Midterm Review for Business Information Systems
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Information age
The present time, during which infinite quantities of facts are widely available to anyone who can use a computer.
Data
Raw facts that describe the characteristics of an event or object.
Information
Data converted into a meaningful and useful context.
Structured data
Stored in a traditional system such as a relational database or spreadsheet.
Machine-generated data
Created by a machine without human intervention.
Human-generated data
Data that humans, in interaction with computers, generate.
Unstructured data
Not defined and does not follow a specified format.
Systems thinking
A way of monitoring the entire system by viewing multiple inputs being processed or transformed to produce outputs while continuously gathering feedback on each part.
Management Information Systems (MIS)
A business function, like accounting and human resources, which moves information about people, products, and processes across the company to facilitate decision-making and problem-solving.
Supply Chain Management (SCM)
The management of information flows between and among activities in a supply chain to maximize total supply chain effectiveness and profitability.
Customer relationship management (CRM)
Involves managing all aspects of a customer's relationship with an organization to increase customer loyalty and retention and an organization's profitability.
Cross-selling and up-selling
Techniques used in marketing operational CRM to encourage customers to purchase additional products.
Sales force automation
A system that automatically tracks all of the steps in the sales process.
Contact center
A customer service operational CRM technology that manages customer interactions via phone.
Web-based self-service system
A customer service operational CRM technology that allows customers to resolve issues online.
Call scripting system
A customer service operational CRM technology that provides scripts for customer service representatives.
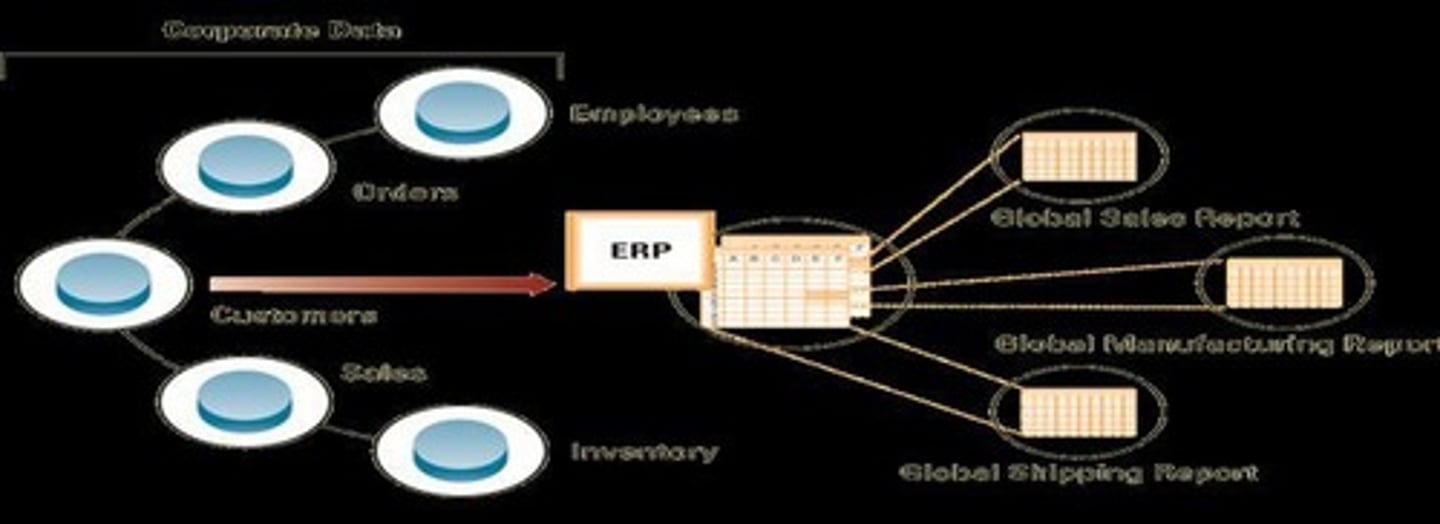
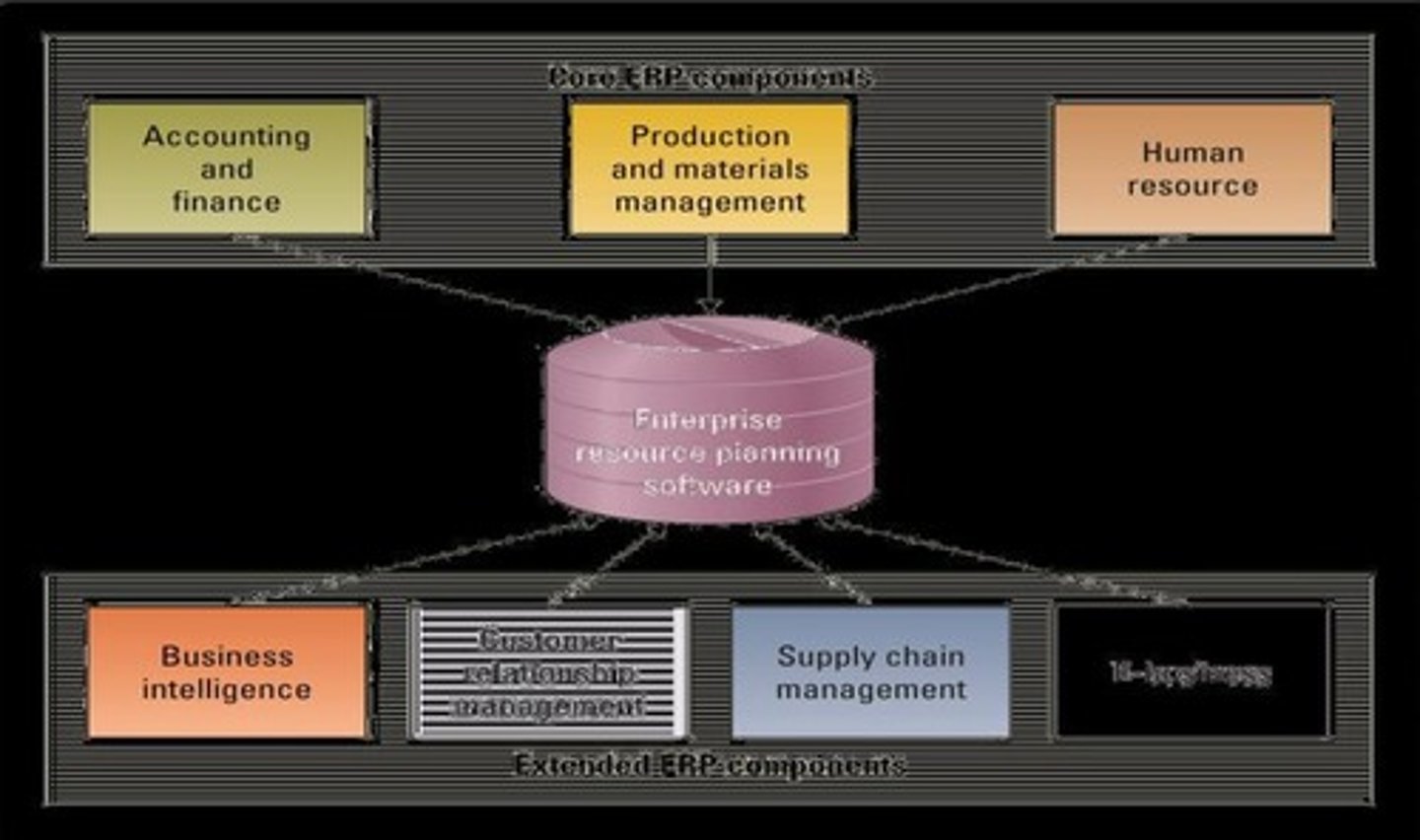
Enterprise resource planning (ERP)
Integrates all departments and functions throughout an organization into a single IT system to facilitate enterprisewide decision-making.
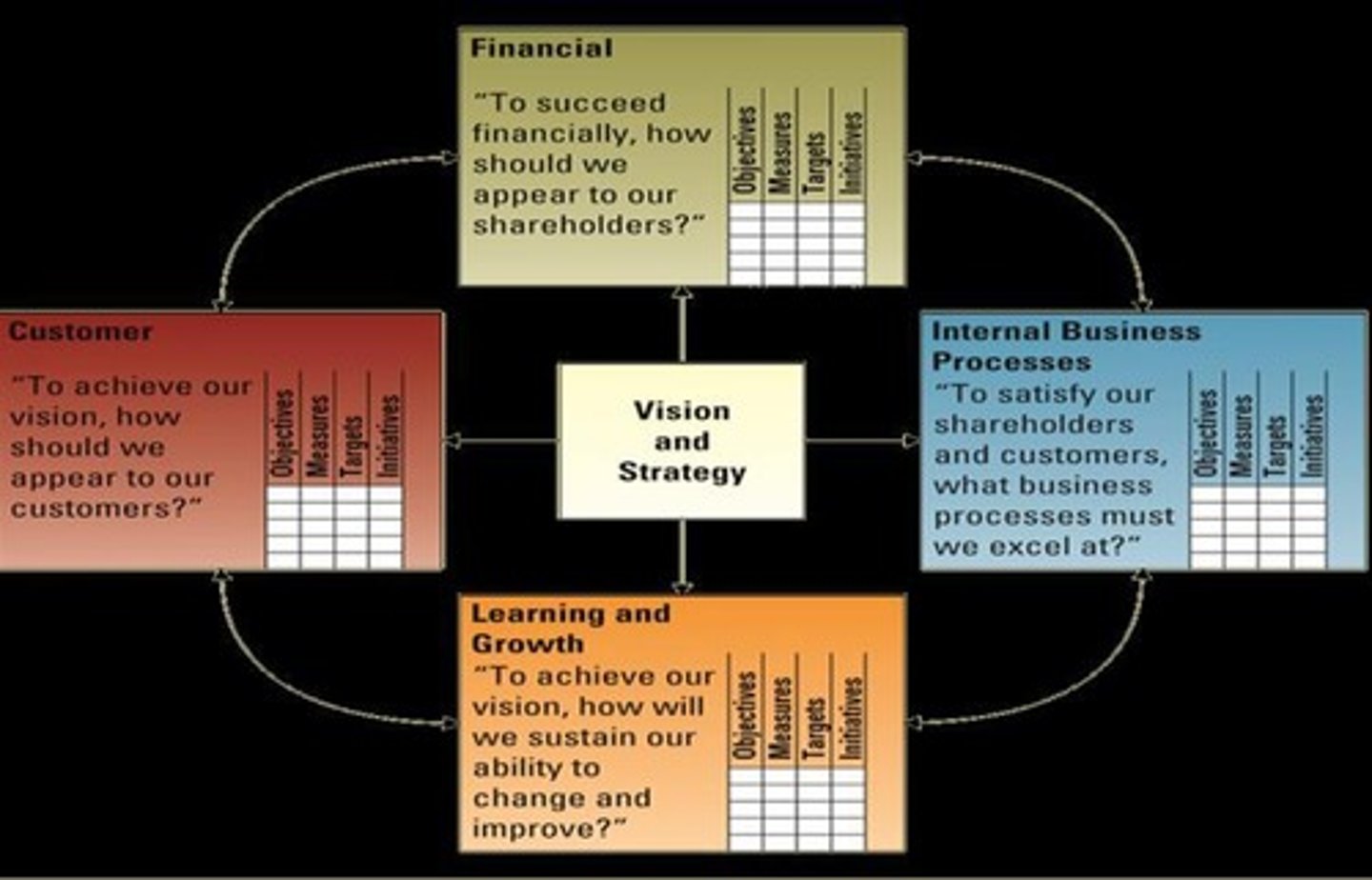
Balanced scorecard
Enables organizations to clarify their vision and strategy and translate them into action, viewing the organization from four perspectives: Learning and growth, Internal business process, Customer, Financial.
Major Limitations of ERP Implementations
ERP systems can be complex, expensive, and time-consuming to implement, and companies may need to change their methods of achieving business objectives.
ERP Implementation Failure
Causes include poor employee involvement and training.
On-Premise ERP Implementation
ERP systems hosted on local servers.
Vanilla Approach
Standard ERP implementation with minimal customization.
Custom Approach
Tailored ERP solutions to specific business needs.
Best of Breed Approach
Combining best individual software solutions.
Business Process
Standardized activities to accomplish specific tasks.
Business Process Reengineering (BPR)
Redesigning workflows within and between enterprises.
Business Process Modeling
Creating detailed flow charts of work processes.
As-Is Process Model
Current state of a business process.
To-Be Process Model
Future state of a business process after improvement.
Supply chain visibility
The ability to view all areas up and down the supply chain in real time.
CRM reporting technology
Helps organizations identify their customers across other applications.
CRM analysis technologies
Helps organizations segment their customers into categories such as best and worst customers.
CRM predicting technologies
Helps organizations make predictions regarding customer behavior such as which customers are at risk of leaving.
Operational CRM
Focuses on managing the day-to-day interactions with customers.
Analytical CRM
Focuses on analyzing customer data to improve business decisions.
List generator
A marketing operational CRM technology that helps create lists of potential customers.
Campaign management system
A marketing operational CRM technology that helps manage marketing campaigns.
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN)
Graphical representation for specifying business processes.

Flow Objects
Includes events, tasks, and gateways in BPMN.
Spreadsheet
Grid format of rows and columns for data.
Cell
Intersection of a row and column in a spreadsheet.
Record
A row of data in a spreadsheet.
Attribute
A column of data in a spreadsheet.
Excel Function
Pre-built formula for performing operations on data.
Function Syntax
FunctionName(argument1,...,argumentN) format.
Cell Reference
Identifies a specific cell in a spreadsheet.
Cell Range
Group of adjacent cells identified by references.
Robust Formulas
Formulas that adapt to changes in data.
Constants in Formulas
Hard-coded values that do not change automatically.
Parameters
Values stored in cells for specific purposes.
3D Reference
Reference including workbook and worksheet names.
Absolute Cell Reference
Reference that does not change when copied.
Dollar Symbol ($)
A dollar symbol ($) creates an absolute cell reference when placed in front of both the column and row designation.
VLOOKUP
Locates data in a table based on comparison values, which must be located in the 1st column of the lookup table range.
HLOOKUP
Identical to VLOOKUP, except data is organized horizontally.
VLookup Function
Used mostly to display data from one worksheet (or workbook) into another.
VLookup Function Arguments
Four arguments: lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup].
Logical IF Function
Used to evaluate data and provide conditional output based on a logical test.
Logical Test
Test results must evaluate to either TRUE or FALSE.
Logical Conjunction Functions
Evaluate multiple logical tests and enable linking or joining of functions or formulas to perform logical tests.
AND Function
Returns TRUE only if all logical tests are TRUE.
OR Function
Returns TRUE if at least one logical test is TRUE.
Direct Conversion Strategy
All users change at once during the implementation of a new system.
Pilot Conversion Strategy
A small group of users change first, then a full rollout occurs.
Phased Conversion Strategy
A small section of the system is rolled out first, followed by a full rollout.
Parallel Conversion Strategy
Old and new systems run simultaneously during the transition.
Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
The overall process for developing information systems from planning and analysis through implementation and maintenance.
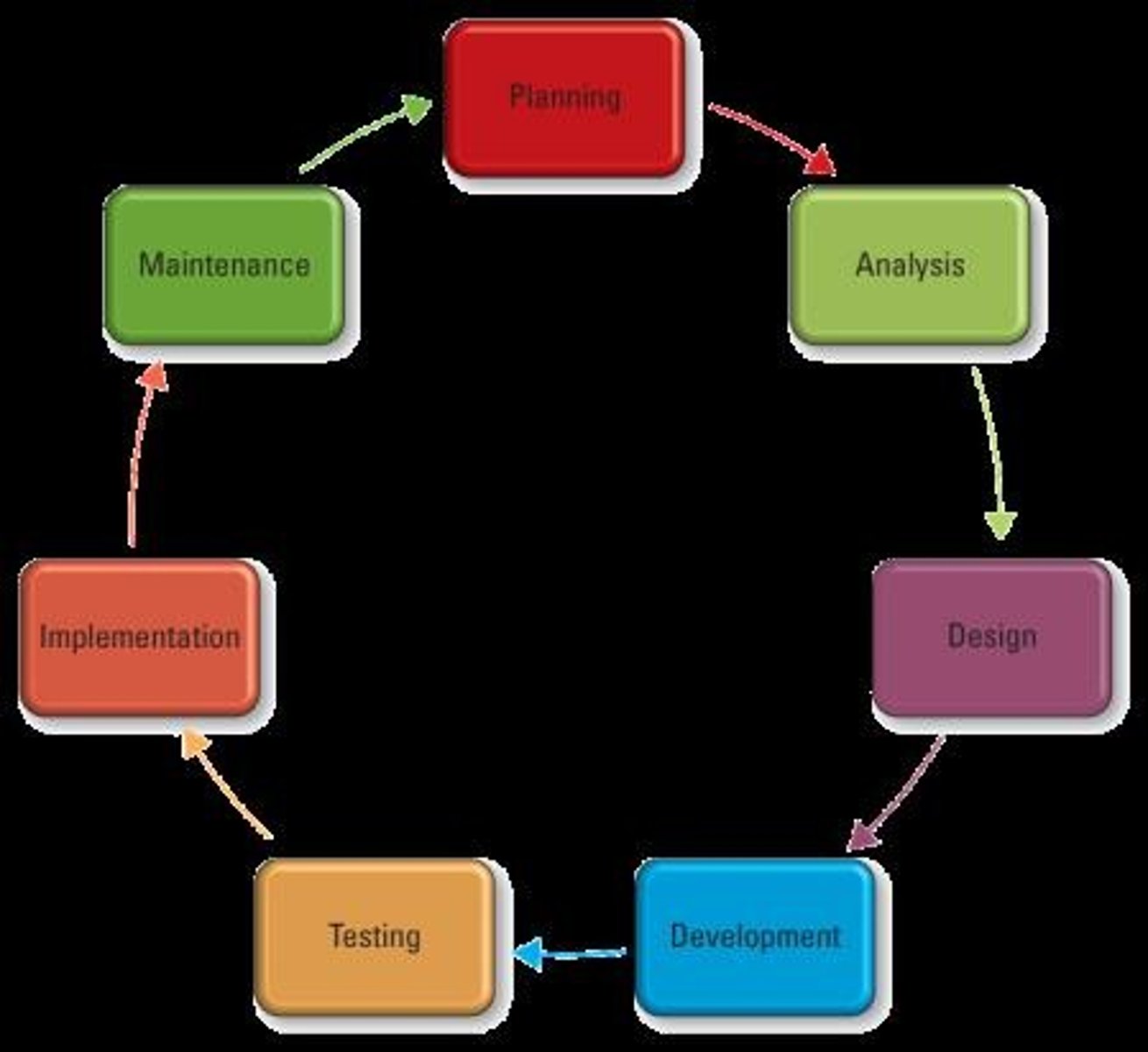
Planning Phase
Establishes a high-level plan of the intended project and determines project goals.
Analysis Phase
Involves analyzing end-user business requirements and refining project goals into defined functions and operations of the intended system.
Design Phase
Establishes descriptions of the desired features and operations of the system including screen layouts, business rules, process diagrams, pseudo code, and other documentation.
Development Phase
Involves taking all of the detailed design documents from the design phase and transforming them into the actual system.
Testing Phase
Involves bringing all the project pieces together into a special testing environment to eliminate errors and bugs, and verify that the system meets all of the business requirements defined in the analysis phase.
Implementation Phase
Involves placing the system into production so users can begin to perform actual business operations with it.
Maintenance Phase
Involves performing changes, corrections, additions, and upgrades to ensure the system continues to meet its business goals.
Market Segments
Groups of potential customers for a company's product or service.
Target Market
A chosen market segment to pursue.
Majority Fallacy
The inefficient targeting of all females, which is an inefficient use of marketing funds.
Niche Market
A smaller, highly defined market segment, such as males aged 21-25 who live in Savannah, GA and drive Subaru Foresters.
Brand Power
The specific image evoked by a brand name, usually proportional to its focus.