Histo Exam 1 Picture Identification
1/135
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
Reticular fibers stained with silver salts or PAS
What is this an image of
reticular collagen (type III)
What is the arrow pointing to
elastic fibers; stained with urchin or resorcin-fuchsin
What is this an image of?
elastic fibers; stain dark purple
What is this an image of?

collagen fibers; stain light pink
What is this an image of?

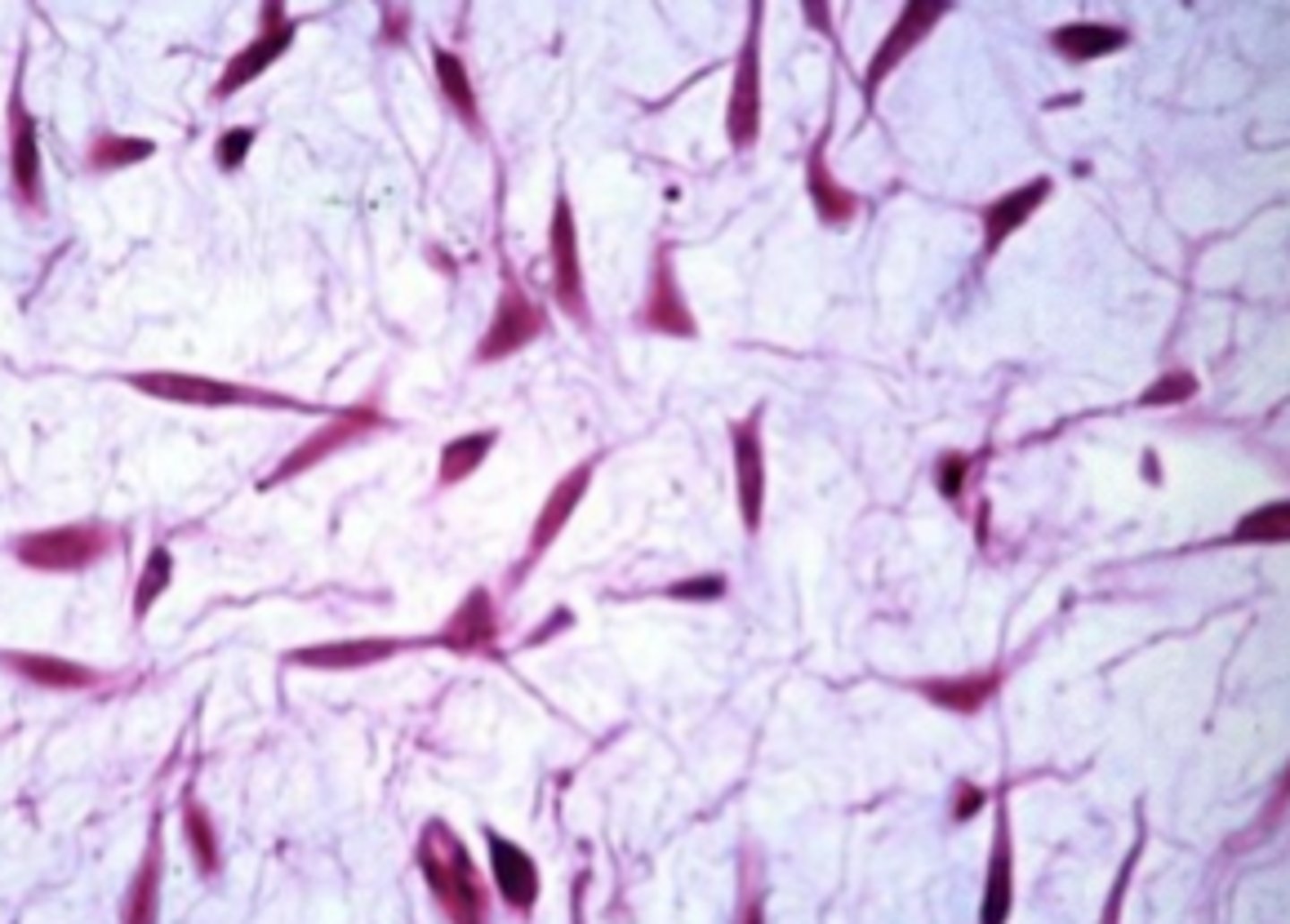
fibroblasts (the principle connective tissue cells)
What cell type is shown
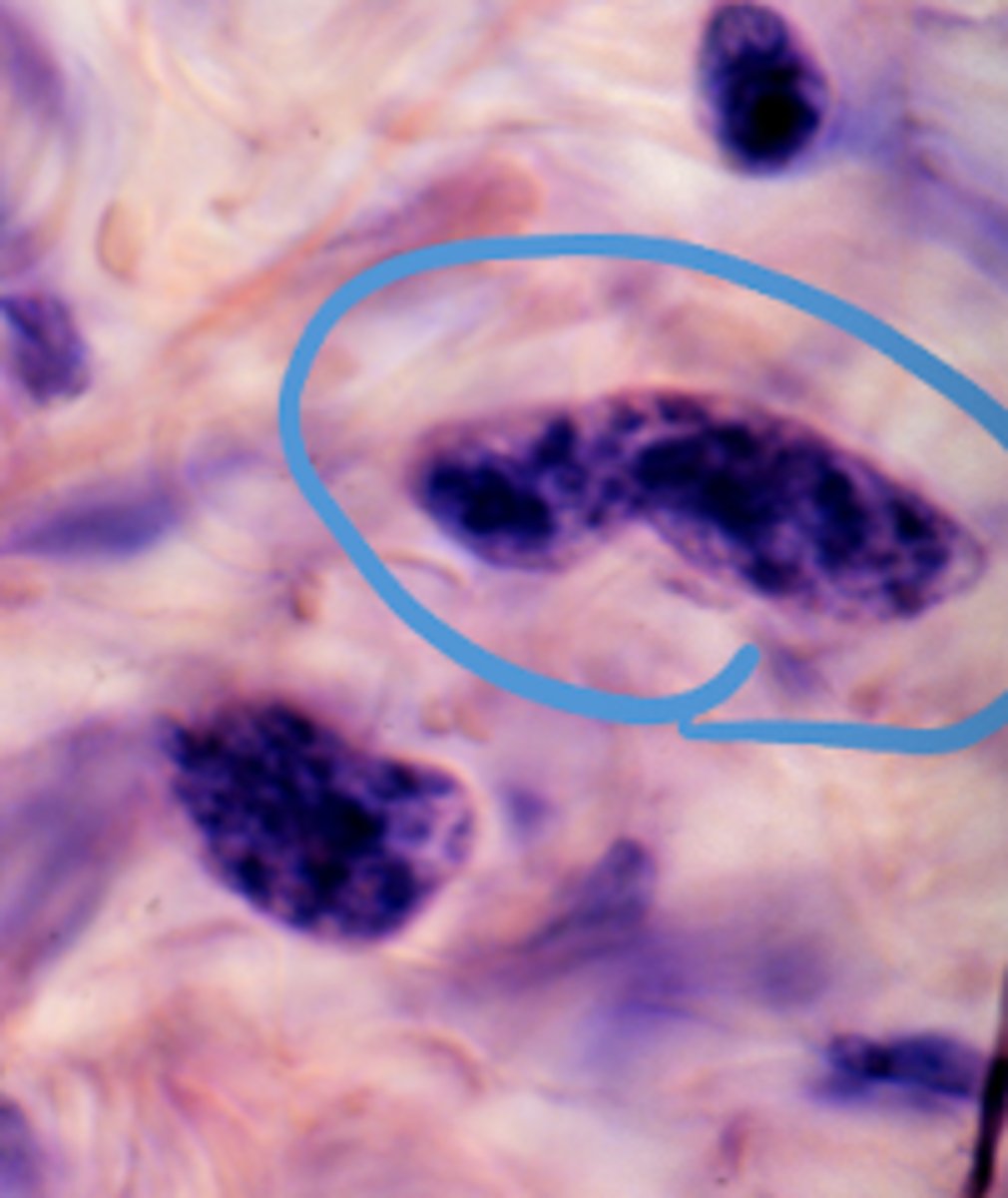
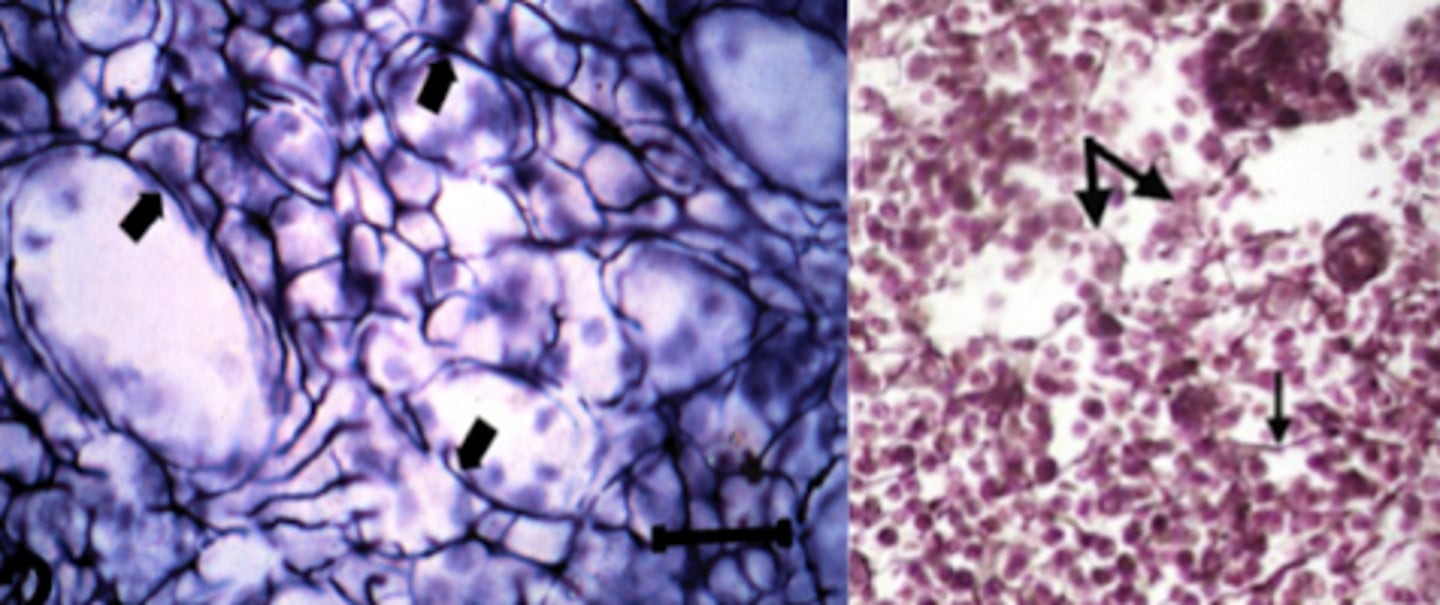
Macrophage
What is this an image of?
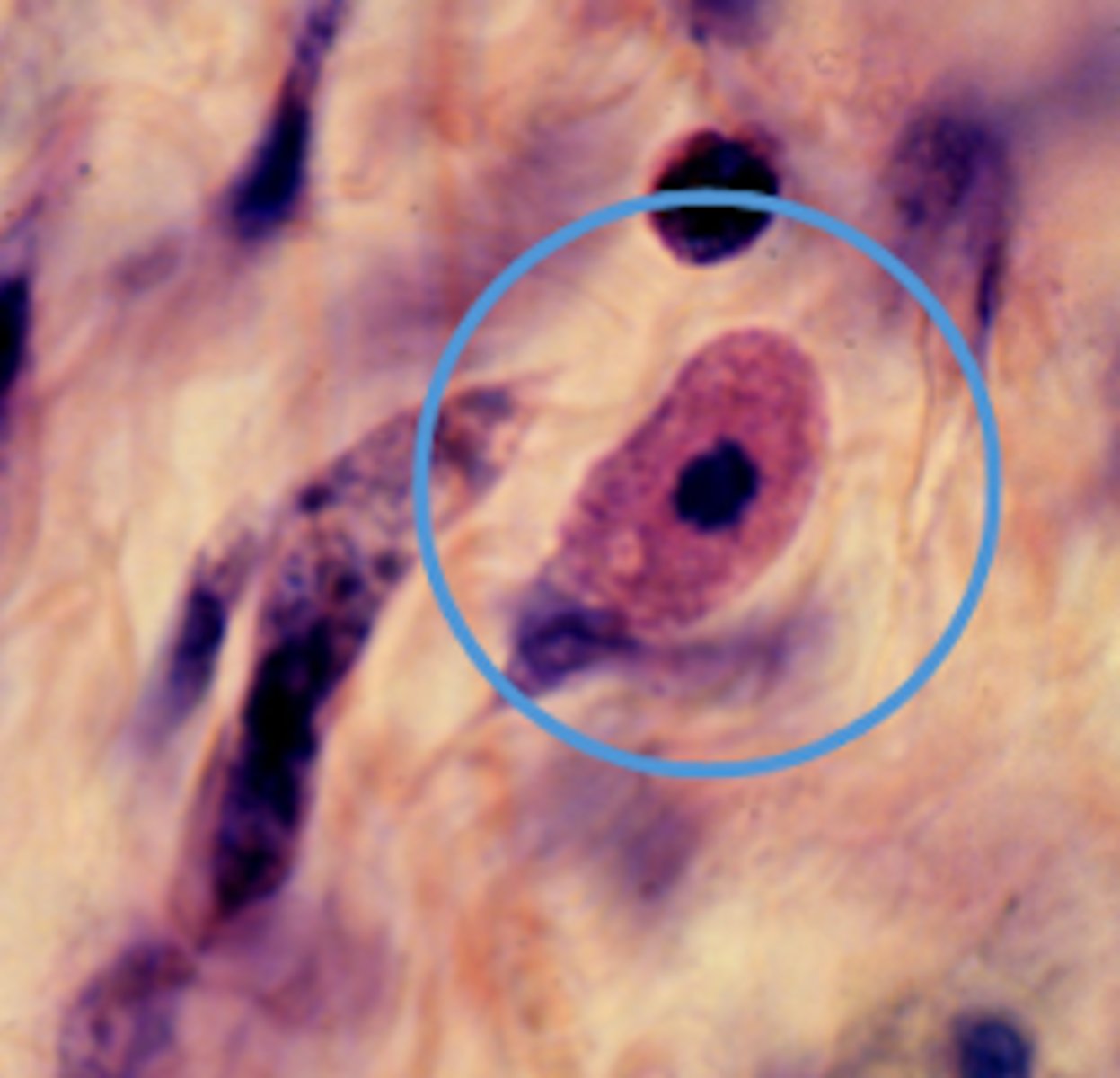
Mast cells
What is this an image of?
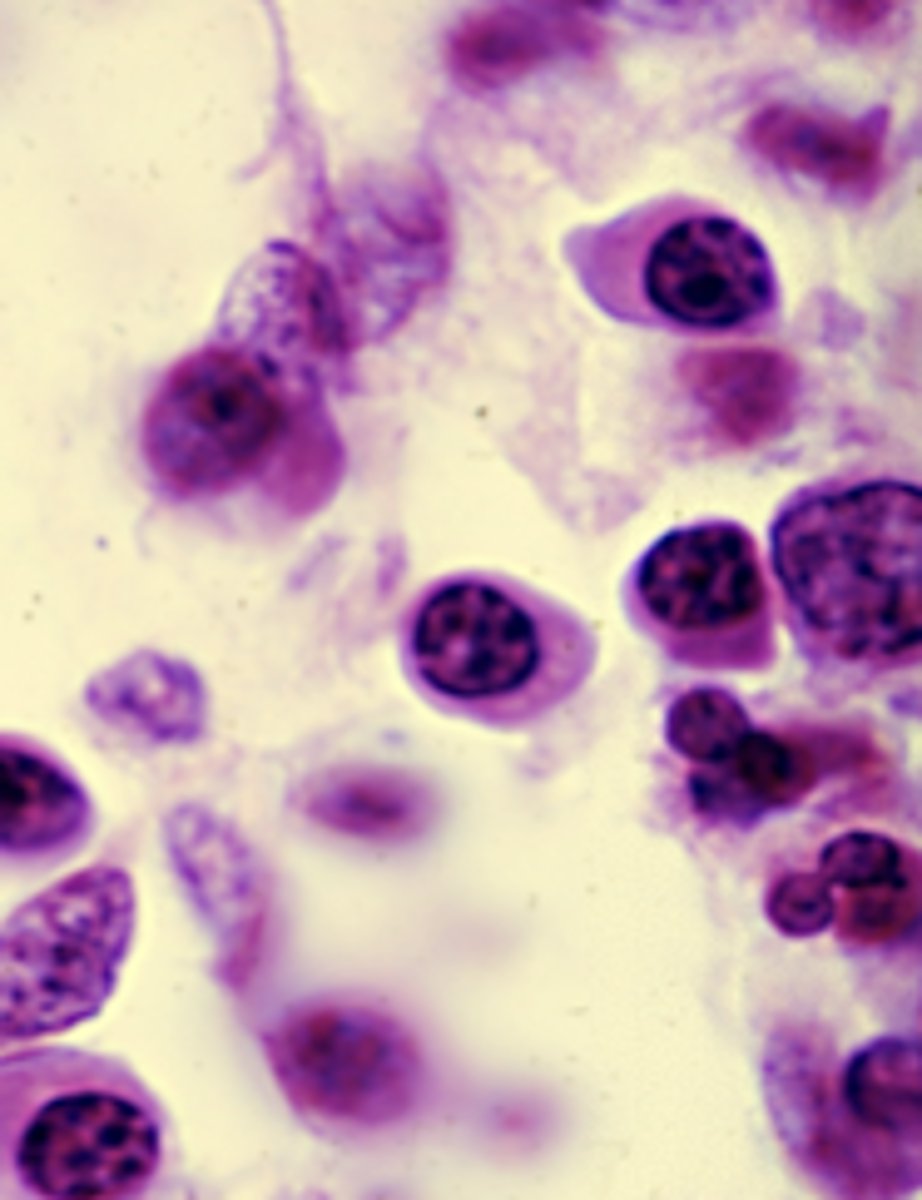
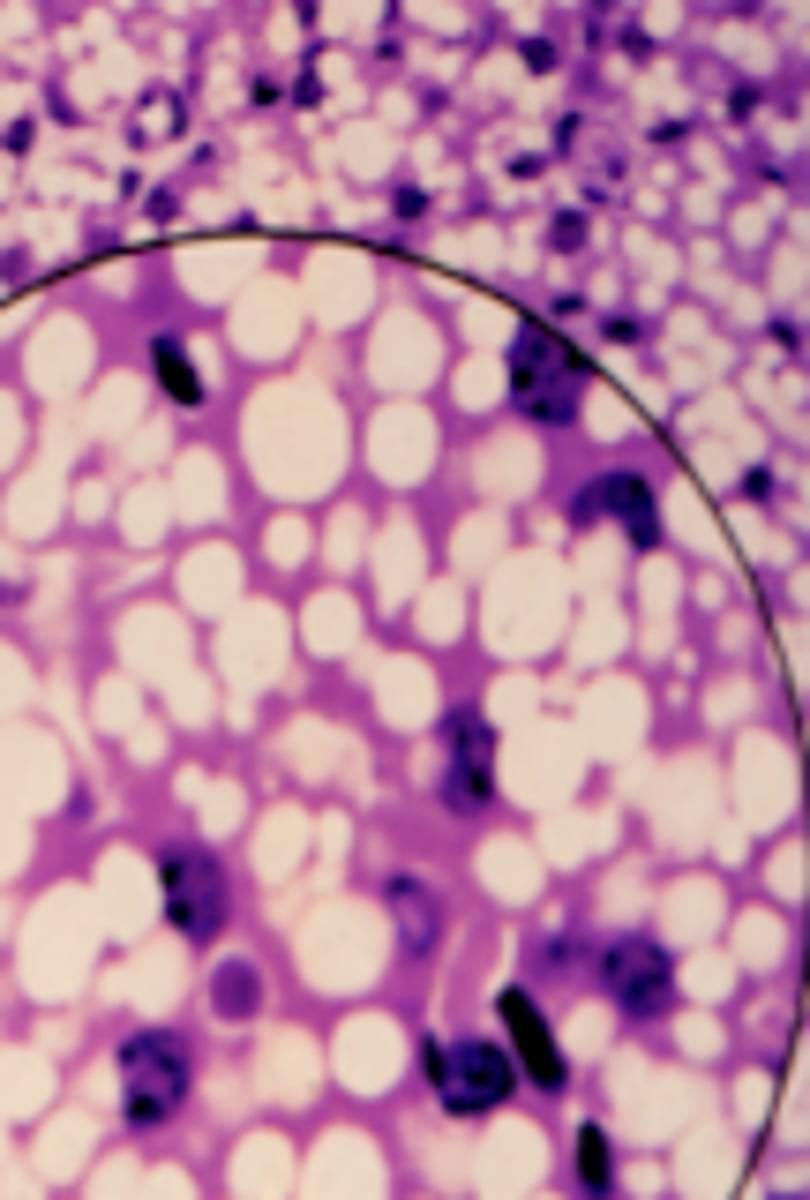
plasma cells
What is this an image of?
reticular cells
What cell type is shown
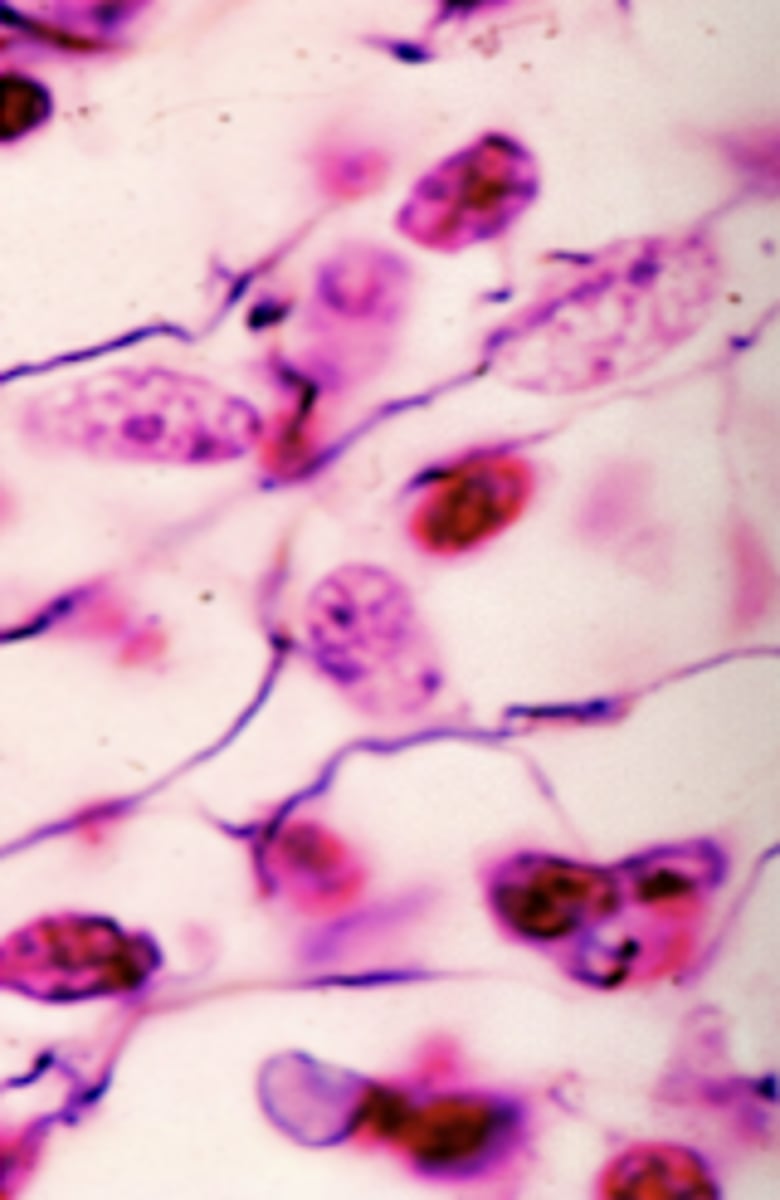
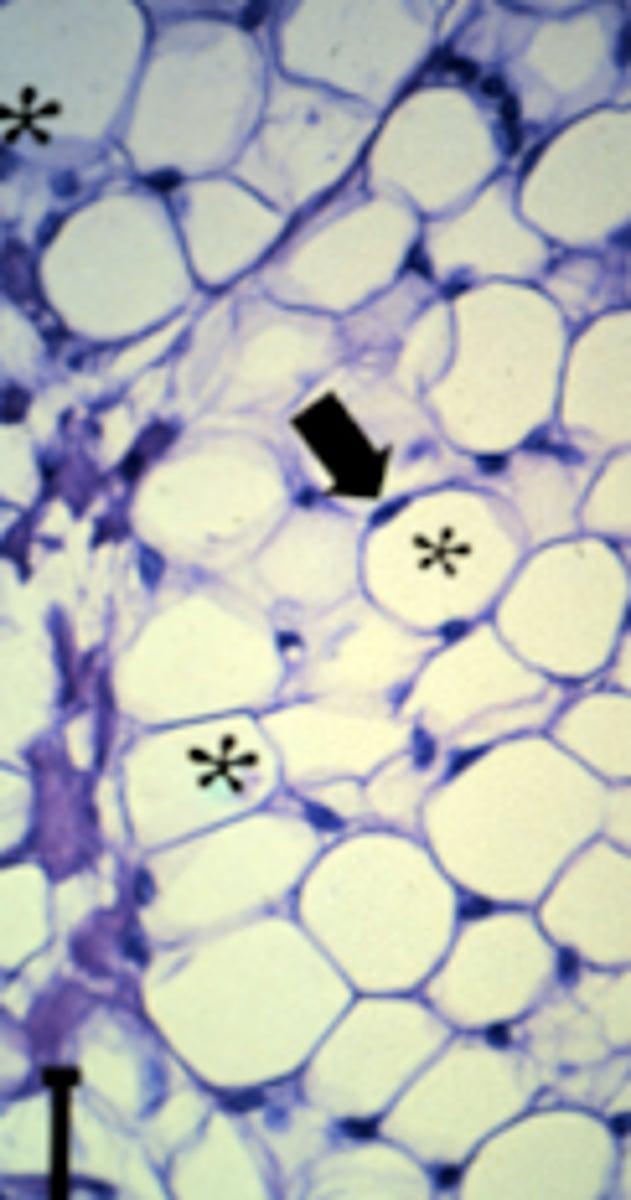
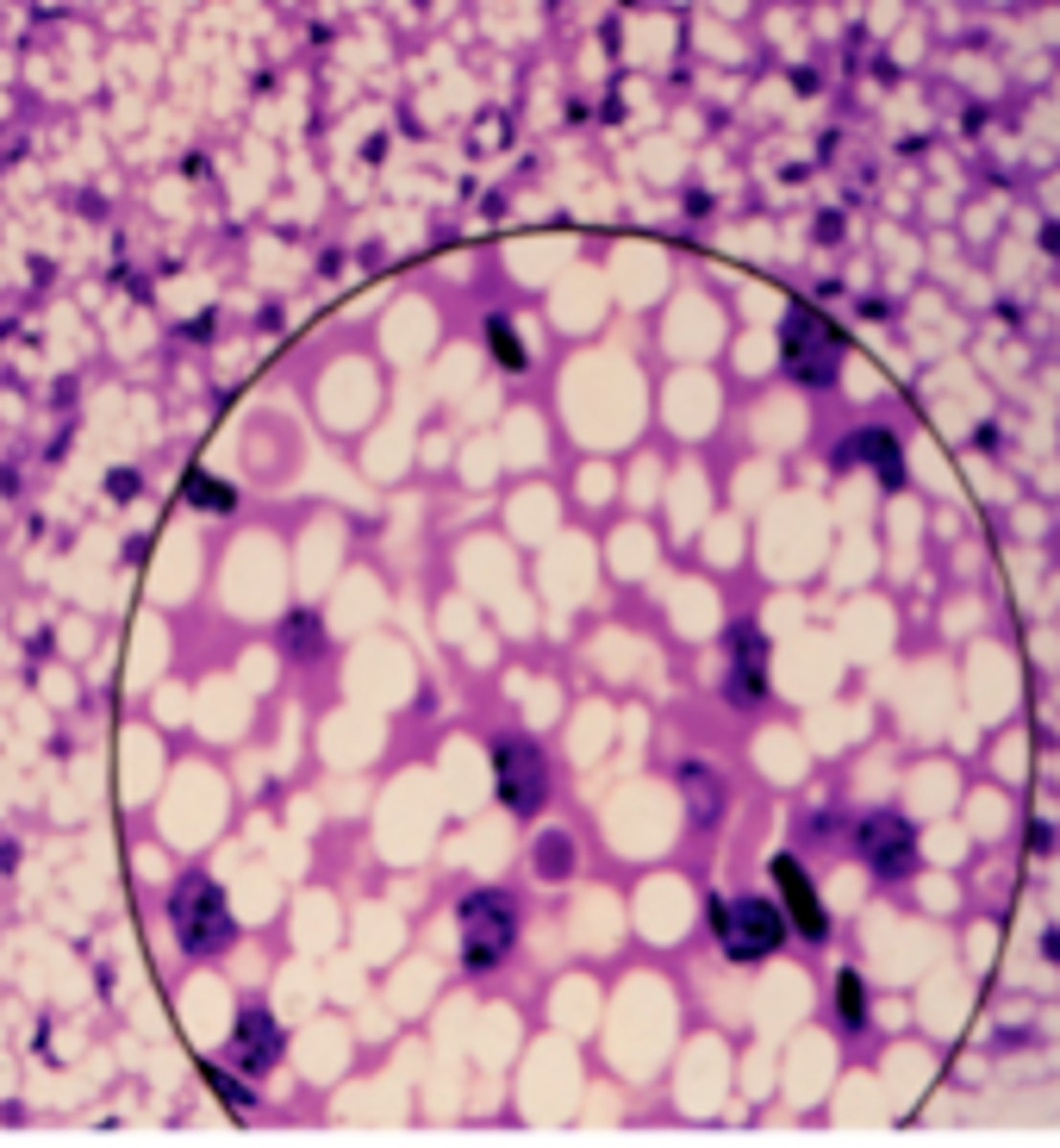
adipocytes
What is this an image of?
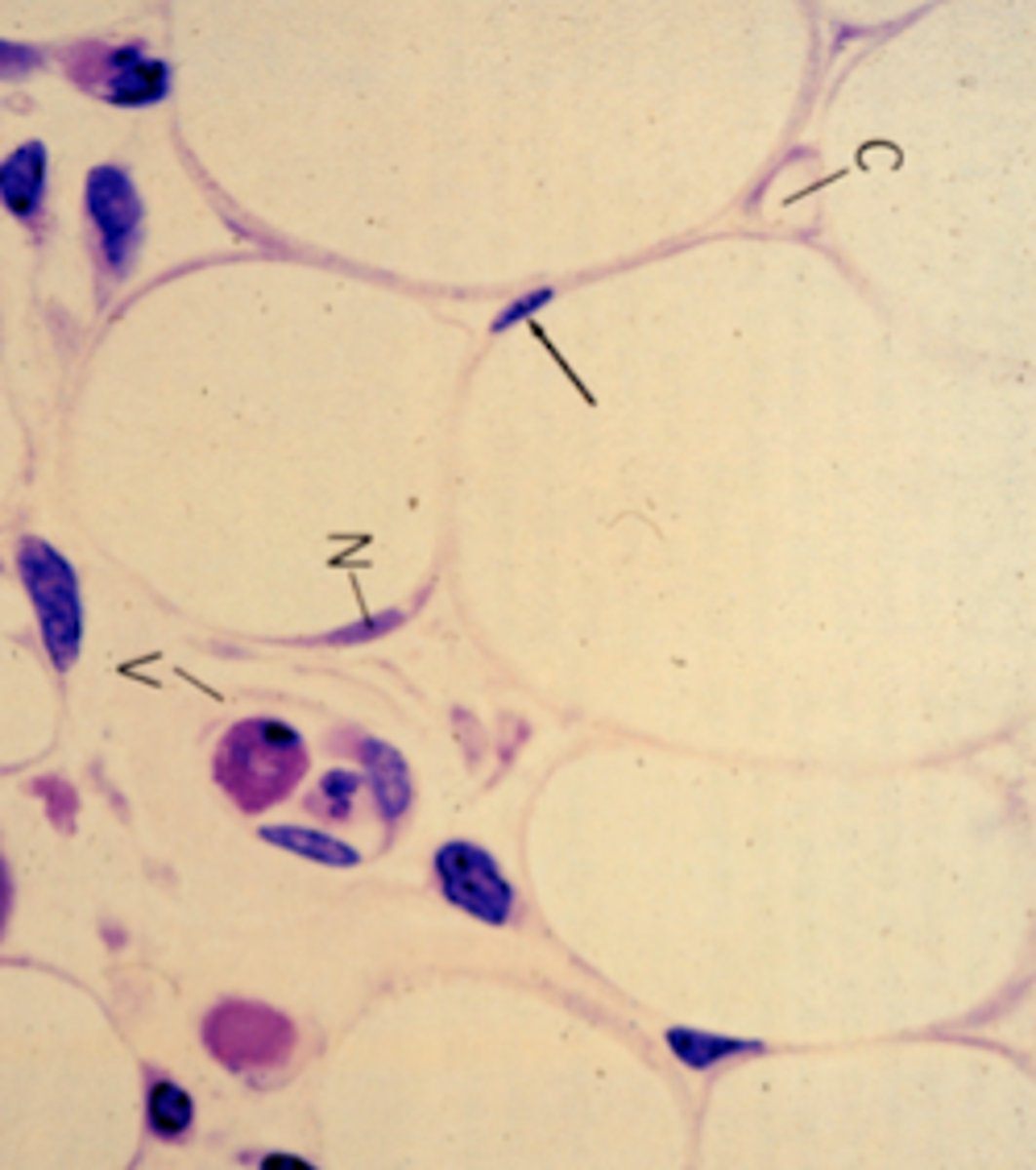
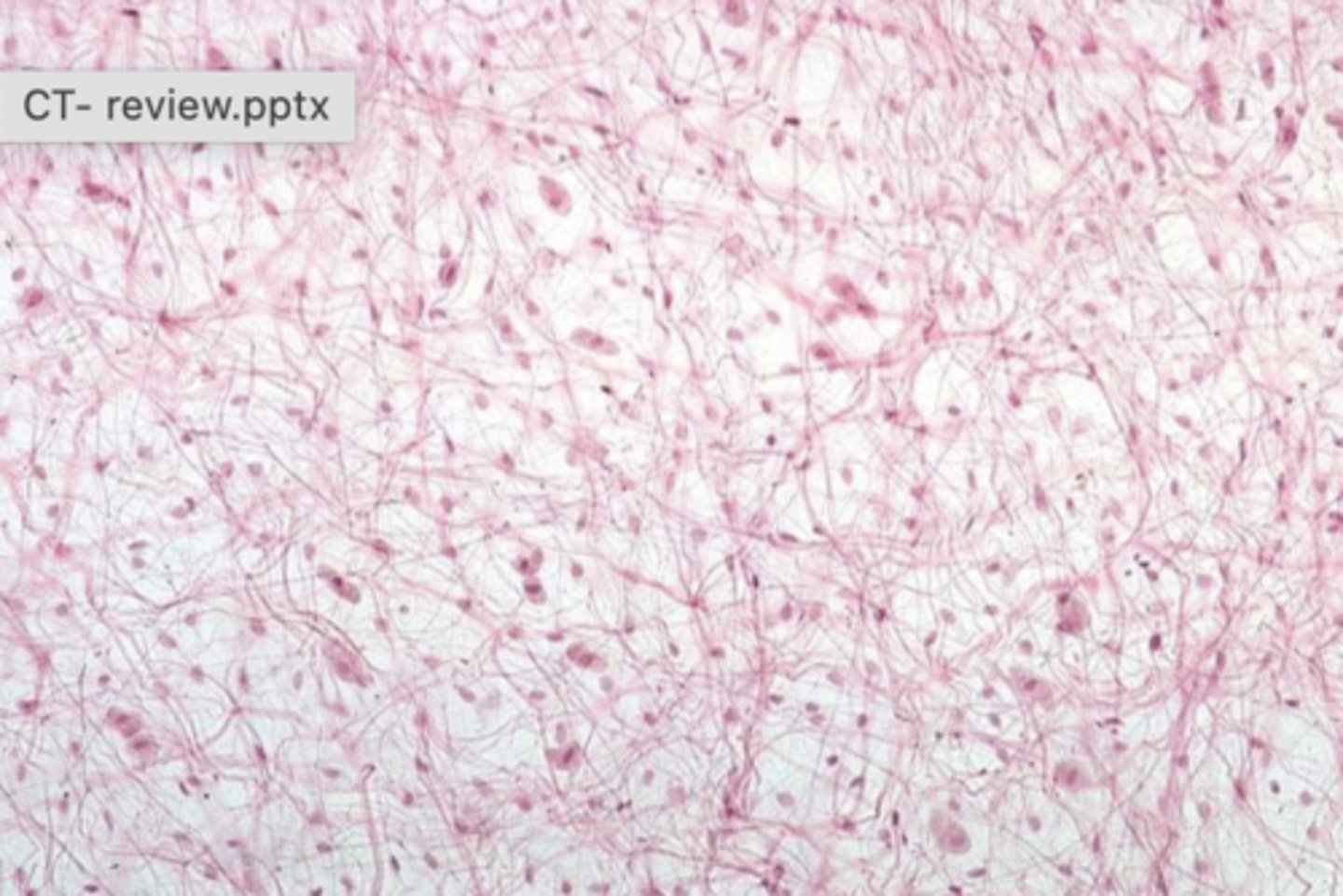
loose (areolar) connective tissue; part of the connective tissue proper
What tissue is shown?
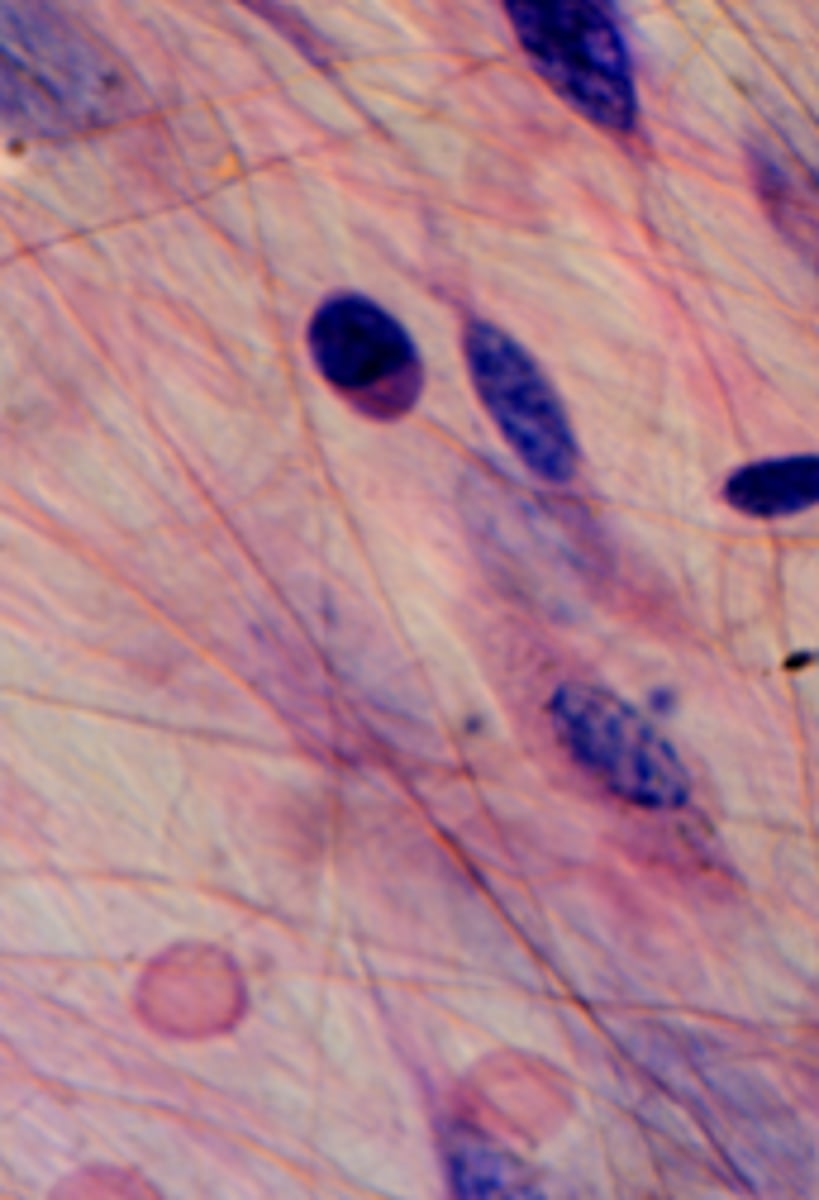
dense regular connective tissue; part of the connective tissue proper
What tissue type is this?
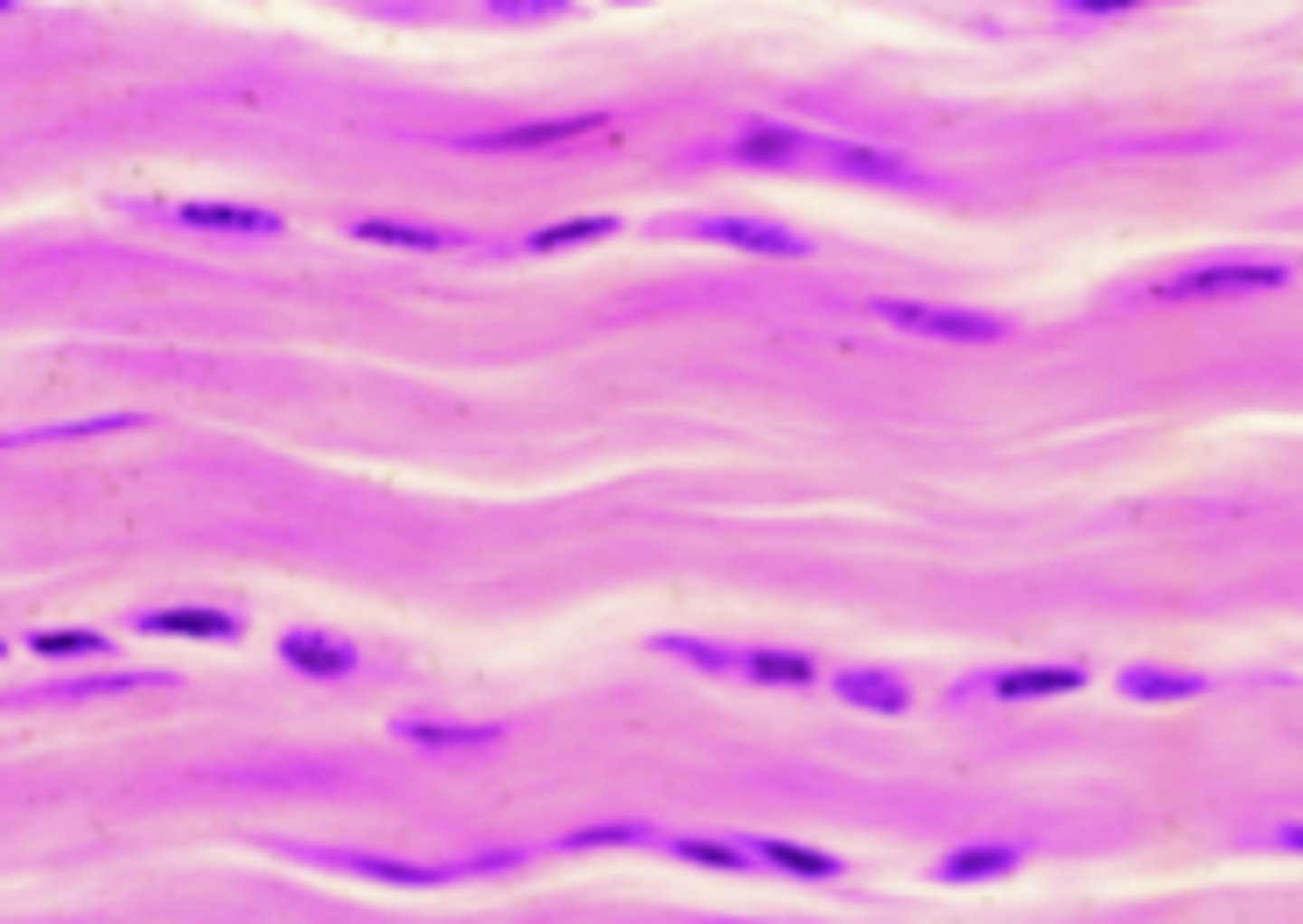
reticular tissue (type III collagen predominates here)
What tissue type are these?
elastic tissue - ligaments
What tissue type is this?
white (unilocular) adipose tissue
What is this an image of?
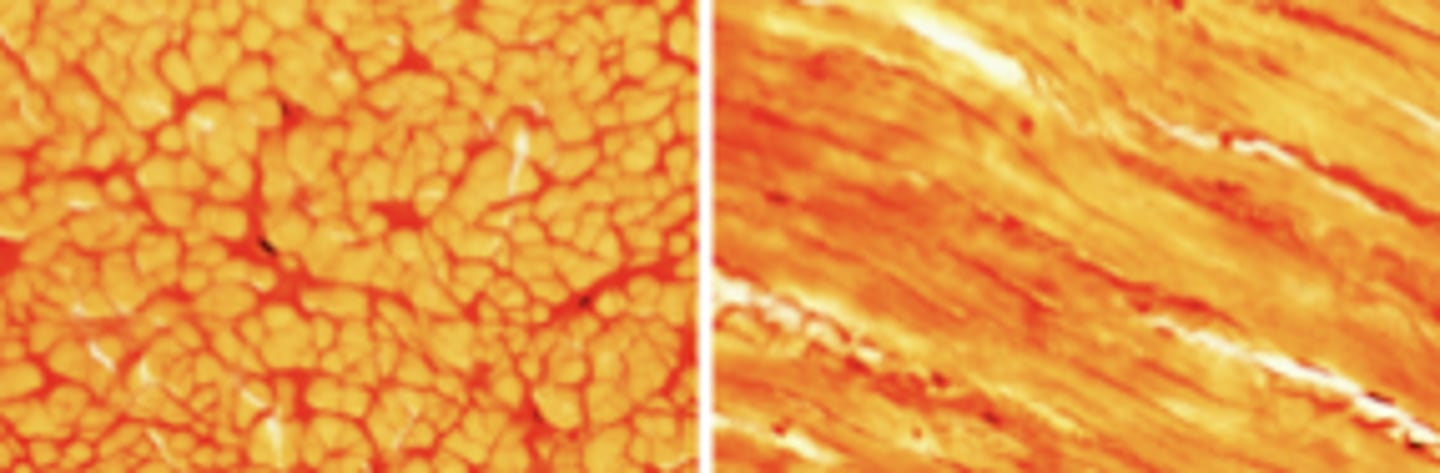
brown adipose tissue
What is this an image of?
brown fat (brown adipose tissue)
What is this an image of?

white fat (white adipose tissue)
What is this an image of?
an elastic artery
What is this an image of?
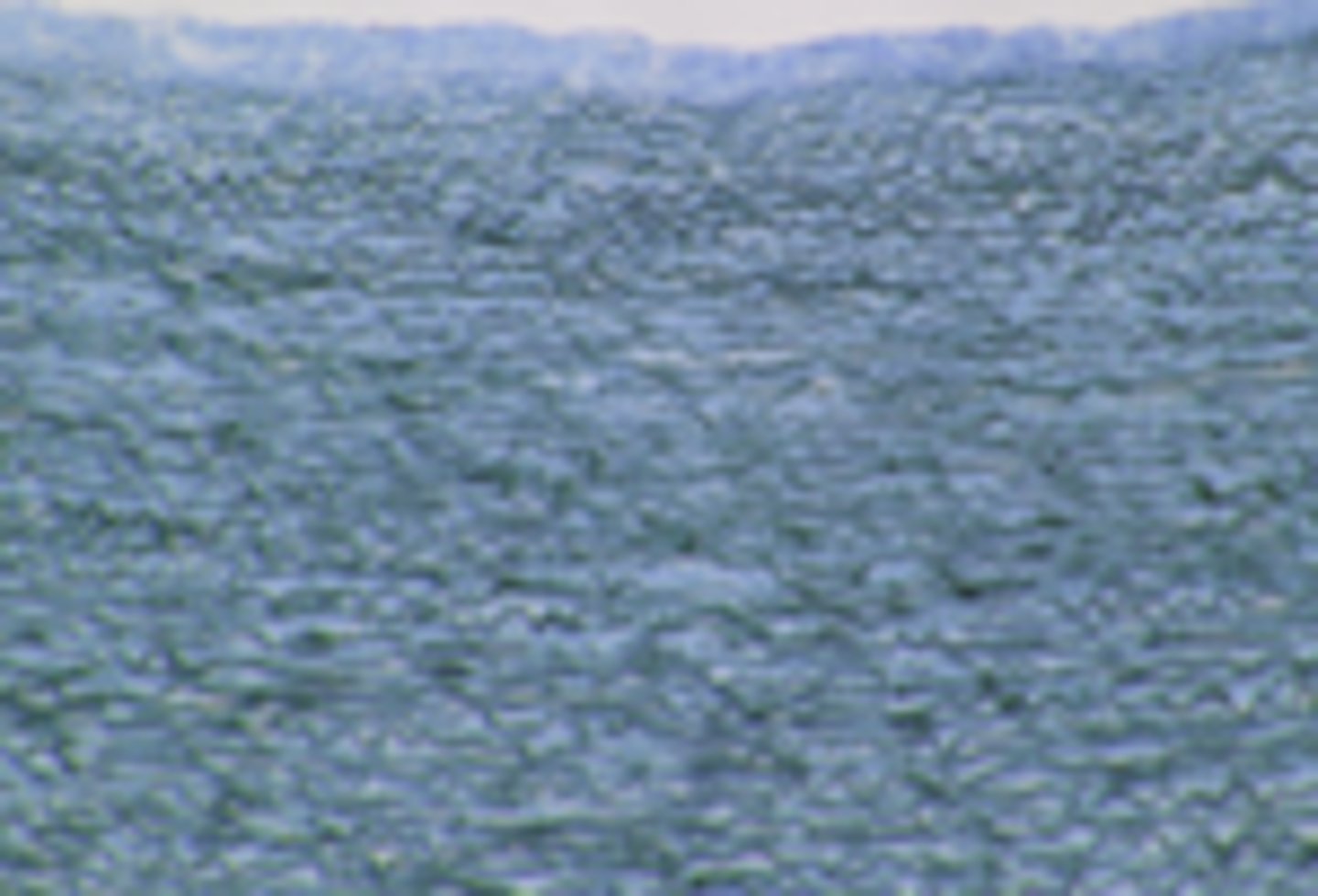

loose connective tissue
What tissue type is shown?
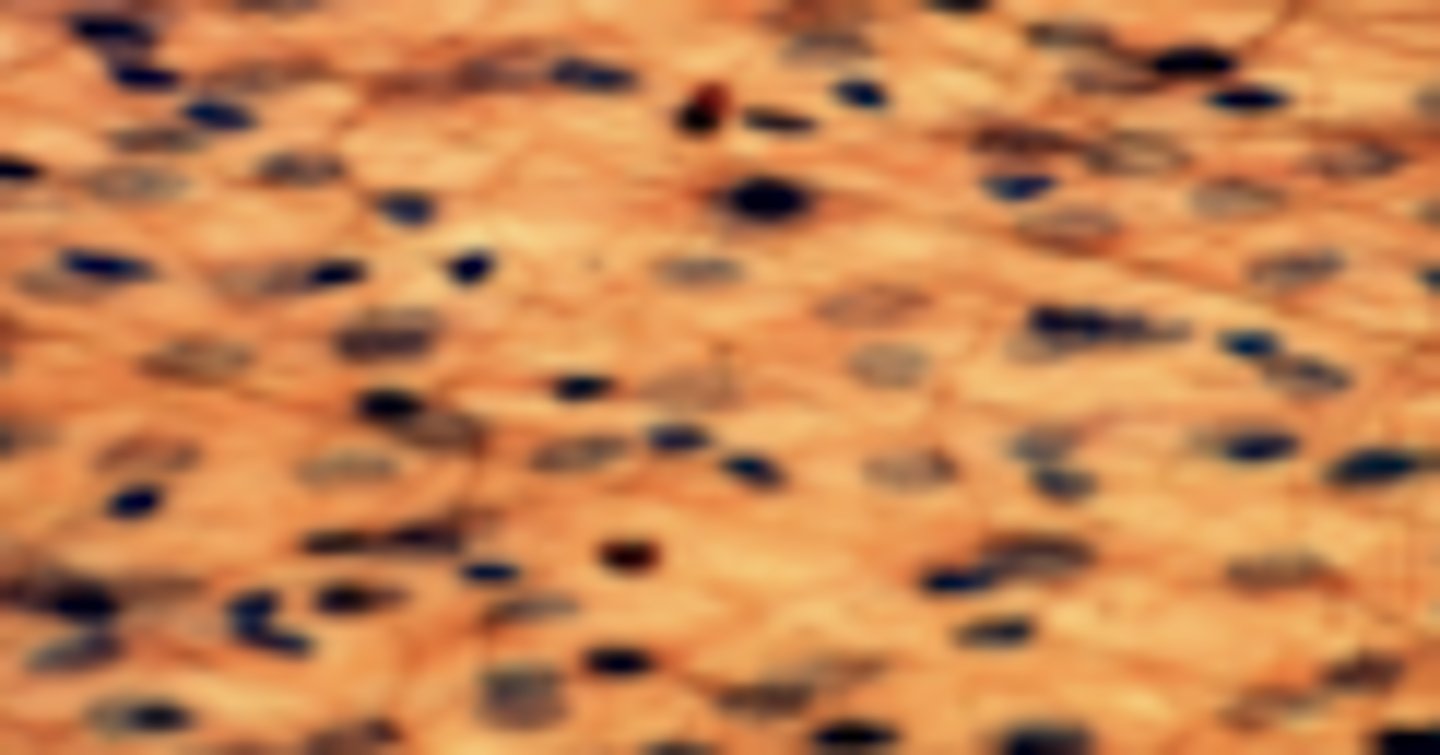

connective tissue - dense regular
What tissue type is shown?
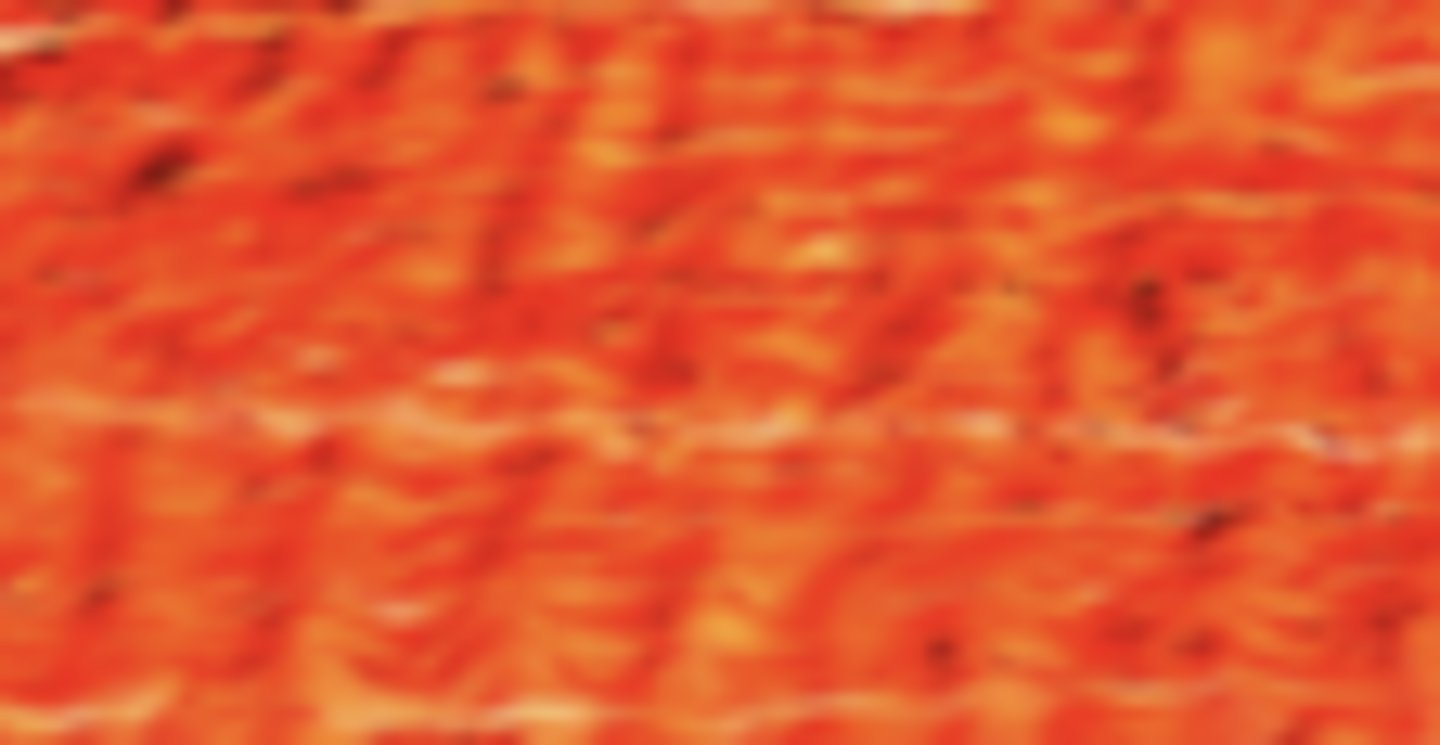

Dense connective tissue
What is the type of tissue circled in green?
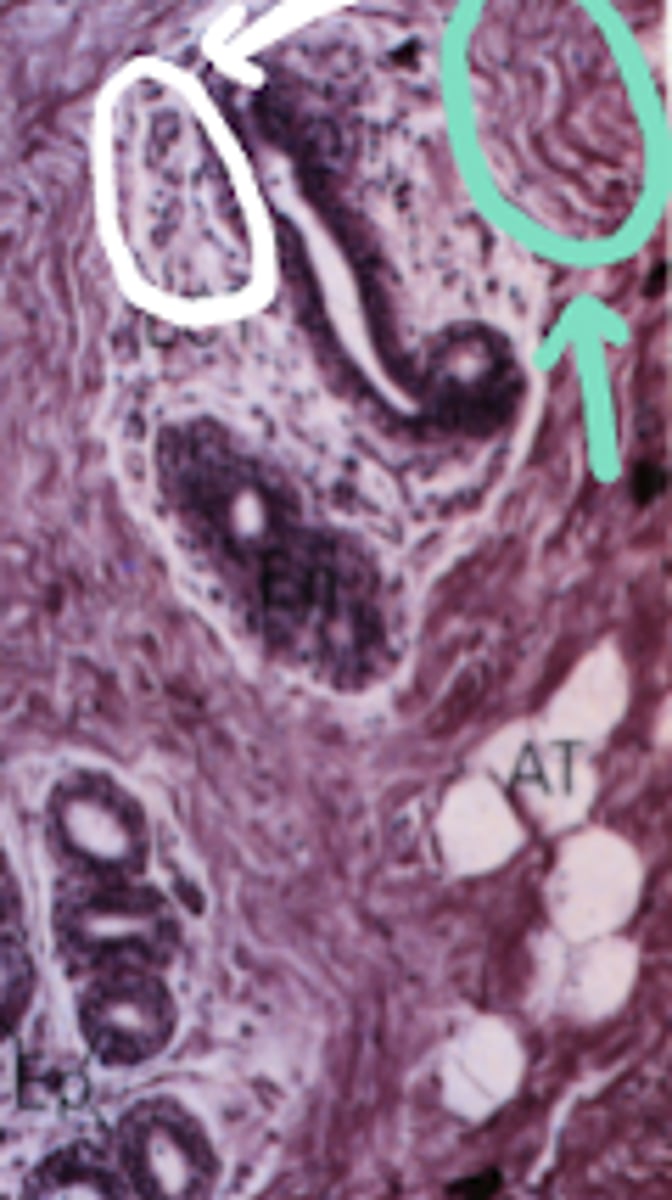
loose connective tissue
What type of tissue is circled in white?
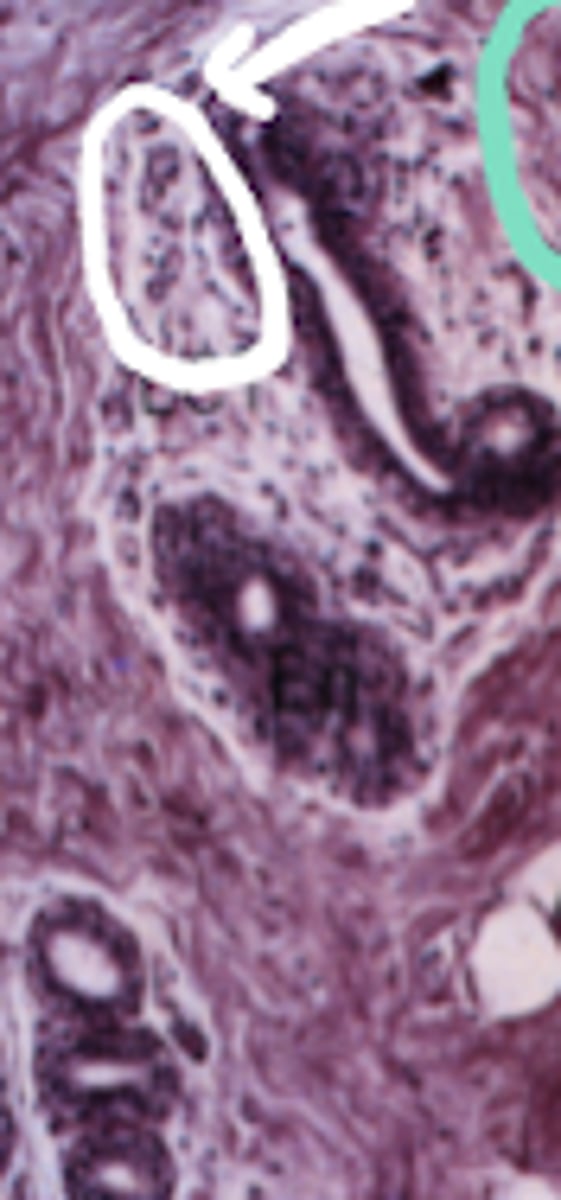
stroma of bone marrow, spleen, lymph nodes
Where is this type of tissue located in the body?
Brown (multilocular) adipose tissue - specialized for heat production
What is this tissue specialized for?
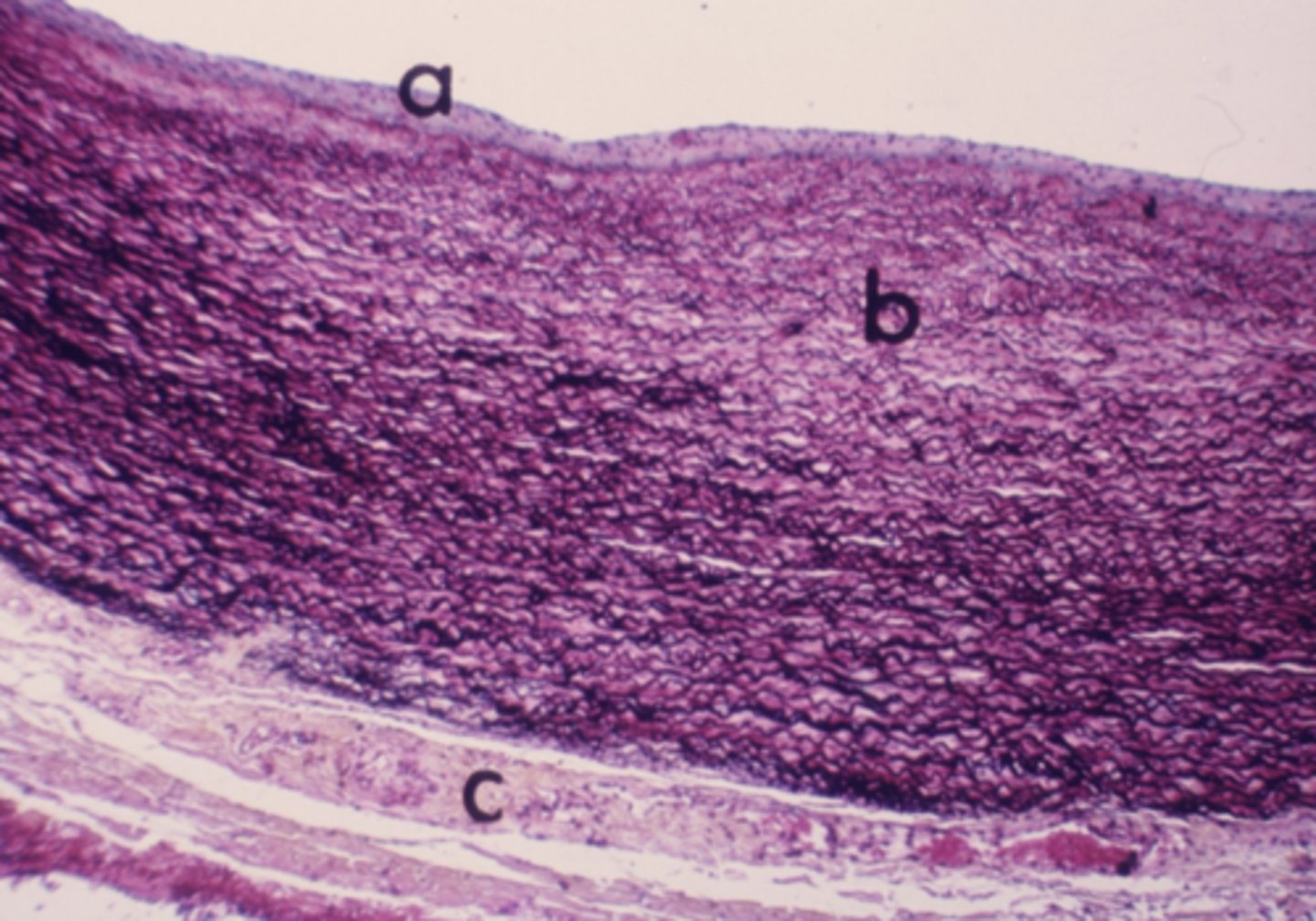
Elastic
What type of connective tissue is located in the area labeled "b"?
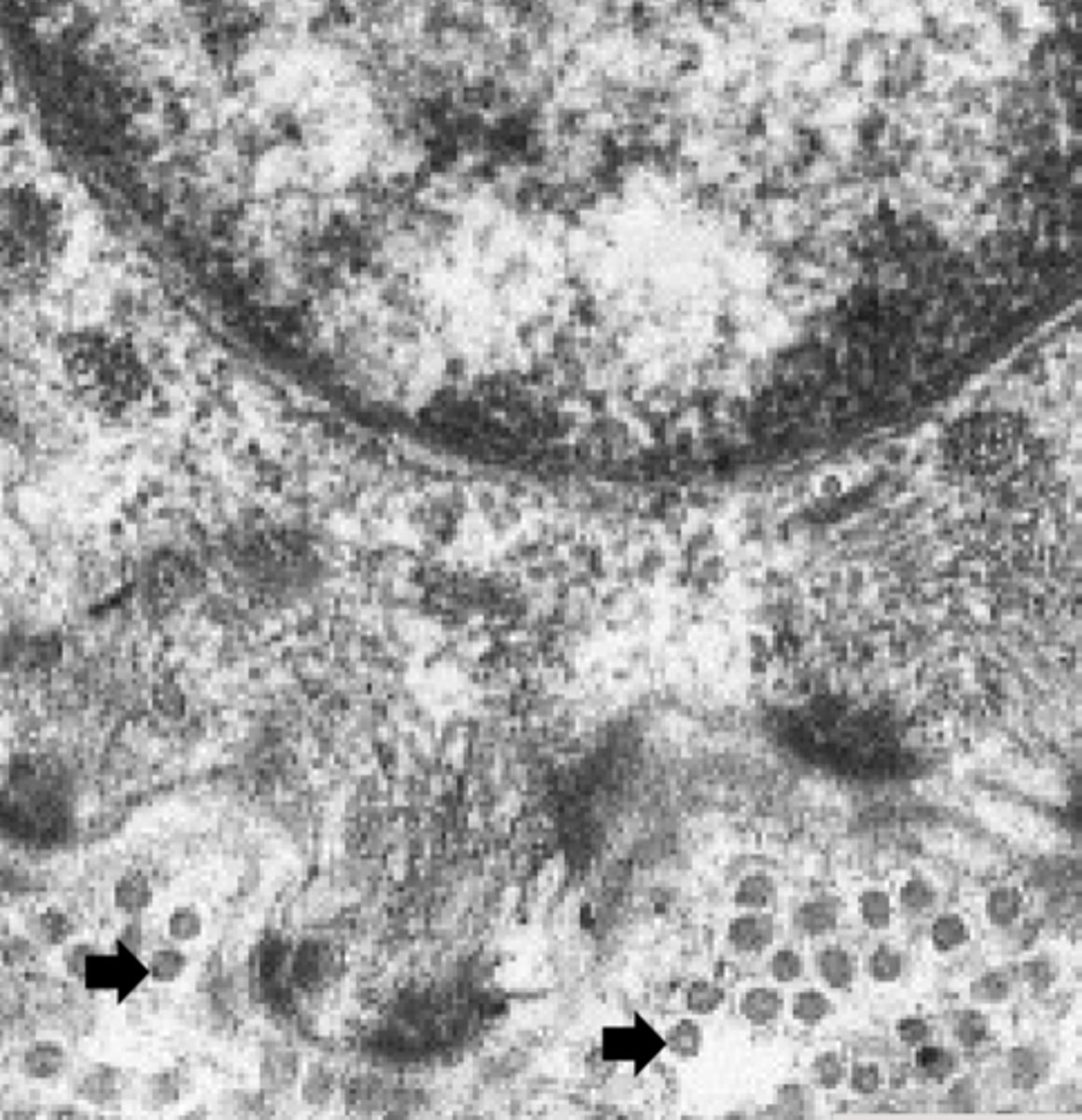
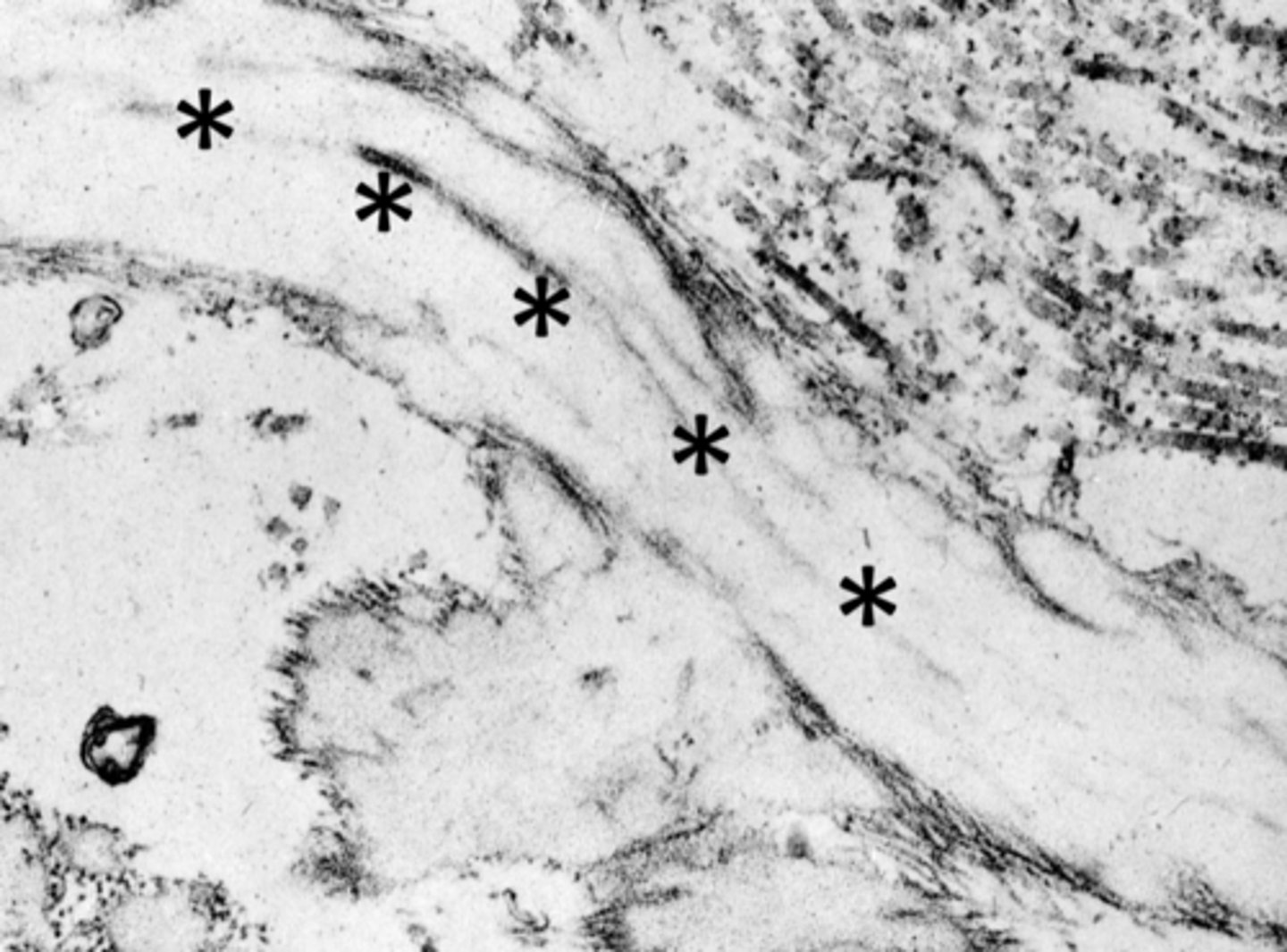
reticular fibers
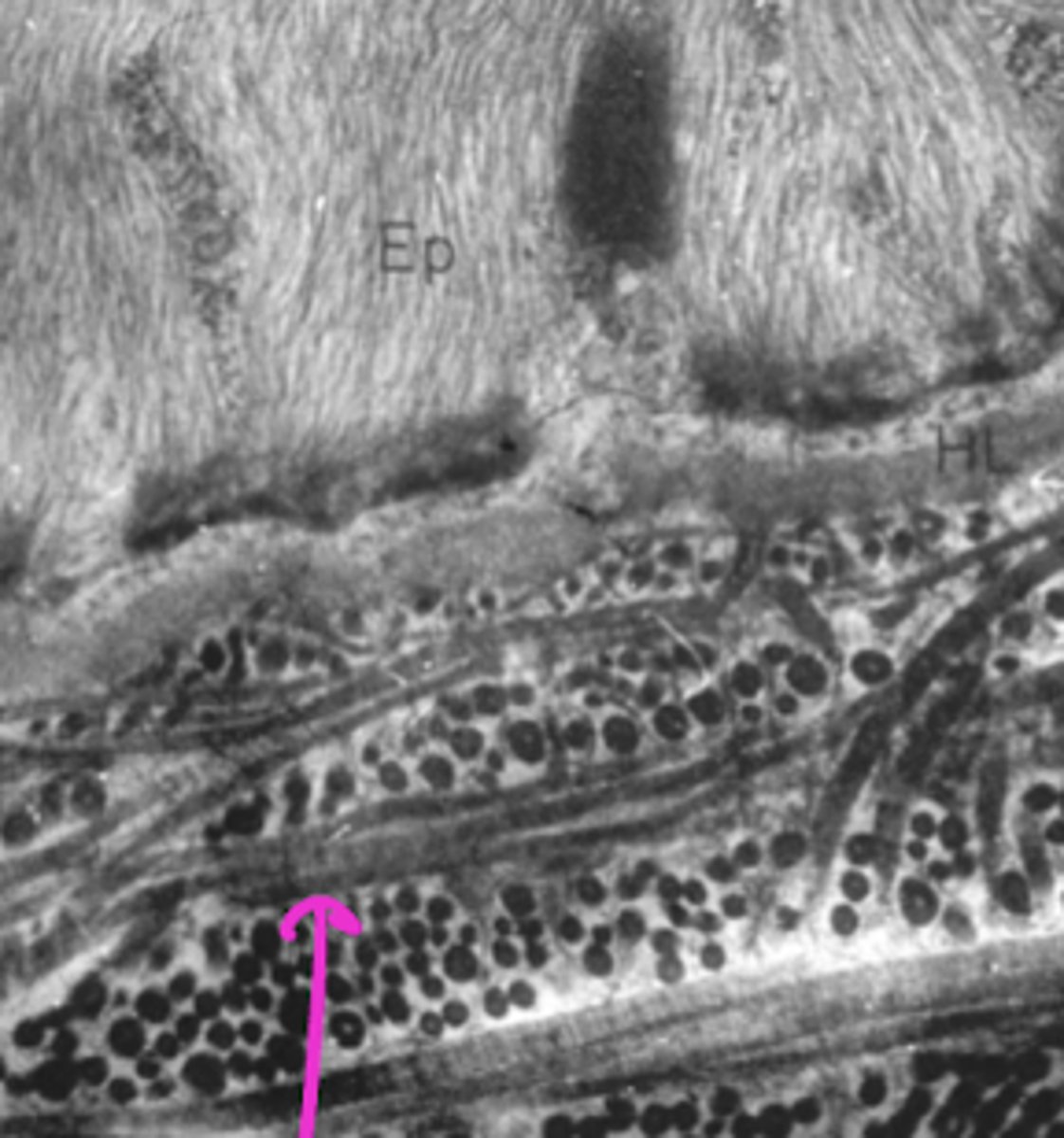
What are the arrows pointing to in this electron micrograph?
loose
Identify the connective tissue type
elastic fiber
What are the arrows pointing to in this electron micrograph?
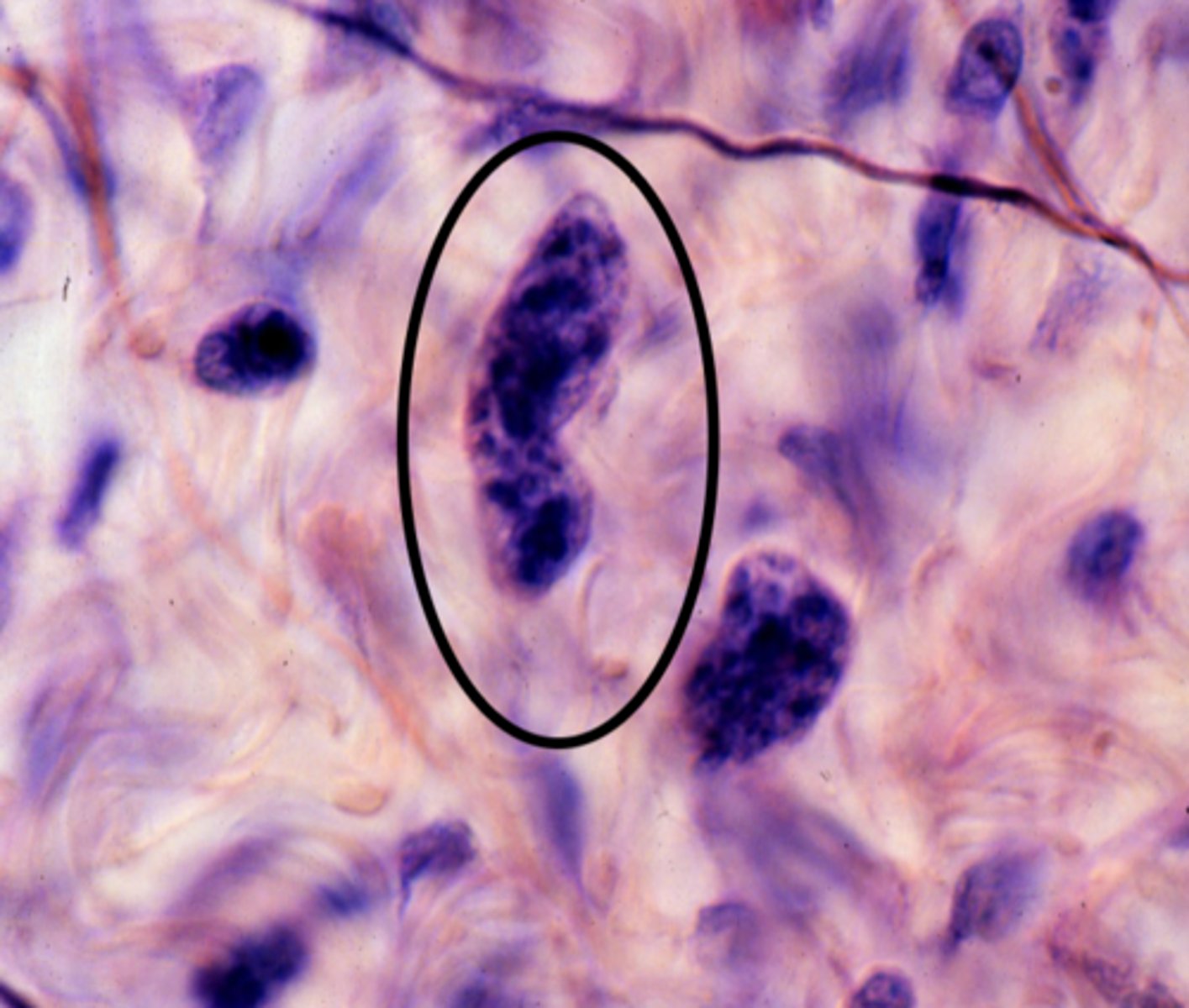
macrophage
This specimen is from a trypan-blue treated rat, what cell-type iscircled?
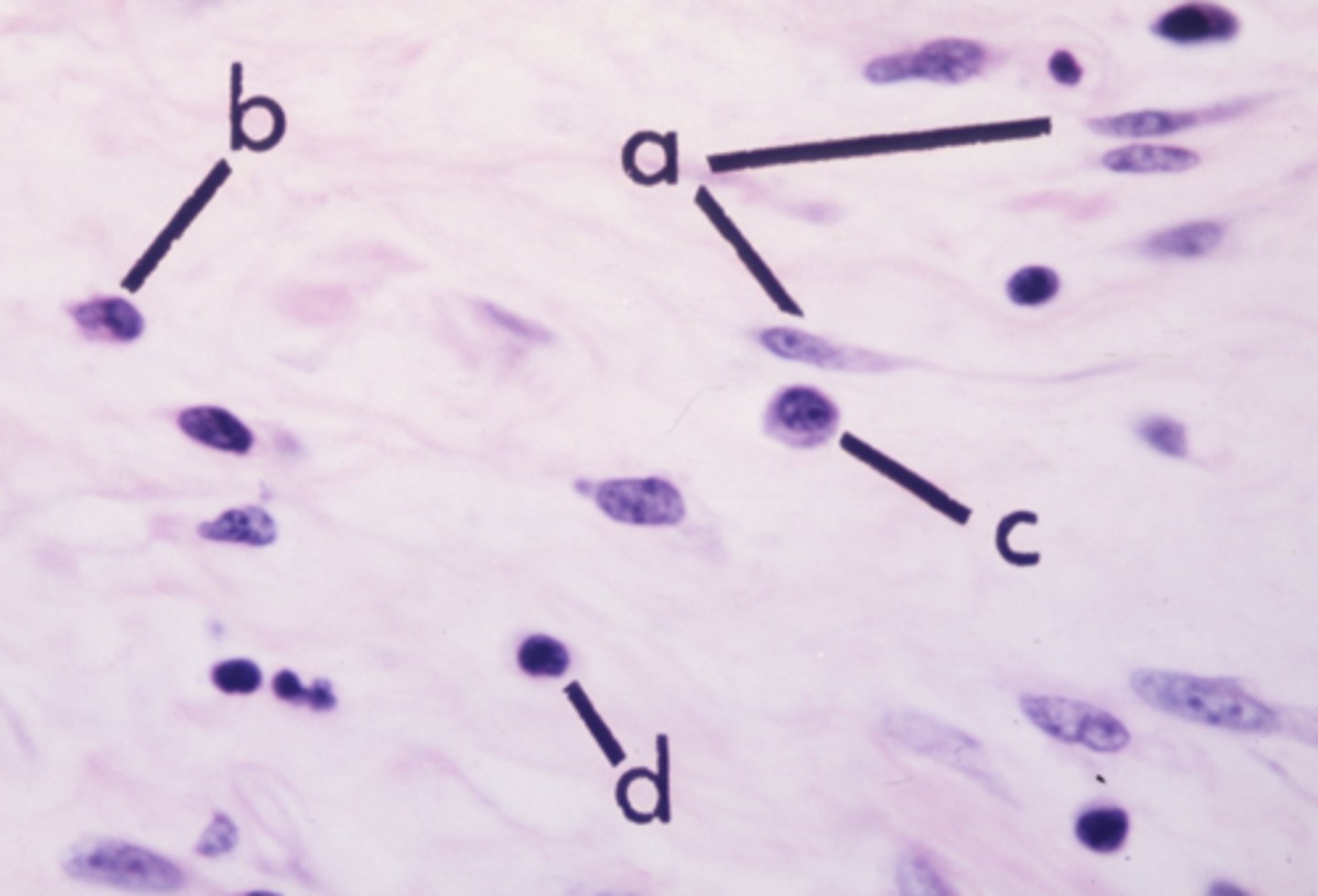
plasma cell
what cell type is letter c?
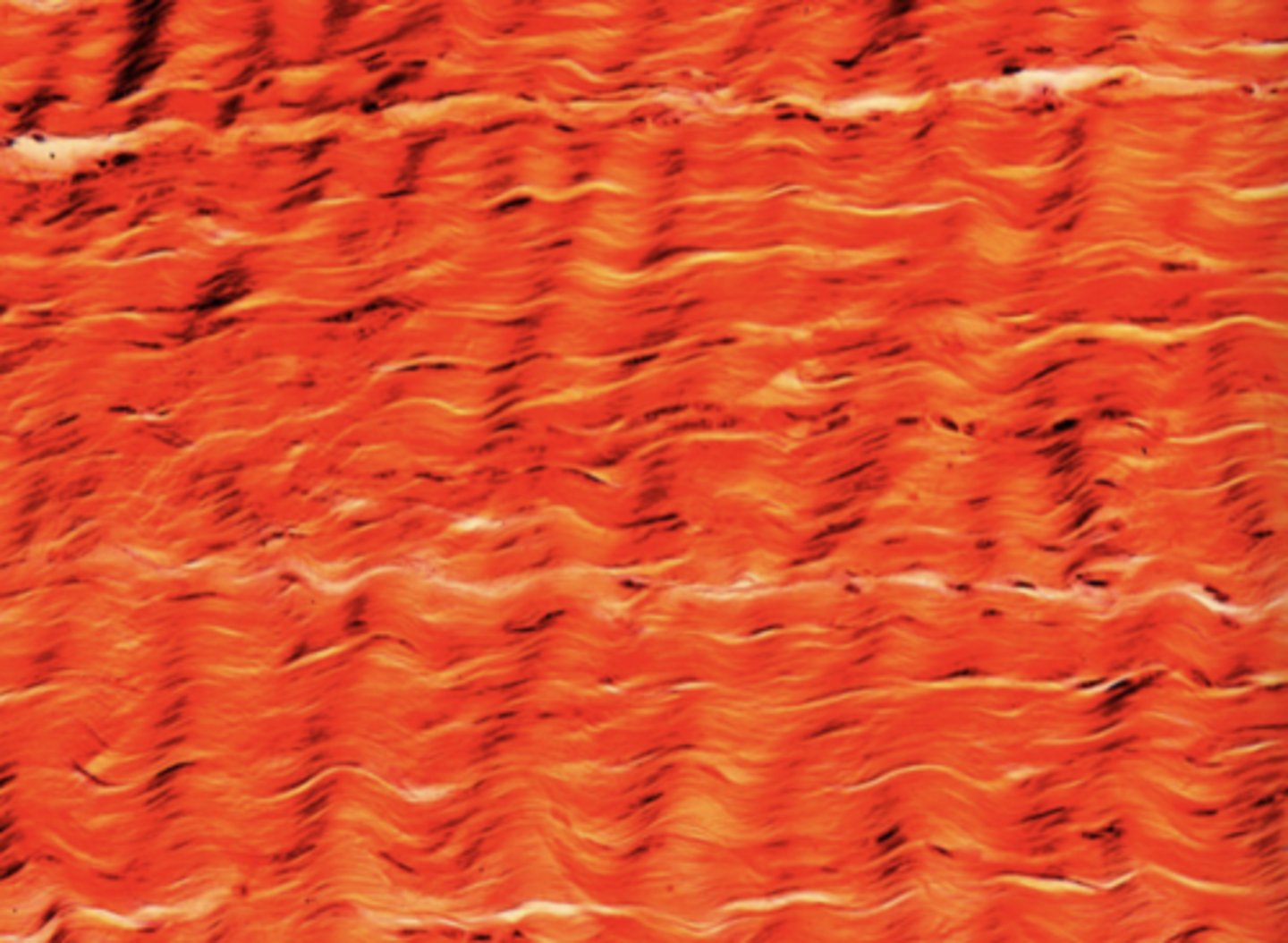
tendon (dense regular)
What body structure could contain the tissue in the image?
reticular
What type of connective tissue is demonstrated in this image?
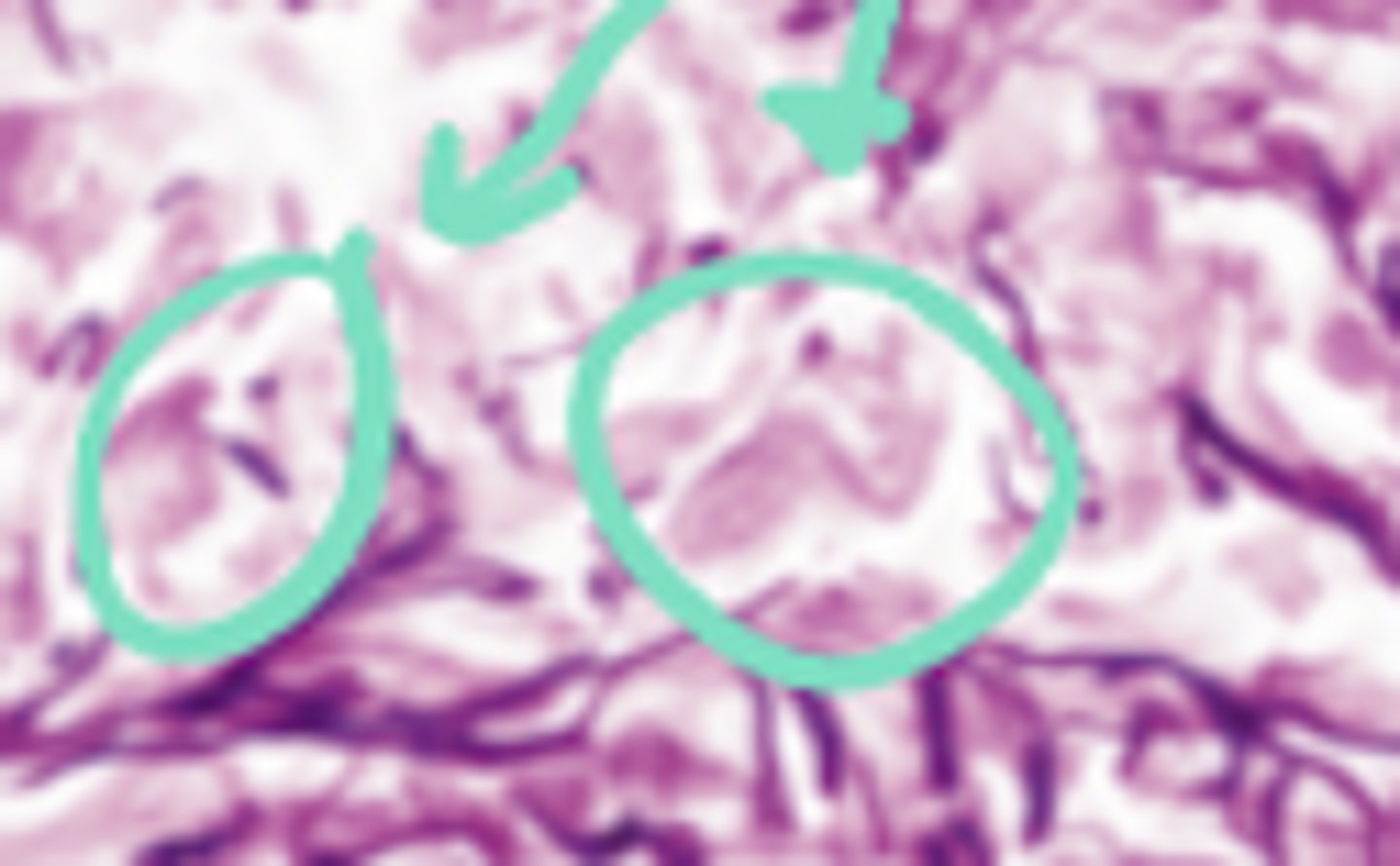
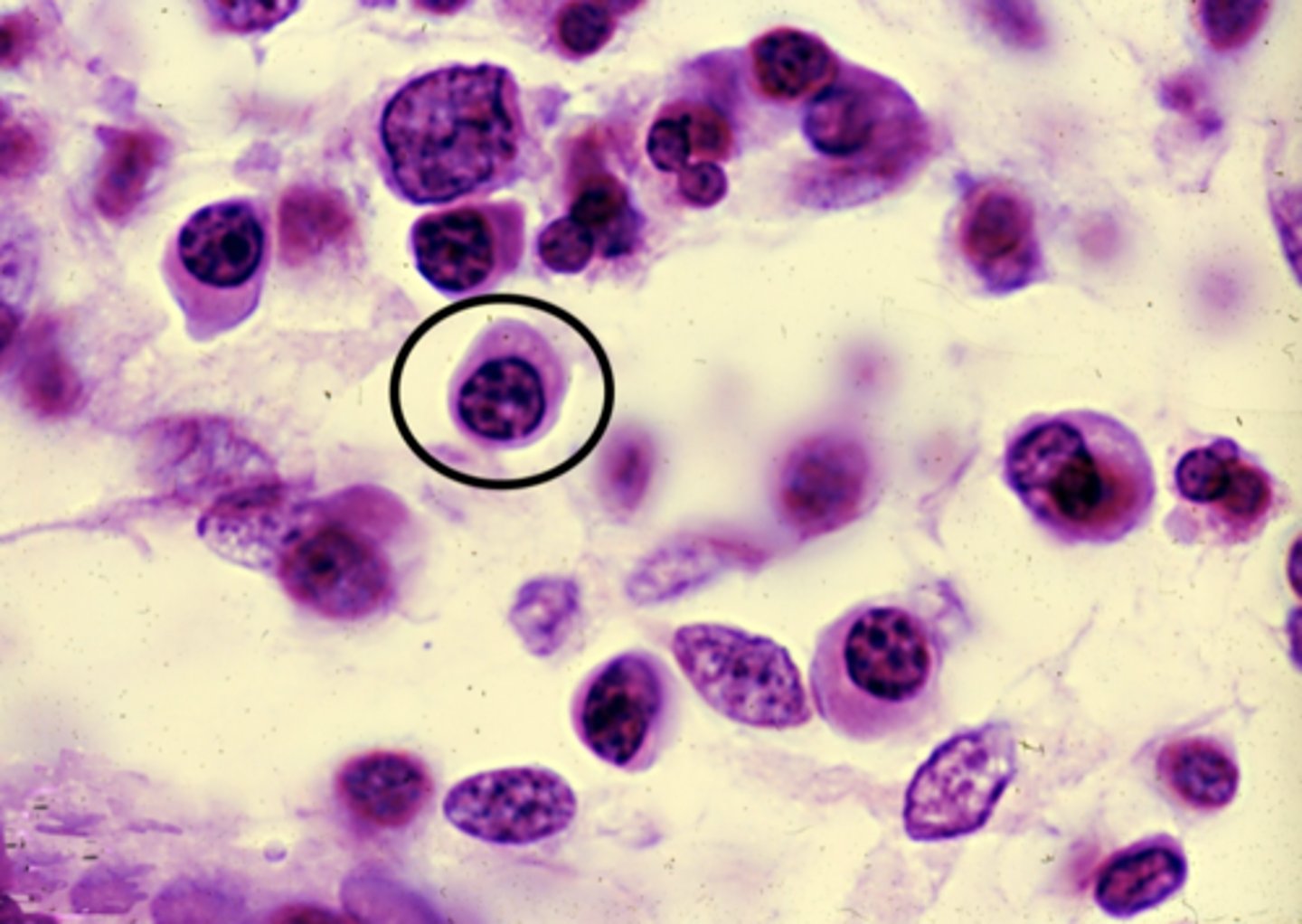
plasma cell
what cell type is circled?
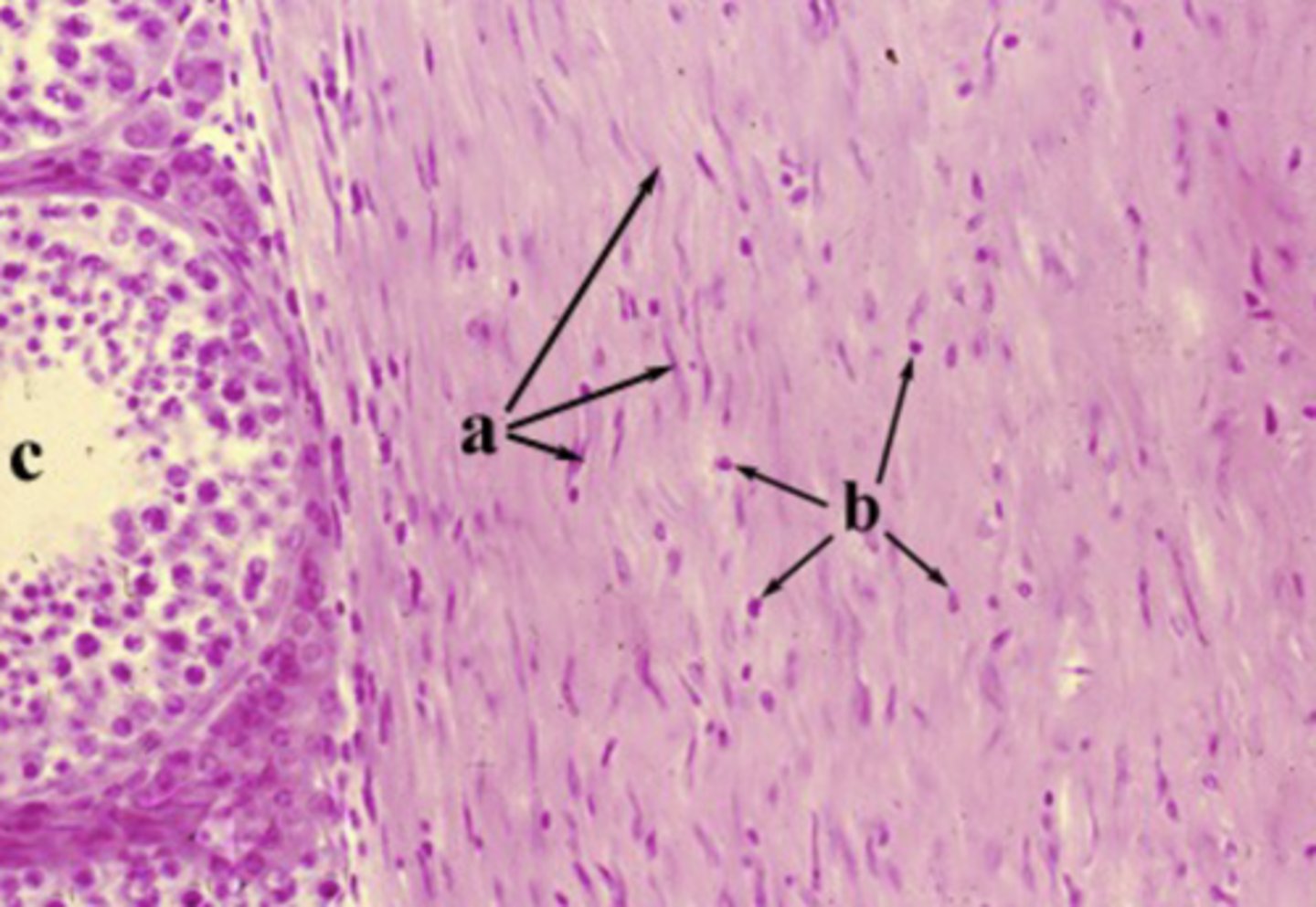
dense irregular
What connective tissue type are the cells label "b" residing?
plasma cell
Identify the cell type
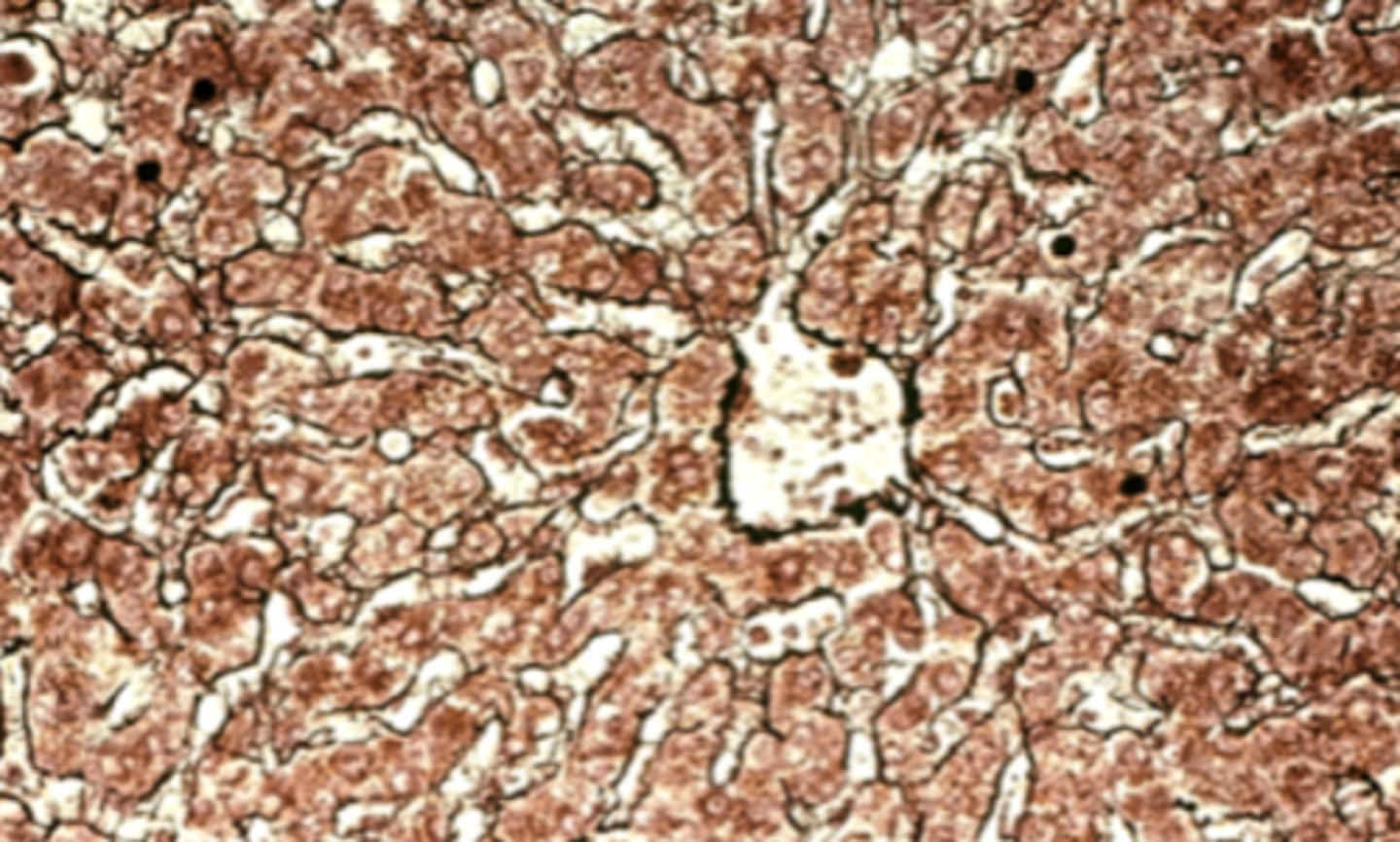
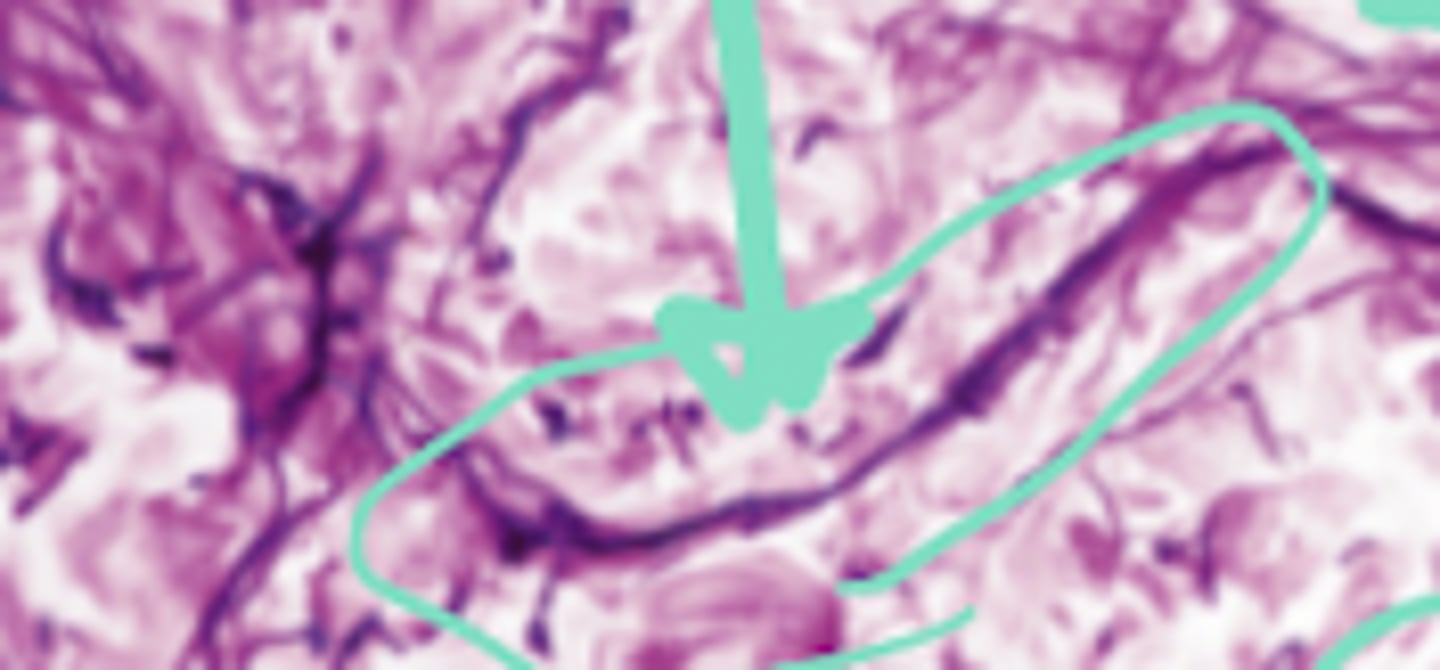
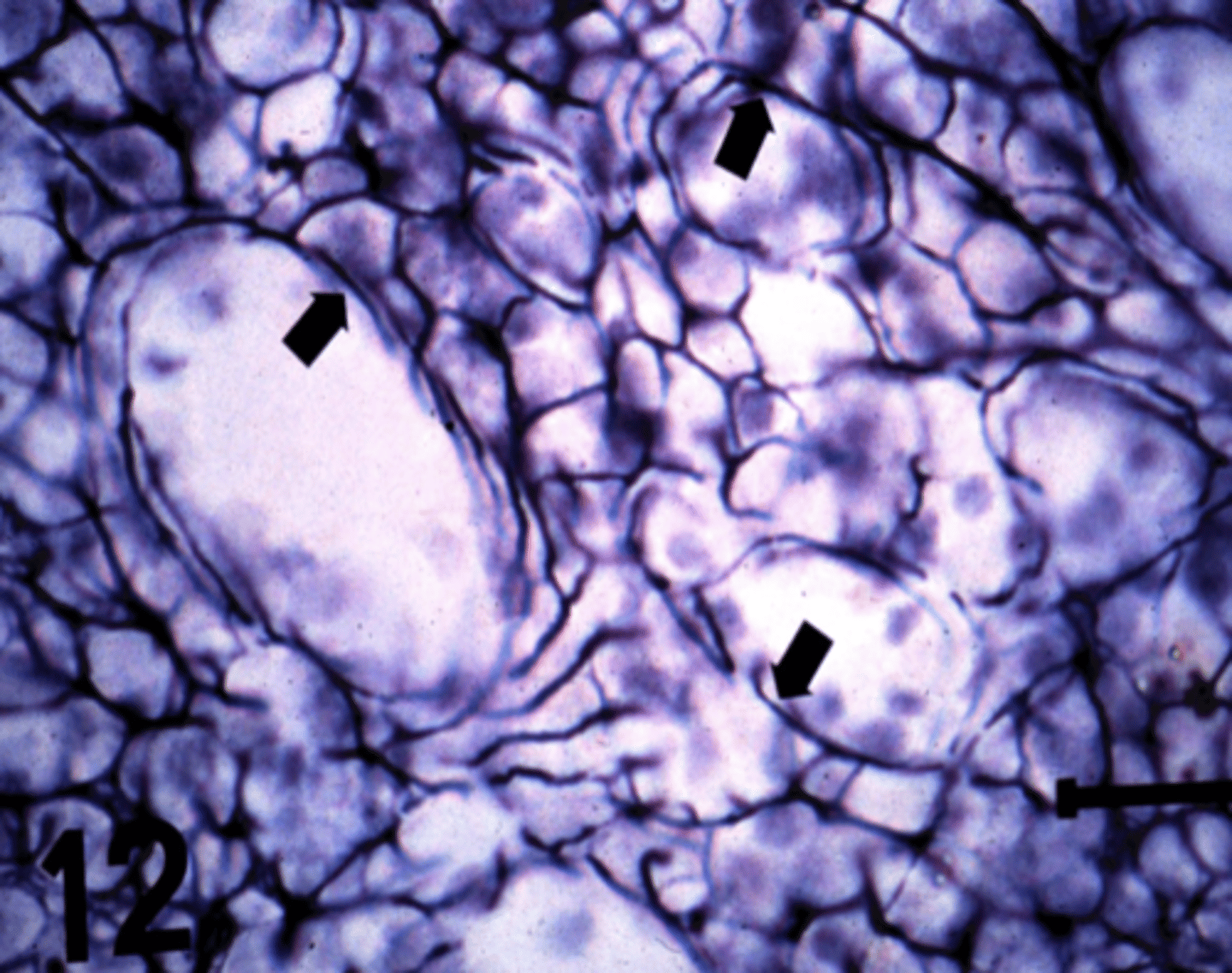
reticular fibers
What is found in high concentrations in the structure indicated by arrows?
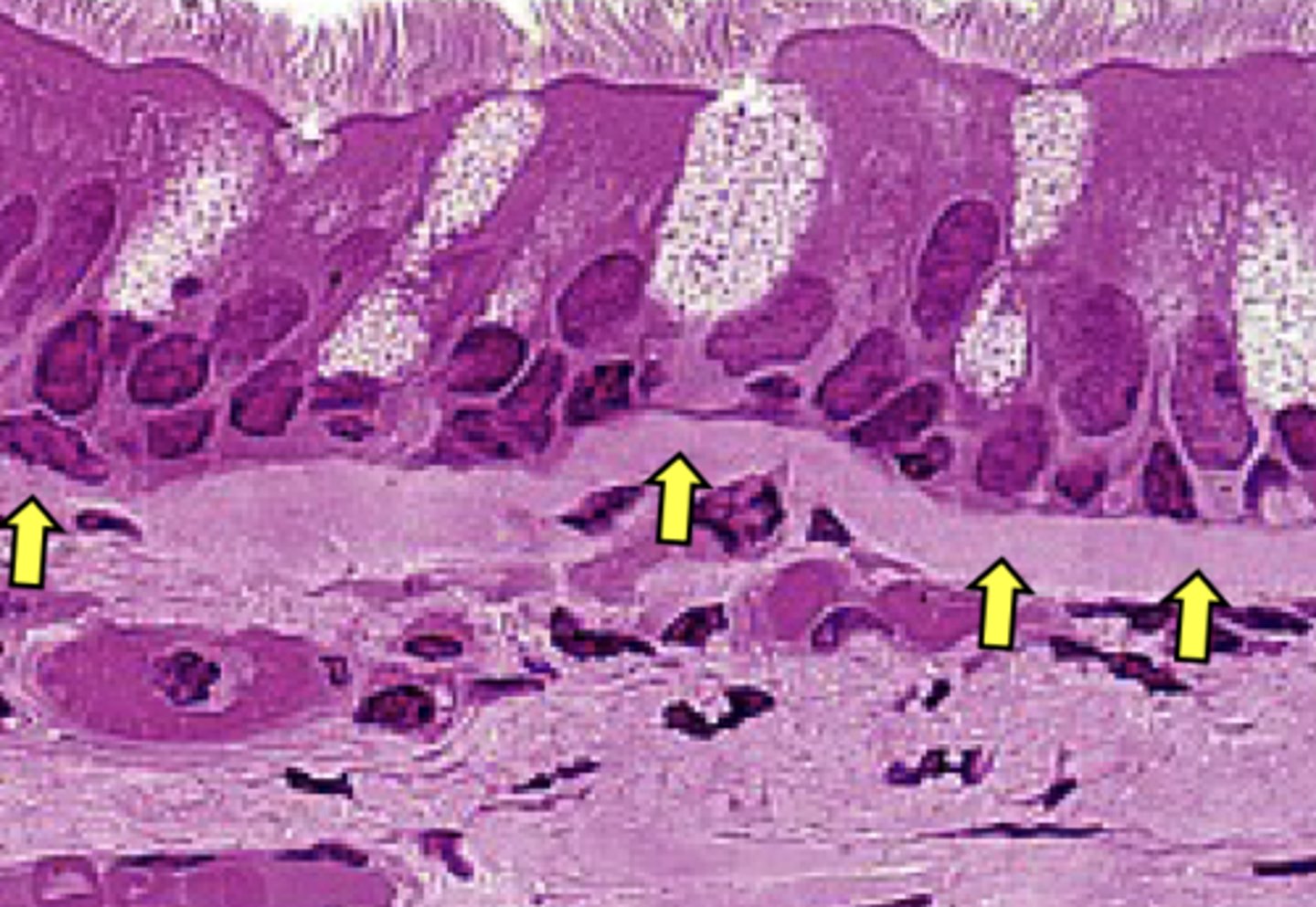
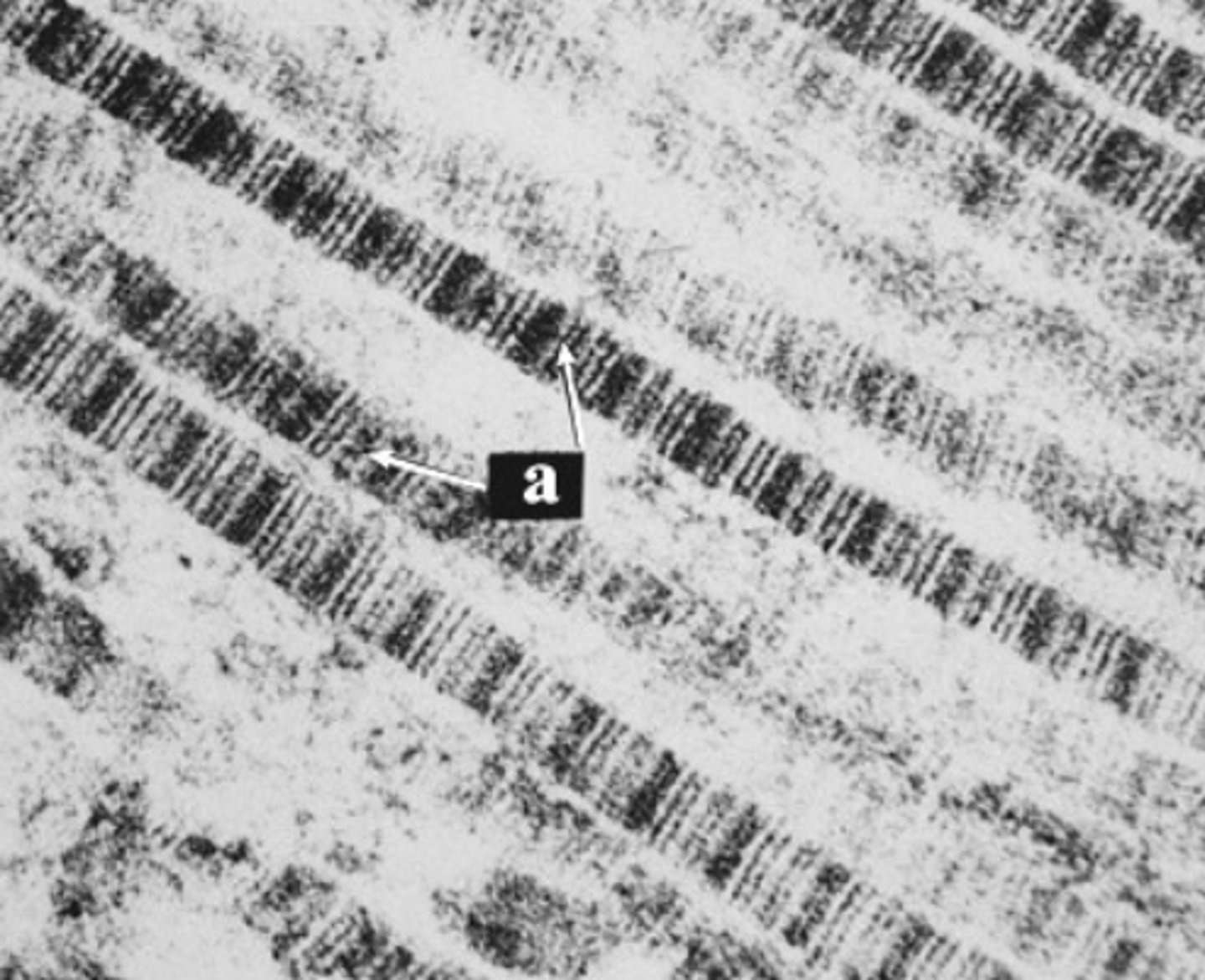
dense regular
What connective tissue type is labeled "a"?
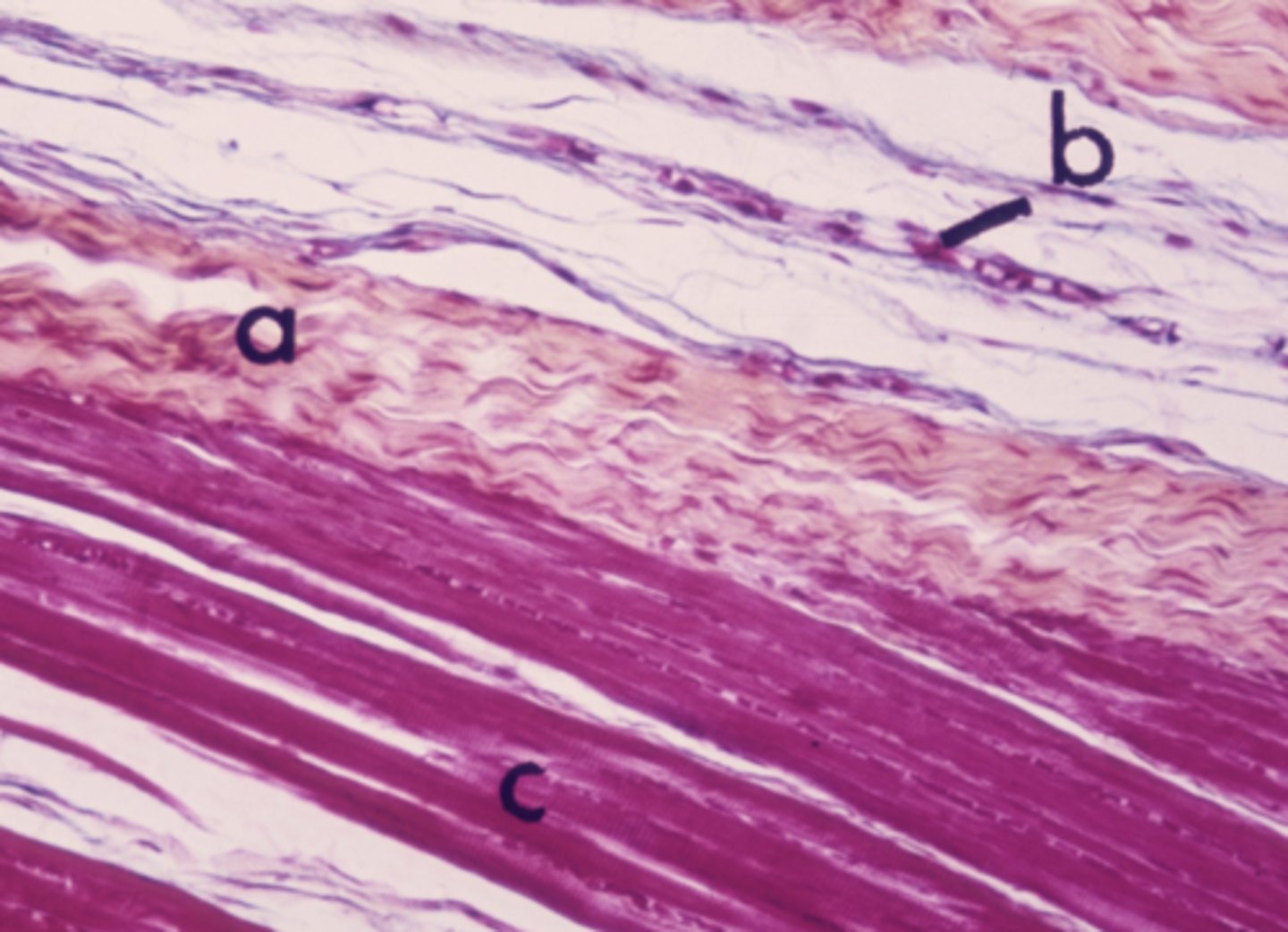
mast cell
Identify the cell type labeled "b"
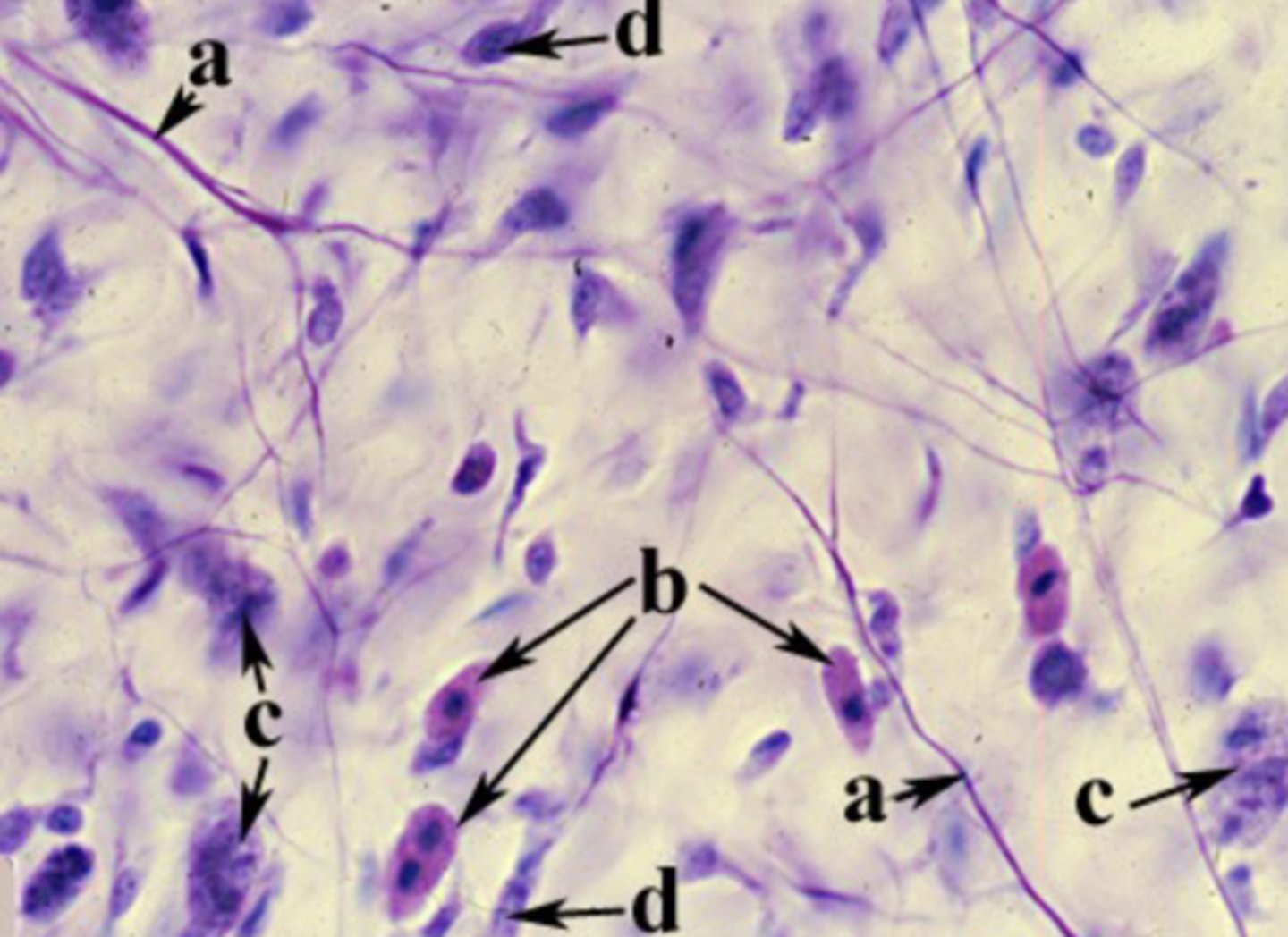
elastic fiber
What is the structure is labeled "a"?
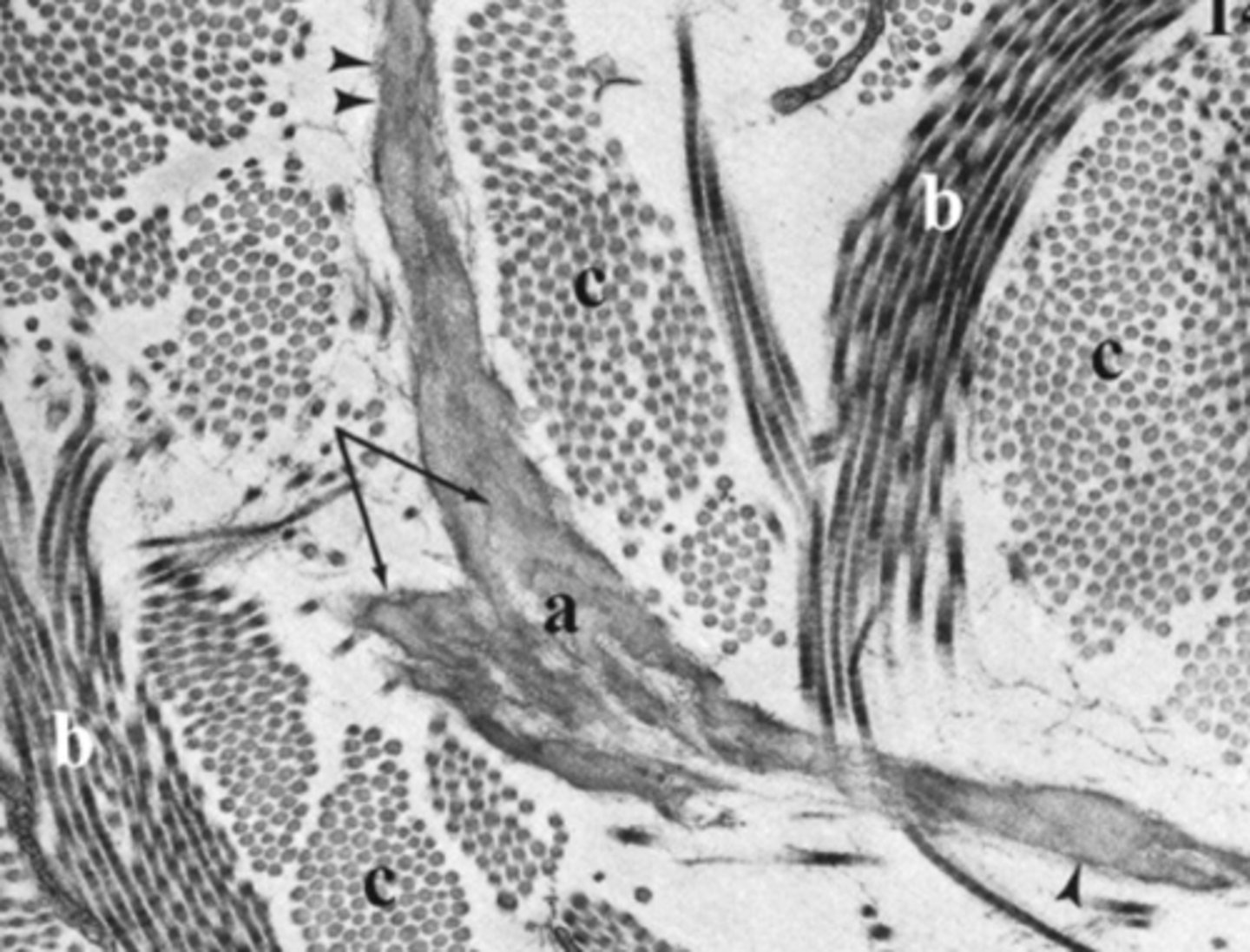
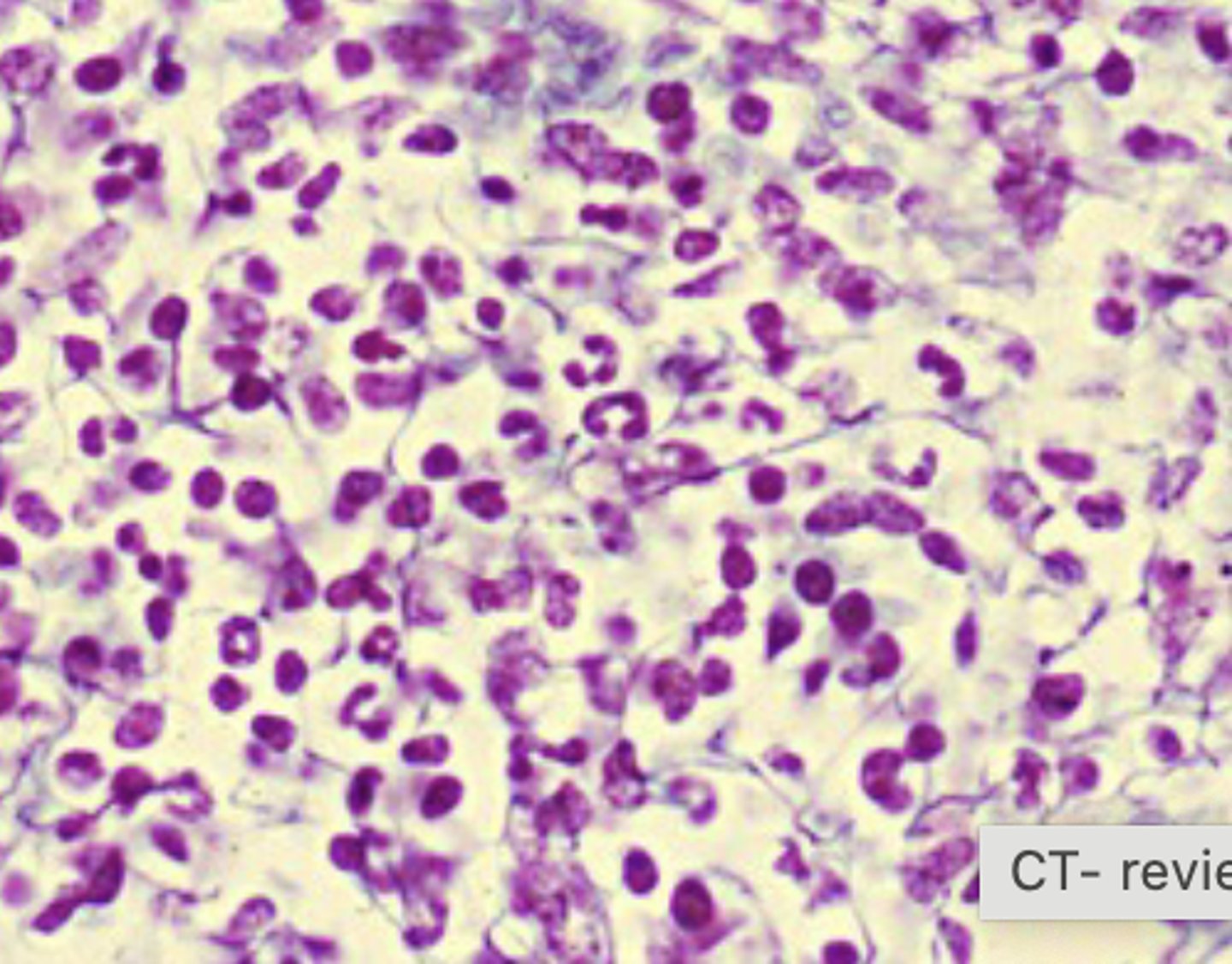
reticular
What connective tissue type is shown in this image?
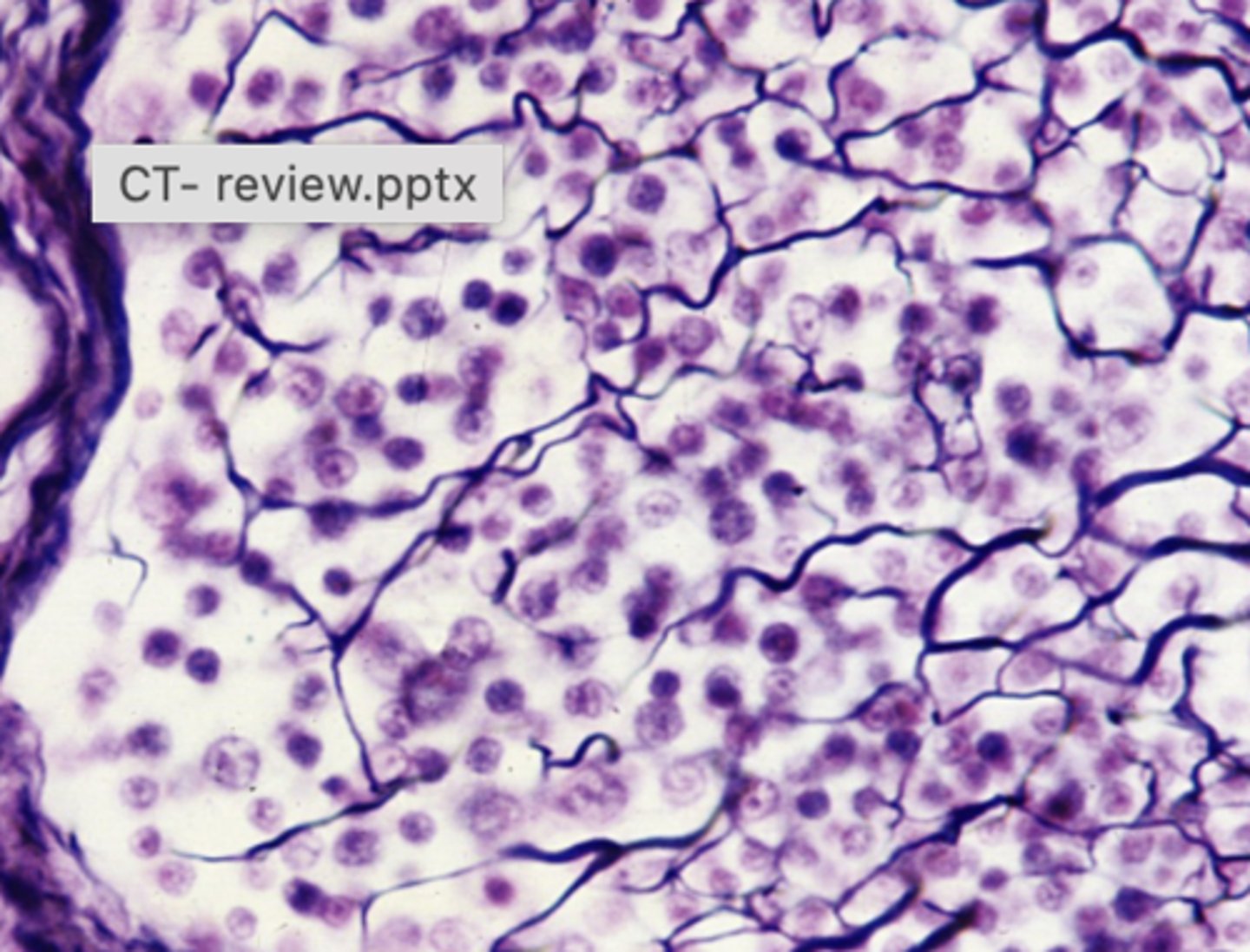
reticular
What connective tissue type is shown in this image?
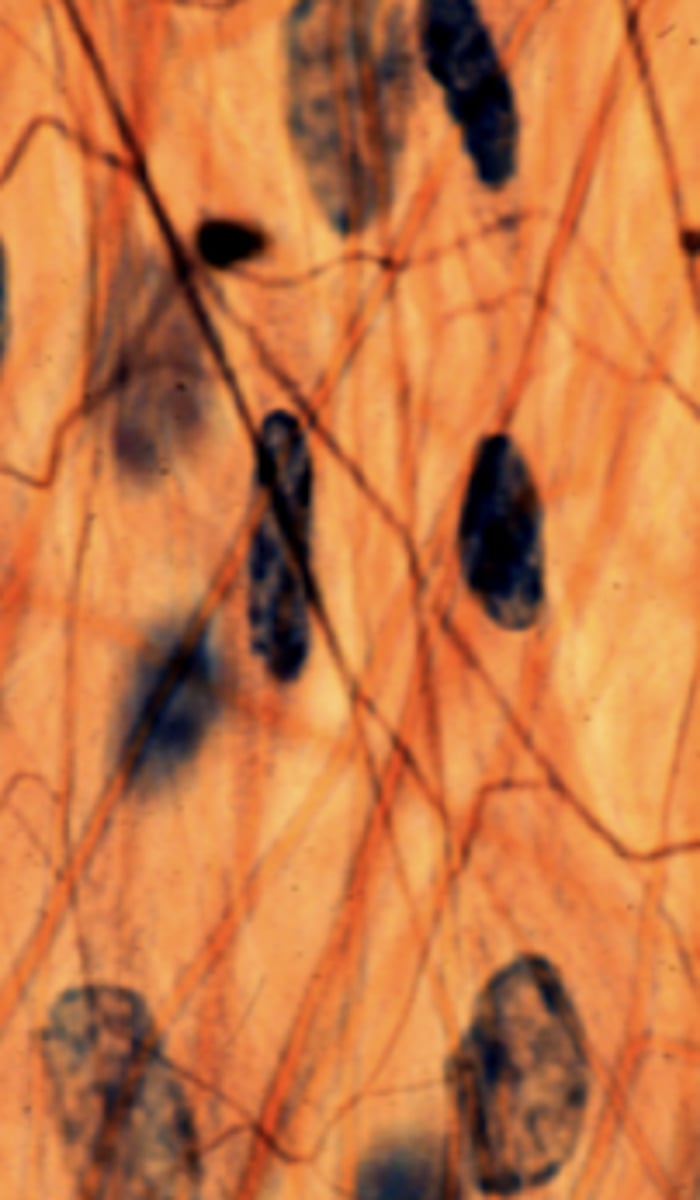
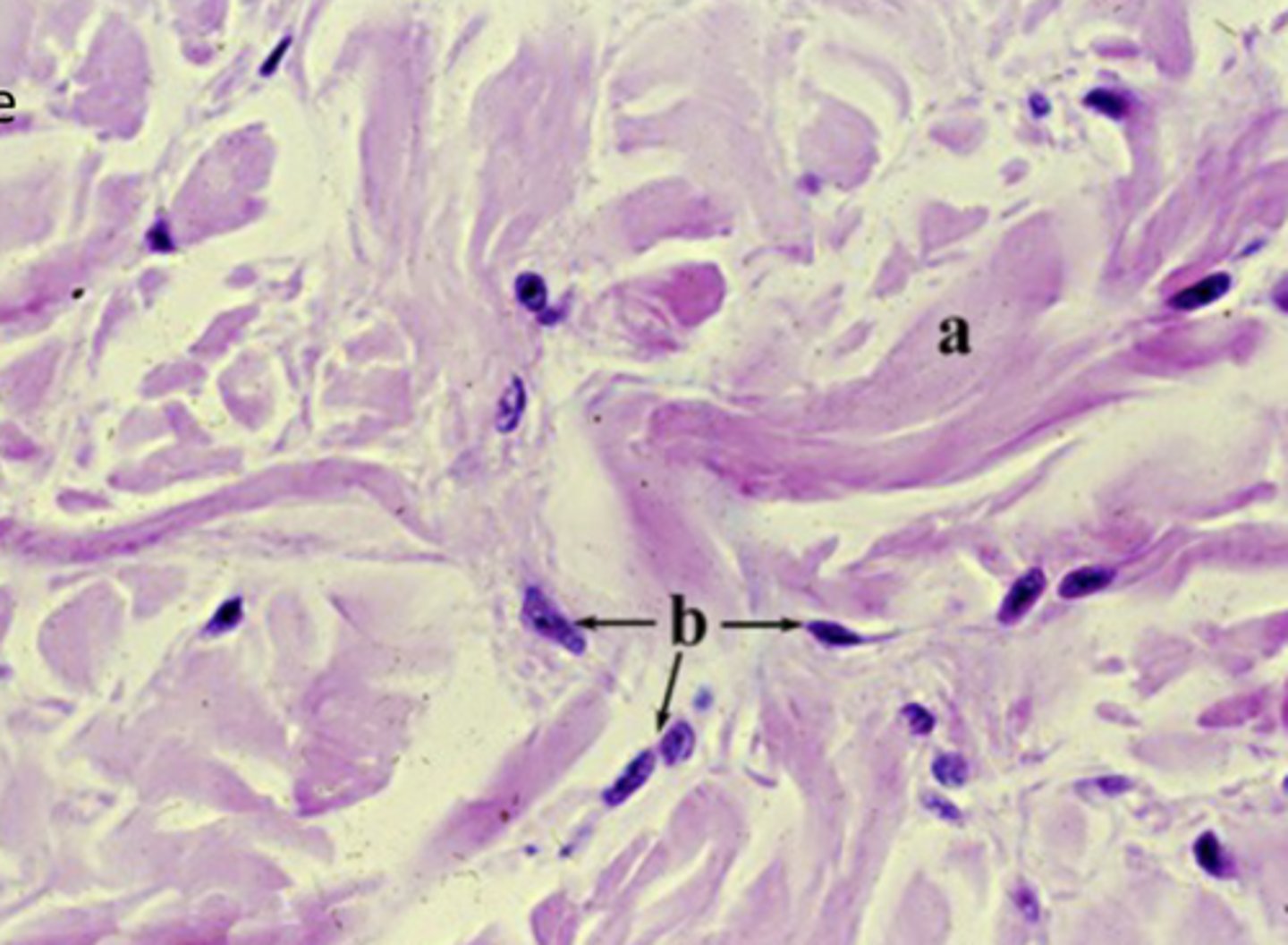
collagen fibers
what is labeled "a"?
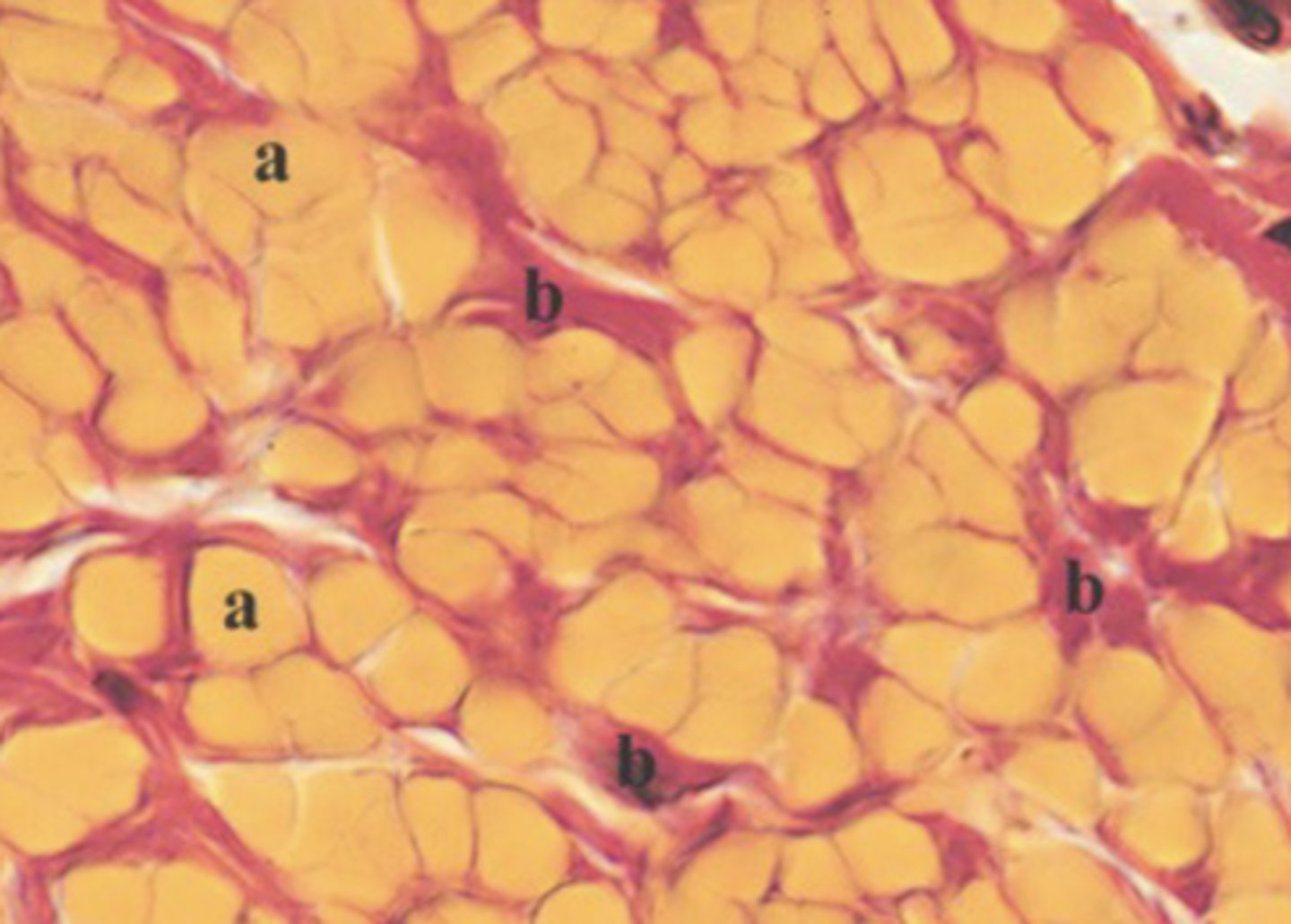
elastic
What type of connective tissue is shown in the image?
collagen fiber
what is the structure labeled "a"?

pink - collagen fibers; yellow - elastic fibers
what structure is stained pink? what structure is stained yellow?
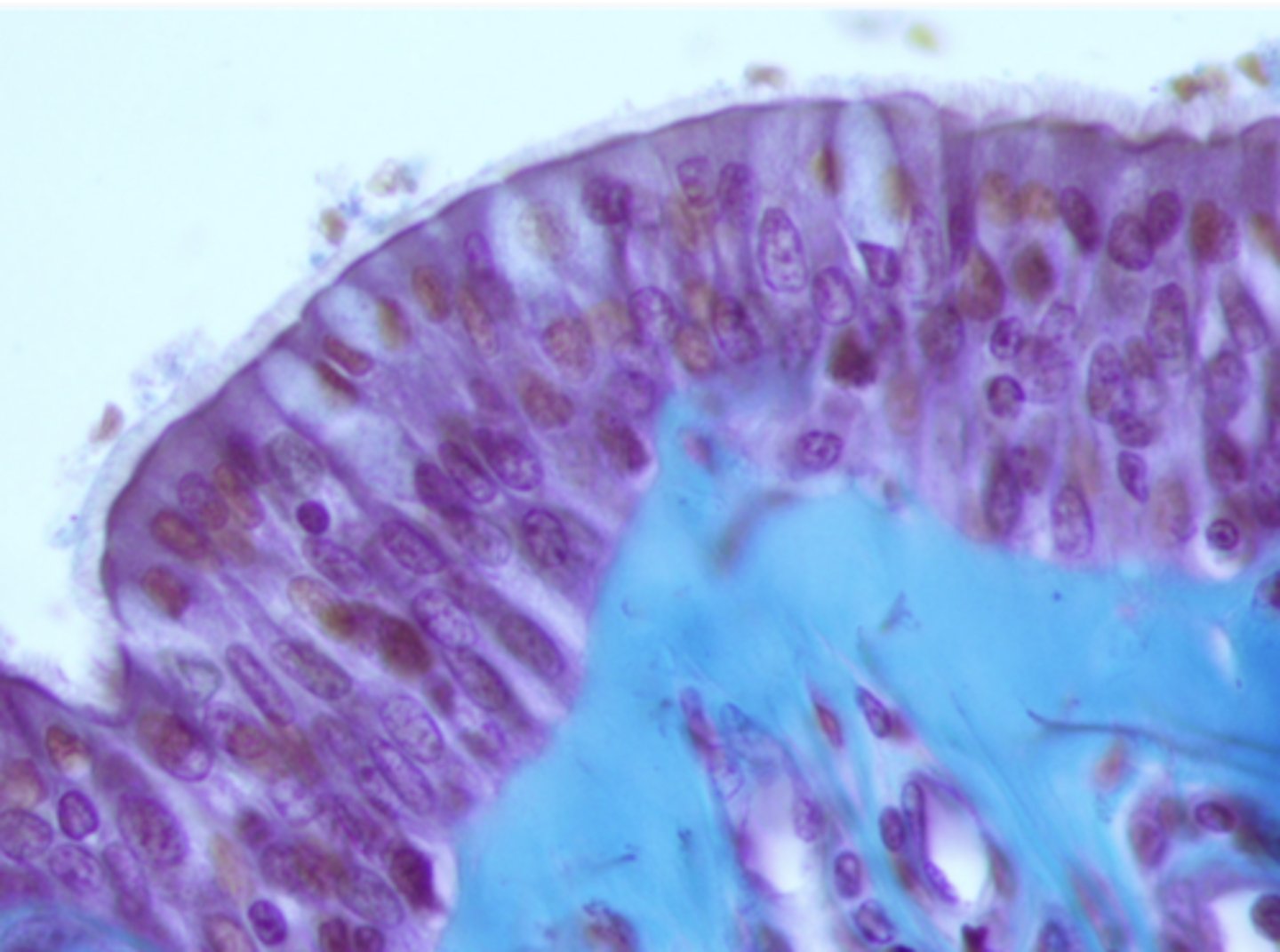
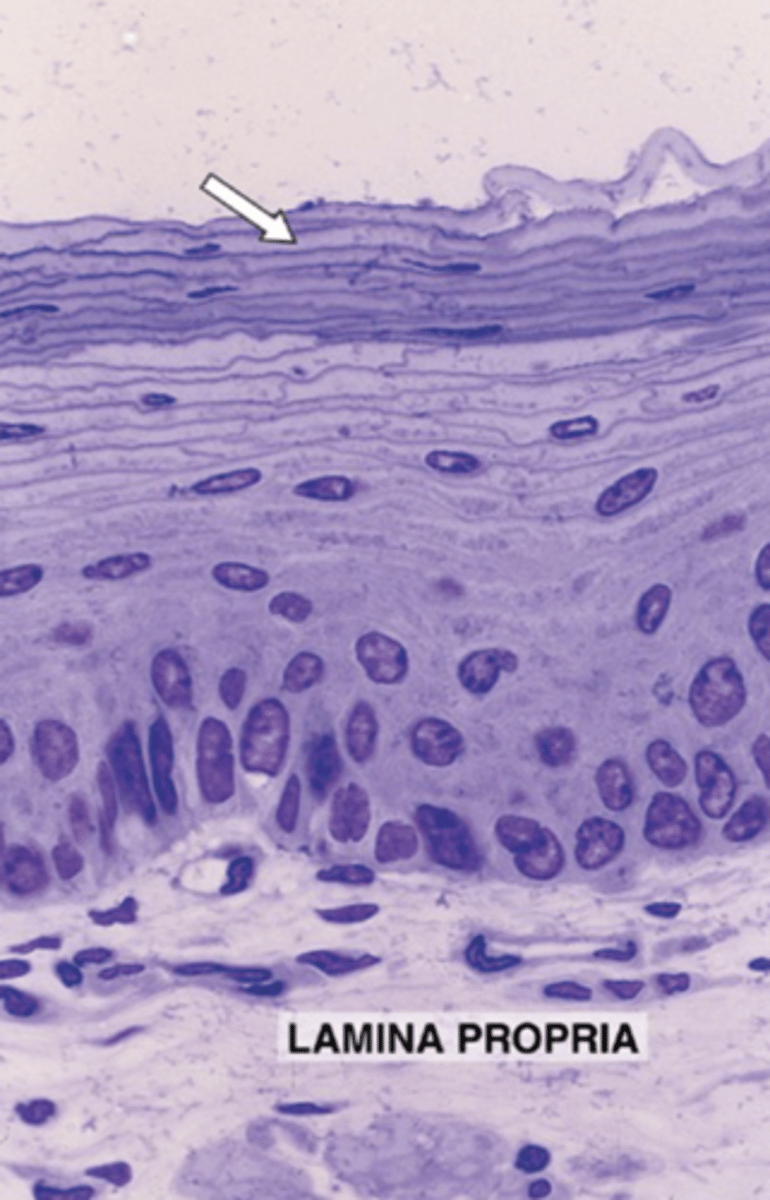
transitional epithelium
what cell type is this
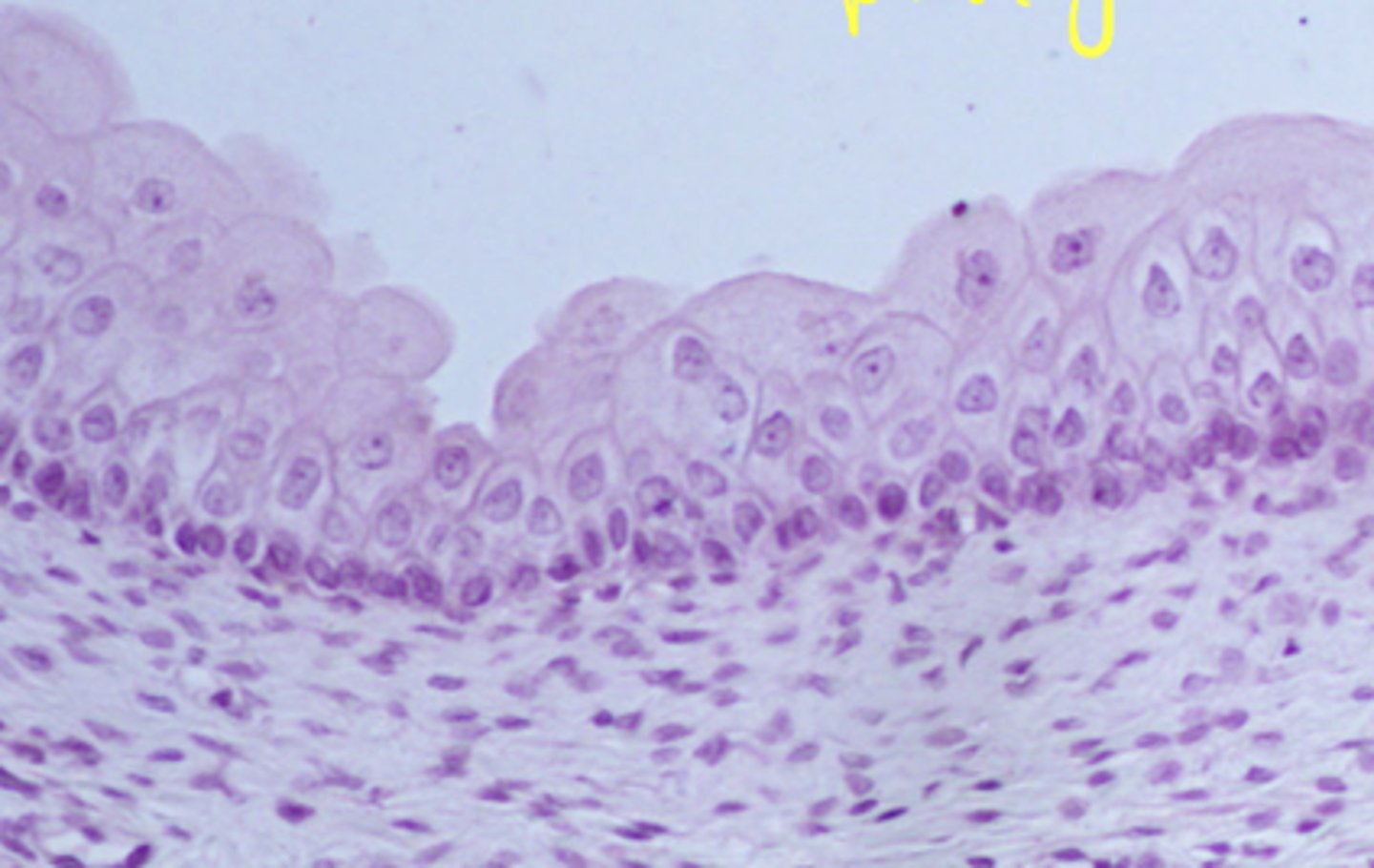
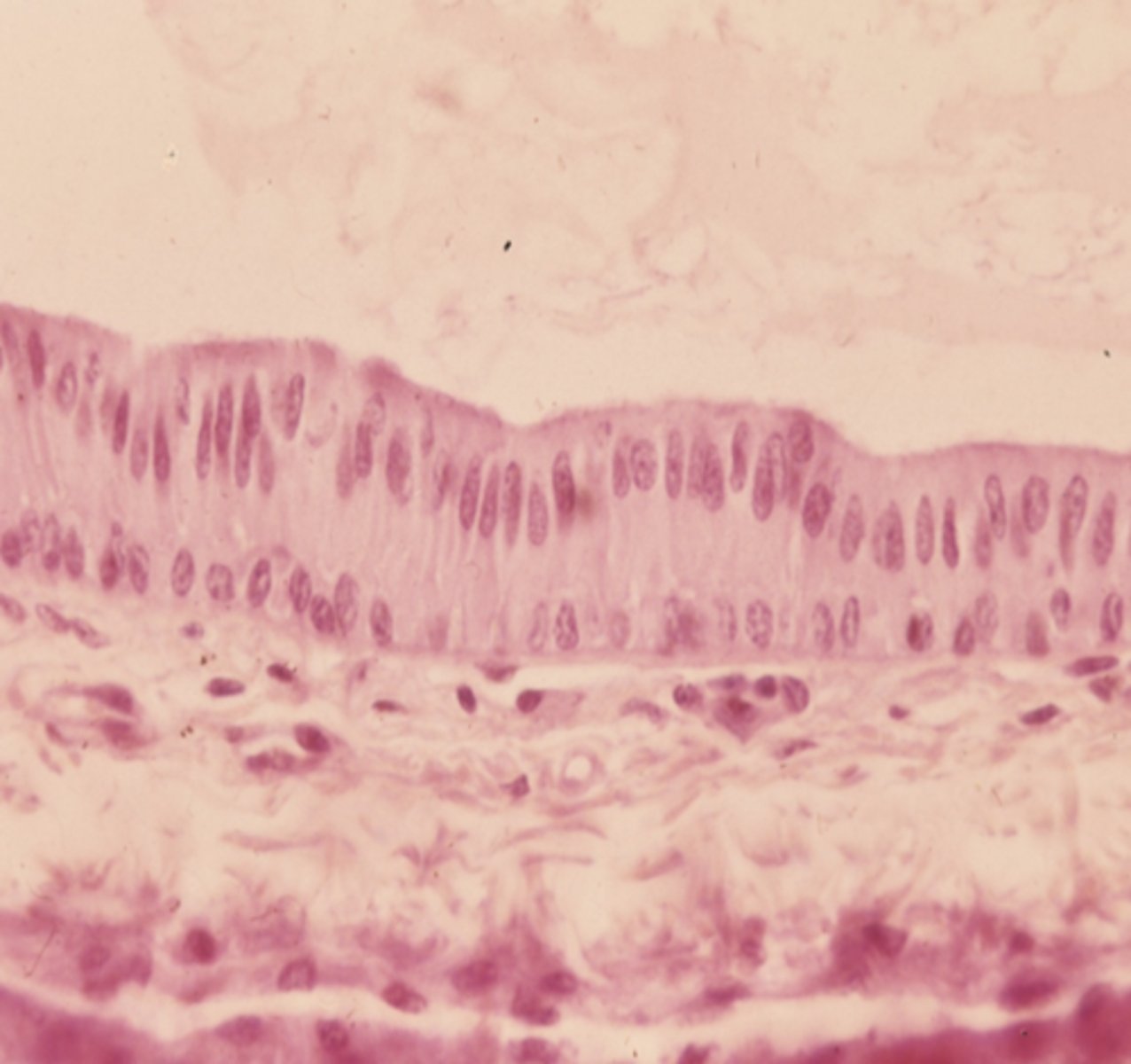
stratified columnar epithelia
what type of tissue is this
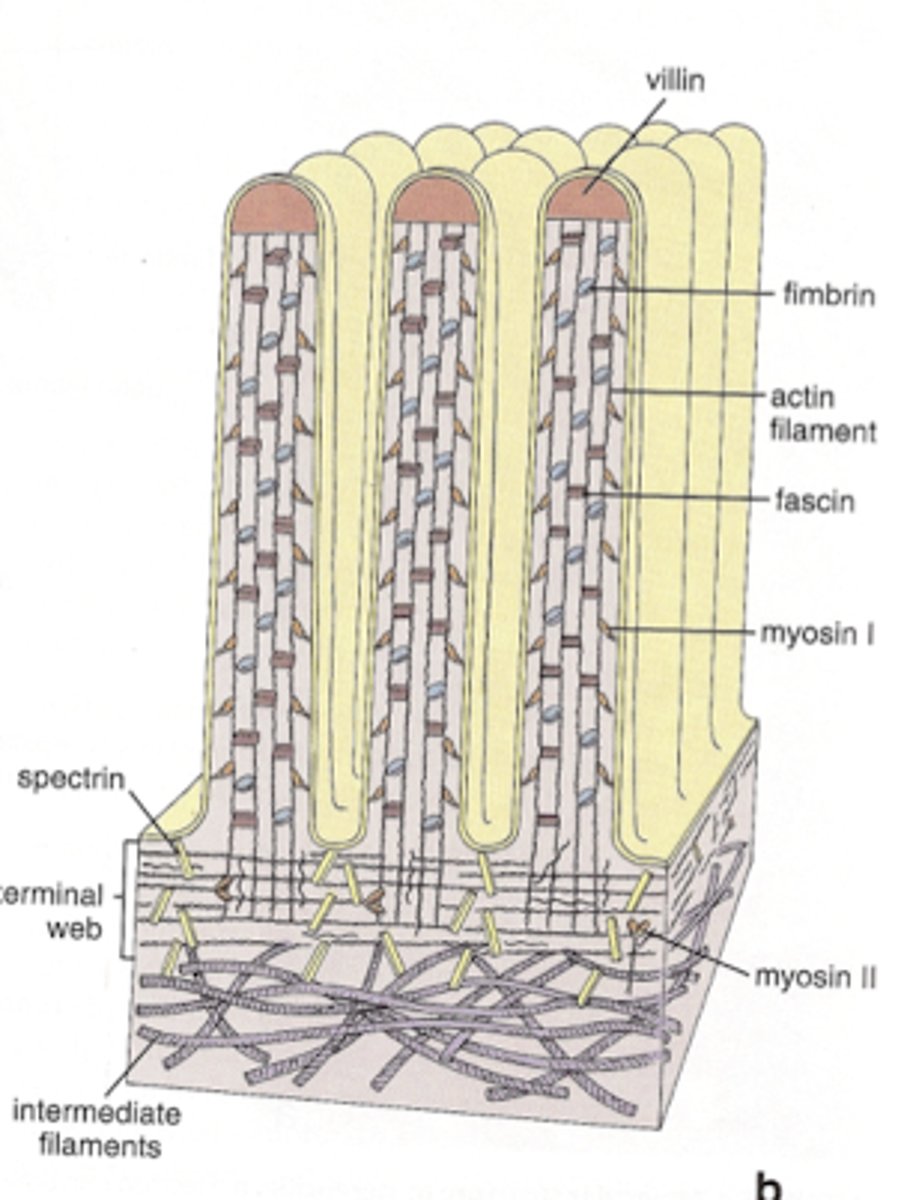
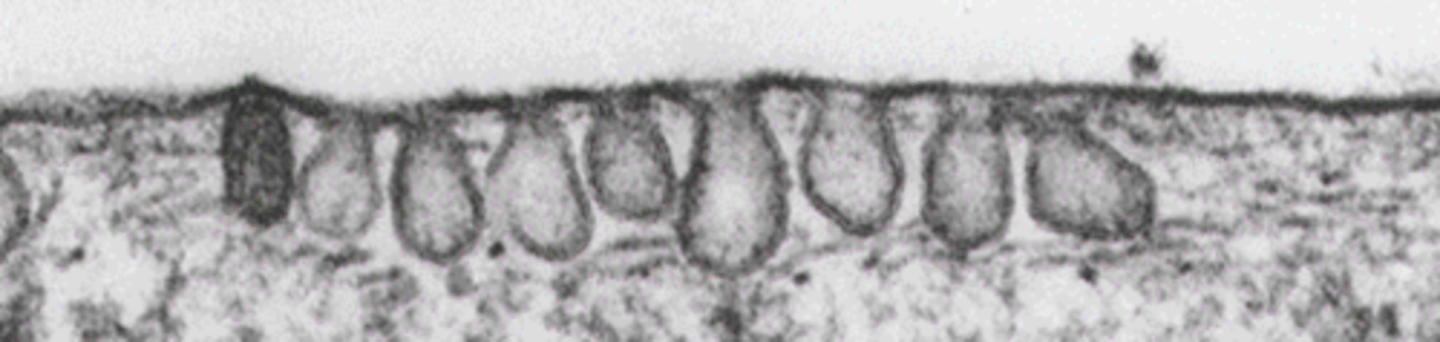
microvilli
what type of surface modification is this
mucous glands
what type of glands are shown
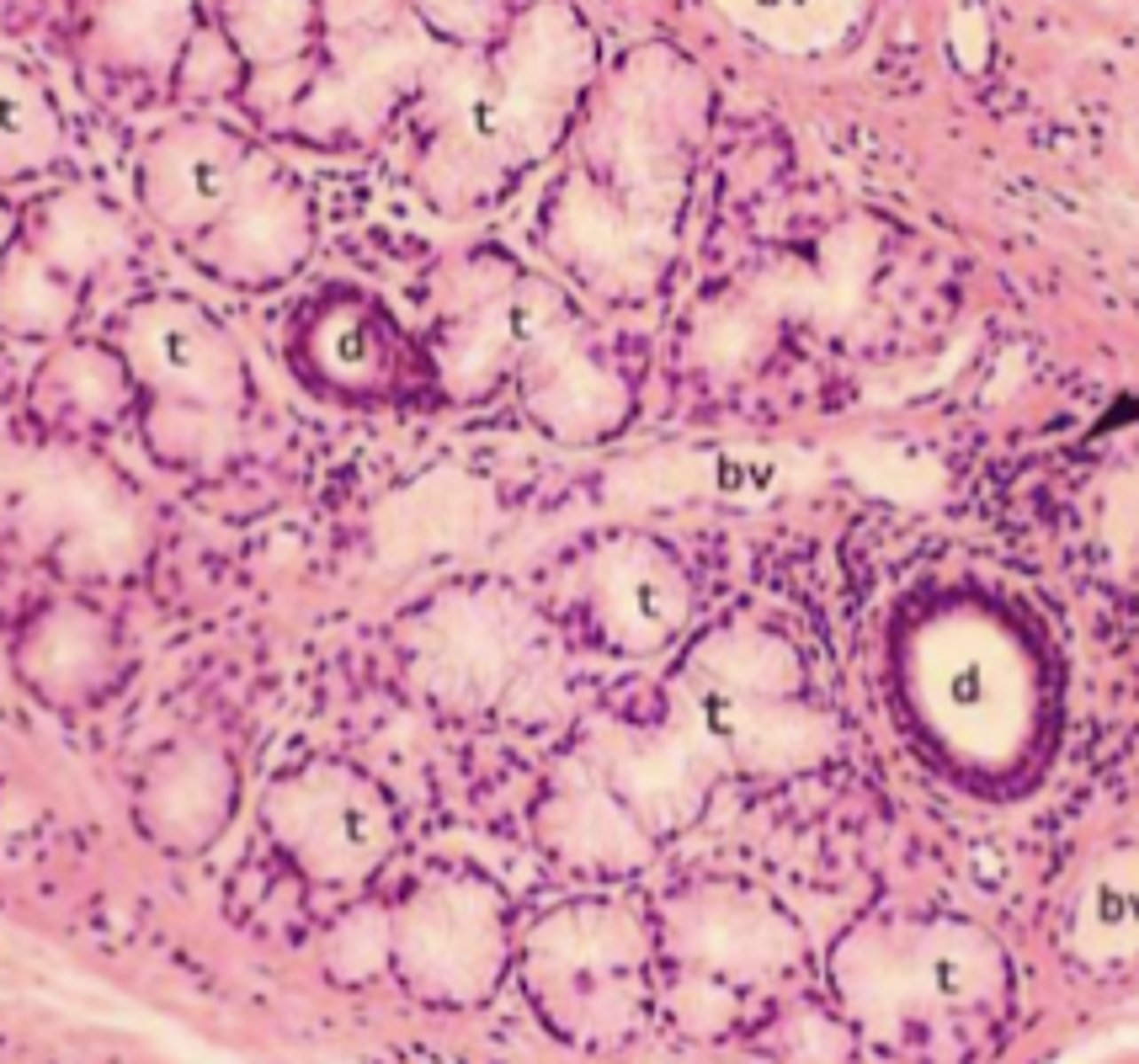
serous glands
what type of glands are shown
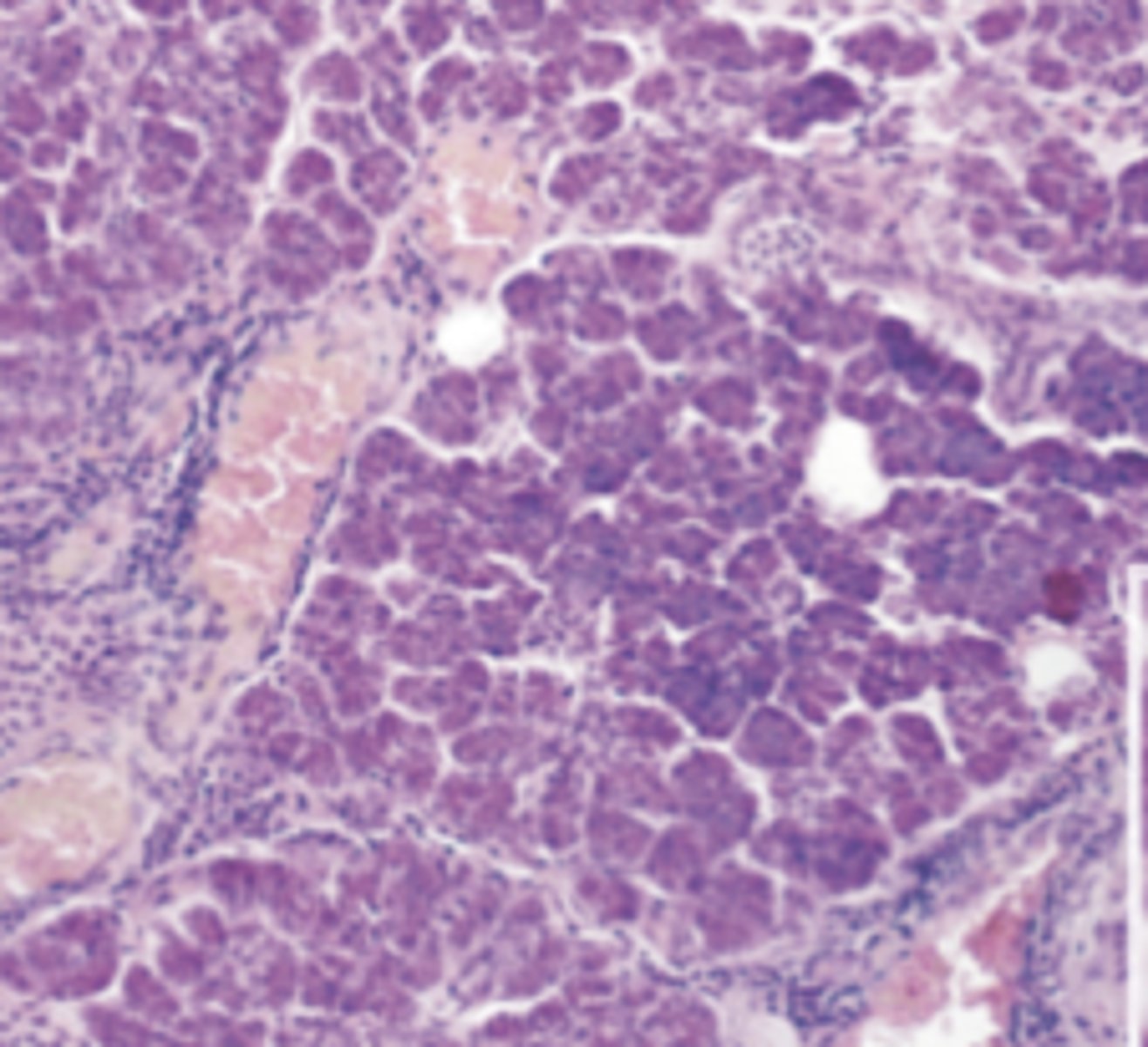
serous
what type of glands are shown
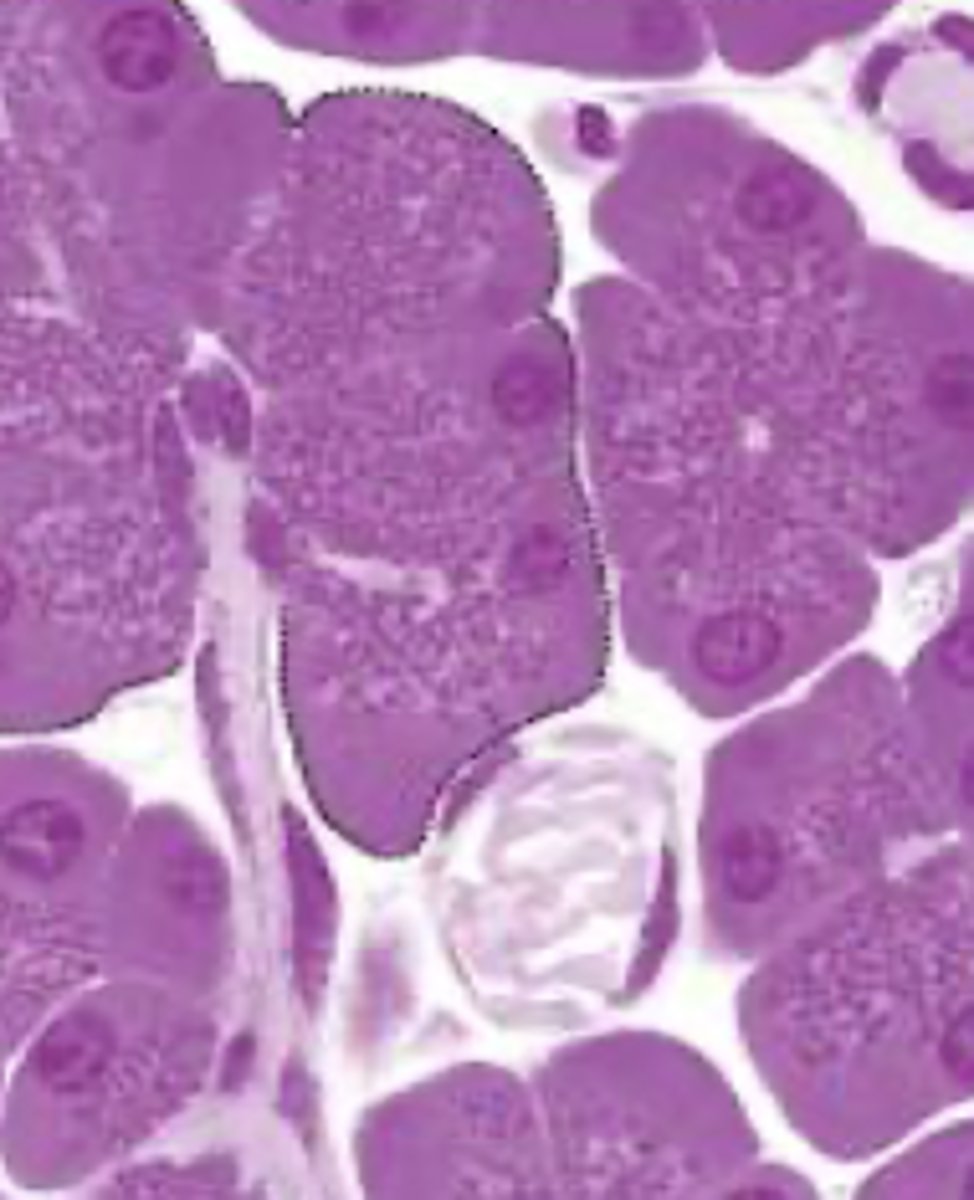
mucous
what type of glands are shown
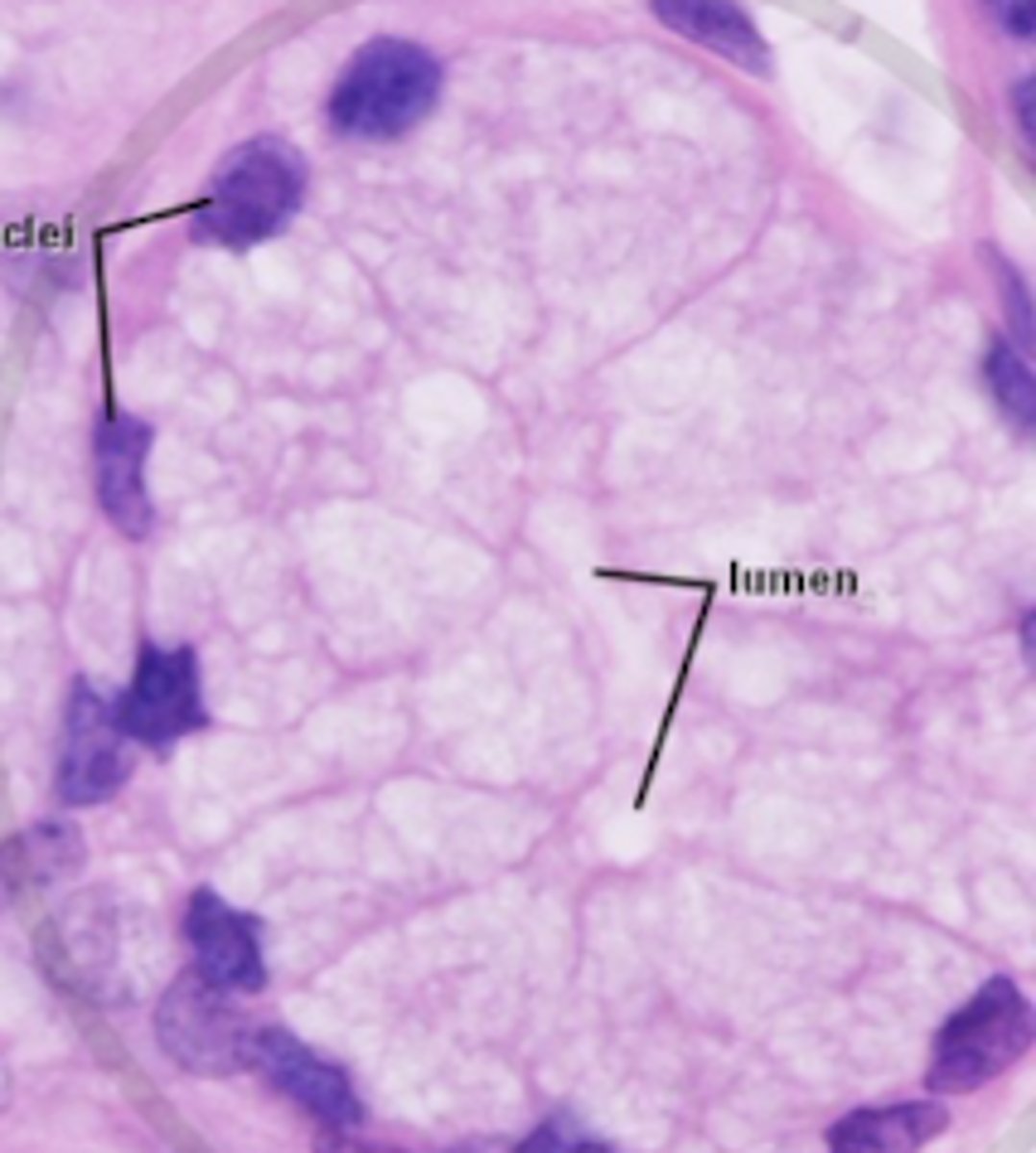
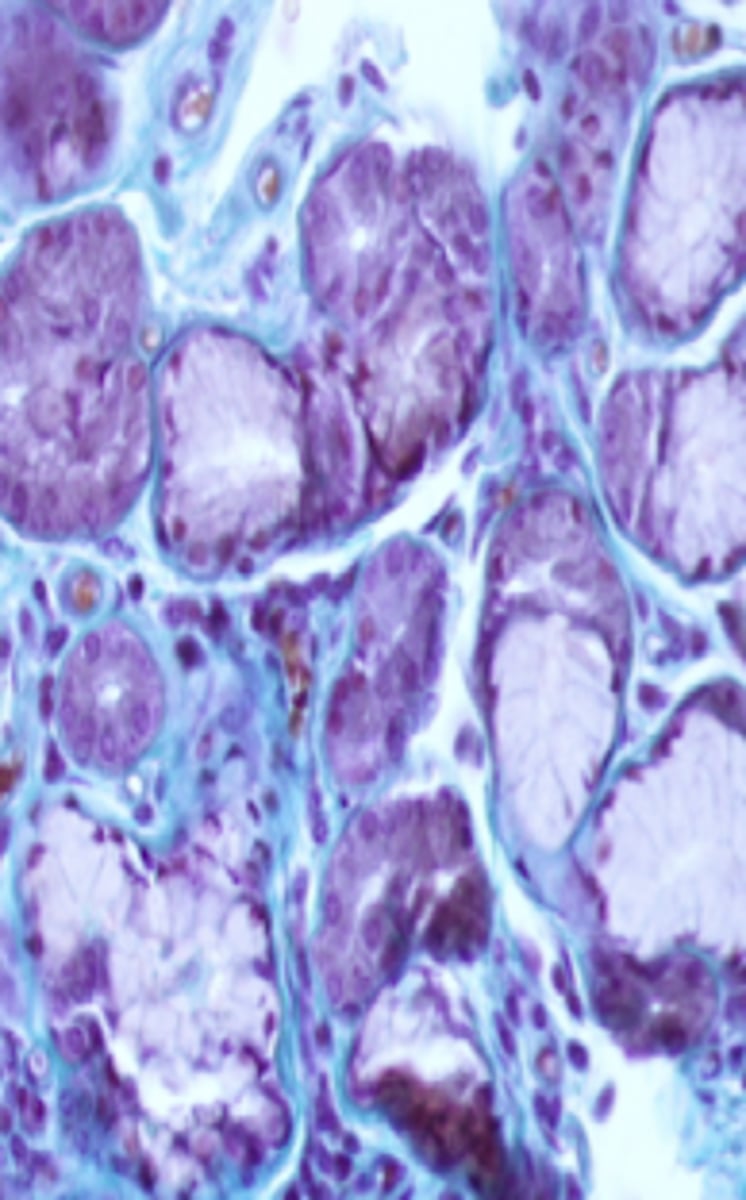
mixed - serous (dark purple) and mucous (light purple)
what type of glands are shown
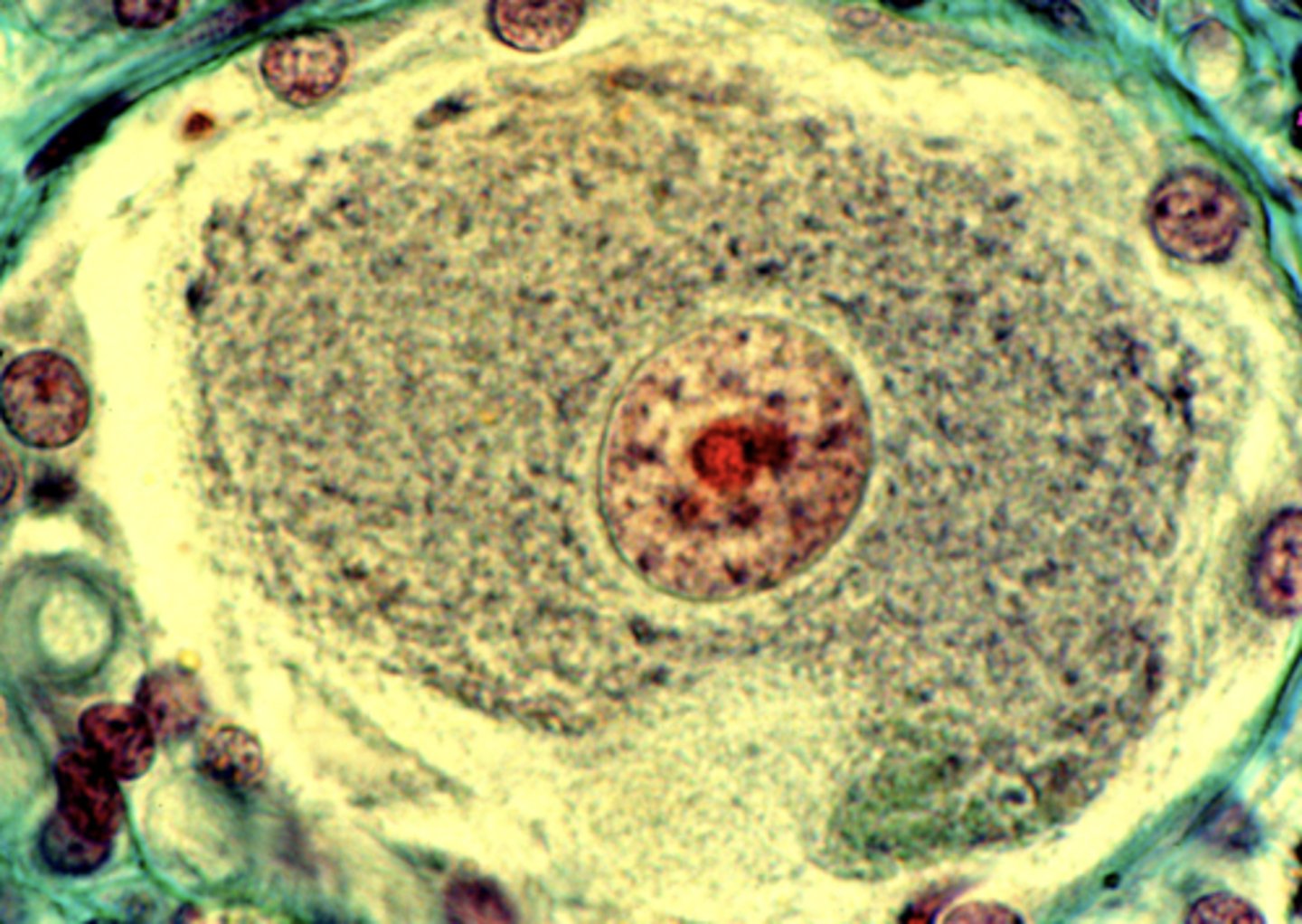
ACTIVE - there is lots of euchromatin in the cell (rather than dark, inactive heterochromatin)
is this cell active or inactive?
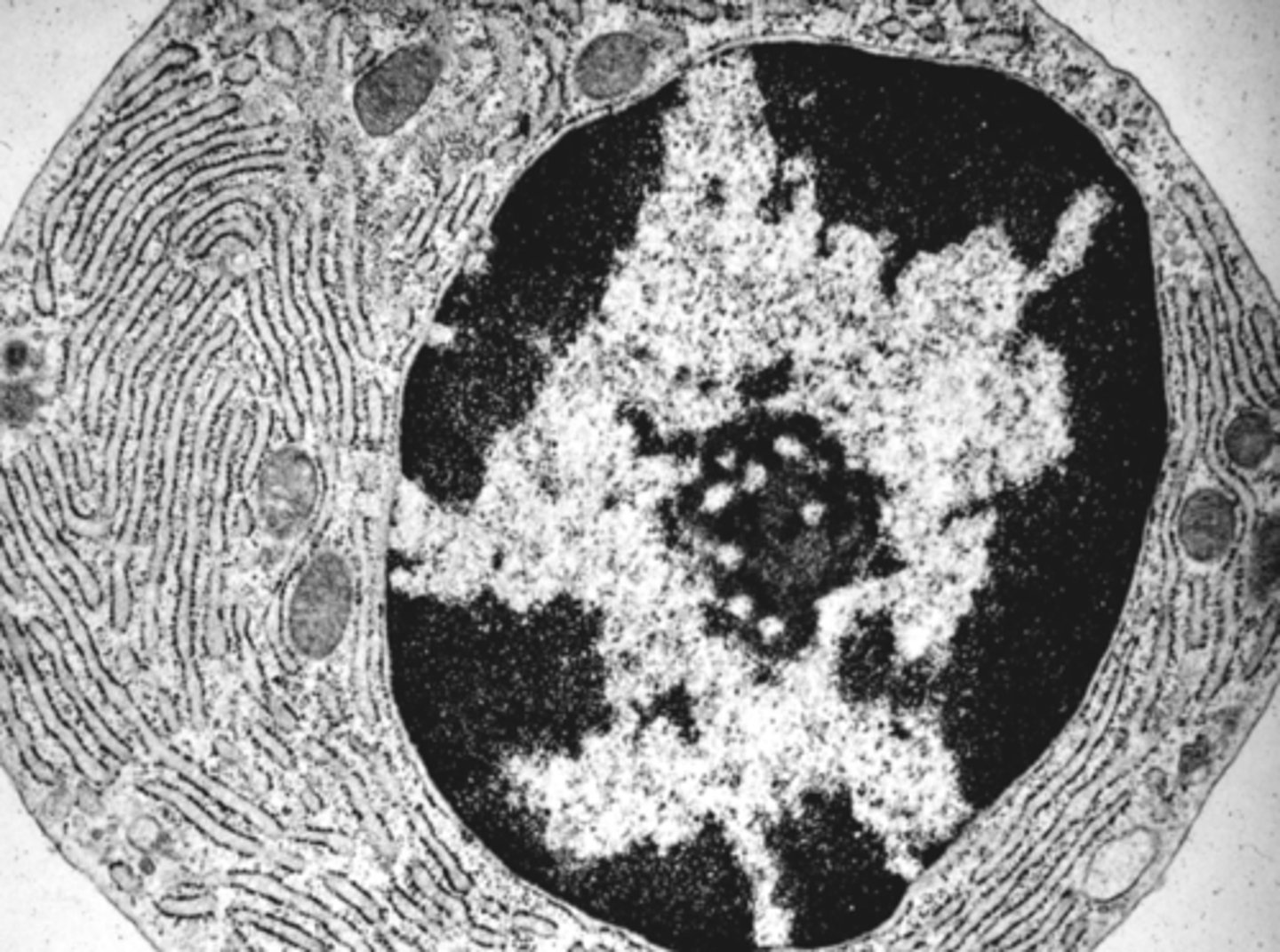
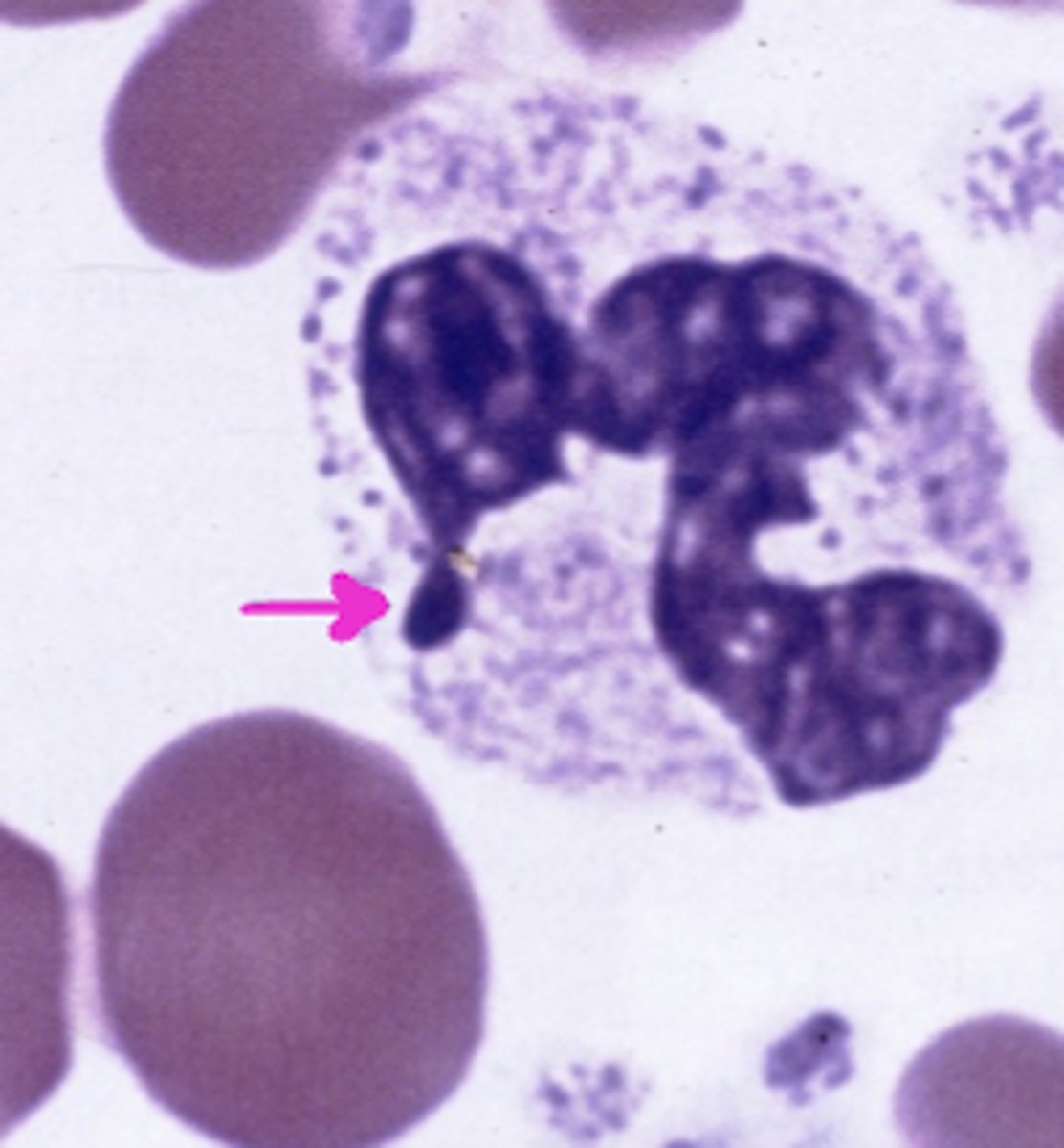
Barr body
what does the arrow point to?
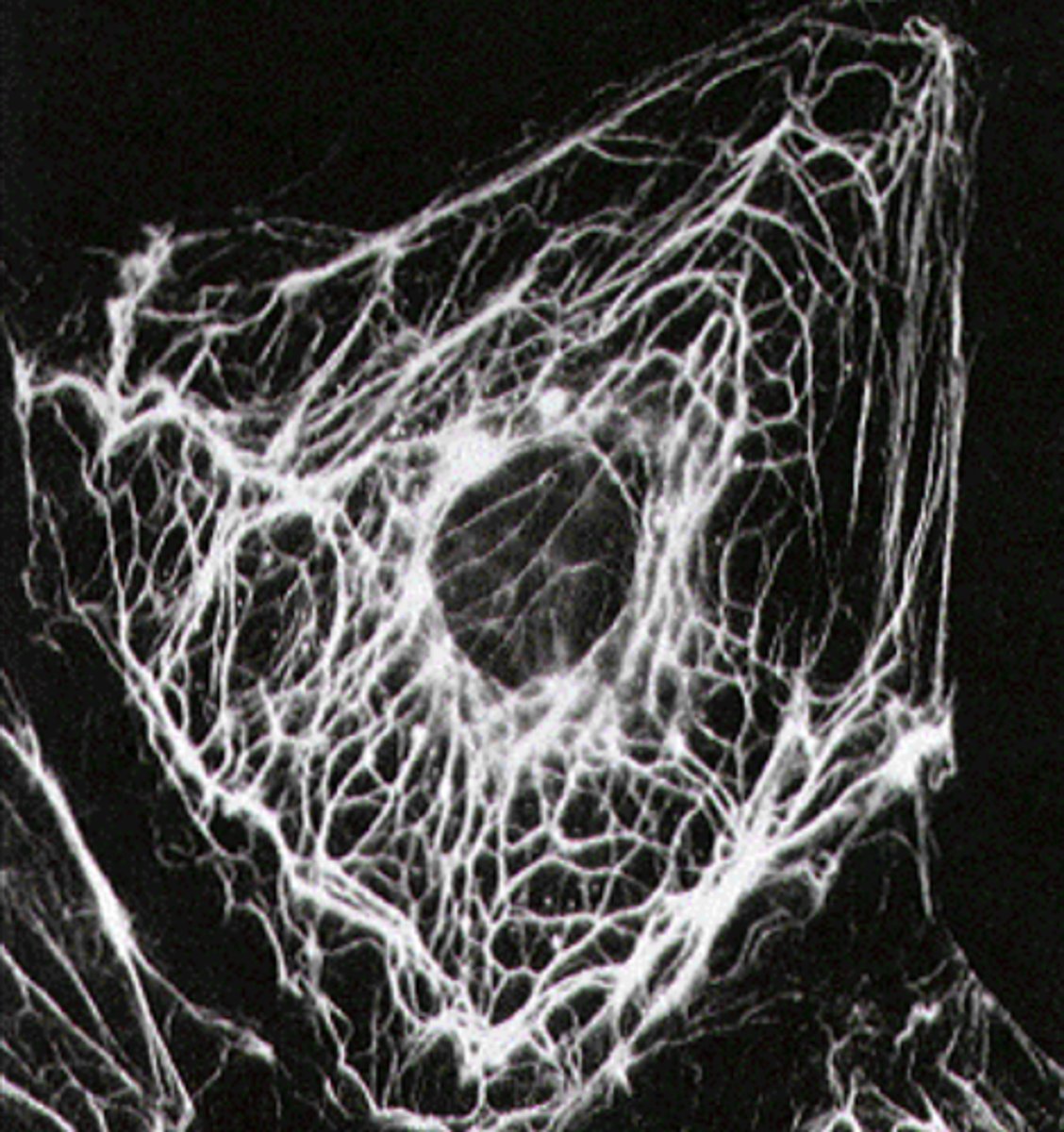
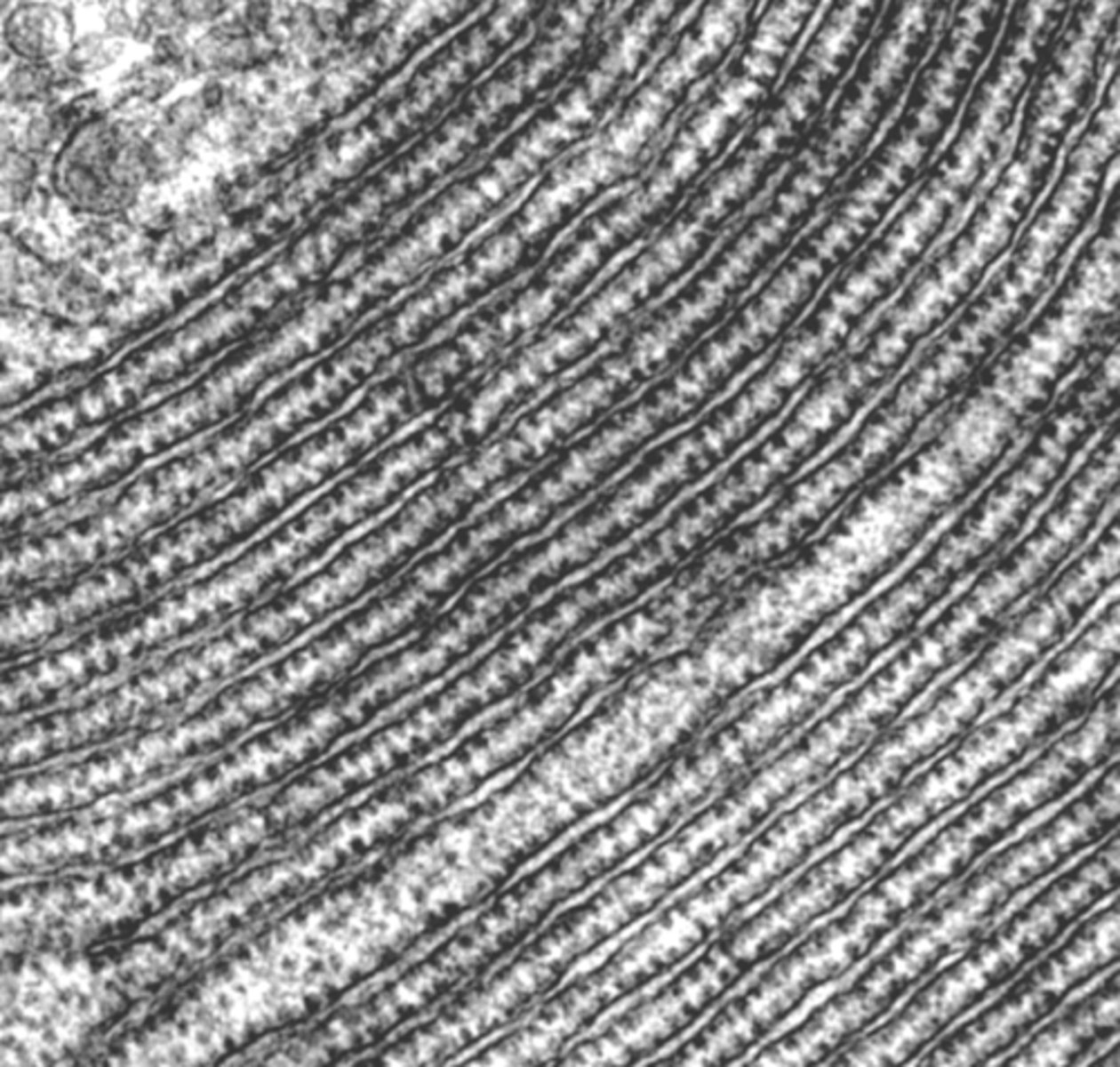
Intermediate filaments
what cytoskeletal structure is this?
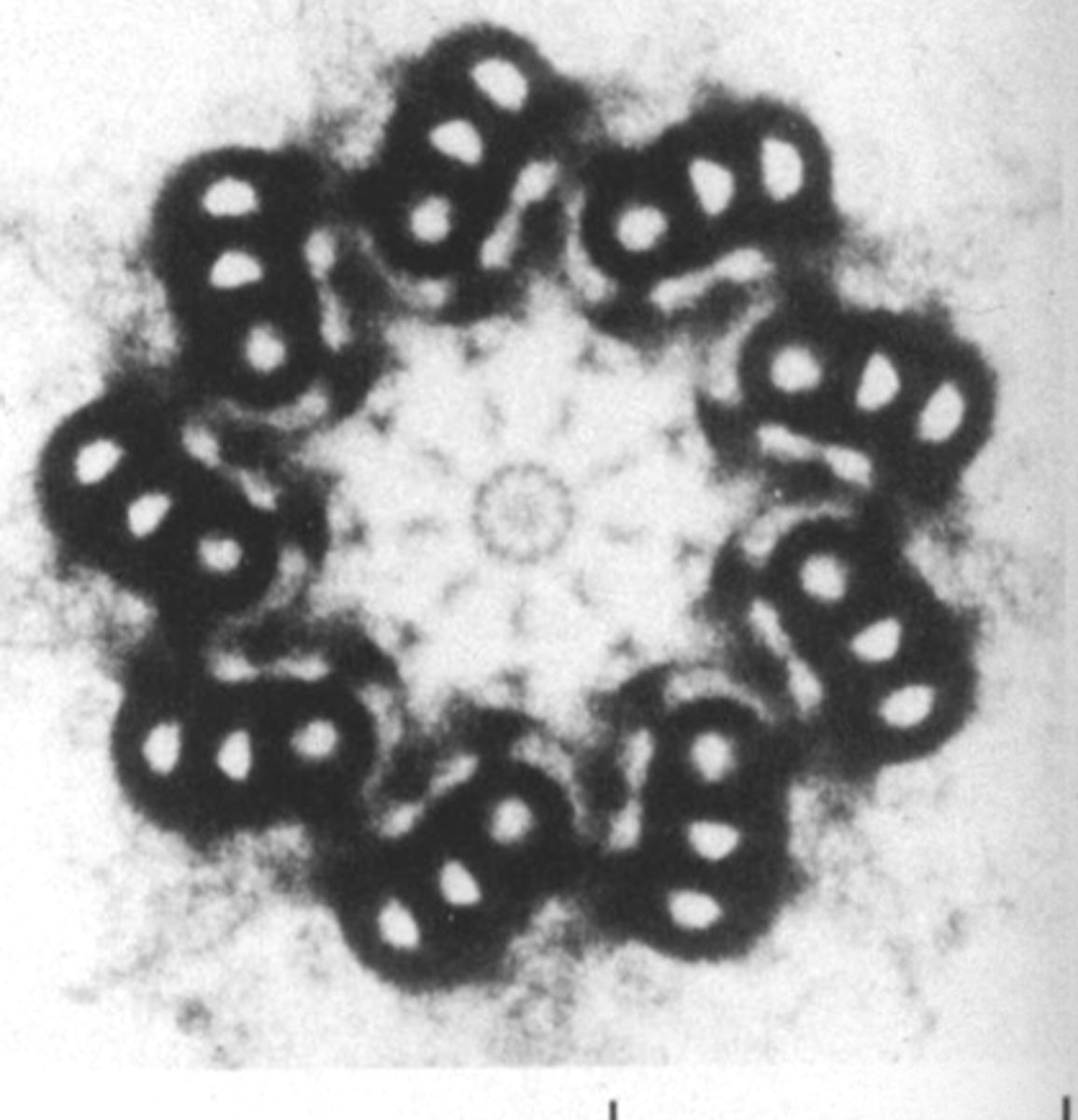
centriole - composed of 9 triplet Mts
what cell structure is this
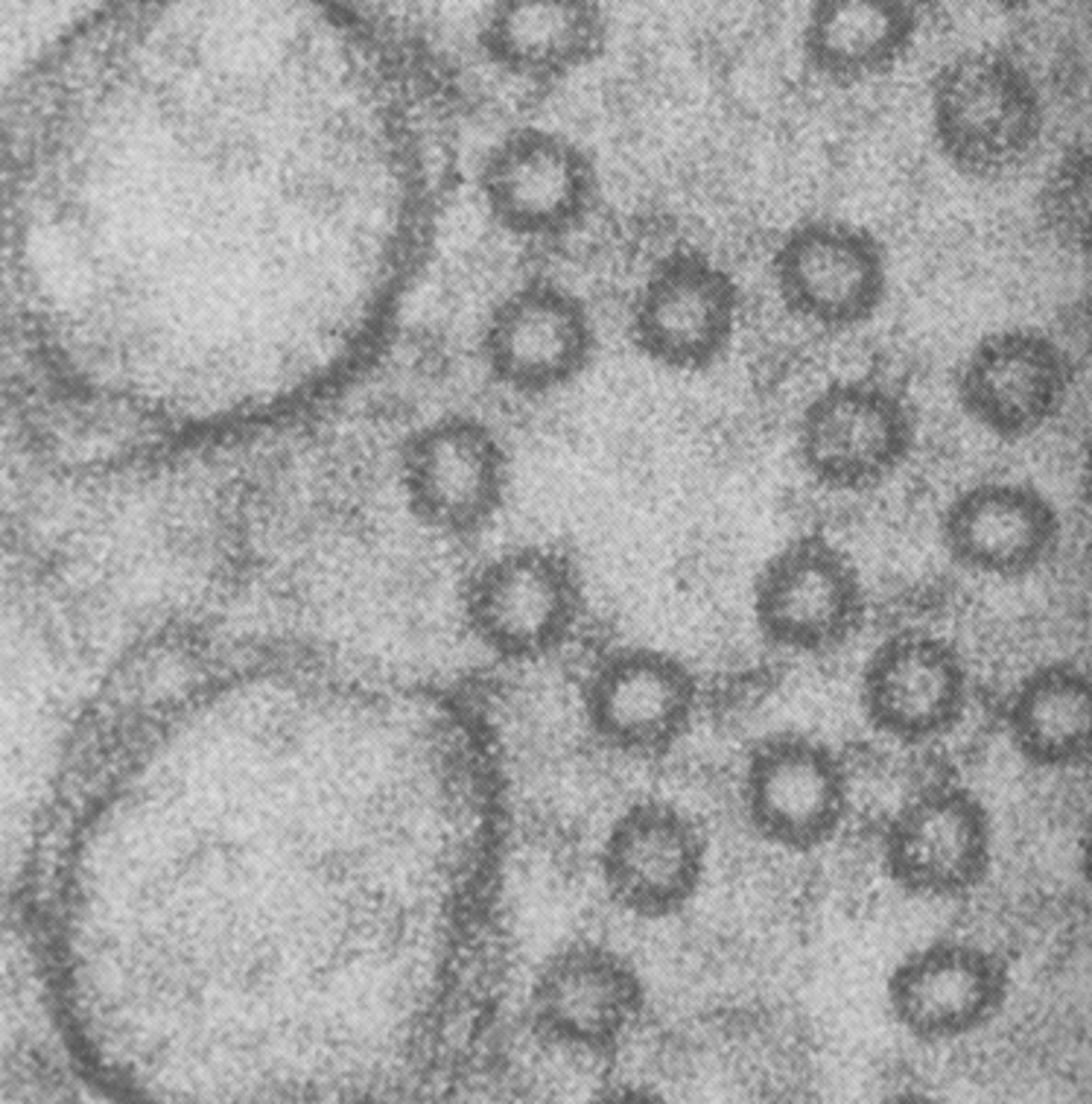
microtubule associated proteins (MAPs)
what are the smaller circles in this image
cancerous - NOT NORMAL
is this a normal or cancerous cell?
smooth ER
what cell organelle is shown

rough ER
what cell organelle is shown
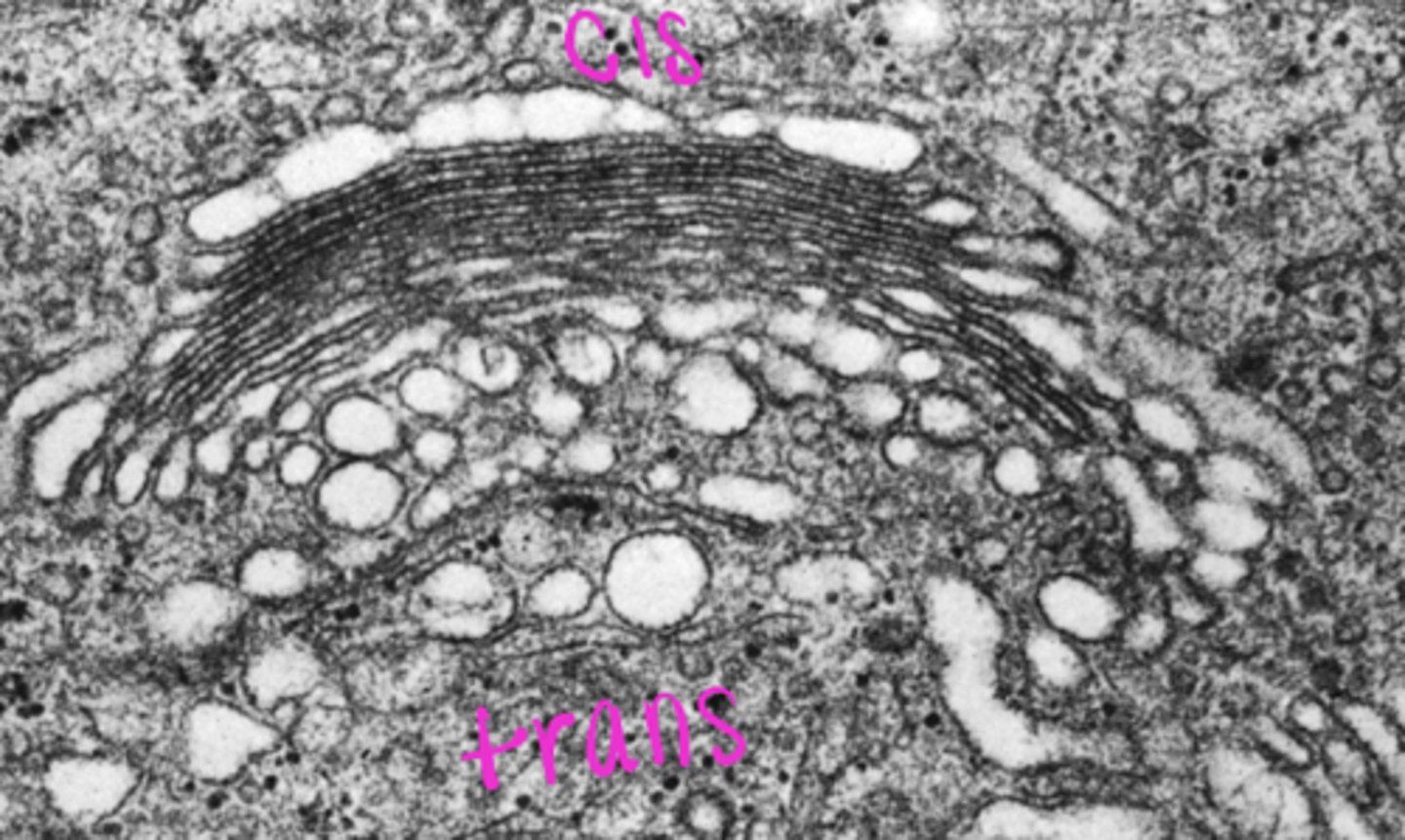
Golgi apparatus
what cell organelle is this
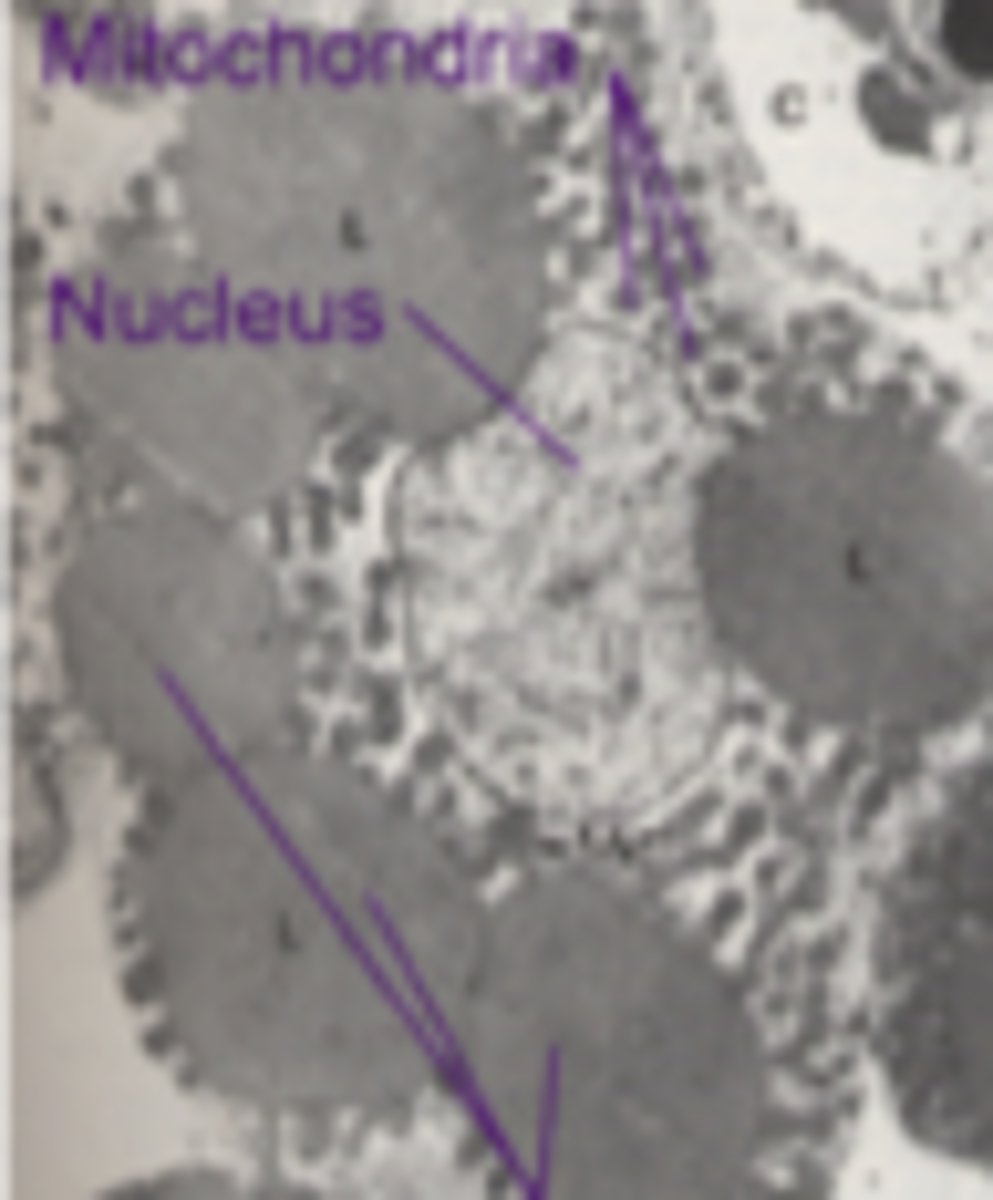
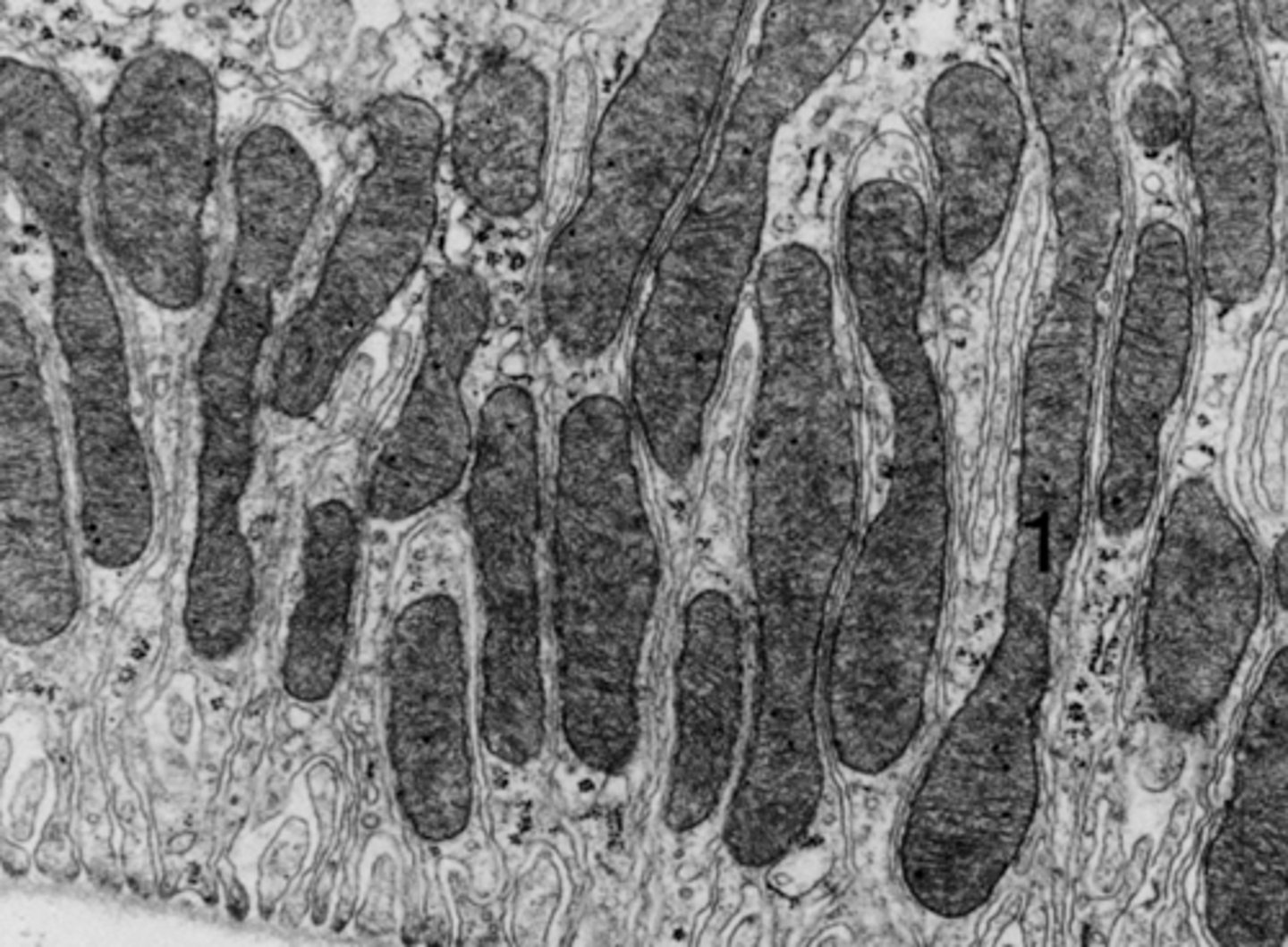
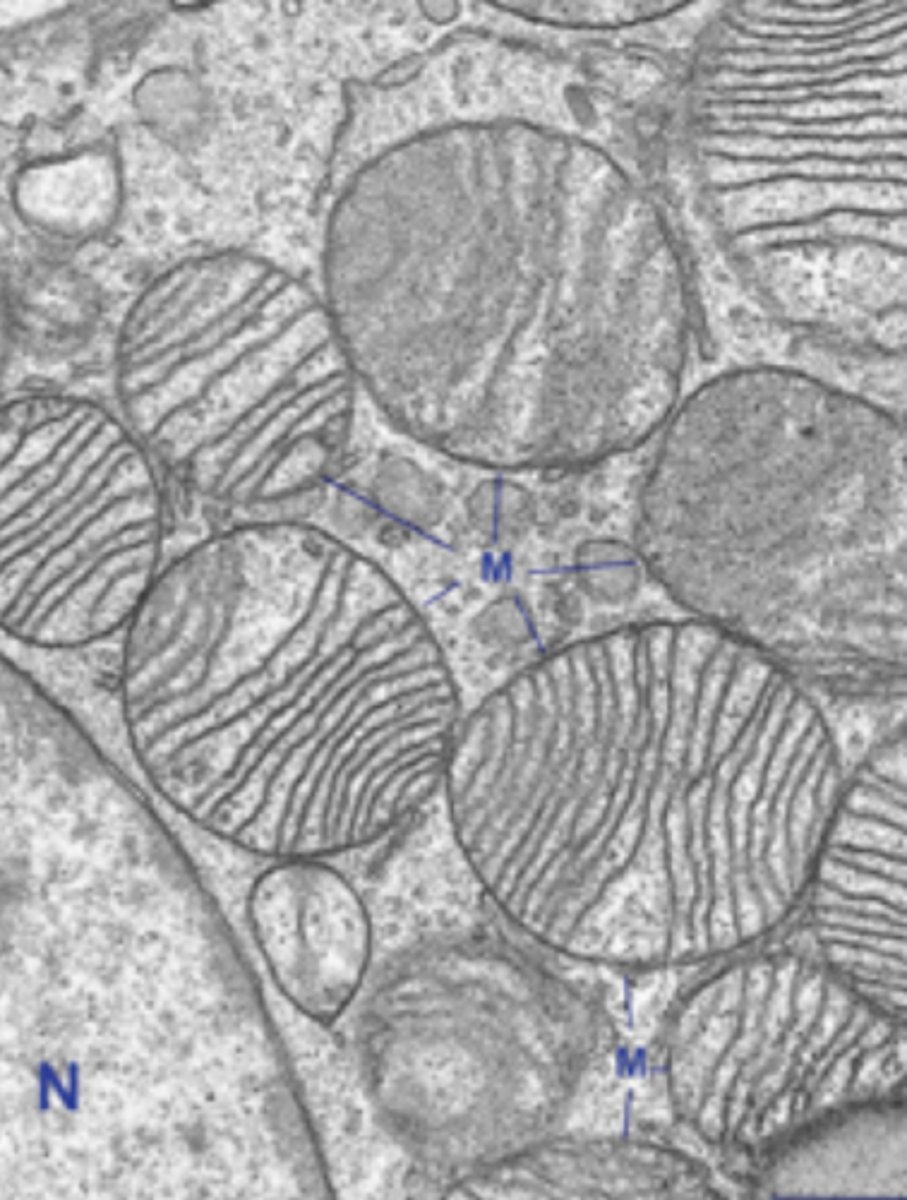
mitocondria
what cell organelle is shown (stained with PTAH)
mitochondria
what cell organelle is shown
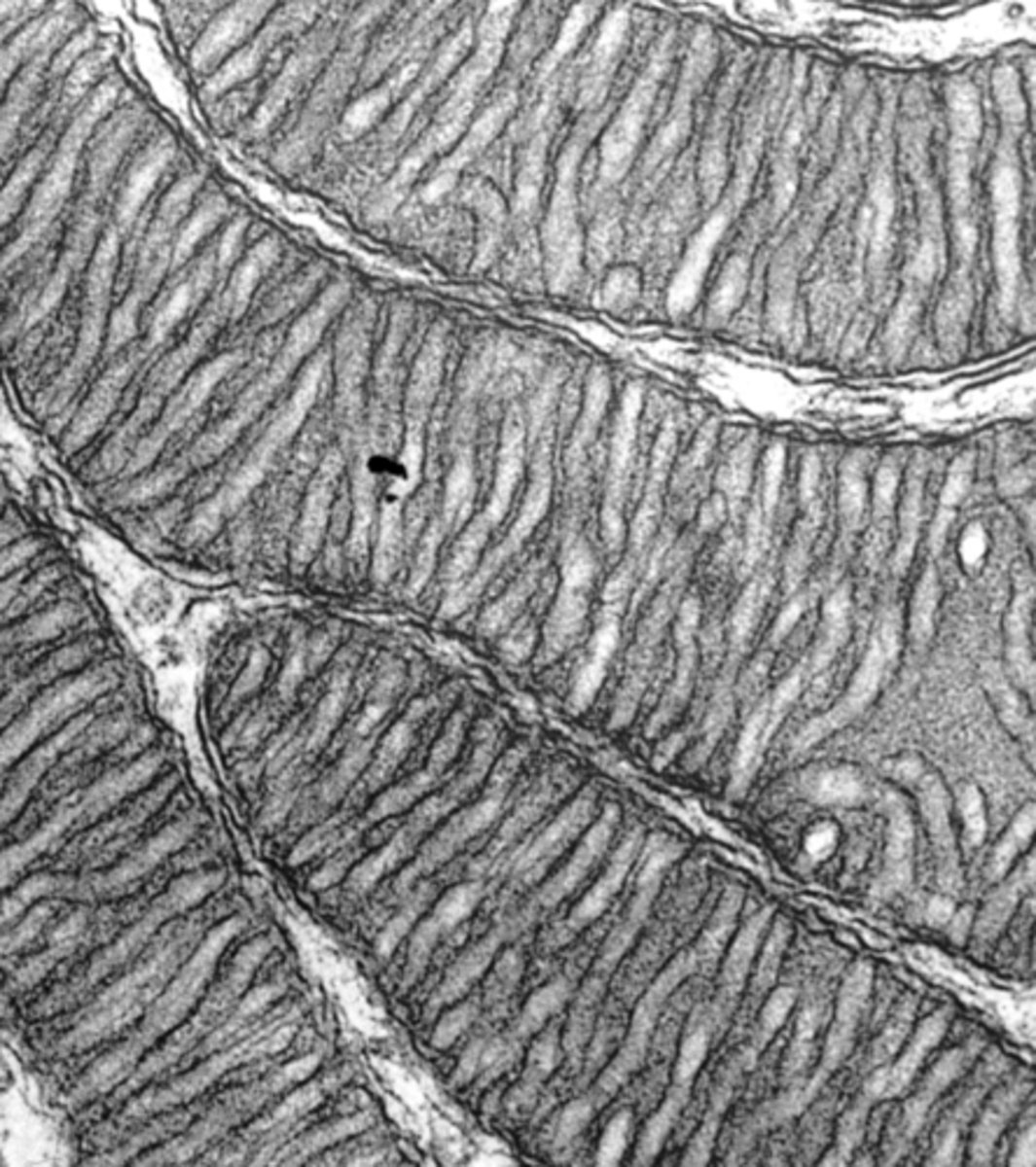
cristae
what organelle structure is shown within these mitochondria?
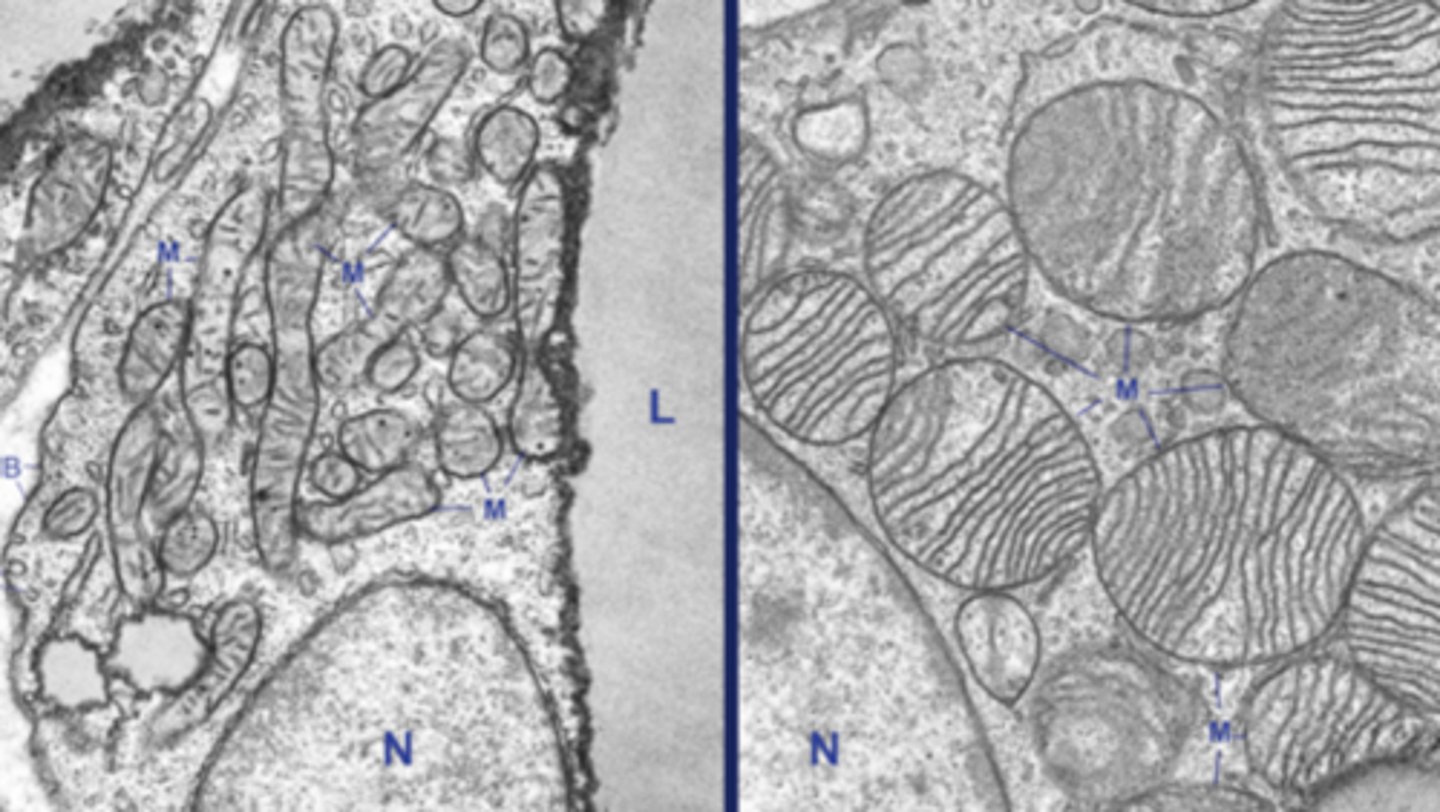
Left - WHITE
Right - BROWN
what type of mitochondria is shown on the right vs the left?
brown mitochondria - specialized for heat production
what function is this type of mitochondria specialized for?
clathrin-coated vesicle - performs mediated endocytosis
what is the function of this type of vesicle
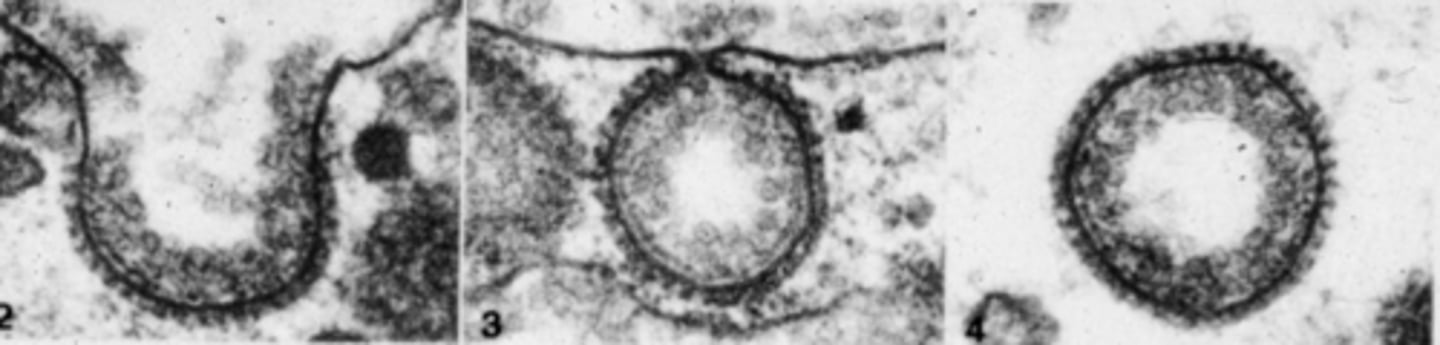
caveolae - function in clathrin-independent endocytosis; also important for transcytosis
what is this structure and what is its function
melanin
What is the brown staining in this cell?
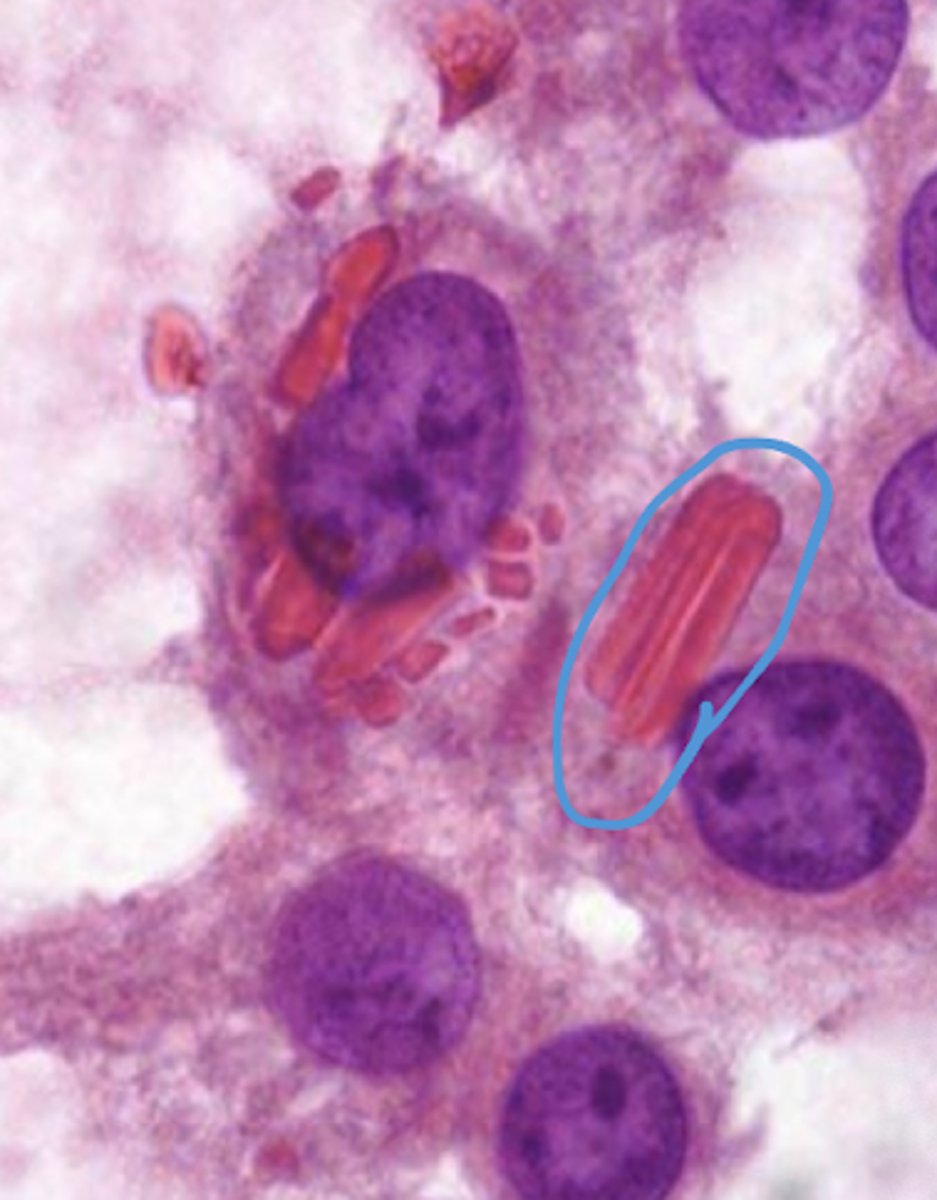
crystals (byproduct in steroid formation)
what is the structure shown
simple cuboidal
what type of epithelium is this
simple columnar
what type of epithelium is shown
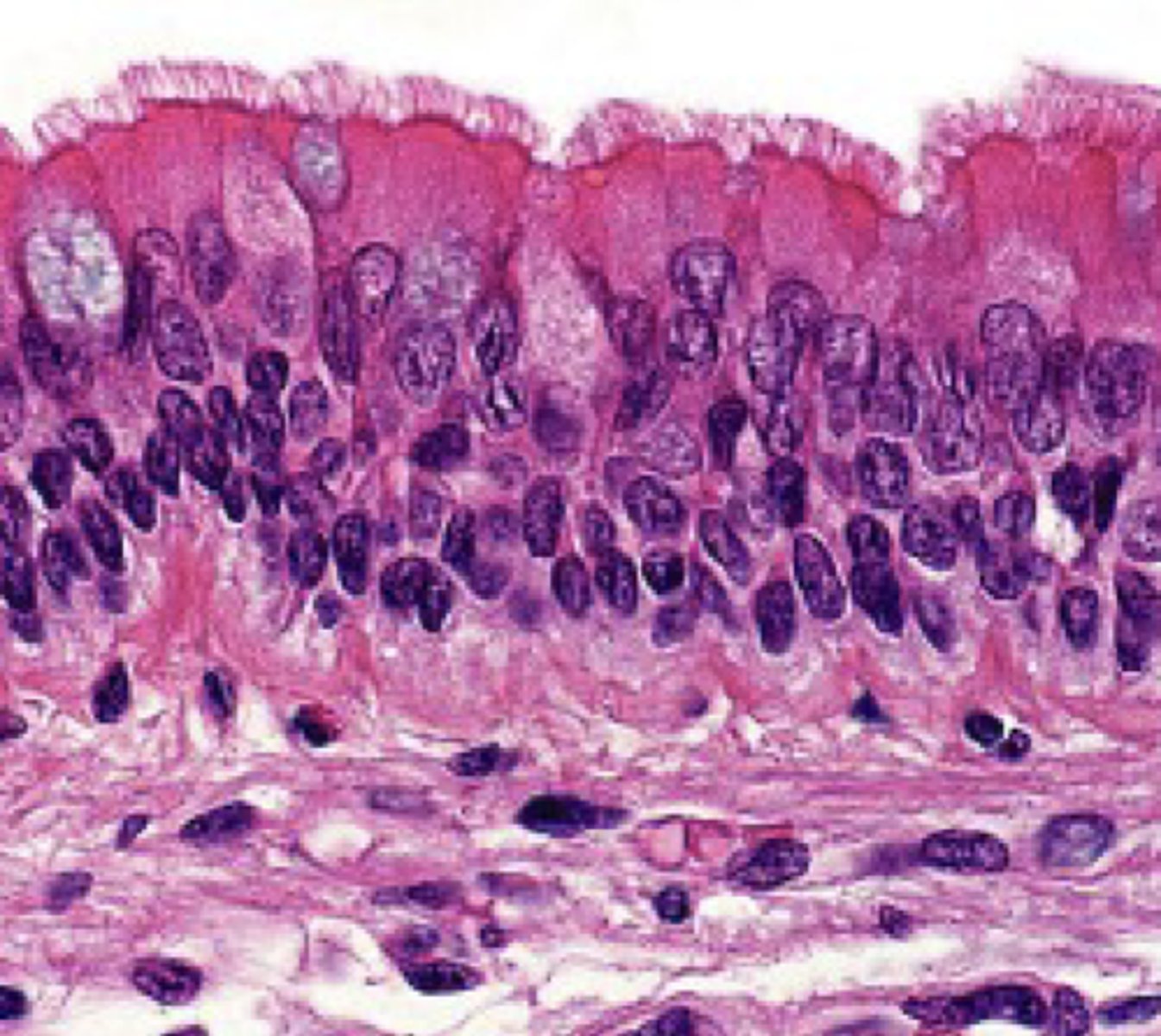
pseudostratified
what type of epithelium is shown
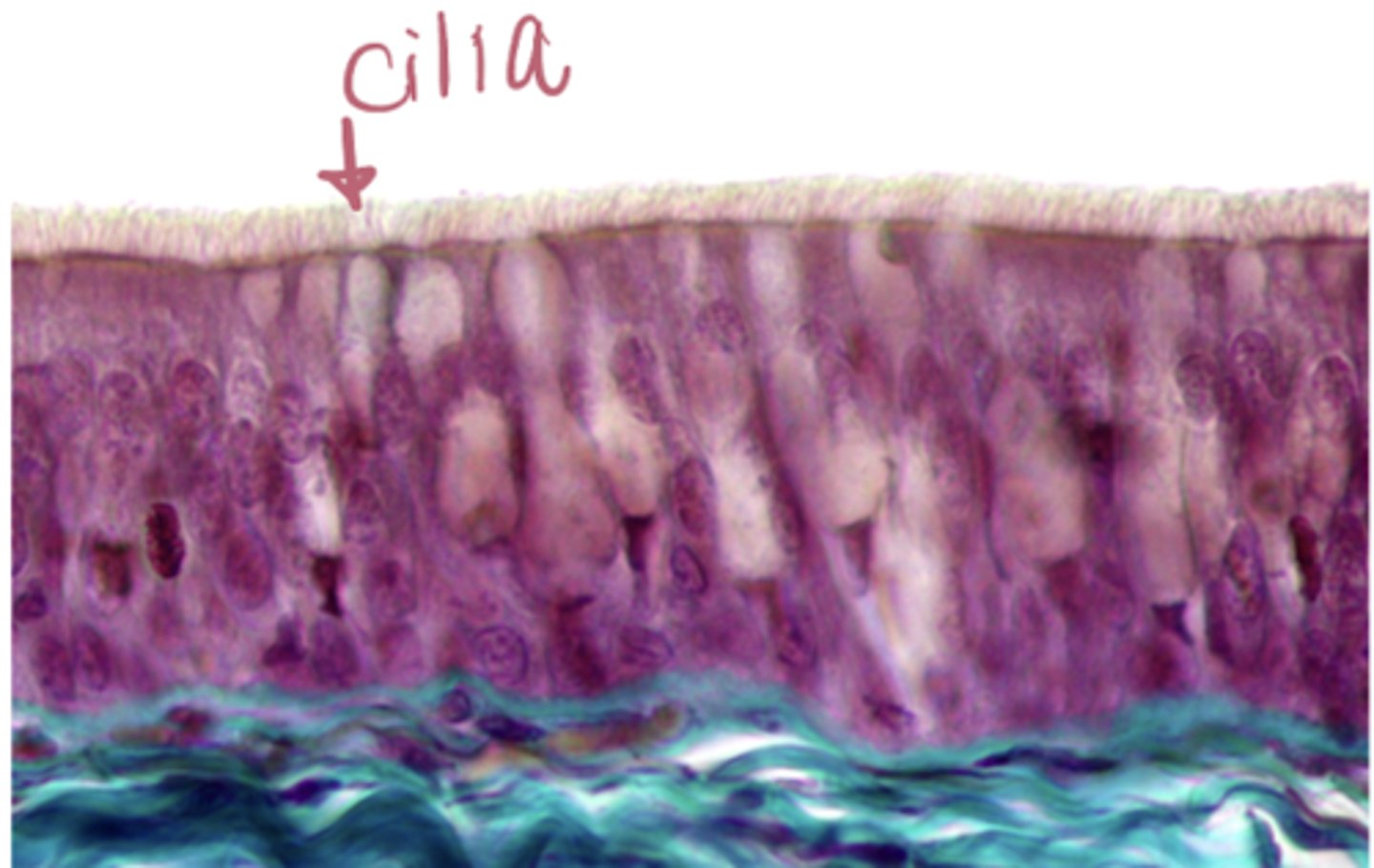
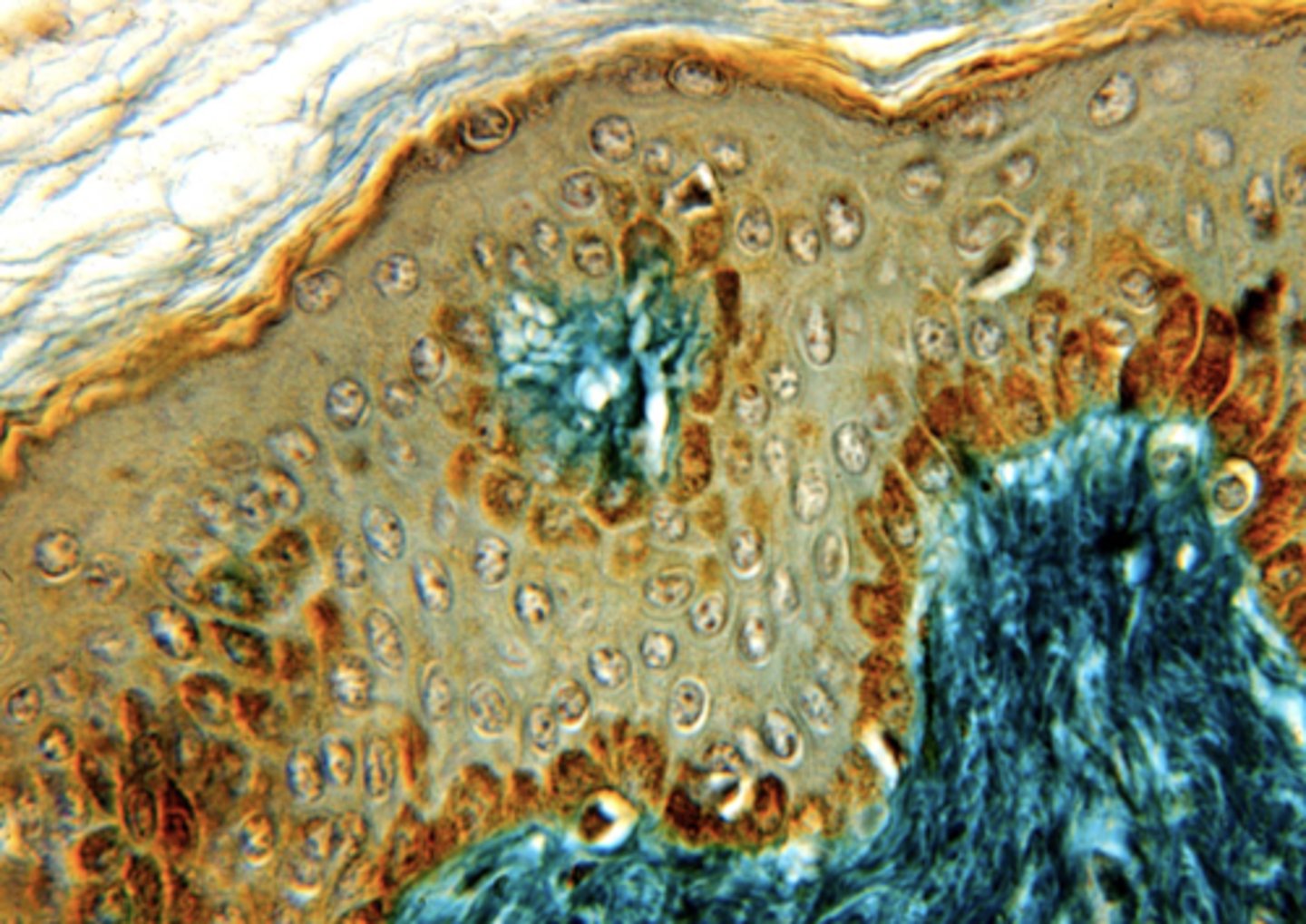
stratified squamous
what type of epithelium is shown
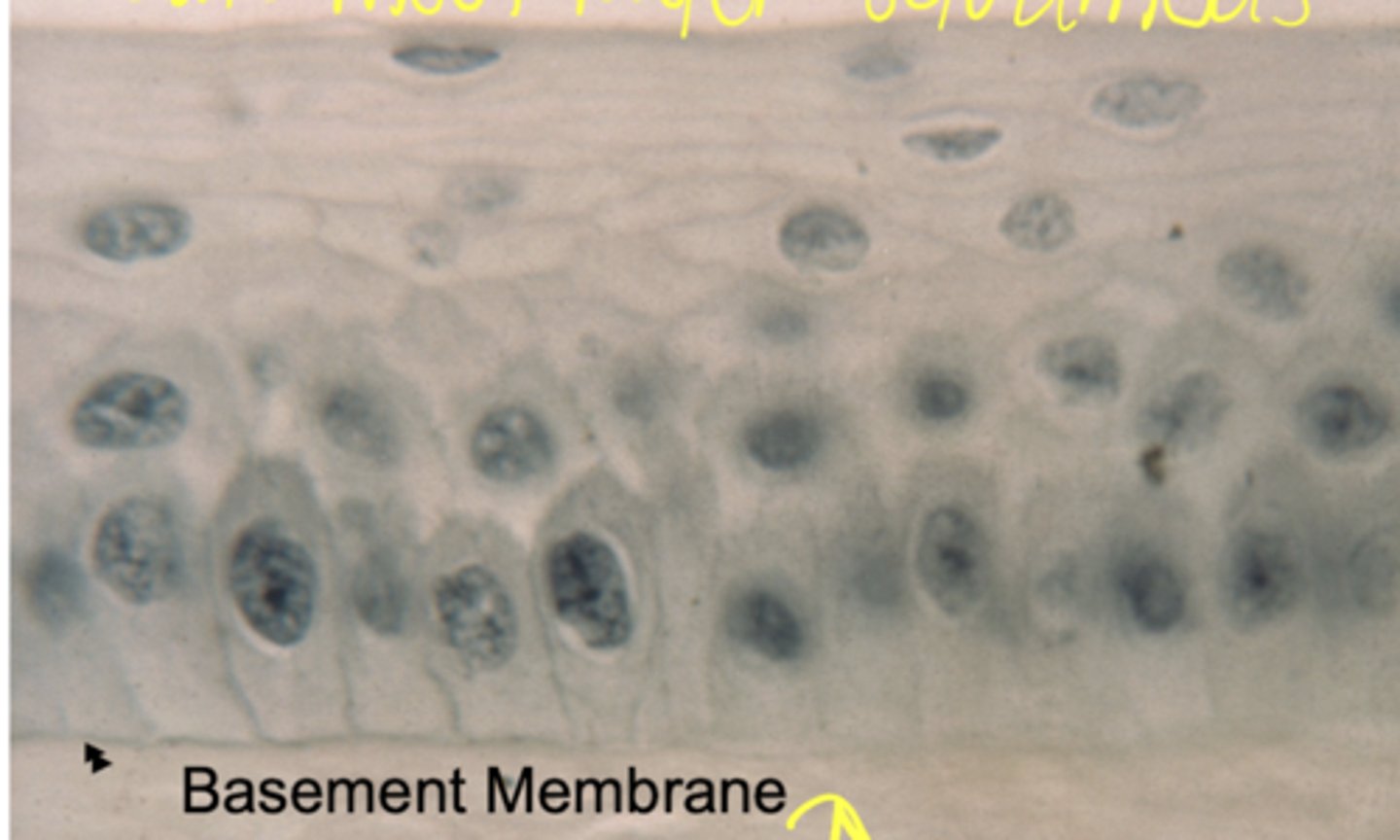
stratified cuboidal
what type of epithelium is shown
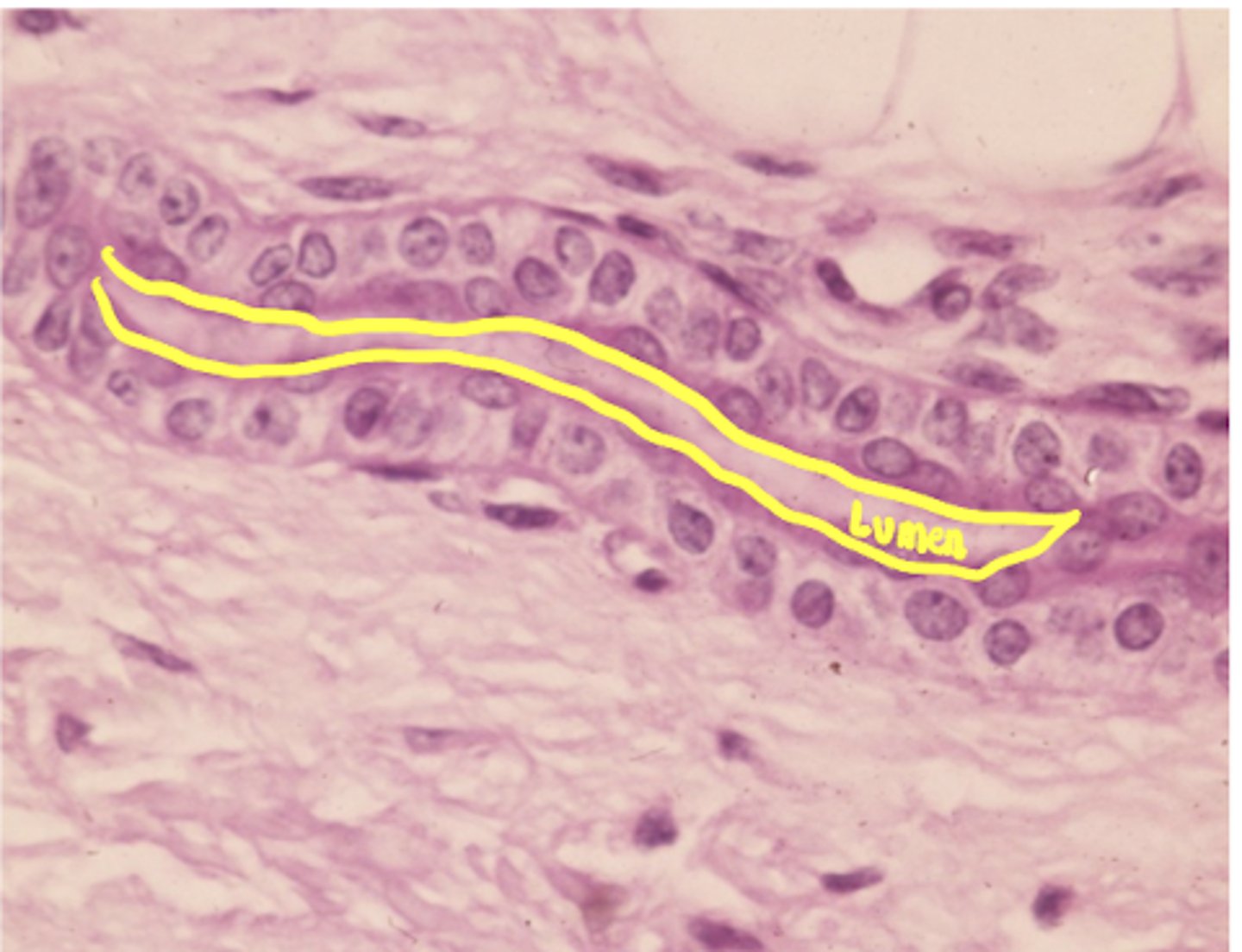
transitional
what type of epithelium is shown
motor proteins
what cell structure is shown
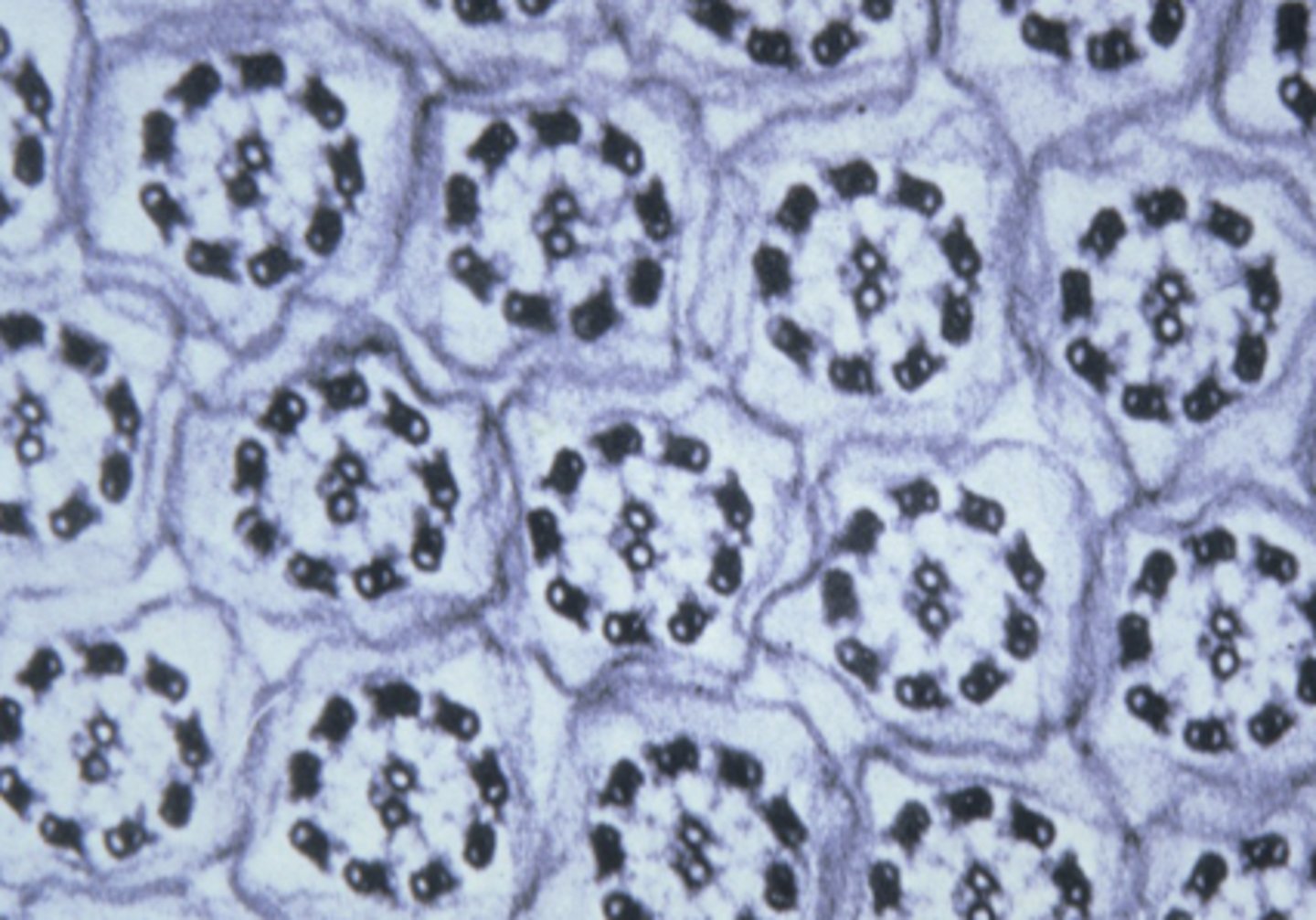
simple columnar
What type of epithelium is shown?
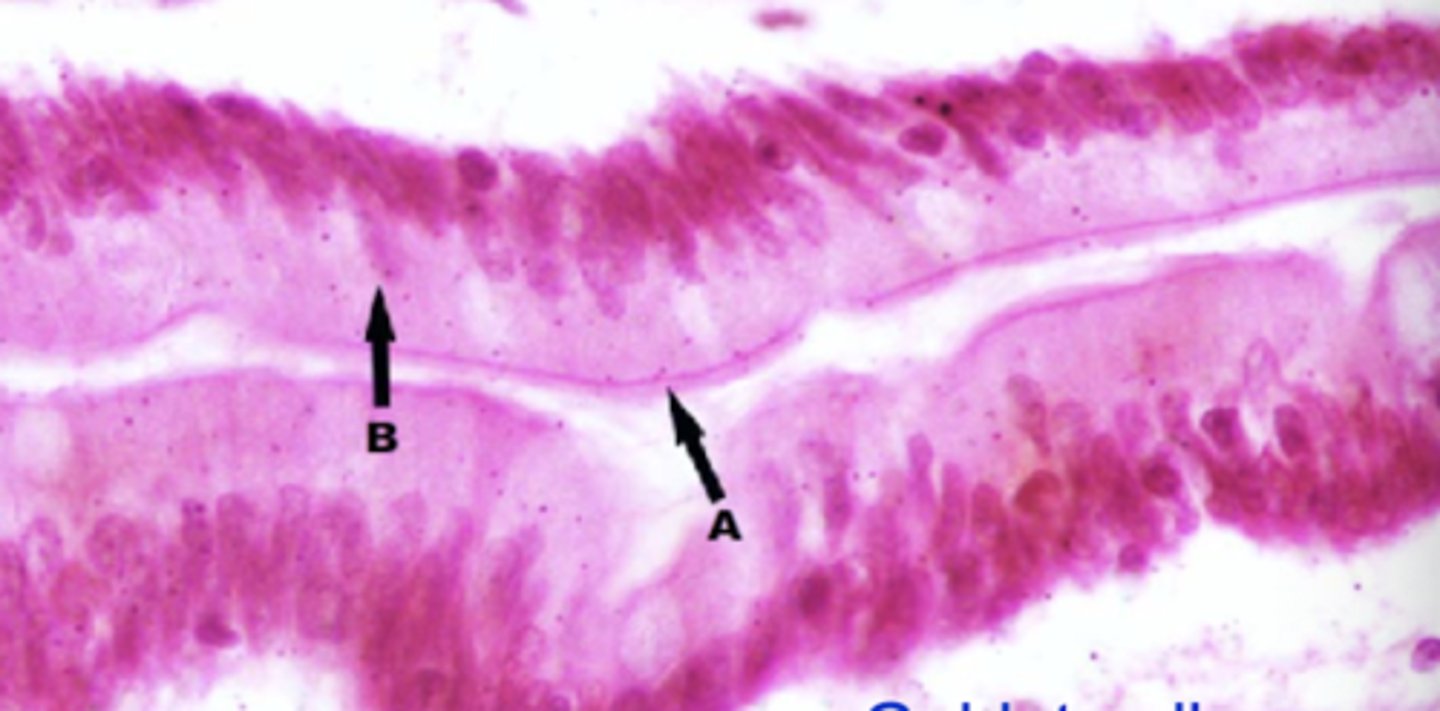
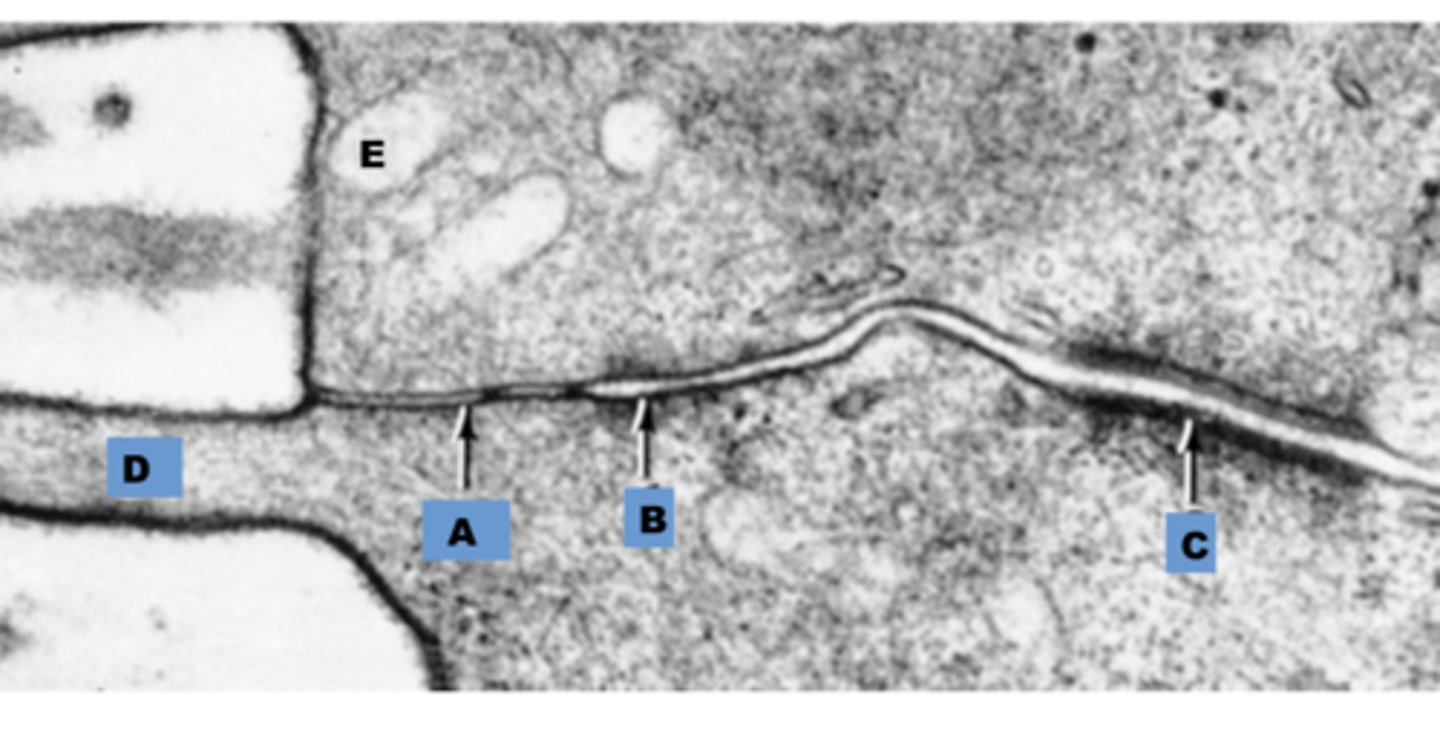
c
which letter is labeling a desmosome
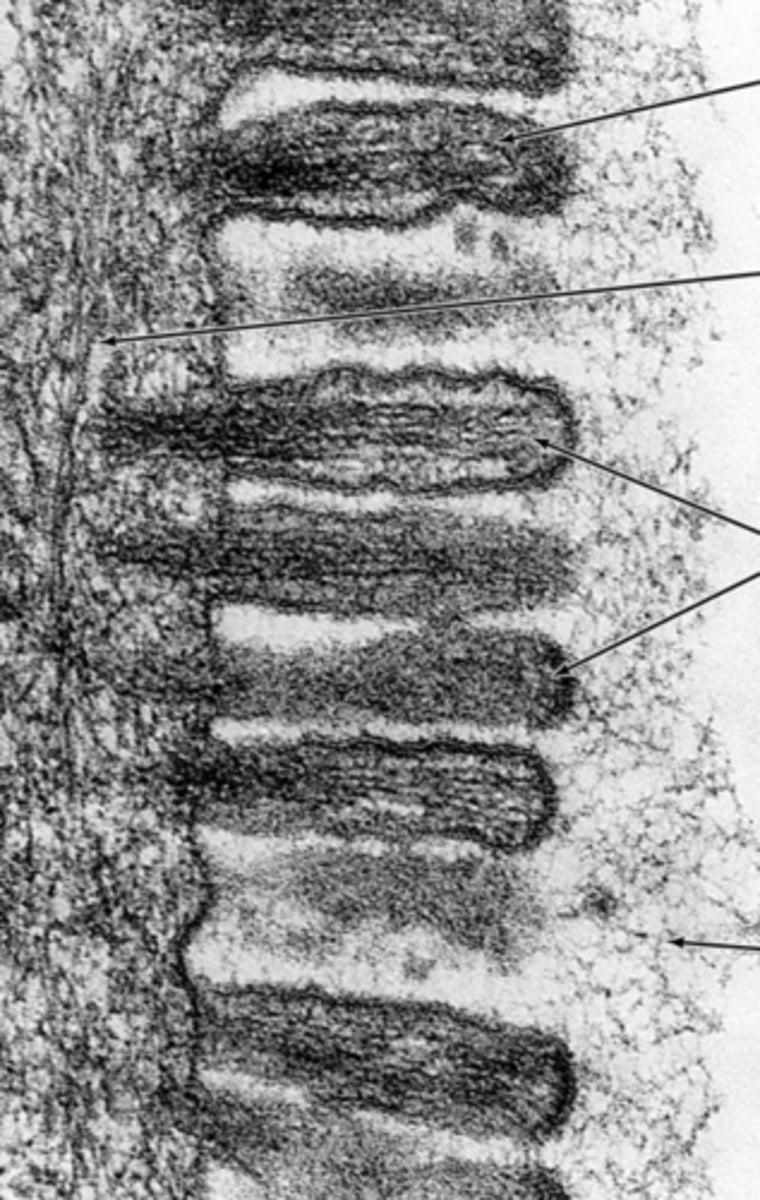
microvilli
Identify the apical membrane modification demonstrated in the EM
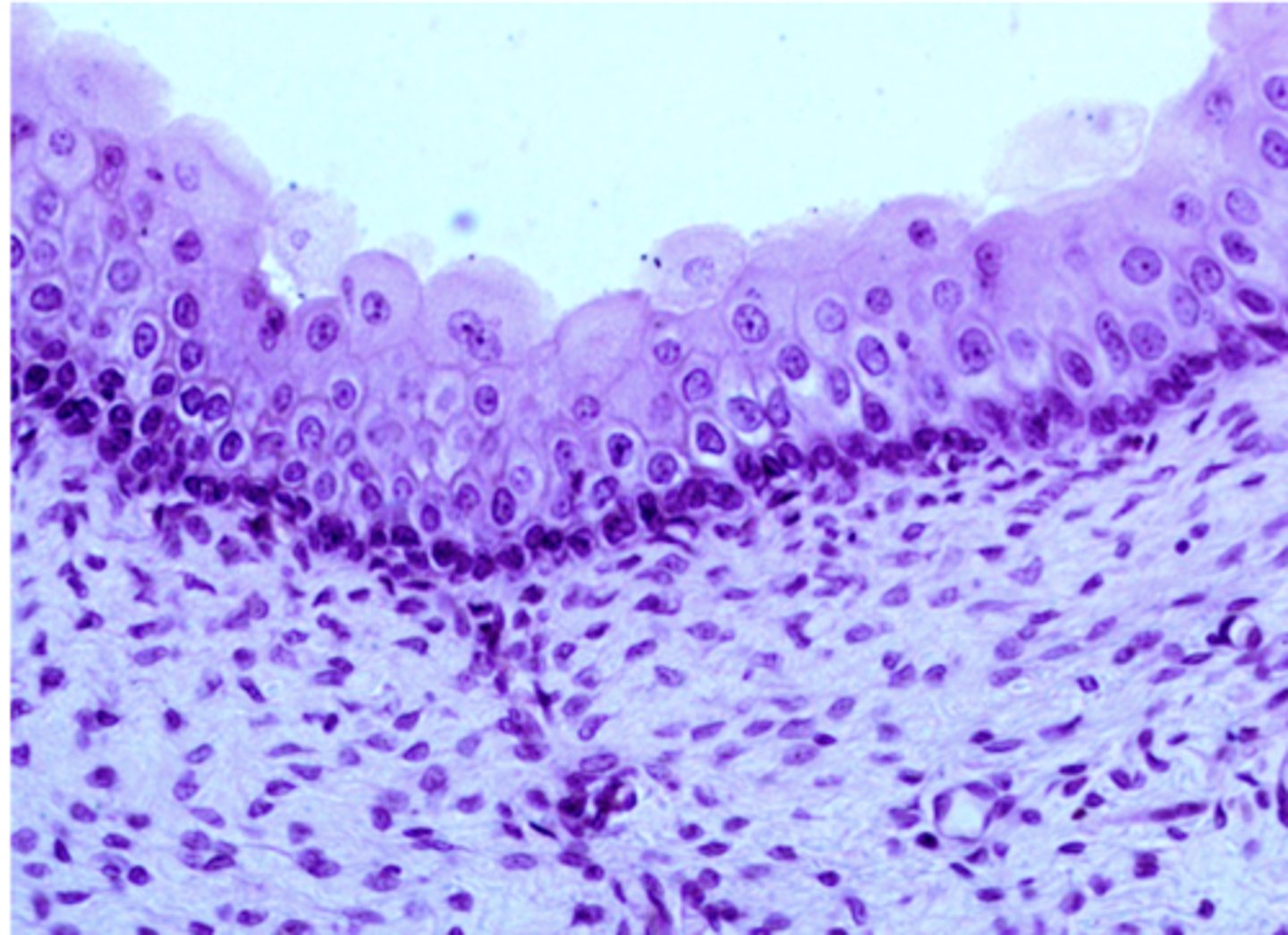
stratified squamous
Classify the epithelium indicated by the arrow.
simple cuboidal
classify the epithelium
psuedostratified
classify the epithelium
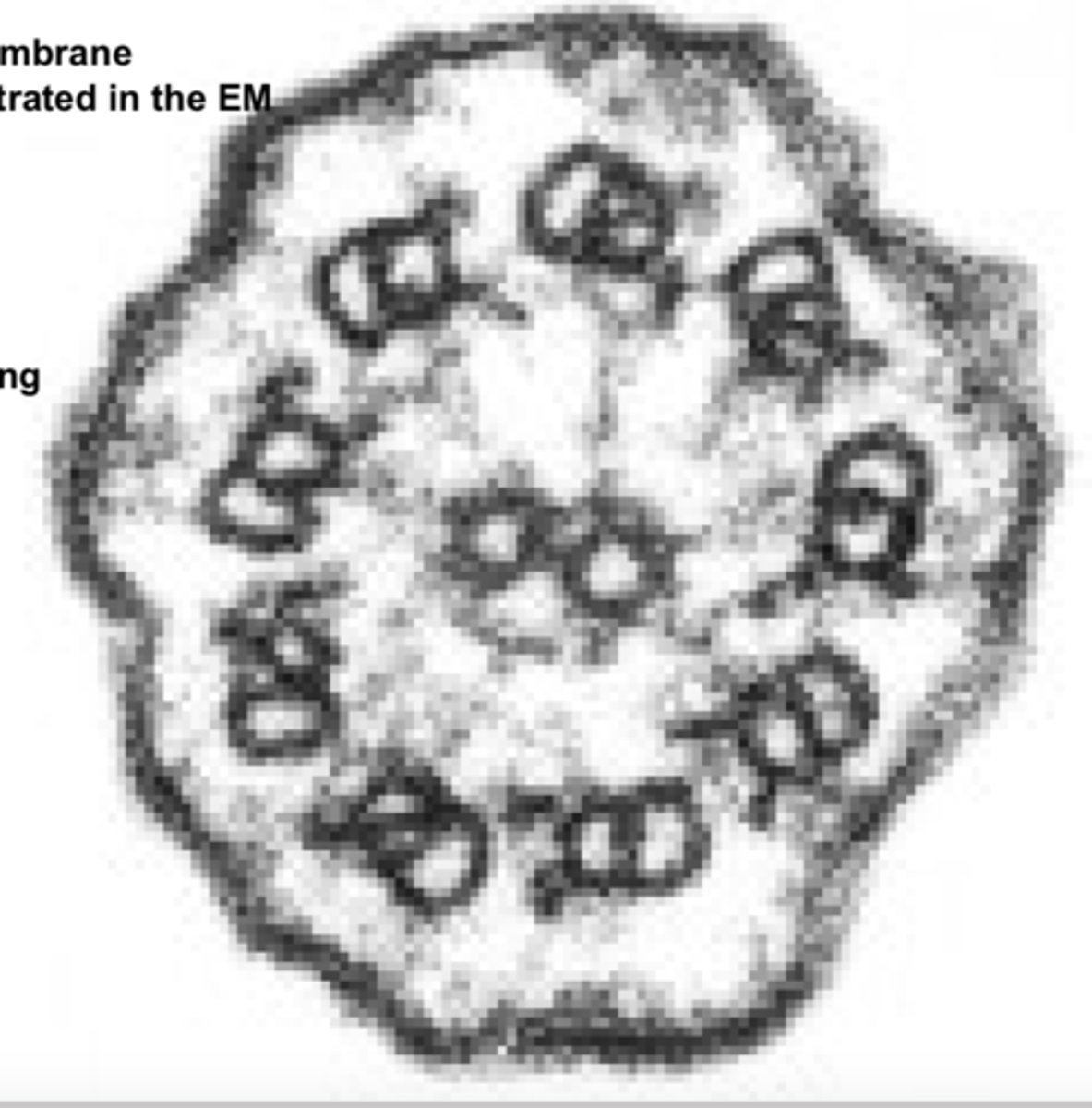
cilia
Identify the apical membranemodification demonstrated in the EM
simple squamous
Classify the epithelium indicated by the arrow
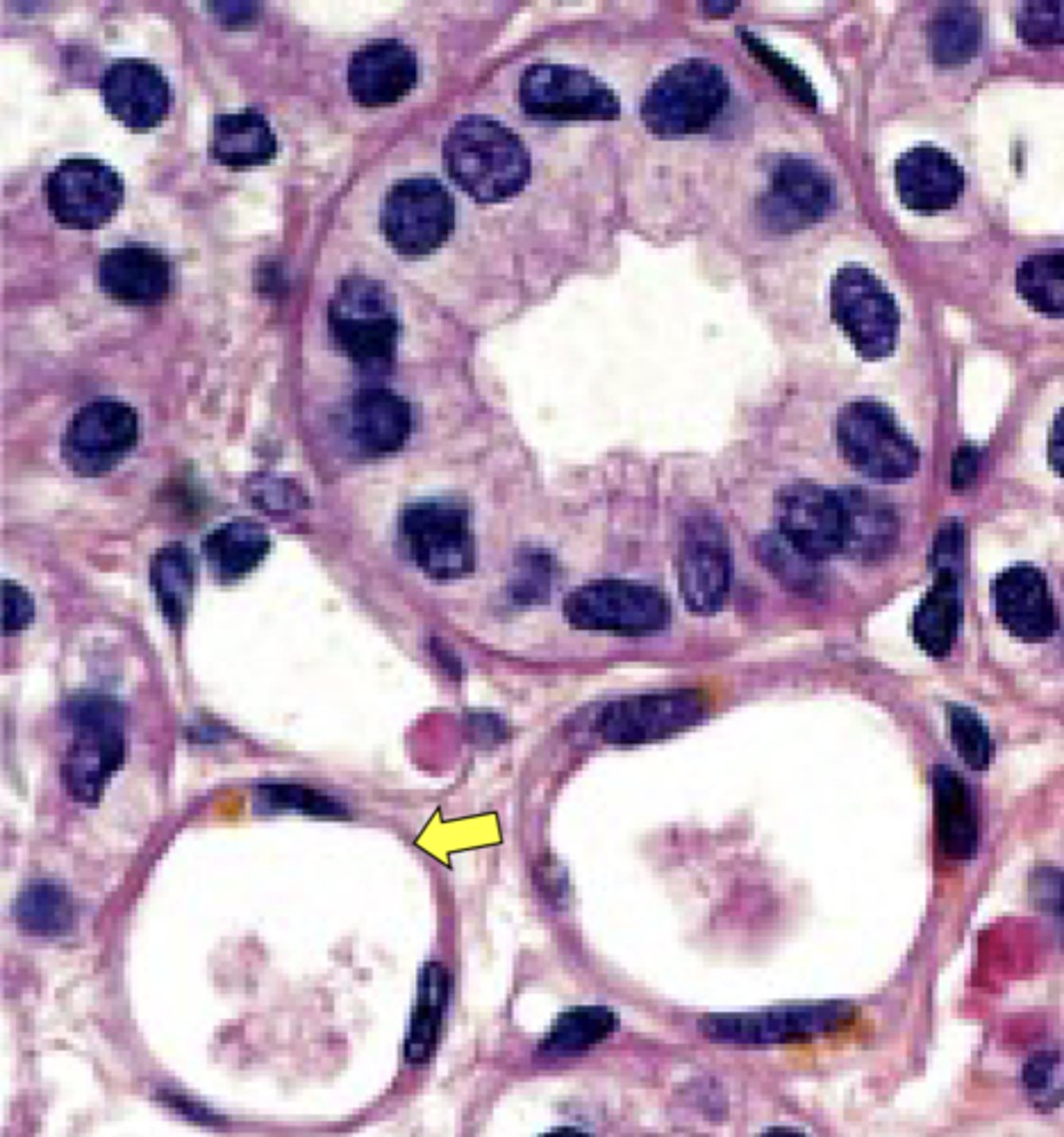
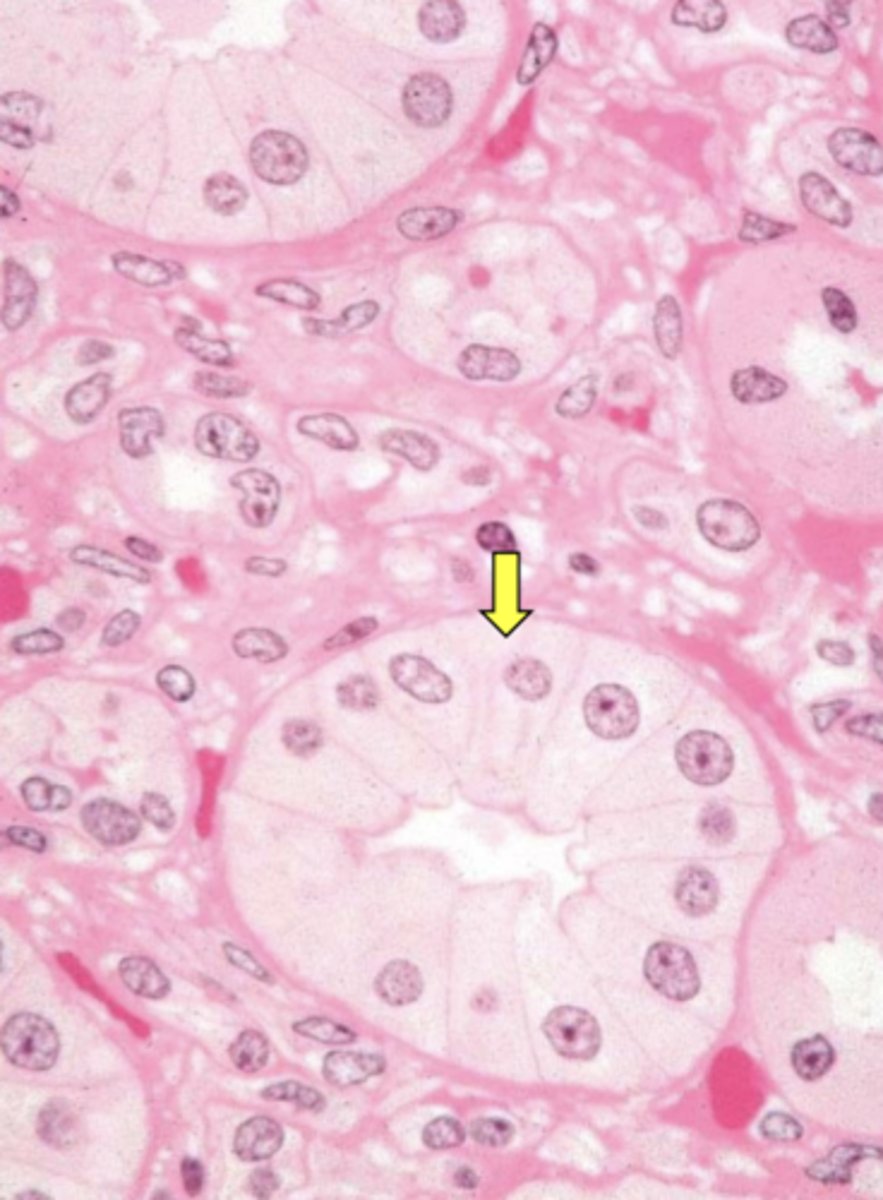
macula densa
Identify the membrane modification indicated by the arrow.
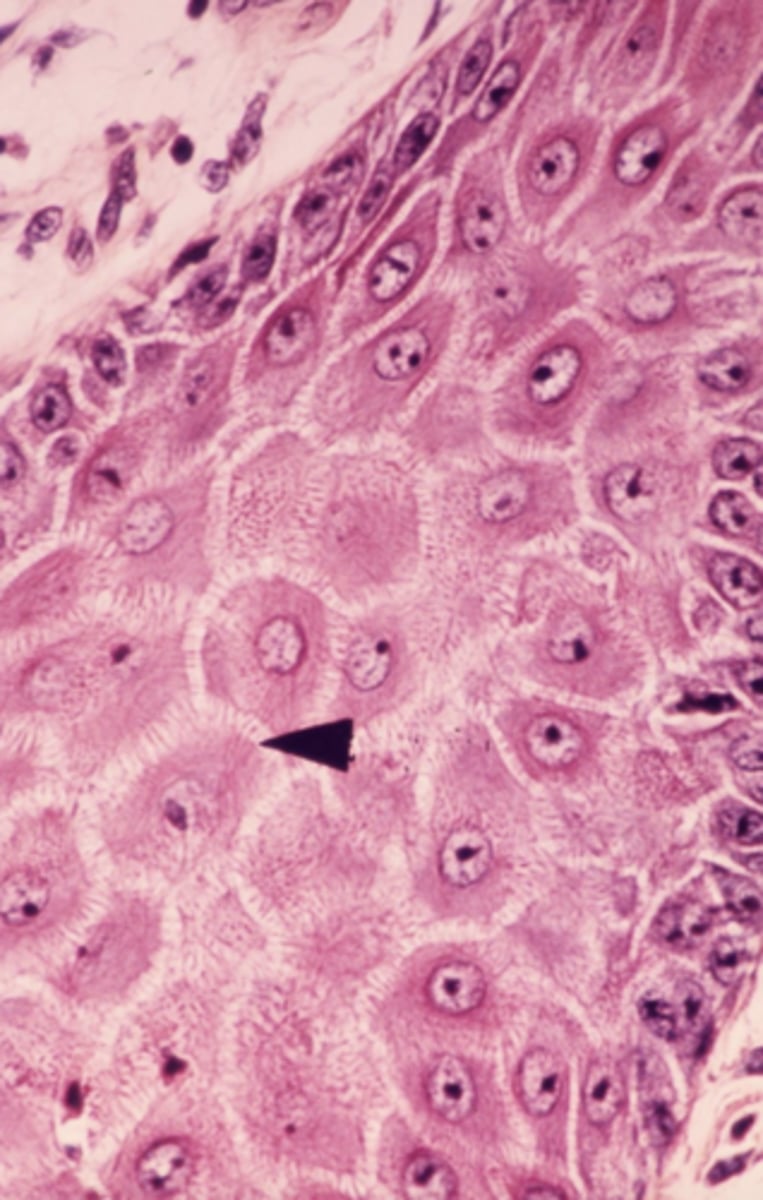
starved animal (minimal glycogen staining)
Is this from a starved animal or well fed animal?
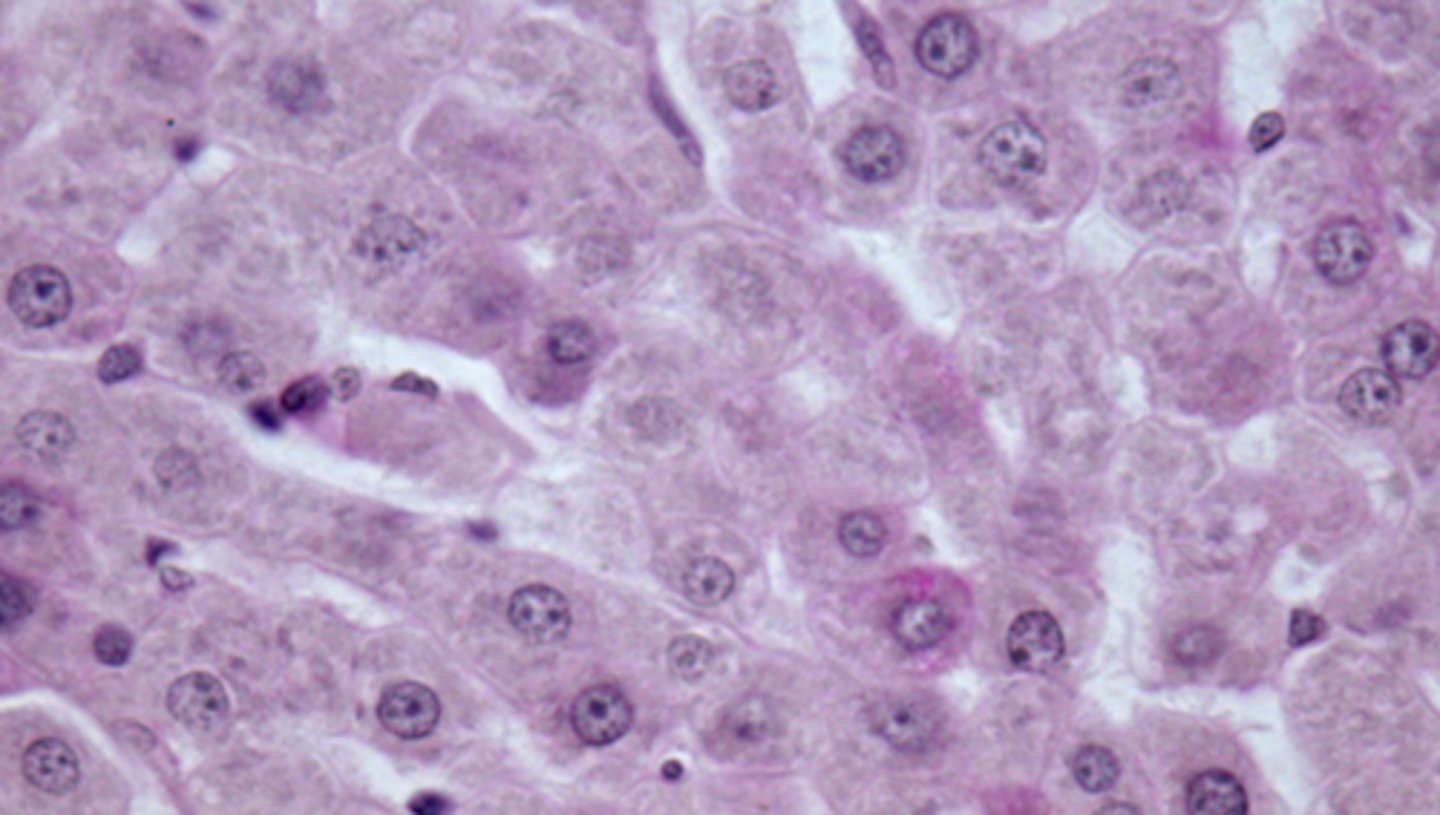
well fed (lots of glycogen staining)
Is this from a starved animal or well fed animal?
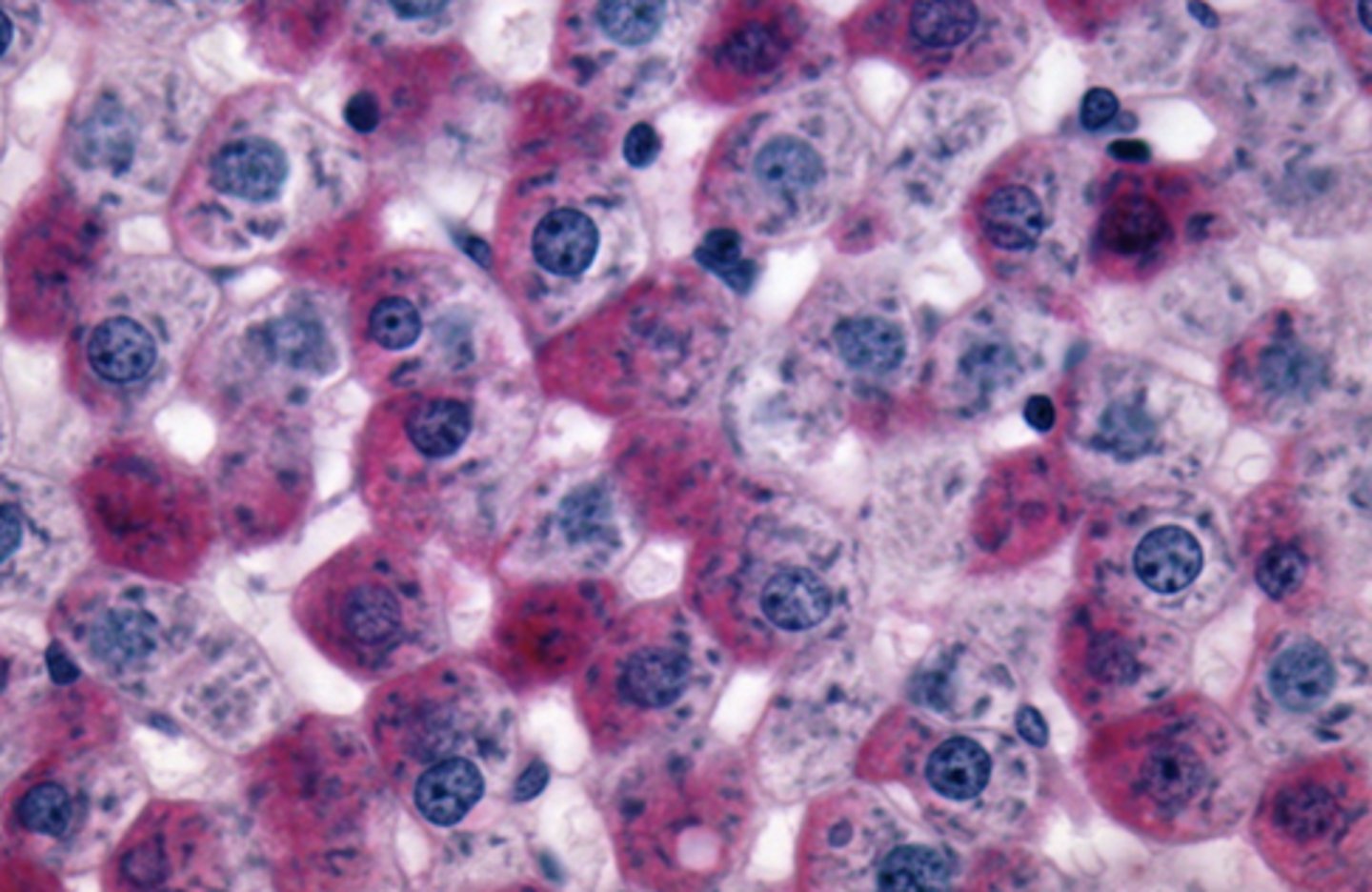
FALSE
(H&E stain does not bind to glycogen well)
true or false - H&E stain binds to glycogen well
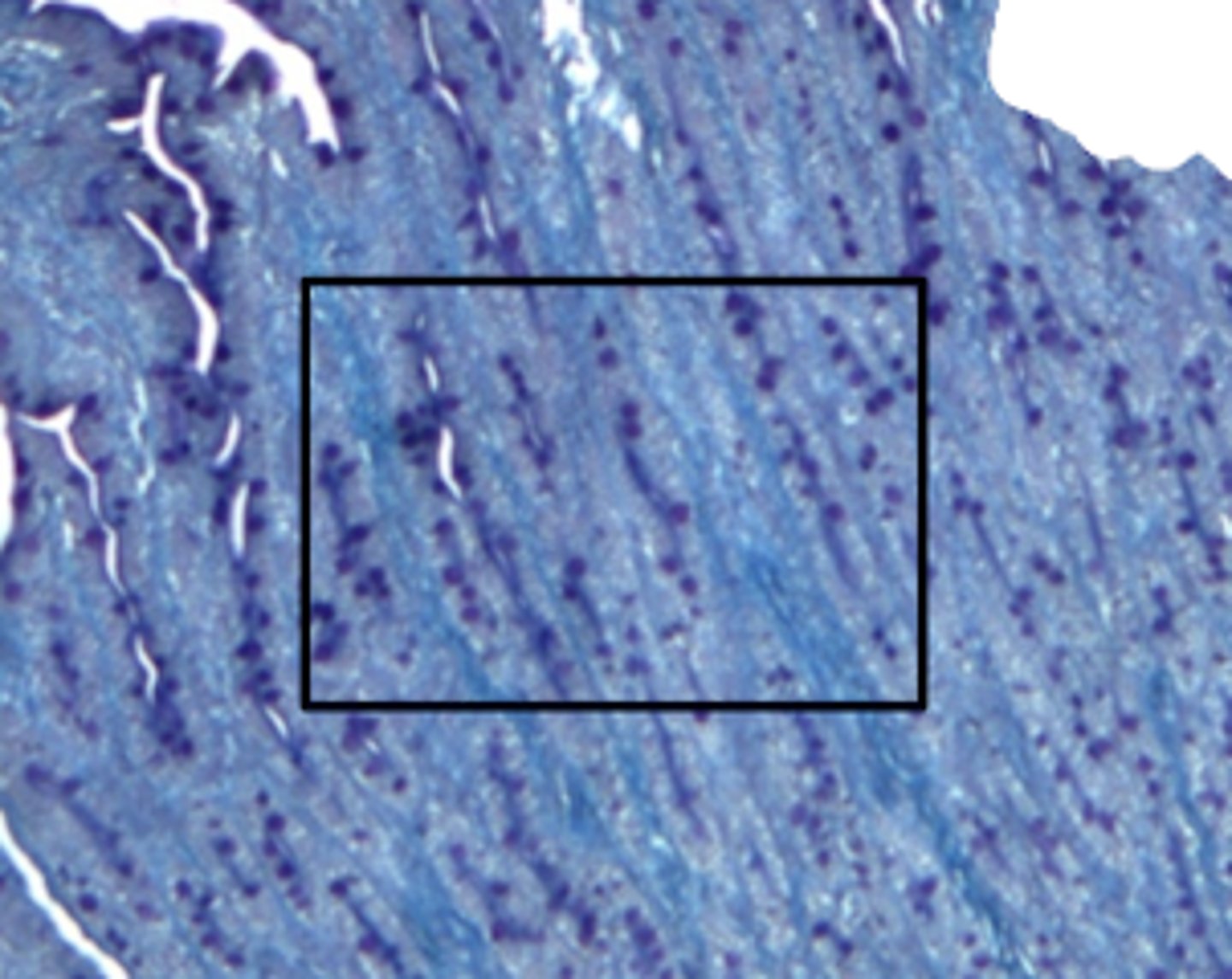
lipid ridges
what is the predominate structure in this image
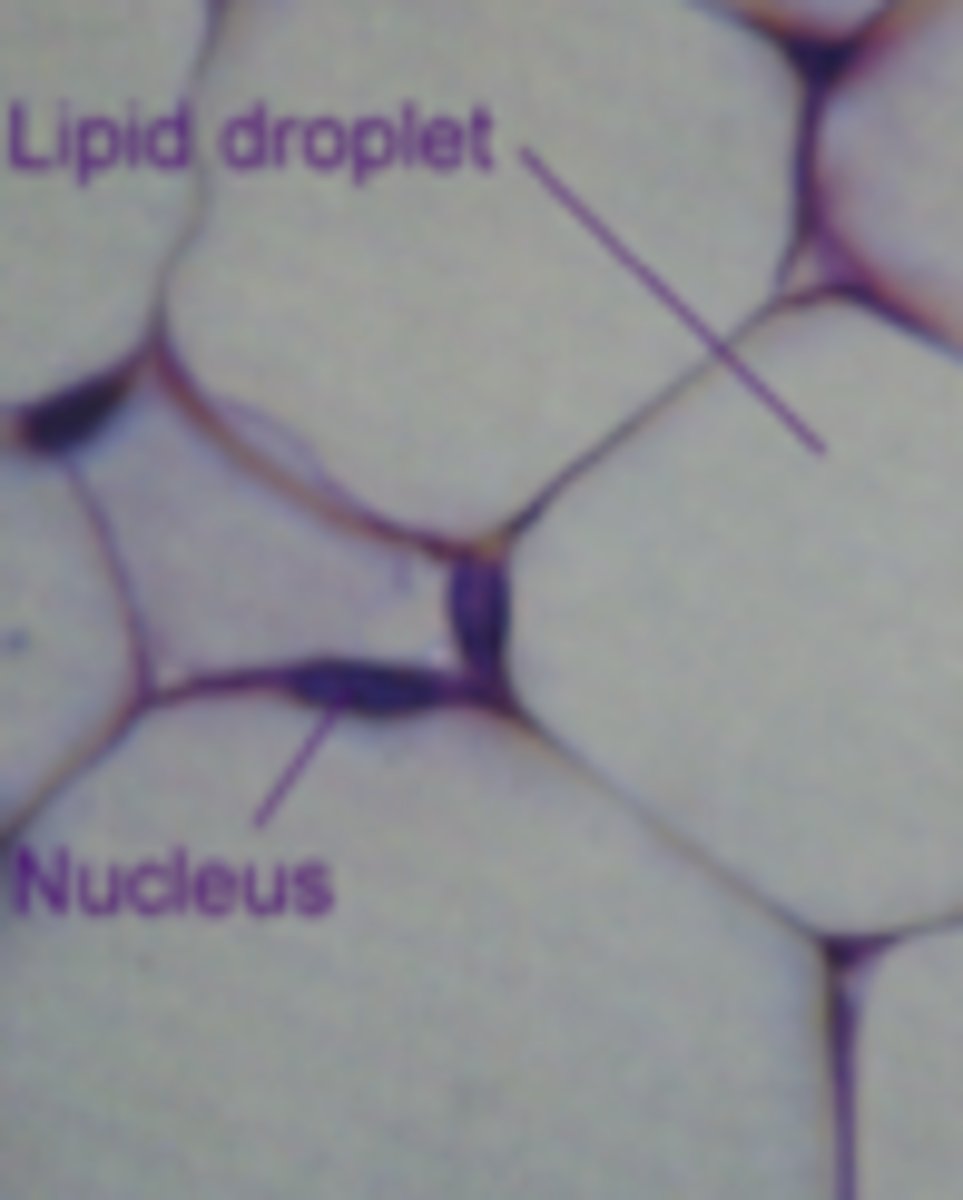
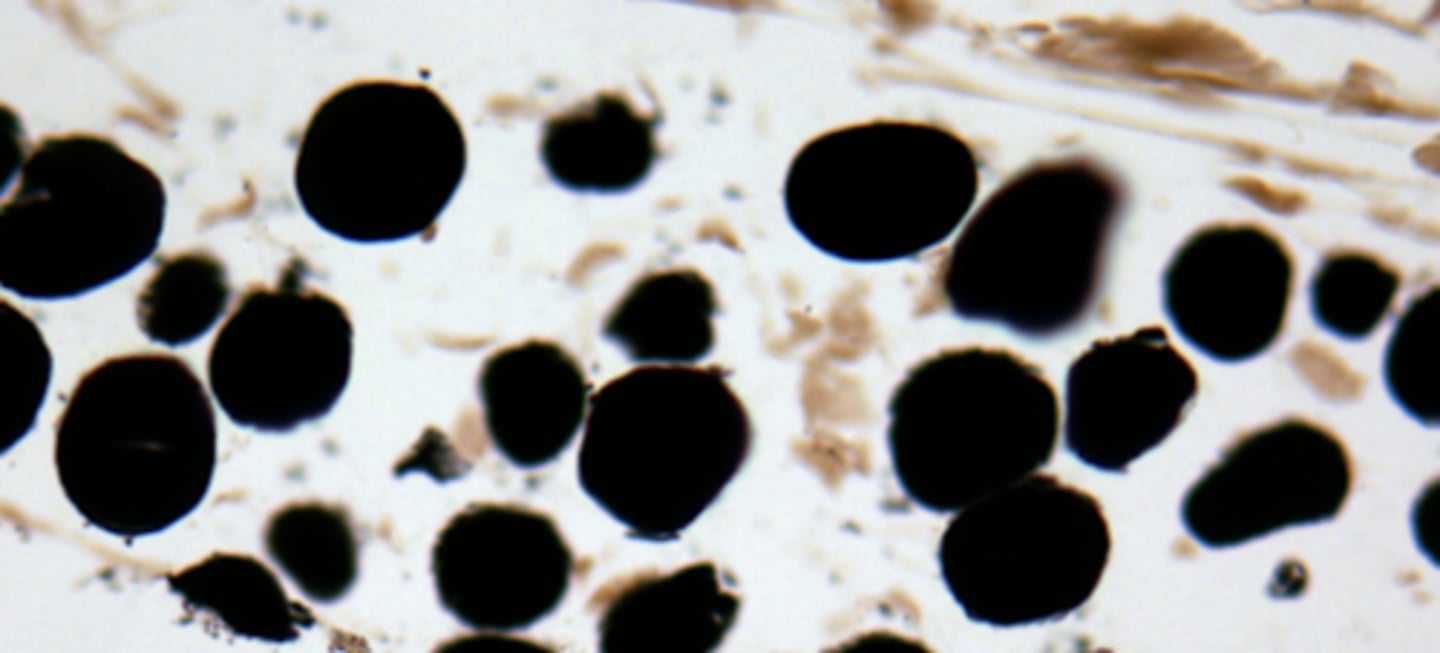
lipid droplets / lipid inclusions in adipose cells
what cell structure is shown
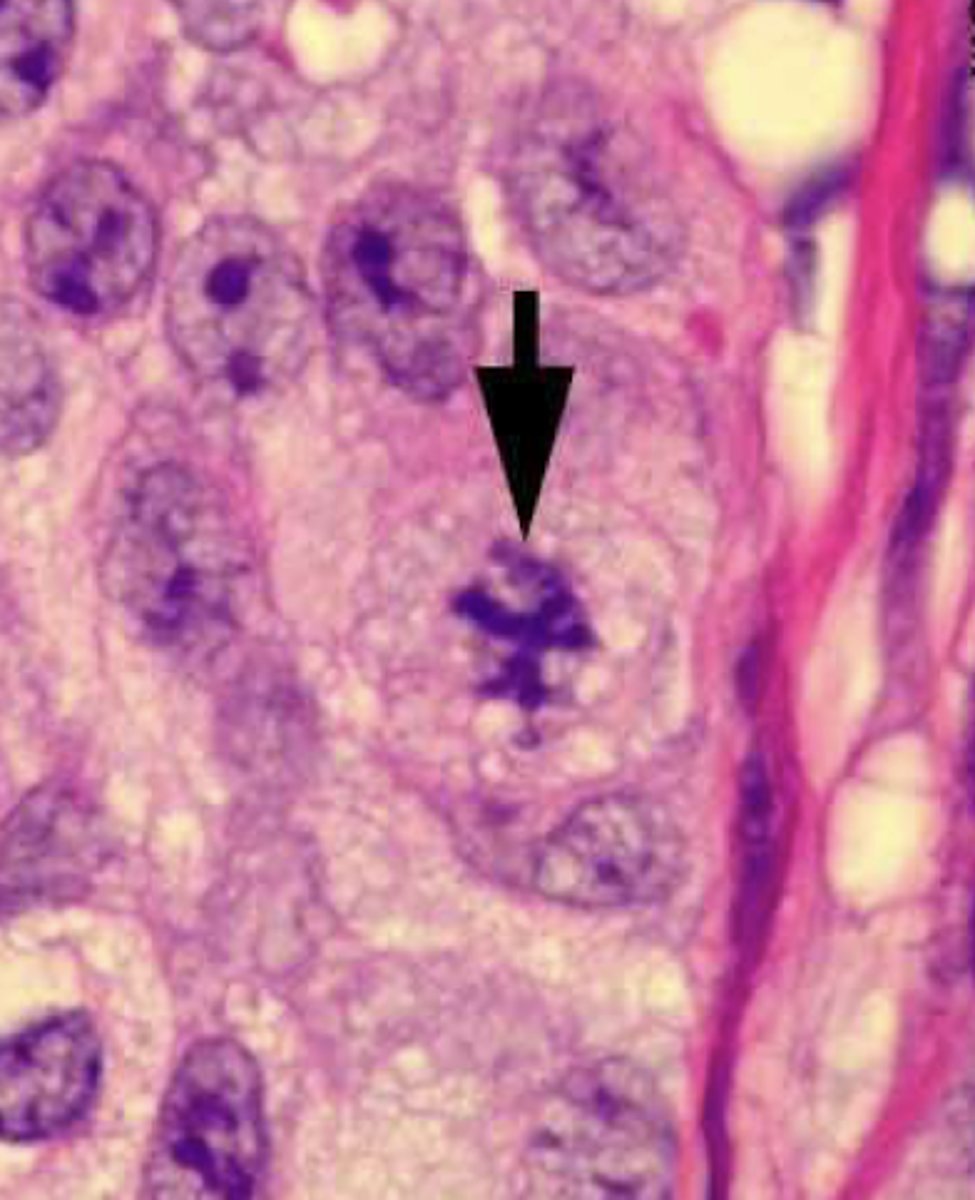
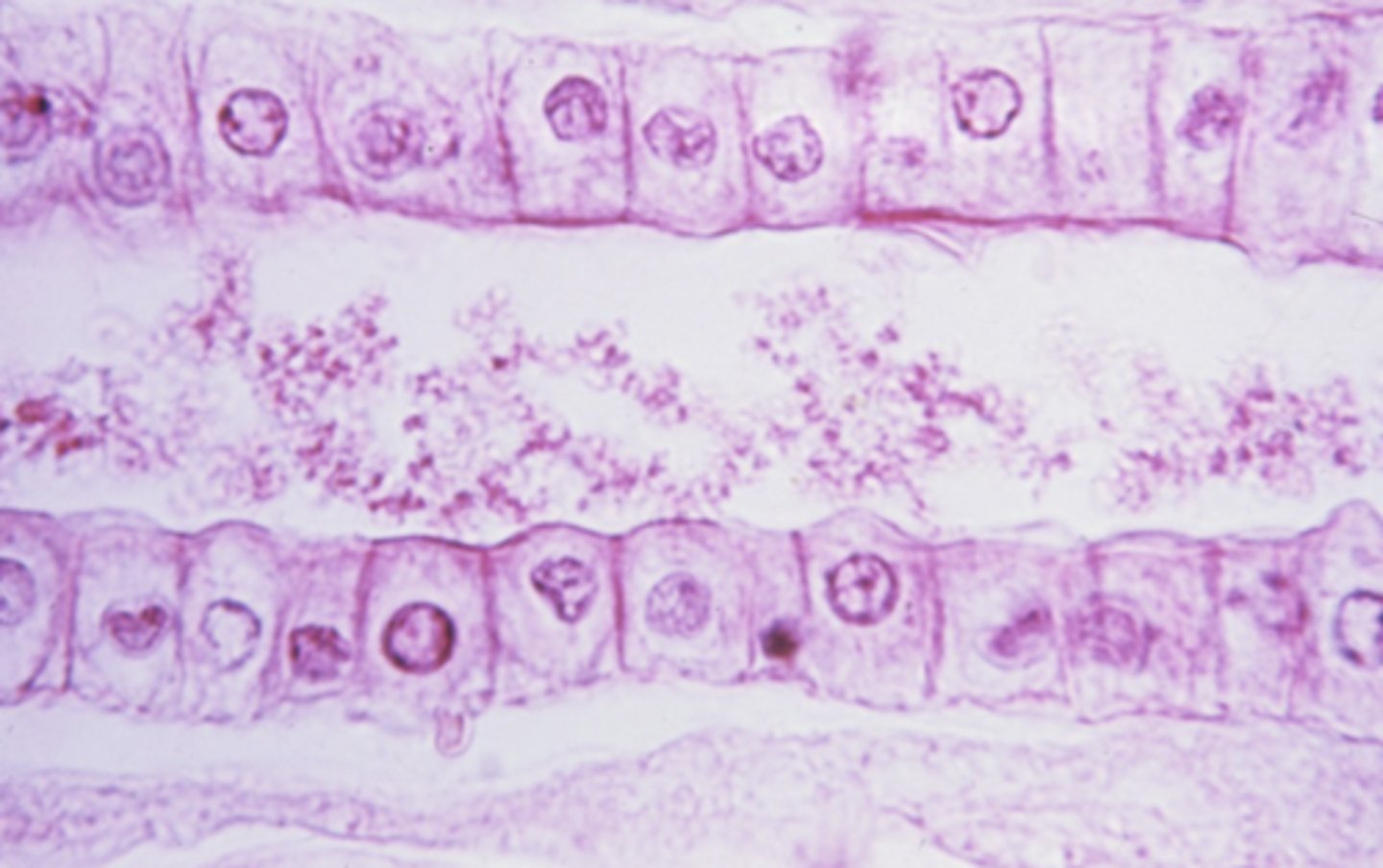
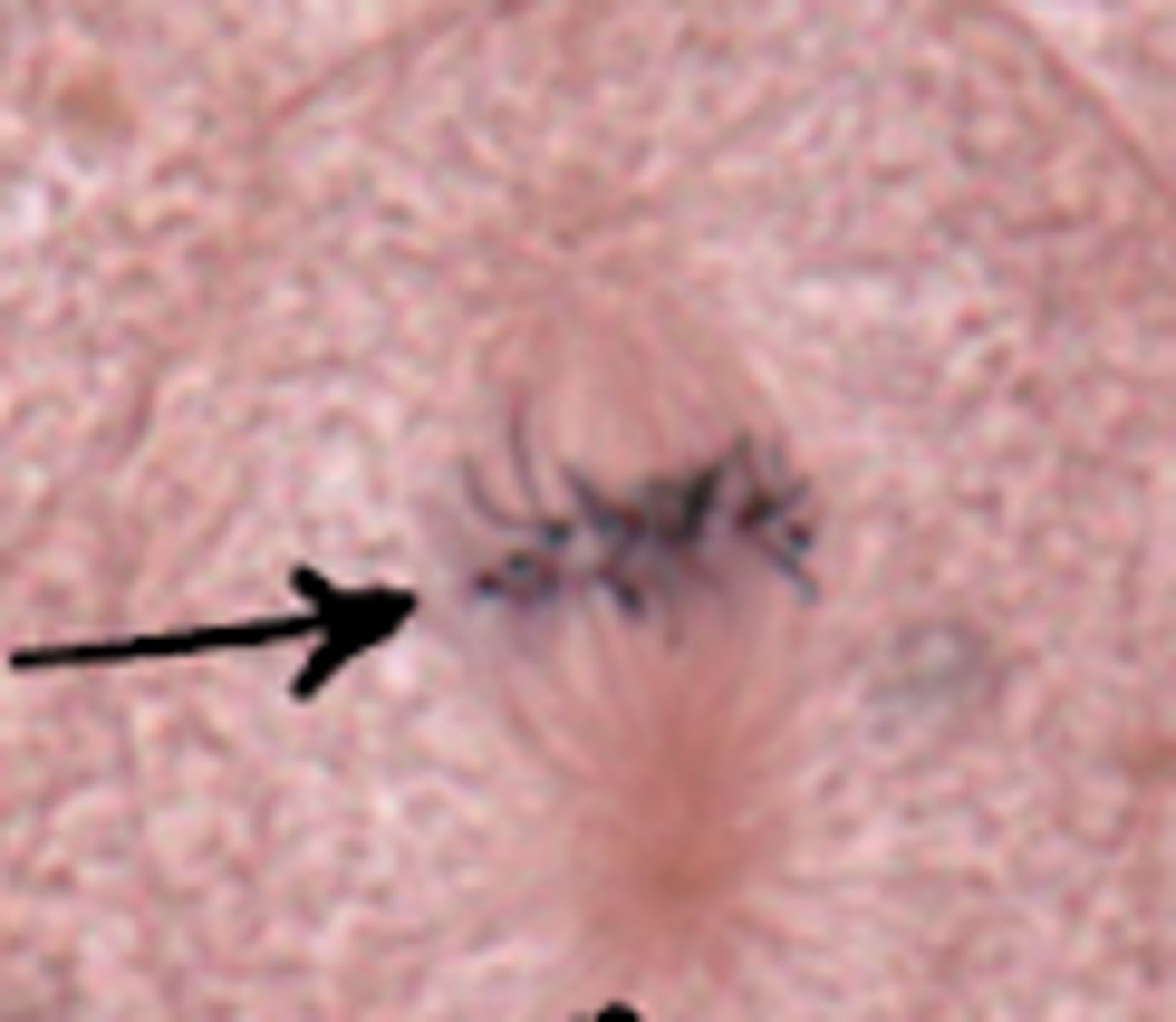
metaphase
what cell stage is shown
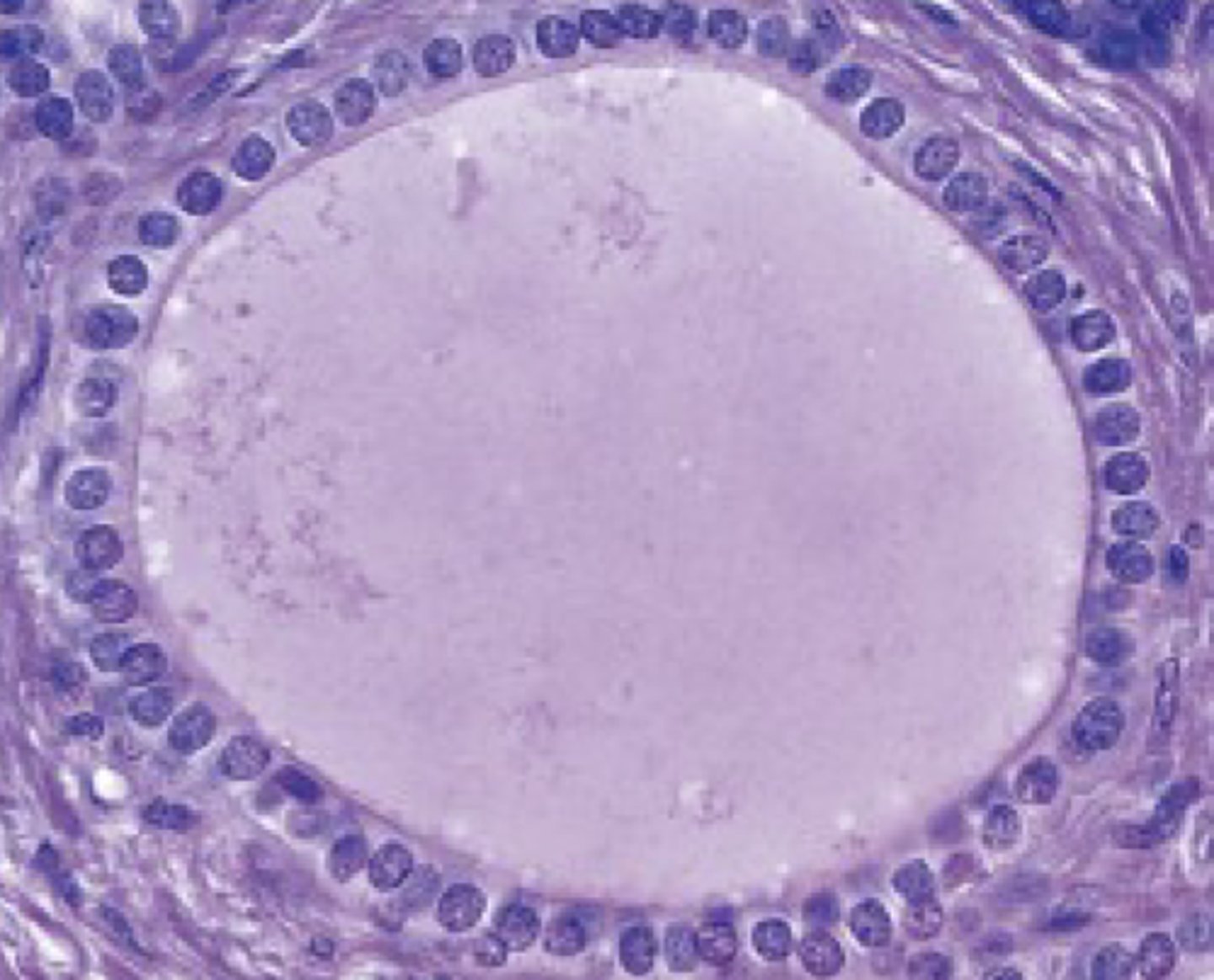
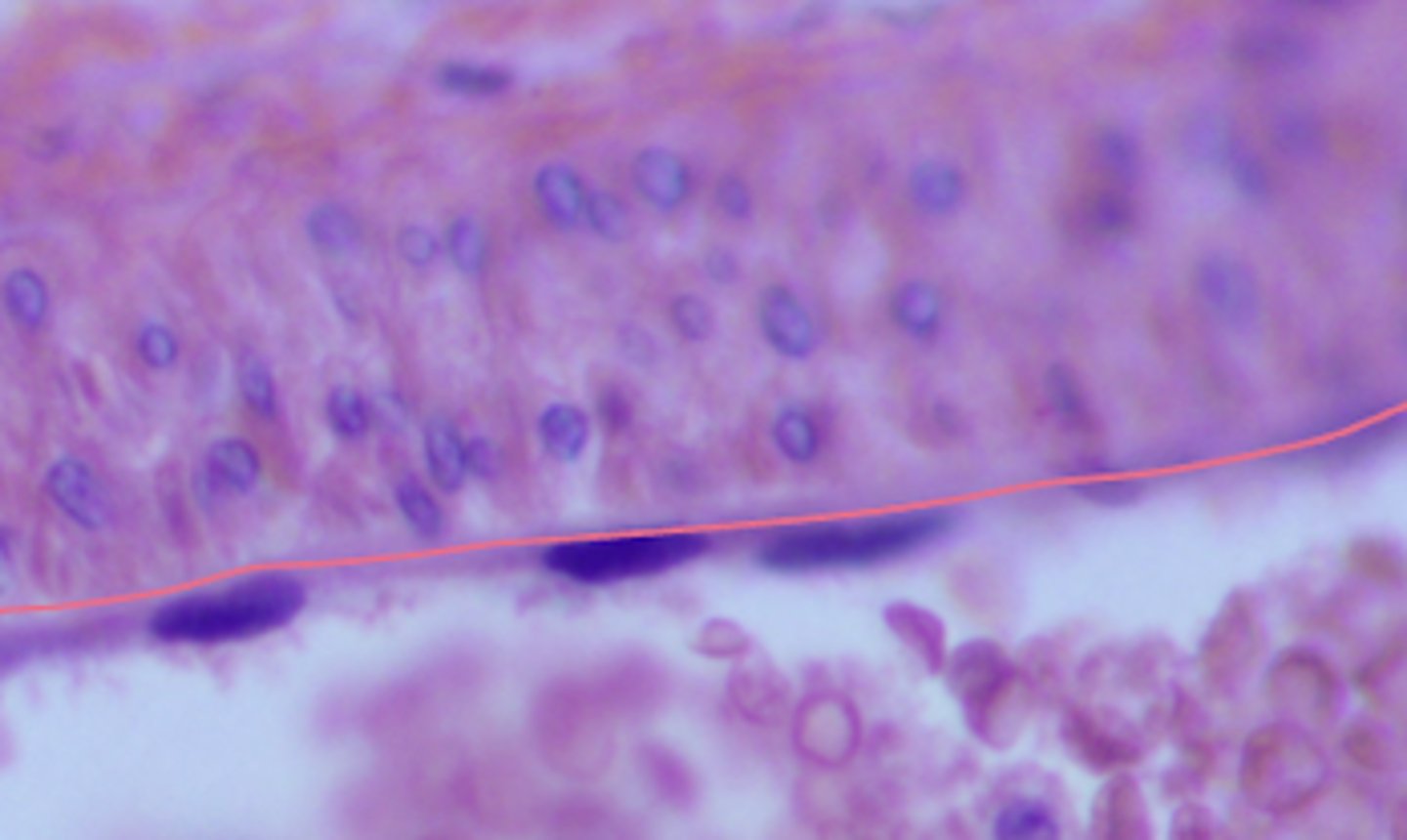
simple squamous
what type of epithelium is shown
simple cuboidal
what cell type is shown
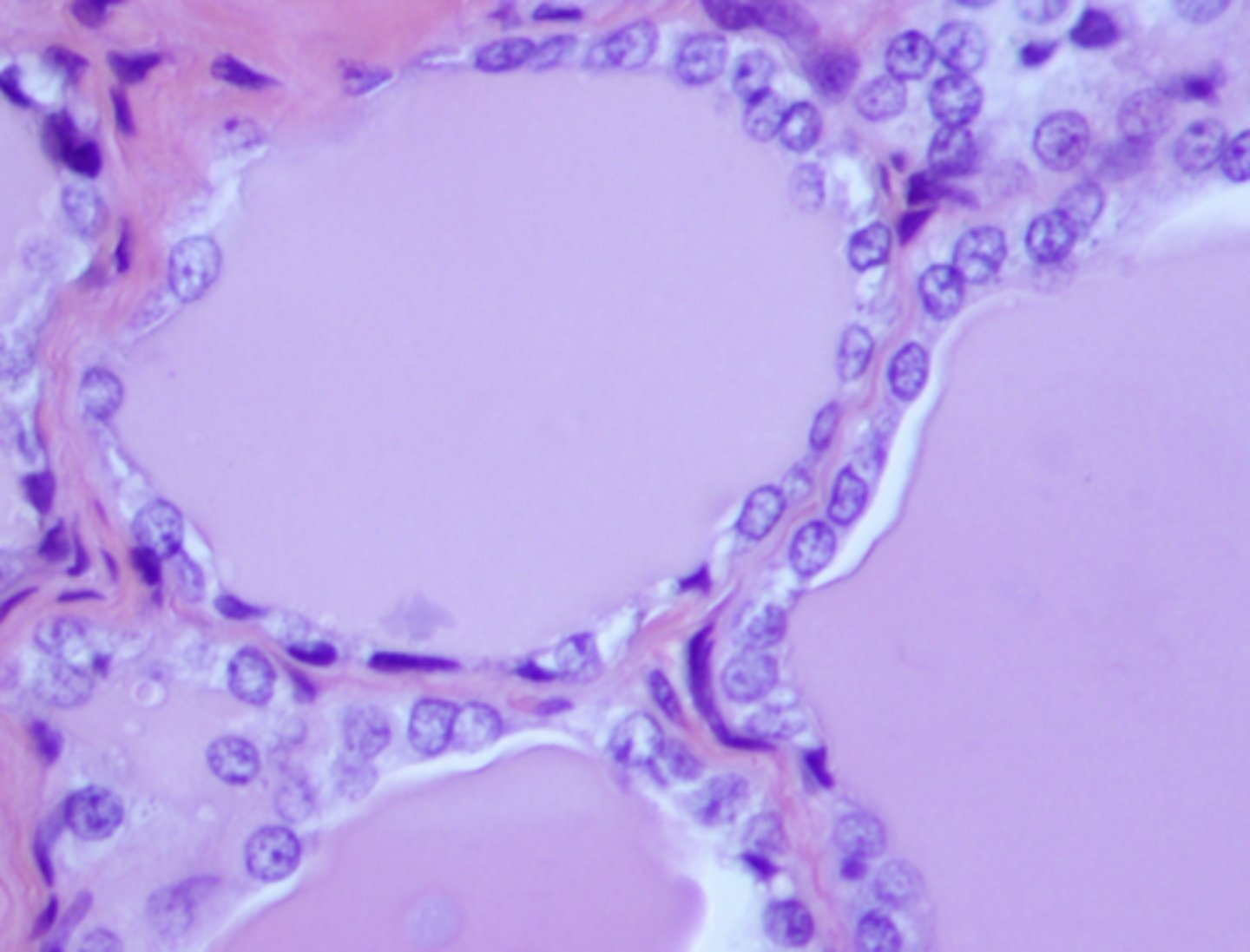
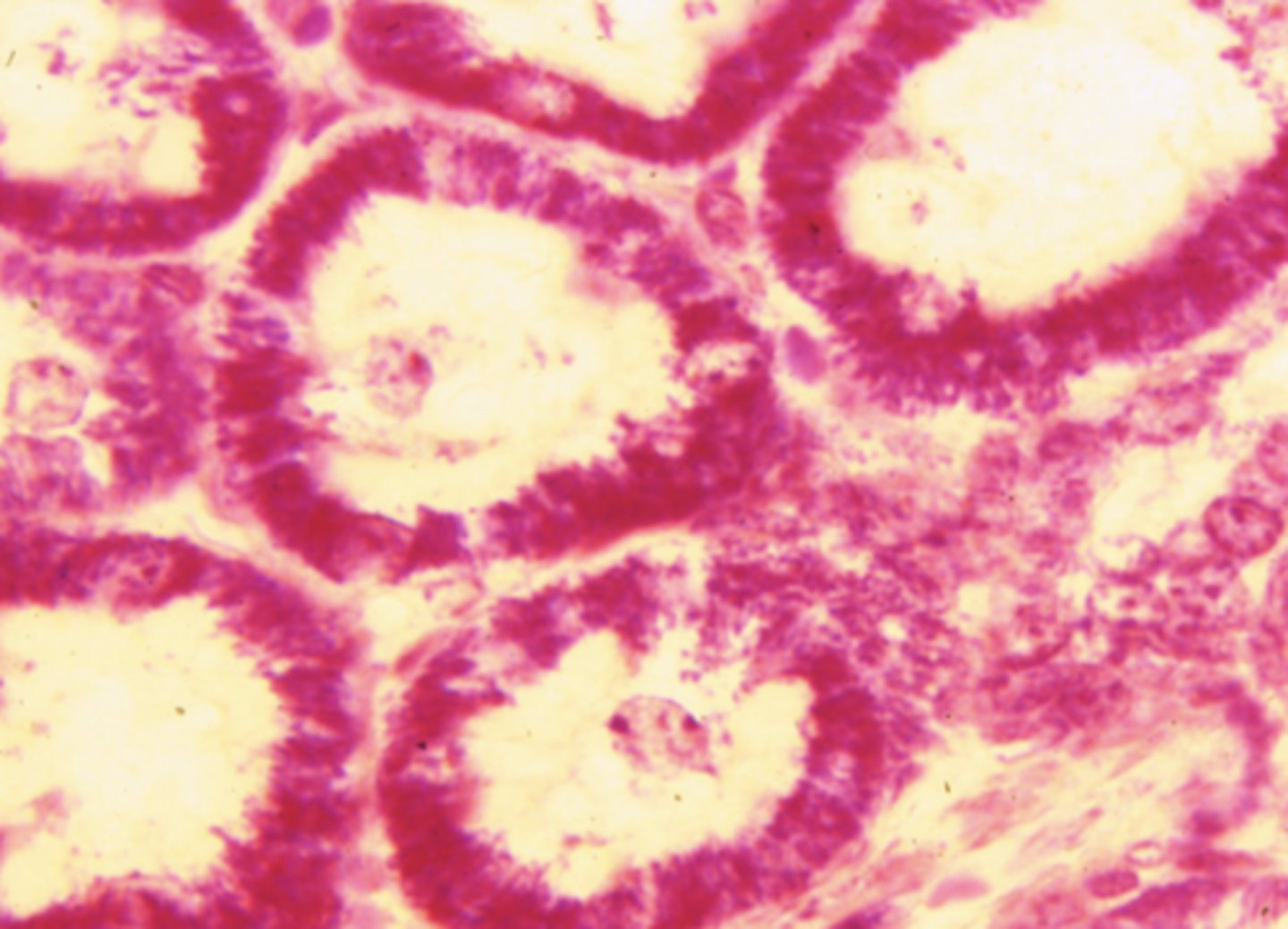
simple columnar
what cell type is shown
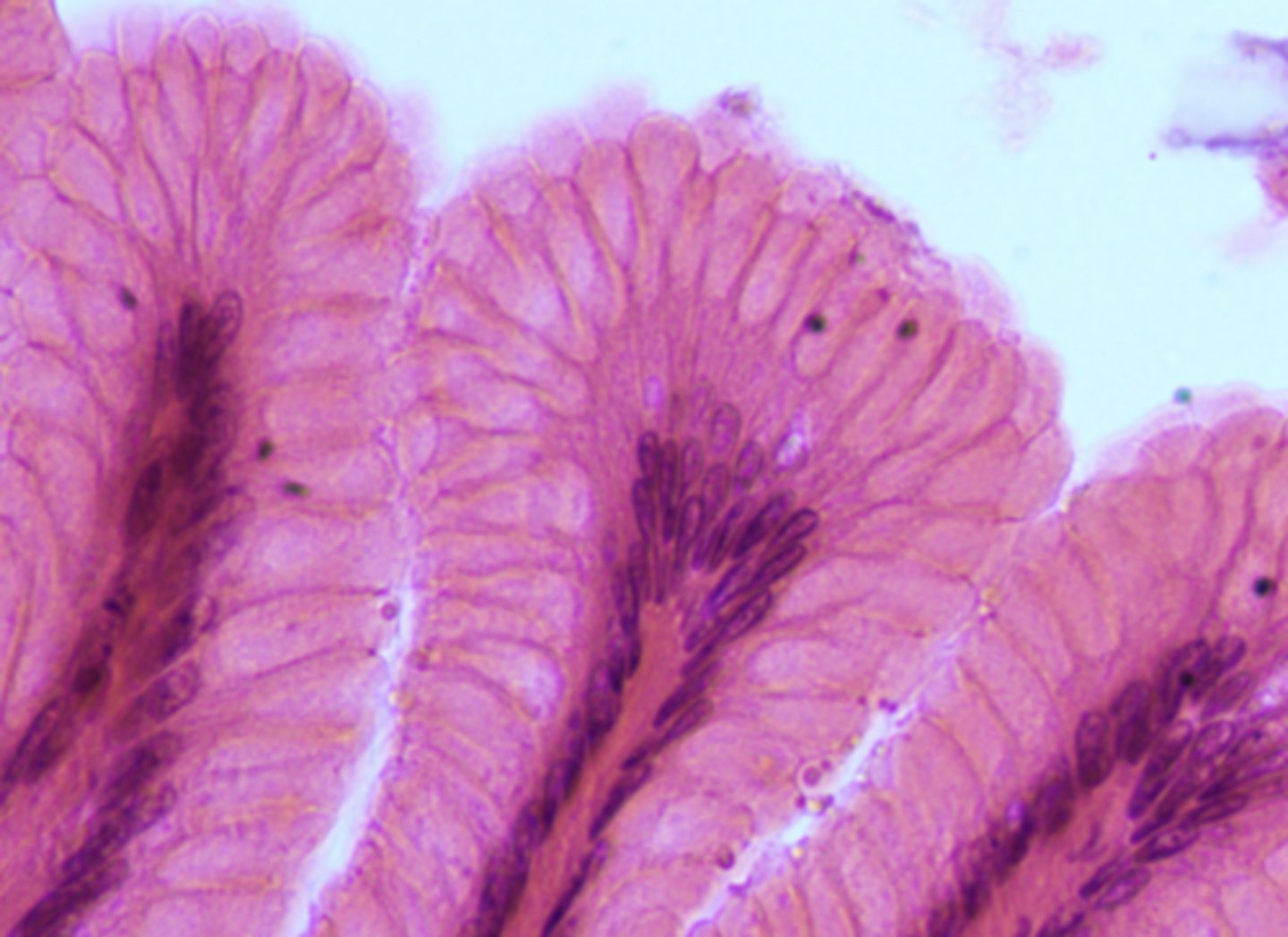
simple columnar epithelium
what cell type is shown
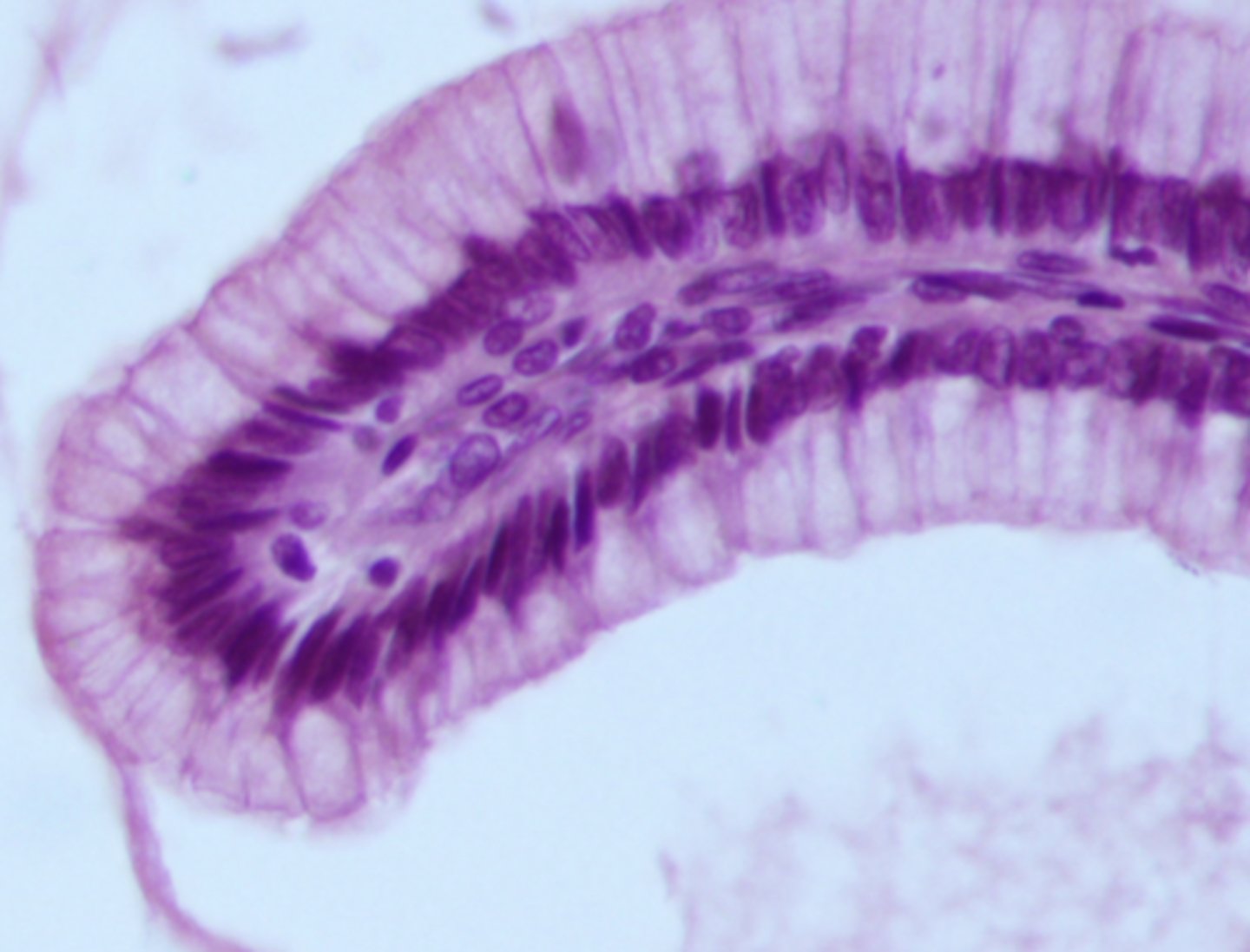
pseudostratified
what cell type is shown