Bones and Cartilage
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Spongy bone
also called cancellous
or trabecular bone. It is found in the long
bones and it is surrounded by compact bone.
haphazardly
arrangement of spongy bone
Compact bone
also called cortical bone, surrounds spongy bone. They are heavy,
Connective
Fundamental type of tissue of Compact bone
Bone or Osseous
Subtype of Compact bone
Compact
Specific subtype of of Compact bone
Osteocytes
Parenchyma of of Compact bone
Lamellae
Structure of bone of Compact bone
Concentric
Arrangement of Compact bone
Connective
Fundamental type of Spongy bone
Bone or Osseous
Subtype of Spongy bone
Cancellous / Spongy
Specific subtype of of Spongy bone
Osteocytes
Parenchyma of Spongy bone
Lamellae
Structure of bone of Spongy bone
Connective
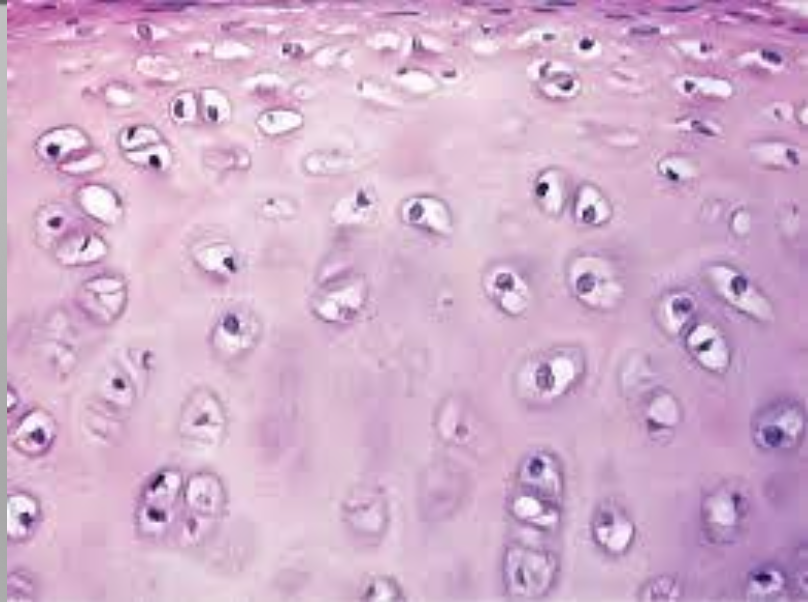
Fundamental type of tissue of Trachea
Cartilage
Subtype of Trachea
Hyaline
Specific Subtype of of Trachea
Chondrocytes
Parenchyma of Trachea
Singly or isogenous groups
Arrangement of of Trachea
Yes
Perichondium of Trachea
Connective
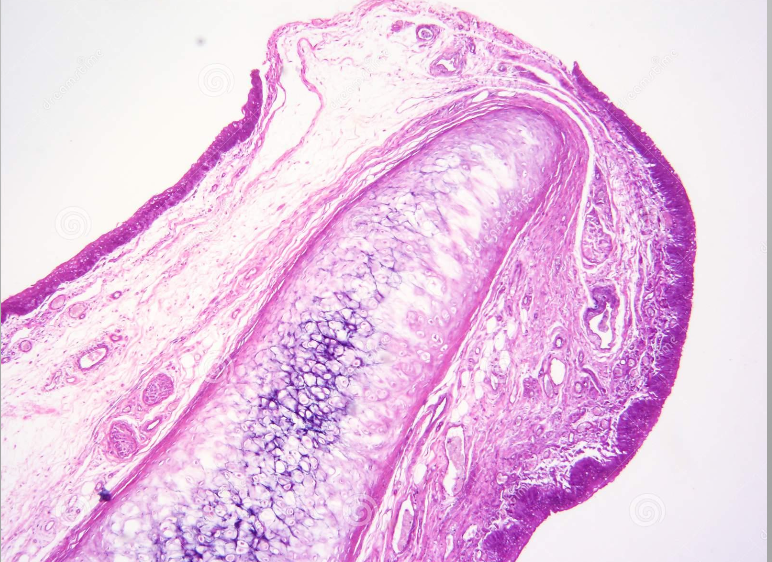
Fundamental types of tissue of Epiglottis
Cartilage
Subtype of Epiglottis
Elastic
Specific subtype of of Epiglottis
Chondrocytes
Parenchyma of Epiglottis
Singly or isogenous groups
Arrangement of Epiglottis
Yes
Perichondium of Epiglottis
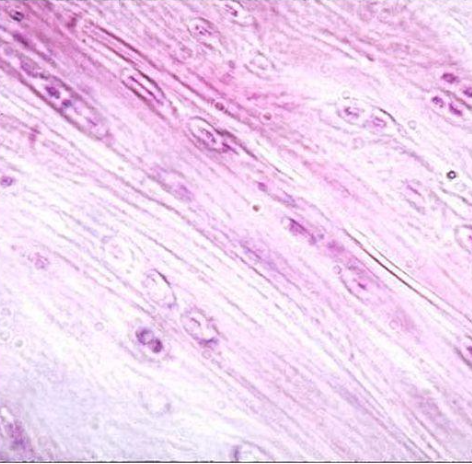
Fibrocartilage
Functions:
Resists compression
Prevents bone-to- bone contact
Locations:
Meniscus of knee
Pubic symphysis
Intervertebral discs
Connective
Fundamental type of Intervertebral disk
Cartilage
Subtype of Intervertebral disk
Fibrocartilage
Specific subtype of Intervertebral disk
Chondrocytes
Parenchyma of Intervertebral disk
Singly or in rows
Arrangement of of Intervertebral disk
No
Perichondium of of Intervertebral disk
Hyaline
Homogenous with type II collagen
Chondrocytes; Chondroblasts
Isolated; Isogenous groups
Yes
Upper respiratory tract / Trachea; articular ends and epiphyseal plates of long bones
Provides smooth, low friction surfaces in joints; structural support for respiratory tract
Elastic
Type II collagen and darker elastic fibers
Chondrocytes; Chondroblasts
Isogenous
Yes
External ear, Epiglottis
Provides flexible shape and support of soft tissues
Fibrocartilage
Type II collagen and large areas of dense connective tissue
Chondrocytes; Fibroblasts
Isolated; Isogenous groups arranged axially
No
Intervertebral disc, Pubic symphysis
Provides cushioning, tensile strength and resistance to tearing and compression
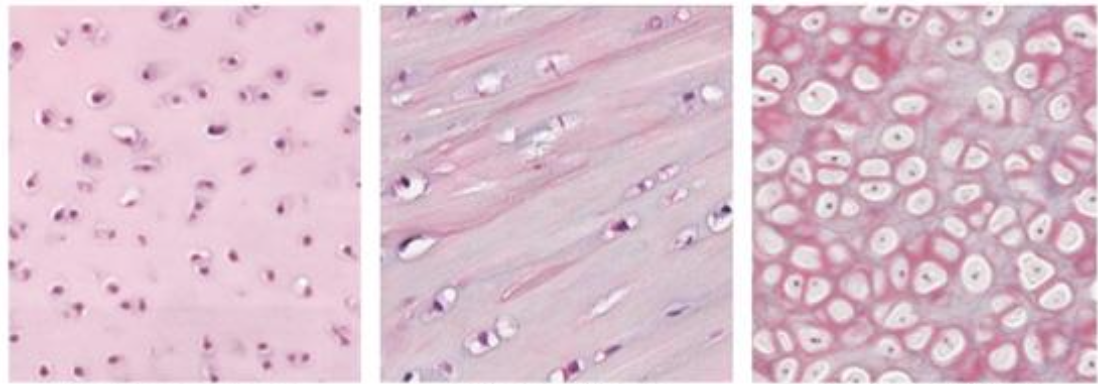
Epiglottis
Trachea
Fibrocartilage
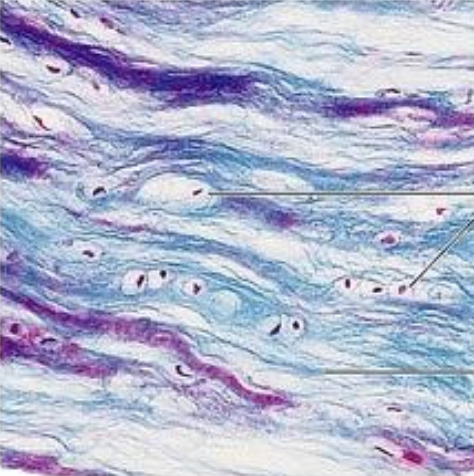
Intervertebral disk
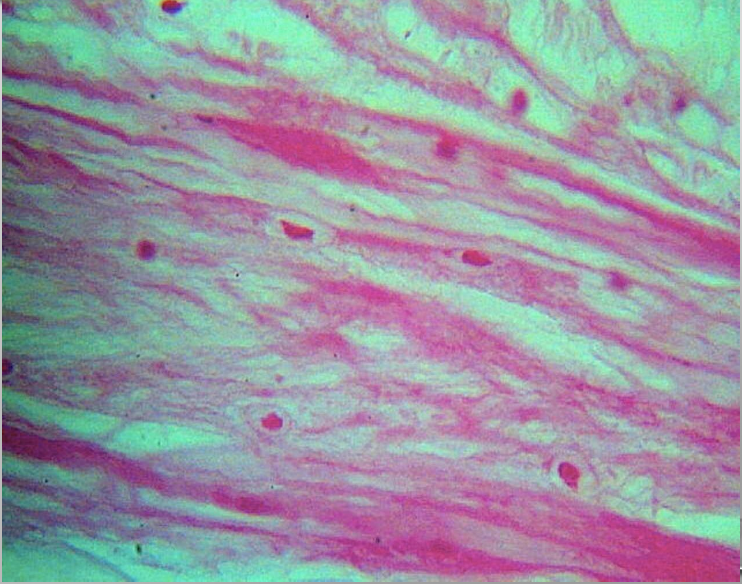
Hyaline cartigae
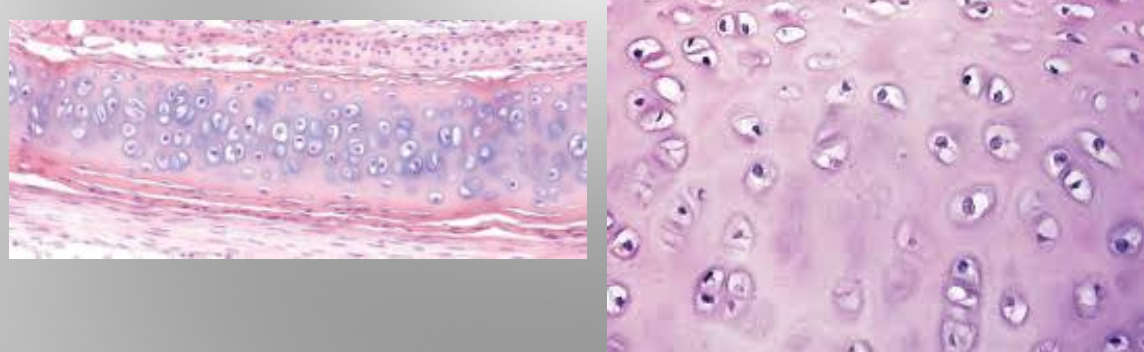
Epiglottis
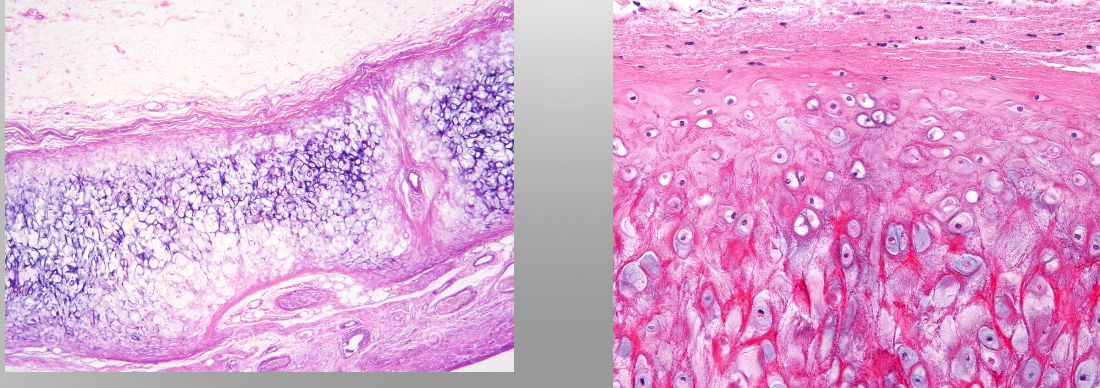
Fibrocartilage
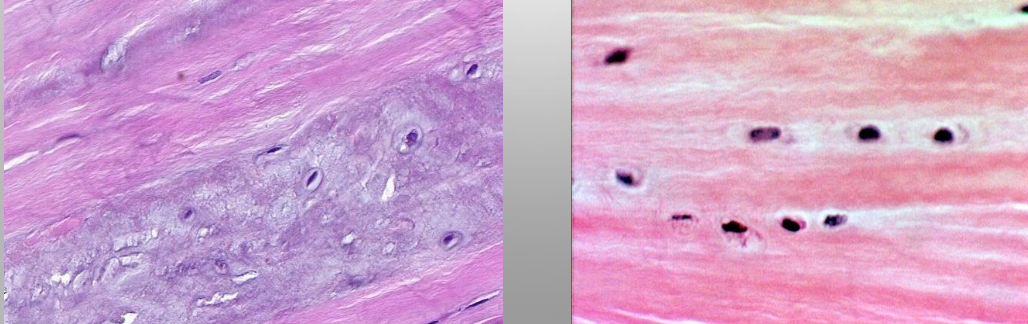
Hyaline cartilage
Fibrocartilage
Elastic cartilage