Histology
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Four Types of basic tissue
Epithelial
Connective
Muscular
Nervous
Epithelial tissue
sheets of cells covering body surfaces and lining cavities
Function of epithelial cells
protection, secretion, absorption, and filtration
endothelium
inner lining of blood vessels and lymph vessels
mesothelium
lines abdomen, heart and pleural cavities
characteristics of epithelium and what they mean
cellularity- how many layers (simple or stratified)
polarity- has two domains (apical- top and basal-bottom, and lateral- side domain)
avascularity: no direct blood supply
high mitotic rate- high turnover and regeneration
pseudo-stratified epithelium
single layer of epithelium with all cells attached to the basement membrane , and the orientation appears to have it layers
squamous epithelial cells
flat and thin cells that facilitate diffusion and filtration.
cuboidal epithelium
they are as wide as they are long and are involved in secretion and absorption.
columnar epithelium
they are longer than they are wide and are primarily involved in absorption, secretion, and protection.
what are the special surface modifications that epithelial cells can have
cilia
microvilli
stereocilia
Cilia
motile, hair like fibers- these can move materials and are found in places like the respiratory tract and the fallopian tubes
microvilli
nonmotile hair like structures, shorter hairs- these can be found in the small intestine and the kidneys
stereocilia
these are loner hairs that are nonmotile, and can be found in the the epididymus and the inner ear
list the junctional complexes in epithelial cells
tight junctions
adhering junctions
desmosomes
hemidesmosomes
gap junctions
tight junctions
these prevent all material from passing through- this is when we don’t want material to infiltrate cells
cells touch at these junctions, almost like a buttoned up shirt that doesn’t fit someone
adhering junctions
These junctions have firm cell adhesion, and resist tensile forces
desmosomes
resist against shear forces
hemidesmosomes
allows for attachment to the basement membrane
gap junctions
allows molecules to diffuse, and cell communication- good for nutrition purposes since these tissues are avascular
Where can you find simple squamous epithelium?
2 types
endothelium: lines the heart and blood vessels
mesothelium- lines the abdomen, pleural and heart chambers
Where can you find simple cuboidal epithelium?
these can be found in small ducts, and kidney tubules
where can you find simple columnar epithelium?
digestive tract and uterine tubes
what are the two kinds of stratified squamous epithelium?
keratinized and nonkeratinized
where can you find keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
skin
Where can you find nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
mouth, esophagus, vagina, anal canal
where can you find stratified cuboidal and columnar cells?
these are rare but can be found in some ducts and glands
where can you find pseudostratified epithelium?
you can find this in the respiratory tract, vas deferns, and epididymis
where can you find psuedostratified epithelium that has cilia on it?
trachea and bronchi
where can you find pseudostratified epithelium with stereocilia on it?
epididymis and vas deferens
what are glands?
they are composed of epithelial tissue, and they develop from epithelial cells that are specialized in secretion
what are the types of glands?
exocrine and endocrine
Exocrine glands
these are connected to the surface via ducts and secrete onto surfaces or into lumens
endocrine glands
these secrete directly into the blood stream or interstitial fluid (no ducts)- they use the capillaries
what are the ways to classify exocrine glands?
secretory product
mechanism of secretion
cell number
morphology
Serous glands- what they secrete and examples
they secrete a watery, protein/enzyme rich secretion
ex. parotid gland, pancreas and sweat glands
Mucous glands- what they secrete and examples?
they secrete viscous mucus (glycoprotein and water), which provides some level of lubrication- this is a very thick material
examples: goblet cells, respiratory and stomach epithelium
Mixed “seromucous” glands- what do they secrete and examples
-they secrete a mixture of both the serous (watery, protein/enzyme rich substance) and mucus (glycoprotein and water)
examples: submandibular, sublingual, and tracheal glands
Sebaceous glands- what do they secrete and where are they located?
these secrete a lipid/ sebum secretion
example: skin sebaceous glands
What are the mechanisms of secretion?
Merocrine
Apocrine
Holocrine
merocrine secretion
this deals with no release of cytoplasm
this can be found in the pancreatic acinar cells, and the salivary glands
apocrine secretion
this deals with some loss of cytoplasm from the apical surface of the epithelial cells
these can be found in the mammary glands
holocrine secretion
this is where the entire cells dissolves/ gets released with secretion
ex. the sebaceous glands
what are the classifications by cell number for exocrine glands
unicellular
single secretory cell performing the secretion
ex. goblet cells in the intestines and the respiratory tract
multicellular
formed into ducts and units
there is a secretory portion (end piece) and the excretory duct
there are a bunch of subtyoes based on morphology
what are the types of morphology classification of the ducts?
simple glands (unbranched or uncoiled)
compound glands (branched)
tubular
acinar
tubuloacinar
where can you find a simple tubular gland?
these can be found in the small and large intestine
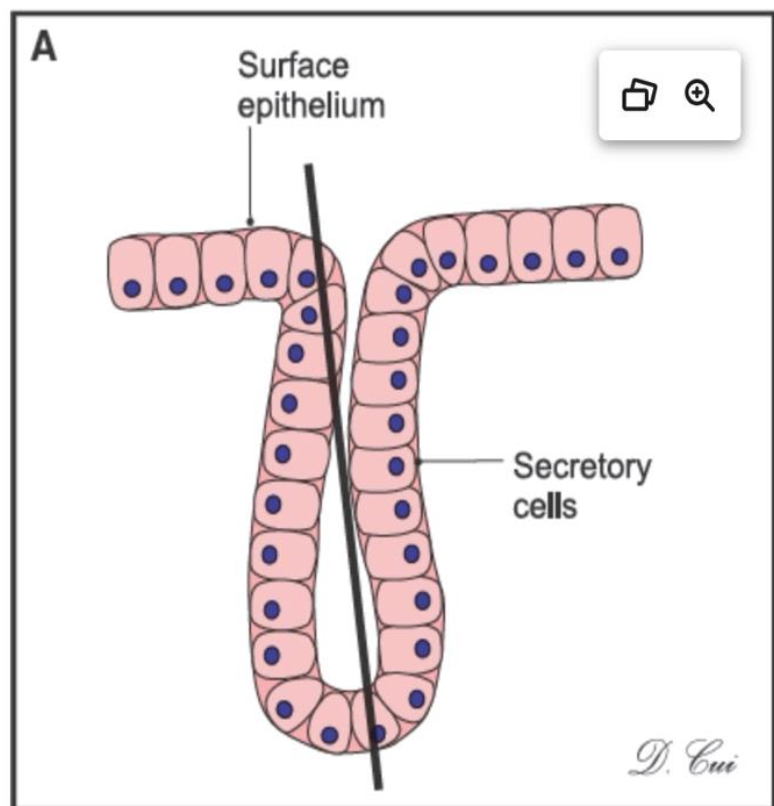
What type of gland is this?
simple tubular and it can be found in the large and small intestines
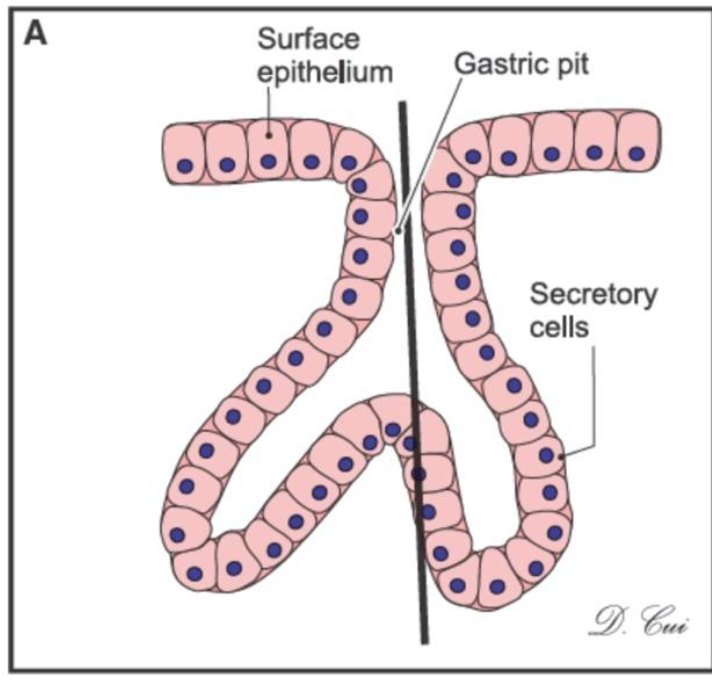
What kind of gland is this?
this is a simple branched tubular gland, and you can find this in the stomach and the uterus
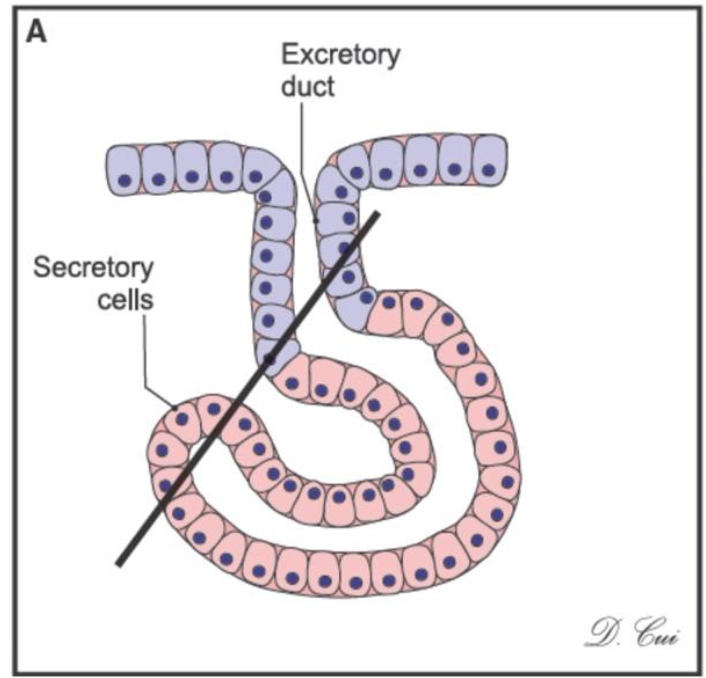
What kind of gland is this?
simple coiled tubular gland and it can be found in the sweat glands
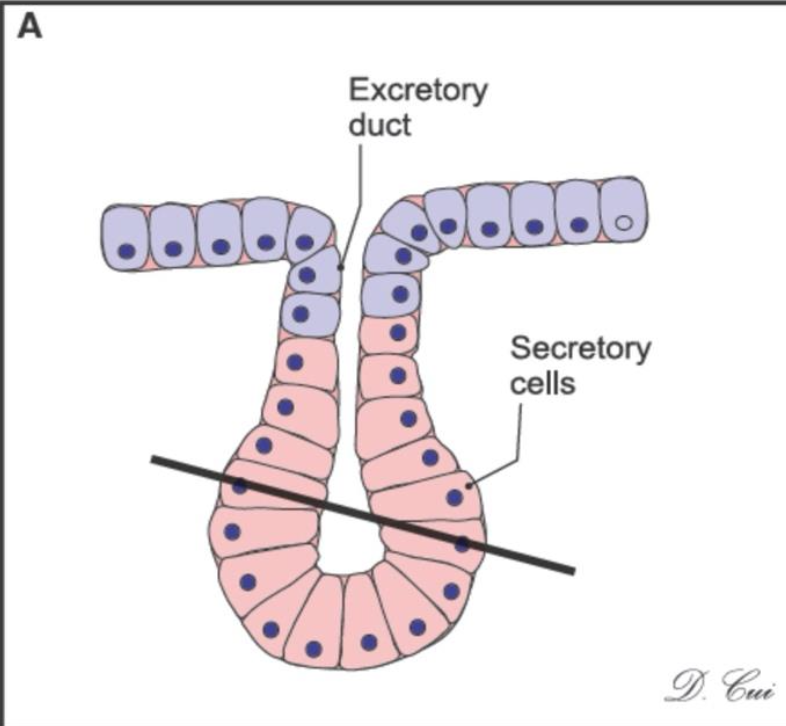
What kind of gland is this and where is it located?
this is a simple acinar gland and can be found in the urethra
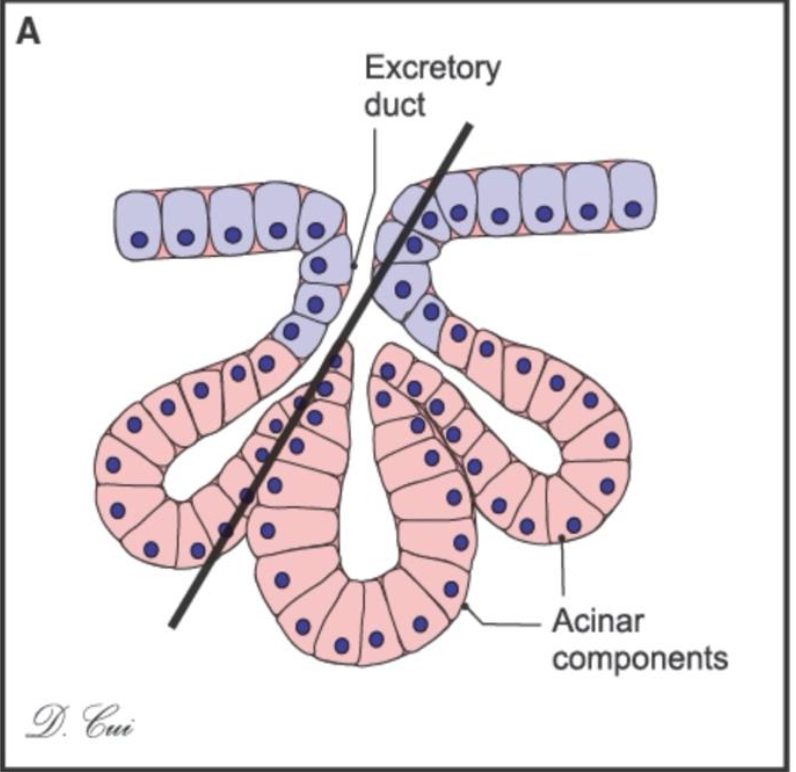
What kind of gland is this and where can you find it?
Simple branched acinar glands, and this can be found in the sebaceous glands of the skin
What are the compound gland morphologies?
compound tubular
compound acinar
compound tubuloacinar
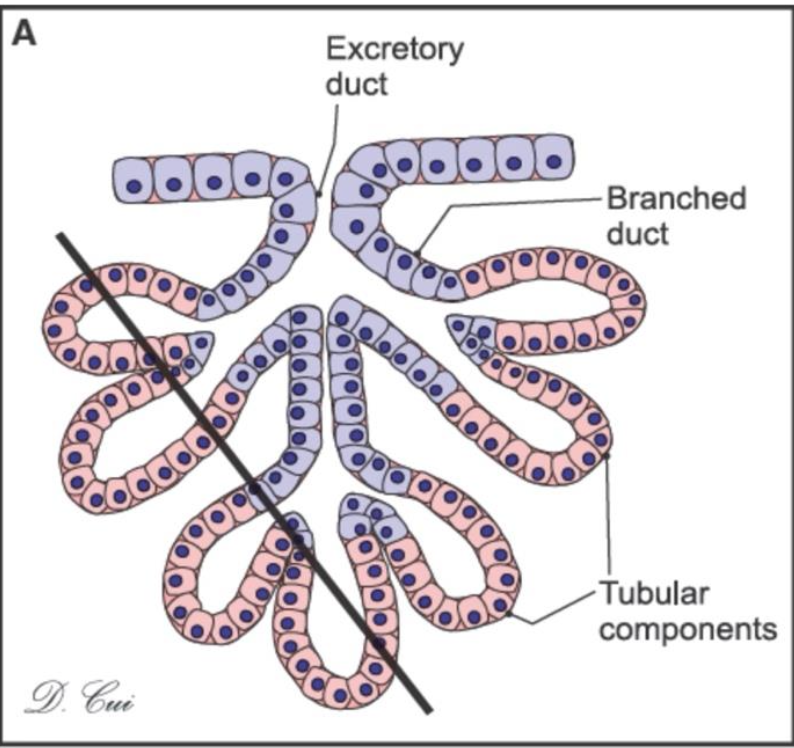
what kind of gland is this and where can you find it?
compound tubular gland and you can find it in the glands of the duodenum
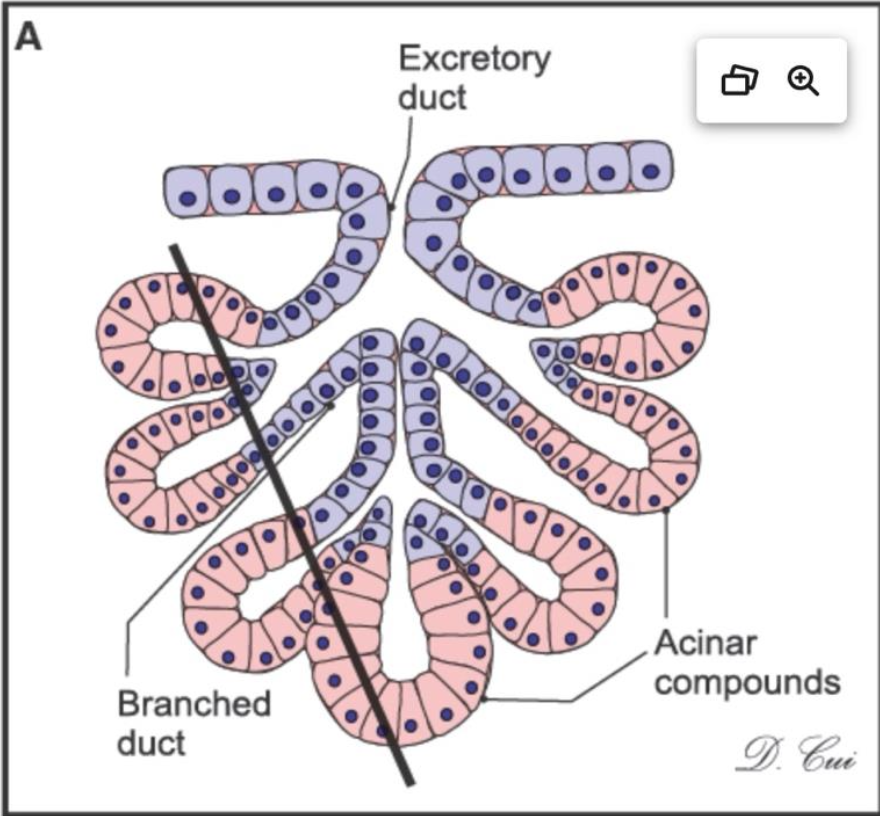
what kind of gland is this and where can you find it?
compound acinar gland and you can find it in the lacrimal glands, pancreas, and mammary glands
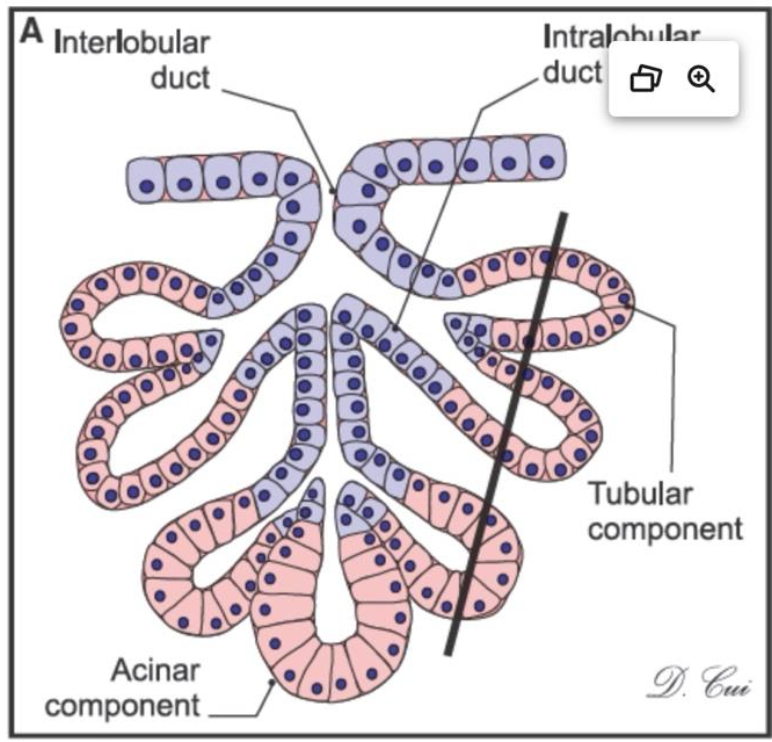
what kind of gland is this and where can you find it?
compound tubuloacinar gland and these can be located in the submandibular and sublingual glands
what is the hierarchy of ducts
secretory units to intercalated ducts (small intralobular) into striated ducts (larger intralobular) into interlobular ducts (in connective tissue septa) into lobar ducts and then the main excretory duct
characteristics of the endocrine glands
there are mo ducts and it has a high vascularity, the secretory cells are surrounded by capillaries, and the hormones are released directly into the bloodstream
major endocrine glands
pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal glands
functions of the endocrine glands
synthesize store and secrete hormones into circulation