Innate immunity: components and fxns pt 1
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
main idea sentinel cells
continuously monitor issues for infection and damage serving as the first line of immune detection
ex. macrophages
epithelial cells
dendritic cells
mast cells
pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) main idea
germline-encoded receptors that recognize conserved microbial structures (PAMPs) and endogenous danger signalsn (DAMPs)
PAMPs main idea
conserved aspects of microbial molecules such as LPS, flagellin, dsRNA, and unmethylate CpG DNA
DAMPs main idea
host derived molecules that signal sterile cellular damage (apoptosis > necrosis)
PRRs are categorized into
families based on their structure and localization: primarily TLRs, RLRs, and NLRs
PRR engagement initiates
intracellular signaling cascades involving adaptor proteins like MyD88, TRIF, and MAVS leading to transcriptional activation
Key transcription factors activated by
PRR signaling include NF-kB, IRF3/7, and AP-1 which regualte expression of inflammatory cytokines, interferons, and antimicrobial peptides
JAK/STAT signaling is a major downstream pathway of
many cytokine receptors activated during PRR signaling, and is targeted therapeutically in chronic inflammatory diseases
sentinel cell activation results in
cytokine and chemokine release (ex. TNF-a, IL-6, IL-1B)
***upregulation of costimulatory molecules used in adaptive immunity and recruitment of leukocytes and antigen presentation cells
dysregualted PRR signaling
contributes to disease states such as autoimmunity, autoinflammatory syndromes, sepsis, and chronic inflammatory conditions
therapeutic exploitation of PRR pathways includes
vx adjuvants (TLR agonists)
immunotherapies (STING agonists in cancer)
anti-inflammatory agents (NLRP3 inhibitors, JAK inhibitors)
cytokines
immune modulating agents made up of proteins
“cellular proteins’ that initiate immune responses from other cells
cell signals, “cell mail”
chemokines
super family of CYTOKINES that mediate chemotaxis
chemotaxis
movement towards or against cellular gradient
help direct cells in immune system to the site of infection/damage
interferons
type of cytokine that alerts the immune system
type I, II, III
help with antiviral defenses, inflammation, modulating immune responses, slowing down growth of cells
interleukin
class of glycoprotein made by leukocytes (WBCs) for regulating immune responses
innate immunity
first line of defense against pathogens
recruit other cells and stimulate inflammation
cellular receptors are
NON specific : self vs nonself
PATTERN RECOGNITION RECEPTORS (PRRs)
-recognize large patterns of molecules conserved across large classes of pathogens; Pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs)
can also recognize cellular damage (DAMPs)
innate cells
**myeloid progenitors
mast cells
granulocytes
phagocytes
natural killer cells (overlap)
granulocytes
eosinophils, basophils, neutrophils
phagocytes
monocytes, dendritic cells, macrophages
sentinel cells THE FRONTLINE
innate immune cells embedded in tissues
recognizes PAMPs and DAMPs via specialized PRRs
macrophages and dendritic cells
kupffer cells (liver)
Langerhans cells (skin and mucosa)
alveolar macrophages (lung)
microglia (brain)
macrophages
engulfs and digests pathogens, damaged cells, debris, and foreign materials (PACMAN)
dendritic cells (DC)
processes antigen and presents it to circulating T/B cells (antigen-presenting cell or APC)
engulf with tentacles
mast cells
resident cell of connective tissues with histamine and heparin granules; roles in allergy
ex. mast cell tumor give antihistamine then send to onco.
epithelial cells
physical barriers with PRRs (pattern)
tissue-resident lymphoid cells
tissue resident natural killer cells
monocyte vs macrophage
circulating vs tissue-resident monocyte
get special name based on their tissue tropism
dendritic cell residing or circulating?
tissue resident
granulocytes reside or circulate?
circulate
mast cells are a non circulating granulocyte that lives in the tissue
WBC circulate or reside
circulate
role of skin cells
langerhans cells
specialized DCs that capture antigens and migrate to draining lymph nodes to prime T cells
macrophages clear debris and recuit monocytes as needed
role of respiratory sentinel cells
alveolar macrophages patrol airway lumen and phagocytose pathogens
mast cells near blood vessels and mucosa release histamine upon allergen detection
role of GI tract sentinel cells
peyer’s patches are specialized lymphoid tissue patches where immune cells reside and process luminal contents
once sentinel cells are activated they initiate
cytokine and chemokine production
upregulation of costimulatory molecules and adaptive immune cell molecules (T cells)
type I IFN response
phagocytosis and ROS nitric oxide production
pattern recognition receptors (PRRs)
cellular protein receptor that recognizes molecules frequentyl found in pathogens or molecules released by damaged cells
pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs)
damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs)
can be on the cell surface or in the cytosol (usually in endosome)
types of PRRs
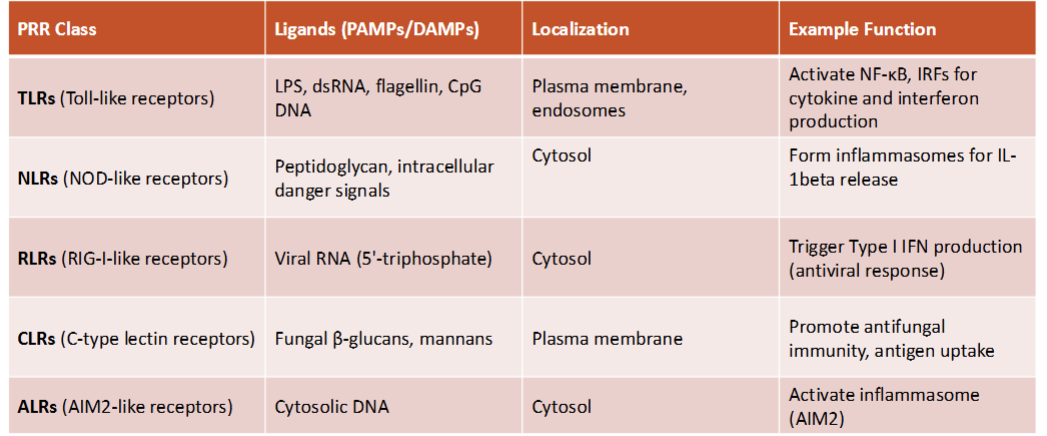
cellular localization of PRRs
cell surface: TLR2, TLR4, TLR5
endosomal: TLR3, TLR7,TLR8, TLR9—→ endosome addresses intercellular problems such as double stranded DNA = virus!
cytosolic PRRs= RIG-1, MDA5 (floating through cell)
PAMPs are conserved
molecular motifs found on or made by microorganisms but NOT host cells
do not readily mutate, highly conserved across broad microbe classes
should be absent in host cells
DAMPs are host
host-derived molecules released from stressed, injured or dying cells—signal sterile tissue damage (necrosis not apoptosis) and alert the immune system often in the absence of infection
act as **alarmins to promote inflammation, repair, and immune recruitment
originate from host cells, especially after **necrosis
PAMPs (infxn)
non self
DAMPs (injury)
altered self
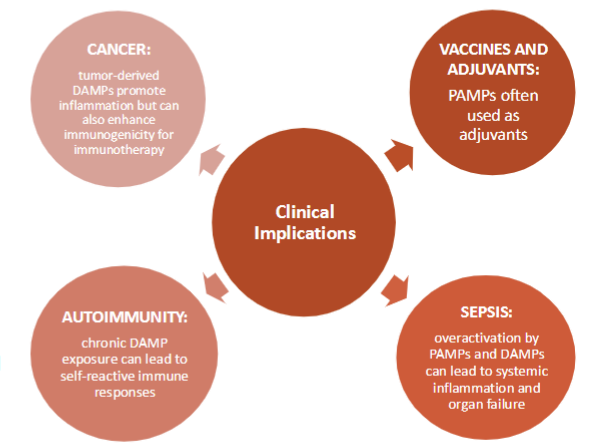
clinical implications
most PRRs require
adapter proteins
key downstream transcription factors
NF-kB: master regulator of inflammation
a. activated by MyD88 (TLRs), NOD1/2, MAVS, and CLRs
induces transcription of
a. cytokines IL-1B, TNF-a, IL-6
b. chemokines CCL2, CXCL8
c. adhesion molecules ICAM-1, VCAM-1
NF-kB is held inactive in the cytoplasm until activation leads to nuclear translocation (MASTER REGULATOR)
JAK/STAT pathway
arguably the most targeted immunological pathway in clinical medicine
clinical disorders linked to PRR dysregulation
sepsis and systemic inflammatory syndrome (SIRS)—hard to control once this occurs
autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases
viral infxns and immune invasion
therapeutic and diagnostic applications
PRRs as drug targets
modulation of PRR pathways—autoimmune diseases (inhibition of inflammasomes);cancer immunotherapy; chronic infections
vaccine adjuvants—many adjuvants are PAMP mimics that activate PRRs to enhance immune responses and memory formation
biomarker discovery—circulating DAMPs serve as biomarkers for tissue injury, cancer, and autoimmune flares
cytokine profiling helps monitor disease activity and therapeutic responses
actual drugs—JAK/STAT inhibitors
critical downstream signaling cascade for many cytokine receptors including those induced by PRR activation
**inib=inhibitor
sentinel cells include
macrophages, dendritic cells, mast cells, and epithelial cells are the body’s first responders continously surveilling tissues for signs of infection or damage
pattern recognition receptors (PRRs)
detect conserved microbial motifs (PAMPs) and host derived signals of damage (DAMPs) initiating innate immune responses
major PRR families include
TLRs, NOD-like receptors (NLRs) and RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs) each recognizing specific molecular patterns in distinct cellular compartments
PRR engagement triggers intracellular signaling cascades that activate
key transcription factors such as NF-kB, IRFs, and AP-1 leading to cytokine and interferon production
sentinel cells integrate
multiple signals to mount tailored responses—recruiting leukocytes, initiating phagocytosis, presenting antigen, and directing adaptive immunity
failure to regulate PRR signaling can lead to
pathological inflammation as seen in sepsis, autoimmune diseases, and autoinflammatory syndromes
PRRs are being leveraged in
clinical applications including vx adjuvants, immune therapies, and biomarkers for inflammation and infection