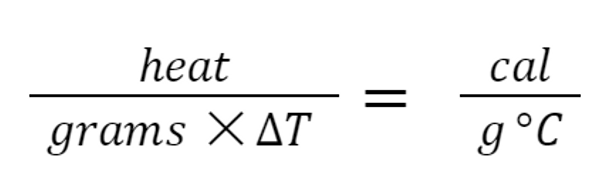Chapter 3: Matter and Energy
0.0(0)Studied by 3 people
Card Sorting
1/83
Last updated 5:28 AM on 1/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
1
New cards
Physical processes
________ can be used to separate mixtures because there are no chemical interactions between the components.
2
New cards
Bonds
________: Happens when atoms are held together by attractions.
3
New cards
Pure substances
________ that are compounds can be broken down by chemical processes into their elements.
4
New cards
Calorie
________ (cal): Defined as the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1 °C.
5
New cards
Sugar
________ dissolves in water to form a solution.
6
New cards
Strong attractive forces
________ hold the particles such as atoms or molecules close together.
7
New cards
piece of wood
A(n) ________ burns with a bright flame, and produces heat, ashes, carbon dioxide, and water vapor.
8
New cards
Celsius
Temperatures in science, are measured and reported in ________ (°C) units.
9
New cards
everyday temperatures
In the United States, ________ are commonly reported in Fahrenheit (°F) units.
10
New cards
Condensation
________: The water vapor is converted back to liquid as the water molecules lose kinetic energy and slow down.
11
New cards
Deposition
________: The reverse of sublimation; the gas particles change directly to a solid.
12
New cards
Pepper
________ is ground into flakes.
13
New cards
Filtration
________: It helps in separating solids from liquids, which involves pouring a mixture through a filter paper set in a funnel.
14
New cards
Evaporation
________: It is taking place as water molecules with sufficient energy escape from the liquid surface and enter the gas phase.
15
New cards
Compound
________: A pure substance that consists of atoms of two or more elements, always chemically combined in the same proportion.
16
New cards
nutrition laboratory
In the ________, foods are burned in a calorimeter to determine their energy value.
17
New cards
Freezer Burn
________: This occurs when a solid is left in the freezer for a long time, and so much water sublimes that solids become dry and shrunken.
18
New cards
Gas
________: It does not have a definite shape or volume.
19
New cards
Kinetic energy
________ is lost, the particles slow down, and attractive forces pull the particles close together; therefore, the substance is freezing.
20
New cards
Chromatography
________: Different components of a liquid mixture separate as they move at different rates up the surface of a piece of chromatography paper.
21
New cards
carbohydrate reserves
If the ________ are exhausted, fats and then proteins are used for energy.
22
New cards
Copper
________ is drawn into thin copper wires.
23
New cards
Sublimation
________: The particles on the surface of a solid change directly to a gas with no temperature change and without going through the liquid state.
24
New cards
Physical properties
________: These are those characteristics that can be observed or measured without affecting the identity of a substance.
25
New cards
Atoms
________: These are extremely tiny particles that make up each type of matter.
26
New cards
solid gain
Melting Point: The particles of a(n) ________ sufficient energy to overcome the attractive forces that hold them together.
27
New cards
Liquid
________: It has a definite volume, but not a definite shape.
28
New cards
Carbohydrates
________ are the primary fuel for the body.
29
New cards
tiny pieces of confetti
Paper is cut into ________.
30
New cards
Kelvins
________ (K): The unit of Kelvin Scale, no degree symbol is used.
31
New cards
metal
Shiny, silver ________ reacts in air to give a black, grainy coating.
32
New cards
Specific Heat
________: The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of exactly 1 g of a substance by exactly 1 °C.
33
New cards
Curve
Cooling ________: A diagram of the cooling process in which the temperature decreases as heat is removed.
34
New cards
Heat Equation
________: Specific heat expression that is arranged to solve for heat.
35
New cards
Chemical properties
________: These are those that describe the ability of a substance to change into a new substance.
36
New cards
State of Matter
________: The physical forms of matter.
37
New cards
Heat Fusion
________: The energy that must be added to convert exactly 1 g of solid to liquid at the melting point.
38
New cards
Kelvin scale
On the ________, 273 °C temperature, is called absolute zero, has the value of 0 K.
39
New cards
solid separate
The particles in the ________ and move about in random patterns.
40
New cards
Homogenous Mixture
________: Also called a solution, the composition is uniform throughout the sample.
41
New cards
large mass of water
A(n) ________ near a coastal city can absorb or release five times the energy absorbed or released by the same mass of rock near an inland city.
42
New cards
Pure Substances
________: A matter that has a fixed or definite composition.
43
New cards
Matter
Anything that has mass and occupies space
44
New cards
Pure Substances
A matter that has a fixed or definite composition
45
New cards
Element
The simplest type of pure substance
46
New cards
Atoms
These are extremely tiny particles that make up each type of matter
47
New cards
Compound
A pure substance that consists of atoms of two or more elements, always chemically combined in the same proportion
48
New cards
Bonds
Happens when atoms are held together by attractions
49
New cards
Molecules
Small groups of atoms
50
New cards
Homogenous Mixture
Also called a solution, the composition is uniform throughout the sample
51
New cards
Heterogeneous Mixture
The components do not have a uniform composition throughout the sample
52
New cards
Filtration
It helps in separating solids from liquids, which involves pouring a mixture through a filter paper set in a funnel
53
New cards
Chromatography
Different components of a liquid mixture separate as they move at different rates up the surface of a piece of chromatography paper
54
New cards
State of Matter
The physical forms of matter
55
New cards
Solid
It has a definite shape and volume
56
New cards
Liquid
It has a definite volume, but not a definite shape
57
New cards
Gas
It does not have a definite shape or volume
58
New cards
Physical properties
These are those characteristics that can be observed or measured without affecting the identity of a substance
59
New cards
Chemical properties
These are those that describe the ability of a substance to change into a new substance
60
New cards
Degrees
Smaller units of temperature
61
New cards
Kelvins (K)
The unit of Kelvin Scale, no degree symbol is used
62
New cards
Energy
The ability to do work
63
New cards
Kinetic Energy
The energy of motion
64
New cards
Potential Energy
Determined by the position of an object or by the chemical composition of a substance
65
New cards
Heat
The energy associated with the motion of particles
66
New cards
Joule (J)
The SI unit of energy and work
67
New cards
Calorie (cal)
Defined as the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1 °C
68
New cards
Specific Heat
The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of exactly 1 g of a substance by exactly 1 °C
69
New cards
Heat Equation
Specific heat expression that is arranged to solve for heat
70
New cards
Change of State
It occurs when the matter is converted from one state to another
71
New cards
Melting Point
The particles of a solid gain sufficient energy to overcome the attractive forces that hold them together
72
New cards
Freezing Point
Occurs when a liquid changes to a solid
73
New cards
Heat Fusion
The energy that must be added to convert exactly 1 g of solid to liquid at the melting point
74
New cards
Evaporation
It is taking place as water molecules with sufficient energy escape from the liquid surface and enter the gas phase
75
New cards
Boiling Point (bp)
The molecules within a liquid have enough energy to overcome their attractive forces and become a gas
76
New cards
Condensation
The water vapor is converted back to liquid as the water molecules lose kinetic energy and slow down
77
New cards
Sublimation
The particles on the surface of a solid change directly to a gas with no temperature change and without going through the liquid state
78
New cards
Deposition
The reverse of sublimation; the gas particles change directly to a solid
79
New cards
Freezer Burn
This occurs when a solid is left in the freezer for a long time, and so much water sublimes that solids become dry and shrunken
80
New cards
Heat of Vaporization
The energy that must be added to convert exactly 1 g of liquid to gas at its boiling point
81
New cards
Cooling Curve
A diagram of the cooling process in which the temperature decreases as heat is removed
82
New cards
calorimeter
In the nutrition laboratory, foods are burned in a _______ to determine their *energy value.*
83
New cards
energy values
The _____ for food are the kilocalories or kilojoules obtained from burning 1 g of carbohydrate, fat, or protein.
84
New cards
Specific Heat Formula