Breast Cancer (Riley)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
table of tx for reference
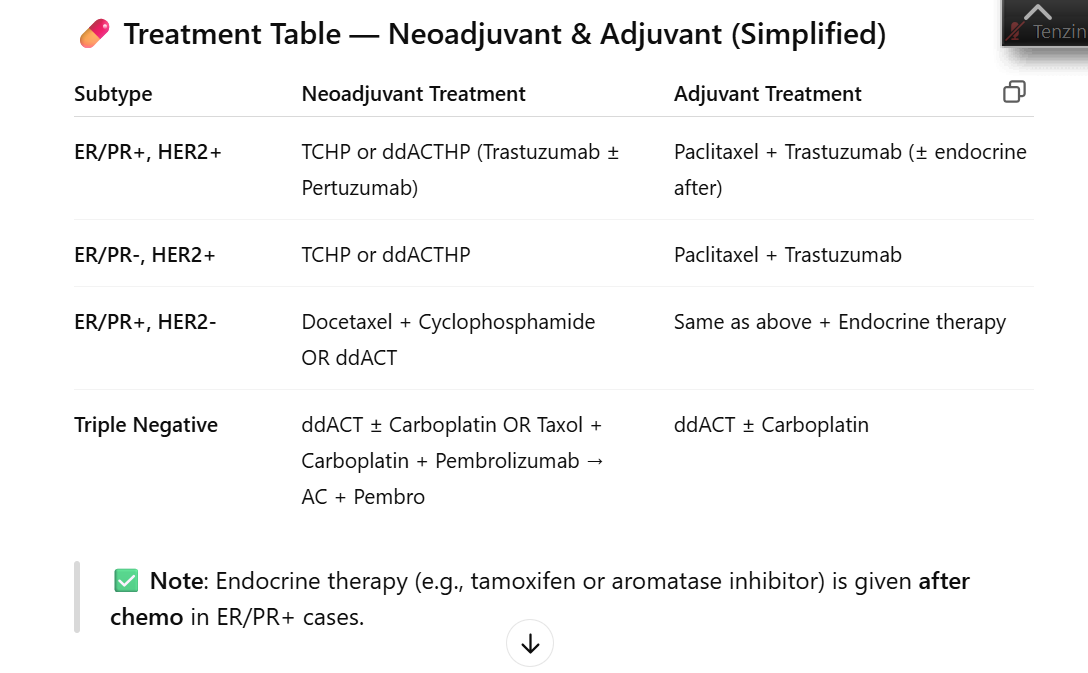
Recommended treatment plan for ER/PR+, HER2+ breast cancer: neoadjuvant (2)
1. TCHP
2. ddACTHP - trastuzumab ± pertuzumab to complete in 1 year
Recommended treatment plan for ER/PR-, HER2- breast cancer: neoadjuvant (2)
1. ddACT ± carboplatin
2. Taxol/carboplatin/pembrolizumab followed by AC/pembrolizumab
Recommended treatment plan for ER/PR-, HER2- breast cancer: adjuvant
ddACT ± carboplatin
Recommended treatment plan for ER/PR+, HER2- breast cancer: neoadjuvant/adjuvant (2)
1. Docetaxel + cyclophosphamide
2. ddACT
Recommended treatment plan for ER/PR-, HER2+ breast cancer: neoadjuvant (2)
1. TCHP
2. ddACTHP - trastuzumab ± pertuzumab to complete in 1 year
Recommended treatment plan for ER/PR-, HER2+ breast cancer: adjuvant
Paclitaxel + trastuzumab
Recommended treatment plan for ER/PR+, HER2+ breast cancer: adjuvant
Paclitaxel + trastuzumab
Recommended treatment for breast cancer with BRCA1/2 mutation
Olaparib
Recommended treatment for breast cancer with PIK3CA mutation (3)
1. Capivasertib
2. Alpelisib
3. Inavolisib
Recommended treatment for breast cancer with MSI-H/dMMR
Pembrolizumab
Recommended treatment for breast cancer with CDK4/6 over-expression (2)
1. Abemaciclib
2. Ribociclib
What is the most common dose-limiting side effect with the combination of trastuzumab + pertuzumab?
diarrhea
What drugs are specifically used in ER+/PR+ breast cancer?
endocrine therapy, should be initiated AFTER chemotherapy (adjuvant)
Unique adverse effects for Tamoxifen (SERM) (3)
1. Hot flashes
2. DVT and PE risk
3. Increased risk of endometrial cancer
Unique adverse effects for aromatase inhibitors (ex. anastrozole, letrozole) (3)
1. Hot flashes
2. Arthralgias
3. Osteopenia and osteoporosisis
Why are GNRH inhibitors used with aromatase inhibitors in premenopausal patients and not (usually) in post-menopausal patients? (2)
1. In premenopausal women, aromatase inhibitors (AIs) must be combined with a GnRH agonist to suppress ovarian function (estrogen production), rendering the patient functionally postmenopausal so the AI can effectively lower systemic estrogen levels.
2. After menopause, the ovaries no longer produce significant estrogen. Therefore, AIs are effective as monotherapy in postmenopausal women, with no need for additional ovarian suppression
What is the likely dose limiting adverse effect for the breast cancer drug ribociclib used for CDK4/6 over-expression?
neutropenia
How is the mucositis associated with everolimus mitigated for breast cancer treatment?
swishing with dexamethasone oral solution
What screening modalities are available for breast cancer?
Brest Self Examination (BSE)
generally not recommended d/t false positives
Clnical Breast Exam (CBE)
not uniformly recommended
Mammography
Starting at age 40 yearly (American cancer society) or q2 years (USPTF)
Breast MRI → adjunct to mammogram in high-risk patients (ex: BRCA mutation carrier)
What are the risk factors for developing breast cancer?
Age
Family history of breast cancer
Endogenous Estrogen Exposure
Exogenous Estrogen Exposure
Benign Breast Disease/Dense Breast Tissue on mammogram
Radiation exposure to the breast or chest
Obesity and BMI
Physical activity
Alcohol intake
Which mutations are common in breast cancer?
HER2 (20-30%)
Which molecular tests are routinely obtained for breast cancer?
Hormone Receptor Status (ER/PR) | HER2 | TNBC |
-Used to predict response to endocrine therapy - Presence of estrogen receptors (ER) or progesterone receptors (PR) occur in 60-75% of breast cancers - Positive test common in post-menopausal women → higher response to endocrine therapy and longer disease free survival | - overexpression of HER2 associated with transmission of cancer growth signals - occurs in 20-30% of breast cancers - higher mortality rates | 15% of cancers |
What is the difference in meaning between neoadjuvant treatment vs adjuvant treatment?
Neoadjuvant treatment - preoperative, treatment given BEFORE surgery to shrink tumor
Adjuvant - postoperative, treatment given AFTER surgery to prevent recurrence
in early breast cancer, pembrolizumab is only indicated in ________
triple negative
How does the mechanism of action of tamoxifen differ from that of the aromatase inhibitors?
Aromatase Inhibitor | MOA |
Anastrozole | Decreases estrogen biosynthesis by selective inhibition of aromatase (estrogen synthase) |
Exemestane | Irreversible steroidal aromatase inactivator, decreases estrogen biosynthesis in peripheral tissues |
Letrozole | Decreases estrogen biosynthesis by selective competitive inhibition of aromotase in peripheral tissues (estrogen synthetase) Inhibition of aromotase reduced conversion of adrenal androgens (testosterone + androtenedione) to estradiol/estrone |
What are the typical side effects of tamoxifen, the aromatase inhibitors, and the GNRH inhbitors?
Tamoxifen | BBW: → increased risk of uterine malignancies → thromboembolic events: DVT + Stroke & PE |
Aromatase inhibitors | Hot flashes |
GNRH inhibitors | Tumor flare (temporary worsening of sx) |
How is the mucositis associated with everolimus mitigated?
Stomatitis - risk for mouth sores,
SWISH Trial: Preventative Dexamethasone rinse