BLG316- Zoology- Mollusca
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Phylum Mollusca def'n
soft body contained within shell (lost in 3 classes)
- all are coelomate
How many classes are in phylum Mollusca?
8
Molluscan form and function:
Body plan
head-foot portion- feeding, sensory and locomotion
viceral mass portion- digestion, circulation, respiration, reproduction
- all housed within the mantle cavity
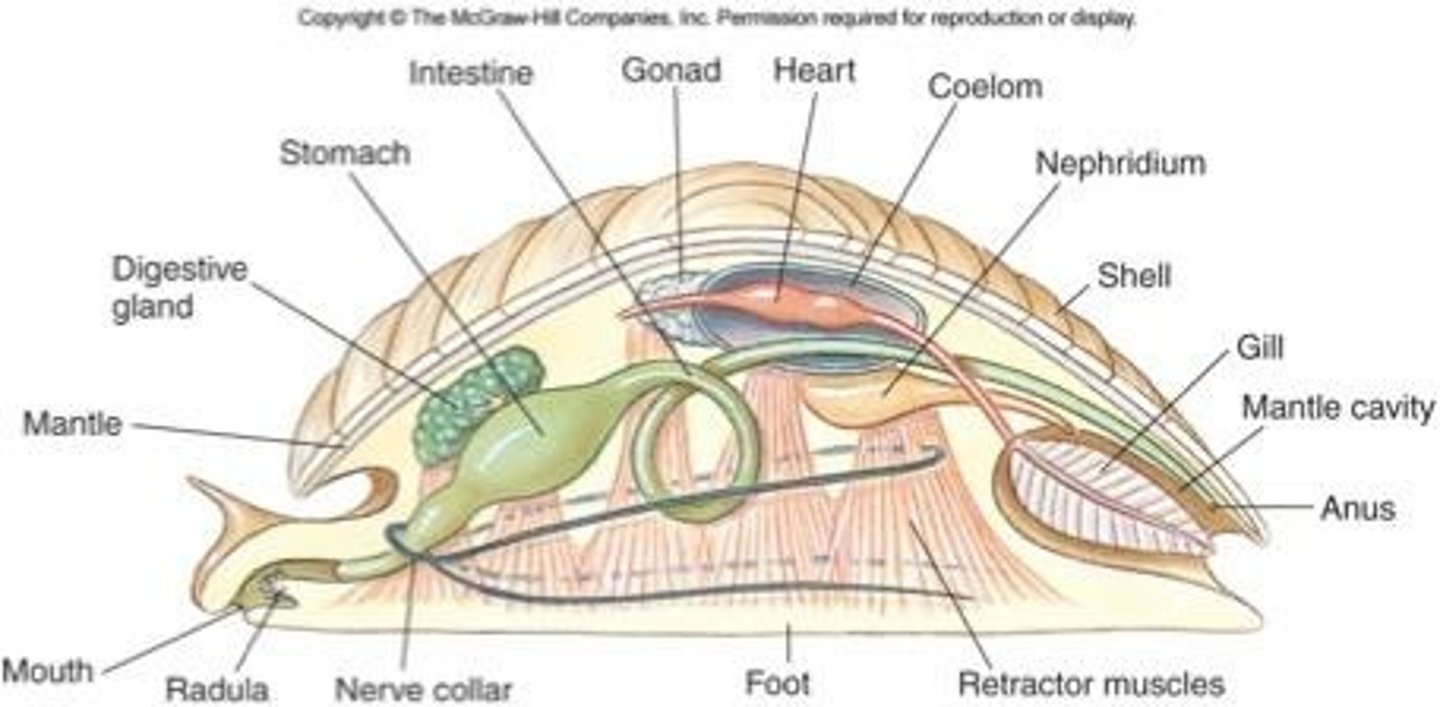
Mantle def'n
tissue fold draping over visceral mass
- secretes shell
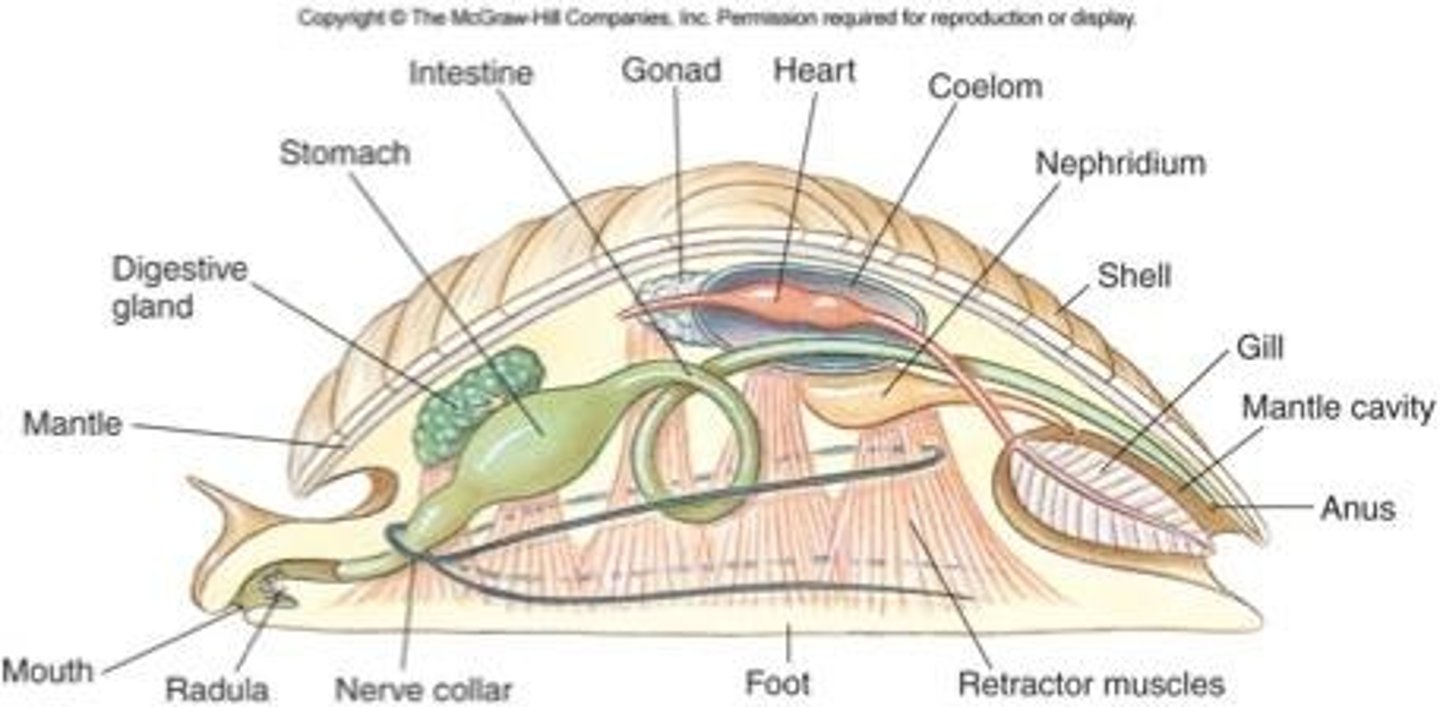
Nephridium def'n
excretory pores
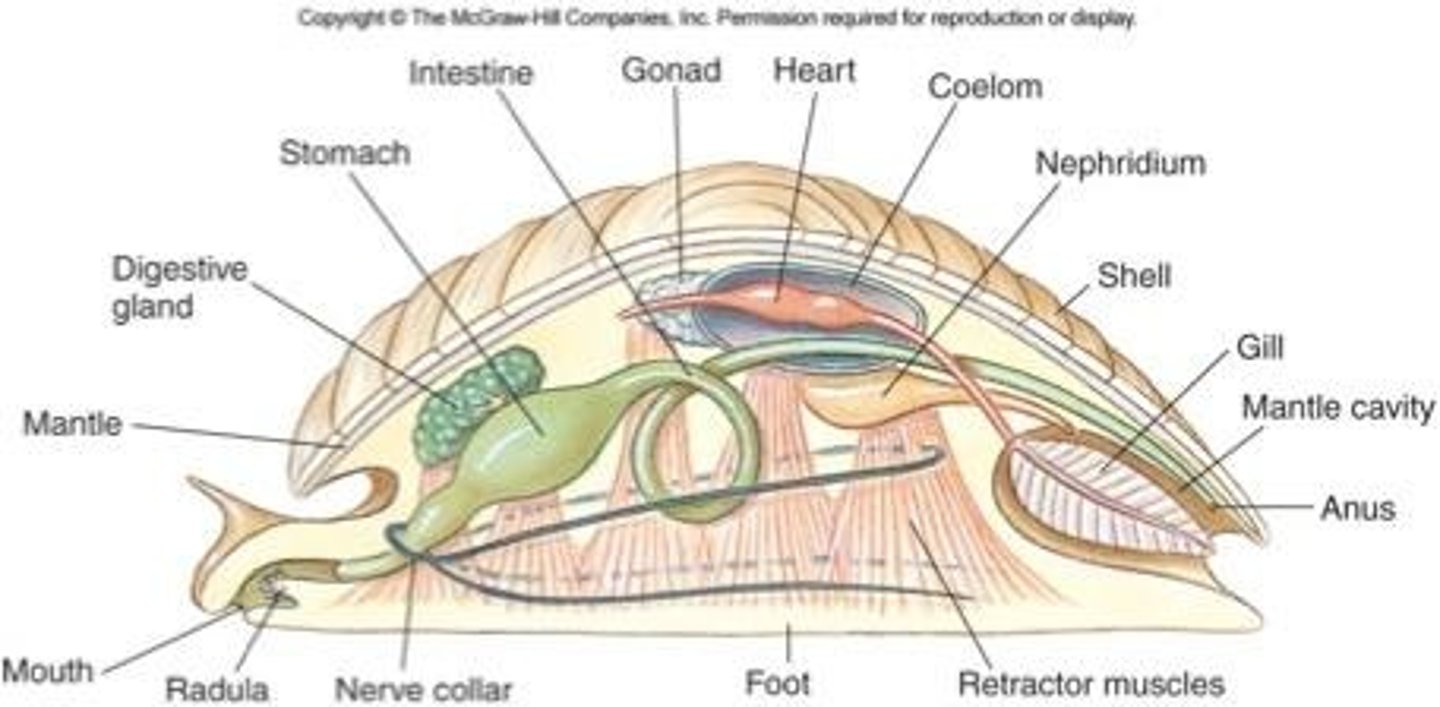
Mantle cavity def'n
mantle extension beyond visceral mass
- water-filled chamber with gills, anus, excretory pores
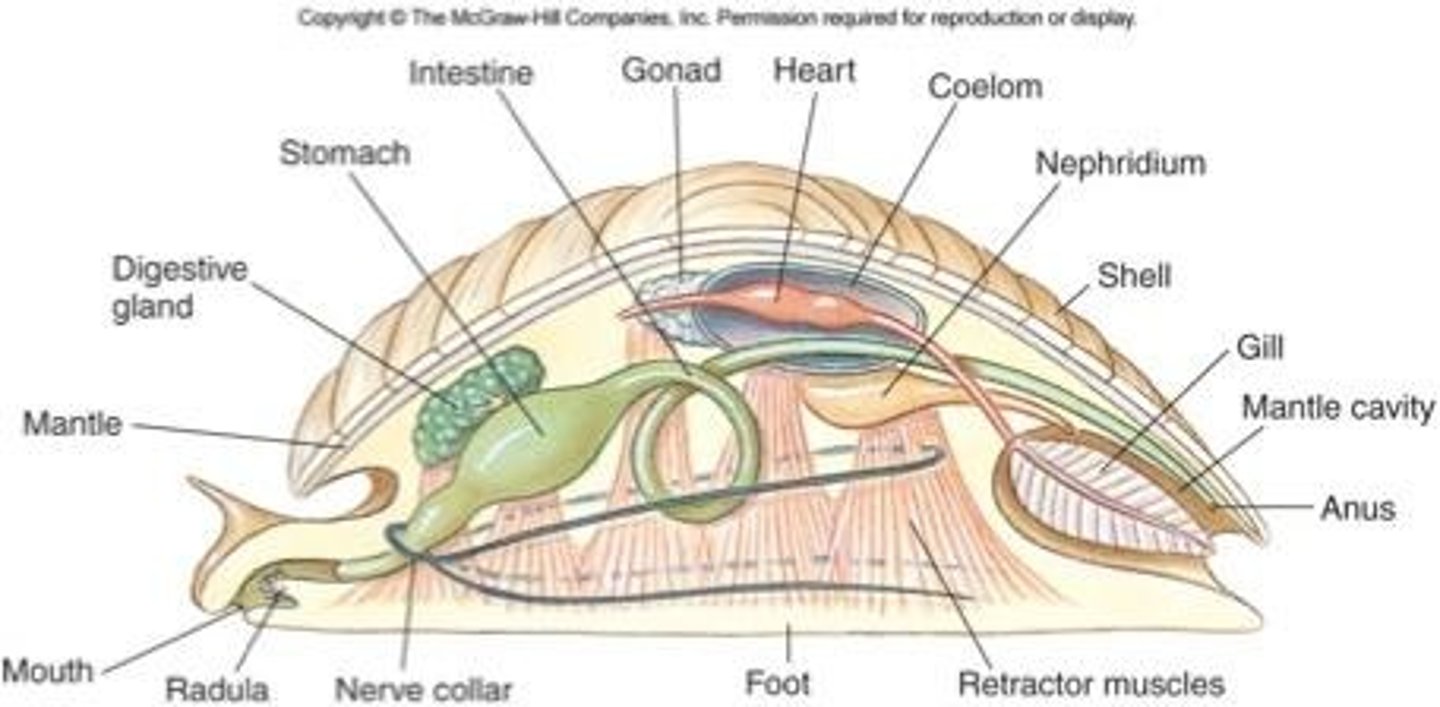
What is the name of the circulatory fluid?
Hemolymph
What kind of circulator system do phylum mollusca have?
open circulatory system
Radula def'n
backwards curved teeth
- scrapping action for feeding (structure inverts to do this)
Phylum Mollusca :
Shell def'n
not always present
- secreted by the mantle
- typically 3 layers
What is the inner most layer of the shell?
Nacre
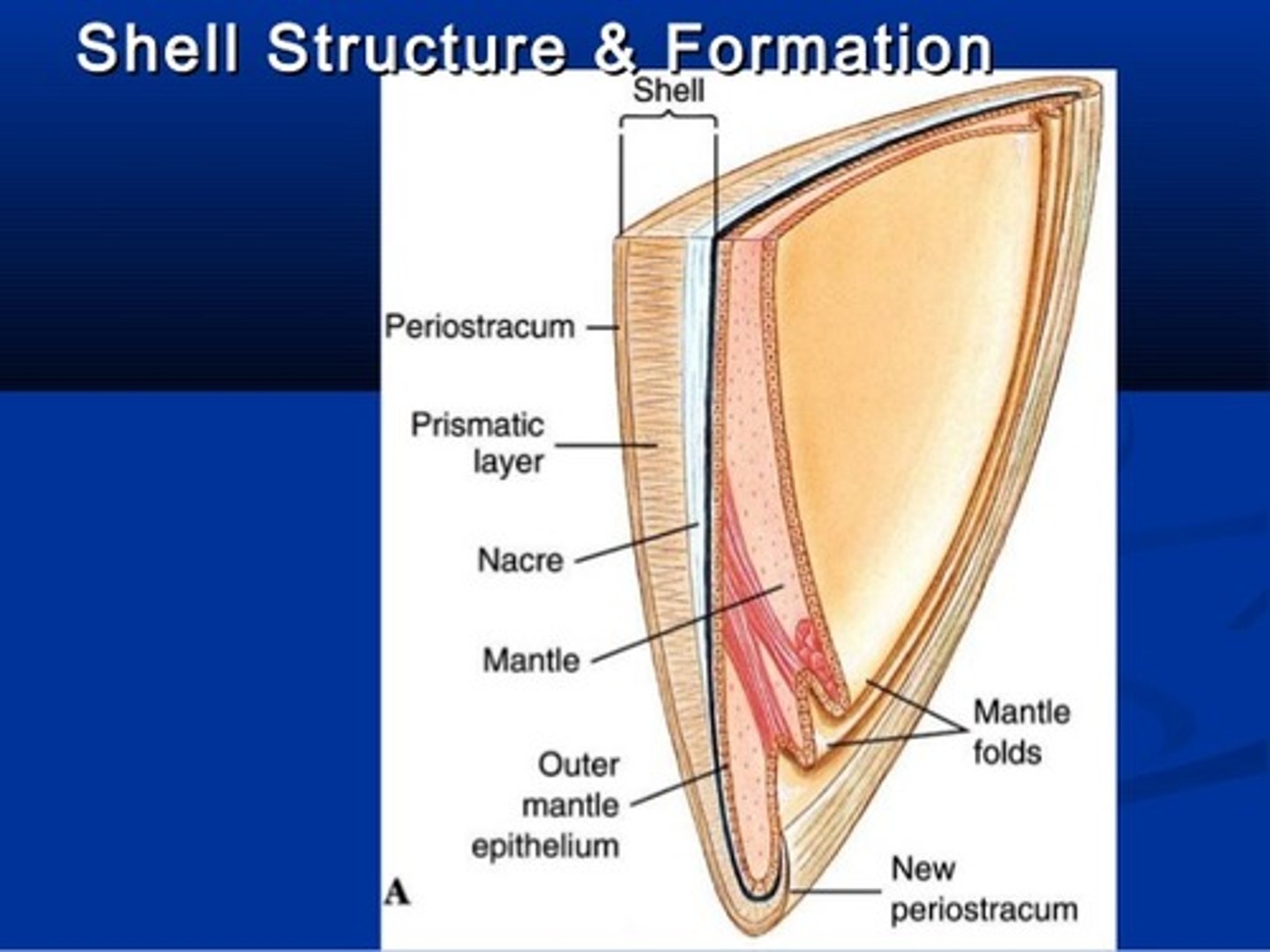
What does the nacre continually excrete?
CaCO3
Phylum Mollusca :
Reproduction
Most are dioecious
- aquatic members usually have ciliated free swimming larval stage
What are the distinct characteristics of the two clades that divide phylum Mollusca?
1 has univalve shell and the other has multiple shell plates
Class Caudofoveata & Solenogastres def'n
m.c.: worm like and shell-less
- calcareous scales/ spicules in integument
- reduced head and no nephridia
Class Polyplacophora (chitons) def'n
m.c.: flat with convex shell containing 8 plates
- mantle forms protective girdle around plates
- shell sometimes with eyes osphradia
Osphradia def'n
chemosensory organ that samples water
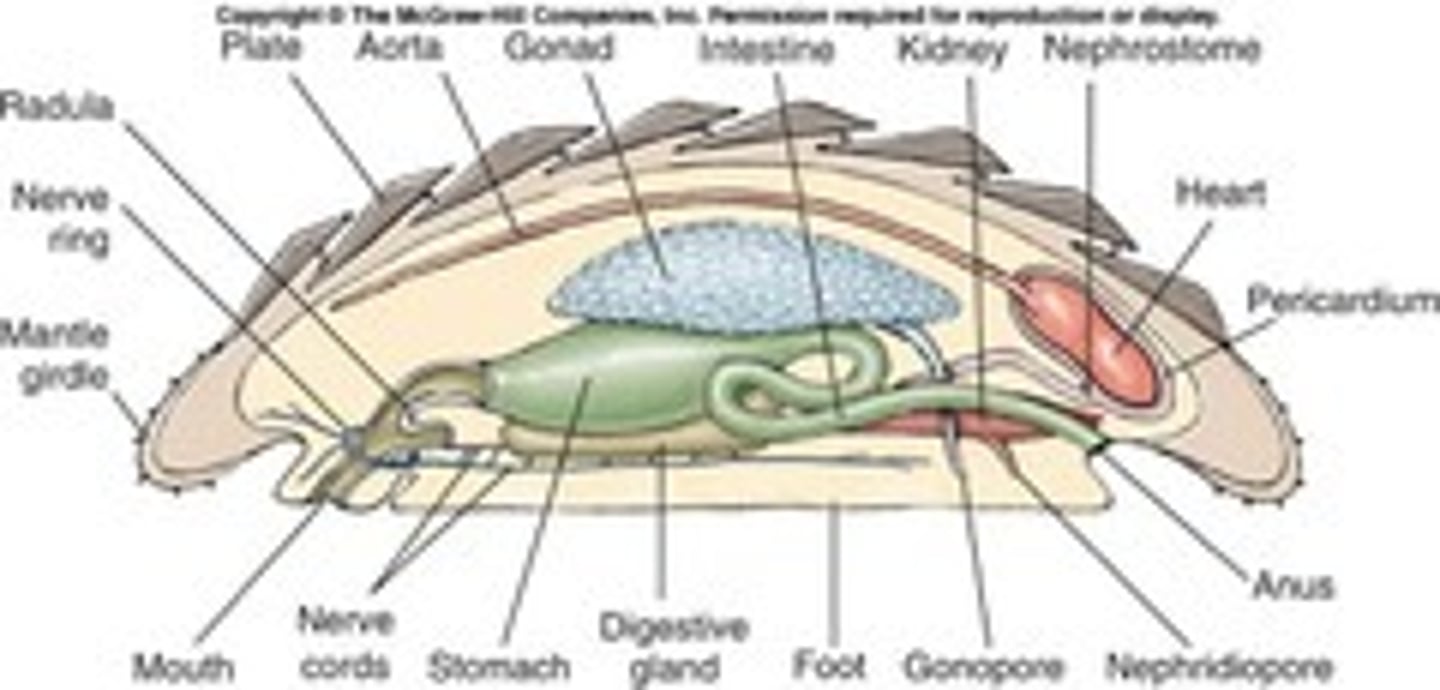
Class Monoplacophora def'n
m.c.: small low rounded shell
- many serially repeated segments
- univalve shell
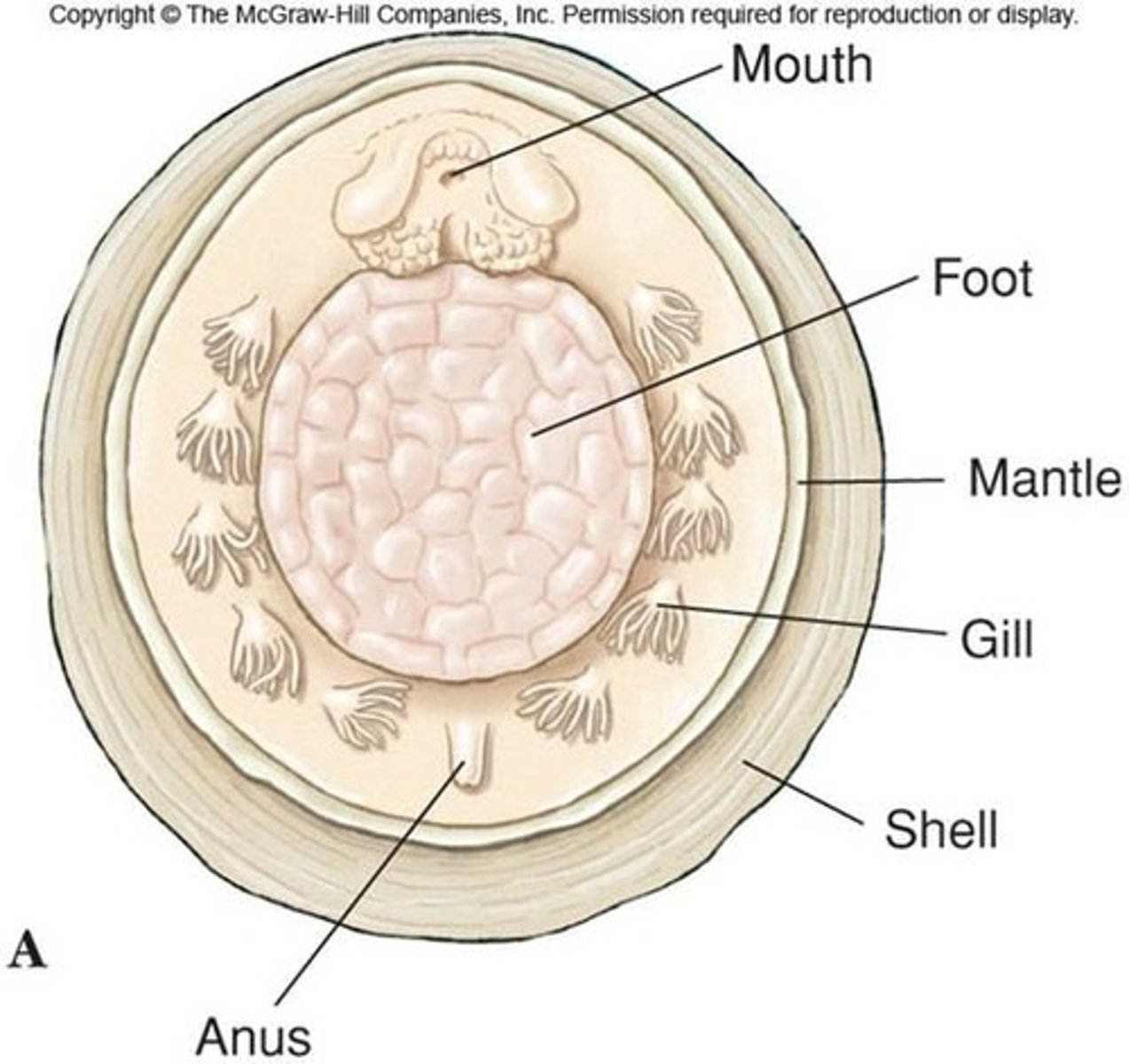
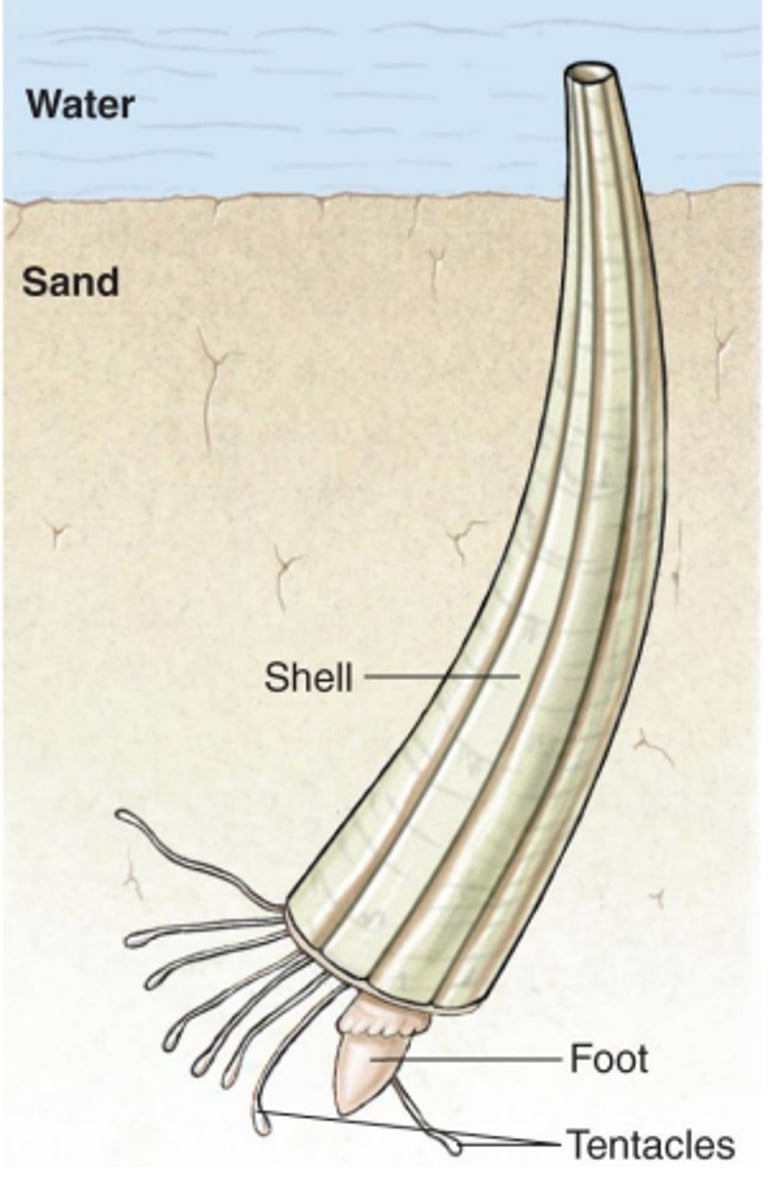
Class Scaphopoda (tusk/tooth shell) def'n
m.c.: sedentary and slender
- tubular shell opened at both ends due to mantle being wrapped around viscera
Class Gastropoda def'n
m.c.: extreme variety
- torsion and coiling
members: snails, limpets, slugs, periwinkles, whelks
Class Gastropoda:
form and function:
Torsion
development usually as ciliated larval stage with gradual shell formation
- mouth anterior and anus posterior initially (relative position of body parts change)
Why might digestive tracts reposition to have anus above head within mantle cavity?
Osphradia located in mantle structure
- advantage to have them located upfront
-
Class Gastropoda:
form and function:
Coiling
spiral winding of shell
- shell becomes whorled and weight is unevenly distributed
- shell is shifted to oblique position but there is a loss of gill and kidney on right side
- bilateral asymmetry
Class Gastropoda:
How do they avoid fouling?
-loss of right gill
- water flows one way from left to right in modern species)
- those with 2 gills vent water through dorsal clef/ hole
- some undergo detorsion as adults
Class Gastropoda:
Feeding
- all use some form of radula
- many herbaceous
- some are predatory (radula for boring holes and tearing tissue)
- Cone snail shoots modified radula harpoon with neurotoxin
Class Gastropoda:
RESPIRATION
- many aquatic members use gills
- vascularized mantle acts as lung
- anus and nephridiophore open near lung opening to outside (pneumostome) to expel waste with air
Class Gastropoda:
Sensory and nervous
3 pairs of ganglia connected to nerves
- eyes, statocysts and tactile organs
Class Gastropoda:
Reproduction
Monoecious and dioecious
- exchange spermatophores
- lay eggs on land
- ciliated larvae for marine
Class Bivalvia def'n
2 shelled (bivalve)
- mostly suspension feeders
- no head
- radula and little cephalization
members: mussels, clams, scallops
Class Bivalvia
Shell
Laterally compressed
2 halves (valves) held together dorsally by hinge ligaments
- abductor muscles draw halves together to close

Class Bivalvia :
What is the name of the raised bump on the shell?
umbo
- oldest part of the shell
Class Bivalvia :
Body and mantle
visceral mass suspended dorsally
- gills on each side covered by mantle folds
- folds form incurrent and excurrent openings
- cilia on gills direct water over gills (food and oxygen)
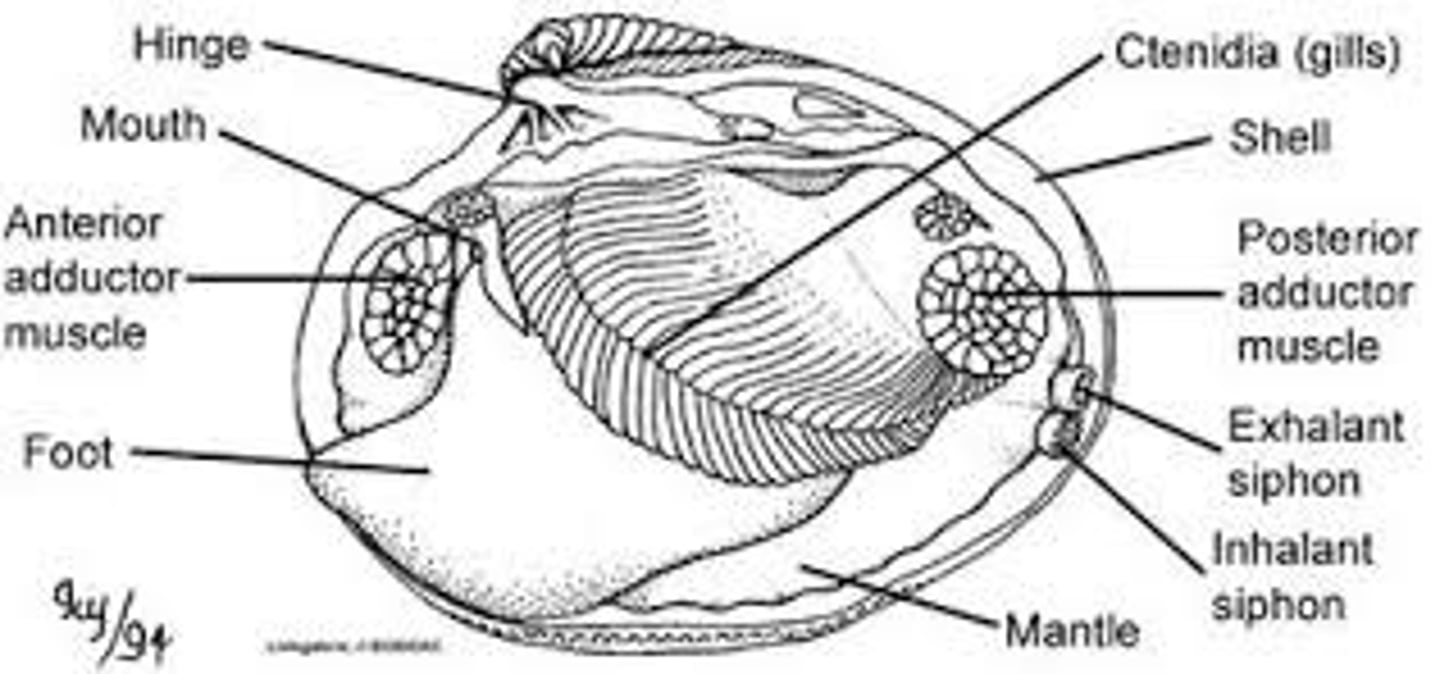
What kind of heart does Class Bivalvia have?
3 chambered heart
- pumps blood through gills to kidneys to excrete waste
Class Bivalvia :
Feeding
Suspension feeder
- glands on gills and palps- secrete mucus
- cilia move particles to mouth
- crystalline rod in stomach rotates to aid digestion
Class Bivalvia:
Locomotion
- most move by extending foot between valve
- pump fluid into foot
- some sessile and attach shell to surface (anchoring threads or cement like substances secreted)
Class Bivalvia :
Reproduction
dioecious
- usually separate sexes and external fertilization
- marine often 3 larval stages
- internal fertilization in FW clams (bring sperm in to shell)
- hitchhiking larvae to disperse
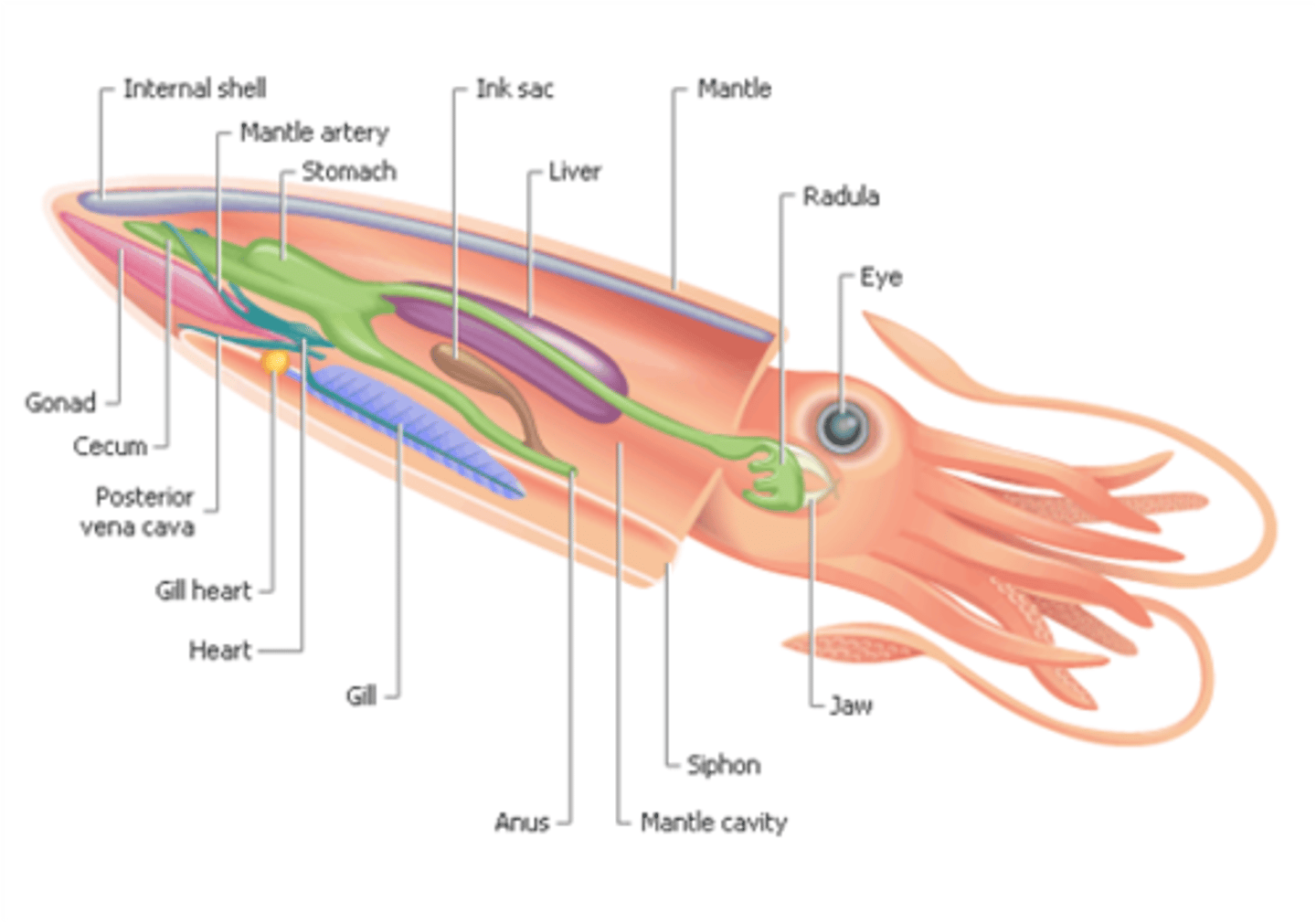
Class Cephalopoda def'n
"Head foot"
- shell reduced and internal or lost
- still have mantle
- active predators
- only mollusc with closed circulatory system
- Well developed sense organs and complex brain
Squid anatomy
have a main heart and accessory heart
- radula (aka beak)
- 8 arms and 2 tentacles are highly modified foot
- siphon expels water for propulsion
- mantle cavity draws in water
Cuttle fish anatomy
8 arms and 2 tentacles
- excellent at camouflage- chromatophores
- eye is equally complex as human eye (convergent evolution)
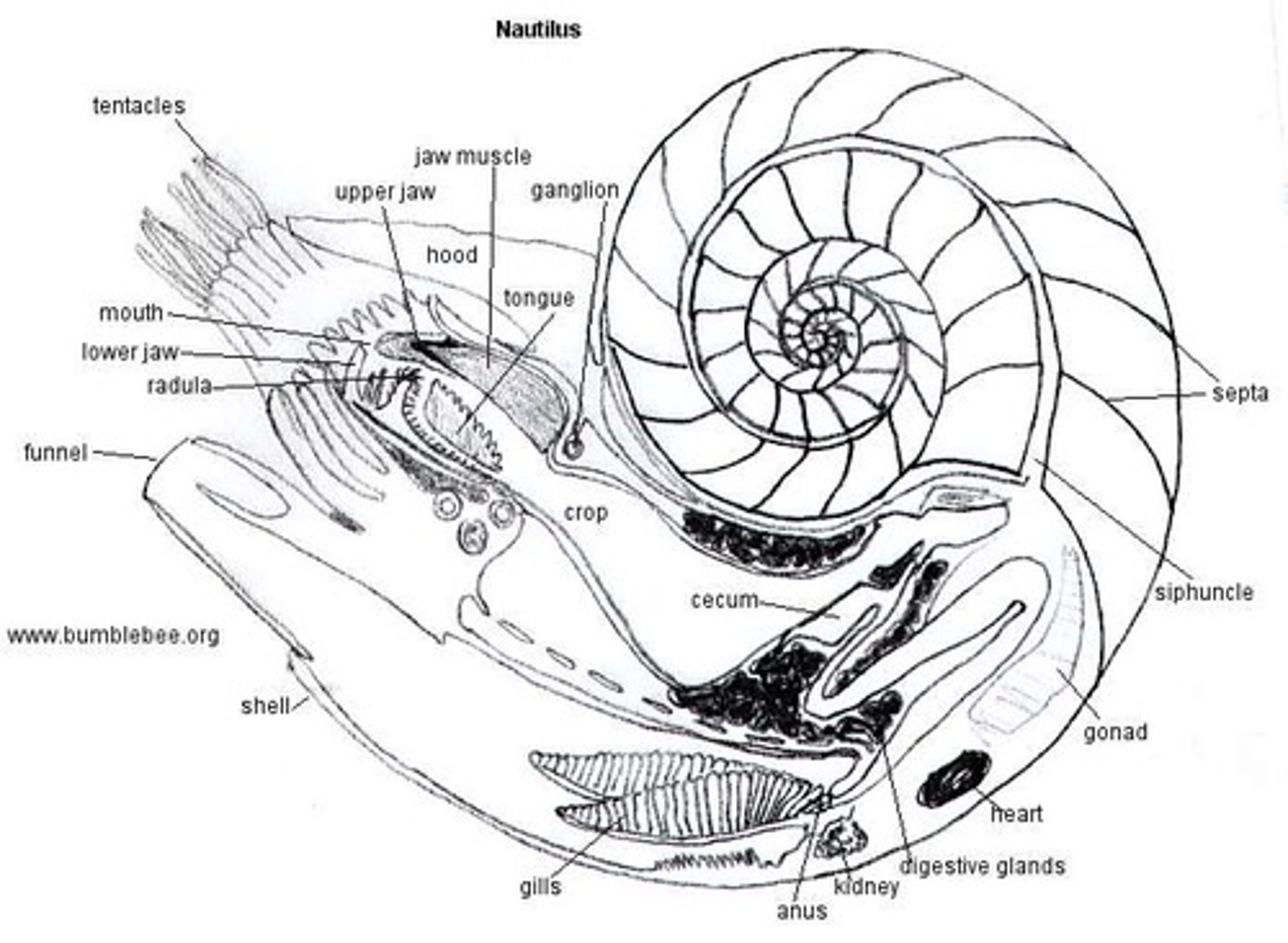
Nautiluses def'n
only living cephalopod with external shell
- numerous internal gas chambers
- non-suckered tentacles extrude from shell to grasp prey
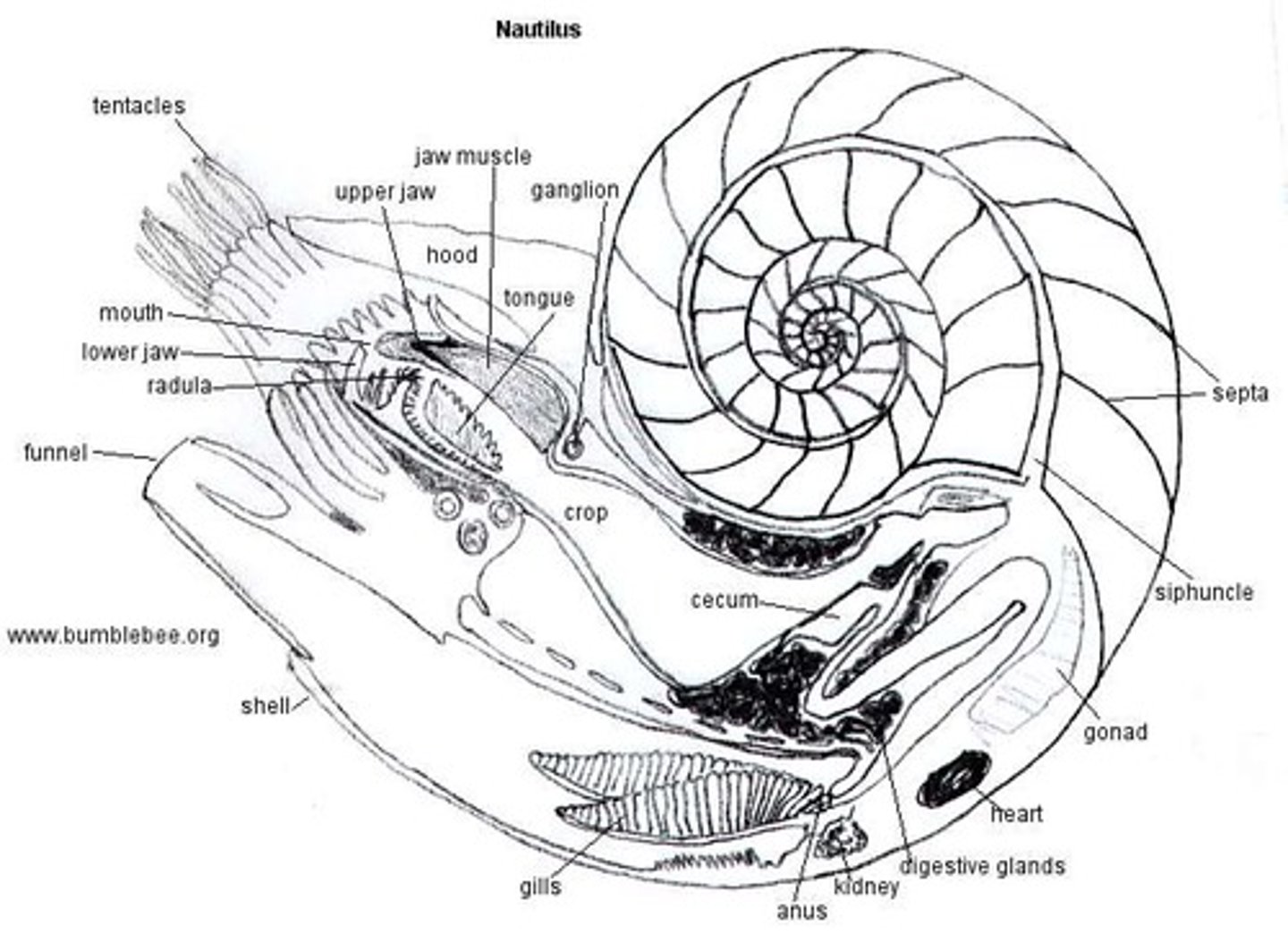
What are the chambers of the Nautilus shell connected by?
chord of living tissue called Siphuncle