Zoology Chapter 12 Sponges
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Phylum Porifera and Placozoa
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
What are the advantages of multicellularity?
Increased surface area for metabolic activities; highly adaptive path towards larger body sizes; leads to division of function & greater complexity
Choanoflagellates
aquatic unicellular eukaryotes; each cell has a flagellum surrounded by a collar of microvilli; sponges have something similar called- choanocytes; closest relative to multicellular animals
Phylum Porifera
Sponges; simplest multicellular animals; asymmetry or radial symmetry; no mouth, digestive tract, or tissues; has mesophyll, spicules, and spongin; about 8600 species today; few mm to over 2 m in diameter
mesophyl
Gelatinous matrix of protiens where all other cells reside; contains skeletal elements
spicules and spongin
tiny silica or calcium carbonate(spicules) and collagen proteins(spongin) skeletons that supports the matrix of a sponge
Sponge Ecology
Free-swimming embryos & sessile adults; can attach to anything submerged; shape & size dependent on environment & space
What biochemicals do sponges & microorganisms that live on crabs, fish, etc produce?
Antimicrobial, antiviral, antiparasitic activity
How do sponges Filter feed?
Suspension feeding; collecting suspended particles from the water
Dermalostia
pores used to draw water into an asconoid sponge
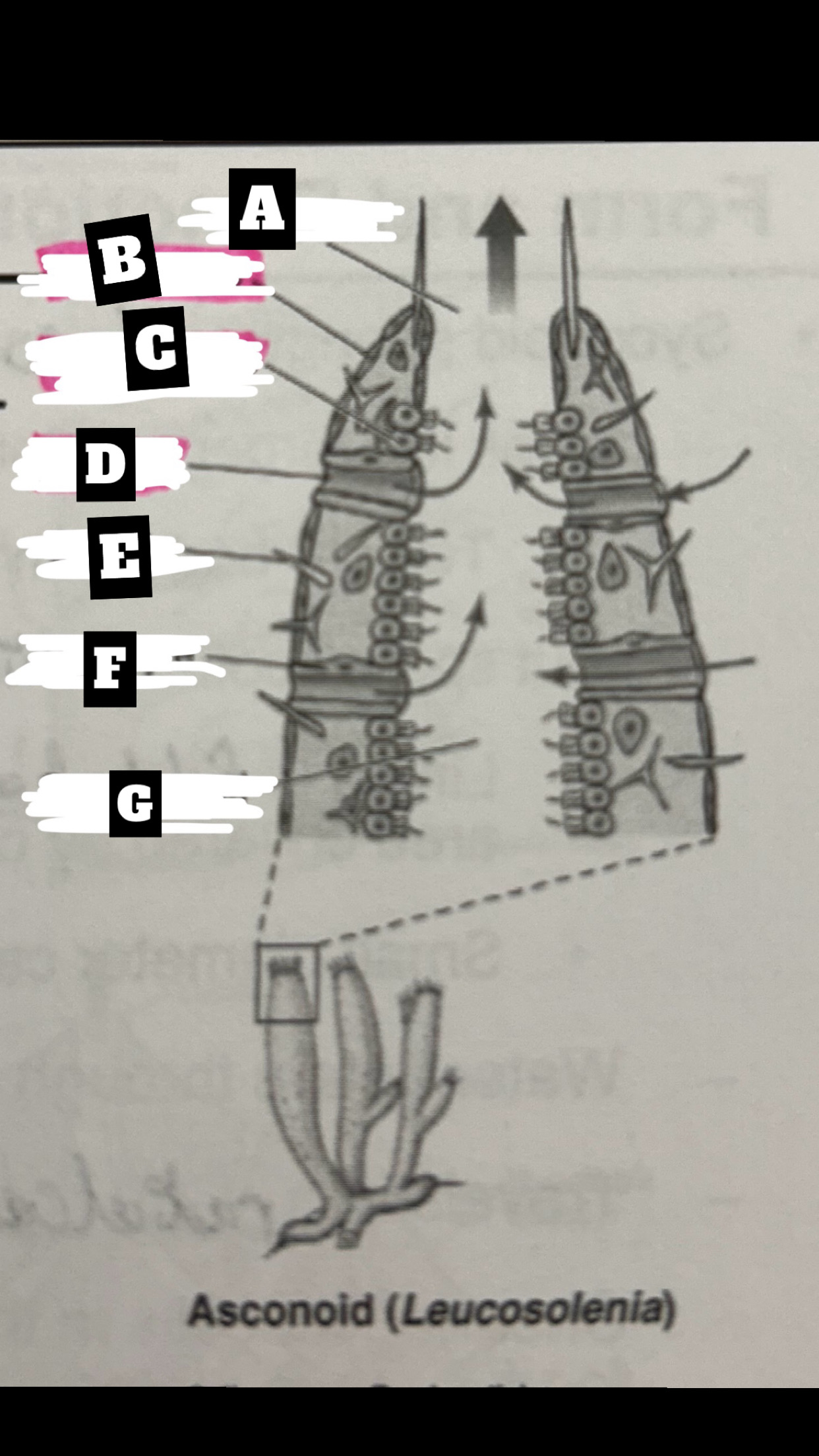
What is A
Osculum
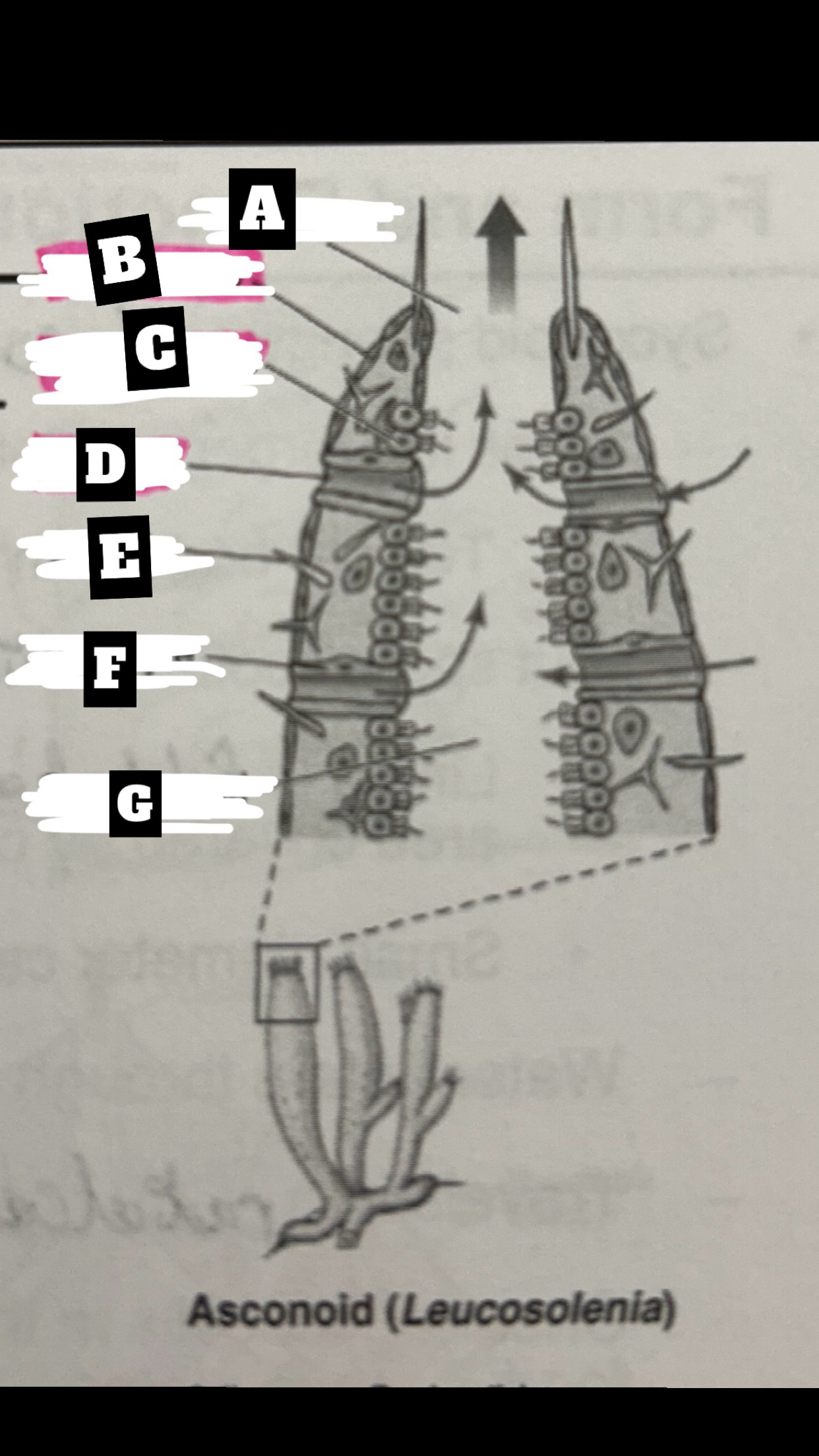
What is B
Pinacocyte
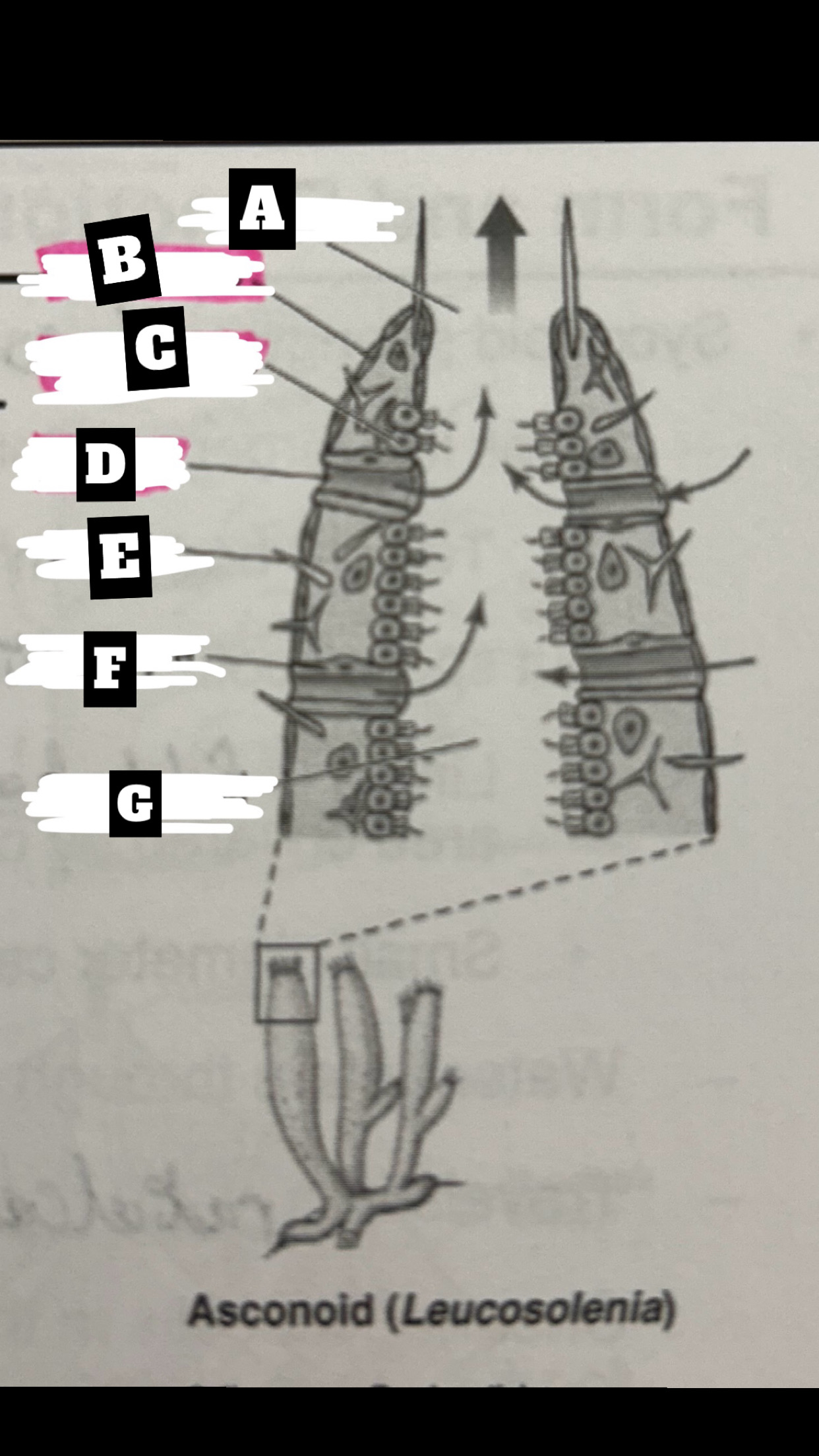
What is C
Chanocyte
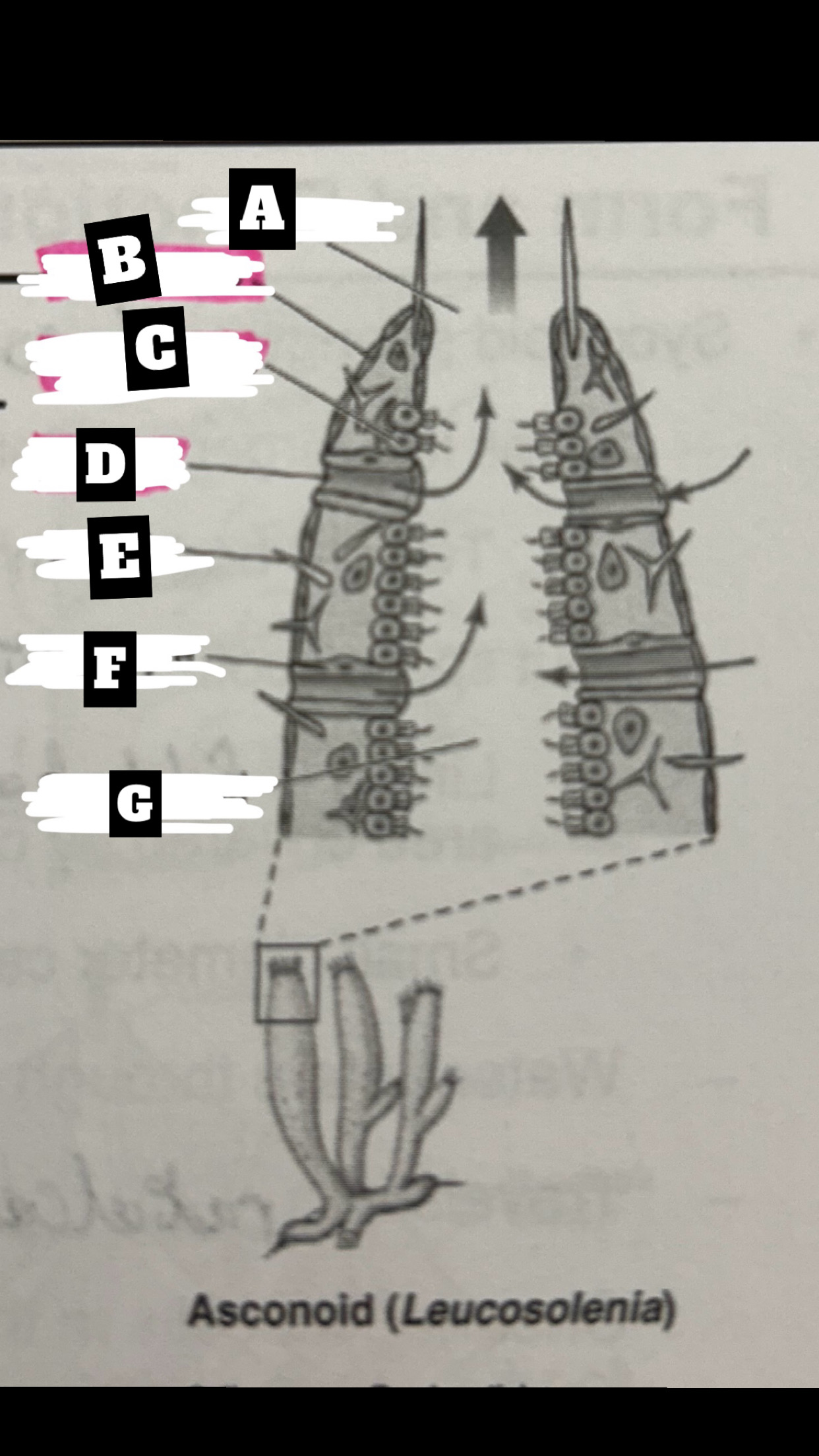
What is D
Ostium
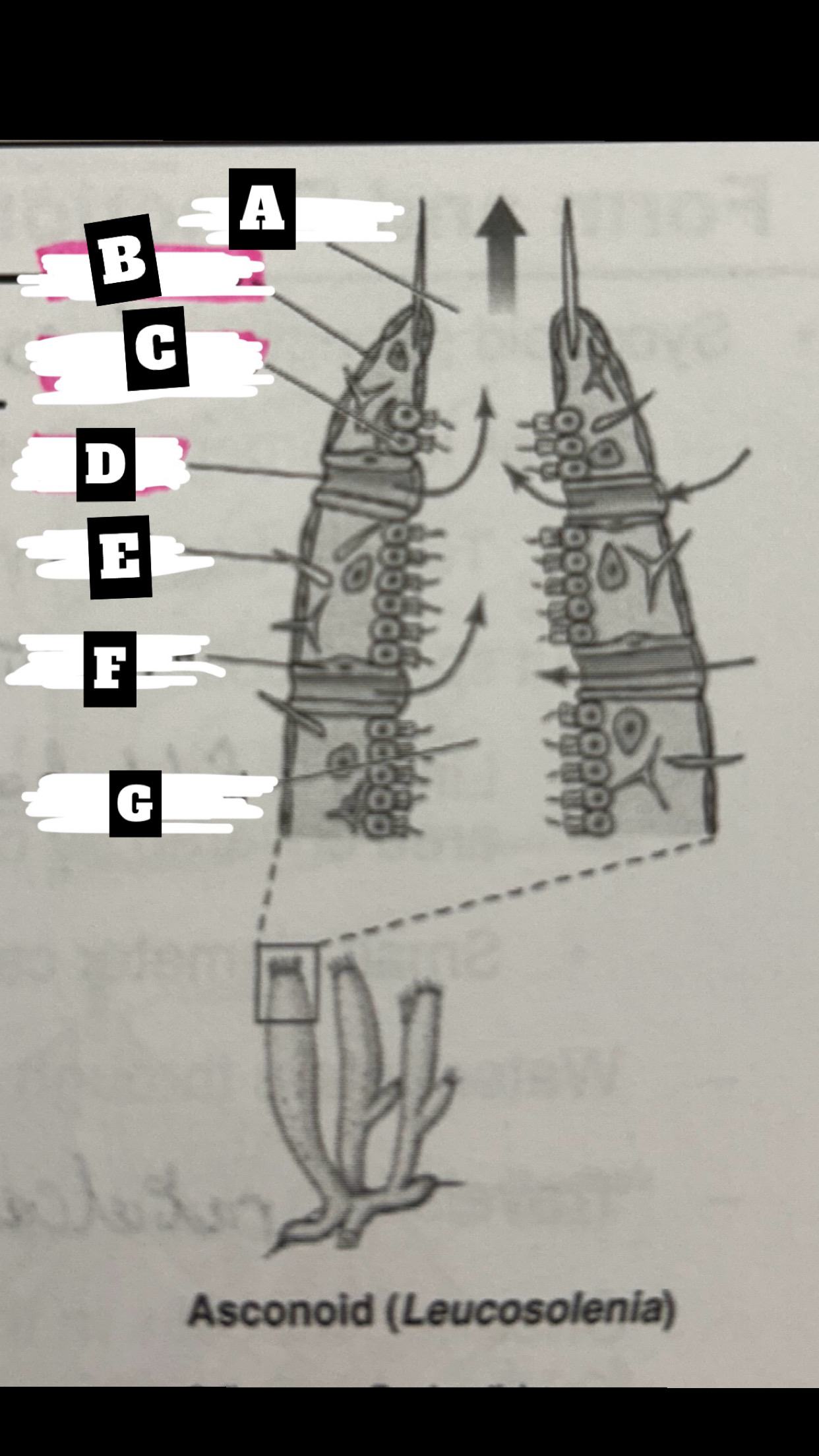
What is E
Spicule
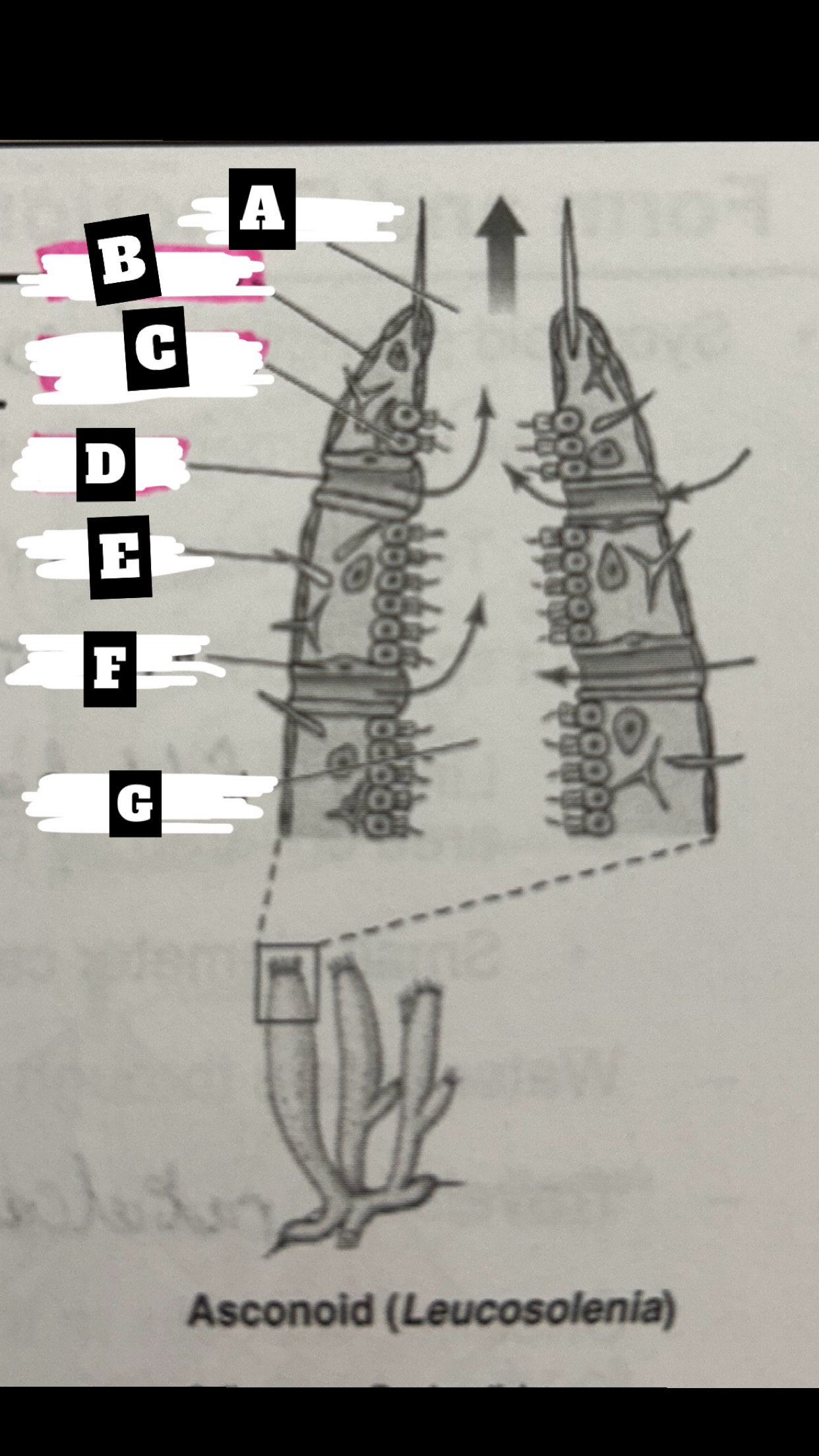
What is F
Porocyte
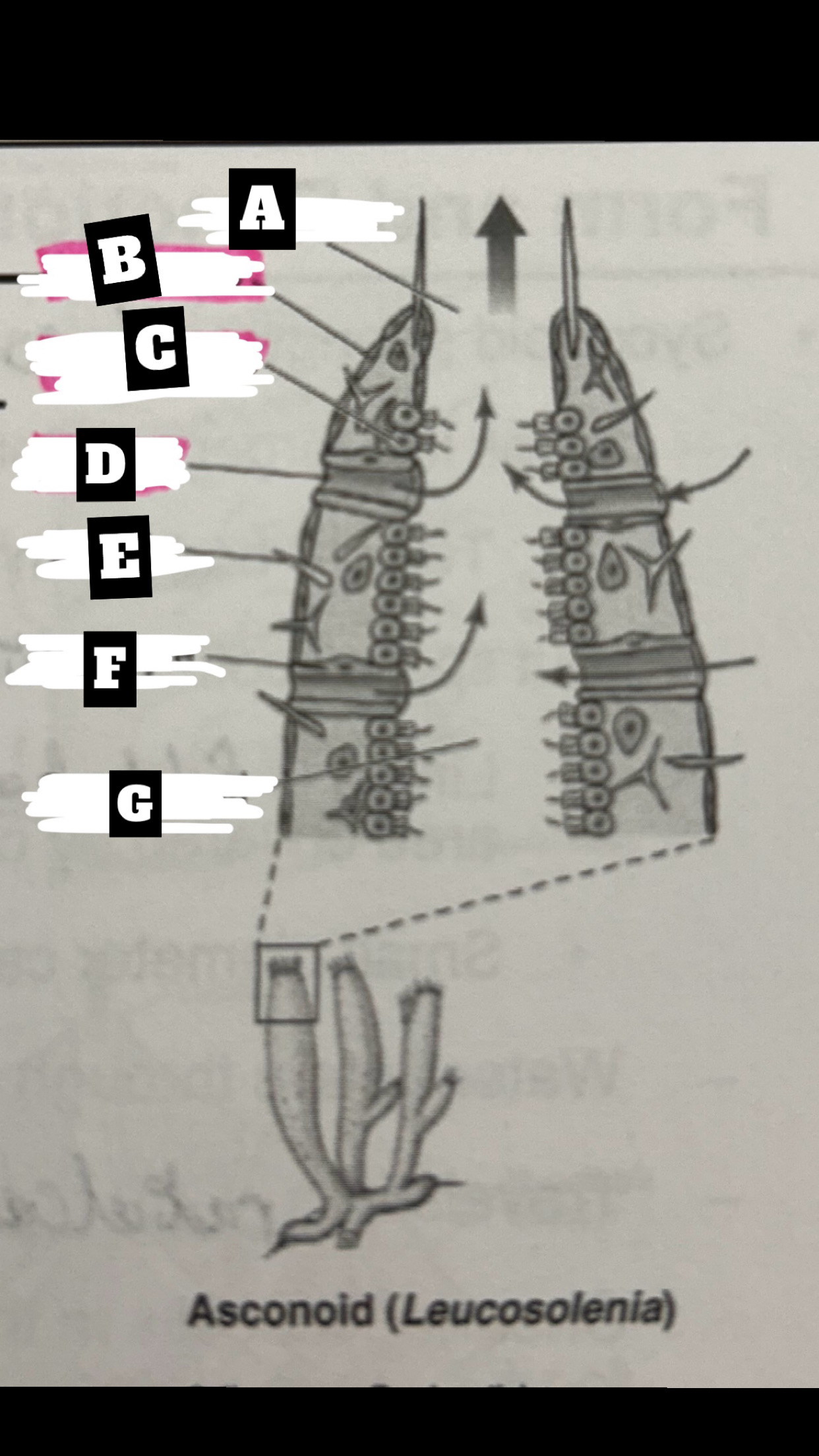
What is G
Spongocoel
Pinacoderm
the outermost layer of cells in sponges
Chanocytes
Ovoid cells tat line canals & chambers; one end is embedded in the mesophyl; Flagellum & surrounding collar extend from exposed side
Flagellum of Choanocyte structure
collar consists of microvilli connected to each other by fine microfibrils = fine filtering device; the beating flagellum moves water through the collar sieve; large particles are trapped in the collar mucus & are phagocytized
Microvilli
;used to trap food in Sponges
Phagocytosis
a process in which specialized cells called phagocytes engulf and destroy foreign particles, such as bacteria, viruses, and dead cells
Describe a Asconoid Sponge’s form and function
Simplest body organization; water is drawn through dermal ostia(porocytes), is drawn into the spongocel(central cavity) by beating flagella of choanocytes(also traps & phagocytizes food particles), the is expelled from top through osculum
Describe a Syconoid Sponge’s form and function
Tubular body with single osculum; thicker and more complex spongocoel with outward folding for more surface area; water enters through dermal ostia, travels into radial canal through prosopyles, choanocyte cells trap food and move water that exits radial canal into spongocoel through apopyles, before being expelled at top through osculum
Describe a Leuconoid Sponge’s form and function
Most common and complex organization with greatest surface area for food gathering; Choanocytes line the walls of small chambers; permits an increase in size= can filter all water; water is drawn into chambers through incurrent canal then exits chambers through excurrent canals, the expelled at the top through osculum(oscula)
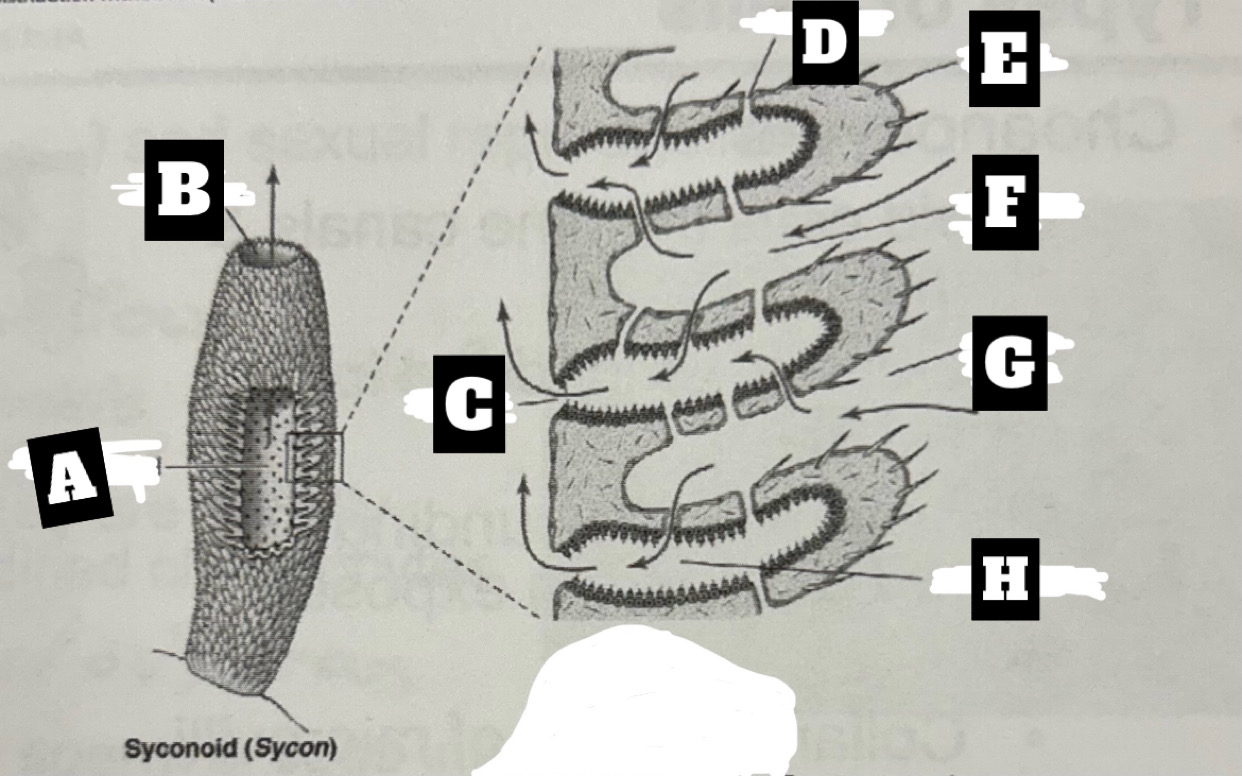
What is A
Spongocel
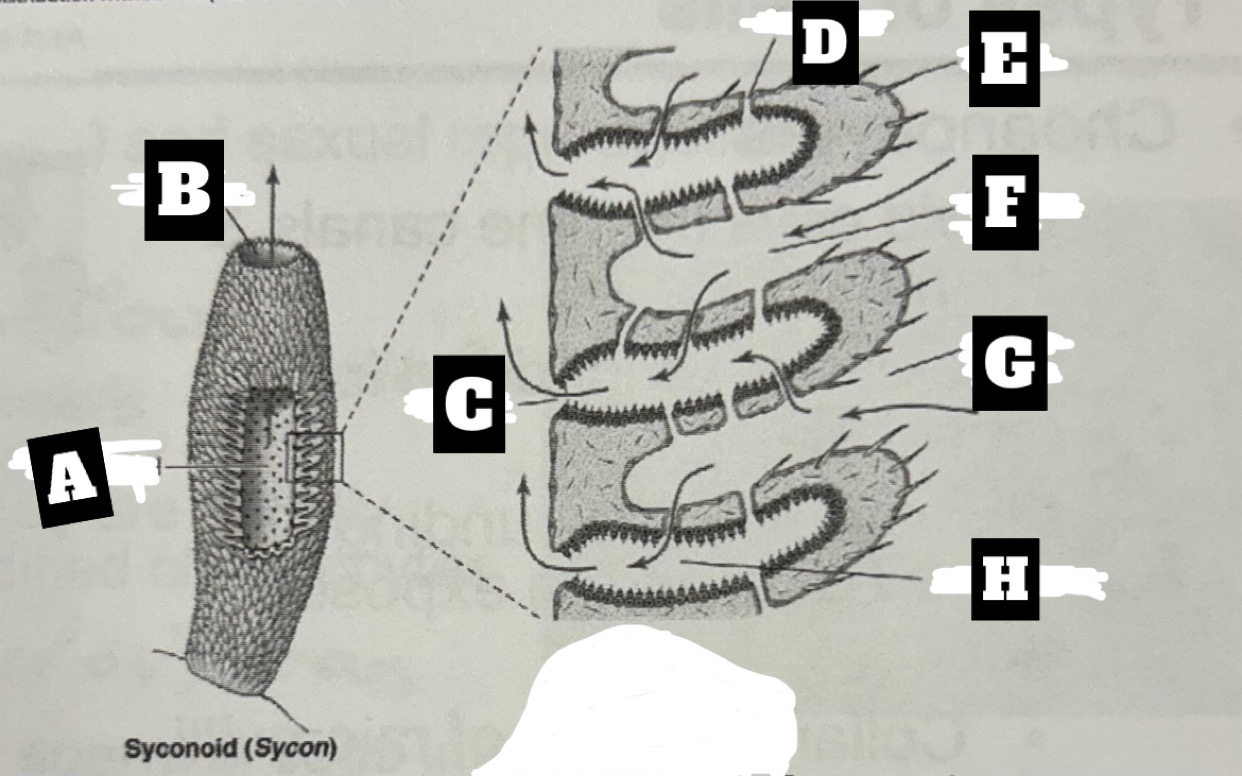
What is B
Osculum
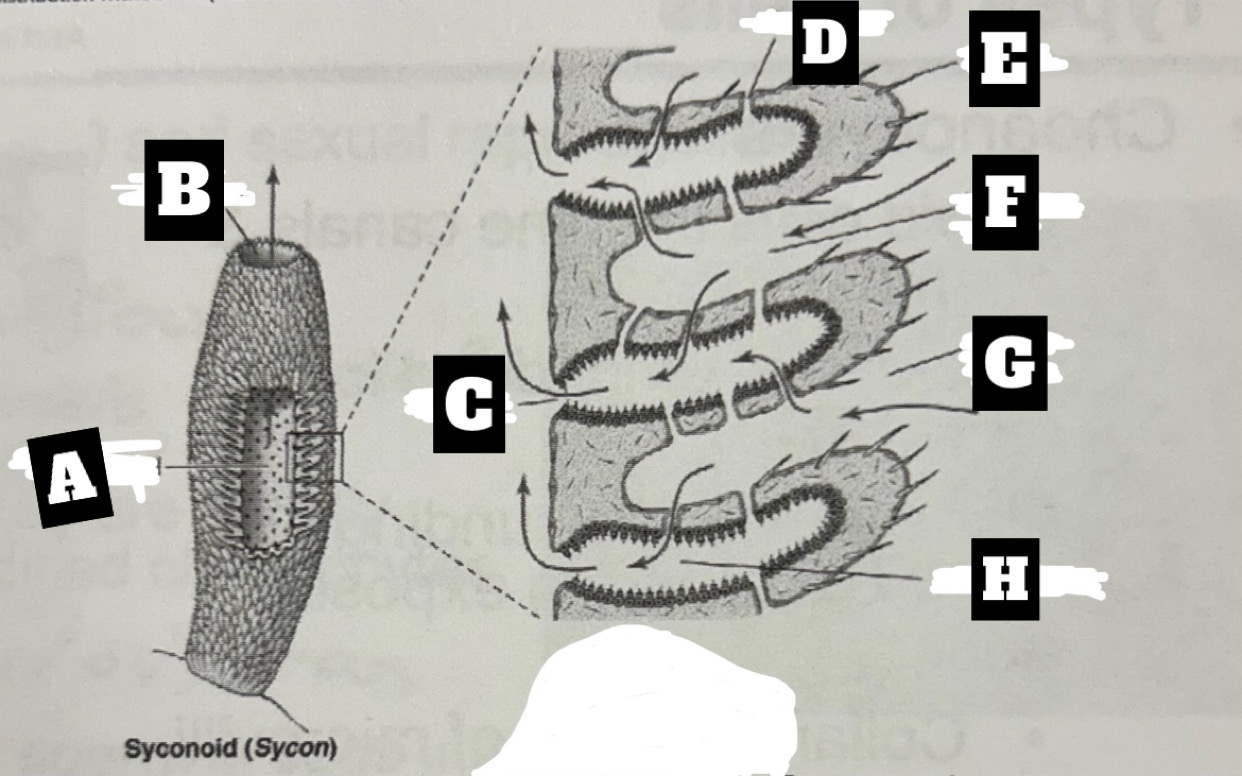
What is C
Apopyle
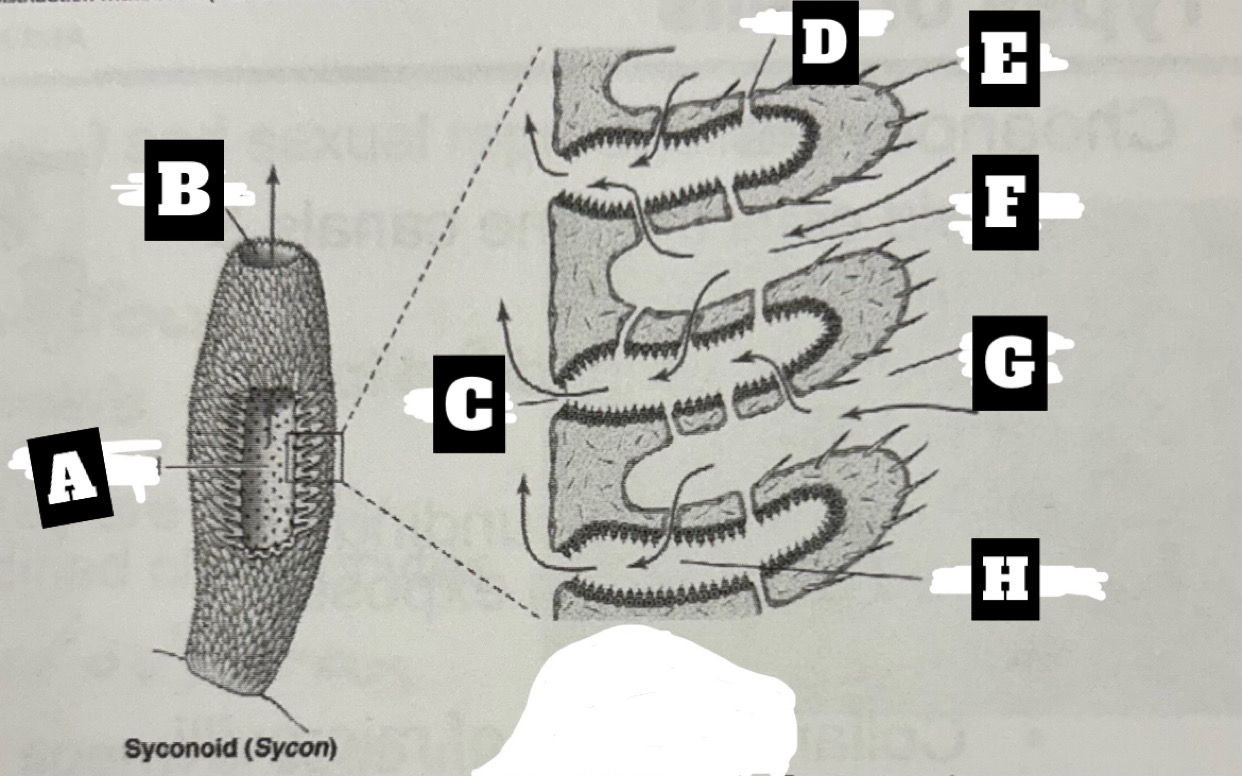
What is D
prosopyle
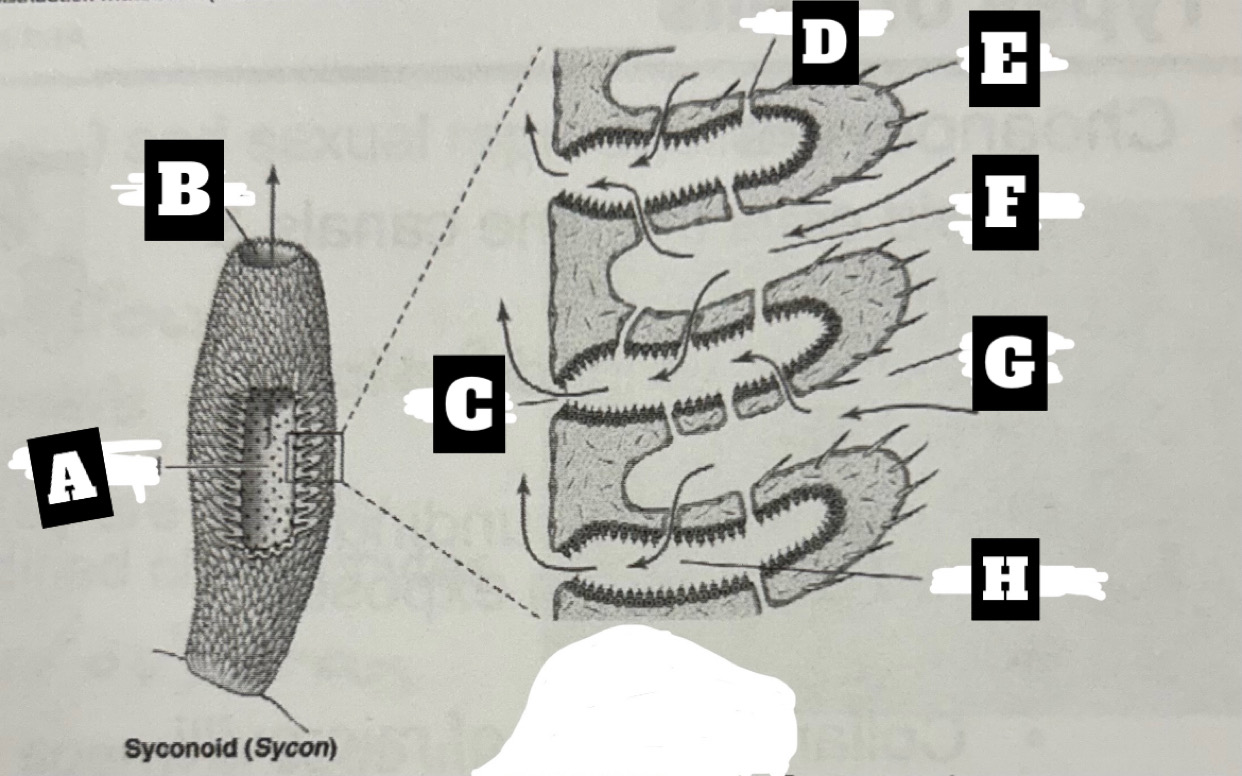
What is E
Spicule
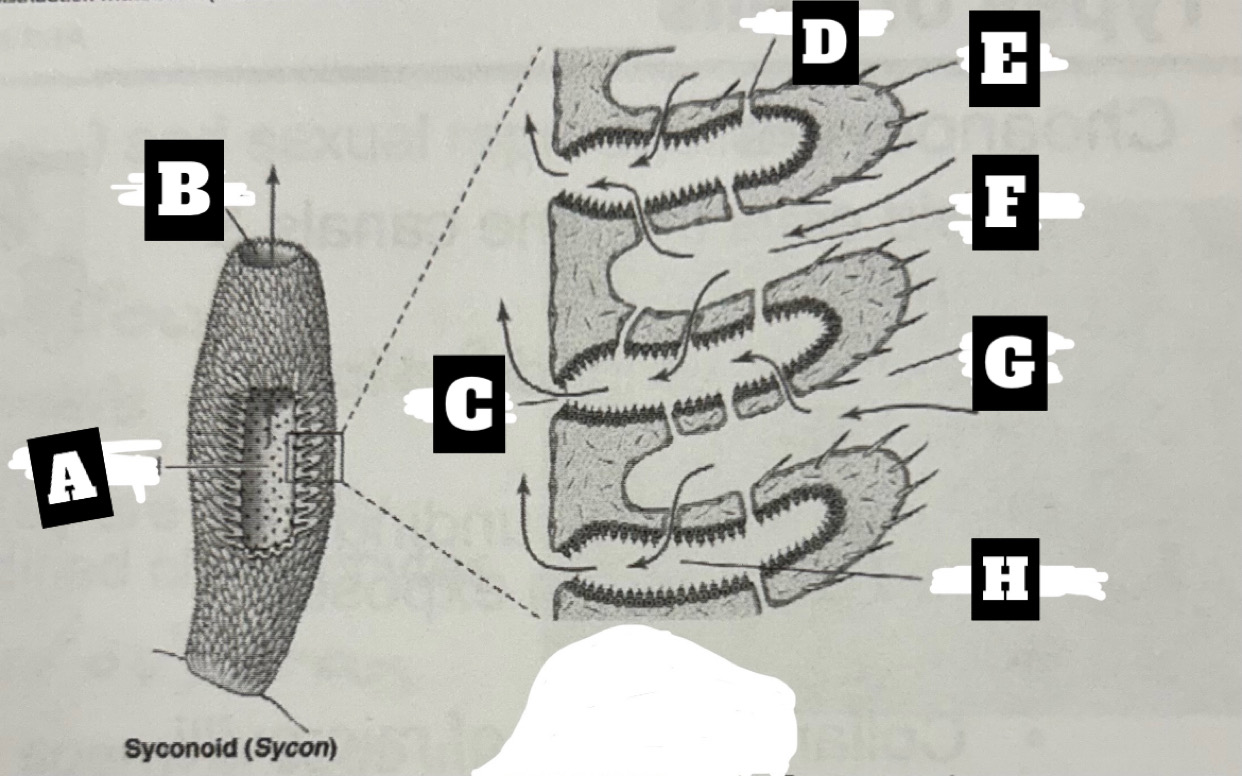
What is F
Incurrent canal
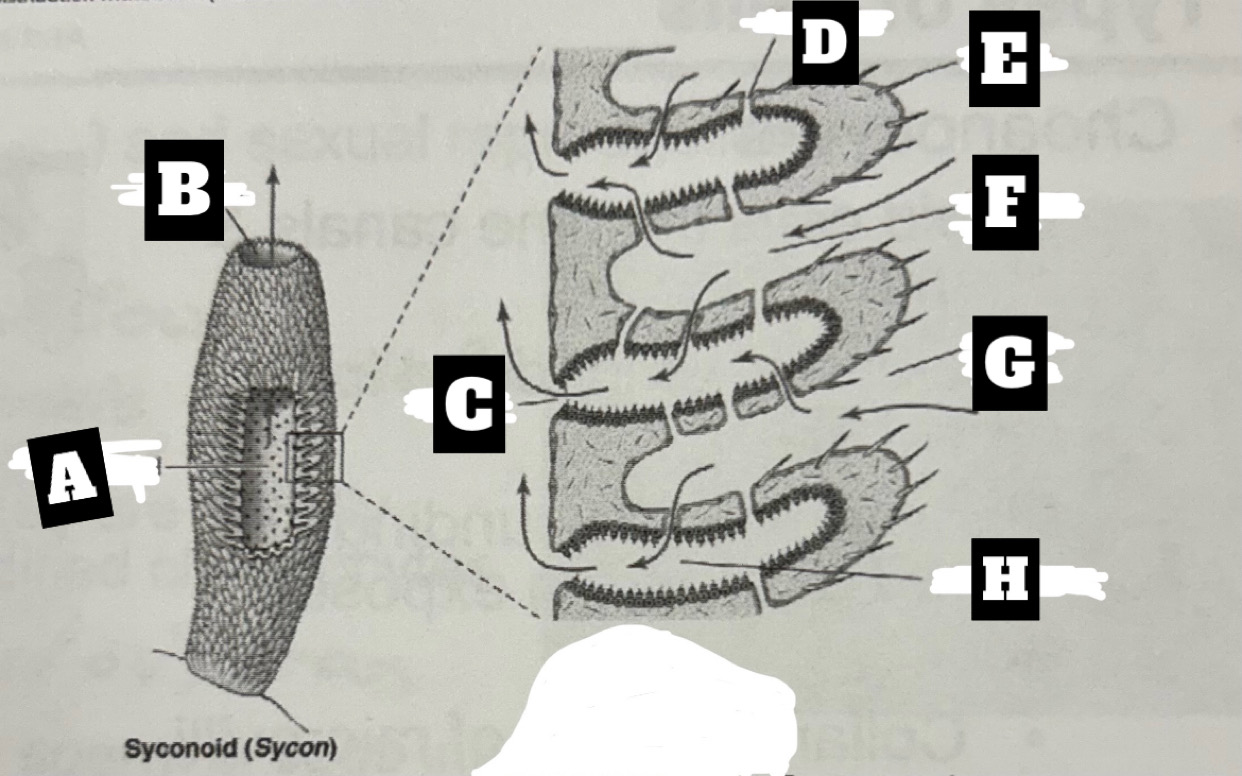
What is G
Dermal Ostium
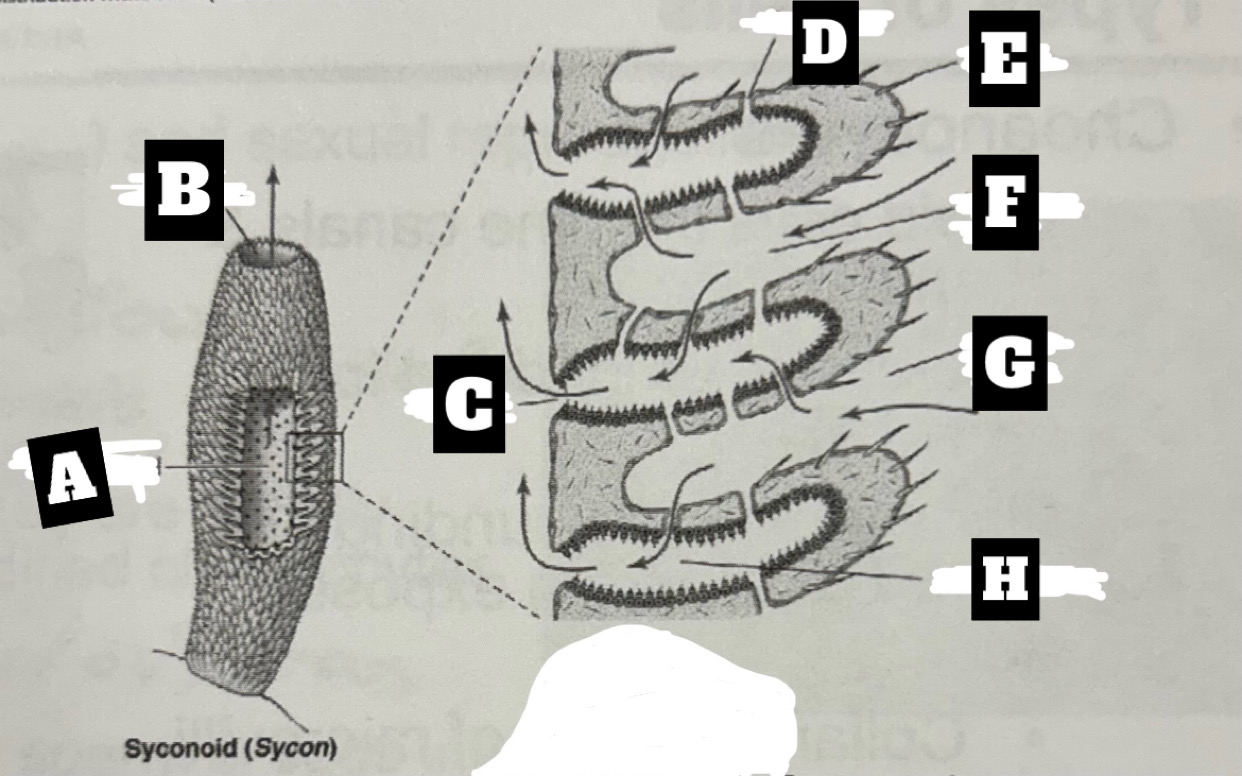
What is H
Radial canal
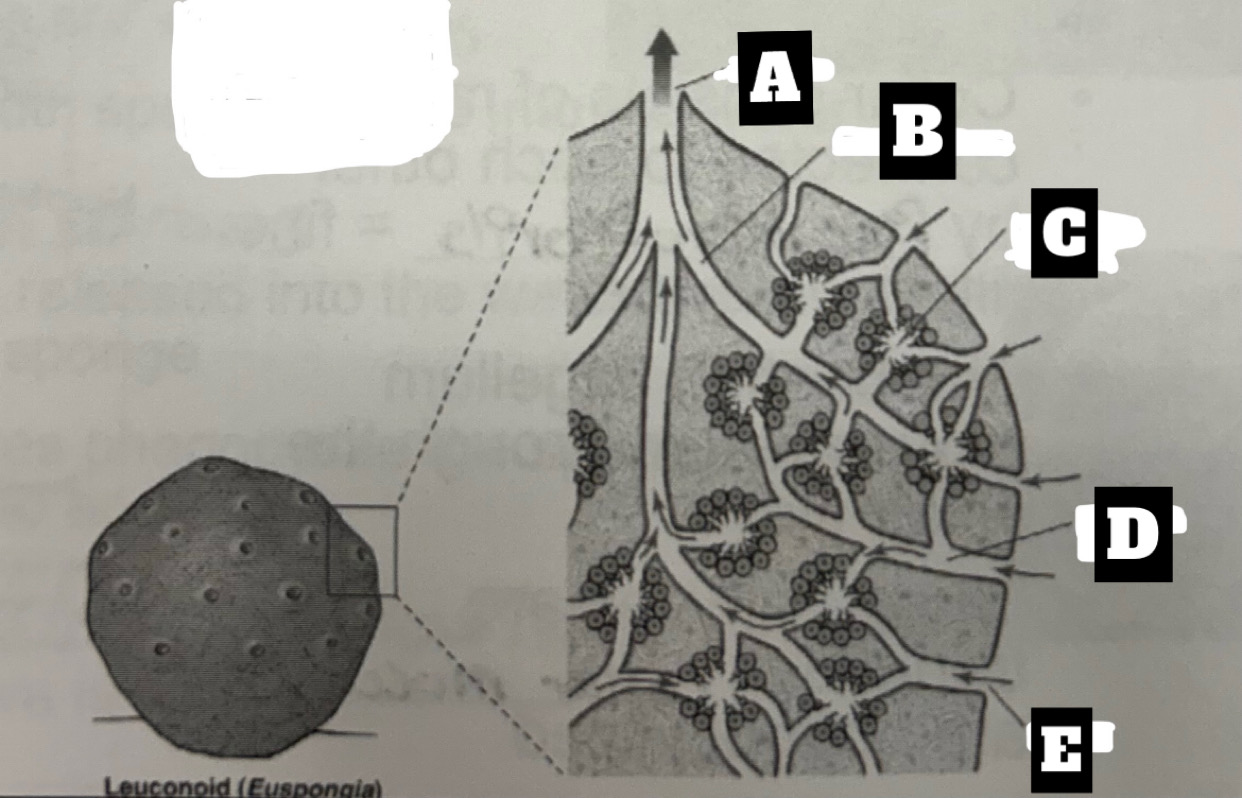
What is A
Osculum
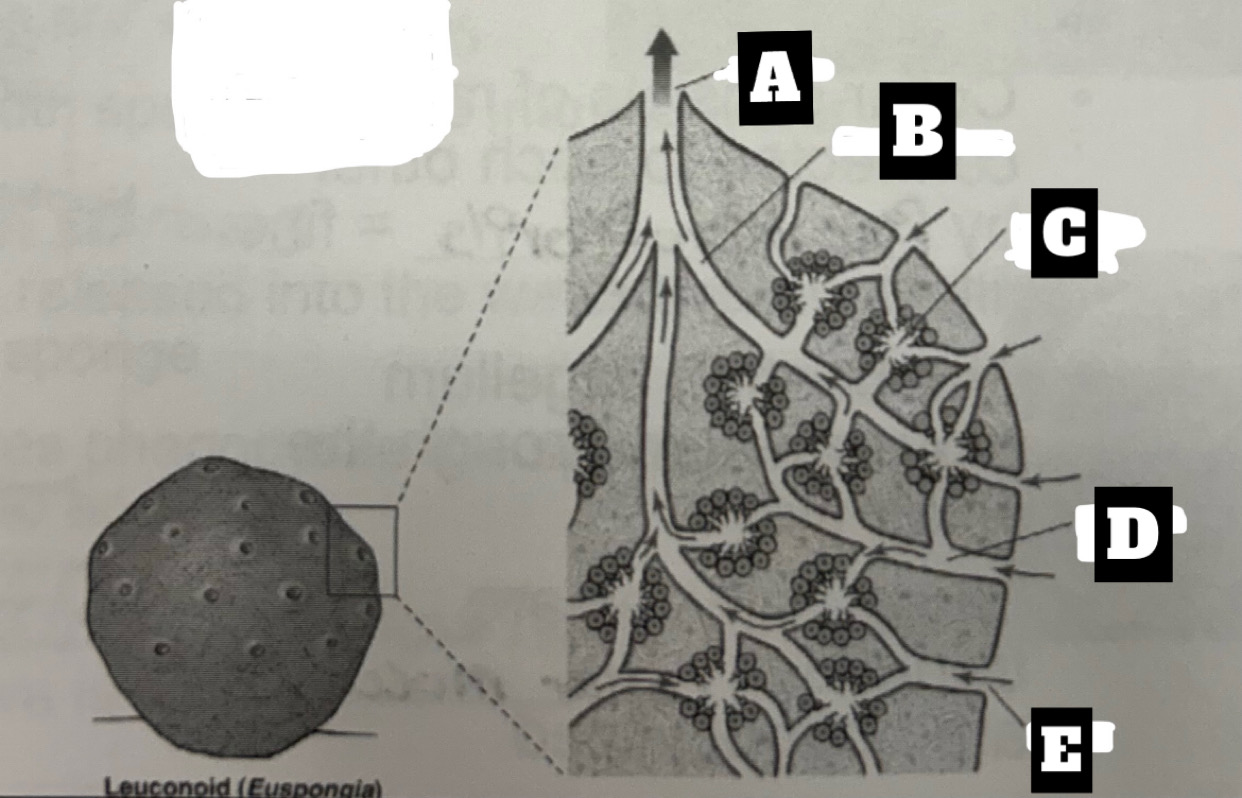
What is B
Excurrent canal
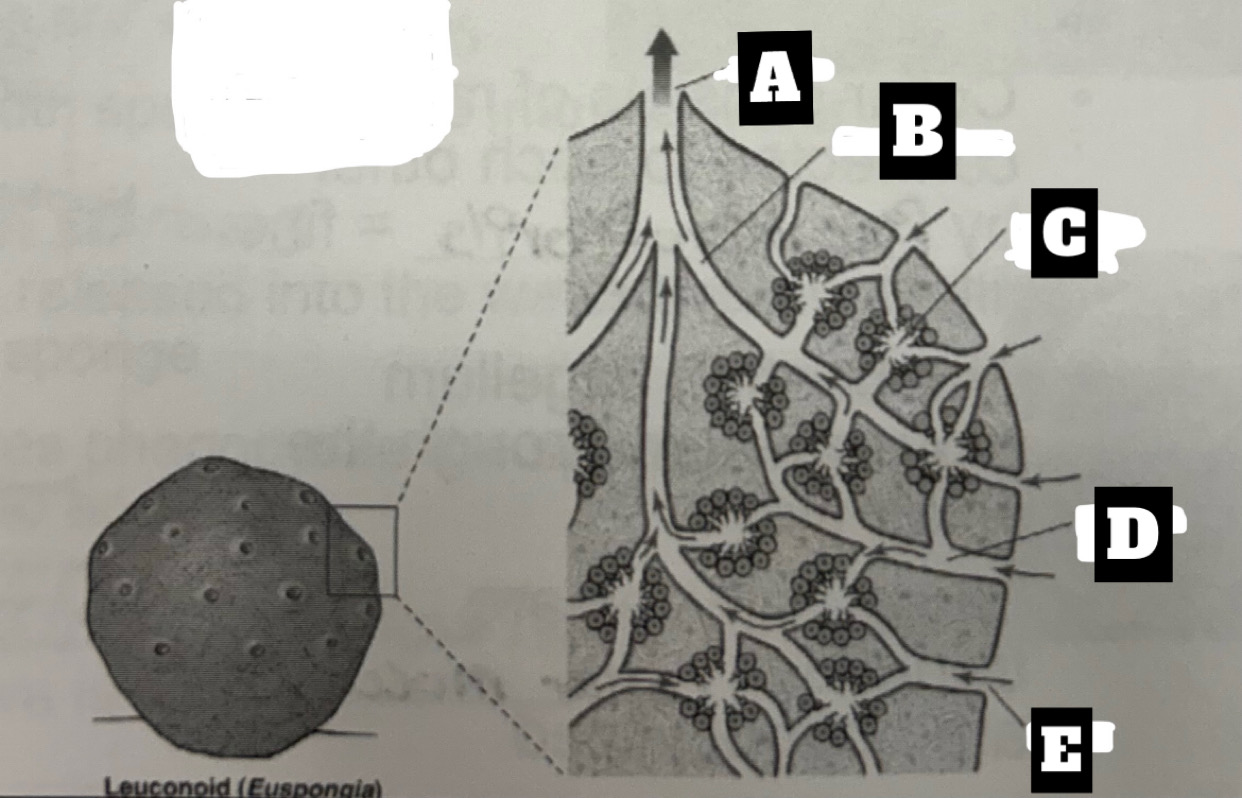
What is C
flagellated chamber
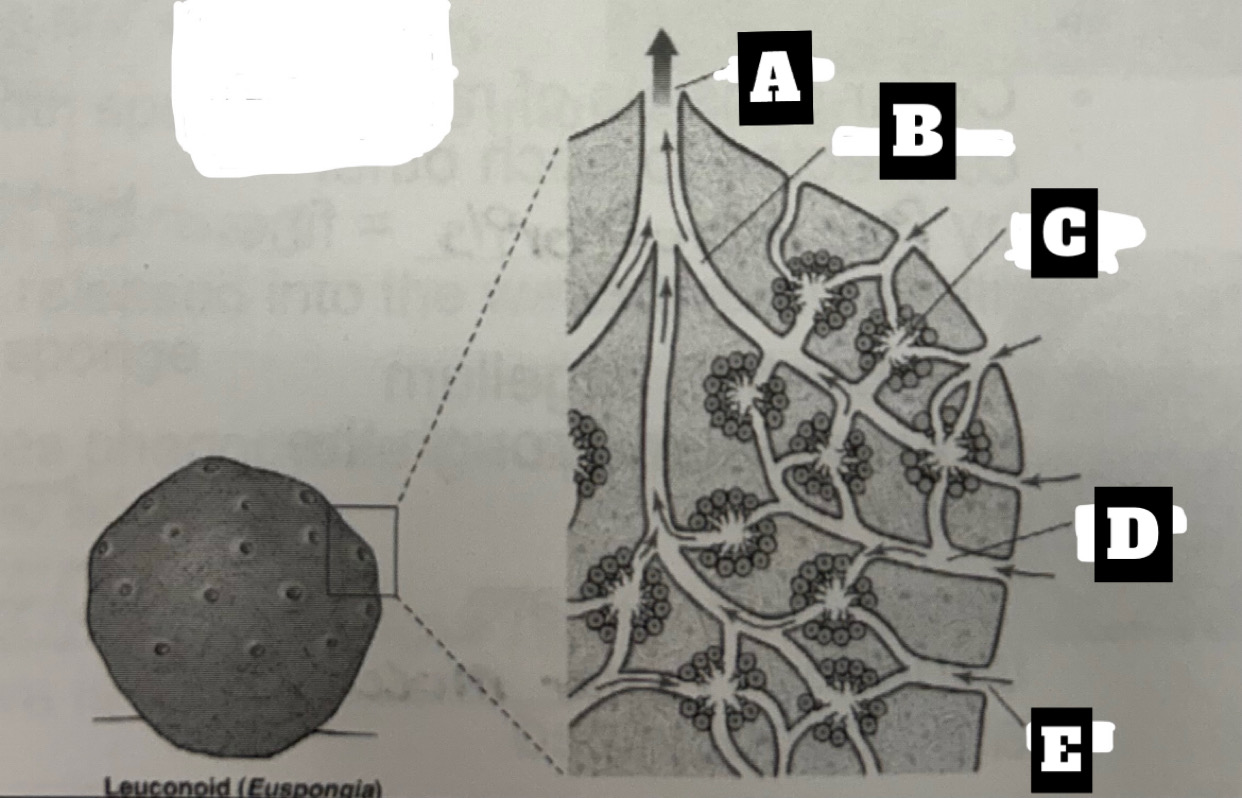
What is D
Incurrent Canal
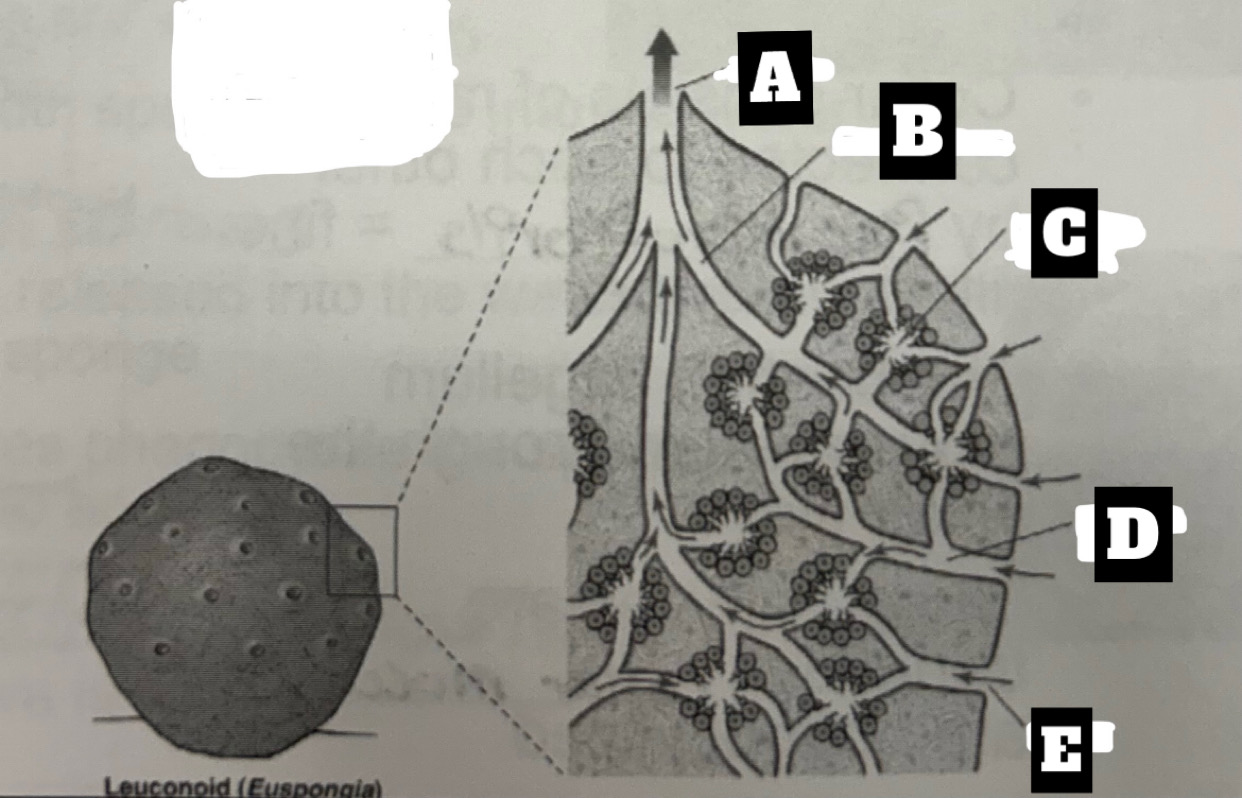
What is E
ostium
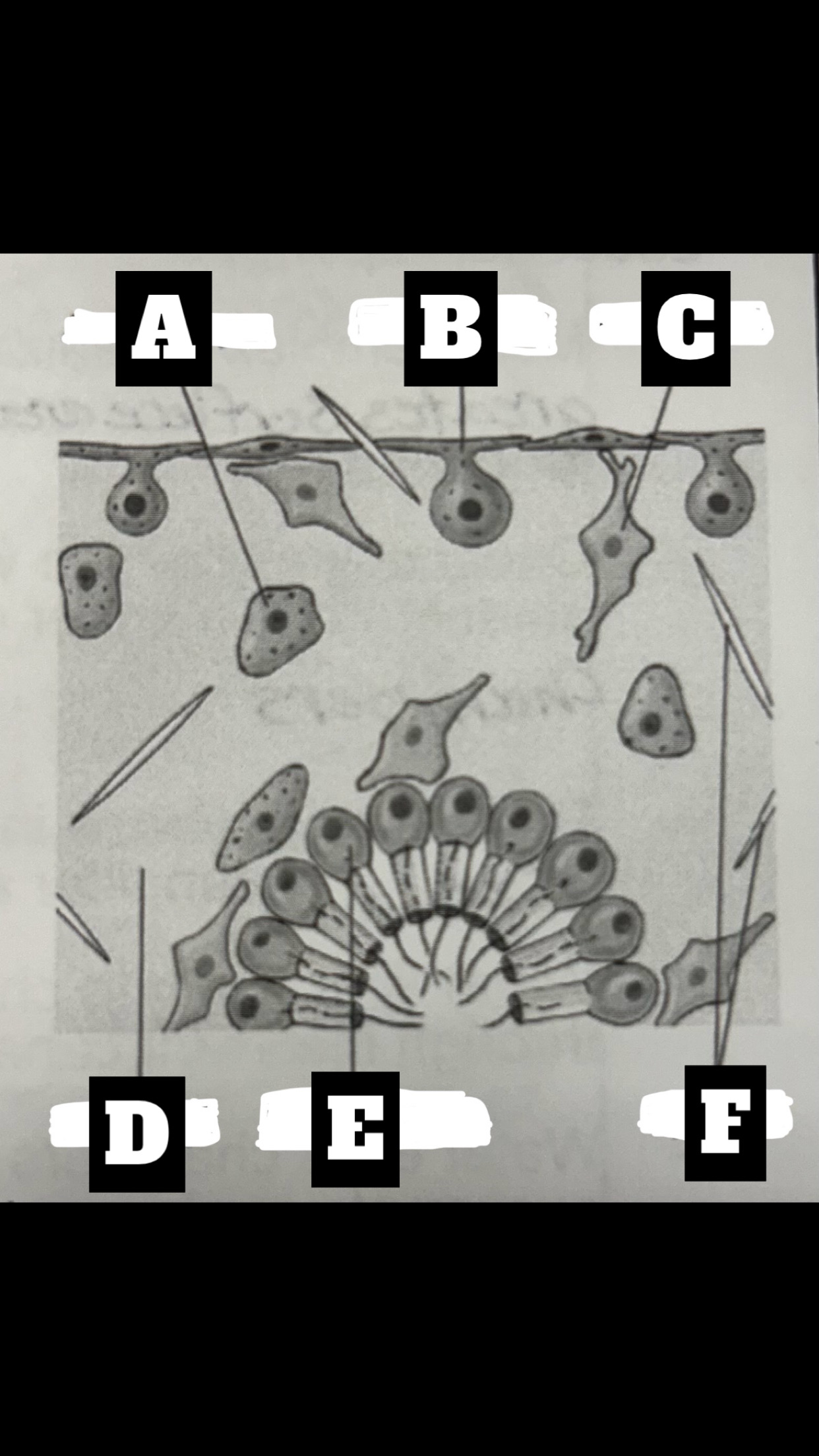
What is A
Archaeocyte
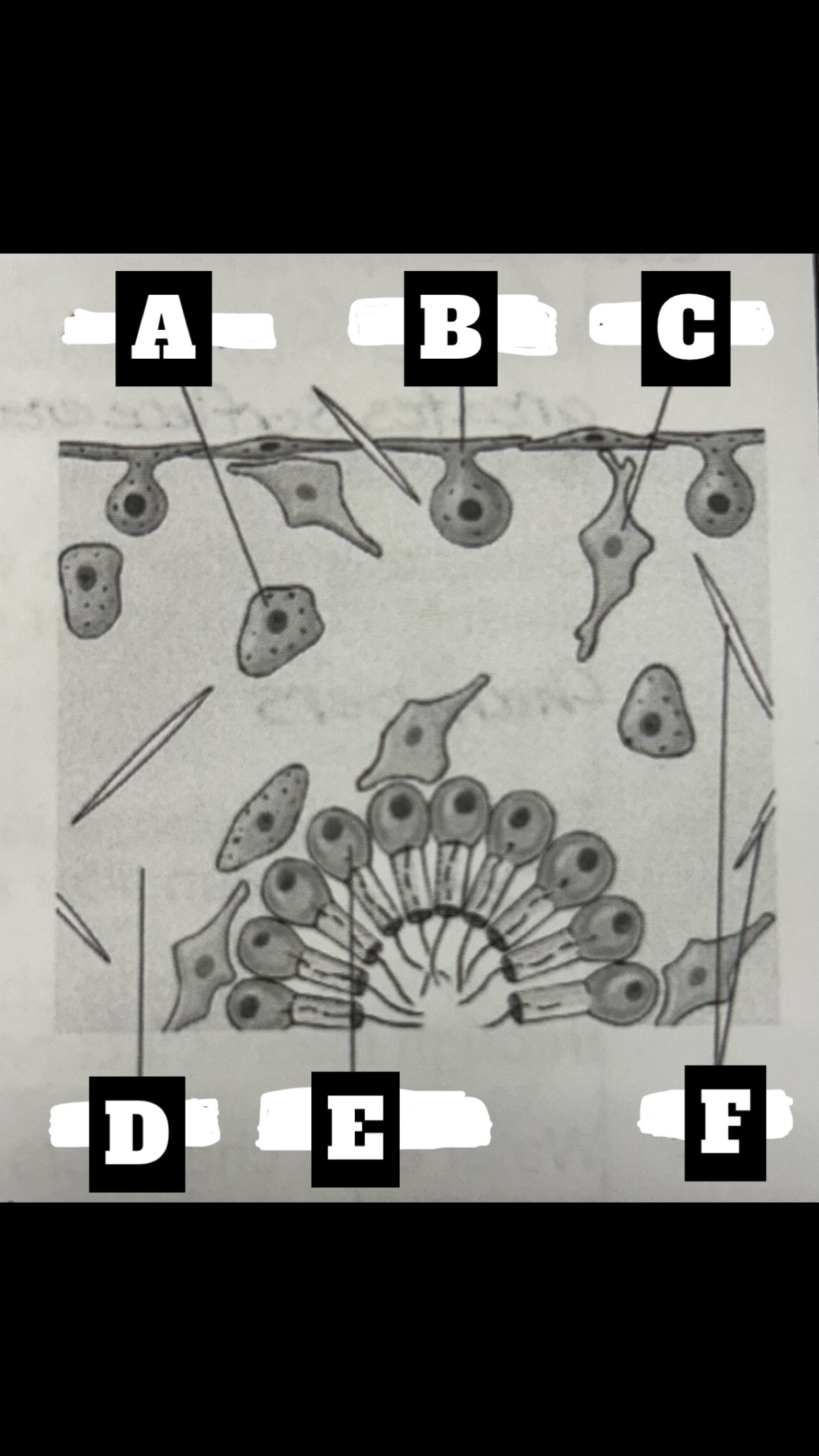
What is B
Pinacocyte
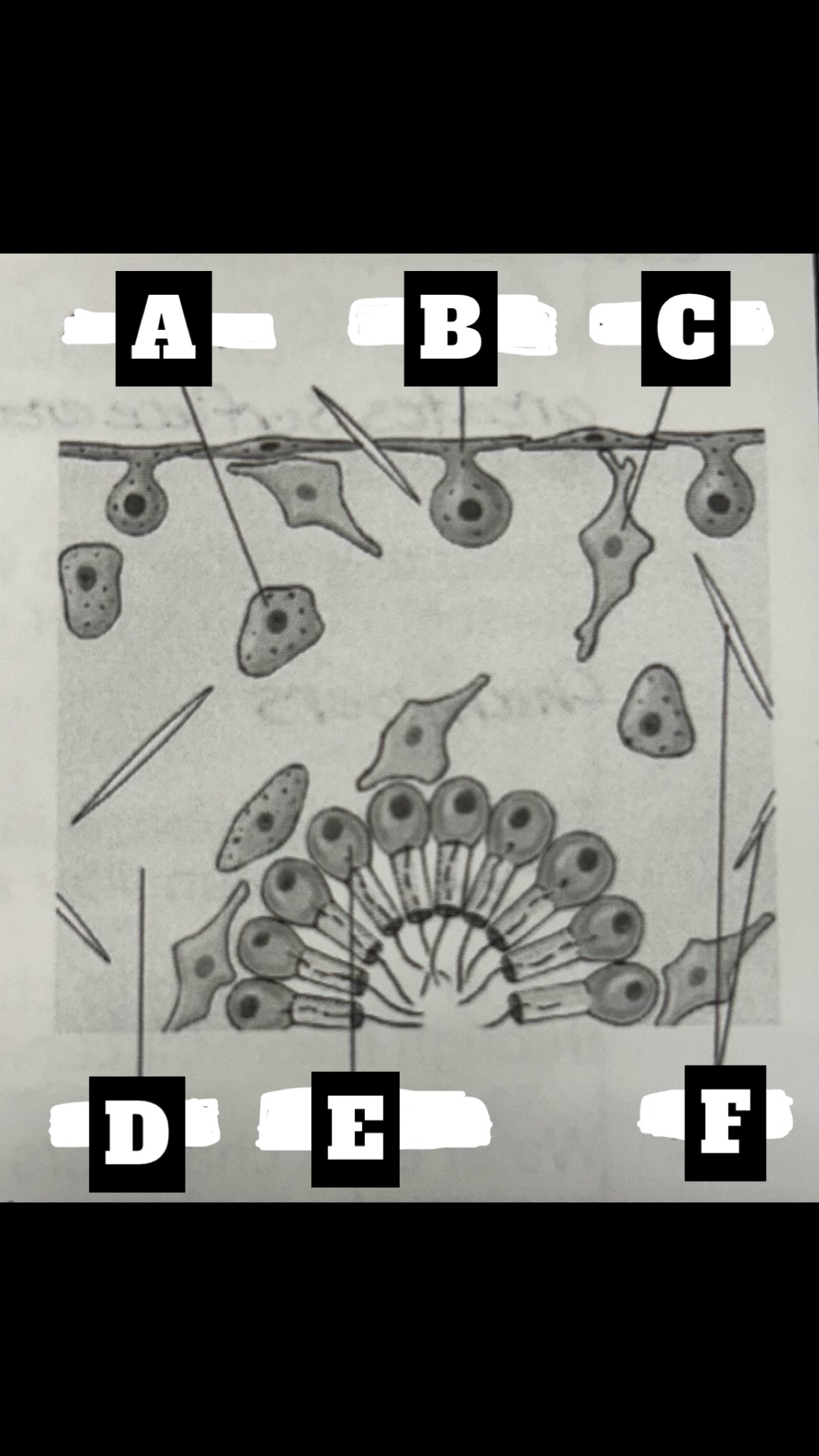
What is C
Collencyte
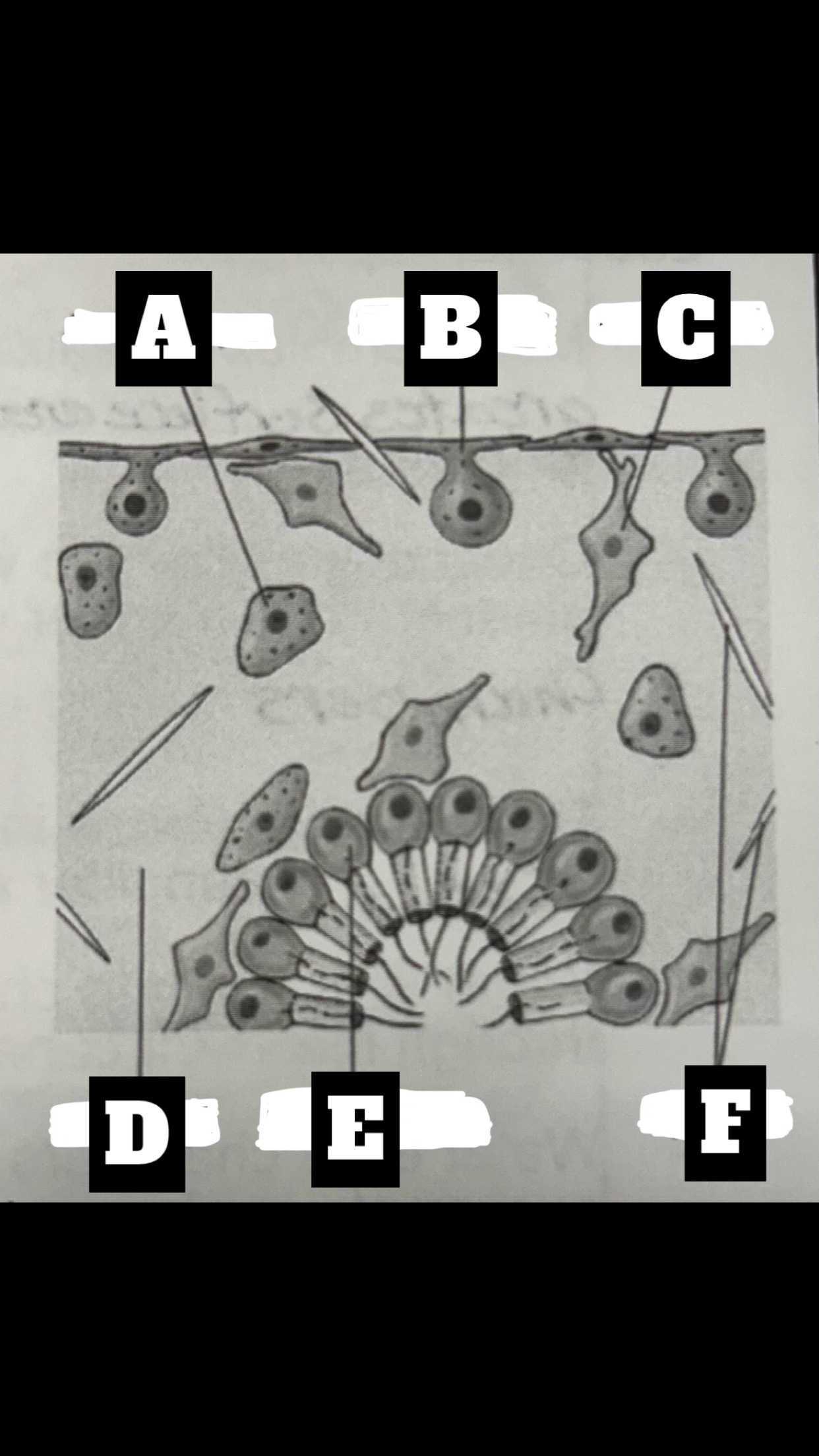
What is D
Mesohyl
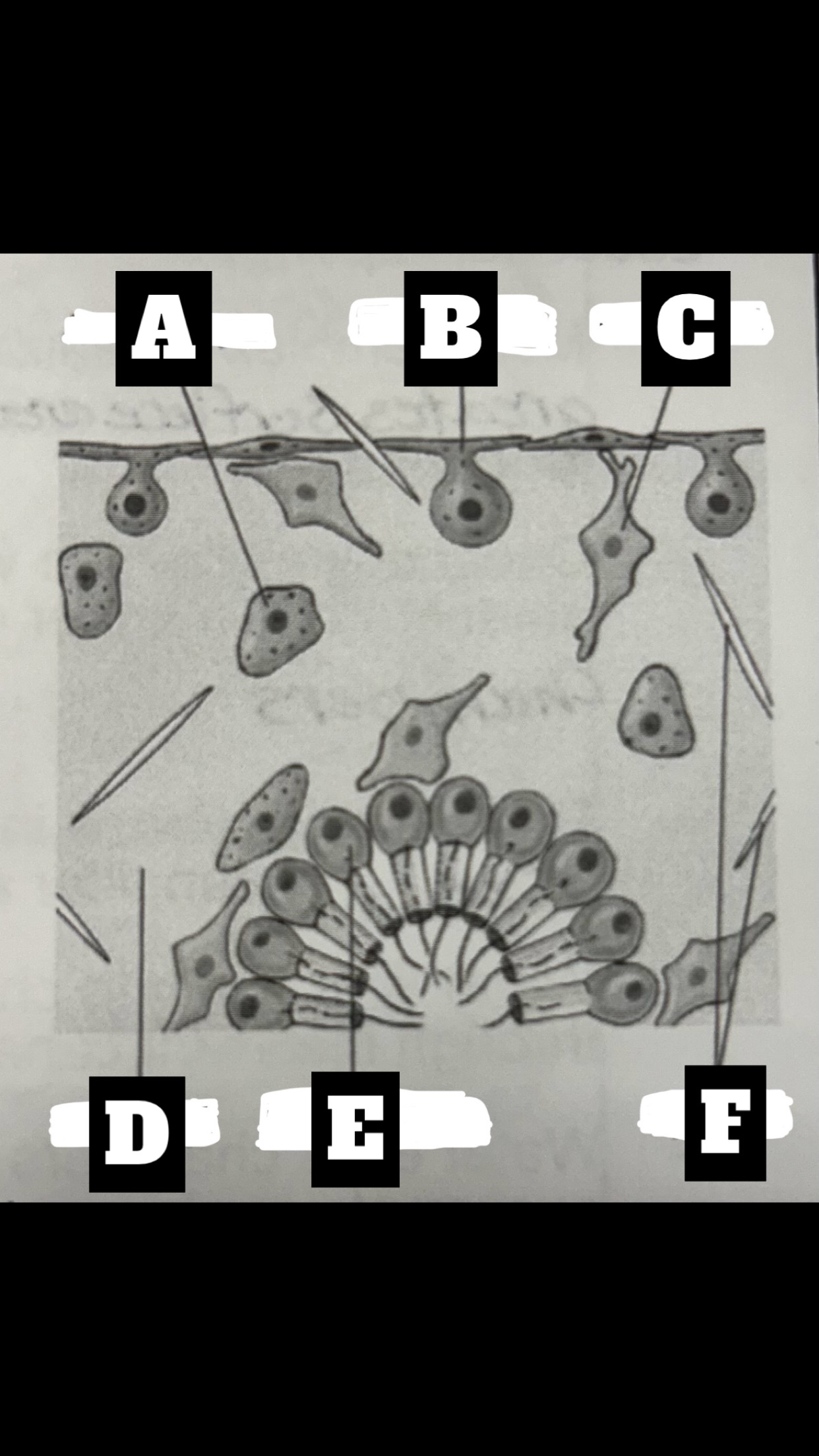
What is E
Choanocyte
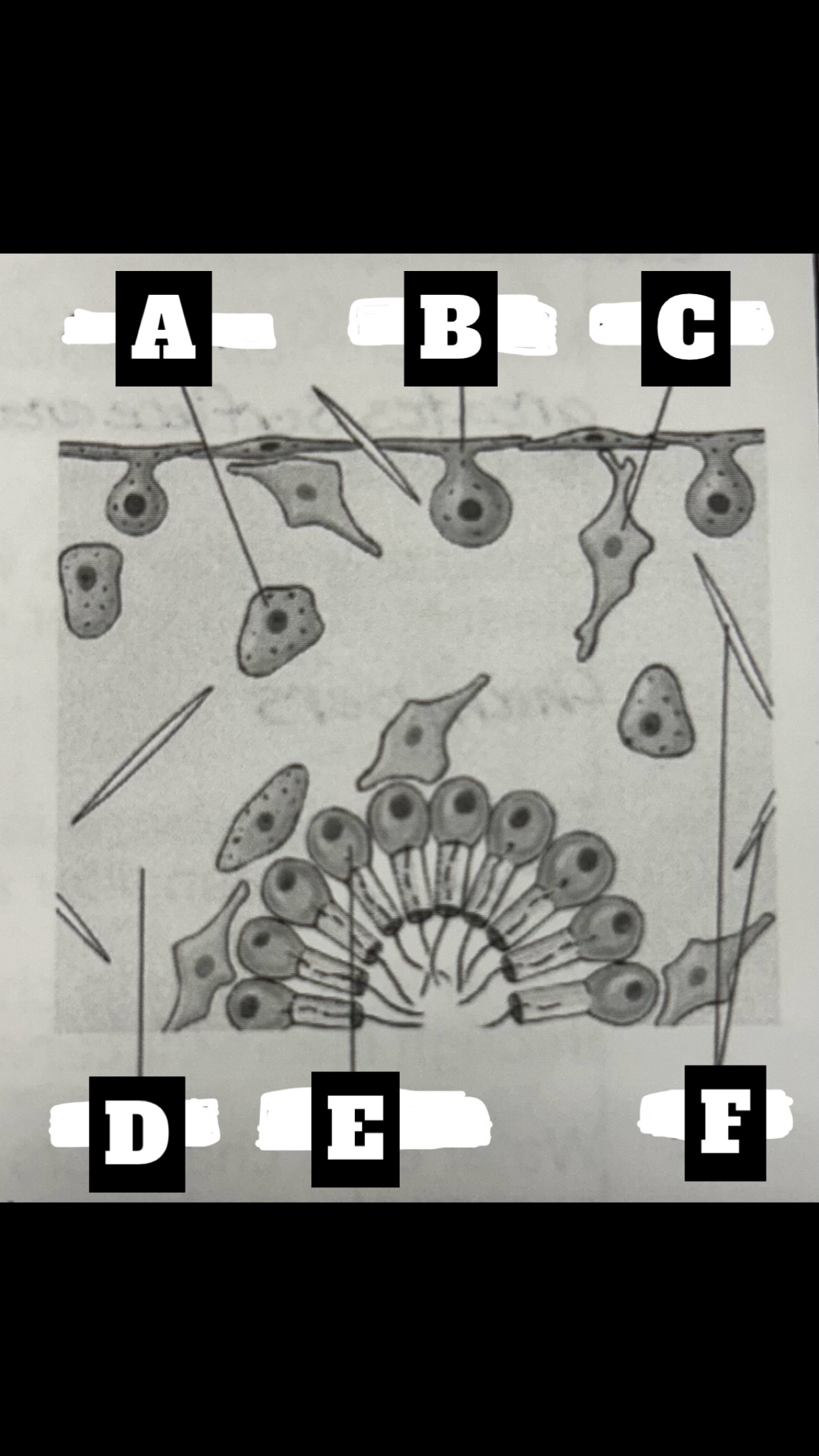
What is F
Spicules
Pinacocytes
thin flat, epithelial-like cells that make up the pinacoderm; closest thing to a tissue; some are modified into mycocytes, located around oculsa or pores to contract to regulate water flowa
Choanocytes
ovoid cells that line canals & chambers; one is embedded in the mesophyll
Choanocyte Flagellum
extend from exposed side; collar consists of microvilli connected to each other be fine microfibrils = fine filtering device; beating flagellum moves water through collar sieve; large particles are trapped in collar mucus &are phagocytized
Archaeocytes
ameboid cells that move about the mesohyl and receive particles form choanocytes for intracellular digestion; can also phagocytize particles at the pinacoderm
Archaeocytes specialized cells
Sclerocytes, spongocytes, collencytes
Sclerocytes
specialized cells that create spicules
Spongocytes
specialized cells that produce spongin, secrete spongin fibers
Collencytes
secrete collagen
Asexual reproduction for sponges
budding
Sexual reproduction for sponges
Monoecious; both female and male sex cells in one individual; sperm and oocytes are usually produced by modified choanocytes; most are viviparous, some are oviparous
Oviparous
Releases sperm and eggs into water; offspring develops outside of mother
Viviparous
Live birth; offspring develops outside
Development of sponges
Free swimming larva(parenchymula) settles, flagellated cells migrate to the interior & become choanocytes
External buds
Fragments or buds break off
Gemmules
Internal buds; collected in Mesohyl; are covered with a tough spongin and spicule coat; can survive harsh, environmental conditions
Four sponge classes
Calcispongiae, Hexactinellida, Demospongiae,
Homoscleromorpha
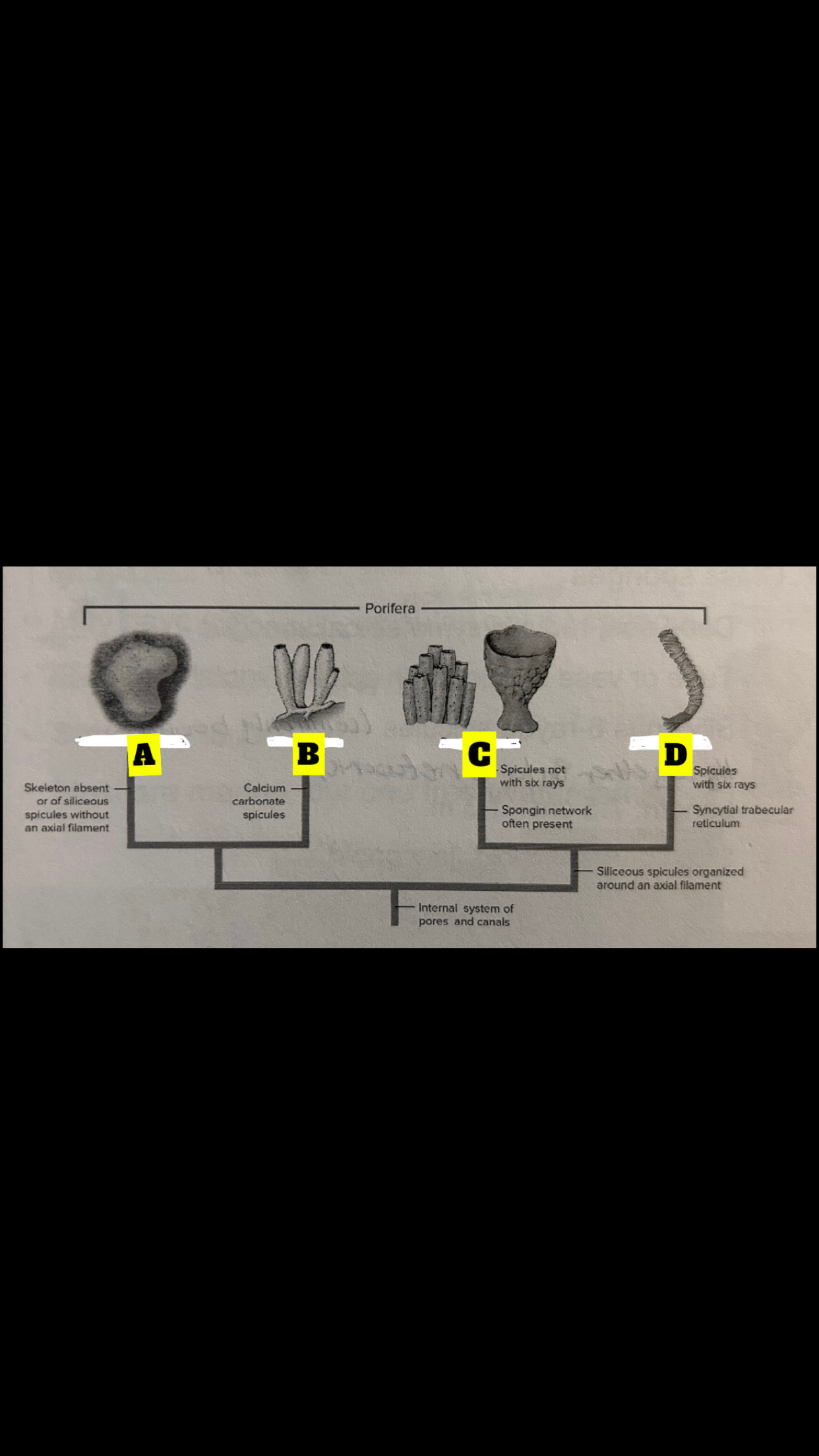
What is A
Homoscieromorpha
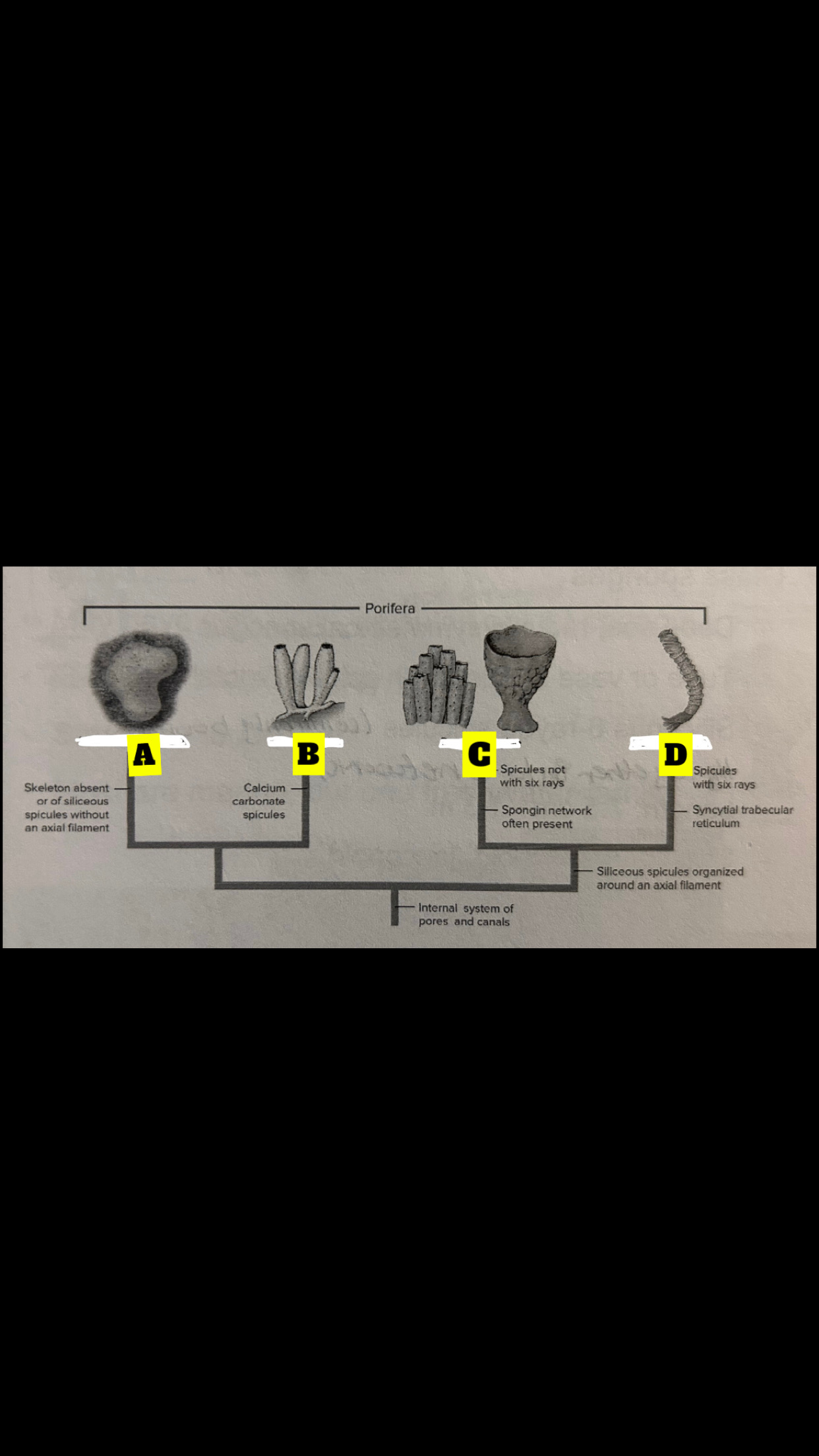
What is B
Calcispongiae
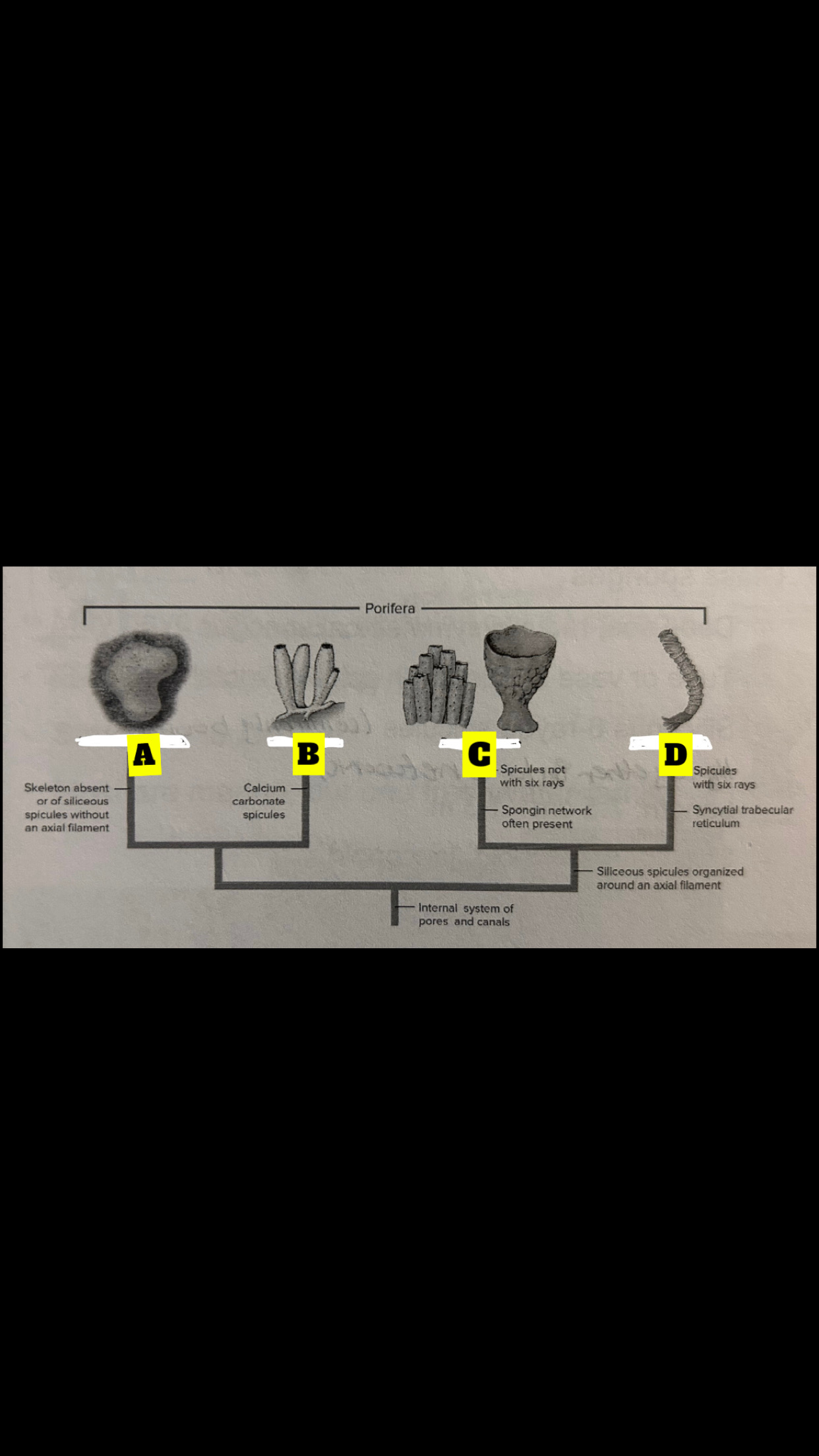
What is C
Deospongiae
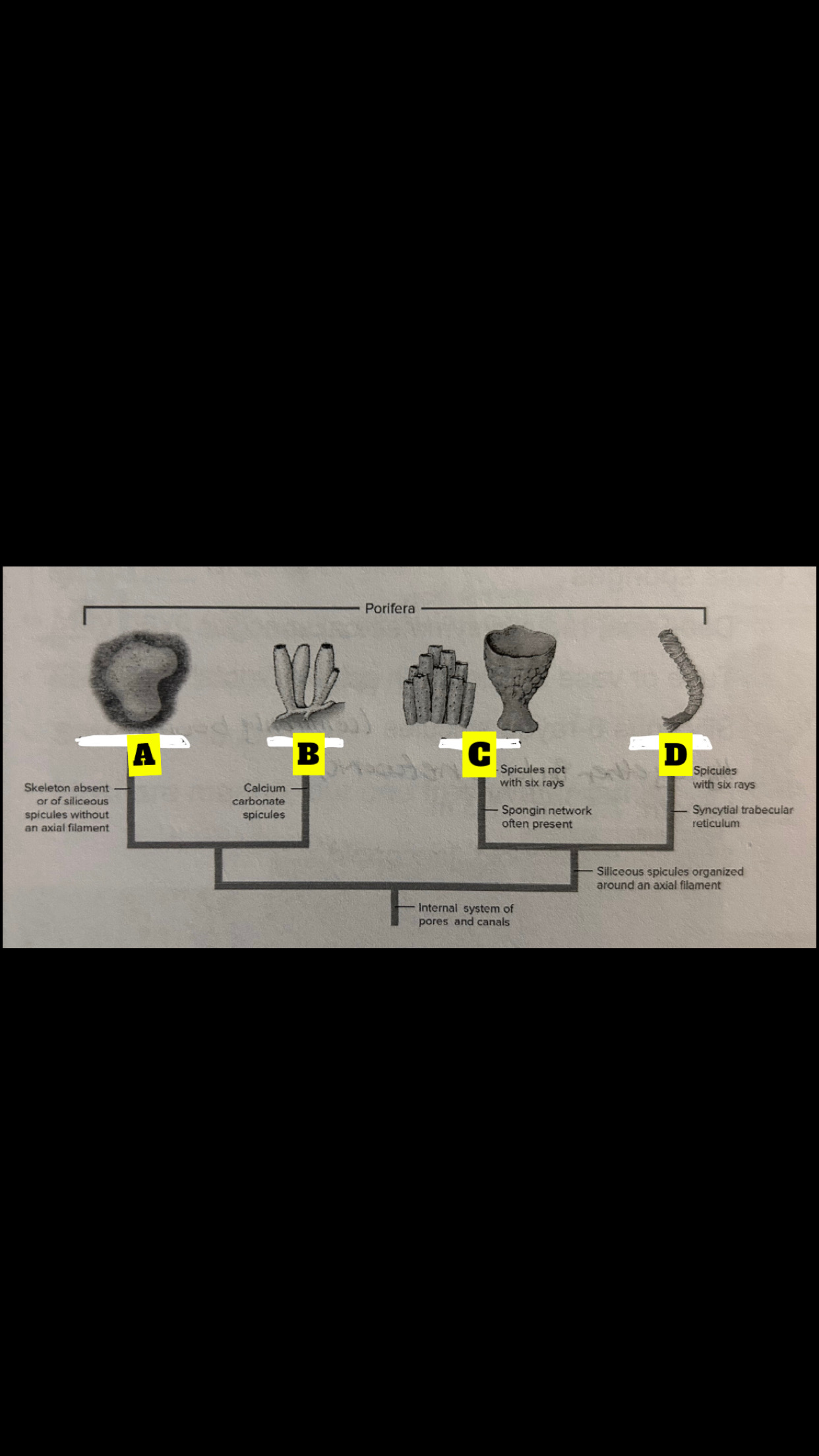
What is D
Hexactinellida
Class Calcispongiae
Calcium carbonate, Monaxon(straight) spicules or with 3-4 rays; <10cm in length; tubular or vase shaped; asconoid, synconoid, leuconoid
Class Hexactinellida
Glass Sponges; deep sea, radial symmetry, tube or vase shaped with spicule roots; siliceous 6-rated spicules(commonly bound together in a network); length 7.5 cm to 1.3 m: synconoid and leuconoid
Choanoblasts
2 collar bodies; responsible for the formation of cartilage by actively producing the extracellular matrix components that give cartilage its structure and strength
Class Demospongiae
95% of sponges; May have silious spicules(not 6 rayed) or just spongin; length and shape are highly variable; leuconoid structure; most our marine, one freshwater family
Class Homoscleromorpha
Two clades:one with spicules and one without; length and shape highly variable; Leuconoid; occur in cryptic marine habitats
Pinacoderm layer is an incipient tissue(early stage; has a true basement layer; cells connected via one type of cell junction(two tissues in one
Silicous Demospongiae
Predatory sponges that live in deep nutrient poor water. They’re coated with tiny hook-like spicules that ensnare tiny crustaceans that grow over prey and digest them. Have no choanocytes and internal canals
Phylum Placozoa
Tiny marine animals 2 to 3 mm in length; plate like body with no symmetry organs, muscular system or nervous system; no ECM but gene suggest otherwise, have four cell types, external digestion(secretes digestive enzymes)
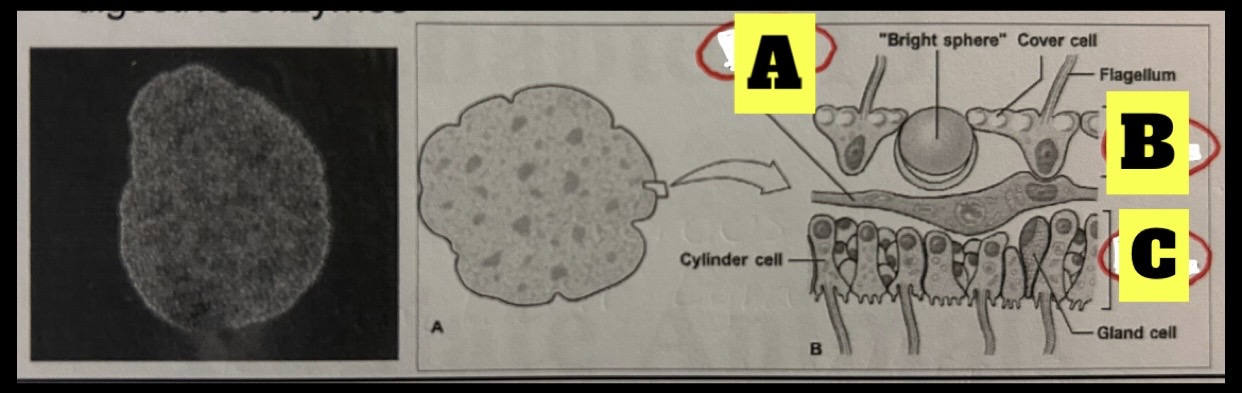
What is A
Contractile fiber cell
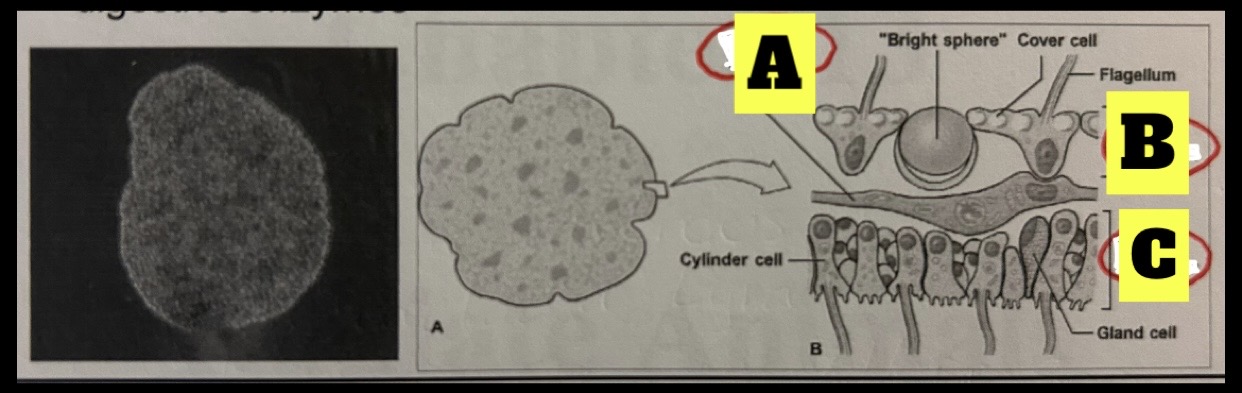
What is B
Dorsal epithelium
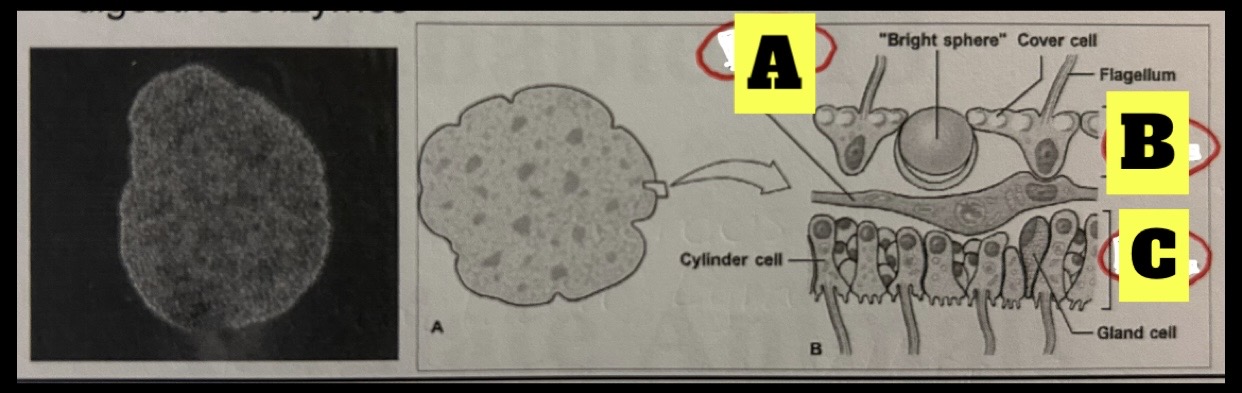
What is C
Ventral epithelium