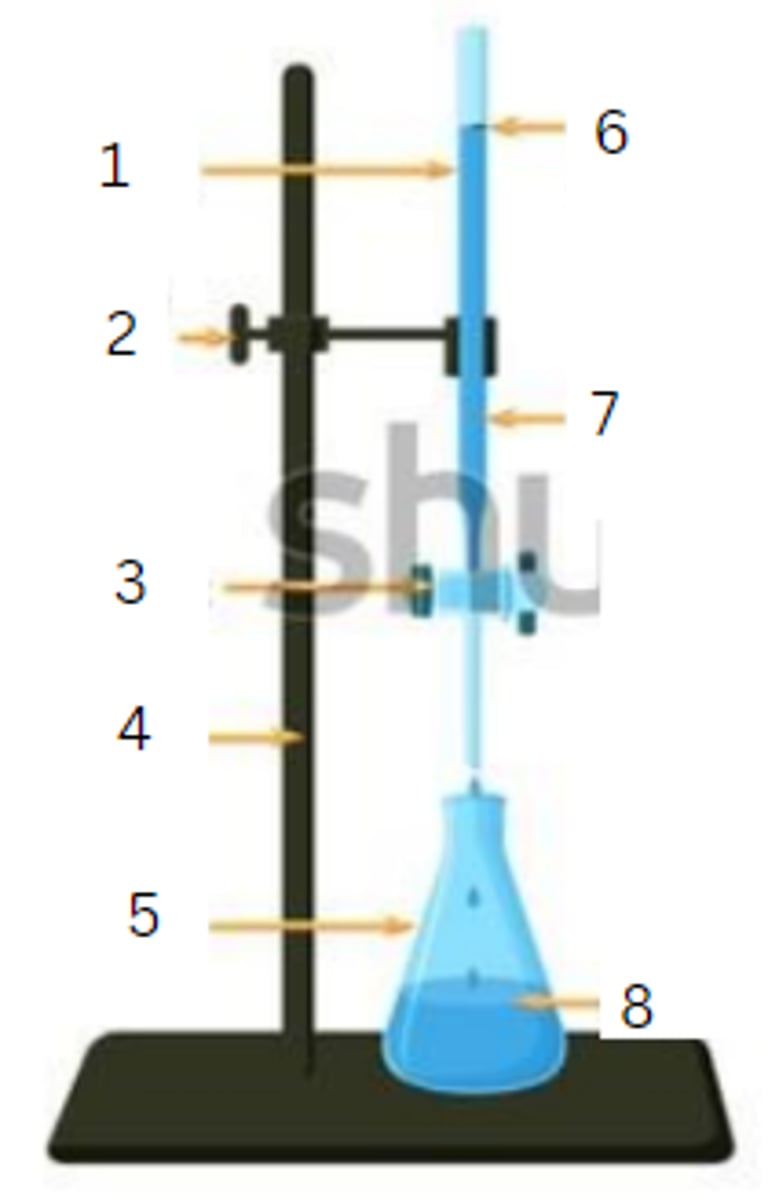
initial reading
6
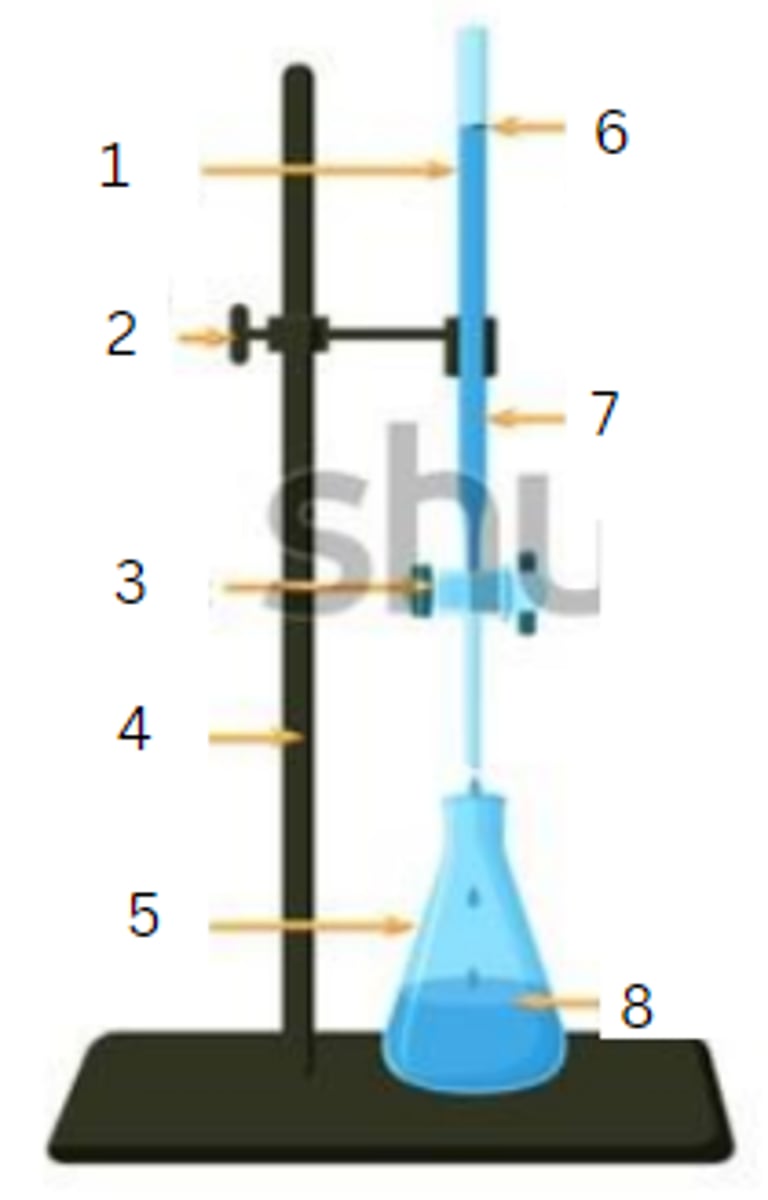
titrant
7
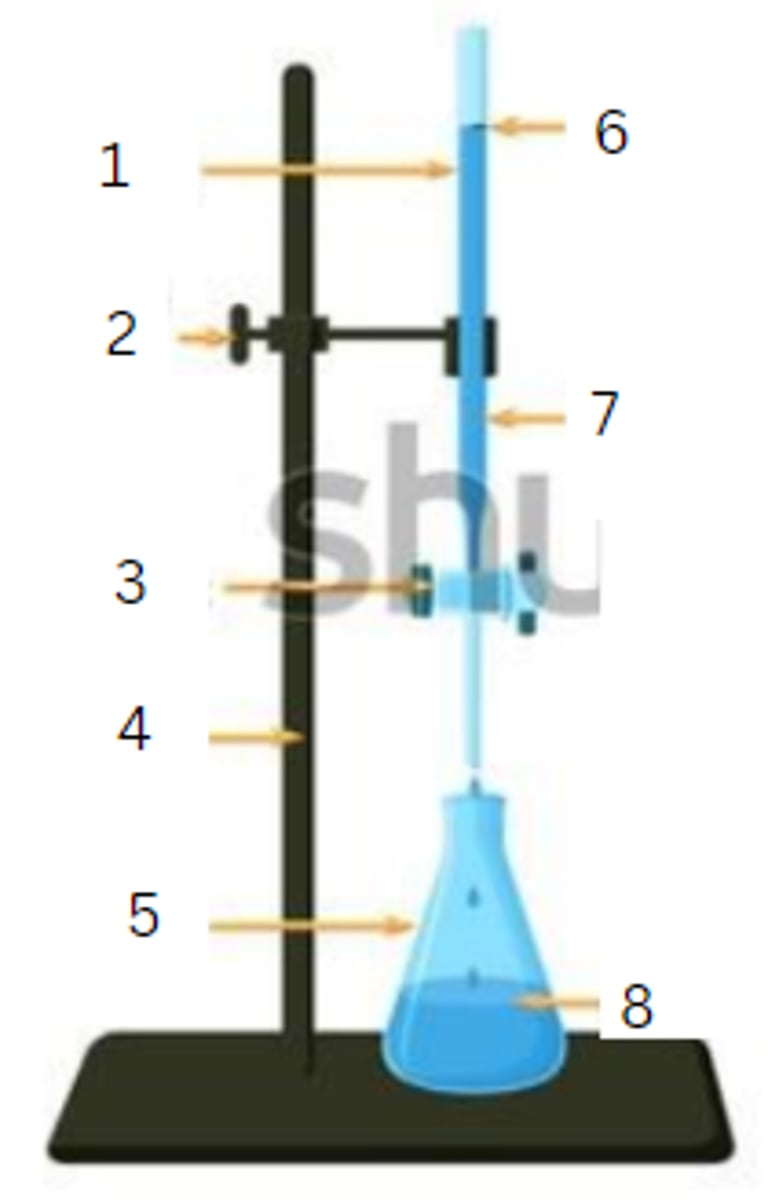
analyte
8
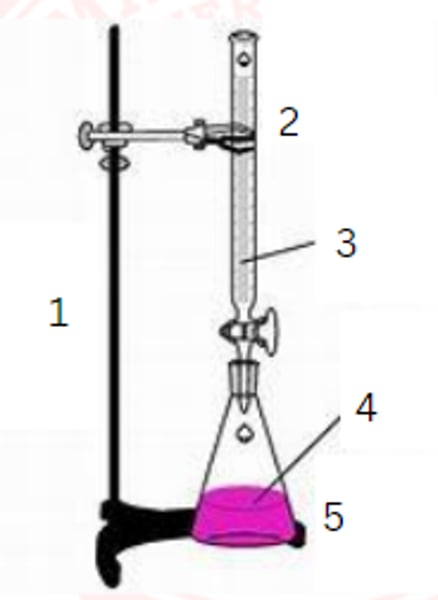
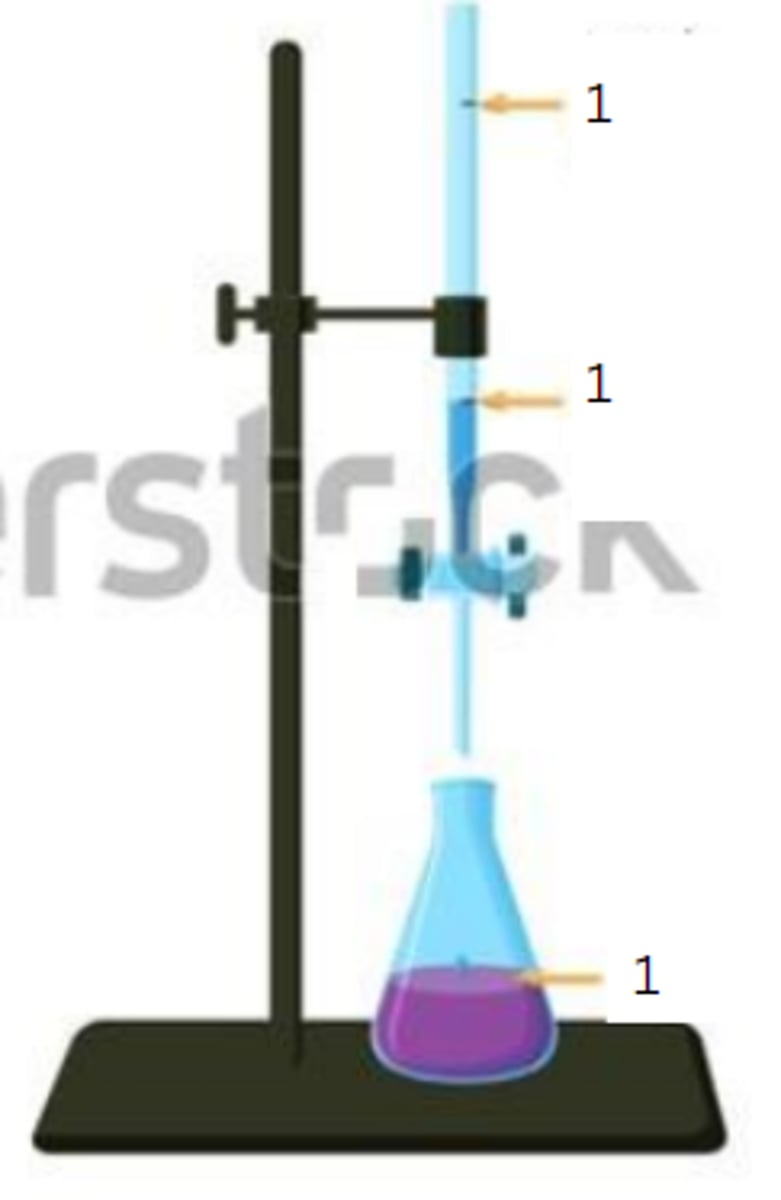
initial reading
1
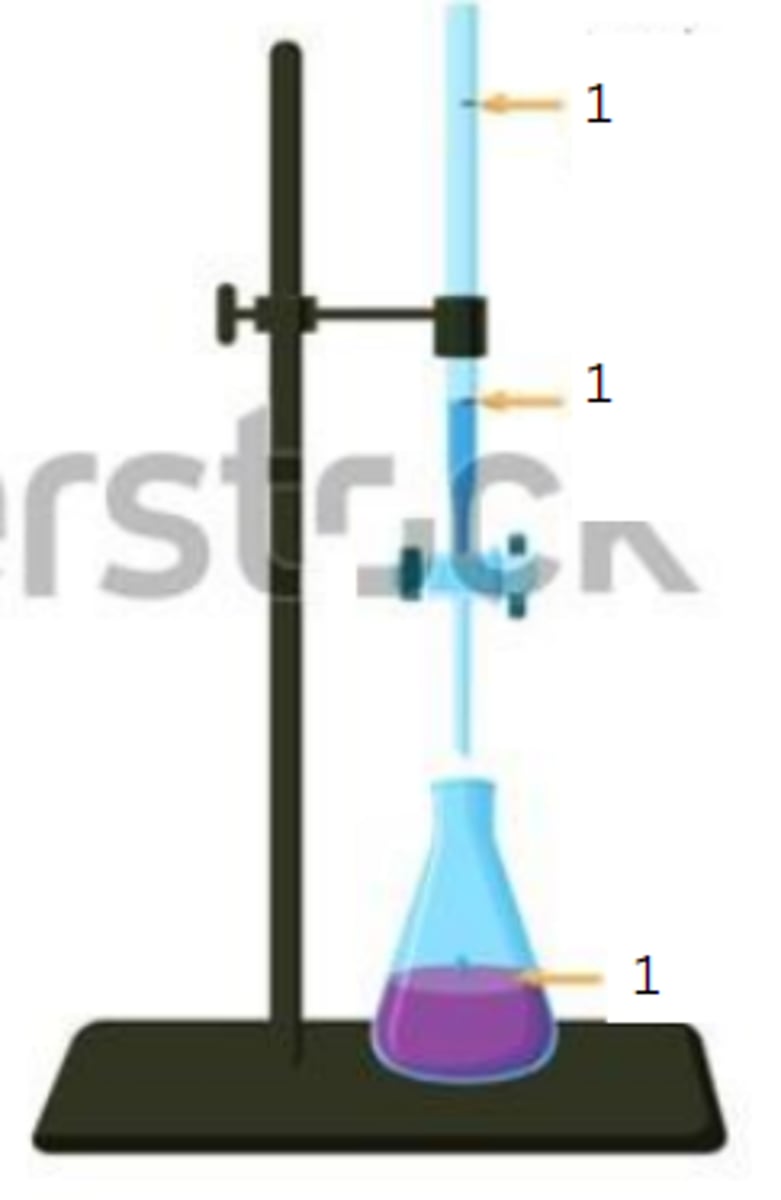
final reading
2
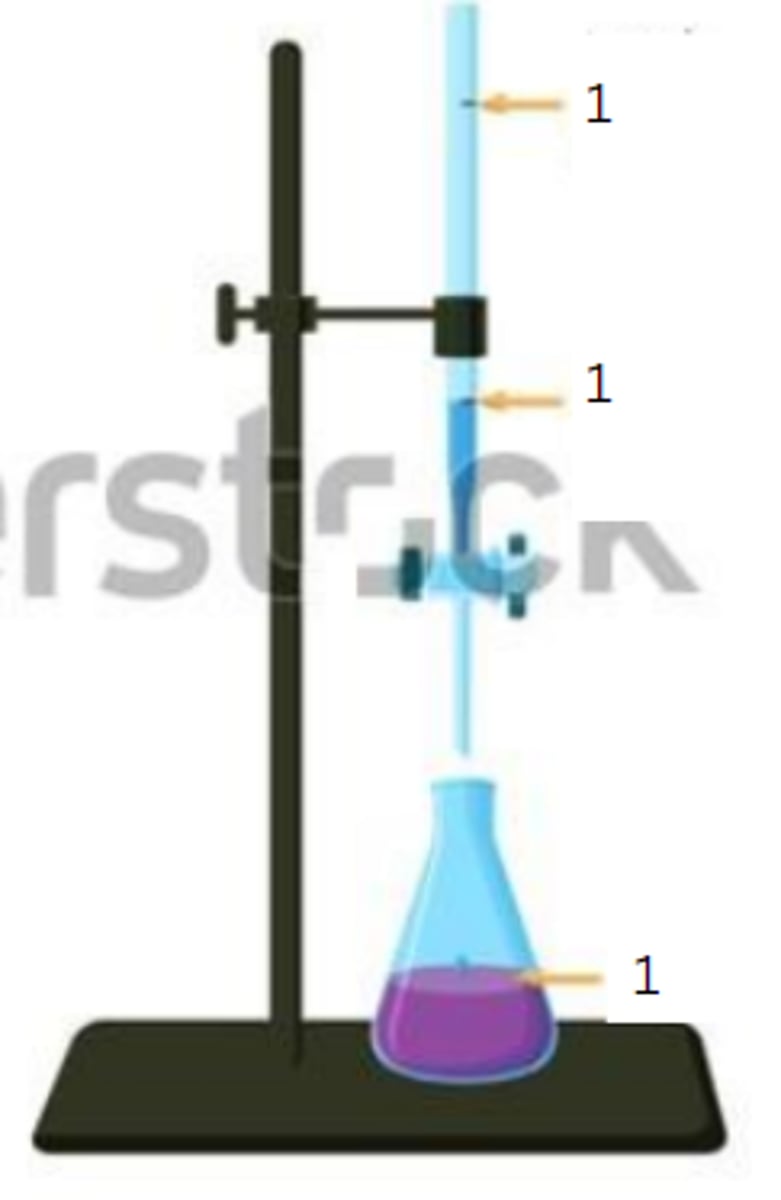
end point
3
10s
when the indicator stays this color for ____________ or so and clears, the acid is neutralized
(Vf - Vi)/M
formula for resolving power
burette
a volumetric measuring glassware which is used in analytical chemistry for the accurate dispensing of a liquid, especially of one of the reagents in a titration
titrant
this is added from a burette to a known quantity of the analyte until the reaction is complete
pipette
this is used to measure the quantity of the analyte
pipette
this is used to put an accurate volume of reactant in the conical flask
burette clamp
is a scientific equipment which is used specifically to hold and secure a burette on a stand, so that a burette is fixed and more convenient for the experiment
stopcock, valve
found at the tip of burettes, these control the flow of the chemical solution
rubber pipette filler
this is used to safely draw liquids into a pipette
releases air, draws in liquid, regulates and releases the liquid
the rubber pipette filler has three valves. one valve ______________, another _________________, and the third ____________________
"A" valve to release air
1
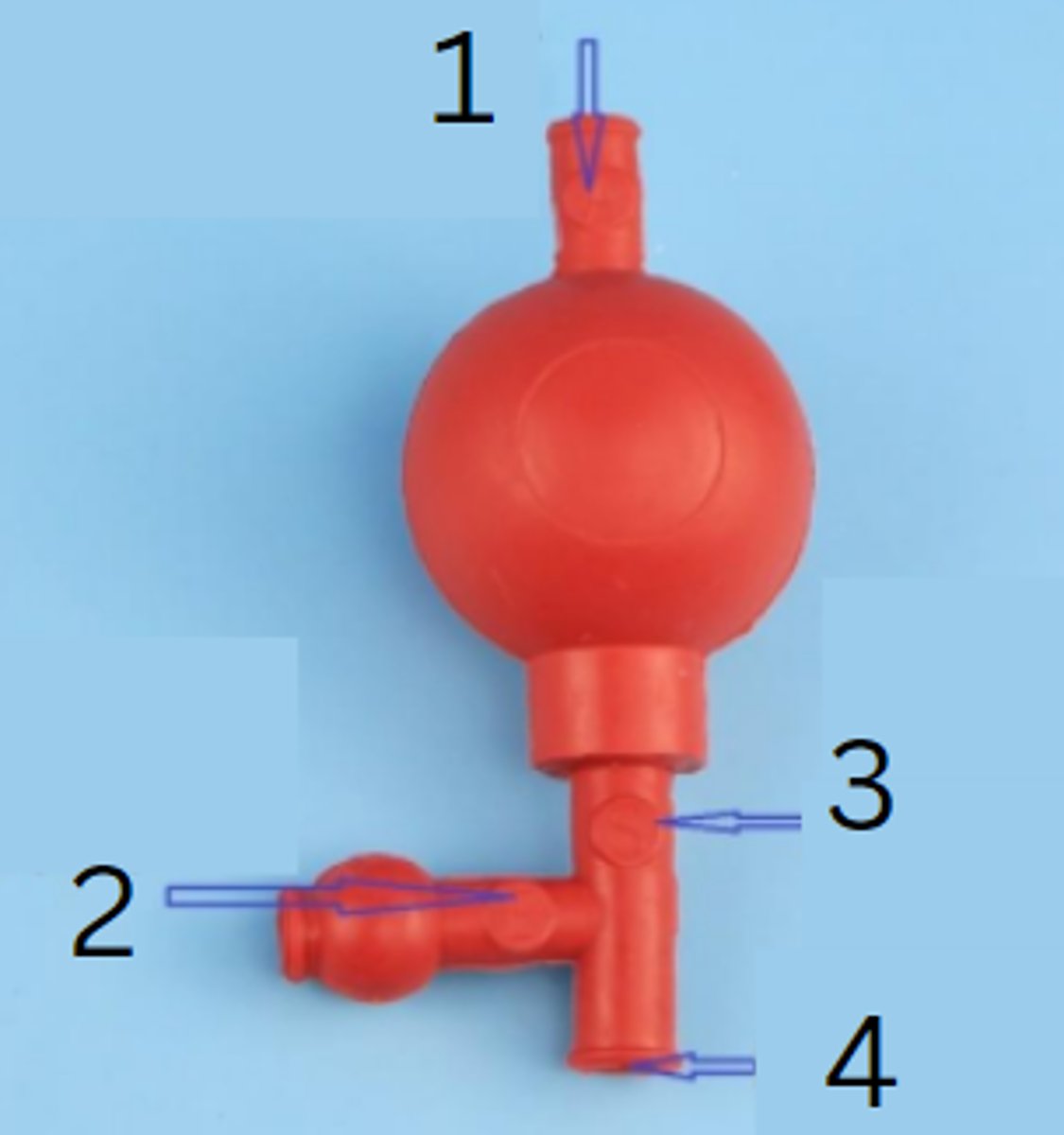

"E" valve to empty pipette
2
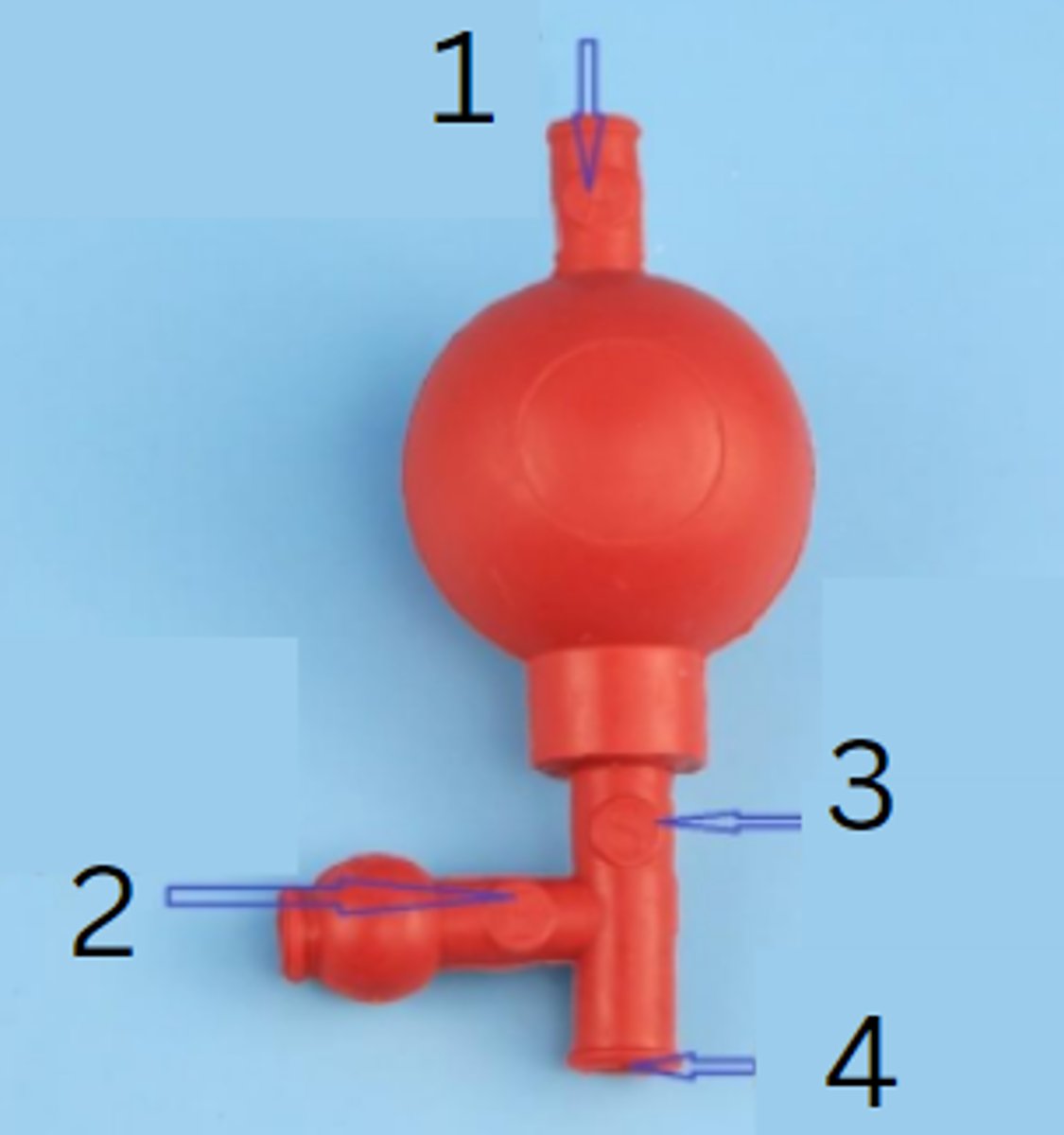

"S" valve to siphon liquid
3
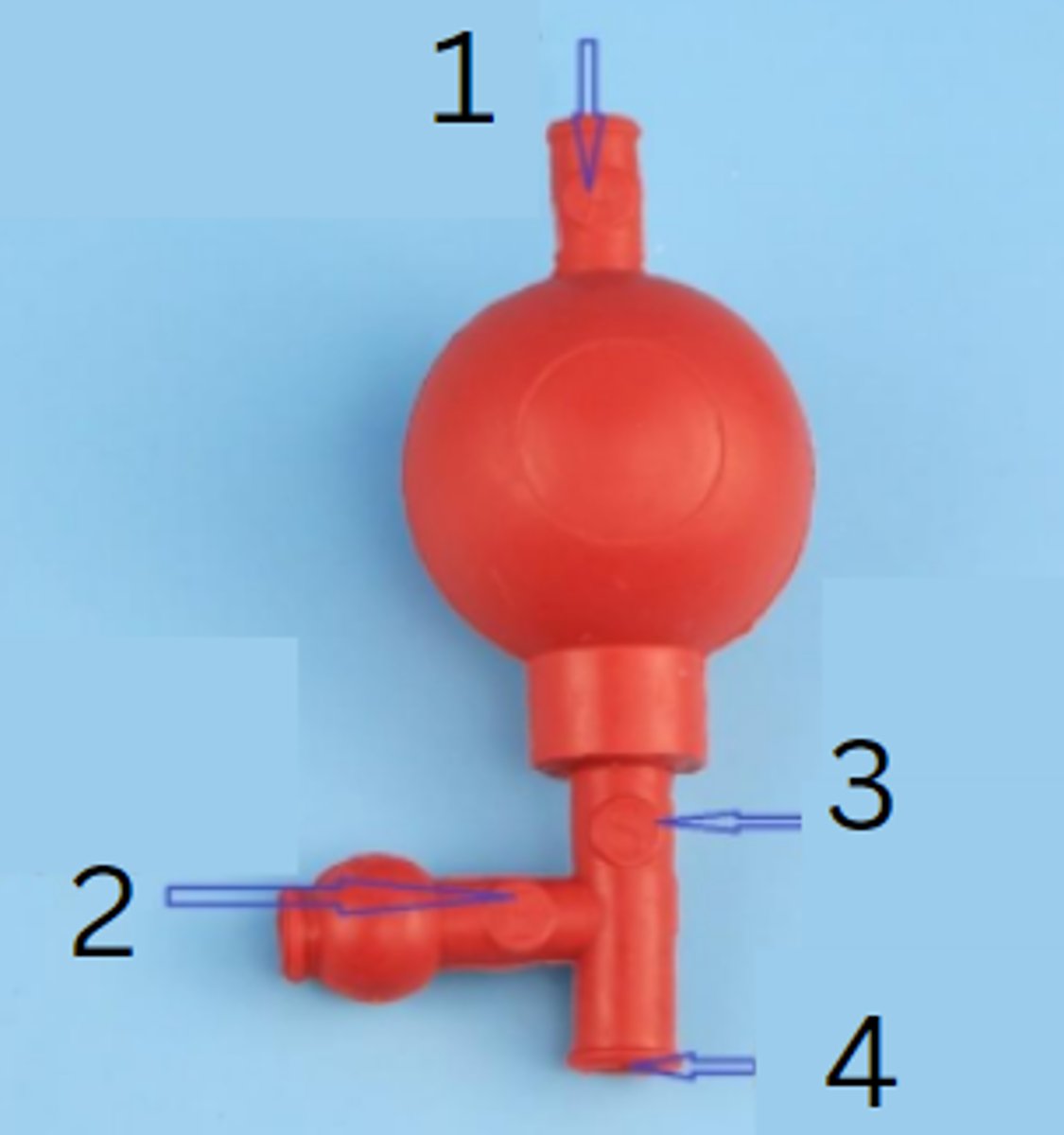

insert pipette port here
4
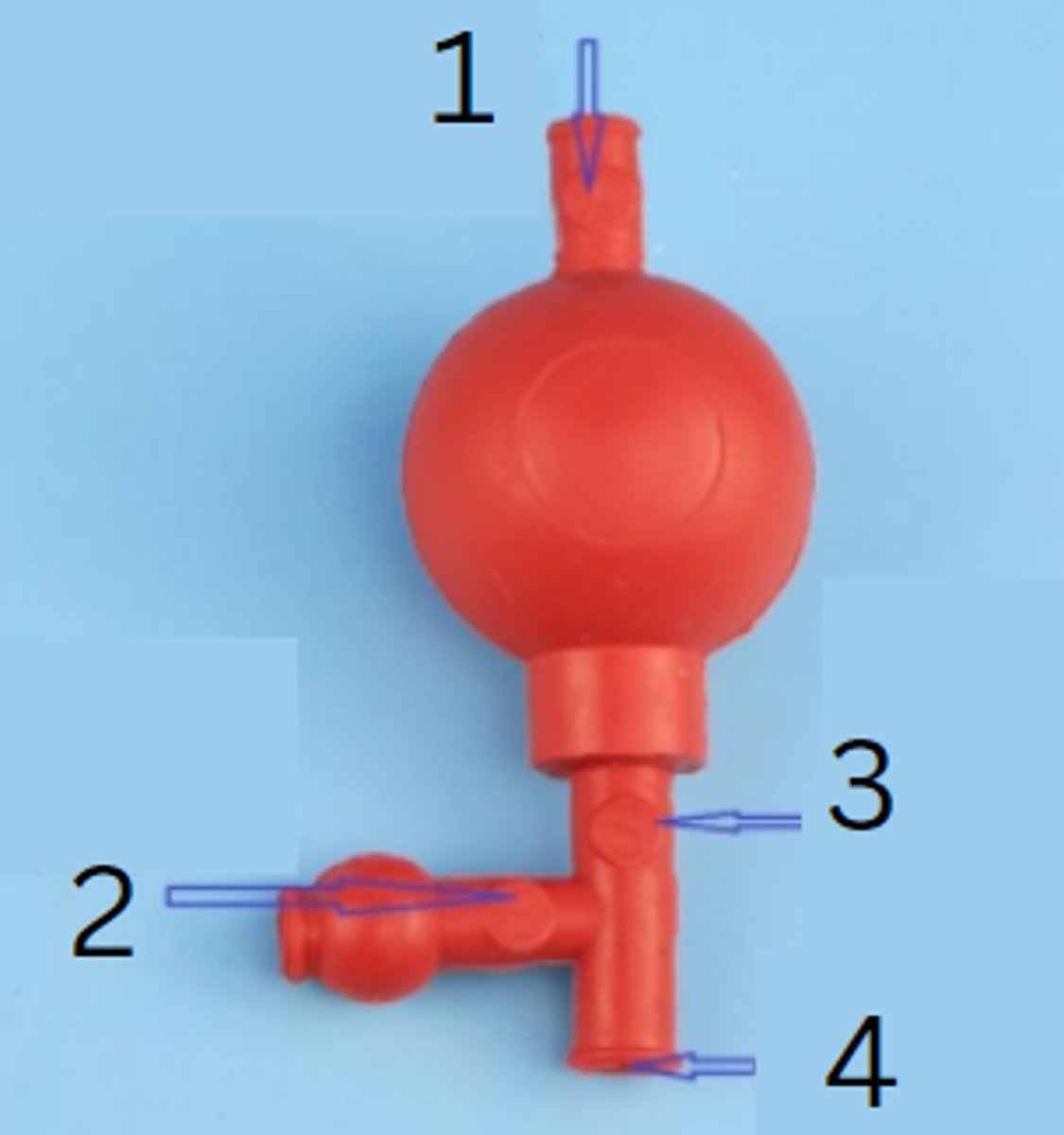

release air
function of the A valve of the rubber pipette filler
empty pipette
function of the E valve of the rubber pipette filler
siphon liquid
function of the S valve of the rubber pipette filler
top of the pipette
for the first step, insert the ____________ in the bottom of the pipette filler
squeezing the bulb
for the second step, release air from the pipette filler by squeezing valve "A" on the top of the pipette filler while simultaneously _______________________
size of the pipette
the amount of air you release is dependent on the _______________ that you are using
tip of the pipette
in the third step, insert the ____________ into the solution to be dispensed
siphon solution
fourth step of using pipette filler
vacuum
squeezing the valve S on the bottom of the pipette filler creates a ________________ to draw solution into the pipette
empty the pipette
fifth step of using pipette filler
desired rate, desired level
squeezing valve E helps to release solution at _________________, and to the _________________
zero mark
in the sixth step of using pipette filler, it works best to fill the pipette past the ______________ on step 4
zero mark
in the sixth step of using pipette filler, after filling the pipette past the zero mark on step 4, draw the level down to the ________________ on step 6
flask
this has a conical base that almost extends into a small, cylindrical neck
bung
the shape of the flask allows the flask to be sealed with a ___________ for heating purposes
erlenmeyer flask
a type of laboratory flask which features a flat bottom, a conical body, and a cylindrical neck
conical flask, titration flask
two other names for erlenmeyer flask
Emil Erlenmeyer
german chemist whose name is the origin for the name of the conical flask
1825-1909
years of emil erlenmeyer
1860
year when the erlenmeyer flask was created
titrant
the solution of a known concentration, which is added to another solution whose concentration has to be determined
analyte
the solution whose concentration has to be determined
titrand
other name for analyte
indicator
this detects the endpoint of the titration
titrator, reagent, standard solution
other names for titrant
analyte
the species of interest during a titration
mole ratio between reactants and products
the key to using titration to determine an unknown concentration of a solution
titration
What analytical technique is widely used in the food industry to determine the quantity of a reactant in a sample, such as the amount of salt or sugar in a product or the concentration of vitamin C or E?
To perform quantitative chemical analysis
What is the purpose of potentiometric titration?
It requires a large amount of material
Why is it difficult to use the traditional titration method in the early stages of drug discovery and development?
5-10 milligrams
What is the minimum amount of sample required for the microtitration method introduced in the report?
n = CV
formula for number of moles