Properties of Water
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Is water polar or non-polar
Polar
Hydrogen bond
slightly negative O attracted to slightly positive H of nearby molecule
How many bonds can H2O form?
4
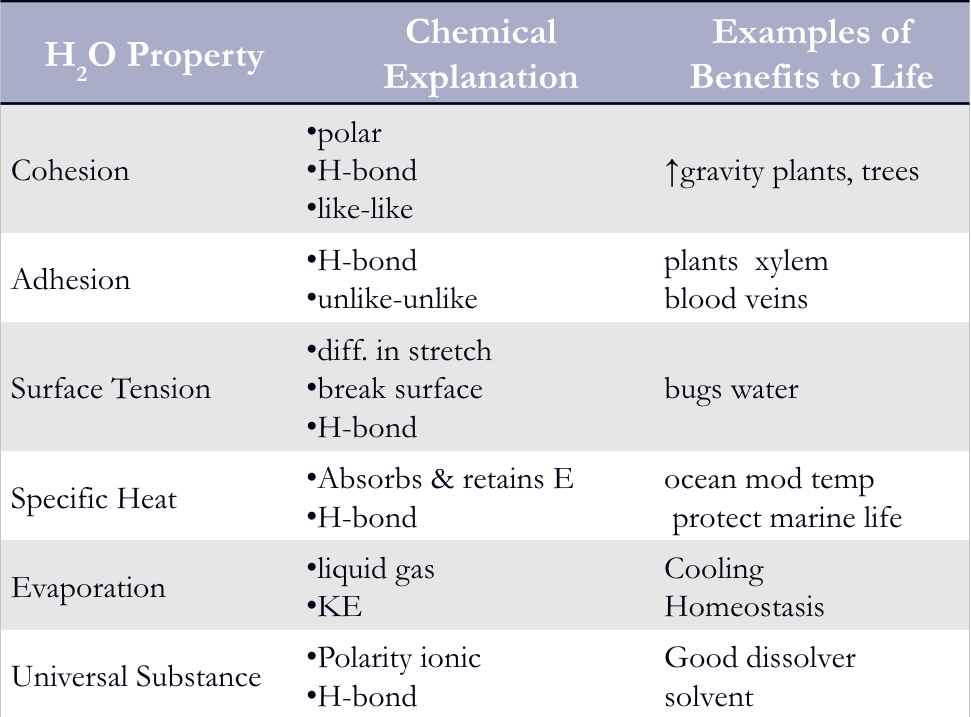
4 important properties of water?
1. Cohesive Behavior
2. Moderation of Temperature
3. Expansion Upon Freezing
4. Solvent
Cohesion
H-bonding between like molecules
Surface Tension
measure of how difficult it is to break or stretch surface of liquid
Adhesion
bonding between unlike molecules
(eg. Adhesion of H2O to plant vessel walls counters downward pull of gravity)
Transpiration
movement of H2O up plants
H2O clings to each other by __________; cling to xylem tubes by ___________
cohesion, adhesion
Transpiration
Water transport in plants
Thermal energy (heat)
Total amount of kinetic energy(KE) in system
Temperature
measure intensity of heat due to average kinetic energy(KE) of molecules
Water specific heat
It has a high specific heat → 4,184 Joules
What does the high specific heat of water contribute to?
Change temp less when absorbs/loses heat
Large bodies of water absorb and store more heat = warmer coastal areas
Create stable marine/land environment
Humans ~65% H2O = stable temp, resist temp. change
Water has high heat of
vaporization
What molecules leave as gas in water vapor
Molecules with greatest KE(kinetic energy)
What does evaporative cooling of water contribute to?
Stable temp in lakes & ponds
Cool plants
Human sweat = natural cooling
Insulation by ice
less dense, floating ice insulates liquid H2O below
What does Insulation by ice contribute to?
Life exists under frozen surface (ponds, lakes, oceans)
Ice = solid habitat (polar bears)
Solution
liquid, homogeneous mixture of 2+ substances
Solvent
dissolving agent (liquid)
Solute
dissolved substance
Water is a….
versatile solvent
Hydrophilic properties
Affinity for H2O
Polar, ions
cellulose, sugar, salt
blood
Hydrophobic properties
Repel H2O
Non-polar
Oils, lipids
cell membrane
Water dissociate equation thing (idk what im doing)
H2O <=> H+ + OH-
acid or base will ________ the balance of these two ions in solution.
change
in a neutral substance, these ion levels
are equal
Acid
increases H+ concentration (HCl)
Base
reduces H+ concentration (NaOH)
Acids are closer to 0? or 14?
0
Bases are closer to 0? or 14?
14
Neutral is
7
pH of water
7 ← neutral
Calculating pH equations (2)
[H+][OH-] = 10-14
pH = -log [H+]
Buffers
minimize changes in concentration of H+ and OH- in a solution (weak acids and bases)
Buffers keep blood at pH?
about 7.4 pH
If blood drops to 7 or up to 7.8 = death :O
Carbonic Acid – Bicarbonate System
important buffers in blood plasma
Here’s a speedy summary: