Gen 4100 Exam 3 | Iowa State University
1/14
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Euchromatin
less condensed
higher gene density
easier to transcribe
a. usually active transcriptionally
generally found on chromosome arms
lightly stained regions of chromosomes
Heterochromatin
more condensed
higher repeat content
harder to transcribe
a. usually inactive transcriptionally
generally found near centromeres
can be split into constitutive/facultative heterochromatin
darker stained regions of chromosomes
isn’t always tied to particular DNA sequences; it can spread

Constitutive Heterochromatin
always condensed
condensed in all cells (ex., Y chromosome)
Facultative Heterochromatin
sometimes condensed
condensed in only some cells and relaxed in other cells (ex., X chromosome)
ATAC-Seq
used to detect open chromatin
the assay for transposase-accessible chromatin with sequencing
Cytogenetics
used to visualize chromosomes
the branch of genetics that studies the structure of DNA within the nucleus
High-Resolution G-Banding
the karyotype of a human male can be examined with high-resolution G-banding
metaphase chromosomes stained with Giemsa have alternating bands of light and dark staining
giemsa stain binds to AT-rich regions of chromosome
Fluorescent in Siti Hybridization (FISH)
used to characterize genomes
depends on hybridization between metaphase chromosomes and a labeled DNA sequence
a. chromosomes are spread on a glass slide and denatured to make them single-stranded
b. a DNA sequence is labeled with a fluorescent tag to make it a probe
c. the probe hybridizes into chromosomes at complementary regions
Histone Tails
it can be modified through acetylation and methylation
histone methylation: often pack chromosomes
histone acetylation: unpack chromosomes
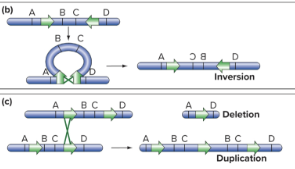
Four Types of Chromosomal Rearrangements
add or remove base pairs
deletions and duplications
relocate chromosomal regions without changing the number of base pairs
inversions and reciprocal translocations
Aberrant Crossing-Over
it can cause deletion, duplication, and inversion
crossing over between repeated sequences on homologous or nonhomologous chromosomes
Using Deletions to Locate Genes
examine a phenotype of a heterozygote for recessive allele and deletion:
a. if the phenotype is mutant, the mutant gene must lie inside the deleted region
b. if the phenotype is wild-type, the mutant gene must lie outside the deleted region
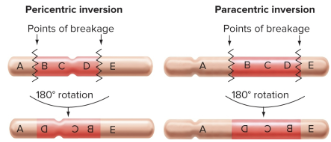
Consequences of Inversions
depends on the relationship of the inversion with the centromere
pericentric inversion: the centromere is within the inverted segment
paracentric inversion: the centromere is not within the inverted segment
Two Classes of TEs
class I: retrotransposons
a. copy-and-paste mechanism of transposition through RNA intermediate
two types:
a. LTR retrotransposons: long terminal repeat
b. non-LTR retrotransposons
class II: DNA transposons
a. cut-and-paste mechanism of direct transposition
two subclasses:
a. TIR transposons: terminal inverted repeat
b. helitrons
Consequences of Transposable Elements on Genomes
TE insertion can result in altered gene expression
TE can be inserted within the coding region of a gene or within the promoter and enhancer, which will affect its expression
gene relocation through TE transposition
due to the formation of composite TE
TEs can trigger spontaneous chromosomal rearrangements
due to unequal crossing over between TEs