Topic 14: Coral Reefs
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Biotic community
Assemblage of organisms that live together within some definable area or habitat
Ecosystem
Biotic plus abiotic community through which organisms transfer and/or exchange energy and nutrients
Reefs
The largest biologically constructed formations; underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building marine invertebrates (corals)
Found throughout the ocean (cold-water corals), focus on those in shallow, warm water areas
Structure of coral reefs
Consist of a living framework with internal cavities filled with sediment and a surrounding area of reef-derived skeletal grains
3 Characteristics of coral reefs
Densely populated and diverse community
Actively growing coral colonies, also contain fragments of dead coral and other material
Higher energy environment (attempt to be 1st to obtain nutrients)
3 main types of coral reefs (based on stages of formation)
Fringing reefs
Barrier reefs
Atolls
Fringing reef
A reef that may connect directly to land with a non-existent or shallow back reef; located nearshore
The most common reef type
Living organisms are concentrated on the seaward edge of reef
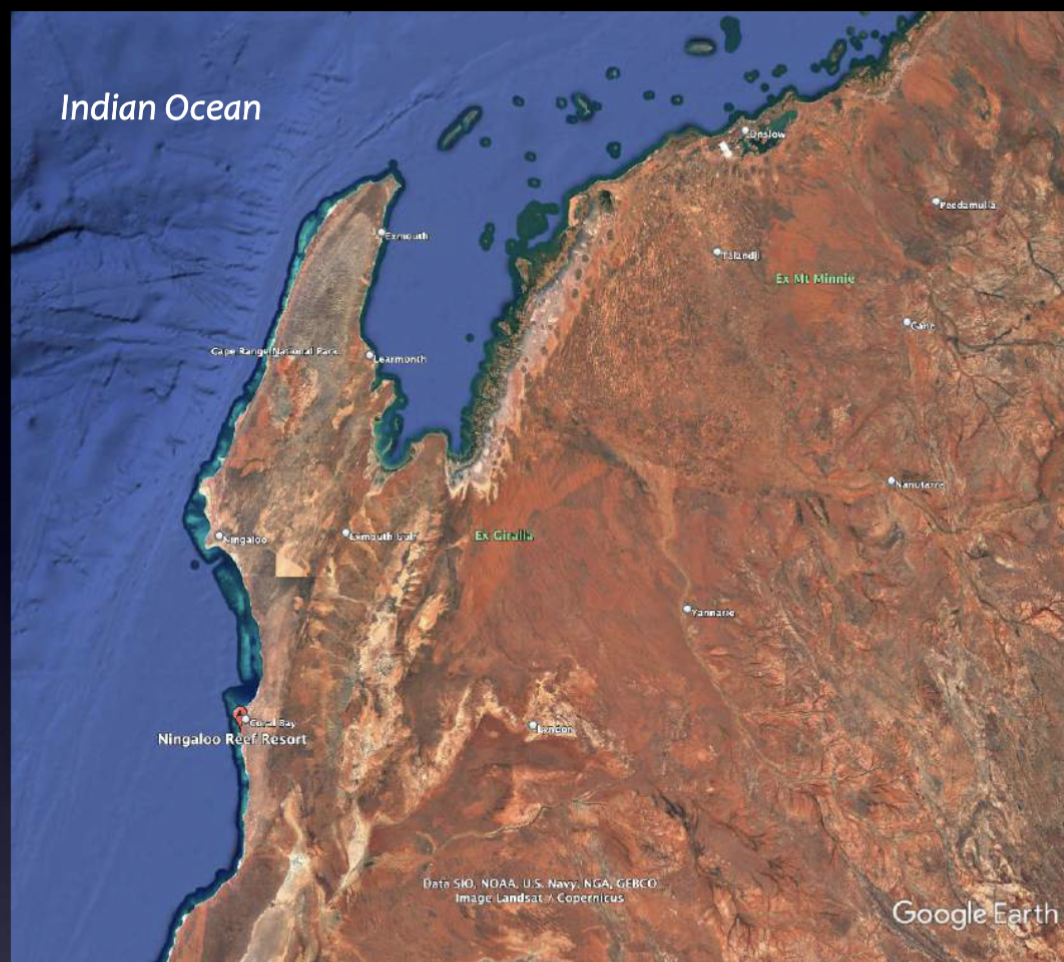
Barrier reef
Reefs separated from land by a deep channel or lagoon with a raised outer (seaward) edge (for greater food supply and therefore faster growth)
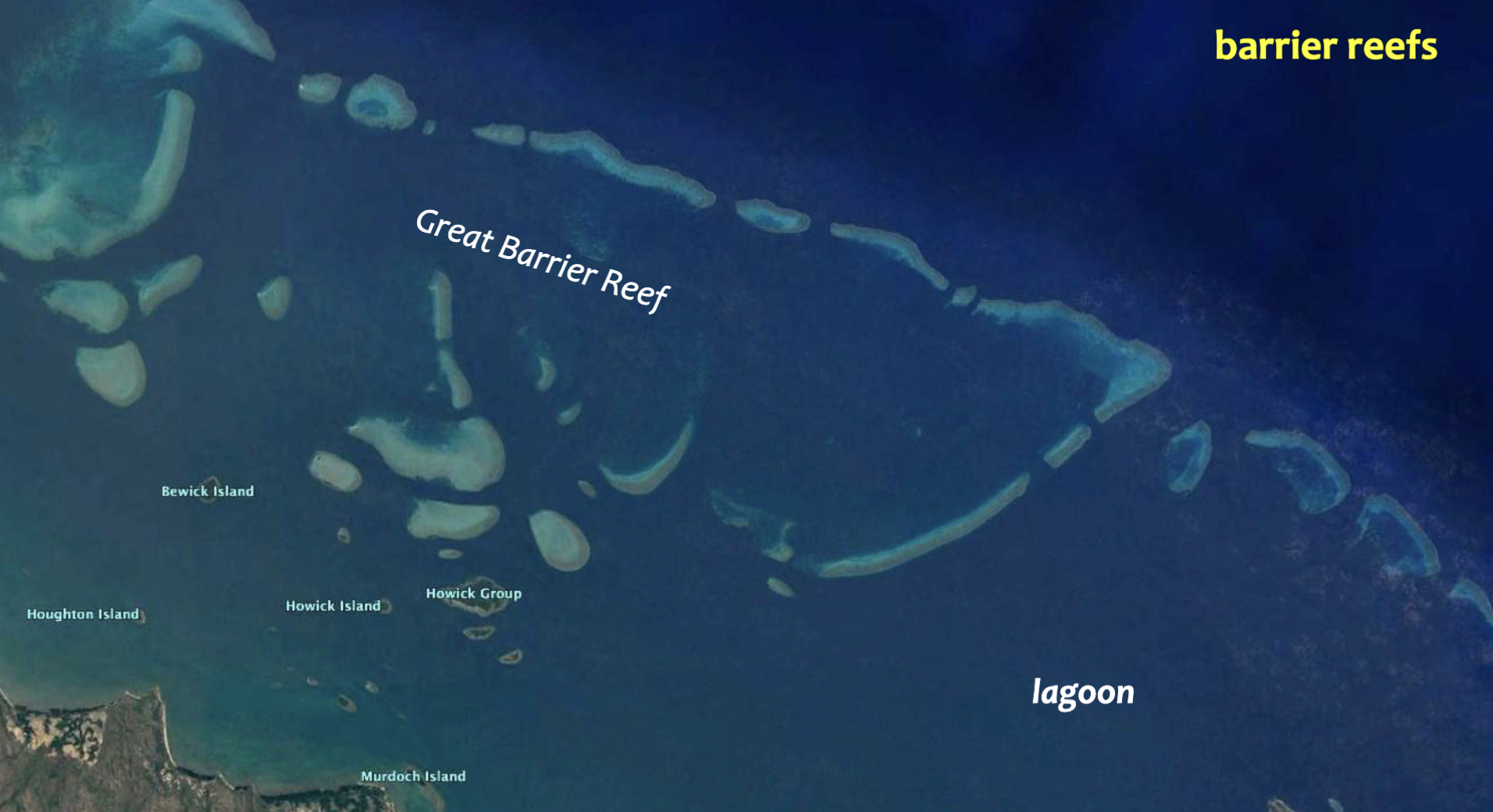
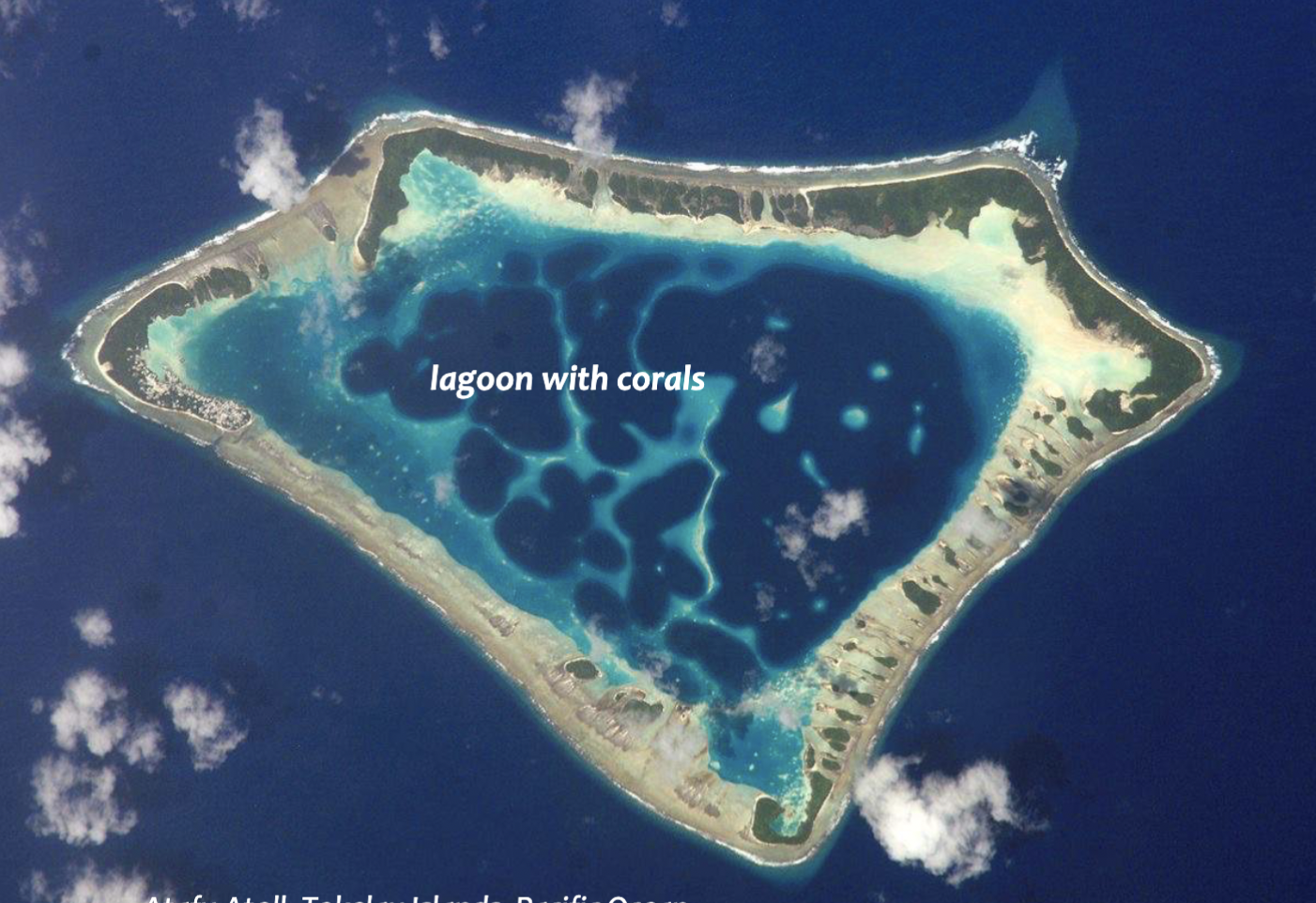
Atoll
A ring-shaped island of coral reefs and coral debris that encloses or partially encloses a shallow lagoon
Potential to be highly affected by sea level rise

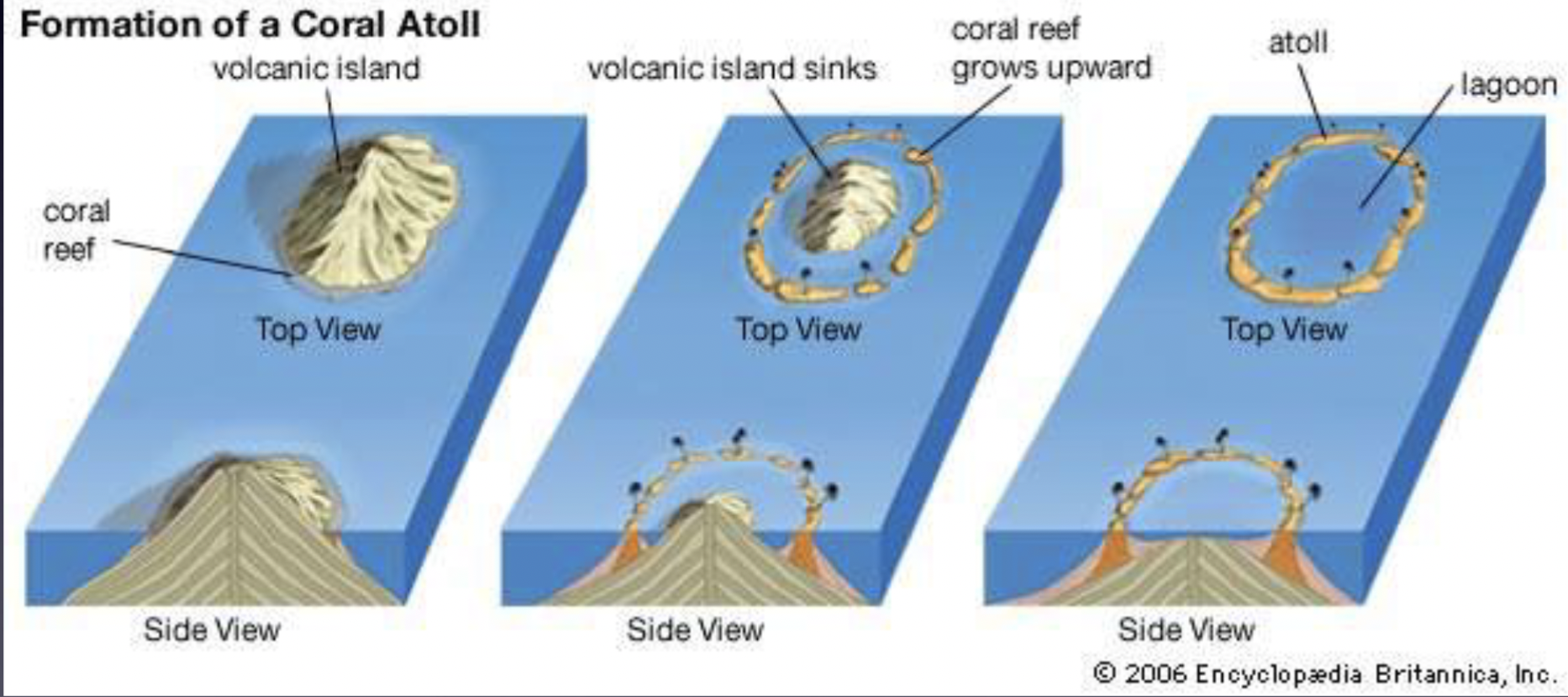
Darwin’s ideas on reef development + flaws
Theory that various types of coral reefs and atolls could be explained by uplift and subsidence of Earth’s crust under the ocean; based on observations made during voyage on the Beagle
Flaw in Darwin’s ideas?
Failed to consider sea level rise and fall due to glaciation (not commonly known in his time)
Who builds the reef?
Phylum Cnidaria (includes corals, sea anemones and jellies)
2 basic body forms of phylum Cnidaria
Free-swimming / floating (nekton) medusae
Sessile/benthic polyps anchored to substrate

Distinguishing feature of phylum Cnidaria
Specialized cells (cnidocytes) used for protection and capturing prey that contain nematocysts (stinging organelles)
Stony/reef-building corals
Any corals that contain zooxanthellae (tiny photosynthetic algae living in their tissue; dinoflagellates)
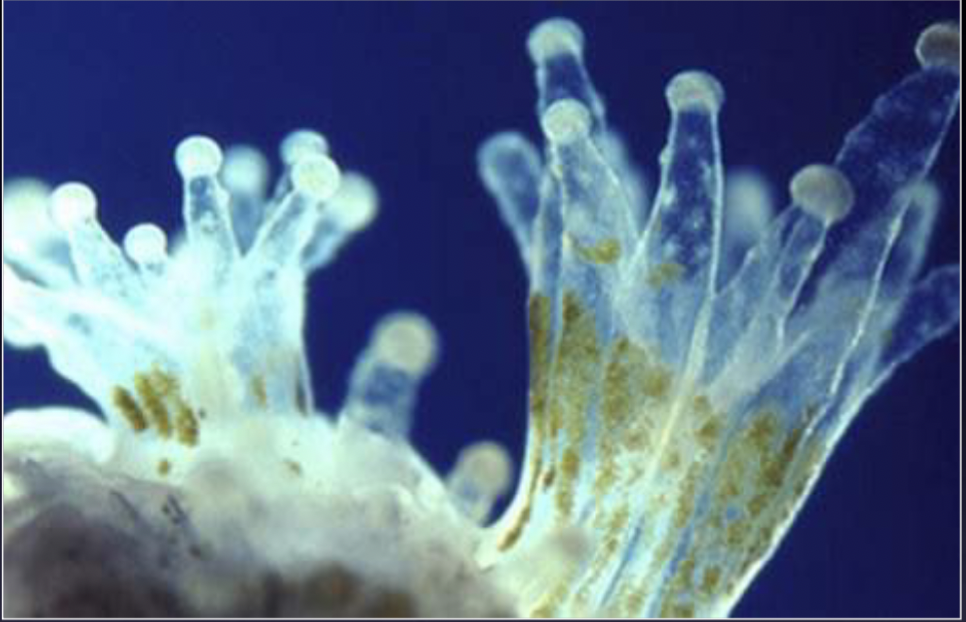
Purpose of zooxanthellae
Create a hard, calcareous skeleton
Mutualism with coral– corals supply nutrients, zooxanthellae supply food!
Gives colour to corals
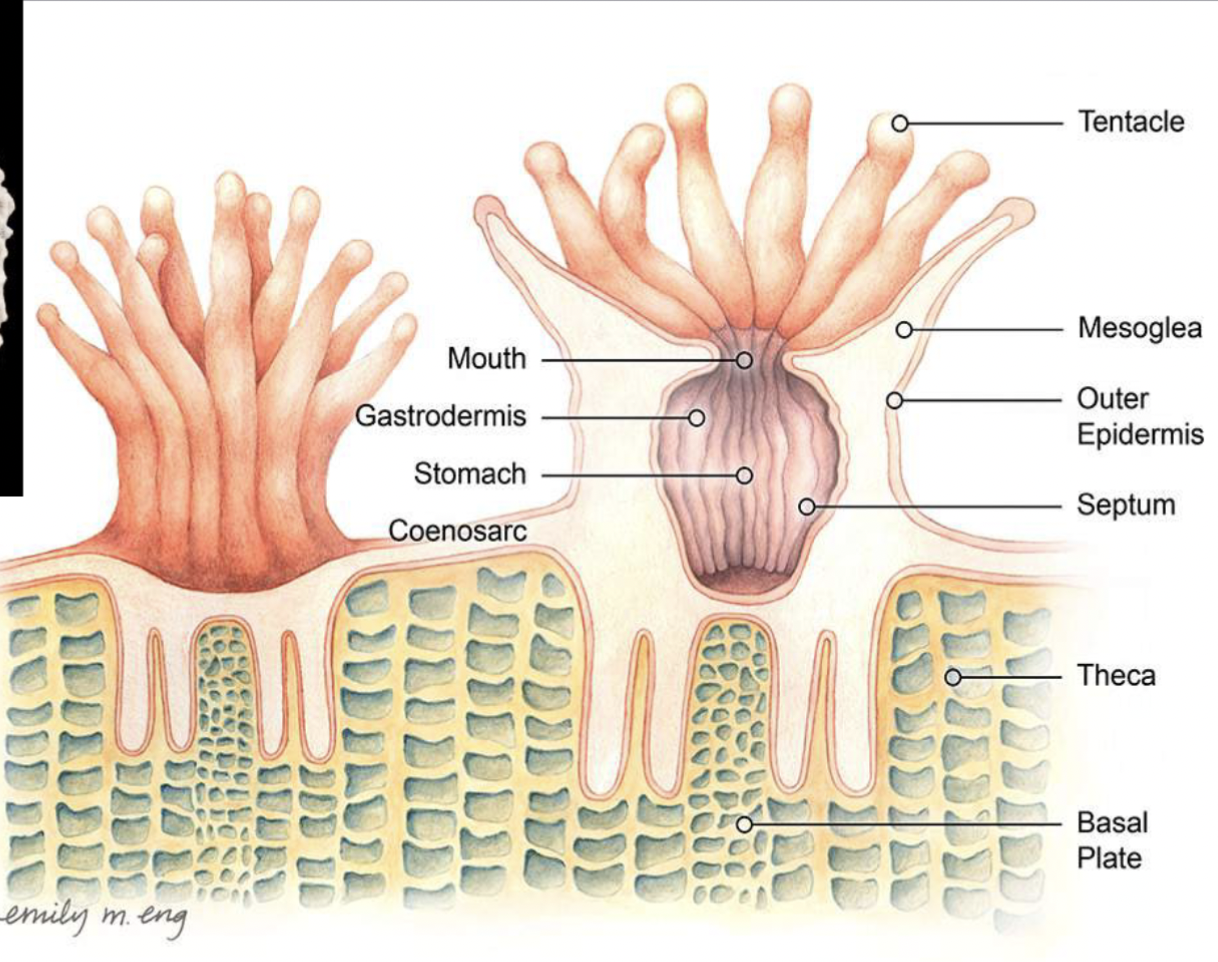
Body of coral polyps
Coral polyps are all stomach and tentacles
With stinging cells on tentacles
They secrete CaCO3 to build a hard outer skeleton
Mixotrophs (i.e reef corals)
Mix of autotrophs (feed themselves) and heterotrophs (feed on others)
How reef corals obtain food
10% from food capture (used for growth and respiration
90% from zooxanthellae
Most of the carbon forms photosynthate (carbs and lipids) which forms a protective mucus
Also used for respiration
Reef-building corals thrive in _______ environments
Oligotrophic (low-nutrient)
How increased nitrate affects reef-building corals
Zooxanthellae retain that nitrate for their own growth which harms the coral’s metabolism, making the coral supsceptible to disease and bleaching
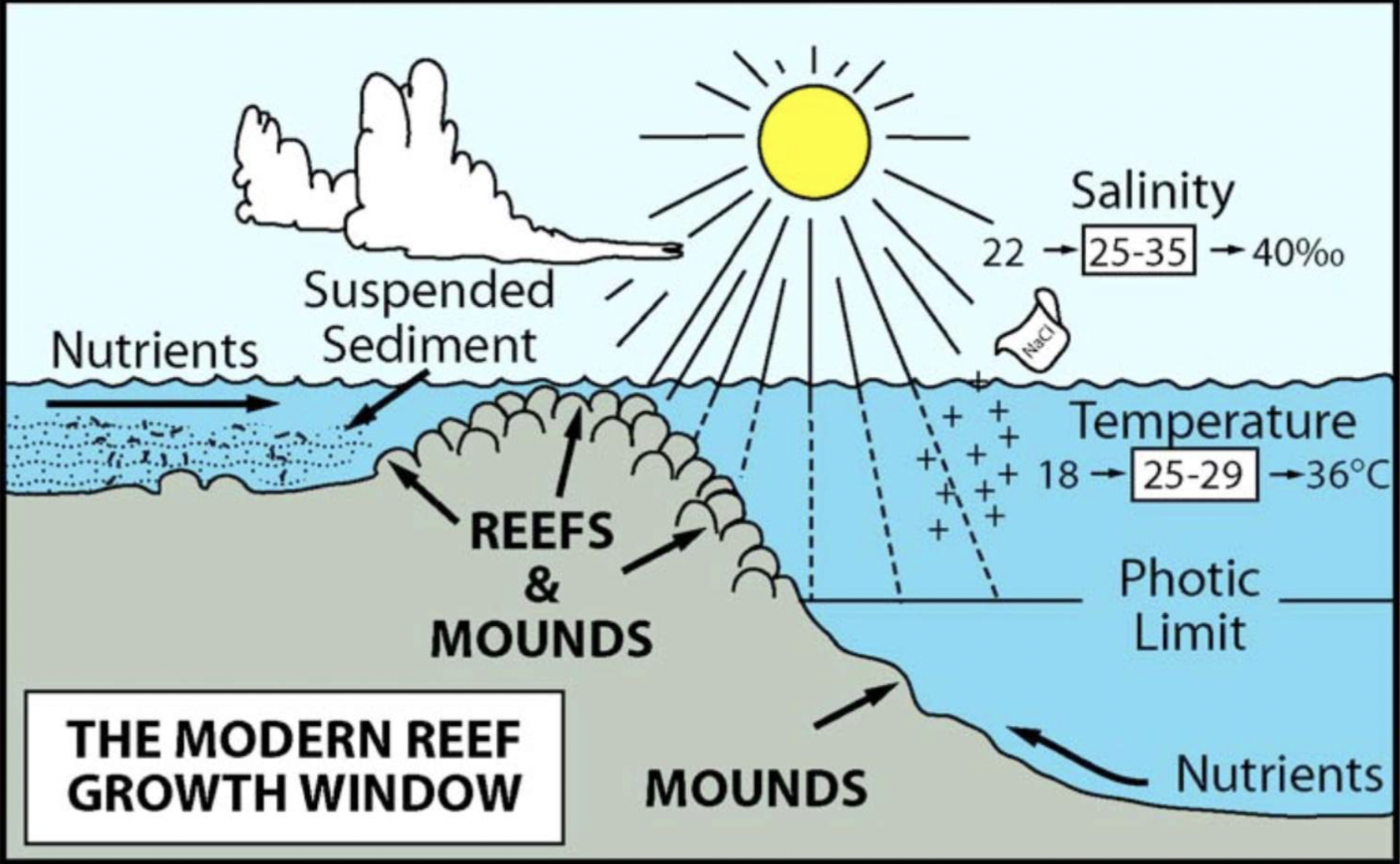
6 necessary conditions for coral reef growth
Clear (nutrient poor) water with low turbidity (little sediment)
Brightly lit (so zooxanthellae can photosynthesize)
Warm, shallow water
Normal to slightly elevated salinity (25 to 35%)
Strong wave or current activity (to bring nutrients and O2 in)
Temperature is 25 to 29 degrees C (temp. that the zooxanthellae like)
Cause of coral bleaching
Death of zooxanthellae due to drastic changes in conditions
Coral reef zonation
They exhibit horizontal and vertical zonation; different coral assemblages and animals live in different places
A result of changes in sunlight as well as other factors (salinity, nutrition, temp)

Growth form and environment of different coral
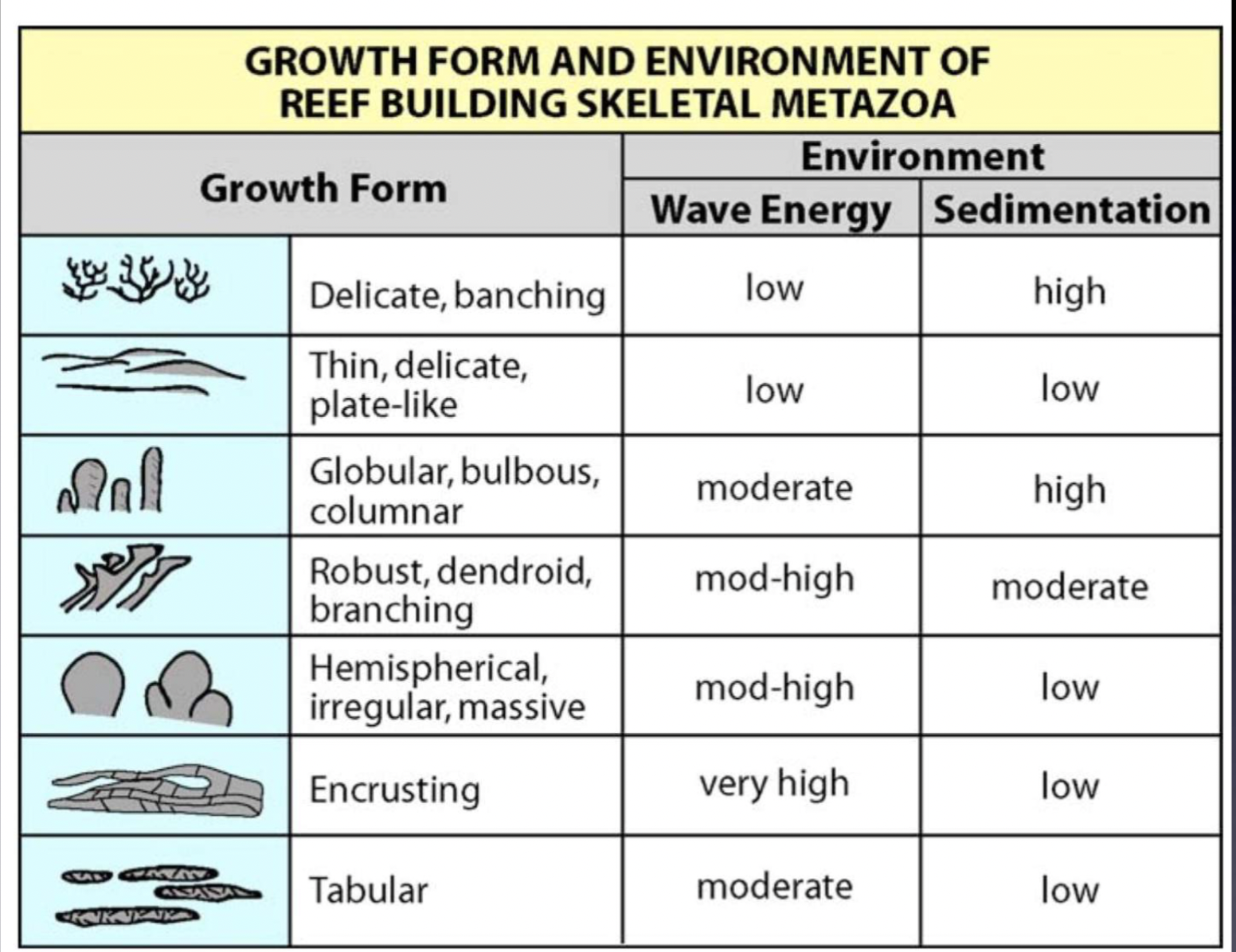
Environment of encrusting corals
Found in very high energy conditions, grow/live directly on the reef substrate
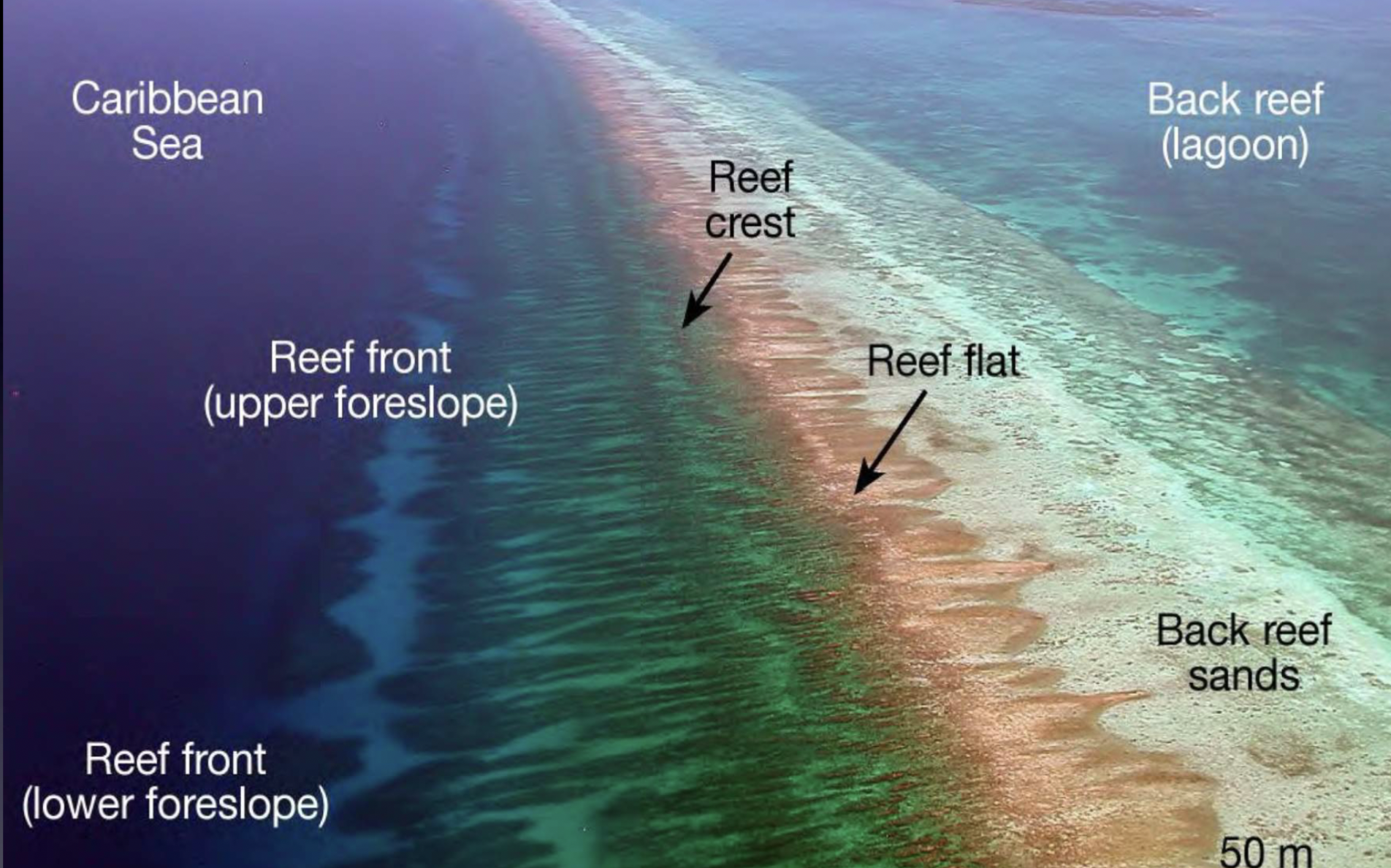
Reef slope
The fore-reef or reef front
Inhabitants of the reef slope
Delicate growth forms and larger corals; species diversity decreases when moving deeper
Reef crest
Highest part of the reef, exposed at low tide with the greatest wave action
Inhabitants of the reef crest
Dominated by robust branching corals and coralline algae
Reef flat
Area of protected calm, shallow water
Inhabitants of the reef flat
Corals and other marine organisms that can tolerate a wide range of temperatures, light intensity, and salinity and adapt to low levels of dissolved oxygen in seawater
Gorgonian corals (soft corals) that do not produce hard CaCO3 structure (also known as sea fans or sea whips); still have polyp
Sea cucumbers (scavengers and deposit feeders; echinoderms)
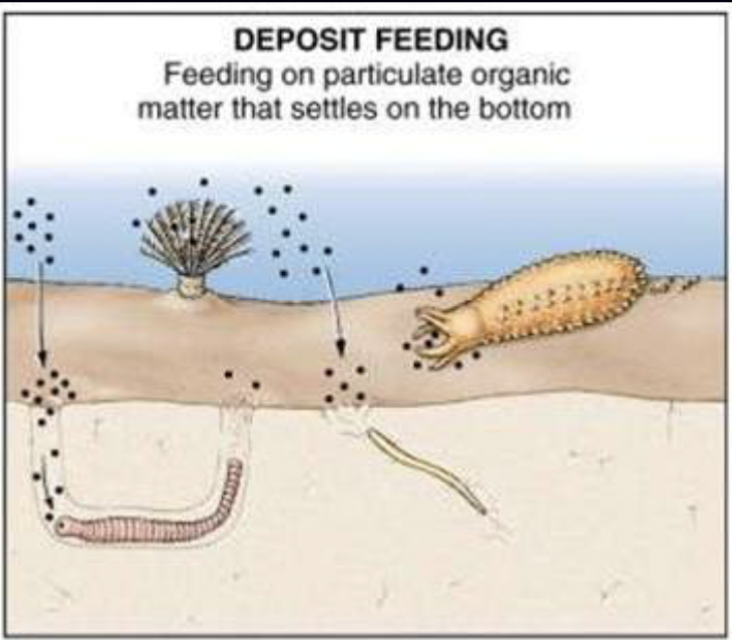
Deposit feeding
Feeding on food items that occur as deposits; some organisms ingest sediment and extract organic matter from it
6 Organisms found in reefs
Calcareous algae
Fish
Sharks and rays
Phytoplankton and zooplankton
Molluscs
Sponges
4 Categories of organisms found in reefs
Builders (corals, calcareous red algae)
Dwellers (bivalves, calcareous green algae, fish, sponges, anemones, crabs…)
Grazers (echinoderms, gastropods, some fish)
Destroyers (sponges, bivalves, annelids)
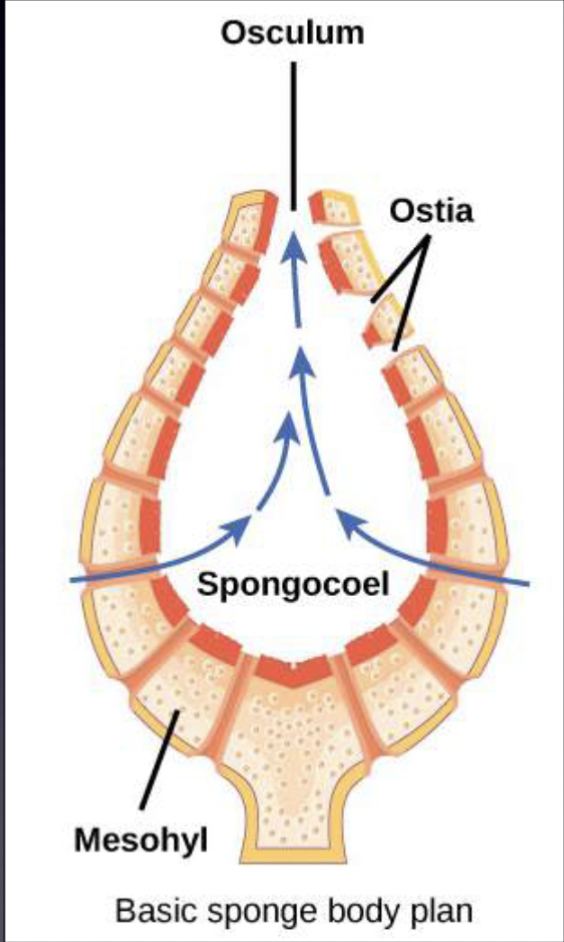
What are sponges
Sessile, benthic filter feeders
Also mixotrophs
Symbiotic relationship with algae where they derive part of nutrition from symbiote
Primitive animals
3 classes of molluscs
Cephalopoda (octopus, squid…)
Bivalvia (clams, oysters, mussels…)
Gastropoda (snails, slugs, periwinkles…)
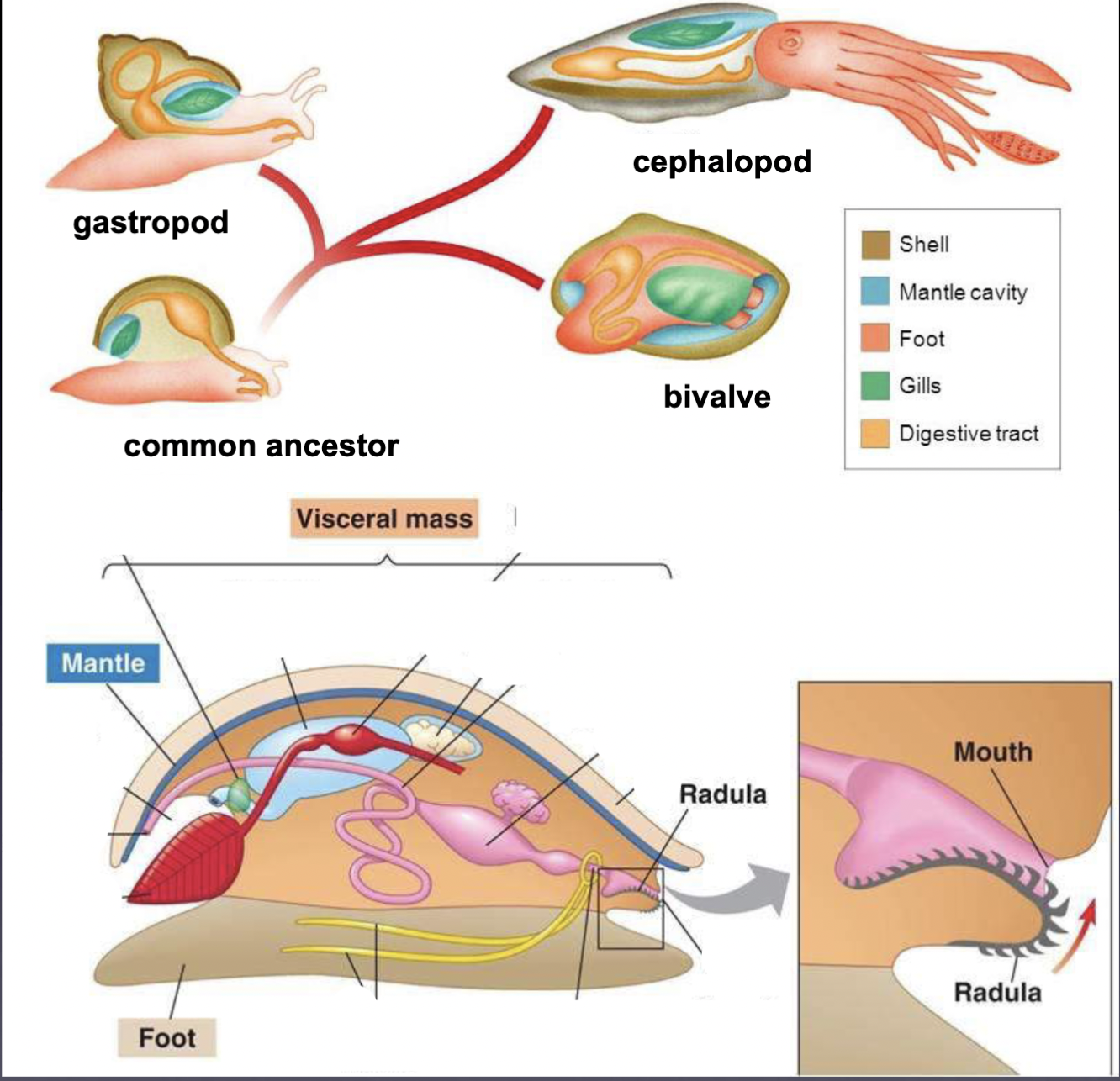
Molluscs
Several classes of organisms (from mussels to octopus) that differ in size, shape, habitat, feeding strategies but have similar body plans and share a common ancestor
4 Parts of a mollusc + their basic function
Foot: movement
Mantle: creates the shell; covers the visceral mass
Shell: protects the visceral mass (‘guts’); 3 layers
Radula: tiny teeth; a scraper
3 life strategies of molluscs
Carnivorous feeding
Siphoning
Filter (suspension) feeding
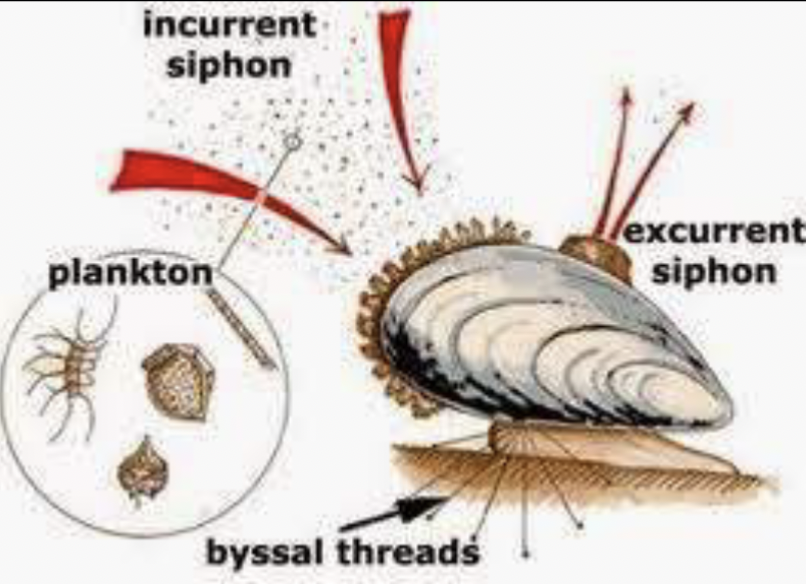
Siphon (molluscs)
Siphon promotes water flow and used for locomotion, feeding, respiration, and reproduction
Symbiotic algae living in its mantle
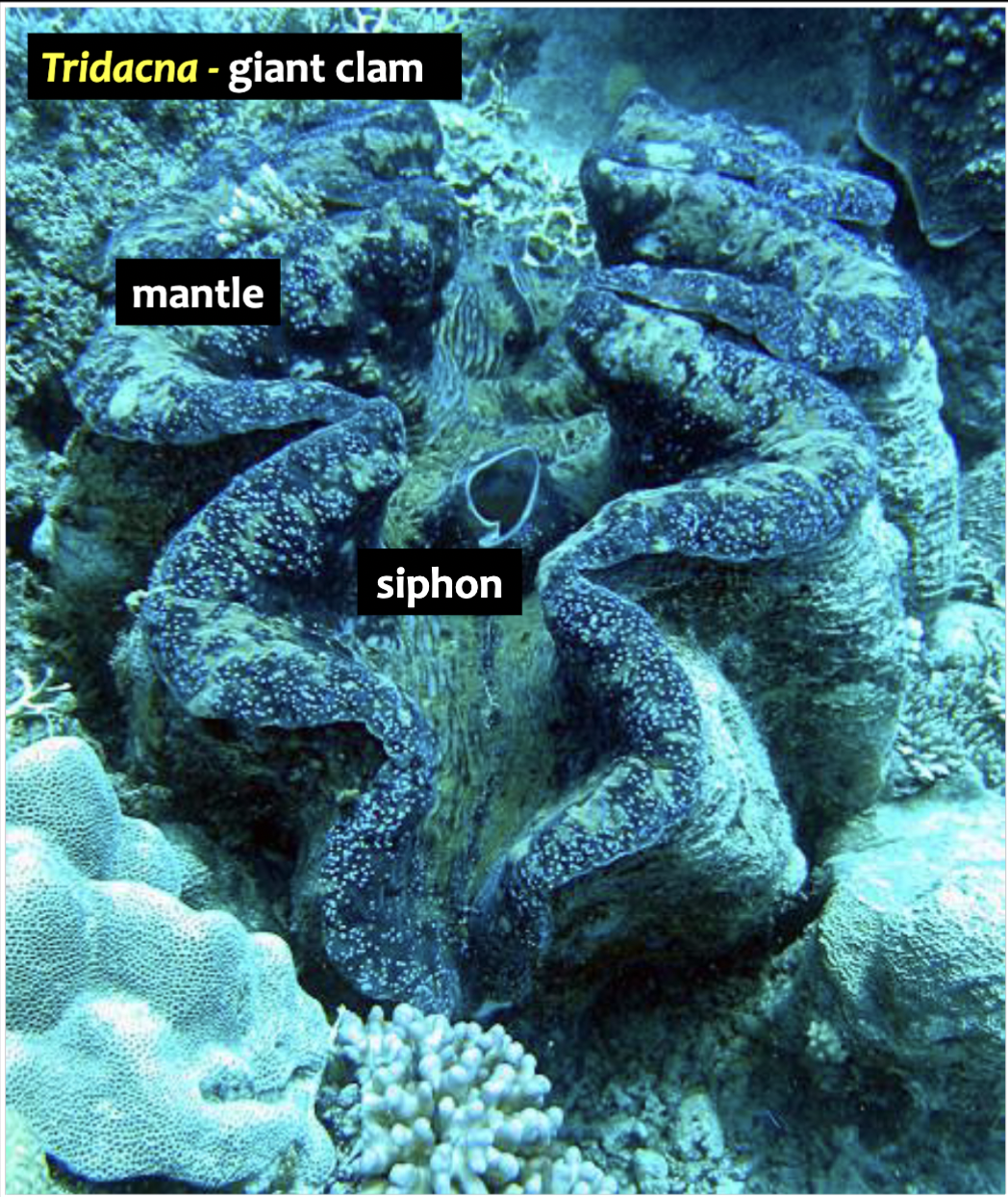

Filter (suspension) feeding
Organism cannot move and attached to a substrate (e.g. clams, oysters)
Have special structures where water passes through – filter food particles out
Ecological role of parrot fish
They browse on and ingest corals and algae; excrete carbonate sand
4 reasons why coral reefs are so important
Home to >> 1 million diverse aquatic species
Have a global estimated value of $3 trillion per year, including tourism and food
Provide coastal protection (reduce shoreline erosion by absorbing energy from the waves) which protects coastal housing, agricultural land and beaches
Home to species that contain pharmaceutical compounds— treatments for illnesses and diseases
4 factors that can lead to coral bleaching
Climate change causing changes in water temp
Extremely low tides causing exposure
Overexposure to sunlight
Pollution