Pulse Wave Operations
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
UT 200 (chapter 4 and 7)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
it takes ___ microseconds to travel 1 cm deep
6.5
it takes ___ microseconds to travel 1 cm round trip
13
pulsed wave ultrasound
creation of images using sound by sending sound waves into the body, timing its return to determine the depth of the reflector
terms to describe pulsed waves
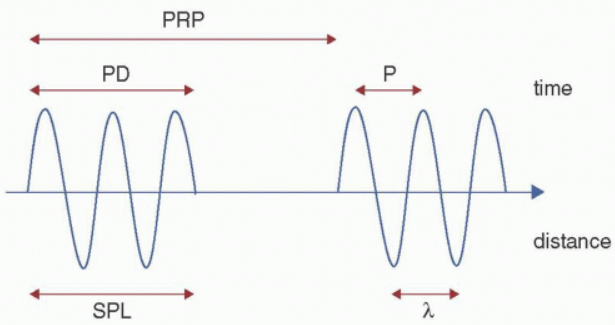
pulse repetition frequency (PRF)
pulse repetition period (PRP)
pulse duration (PD)
duty factor (DF)
spatial pulse length (SPL)
bandwidth
pulse
collection of cycles that travel together
must have a beginning and an end
an entire pulse moves as a single unit
two components of a pulse
transmit or “on” time
receive/listening or “off” time
pulse duration (PD)
group of periods/number of periods in a pulse
actual time from the start of a pulse to the end of that pulse
considered the “on” time or ringing time
ranges from 0.3 to 2.0 microseconds
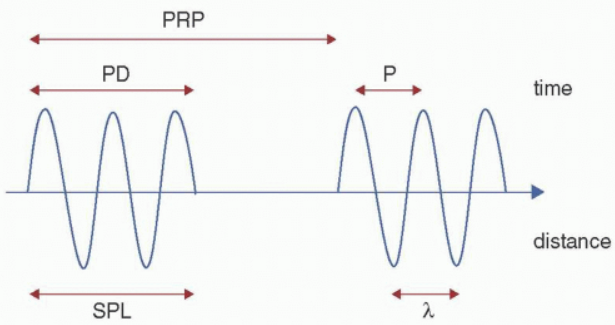
PD is determined by the …
sound source (TDR frequency)
PD formula
PD = n x P
PD = number of cycles in a pulse x period
period and frequency are inversely related (P = 1/f), so if the frequency increases then …
period and PD decrease
pulse repetition period (PRP)
start of one pulse to the start of the next pulse
includes the on (transmit) and off (listening) time
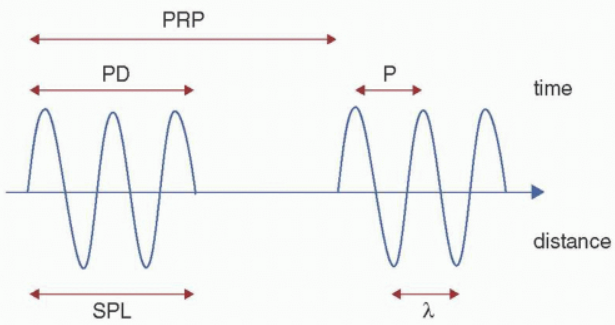
PRP is determined by the …
sonographer (by adjusting depth) and sound source
PRP and PRF are ___ related
inversely
PRP is ___ related to depth
directly
as depth increases, PRP …
increases
as PRP increases, PRF …
decreases
as depth increases, PRF …
decreases
PRF is ___ related to depth
inversely
PRF is not the same as …
TDR frequency
as TDR frequency increases …
depth decreases
difference between PRP and PD
PD is only the on time
PRP is both the on and off time
how the source affects PD
PD is determined by the period
period is determined by the frequency
frequency is determined by the sound source
pulse repetition frequency (PRF)
number of pulses transmitted into the body by the US system each second
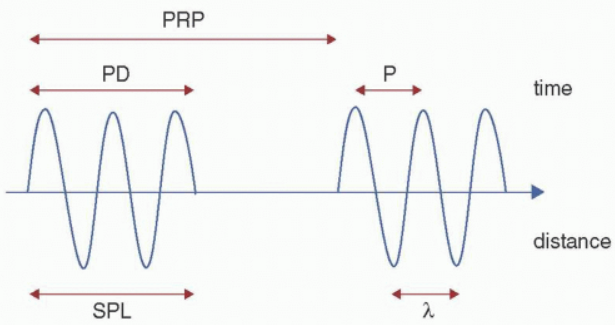
units for PRF
Herz (Hz) or per sec
units for PD
microseconds
units for PRP
milliseconds or microseconds
PRF is determined by the ___ ___ and is inversely related to depth
sound source
as depth increases, PRF …
decreases
PRF is ___ related to depth
only
PRF is ___ related to TDR frequency
not
if the transducer is excited 500 times, then the PRF is …
500 Hz
spatial pulse wavelength (SPL)
distance (length) a pulse occupies in space from start to end
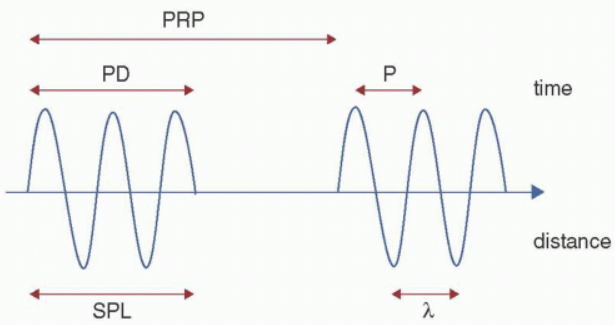
formula for SPL
SPL = number of cycles in a pulse x wavelength
units for SPL
mm
SPL is determined by …
the source and the medium (because wavelength is determined by the source and the medium)
SPL is visually the same as the …
PD
SPL ___ be altered by the sonographer
cannot
US likes ___ pulses
shorter
high frequency = shorter period = shorter PD = shorter wavelength = shorter SPL =
better image quality
low frequency = longer period = longer pulse duration = longer wavelength = longer SPL =
worse image quality
duty factor (DF)
the percentage or fraction of time that the system transmits a pulse
ranges between 0 to 1.0 or 0% to 100%
the DF of continuous wave (CW) ultrasound system is ___ because it is always transmitting
1.0 (100%)
DF formula
DF (fraction) = PD (sec) / PRP (sec)
DF (%) = PD (sec) / PRP (sec) x 100
the DF of pulse wave (PW) ultrasound system is …
less than 1% (ranges from 0.001 and 0.01)
the DF of clinical US imaging is very low because …
there is more receiving time (>99%) than transmitting time (<1%)
DF is determined by the …
source and depth
how PD is affected by the sound source
PD is affected by the period = period is affected by the frequency = frequency is determined by the sound source
as PD increases, DF …
increases
if the PD is 10 sec and the PRP is 100 sec, what is the DF?
10/100 × 100 = 10%
10/100 = 0.10
as PRP increases, DF …
decreases
as PRF increases, DF …
increases
as depth increases, DF …
decreases
as period increases, DF …
increases
DF is directly related to …
PD, PRF, and period
DF is inversely related to …
PRP and depth
factors determined by the sound source
PD, DF, PRP, and PRF
factors affected by depth
DF, PRF, and PRP
factors determined by the source and medium
SPL
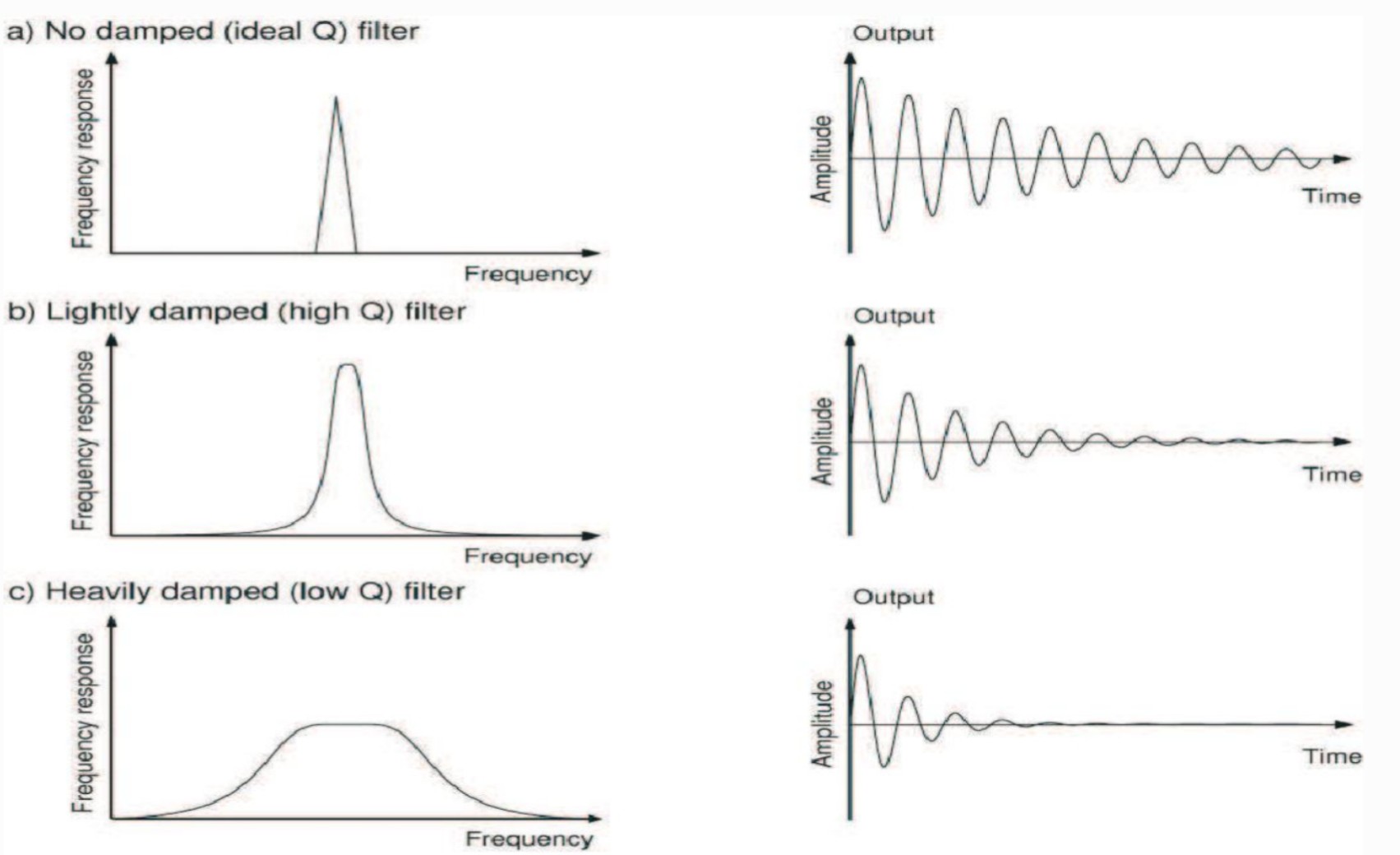
bandwidth
the difference between the highest and lowest frequencies emitted by the TDR
TDRs emit frequencies ___ and ___ the operating frequency
above; below
a TDR with a ___ bandwidth emits few frequencies
narrow
examples of TDRs with narrow bandwidth
CW TDRs (cardiac and vascular)
examples of TDRs with wide bandwidth
PW TDRs (abdominal)
a TDR with a ___ bandwidth has short pulses (emits more frequencies)
wide
damping ___ the ring time
shortens
shorter ring time =
better image
narrow bandwidth
A
medium bandwidth
B
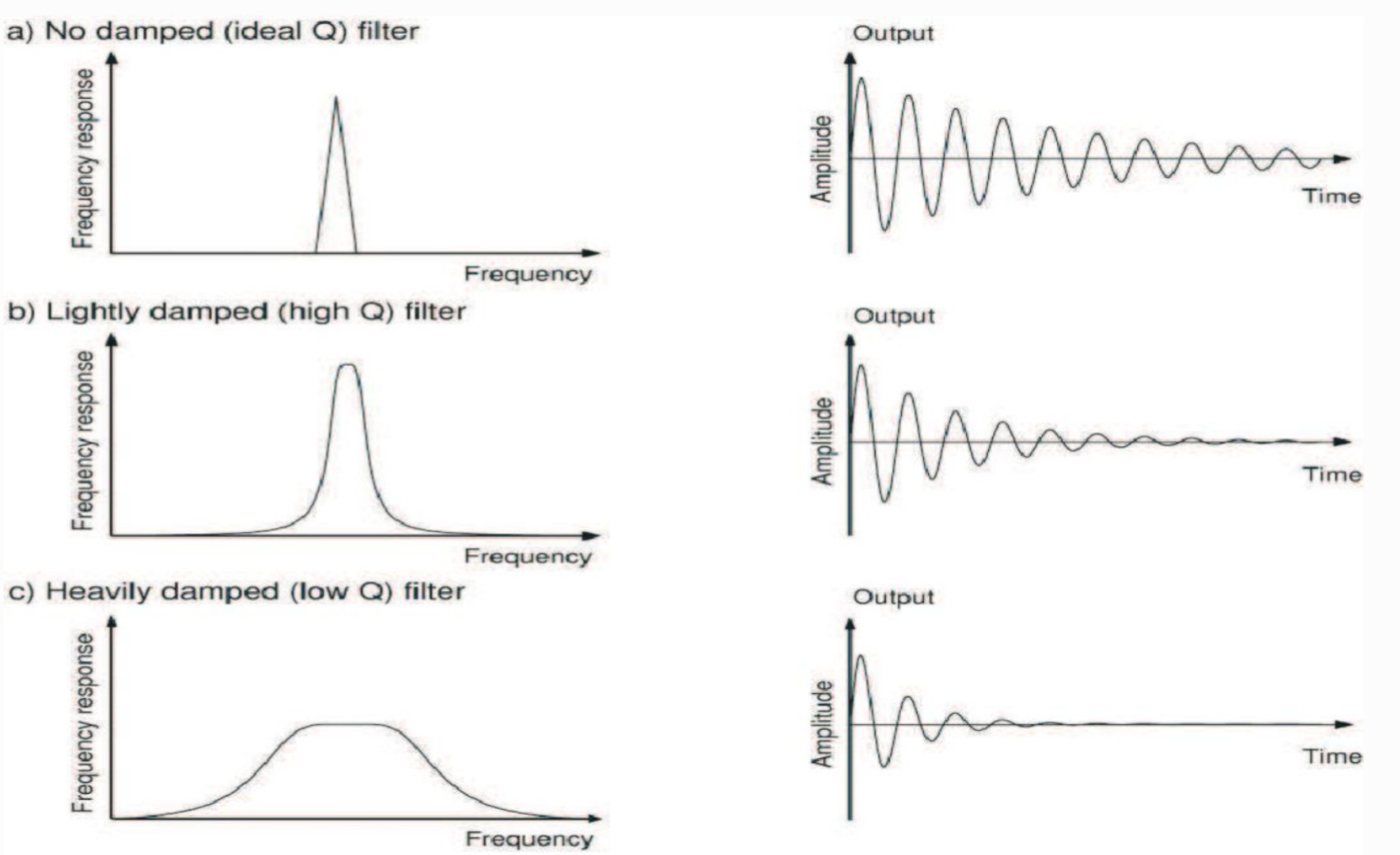
wide bandwidth
C

___ TDRs have damping
imaging (PW)
range equation
AKA time of flight or round-trip time
used to determine how far away a reflector is located to be displayed on the screen
ultrasound assumes that the beam is traveling through soft tissue at a speed of …
1.54 mm/microsecond
1540 m/s
13 microsecond rule
it takes 13 microseconds to travel to a depth of 1 cm and return
only applies in soft tissue (thus reflectors traveling faster or slower than soft tissue will be displayed inaccurately)