Lecture 13 - Animals: Cnidarians, Platyhelminthes, & Annelids
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
General characteristics of the members from phylum Cnidaria
-Eumetazoans (true animals) have embryonic germ layers
-Diploblastic (ectodermis and gastrodermis)
-Radial symmetry
What is the gastrovascular cavity in a cnidarian?
-A central cavity w/ a single opening
-functions as both a mouth and an anus
Cnidarian medusa form
-oral surface faces down
-moves by drifting freely or body contractions
Cnidarian polyp form
-mostly sedentary
-can detach from surface
-oral surface faces up
Oral surface of cnidarian
surface where mouth is located (tentacles)
Aboral surface of cnidarian
surface opposite to mouth
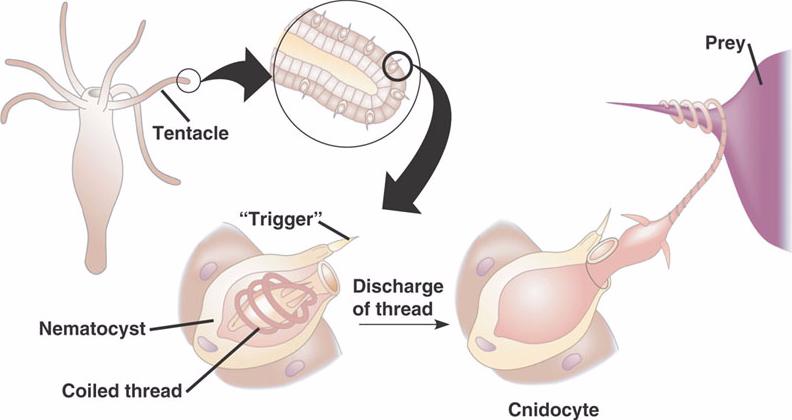
Cnidocytes
-stinging cells that contain cnidae (nettle), capsules capable of exploding outward
-found on tentacles
-used for defense and capture of prey
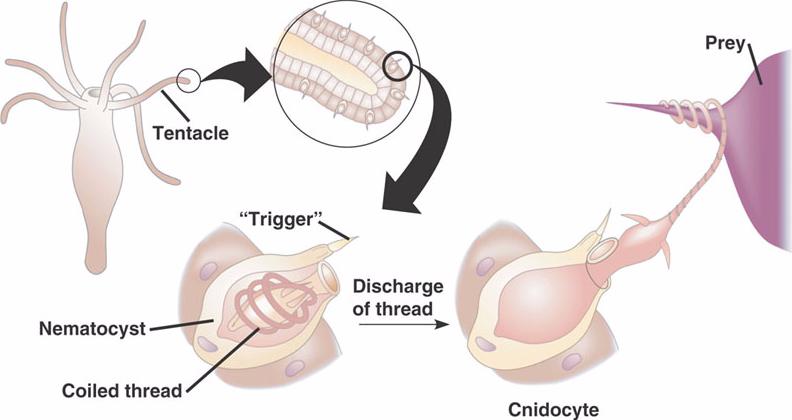
Nematocysts
organelle in Cnidocytes that ejects a stinging coiled thread to entangle or paralyze prey
Medusozoans
-spend majority of life in medusa form
-jellies, box jelly
Anthozoa
-exist only in polyp form
-sea anemone, corals
Coral colony structure: presence of algal endosymbiont
Form symbiosis with zooxanthellae algae
-photosynthetic algae provides sugar to coral
Coral colony structure: formation of exoskeleton
Secret and build exoskeleton of calcium carbonate
-build on top of previous generations’ skeletons
General features of Lophotrochozoans
-Bilateral symmetry
-Protostome development
Either:
~Lophophore: ciliated feeding structure around mouth
~Trochophore: a type of developmental larval stage
General characteristics of Platyhelminthes?
-Protostome
-Acelomates (no internal body cavity)
-Live in aquatic and damp terrestrial environments
-Lack a circulatory system
-Some species are free-living (class Turbellaria), others are parasites (class Cestoda)
-Monoecious
Why are platyhelminthes flat?
-Minimizes surface area
-Gas exchange and waste removal all via diffusion across body
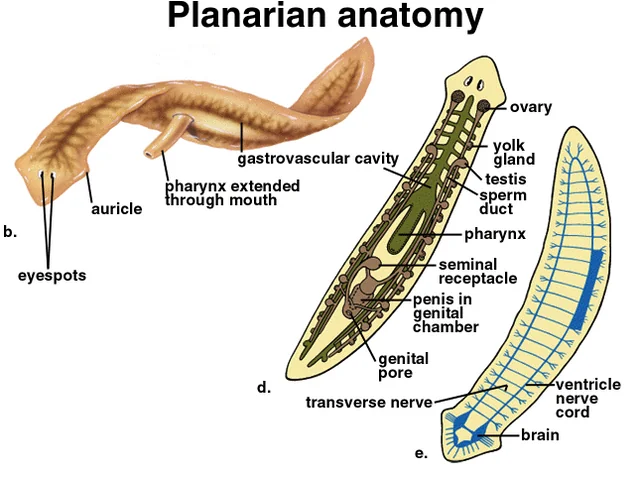
Planarian features: Eyespots
light detection
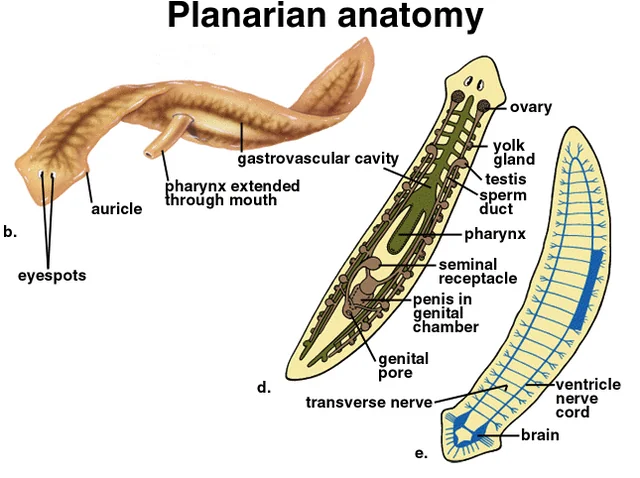
Planarian features: Ganglia
dense nerve cell clusters at front end, centralized nervous system
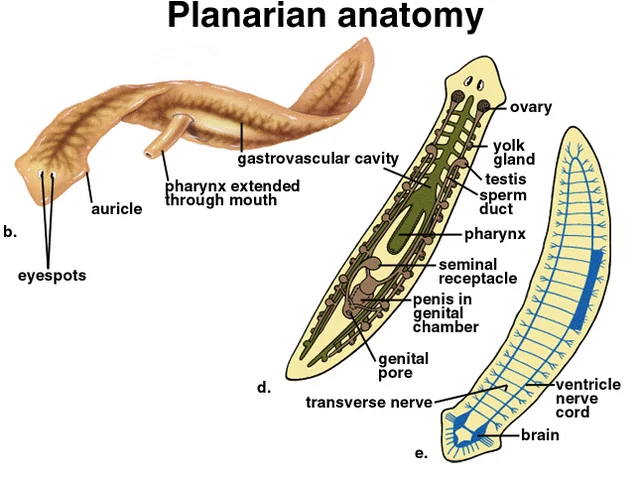
Planarian features: Pharnyx
extended through mouth to feed and take up food, undigested waste ejected here
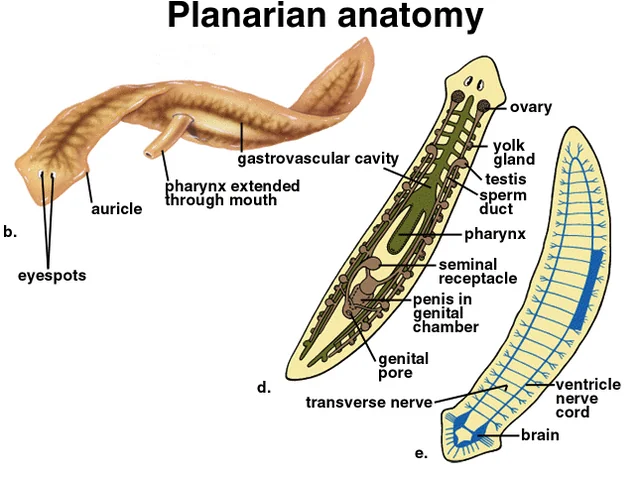
Planarian features: Gastrovascular cavity
highly branched to deliver nutrients to cells
Features of the group Turbellaria
-phylum Platyhelminthes
-free-living
-carnivores
-aquatic and terrestrial flatworms
-move by undulation or gliding along secreted mucus layer
Features of the group Cestoda
-phylum Platyhelminthes
-parasites of vertebrates
-scolex on anterior end has hooks and suckers to attach to intestinal lining of host
-body made of proglottids
-ex: tape worm
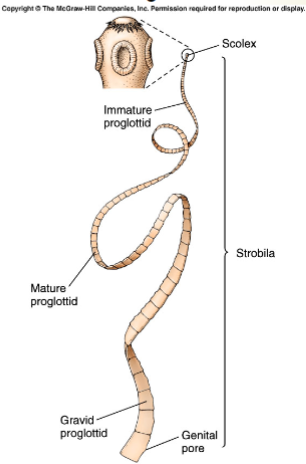
What are proglottids
repeating sacs containing sex organs, sexual reproduction fills up proglottids w/ fertilized eggs and proglottids are shed in feces
What are rotifers
-Microscopic wheel animals
-plylum Syndermata
General features of rotifers?
-Live in freshwater, marine, and damp soil environments
-Psudocoelomates (hemocoel with hemolyph)
-Protostome
-Multicellular but smaller than most protists
-Reproduce via parthenogenesis
-Dioecious
How do rotifers obtain nutrients
-Have ring of cilia around mouth to draw in food via vortex
-Jaws grind up food and digestion and excretion occurs in rest of alimentary canal (GI tract)
What is parthenogenesis
When females produce unfertilized eggs that develop into new females (asexual), some species lack males entirely
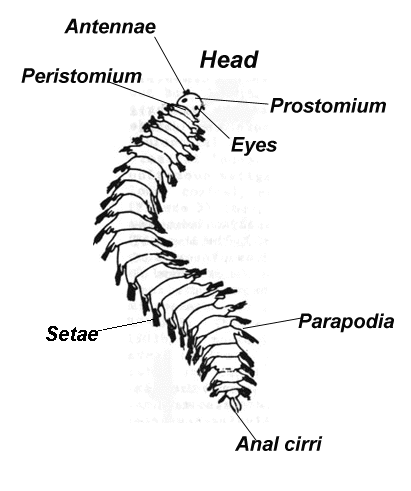
General features of Annelids?
-Protostome
-Coelomates
-Have closed circulatory system and alimentary canal
-well developed nervous system
-segmented internally and externally
-most have chaetae
What are chaetae
external bristles made of chitin (polysaccharide), used for moving and gripping the ground
What are the two made clades of the phylum Annelida?
Errantians and Sedentarians
Errantians
-Annelida
-Highly mobile marine worms
-Predators and grazers
Sedentarians
-Annelida
-Less mobile worms
-Include earthworms and leeches
-Filter feeders or feed on sediment/soil
-Some burrow slowly through marine sediments or soil while others live in tubes
Purpose of parapodia
Lateral paddles with several chaetae used for movement and gas exchange
What are leeches? What’s hirudin used for?
-Parasitic annelid (sedentarians)
-Hirudin (anticoagulant) thins blood and they feed on the blood
Digestive system in earthworms
Mouth, esophagus, crop (temporary food bag), gizzard (grind food), intestine, and anus
Nervous system of earthworms
Cerebral ganglia (brain) coordinates movement towards or away from light, temp, touch, etc
Circulatory system of earthworms
Closed (blood is contained with in blood vessles) and has a heart
What are metanephridia used for by earthworms?
Waste removal and osmoregulation (invertebrate kidney)
How do earthworms reproduce?
By aligning themselves in opposite directions and exchanging sperms (monoecious)