APES UNIT 9
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
☁ Stratosphere
🔹 Contains 97% of atmospheric ozone
🔹 Located 9–25 miles (15–40 km) above Earth
☀ Formation of Stratospheric Ozone
🔹 UV radiation breaks oxygen molecules (O₂) into atomic oxygen (O)
🔹 Atomic oxygen (O) combines with oxygen molecules (O₂) to form ozone (O₃)
🌞 Types of UV Radiation
🔵 UVA → Closest to visible light; causes skin tanning
🔴 UVB → Causes sunburns & skin cancer
🟣 UVC → Forms ozone in the stratosphere
🛡 Ozone Layer
🔹 Found 9–19 miles (15–30 km) above Earth
🔹 Shields Earth from harmful UVB radiation
⚛ Ozone (O₃)
🔹 Highly reactive molecule
🔹 Constantly formed & broken down in the stratosphere
🚨 Ozone-Depleting Chemicals
❌ Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
🛑 Nonflammable chemicals with carbon, chlorine, & fluorine
🛑 Reach stratosphere & break down ozone
❌ Halocarbons (Halons)
🛑 Organic chemicals with carbon & halogens (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine)
🌍 No natural reservoirs of CFCs or halons → Their chemical stability allows them to persist & damage ozone
🔻 Effects of Ozone Depletion
🌾 Lower crop production
🦠 Weaker immune system
🌊 Decline in phytoplankton → Disrupts food webs
🌡 Cooling of the stratosphere
🐾 Harmful effects on animals
👀 Increased cataracts
🧬 Higher DNA mutations → Skin cancer risk
🔥 More sunburns & skin damage
✅ Ways to Reduce Ozone Depletion
📜 Support legislation to ban ozone-depleting chemicals
💰 Tax tariffs on products from countries still using CFCs
🔄 Rebates for recycling old fridges & air conditioners
❄ Use helium, ammonia, propane, or butane instead of HCFCs & CFCs
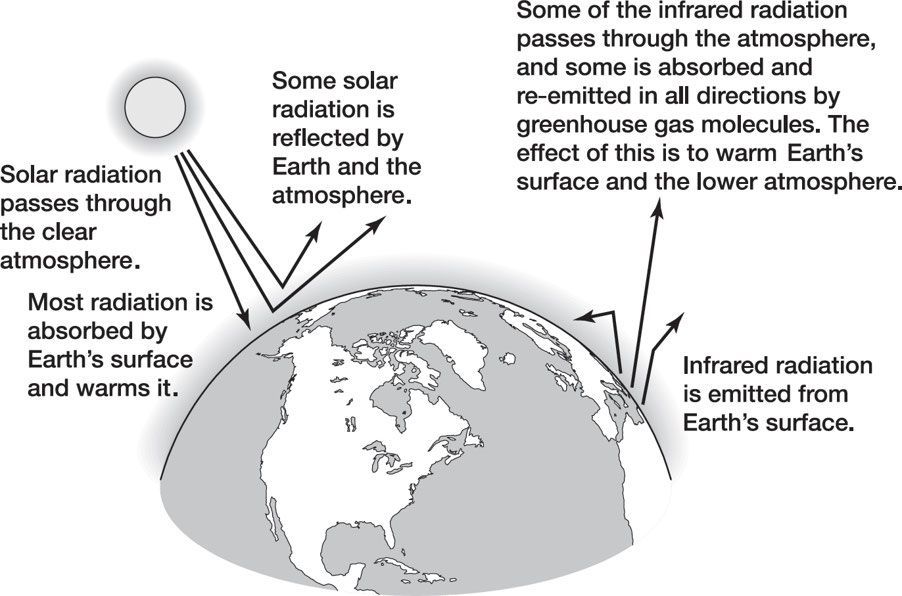
☀ The Greenhouse Effect
🔹 Sunlight strikes Earth's surface
🔹 Some energy is reflected as infrared radiation (heat)
🔹 Greenhouse gases absorb infrared radiation and trap heat in the atmosphere
🌍 Result → Warmer Earth, maintaining temperatures suitable for life
🔥 Major Greenhouse Gases (GHGs)
1⃣ Carbon Dioxide (CO₂)
🔸 From burning fossil fuels, deforestation
🔸 Most abundant human-caused GHG
2⃣ Methane (CH₄)
🔸 From livestock, landfills, natural gas leaks
🔸 Traps 25x more heat than CO₂ over 100 years
3⃣ Water Vapor (H₂O)
🔸 Most abundant natural greenhouse gas
🔸 Warms atmosphere but does not accumulate like CO₂
4⃣ Nitrous Oxide (N₂O)
🔸 From agriculture, fertilizers, fossil fuels
🔸 300x stronger than CO₂ at trapping heat
5⃣ Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) & Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs)
🔸 From refrigerants, aerosols, air conditioners
🔸 Highly potent but in lower concentrations
🌡 Effects of the Greenhouse Effect
🔥 Global warming → Rising temperatures
🌊 Melting glaciers & rising sea levels
🌪 More extreme weather (hurricanes, heatwaves)
🌾 Changes in ecosystems & agriculture
🐾 Threats to biodiversity
✅ Ways to Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions
🌱 Use renewable energy (solar, wind, hydro)
🚗 Reduce fossil fuel use (electric cars, public transport)
🌲 Reforestation & afforestation (plant more trees)
🏠 Increase energy efficiency (LED bulbs, insulation)
🗑 Reduce waste & methane emissions (composting, recycling)
🌍 Sources of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
1⃣ Agriculture
🔸 Emissions mostly from managing agricultural soils
🔸 Livestock and fertilizer use contribute
2⃣ Commercial & Residential Buildings
🔸 On-site energy generation
🔸 Burning fuels for heating and cooking
3⃣ Energy Supply
🔸 Burning coal, natural gas, and oil for electricity and heat
🔸 Largest source of global greenhouse gas emissions
4⃣ Industry
🔸 Burning fossil fuels at facilities for energy
🔸 Cement manufacturing contributes significant CO₂
5⃣ Land Use & Forestry
🔸 Deforestation (removal of carbon sinks)
🔸 Land clearing for agriculture, strip-mining, fires, peat decay
6⃣ Transportation
🔸 Burning fossil fuels for road, rail, air, and marine transport
7⃣ Waste & Wastewater
🔸 Landfill methane (CH₄) emissions
🔸 Waste incineration and wastewater treatment
🌿 Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Gas
1⃣ Carbon Dioxide (CO₂)
🔸 Released by deforestation and burning fossil fuels
🔸 Naturally from respiration and volcanic eruptions
2⃣ Methane (CH₄)
🔸 Contributed by agricultural activities, waste management, and energy use
3⃣ Nitrous Oxide (N₂O)
🔸 Fertilizer use is the primary source of emissions
4⃣ Fluorinated Gases
🔸 Industrial processes, refrigeration, and consumer products
🔸 Includes HFCs, PFCs, and SF6
5⃣ Black Carbon (Soot)
🔸 A solid particle/aerosol, not a gas, but still warms the atmosphere
1⃣ Oceans Contain More CO₂
🔸 The world's oceans contain more carbon dioxide than the atmosphere.
2⃣ Pole-Wide Warming
🔸 Atmospheric temperatures, cloud cover, surface albedo, and water vapor cause pole-wide warming.
🔸 The north and south poles are warming faster due to energy carried through large weather systems.
3⃣ Ocean Currents Carry Heat
🔸 Ocean currents help distribute heat around the Earth.
🔸 As oceans absorb heat, sea surface temperatures rise, and ocean circulation patterns change.
4⃣ Ocean Heat and Global Climate
🔸 Even small changes in ocean heat can affect the global climate significantly.
5⃣ Average Global Air Temperature Rise
🔸 Air temperatures are 5°F to 9°F (3°C to 5°C) warmer than pre-industrial times.
6⃣ Climate Effects of Warming
🔸 Higher temperatures may increase storm frequency/severity, flooding, aquifer recharge, and sedimentation.
7⃣ Coastal Wetland Threats
🔸 Global warming may completely alter estuaries and coastal wetlands.
🔸 Sea-level rise threatens coastal biota, which can't move inland due to coastal development.
8⃣ Displacement due to Coastal Flooding
🔸 The UN estimates 150 million people will need relocation by 2050 due to flooding, erosion, and agricultural disruption.
9⃣ Decrease in Glaciers
🔸 The total surface area of glaciers has decreased by 50% since the end of the 19th century.
🔟 Antarctica's Role in Ice
🔸 Antarctica holds 90% of Earth's ice and 70% of freshwater.
🔸 If Antarctic ice melted, sea levels could rise by 200 feet (60 m).
1⃣1⃣ Greenhouse Gases and Climate
🔸 Greenhouse gases trap solar radiation and warm the Earth's climate.
1⃣2⃣ Health Risks from Global Warming
🔸 Higher temperatures increase heat-related deaths, diseases like malaria, and bacterial infections.
1⃣3⃣ Arctic Species Affected
🔸 Arctic fauna, like polar bears, are severely impacted by the loss of ice floes and disrupted food webs.
1⃣4⃣ Tectonic Movements
🔸 The movement of tectonic plates creates volcanoes and mountains, impacting climate.
1⃣5⃣ Volcanic Gases and Climate
🔸 Volcanic gases in the stratosphere affect climate for long periods.
1⃣6⃣ Solar Cycles and Temperature
🔸 The solar cycle affects global temperatures by ~0.1°C, warmer during solar maximums and cooler during solar minimums.
1⃣7⃣ Fish Migration Due to Warming
🔸 Warm-water fish are moving into areas once inhabited by cold-water species due to river and stream warming.
1⃣8⃣ Arctic Methane Release
🔸 Arctic methane release from melting glaciers creates a positive feedback loop, accelerating global warming.
1⃣9⃣ Historical Sea-Level Rise
🔸 Sea levels have risen 400 feet (120 m) since the last ice age.
🔸 From 1900, sea levels have risen 3 mm per year.
2⃣0⃣ Ocean Acidification
🔸 Atmospheric CO₂ reacts with seawater to form carbonic acid, leading to ocean acidification.
🌍 International Climate Agreements
2⃣1⃣ Kyoto Protocol (2005)
🔸 A UN plan to reduce climate change effects, aiming for emission reductions.
2⃣2⃣ Montreal Protocol (1987)
🔸 An international treaty to phase out substances causing ozone depletion.
2⃣3⃣ Paris Agreement (2016)
🔸 Aimed at keeping global temperature rise below 2°C above pre-industrial levels, with each country setting its own mitigation plans.
🔸 Plants are more vulnerable to habitat loss because:
🔹 Cannot migrate
🔹 Cannot seek nutrients or water
🔹 Seedlings must survive in degraded conditions
🔹 Seed dispersal rates are slow
🔸 Animals can cope with habitat destruction through:
🔹 Migration
🔹 Adaptation
🔹 Acclimatization
What Affects Animal Migration?
🔹 Access routes or corridors
🔹 Magnitude and rate of degradation
🔹 The organism's ability to migrate
🔹 Proximity and availability of new habitats
🧬 Adaptation to Environmental Changes
🔸 Adaptation is the ability of an organism to survive changing environmental conditions.
🔸 Adaptation depends on:
🔹 Birth rate
🔹 Gene flow between populations
🔹 Genetic variability
🔹 Population size
🔹 Length of generation
🔹 Magnitude and rate of degradation
⚙ Acclimatization
🔸 Acclimatization is the process by which an organism adjusts to gradual changes in the environment.
🔸 Acclimatization depends on:
🔹 Physiological and behavioral limitations
🔹 Magnitude and rate of degradation
🌿 Invasive Species
🔸 Invasive species are plants or animals transported to areas where they do not naturally live.
📋 Characteristics of Invasive Species
🔸 Invasive species typically have the following characteristics:
🔹 Abundant in native range
🔹 Broad diet
🔹 High dispersal rates
🔹 High genetic variability
🔹 High rates of reproduction
🔹 Live in close association with humans
🔹 Long-lived
🔹 Pioneer species
🔹 Short generation times
🔹 Tolerant of a wide range of environmental conditions
🔹 Vegetative or clonal reproduction
🌳 Examples of Invasive Species
8⃣ Dutch Elm Disease
🔸 Dutch elm disease is transmitted by elm bark beetles, killing over half of the elm trees in the northern US.
9⃣ European Green Crabs
🔸 European green crabs were introduced to the San Francisco Bay area in 1989, threatening commercial fisheries.
🔟 Water Hyacinth
🔸 Water hyacinth, an aquatic plant from South America, crowds out native aquatic plants, blocks sunlight for submerged plants, and clogs waterways and intake pipes.
1⃣1⃣ Zebra Mussels
🔸 Zebra mussels can attach to almost any hard surface, clogging water intake pipes, attaching to boats, docks, and even native mussels and crayfish.
🦏 Endangered Species
🔸 A species considered to be facing a very high risk of extinction in the wild.
📊 Factors for Endangerment Label
🔹 Breeding success rate
🔹 Known threats
🔹 Population increase/decrease over time
🔹 Number of animals remaining
🌍 Arguments for Protecting Endangered Species
🔸 Reasons for protection include:
🔹 Maintaining genetic diversity
🔹 Keystone species
🔹 Indicator species
🔹 Aesthetic, ecological, educational, historical, recreational, and scientific value
🔹 Preserving the yet-to-be-discovered value of certain species
🌱 Characteristics Contributing to Endangerment
🔸 Factors include:
🔹 Competition for food with humans
🔹 High infant mortality
🔹 Sensitivity to environmental changes
🔹 Hunting for sport
🔹 Introduction of nonnative species
🔹 Limited environmental tolerance
🔹 Limited geographic range
🔹 Loss of habitat
🔹 Low reproductive rates
🔹 Slow movement
🔹 Lack of natural predators
🔹 Difficulty adapting quickly
🔹 Commercial hunting for body parts
🔹 Need for large territory
🔹 Small population size
🔹 Specialized feeding behaviors
🔹 Disease spread by humans or livestock
🔹 Superstitions
🦐 Examples of Species Contributing to Endangerment
🔹 African penguins - Compete for food with humans
🔹 Leatherback turtles - High infant mortality
🔹 Cotton-top tamarins - Sensitive to environmental changes
🔹 Passenger pigeons, blue whales, Bengal tigers - Hunting for sport
🔹 Bandicoots - Threatened by introduced cats
🔹 Frogs - Sensitive to water pollution and habitat destruction
🔹 Pandas - Limited geographic range
🔹 Salmon in the Pacific Northwest - Loss of habitat from human activities
🔹 Red wolves, Whooping cranes - Loss of habitat
🔹 Whales, elephants, orangutans - Low reproductive rates
🔹 Desert tortoises - Slow movement
🔹 Dodo birds, Steller’s sea cows - No natural predators
🔹 Polar bears - Not able to adapt quickly to climate change
🔹 Sharks, elephants, rhinoceros - Commercial value of body parts
🔹 Tigers - Require large territories
🔹 Tigers - Small population size and limited genetic diversity
🔹 Pandas - Specialized diet (Bamboo)
🔹 African wild dogs - Disease spread
🔹 Aye ayes - Killed due to superstition
🌳 Maintaining Biodiversity
🔸 Strategies include:
🔹 Creating and expanding wildlife sanctuaries
🔹 Establishing breeding programs for endangered species
🔹 Managing habitats and monitoring land use
🔹 Updating laws that protect endangered species
🔹 Protecting habitats through private or governmental land trusts
🔹 Reintroducing species into suitable habitats
🔹 Restoring compromised ecosystems
🔹 Reducing nonnative and invasive species