Derm 2025 Lesions
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
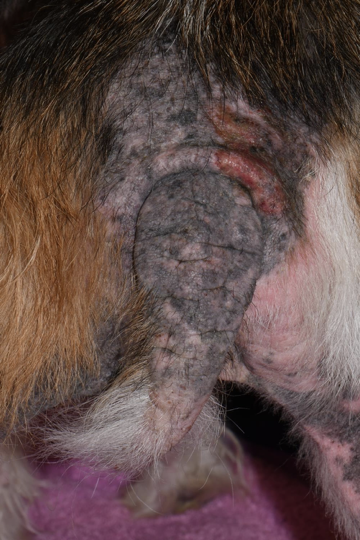
Shar pei’s have a breed disposition to:
Dermal mucinosis - Mucin is the squishy substance between our collagen fibers and the dermis that allow us be squeezed and our tissue does not stay looking deformed.
In sharp peis, there is lack of outflow of mucin, so it starts to leak out.
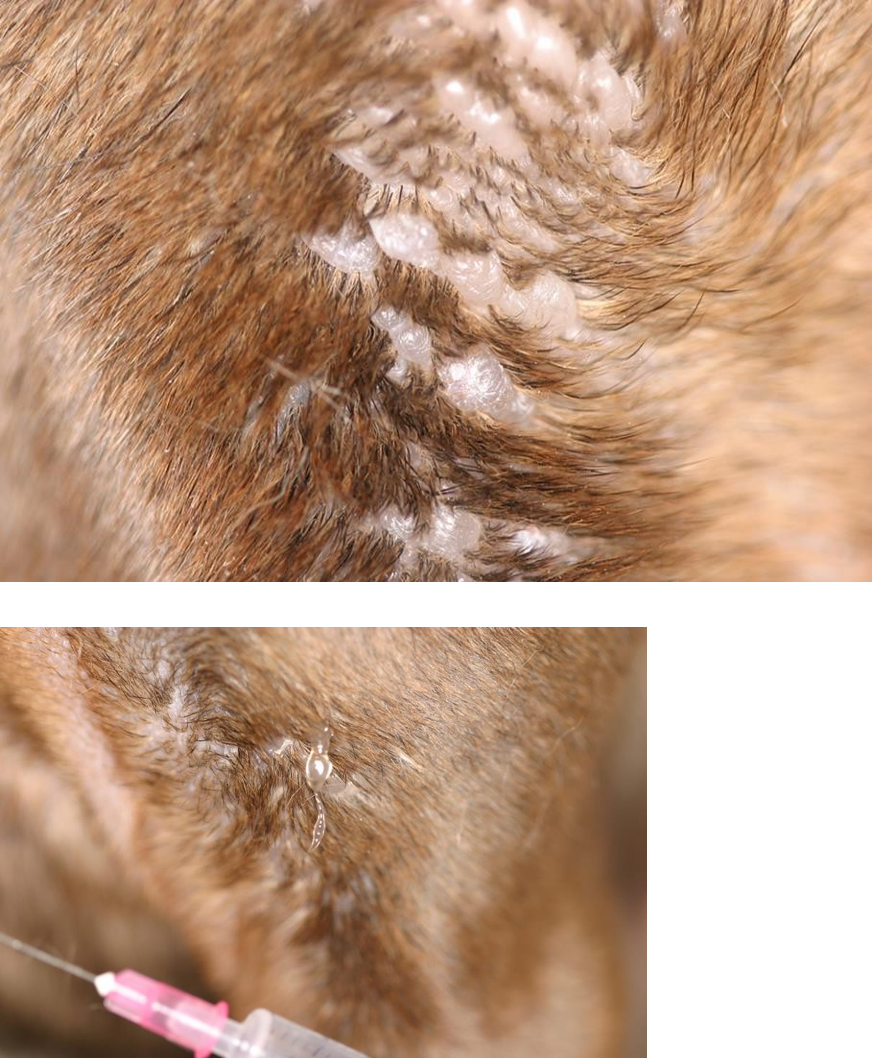
What is sun induced dermatitis?
Sun induced problem can also be seen in animals that have white and black pattern. If the skin lesions are only localized to the white areas, then it is likely a problem.
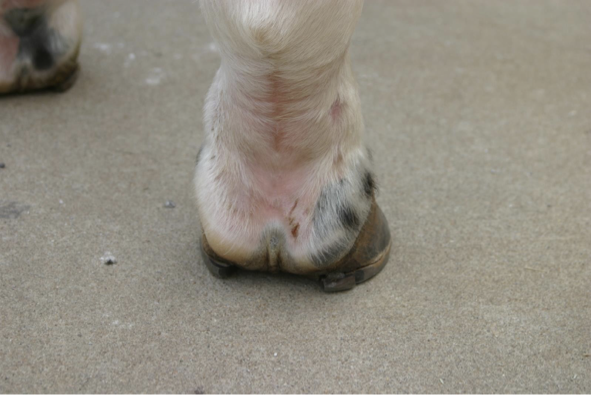
Differentiate between a kitten mass and a senior cat mass in the ear canal. Which one is more concerning?
Kitten more likely to have an inflammatory polyp
Older (senior) cat are more likely to be a malignant growth – adenocarcinoma
But BOTH look the same.
Age matters
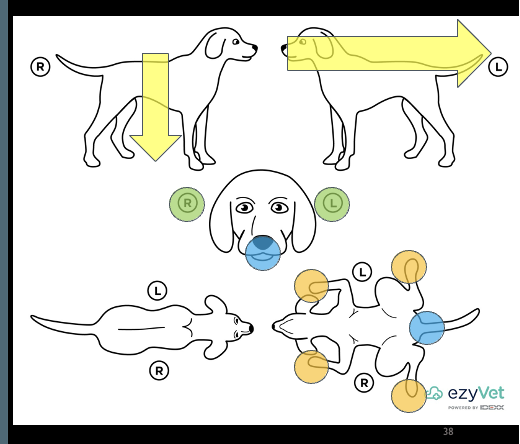
Provide the steps to a dermatological examination with a body map
Body maps are available for all species
Start at tip of nose to the tip of tail
Start at the back and work distally to the paws
Spread the digits to see all of them in all 4 paws
Mucus membranes could have lesions so look at that too and anal/perineal region
Ears should also be covered
Differentiate between primary and secondary skin lesions
initial eruption driven by skin disease ex: pustule
crusty lesion - ex of secondary lesion
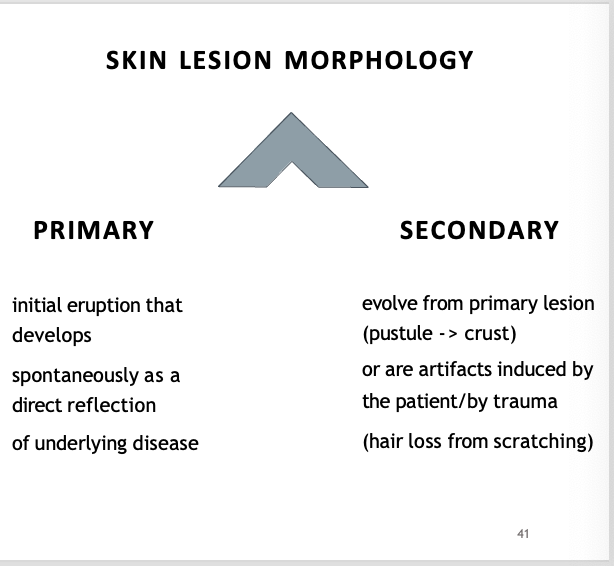
Differentiate between primary and secondary hairloss. Medical term?
Alopecia
Hairloss due to thinning, non itchy - primary
Hairloss and development of pustules due to self induced trauma (scratching) - secondary
Define macule
an area of skin that has changed color
primary lesion
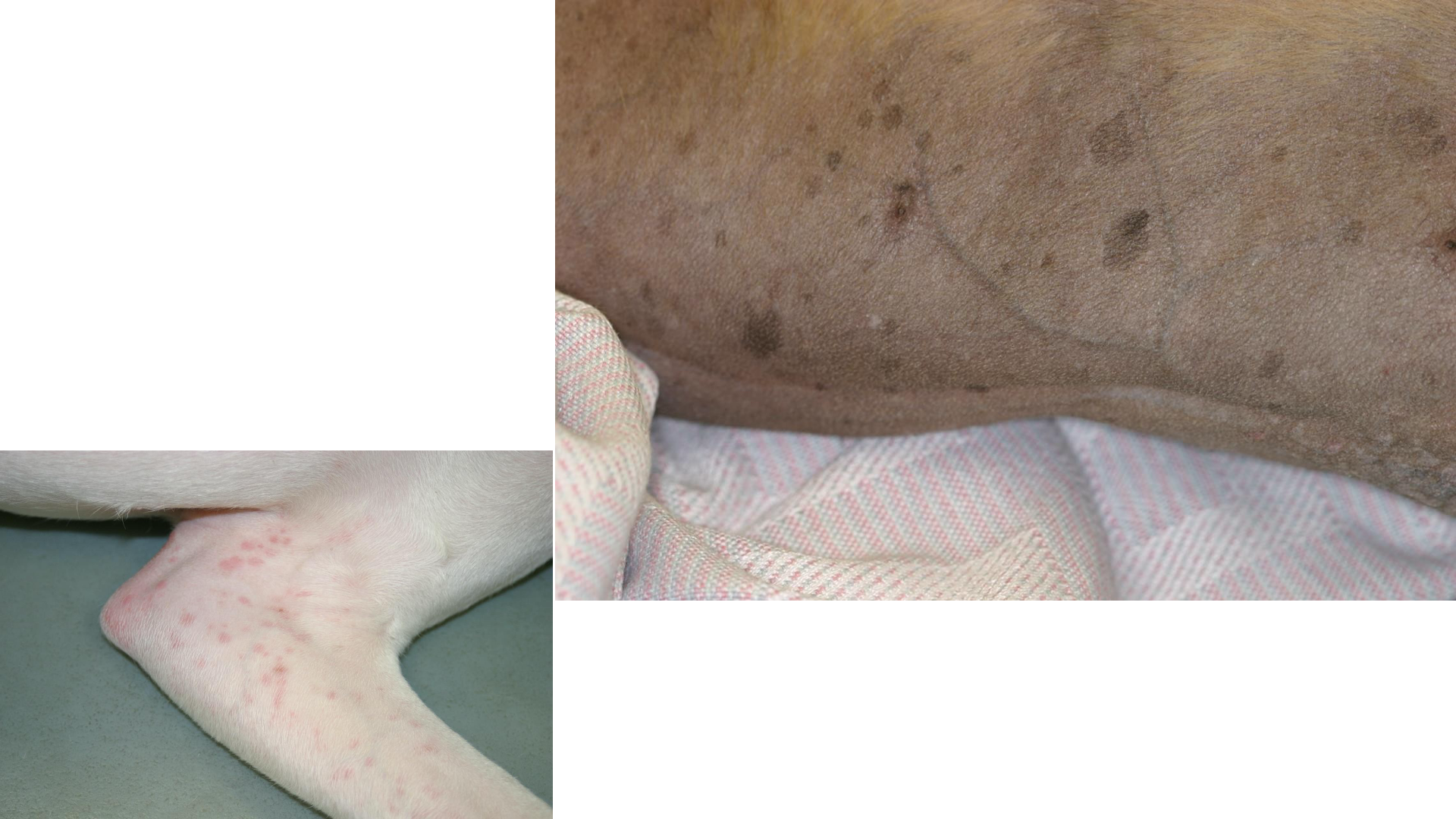
Define papule
Elevated solid, palpable lesion <1cm
can be early stages of pyoderma or skin cancer
primary lesion
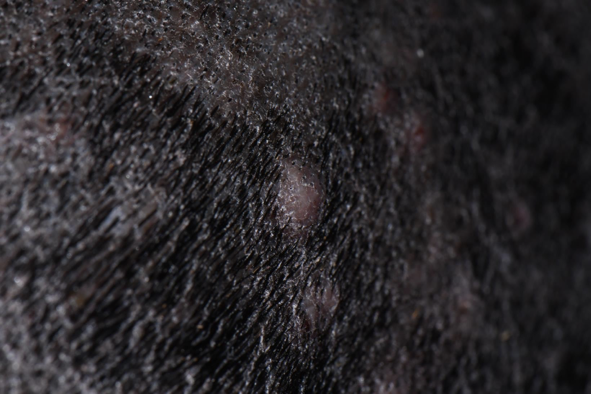
Define Plaque
Elevated solid, palpable lesion >1cm
primary lesion
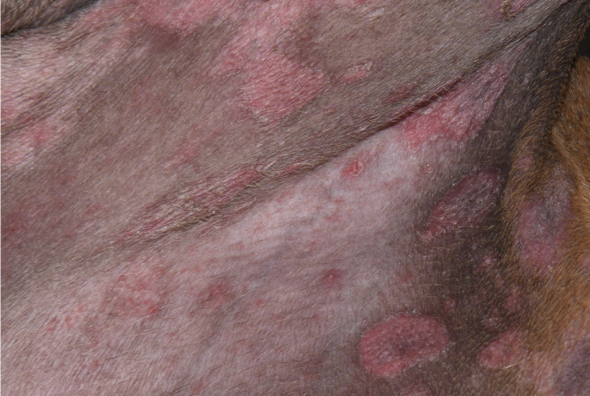
Define Wheal
Circumscribed, raised lesion consisting of edema
Wheal = hives
typically allergic reactions
primary lesion
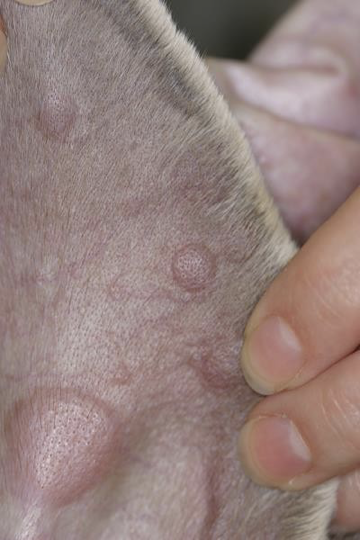
Define nodule
Circumscribed, solid, elevated lesion >1cm. Often extends into the deeper layers of the skin like the dermis
primary skin lesion
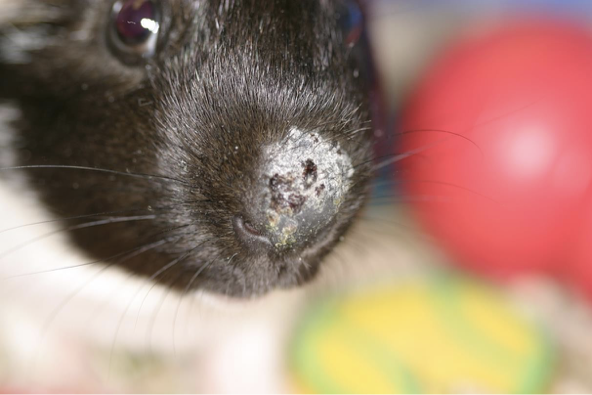
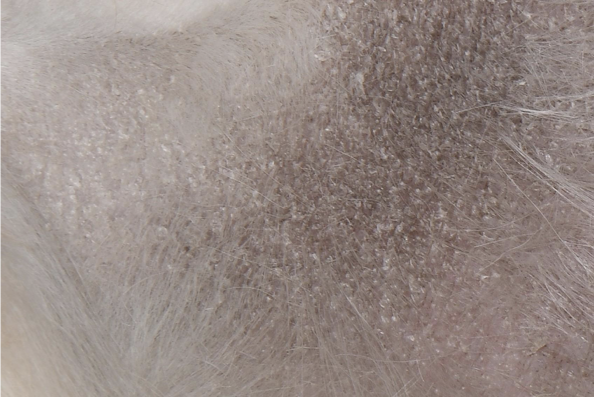
Define Scales
Accumulation of CORNIFIED cells
primary or secondary skin lesion
Hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation may be ___
indicative of underlying issue
can be primary or secondary skin lesion
Define Comedo
Dilated hair follicle filled with sebaceous material and cornified cells. Patients with hormonal diseases, and hair follicle mites have this.
can be primary or secondary lesion
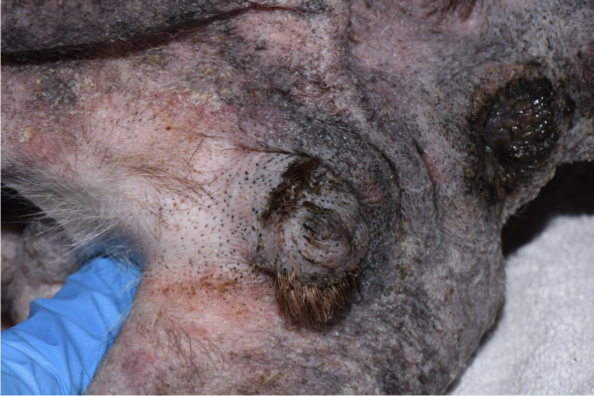
Define Epidermal Collarette
special type of scale arranged in circular rim of loose keratin flakes or peeling keratin. Confused with ringworm.
can be primary or secondary skin lesion
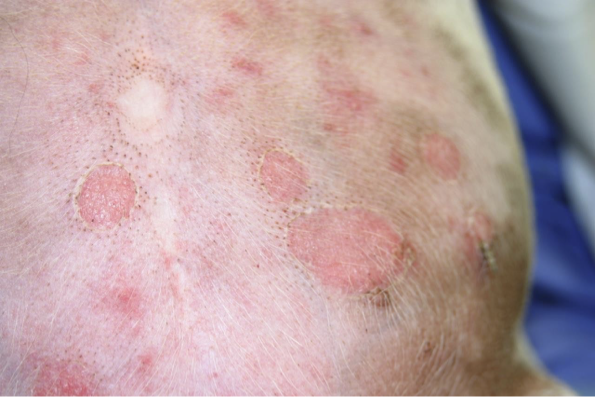
Define excoriation
Self-induced erosions or ulcers (by scratching, biting); often linear
secondary lesion
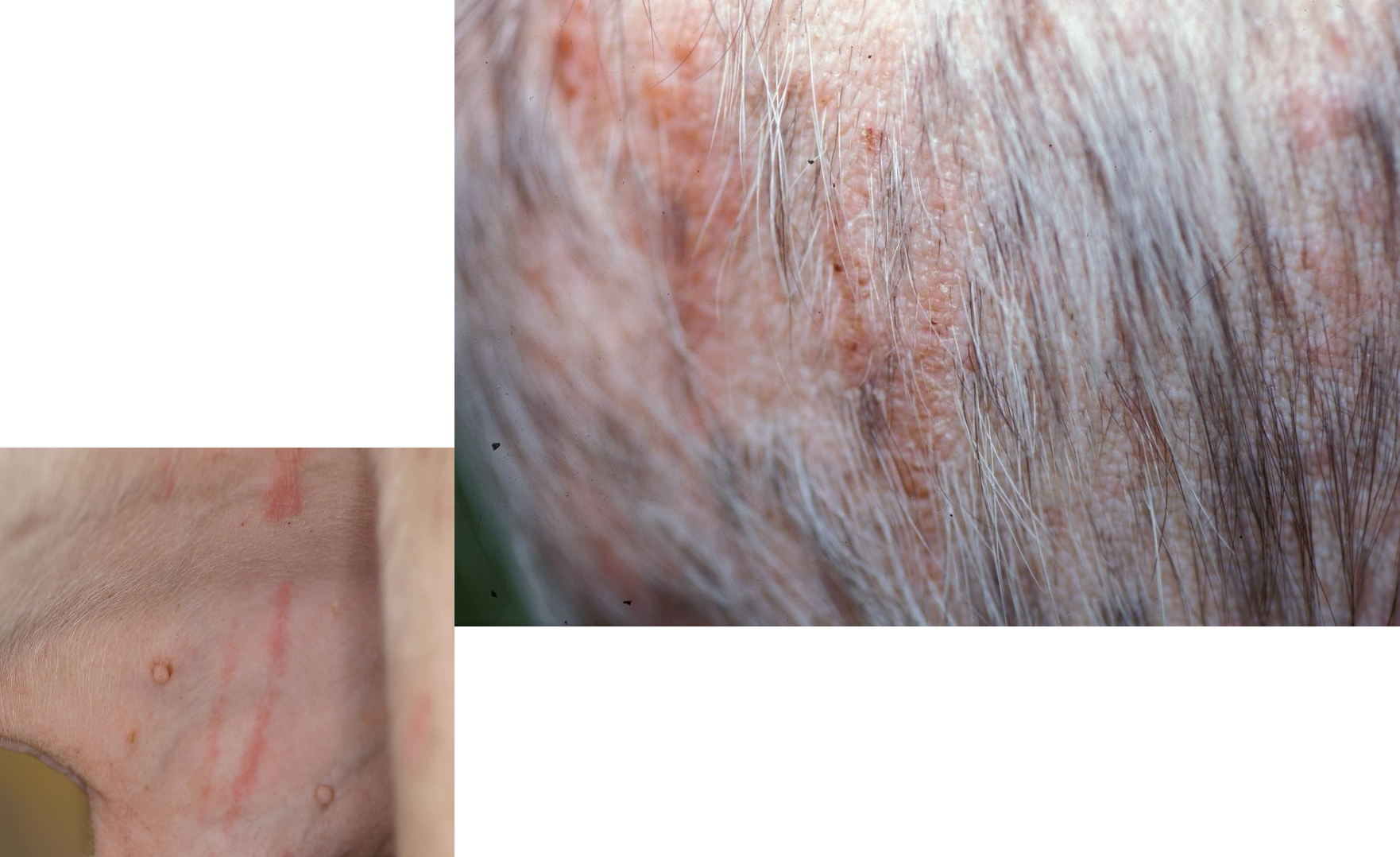
Define erosion
shallow epidermal defect that does not penetrate basal laminar zone
Can simply be caused by disease and heal without a scar.
secondary lesion
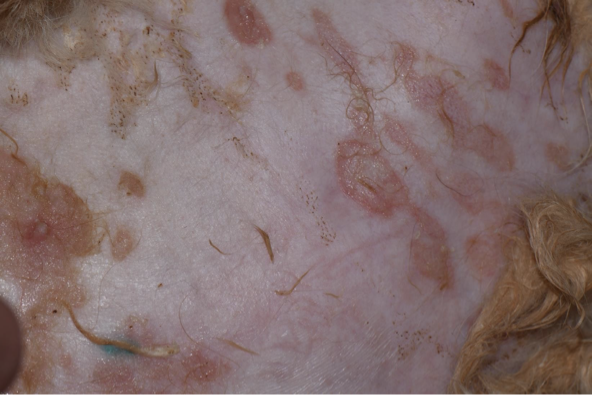
Define ulcer
A break in continuity of epidermis with exposure of underlying dermis. Red, angry, and can bleed. Can heal but with scar.
Secondary lesion
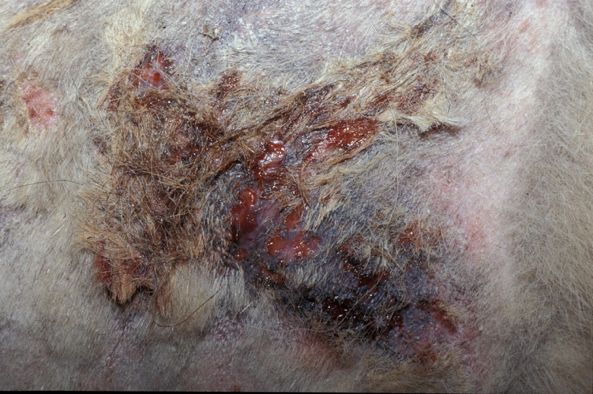
Ulcers in the mouth or other mucosal tissue can is caused by ___
Break in the continuity of mucosa with exposure of underlying dermis. Can also be on the anus, vulva, or gums.
secondary lesion
Define lichenification
elephant like skin surface, exaggeration of superficial surface architecture, thickening of the skin. Constant inflammation and itchy skin leads to lichenification
secondary lesion