words
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
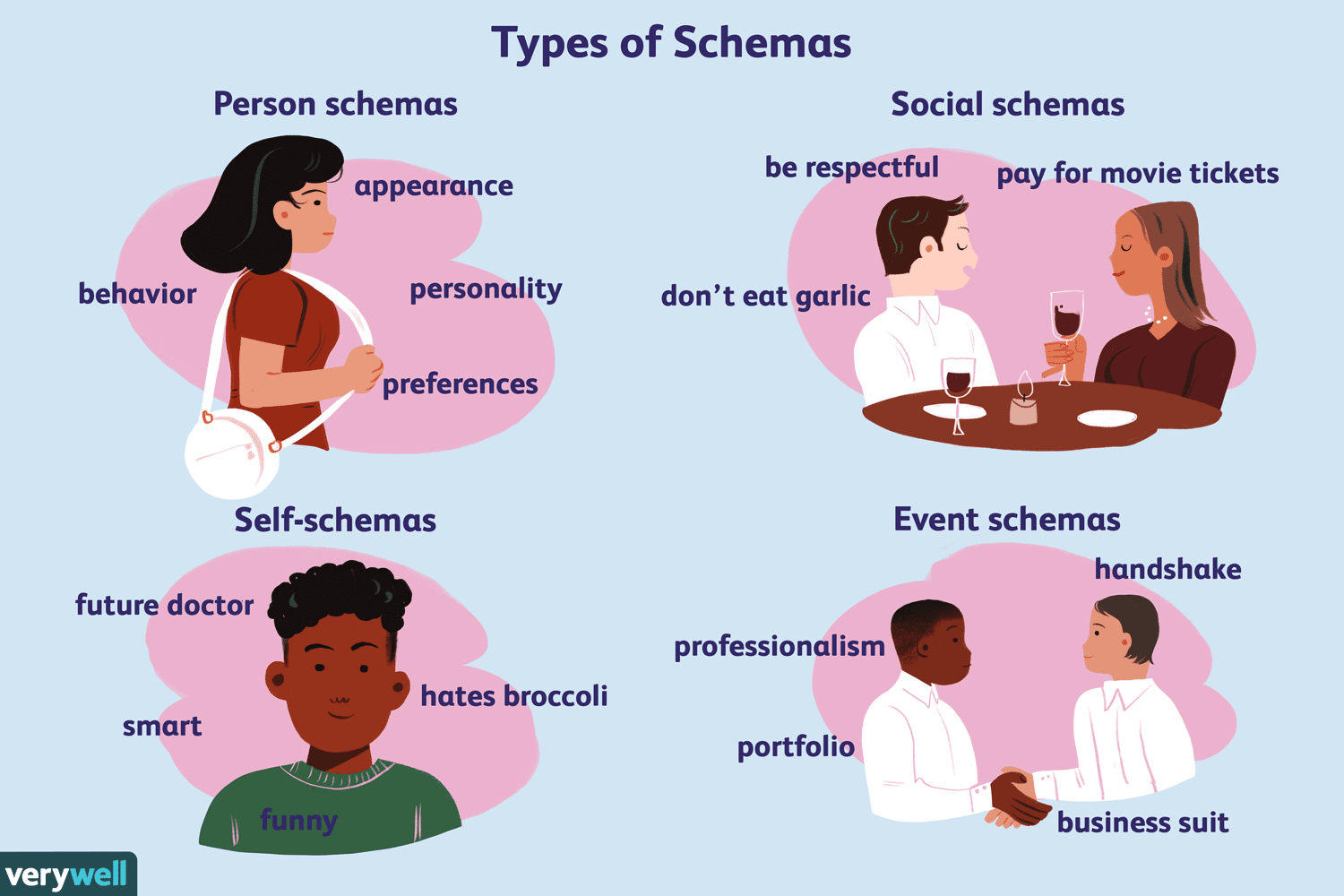
Schema
Mental framework for organizing information
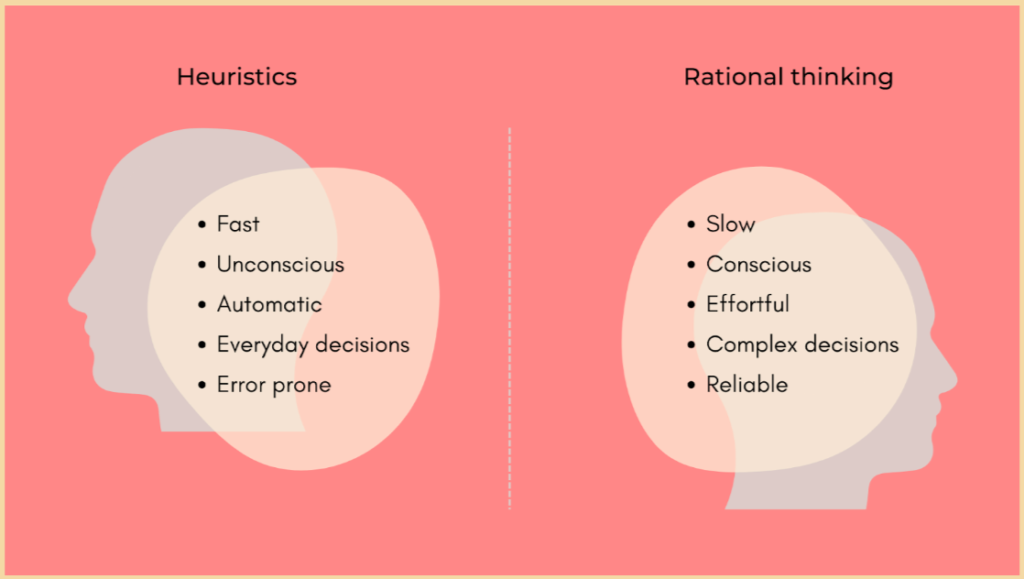
Heuristics
Mental shortcuts or rules of thumb to make decisions
Levels of Processing theory
Theory by Robert Lockheart explaining memory is not based on separate types of memory but the depth of info processing (deeper the encoding = more likely to remember)
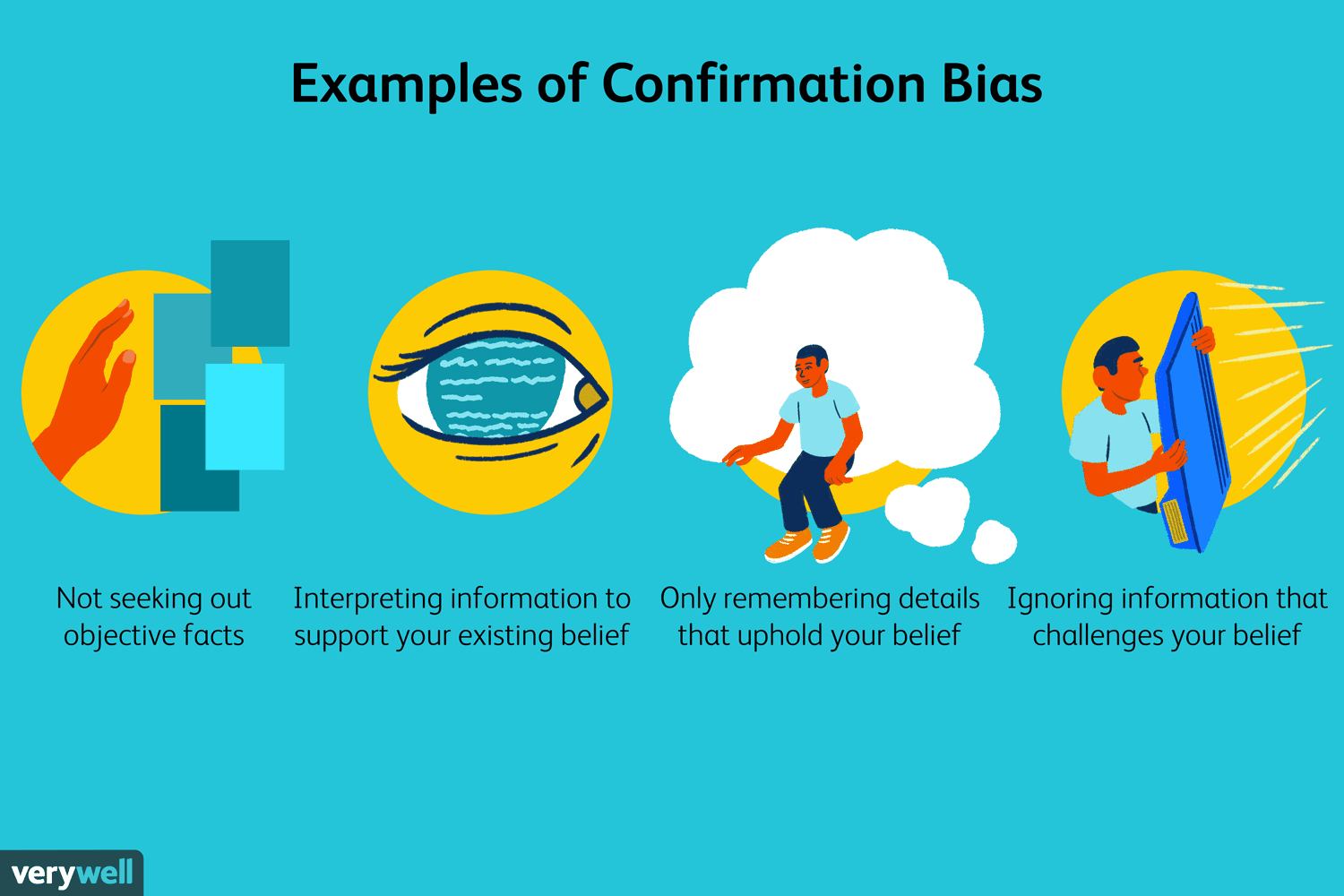
Conformation Bias
tendency to search for info that confirms one’s bias / perception / beliefs
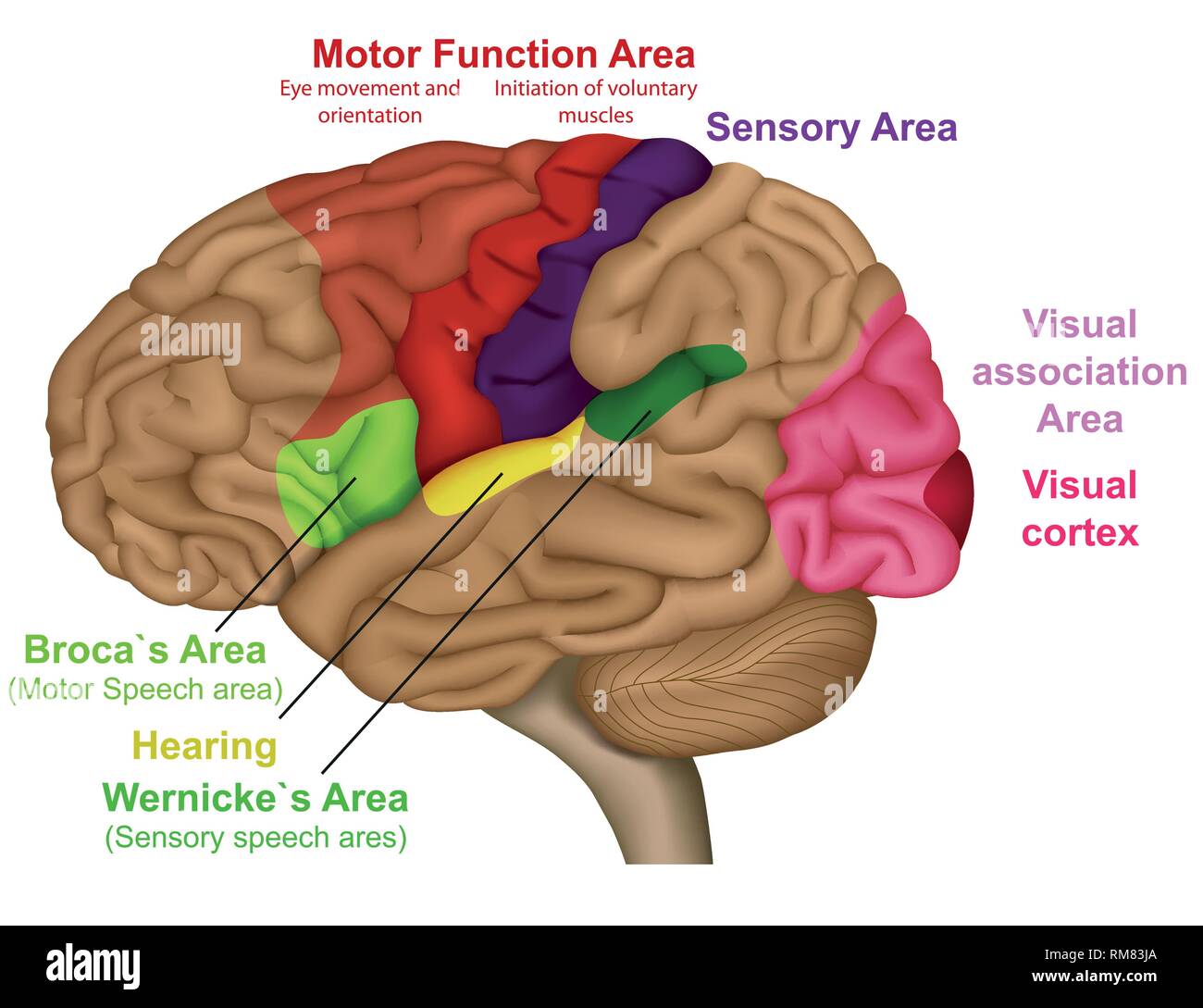
Association Areas
Regions of the cerebral cortex that do not have specific sensory or motor functions but are involved in higher mental functions such as planning, thinking and communication (lobes, cortex, etc.)
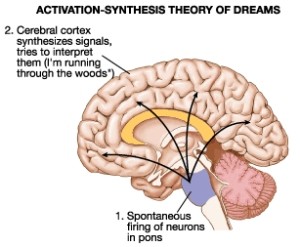
Activation-Synthesis Theory
Theory that dreams are interpretations of random neural activity that occurs during REM sleep
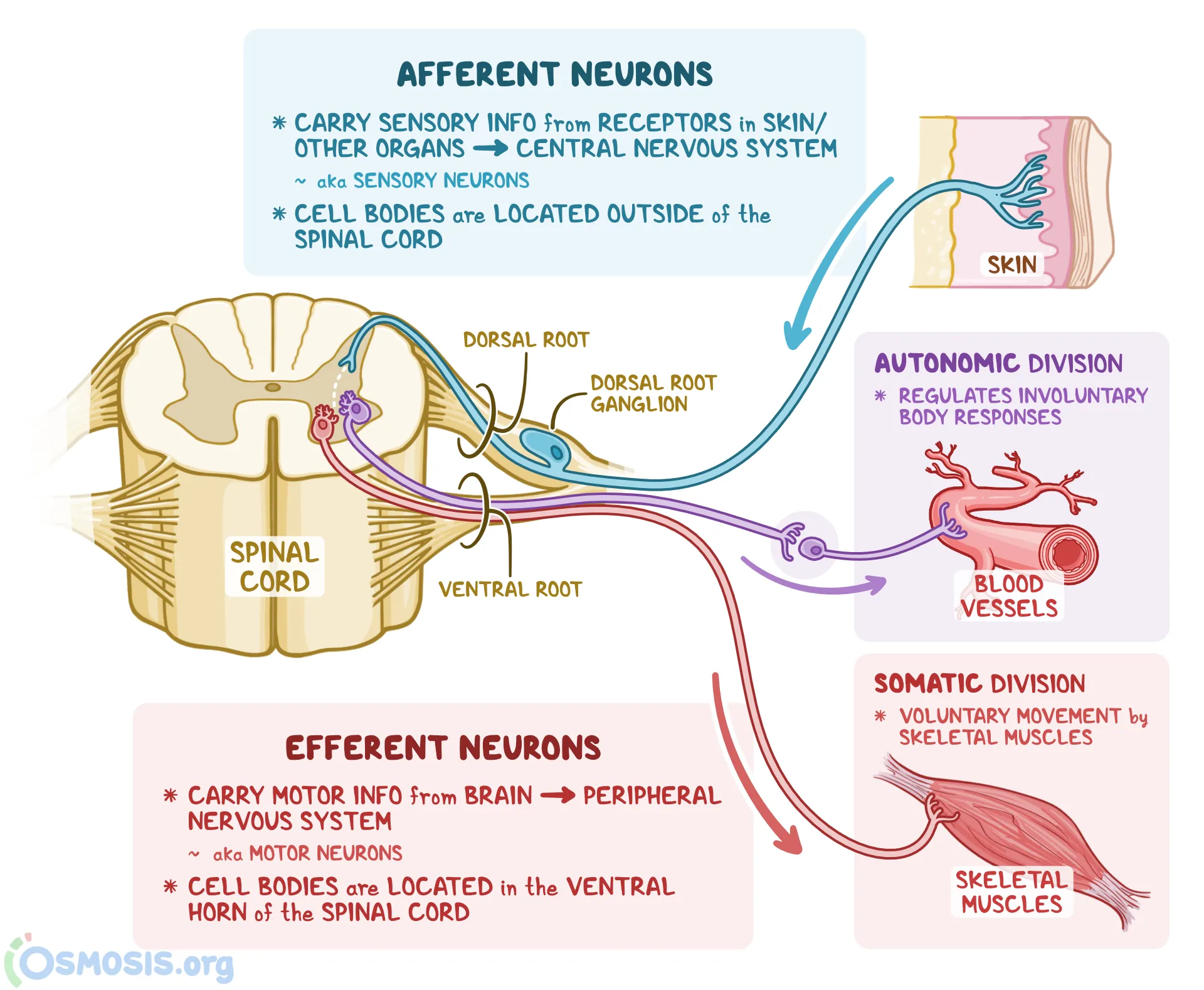
Afferent Neuron
Sensory Neuron that signals to the CNS
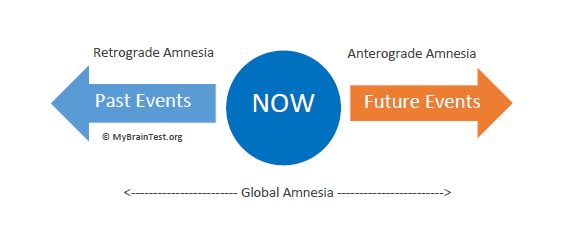
Anterograde Amnesia
Disorder caused by brain damage that interrupts a persons ability to form NEW long term memories that occur after the damage
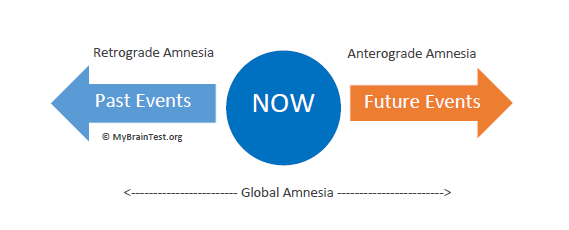
Retrograde Amnesia
Disorder caused by brain damage that interrupts a persons ability to remember past events after the brain damage occurs
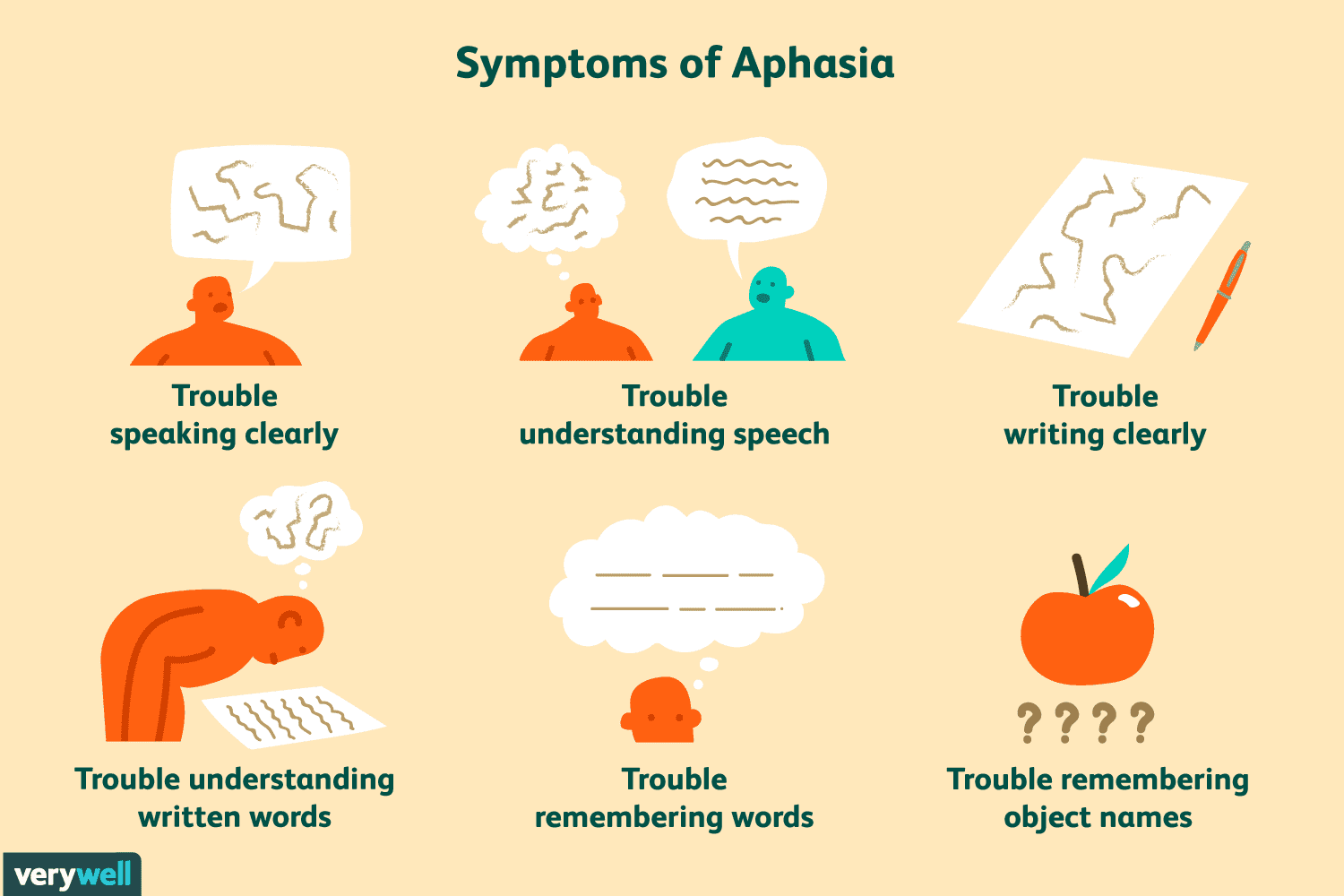
Aphasia
Impairment of the ability to UNDERSTAND or USE language
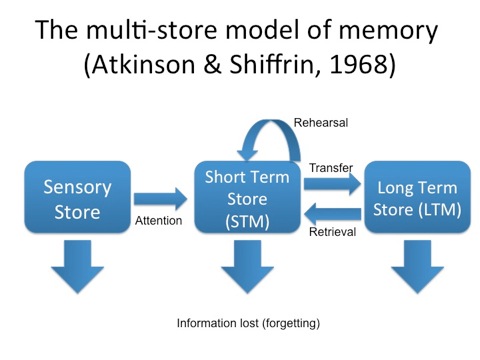
Atkinson-Shiffrin Model
A model of memory that assumes 3 different memory systems - Short term Memory, Long Term Memory and Sensory Memory
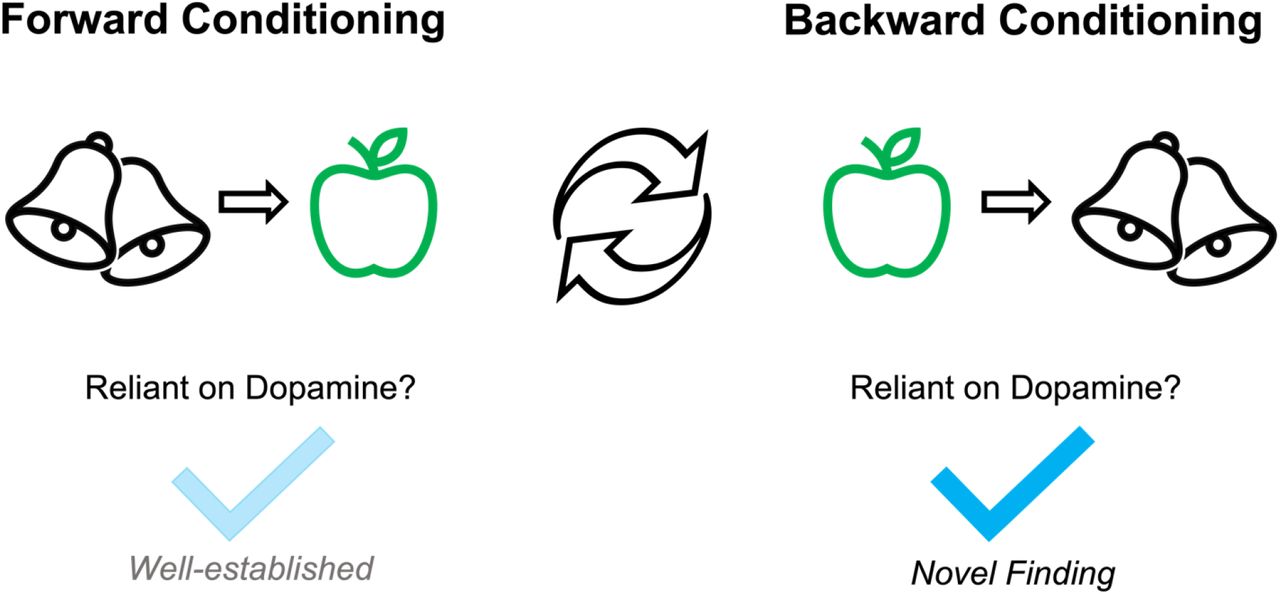
Backwards Conditioning
Conditioning where the US is presented before the CS
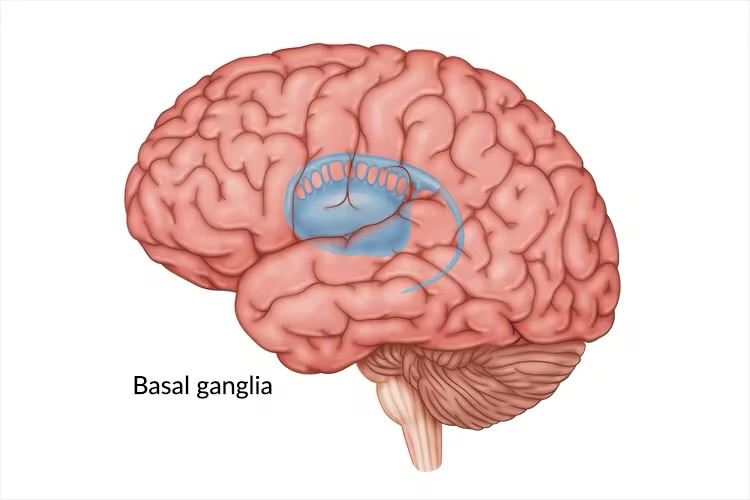
Basal Gangila
Clusters of neurons deep down in the brain that regulate memory, balance, eye movements, etc. Also the function of implicit memories
Big 5
Trait theory that presents 5 traits that our personality is composed of - Openness, Conscientiousness, extroversion, agreeableness and neuroticism

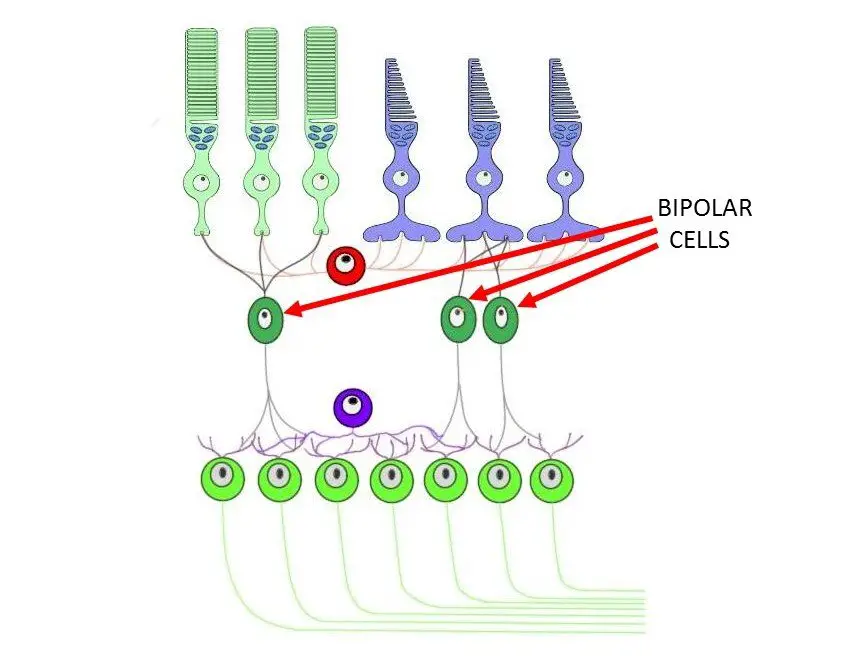
Bipolar Cells
Second layer of neurons in the retina that transmit impulses from rods and cones and ganglion cells
Broca’s Area
Left side hemisphere in the frontal lobe that controls production of speech. If damaged, you can understand speech but can’t talk.
Wernicke’s Area
Right side of your frontal lobe that controls your ability to understand speech, if damaged you can talk but with no coordination.
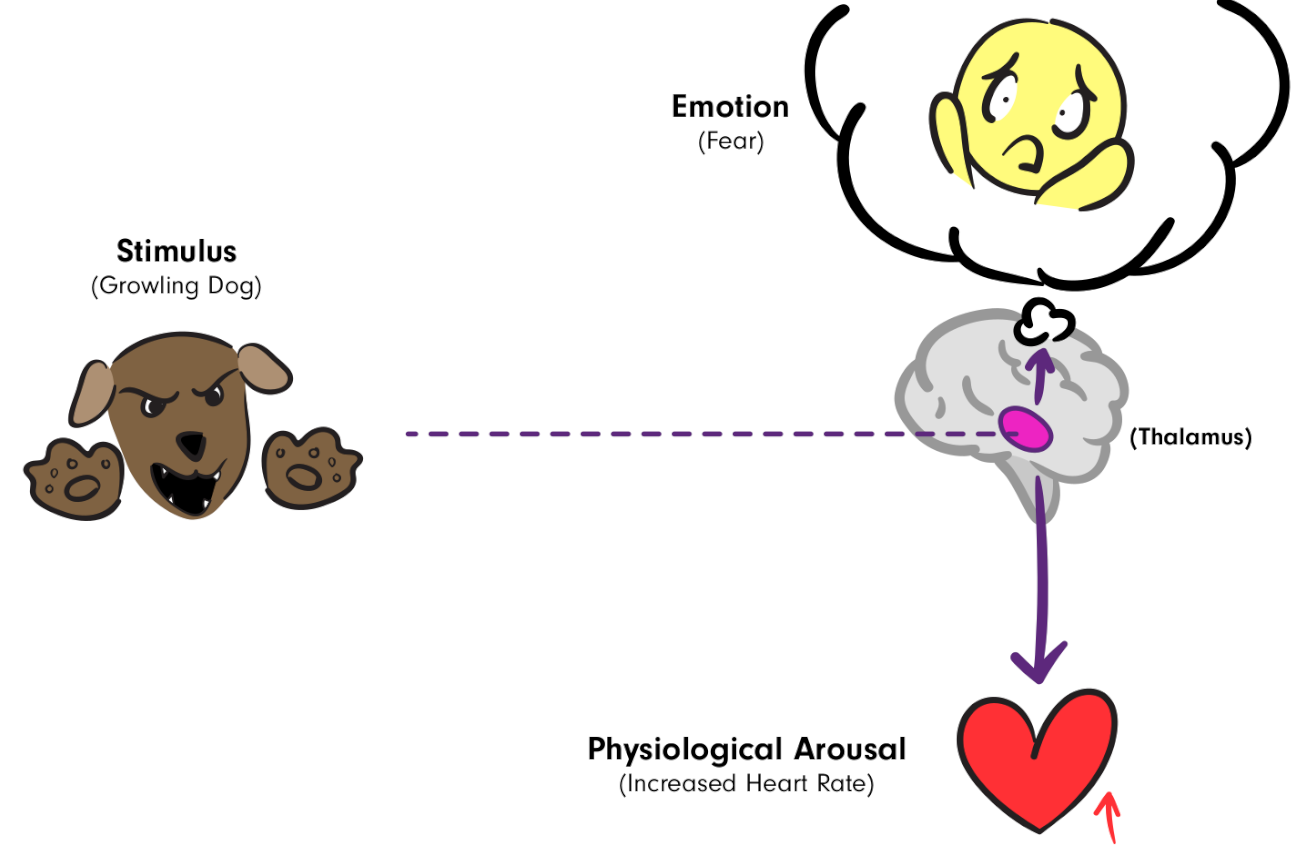
Cannon-Bard Theory
Theory that emotional states and physiological states occur simultaneously
Central Tendency
Average or most typical scores from a data set
CAT scan
X ray passing through the brain to show brain structure and or show a lesion (damage)
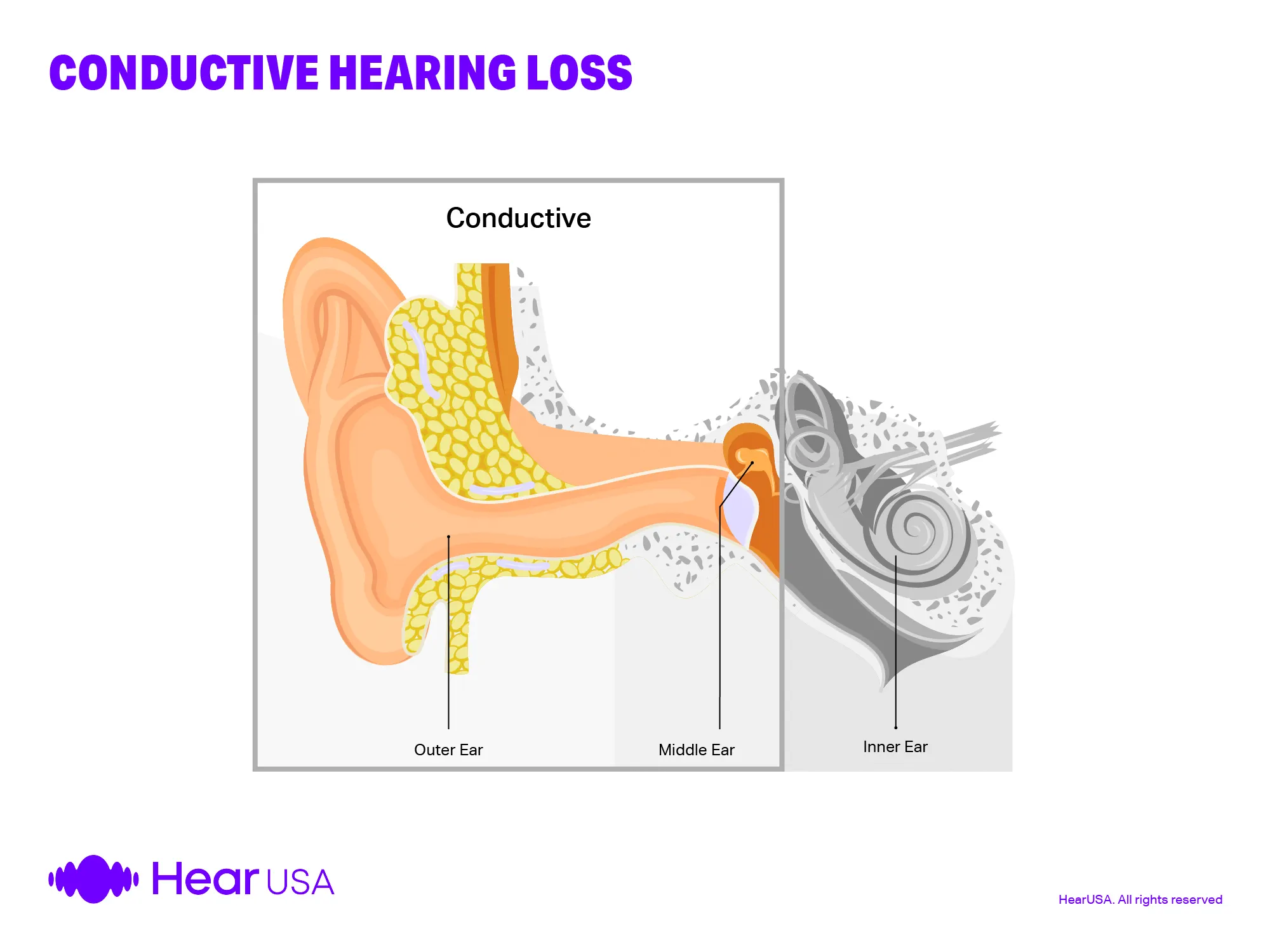
Conduction deafness
Loss of hearing resulting from when an eardrum is punctured or ossicles no longer vibrate. Sounds don’t go through the inner ear. Hearing aids may help with this
Confabulation
Filling in gaps in memory by substituting memories from events other than the one you’re trying to remember. memory you THOUGHT happened

Construct validity
Extent to which the test measures a given characteristic, trait or construct. What it is truly assigned to assess

Criterion related validity
Measure of the extent to which the tests results correlate with other accepted measures of what is being tested
Charles Darwin
English scientist who developed the "Theory of Evolution" by NATURAL SELECTION (survival of the fittest), how species evolved over time
Sigmund Freud
Father of modern psychology, Founder of psychoanalysis, key insight was to dive into the unconscious mind where deep desires lie
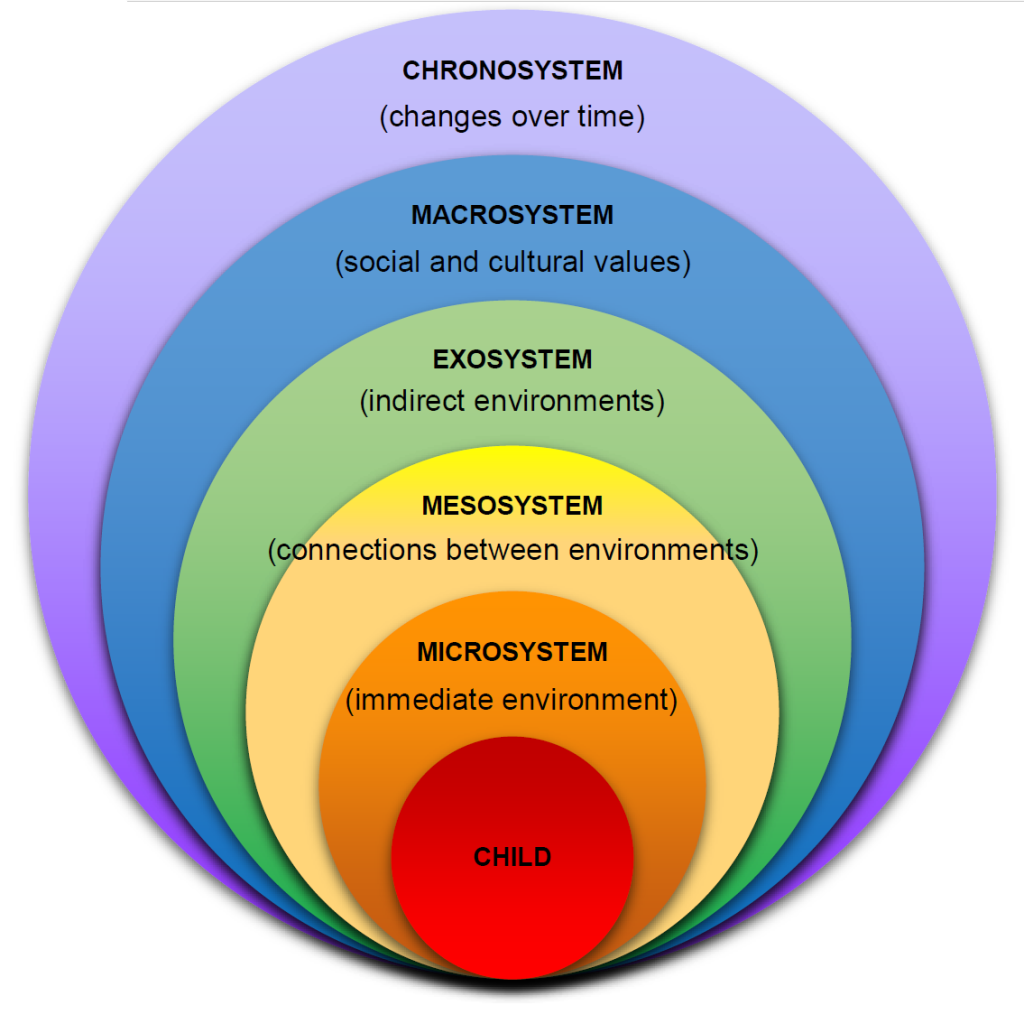
Developmental ecological theory
Systems of human development that start from the individual then to immediate family, then immediate family with others than more external factors to bigger changes in life/world