Animal Evolution - The Deuterostomes
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
echinodermata
• Deuterostomes
• Unsegmented
• Radial symmetry: fivefold arrangement
• Endoskeleton: interlocking plates of calcite
• Fluid-filled canals
• Tube feet!
hermichordates
marine-dwelling bottom feeders or filter feeders.
They are all small in size and are the sister group to the Echinodermata.
- pharyngeal slits
- dorsal hollow nerve cord
not the same body plan as the other deuterostomes.
the echinoderm adult:
- no head
- oral and aboral sides
- moves in any direction
- pentaradial symmetry
Do echinoderms have segmentation
NO!!!!
- It is unclear whether this lack of segmentation is ancestral or derived
- Skeletons ("test") are really interlocking calcium carbonate "plates"
- It is produced by mesoderm and there is ectoderm outside of it...so that means they have an endoskeleton!
echinoderm tube feet
- extensions of the coelom and function in locomotion and/or feeding and/or defense.
- Bulk transport of necessities through canals
- extremely sensitive and highly functional.
4 features of chordates
1. Nerve cord
2. Notochord
3. Pharyngeal slits
4. Postanal tail
Vertebrate Characteristics
- jointed axial skeleton
- jointing provides more mobility than notochord
- The spinal column or backbone is made up of bones called vertebrae with a vertebral disc between each bone and the next
Agnatha: Lamprey: a jawless fish
- Class Hyperoartia
- The lamprey is the most basal extant vertebrate
- Adults of many species are predaceous and migratory
- 'teeth' (made of keratin) on the oral disk and tongue
Agnatha: Hagfish: a jawless fish
• Class Myxini
• Two rows of keratin 'teeth'
• Slime!
• Recently moved back into the vertebrate grouping by DNA evidence
• Scavenger, marine, benthic
• Is an evolutionary 'tween' in its nutrient uptake habits
Chondrichthyes
cartilaginous fish
- Cartilage is flexible, composed of collagen and chondroitin, it is calcified in places needing more rigidity.
- Teeth and scales are remnants of a bony skeleton on the outside of the first fish
- This group includes the sharks and rays. They are entirely carnivorous.
Osteichthyes: 'Bony fish"
• Osteichthyes have an internal skeleton of bone
• Bone is a mineralized collagen matrix, and is harder than cartilage
• They have lungs (but not the way you might think)
• They are divided into two main groups: ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii) and the lobe-finned, or fleshy-finned, fish (Sarcopterygii)
Ray-finned osteichthyans: Actinopterygii
One of two major bony fish groups, the ray-finned fishes, evolved about 420 mya
- In the ray-finned fishes, the paired fins are supported by internal skeletons
- With 24,000 spp, ray-finned fishes are more diverse than other groups of vertebrates
Lobe-finned/Fleshy-finned Fish: Sarcopterygii
In the lobe-finned fishes, there are bones in the fin bases extending out from the body
- There are only 4 'fishy' spp of living lobe-fins
- The rest are the tetrapods!
Transition to tetrapod vertebrates
Eleven animal groups made transitions to land from the water
In vertebrates this transition includes changes to:
- limbs
- rib
- cages
- skulls
Tiktaalik
"missing link" thought to be a transitional form between fish and tetrapods
- transition form with wrist and finger bones plus a true neck and amphibian skull
amphibian life cycle
wide range of sizes
Typical life cycle includes an aquatic larvae with gills and metamorphosis to a lunged terrestrial adult
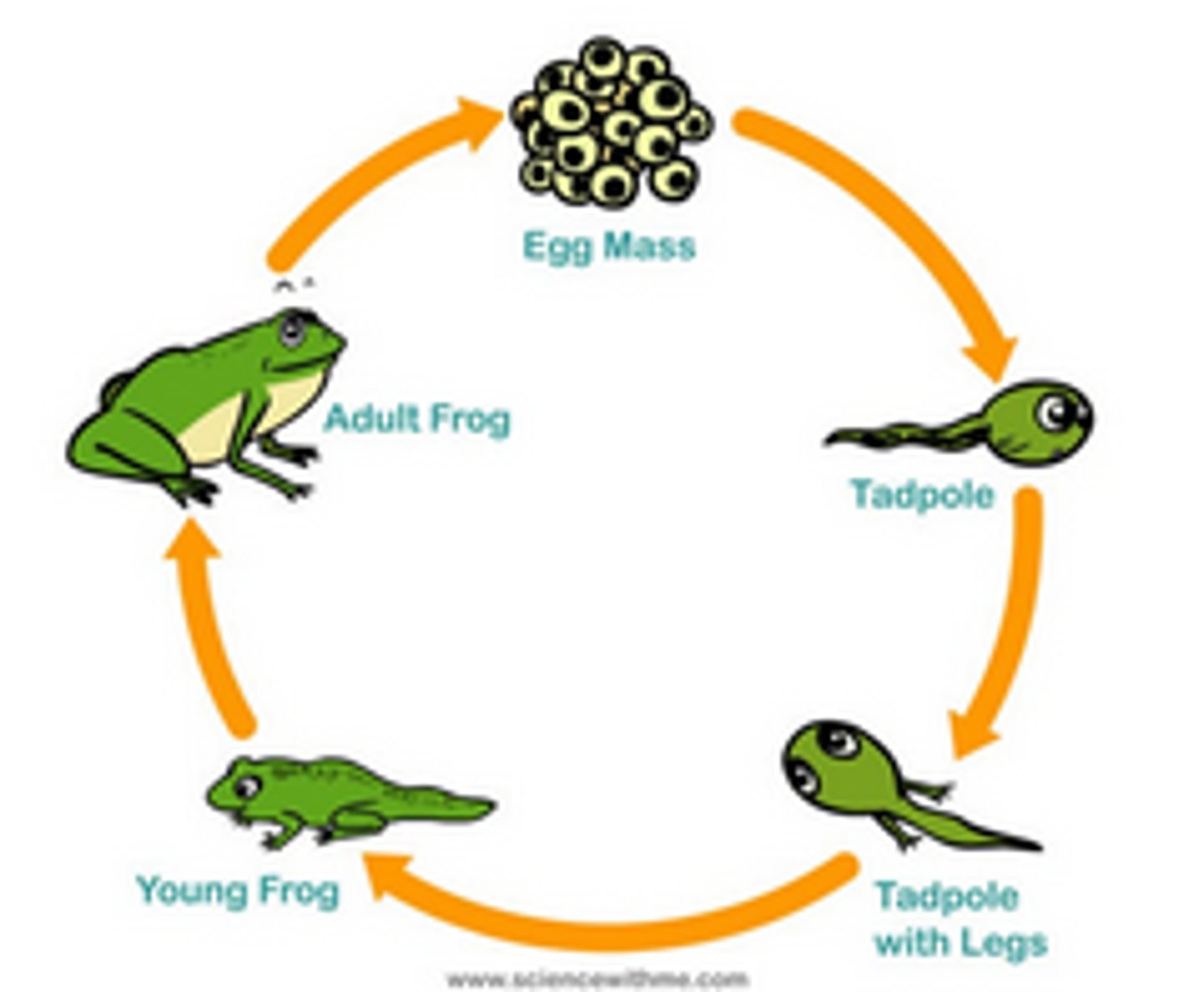
Amphibia
tetrapods that remain dependent on free water for reproduction
• Amphibia means 'double life', both wet and dry.
• Although they evolved from heavily scaled fishes, extant amphibians have thin, porous skin.
• Eggs are always kept in moist environments
• Larvae : metamorphosis : adult
Sauropsids: (Amniotes)
Most have up to four egg membranes, some type of desiccation-resistant shell, plus a yolk ... others have a placenta.
Reptilia
amniotes with scales of keratin
Reptilia evolved several dramatic changes in body plan
- ex. limb loss in snakes and legless lizards
scales grow from the epidermis
includes turtles, lizards, snakes, crocodilians, and birds
endotherms
use internal metabolic heat to sustain elevated and stable internal temperatures
- involves more heat production (through higher metabolism) and less heat loss (decreased with body insulation)
ectotherms
rely entirely on the environment and behavior for heat
matrotrophy
direct nourishment of embryo by mother.
- Hatching occurs within the mother, and the embryo's yolk reserves are supplemented by additional nutrient transfer.
- The result is fewer, bigger offspring
- Offspring are also more developed at birth.
mammal characteristics
amniotes with hair and skin glands
All mammals feed their offspring via lactation, and most are viviparous.
Shared derived characters of the mammals include features of the skin
- Hair, claws, nails, hooves (keratin)
- Glands: sweat and mammary
heterodont teeth
heterodonty
differentiation of the form of the teeth in one mouth (incisors, canines, molars, etc.)
viviparous
live birth
monotremes
- Monotremes are egg layers who make milk but have no nipples.
- 2 spp of echidna and 1 platypus, present only in Australia and New Guinea.
marsupials
Marsupials have a placenta but give birth very early in development.
- <300 spp are present in Australia, N. and S. America
Eutherians
Eutherians have a more complex placenta and are well-developed at birth
- 5000 spp occur in all oceans and continents