BIO 189: Chapter 8- DNA Replication, Binary Fission and Mitosis
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
What is a gene and what is a genome?
A gene is a segment of DNA with instructions for RNA or protein while a genome is the sum of a organism’s DNA
What are the characteristics of a Prokaryotic genome?
Singular circular chromosome
Located in nucleoid region (central region of cell)
Includes plasmids (smaller DNA circles containing one or few genes)
What are the characteristics of Eukaryotic genome?
Multiple linear chromosomes
Located in the nucleus
Associated with histone “packing proteins”
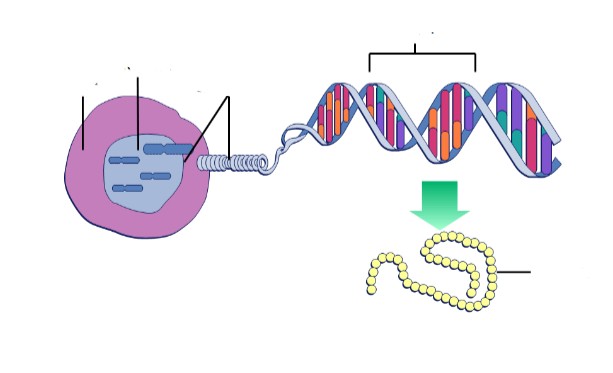
Label from left to right bottom
Cell, nucleus, chromosomes, gene, protein
What is a karyotype?
Karyon: Kernel/seed/nucleus
Typos: General form
What does the human karyotype contain?
23 pairs of chromosomes (1 set from mom and 1 set from dad)
What are the 22 pairs called?
Autosome chromosomes
What is the 23rd pair and what does it determine?
Sex chromosomes and it determines biological sex
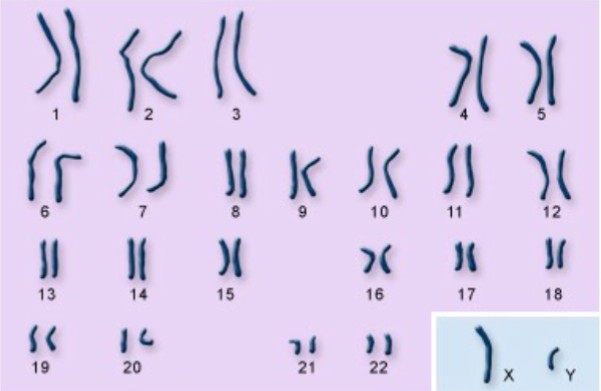
This karyotype represents what?
Typical human karyotype with no chromosomal mutations
Differential gene expression results in different cell types from the?
Same set of instructions
Human DNA is about 99.9% identical to other humans and what else?
99.1% to chimps
90% to mice
85% to zebra fish
50% to bananas
What is cell theory?
All cells come from pre-existing cells
What is cell division?
One “parent” cell duplicates all cellular contents then divides (splits) into two new daughter cells
What is the process of Prokaryotic cell division consist of?
DNA Replication
Chromosome Segregation
Cytokinesis
Binary Fission
What is the process of eukaryotic cell division consist of?
Mitosis which is the cell division in body cells (somatic) in multicellular organisms
What is cell division critical for?
Growth and development
Wound repair
Tissue regeneration
Microbial fission/budding
What is apoptosis?
Programmed cell death, regulated by a class of protein (degrading enzymes called caspases)
What are some reasons for cells to commit suicide?
Development
Injured
Damaged
Infected
What is a somatic cell cycle?
Cell division to cell division
What are the two cell life phases?
Interphase and Mitosis
What is interphase and what does it consist of?
The majority of a cell’s life cycle will be spent here, and it consist of 3 sub phases
What are the 3 sub phases of interphase?
G1: Normal cell function and cell growth
S: DNA replication
G2: Additional growth and preparation for division
What is mitosis and what does it consist of?
The parent cell rapidly divides into two daughter cells and have four stages
What are the four stages of mitosis
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase/Cytokinesis
When does DNA replication occur?
Before cell division
What does a parent cell need to do before dividing and where does this occur?
DNA (genome) and in the S phase (synthesis phase)
What do promotor like regions do and what does it produce?
It recruits various enzymes to the origins of replications and splits DNA strand producing a replication fork
What does a DNA polymerase associate with at replication forks?
Two of the original DNA strands
What is semi-conservative replication?
Each parental strand serves as template for new complementary strand
What are the three essential enzymes in DNA replication?
Helicase: Unwinds and Unzips DNA
DNA Polymerase: Building polymers of DNA
Ligase: Tie up or join strands
What occurs during Prokaryotic Binary Fission?
Parent cell contains one chromosome
DNA replicates and attaches to cell membrane
Membrane growth moves DNA molecules apart into new cell walls
Split occurs and two daughter cells are created
What are the mechanisms of prokaryote evolution?
Random DNA mutations may produce new traits
Horizontal gene transfer (genes coming from something else)
What are the three types of horizontal gene transfer?
Transformation (bacterium takes up foreign DNA & adds it to its genome)
Conjugation (donor cell and recipient form a plasmid and make contact through a pilus)
Transduction (DNA is transferred from a virus)
What is Naked DNA and where is it found?
DNA not associated with any histone proteins, found during DNA synthesis and active gene expression
What is chromatin?
DNA wrapped around histone proteins
What is loose configuration?
DNA compacted but allows for easy access to genes if needed
What is common configuration?
When cell is not undergoing cell division
What are chromosomes and where are they found?
Highly condensed (compacted) chromatin, found only during active cell division/mitosis
What are the same pair of chromosomes called?
Homologous chromosomes
During the S phase of the cell cycle, what does the semi conservative DNA replication result in?
Two identical sister chromatids attached by protein centromere
At what point does DNA fully condense during the cell cycle?
Prophase
When does chromosome duplication occur?
Interphase after the S-phase
The dynamic movements of chromosomes and cellular components during mitosis is dependent on what?
Microtubule cytoskeletal elements (Largest cytoskeletal fibers are made from tubulin protein dimers)
What are centrosomes?
Organelle made of two centrioles that makes and organizes microtubules during mitosis
What occurs during G2 Interphase
DNA replication finished
Cellular resources for mitosis are accumulated
Centrosomes duplicate
What occurs during early prophase?
Chromosomes condense and become visible. Spingdle forms as centrosomes move to opposite poles
What occurs during late prophase?
Nuclear envelop breaks up and spindle fibers attach to chromosomes’ sister chromatids
What occurs during metaphase?
Nuclear membrane is disintegrated
Microtubules have attached to sister chromatids
mitotic spindle is formed (cage like)
All 46 chromosomes are lined up at cell midline or metaphase plate
What occurs during Anaphase?
Microtubules begin to pull sister chromatids apart toward opposite poles, cell membrane elongates
What occurs during telophase?
Spindle fiber microtubules begin to disintegrate
two nuclear membranes form
chromosomes decondense into chromatin
What occurs during cytokinesis?
Cytoplasm and organelles are split
In animal cells how does cytokinesis occur?
Contractile ring of proteins makes cleavage furrow
Cells pinch off
In plant cells how does cytokinesis occur?
Cell wall containing vesicles are sent to midline (cell plate) between nuclei
Vesicles fuse and cell wall is established
What are the cell cycle checkpoints?
G2 phase: Is genome damaged? Does the cell have the resources to continue into mitosis?
Mitosis: Were the genomes separated properly?
G1 phase: Is there a signal to divide?
S phase: Is the genome properly replicated?
How can the cell cycle go wrong?
If DNA mutations are not eliminated and accumulate which could cause tumors or cancer
What are benign tumors?
Uncontrolled cell division contained in a tough capsule (size is limited and does not spread)
What is a malignant tumor?
Uncontrolled cell division with no capsule and can enter into circulatory systems and seed in new regions of the body