BIOL 1020 Lesson 3 Practice Questions
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:12 PM on 10/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
1
New cards
The difference in lipid and protein composition between the membranes of the endomembrane is largely determined by
1. the physical separation of most membranes from each other.
2. the synthesis of different lipids and proteins in each of the organelles of the endomembrane system.
3. the function of the Golgi apparatus in sorting and directing membrane components.
4. the modification of the membrane components once they reach their final destination.
5. the transportation of membrane lipids among the endomembrane system by small membrane vesicles
1. the physical separation of most membranes from each other.
2. the synthesis of different lipids and proteins in each of the organelles of the endomembrane system.
3. the function of the Golgi apparatus in sorting and directing membrane components.
4. the modification of the membrane components once they reach their final destination.
5. the transportation of membrane lipids among the endomembrane system by small membrane vesicles
3. the function of the Golgi apparatus in sorting and directing membrane components
2
New cards
Which of the following statements correctly describes some aspect of protein secretions from prokaryotic cells?
1. proteins that are secreted by prokaryotes are synthesized on ribosomes that are bound to the cytoplasmic surface of the plasma membrane
2. in prokaryotes, the ribosomes that are used for the synthesis of secreted proteins are located outside of the cell.
3. prokaryotes contain large pores in their plasma membrane that permit the movement of proteins out of the cell.
4. the mechanism of protein secretion in prokaryotes is probably the same as that in eukaryotes
5. prokaryotes are unlikely to be able to secrete proteins because they lack an endomembrane system
1. proteins that are secreted by prokaryotes are synthesized on ribosomes that are bound to the cytoplasmic surface of the plasma membrane
2. in prokaryotes, the ribosomes that are used for the synthesis of secreted proteins are located outside of the cell.
3. prokaryotes contain large pores in their plasma membrane that permit the movement of proteins out of the cell.
4. the mechanism of protein secretion in prokaryotes is probably the same as that in eukaryotes
5. prokaryotes are unlikely to be able to secrete proteins because they lack an endomembrane system
1. proteins that are secreted by prokaryotes are synthesized on ribosomes that are bound to the cytoplasmic surface of the plasma membrane
3
New cards
A biologist wants specifically to examine the surfaces of different types of cells in kidney tubules of small mammals. The cells in question can be distinguished by external shape, size, and 3-D characteristics. Which of the following would be the optimum method for her study?
1. scanning electron microscopy
2. cell fractionation
3. transmission electron microscopy
4. light microscopy using stains specific to kidney function
5. light microscopy of living unstained material
1. scanning electron microscopy
2. cell fractionation
3. transmission electron microscopy
4. light microscopy using stains specific to kidney function
5. light microscopy of living unstained material
1. scanning electron microscopy
4
New cards
The fact that the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope has bound ribosomes allows one to most reliably conclude that
1. the nuclear envelope is physically separated from the endoplasmic reticulum
2. nuclear pore complexes contain proteins
3. the nuclear envelope is not part of the endomembrane system
4. small vesicles from the Golgi fuse with the nuclear envelope
5. at least some of the proteins that function in the nuclear envelope are made by the ribosomes on the nuclear envelope
1. the nuclear envelope is physically separated from the endoplasmic reticulum
2. nuclear pore complexes contain proteins
3. the nuclear envelope is not part of the endomembrane system
4. small vesicles from the Golgi fuse with the nuclear envelope
5. at least some of the proteins that function in the nuclear envelope are made by the ribosomes on the nuclear envelope
5. at least some of the proteins that function in the nuclear envelop are made by the ribosomes on the nuclear envelope
5
New cards
Which of the following contain statements concerning bacteria and archaea cells is correct?
1. archaea cells contain small membrane enclose organelles; bacteria do not
2. DNA is present in both archaea cells and bacteria cells
3. archaea cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus; bacteria do not
4. DNA is present in the mitochondria of both bacteria and archaea cells
1. archaea cells contain small membrane enclose organelles; bacteria do not
2. DNA is present in both archaea cells and bacteria cells
3. archaea cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus; bacteria do not
4. DNA is present in the mitochondria of both bacteria and archaea cells
2. DNA is present in both archaea cells and bacteria cells
6
New cards
Why isn’t the mitochondrion classified as part of the endomembrane system?
its structure is not derived from the ER or Golgi
7
New cards
Prokaryotes are classified as belonging to two different domains. What are the domains?
bacteria and archaea
8
New cards
Which of the following produces and modifies polysaccharides that will be secreted?
1. lysosome
2. vacuole
3. mitochondrion
4. golgi apparatus
5. perocisome
1. lysosome
2. vacuole
3. mitochondrion
4. golgi apparatus
5. perocisome
golgi apparatus
9
New cards
white blood cells engulf bacteria through what process?
phagocytosis
10
New cards
According to the fluid mosaic model of cell membranes, which of the following is a true statement about membrane phospholipids?
1. they can move laterally along the plane of the membrane
2. they have hydrophilic tails in the interior of the membrane
3. they occur in an uninterrupted bilayer, with membrane proteins restricted to the surface of the membrane
4. they are free to depart from the membrane and dissolve in the surrounding solution
5. they frequently flip-flop from one side of the membrane to the other
1. they can move laterally along the plane of the membrane
2. they have hydrophilic tails in the interior of the membrane
3. they occur in an uninterrupted bilayer, with membrane proteins restricted to the surface of the membrane
4. they are free to depart from the membrane and dissolve in the surrounding solution
5. they frequently flip-flop from one side of the membrane to the other
1. they can move laterally along the plane of the membrane
11
New cards
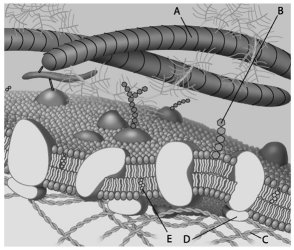
For the following questions, match the labelled component of the cell membrane in the figure with its description. Which of the following is a glycolipid?
B
12
New cards
The fluid mosaic model of the membrane proposes that membranes
1. are a phospholipid bilayer
2. consist of protein molecules embedded in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids
3. are a phospholipid bilare
4. are a single layer of phospholipids and proteins
5. consist of a mosaic of polysaccharides and proteins
1. are a phospholipid bilayer
2. consist of protein molecules embedded in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids
3. are a phospholipid bilare
4. are a single layer of phospholipids and proteins
5. consist of a mosaic of polysaccharides and proteins
consist of protein molecules embedded in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids
13
New cards
proton pumps are used in various ways by members of every domain of organisms: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. What does this most probably mean?
1. cells of each domain evolved proton pumps independently when oceans became more acidic.
2. proton pumps must have evolved before any living organisms were present on Earth.
3. proton gradients across a membrane were used by cells that were the common ancestor of all three domains of life.
4. proton pumps are necessary to all cell membranes.
5. the high concentration of protons in the ancient atmosphere must have necessitated a pump mechanism.
1. cells of each domain evolved proton pumps independently when oceans became more acidic.
2. proton pumps must have evolved before any living organisms were present on Earth.
3. proton gradients across a membrane were used by cells that were the common ancestor of all three domains of life.
4. proton pumps are necessary to all cell membranes.
5. the high concentration of protons in the ancient atmosphere must have necessitated a pump mechanism.
3. proton gradients across a membrane were used by cells that were the common ancestor of all three domains
14
New cards
The movement of potassium into an animal cell requires
1. an energy source such as. ATP
2. low cellular concentrations of sodium
3. high cellular concentrations of potassium
4. a potassium channel protein
5. a cotransport protein
1. an energy source such as. ATP
2. low cellular concentrations of sodium
3. high cellular concentrations of potassium
4. a potassium channel protein
5. a cotransport protein
1. an energy source such as ATP
15
New cards
Which of the following statements correctly describes the normal tonicity conditions conditions for typical plant and animal cells?
1. the animal cell is in a hypotonic solution, and the plant cell is in an isotonic solution
2. the animal cell is in an isotonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypertonic solution
3. the animal cell is in a hypertonic solution, and the plant cell is a hypotonic solution
4. the animal cell is in an isotonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypotonic solution
5. the animal cell is in a hypertonic solution, and the plant cell is in an isotonic solution
1. the animal cell is in a hypotonic solution, and the plant cell is in an isotonic solution
2. the animal cell is in an isotonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypertonic solution
3. the animal cell is in a hypertonic solution, and the plant cell is a hypotonic solution
4. the animal cell is in an isotonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypotonic solution
5. the animal cell is in a hypertonic solution, and the plant cell is in an isotonic solution
4. the animal cell is in an isotonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypotonic solution
16
New cards
The sodium-potassium pump is called an electrogenic pump because it
contributes to the membrane potential
17
New cards
Upon chemical analysis, a particular polypeptide was found to contain 100 amino acids. How many peptide bonds are present in this protein?
99
18
New cards
Which bonds are created during the formation of the primary structure of a protein?
Peptide bonds
19
New cards
If cells are grown in a medium containing radioactive 35S, which of these molecules will be labelled?
1. amylose
2. proteins
3. nucleic acids
4. phospholipids
5. both proteins and nucleic acids
1. amylose
2. proteins
3. nucleic acids
4. phospholipids
5. both proteins and nucleic acids
2. proteins
20
New cards
Which of the following polymers contain nitrogen?
1. starch
2. amylopectin
3. chitin
4. glycogen
5. cellulose
1. starch
2. amylopectin
3. chitin
4. glycogen
5. cellulose
3. chitin
21
New cards
The minimum distance two points can be separated and still discerned as separate is the
1. magnification
2. objective magnification
3. visibility
4. resolution
5. contrast
1. magnification
2. objective magnification
3. visibility
4. resolution
5. contrast
4. resolution
22
New cards
The Golgi apparatus has a polarity or sidedness to its structure and function. Which of the following statements correctly describes this polarity?
1. transport vesicles fuse with one side of the Golgi and leave from the opposite side
2. lipids in the membrane of the Golgi may be sorted and modified as they move from one side of the Golgi to the other
3. soluble proteins in the cisternae (interior) of the Golgi may be sorted and modified as they move from one side of the Golgi to the other
4. proteins in the membrane of the Golgi may be sorted and modified as they move from one side of the Golgi to the other
5. All of the above correctly describe polar characteristics of the Golgi function
1. transport vesicles fuse with one side of the Golgi and leave from the opposite side
2. lipids in the membrane of the Golgi may be sorted and modified as they move from one side of the Golgi to the other
3. soluble proteins in the cisternae (interior) of the Golgi may be sorted and modified as they move from one side of the Golgi to the other
4. proteins in the membrane of the Golgi may be sorted and modified as they move from one side of the Golgi to the other
5. All of the above correctly describe polar characteristics of the Golgi function
5. all of the above correctly describe polar characteristics of the Golgi function
23
New cards
The advantage of light microscopy over electron microscopy is that
1. light microscopy provides for higher magnification than electron microscopy
2. light microscopy allows one to view dynamic processes in living cells
3. specimen preparation for light microscopy does not produce artifacts
4. light microscopy provides higher contrast than electron microscopy
5. light microscopy provides for higher resolving power than electron microscopy
1. light microscopy provides for higher magnification than electron microscopy
2. light microscopy allows one to view dynamic processes in living cells
3. specimen preparation for light microscopy does not produce artifacts
4. light microscopy provides higher contrast than electron microscopy
5. light microscopy provides for higher resolving power than electron microscopy
2. light microscopy allows one to view dynamic processes in living cells
24
New cards
A cell with predominance of free ribosomes is most likely
1. enlarging its vacuole
2. producing primarily proteins for secretion
3. producing primarily cytoplasmic proteins
4. digesting large food particles
5. constructing an extensive cell wall or extracellular matrix
1. enlarging its vacuole
2. producing primarily proteins for secretion
3. producing primarily cytoplasmic proteins
4. digesting large food particles
5. constructing an extensive cell wall or extracellular matrix
3. producing primarily cytoplasmic proteins
25
New cards
Which organelle or structure is absent in plant cells?
1. centrosomes
2. perocisomes
3. Golgi vesicles
4. microtubules
5. mitochondria
1. centrosomes
2. perocisomes
3. Golgi vesicles
4. microtubules
5. mitochondria
1. centrosomes
26
New cards
One of the key innovations in the evolution of eukaryotes from a prokaryotic ancestor is the endomembrane system. What eukaryotic organelles or features might have evolved as a part of, or as an elaboration of, the endomembrane system?
1. nuclear envelope
27
New cards
Signals between the ECM and the cytoskeleton may be transmitted by
1. fibronectin
2. middle lamella
3. integrins
4. collagen
5. proteoglycans
1. fibronectin
2. middle lamella
3. integrins
4. collagen
5. proteoglycans
3. integrins
28
New cards
Hydrolytic enzymes must be segregated and packaged to prevent general destruction of cellular components. Which of the following organelles contain these hydrolytic enzymes in animal cells?
1. lysosome
2. chloroplast
3. glyoxysome
4. central vacuole
5. peroxisome
1. lysosome
2. chloroplast
3. glyoxysome
4. central vacuole
5. peroxisome
1. lysosome
29
New cards
Why are lipids and proteins free to move laterally in membranes?
1. the interior of the membrane is filled with liquid water
2. there are only weak hydrophobic interactions in the interior of the membrane
3. molecules such as cellulose can pull them in various directions
4. lipids and proteins repulse each other in the membrane
5. hydrophilic portions of the lipids are in the interior of the membrane
1. the interior of the membrane is filled with liquid water
2. there are only weak hydrophobic interactions in the interior of the membrane
3. molecules such as cellulose can pull them in various directions
4. lipids and proteins repulse each other in the membrane
5. hydrophilic portions of the lipids are in the interior of the membrane
2. there are only weak hydrophobic interactions in the interior of the membrane
30
New cards
In order for a protein to be an integral membrane protein, it would have to be
1. hydrophobic
2. completely covered with phospholipids
3. amphipathic, with at least one hydrophobic region
4. exposed on only one surface of the mebrane
5. hydrophilic
1. hydrophobic
2. completely covered with phospholipids
3. amphipathic, with at least one hydrophobic region
4. exposed on only one surface of the mebrane
5. hydrophilic
3. amphipathic, with at least one hydrophobic region
31
New cards
A bacterium engulfed by a white blood cell through phagocytosis will be digested by enzymes contained in
1. secretory vesicles
2. peroxisomes
3. lysosomes
4. Golgi vesicles
5. vacuoles
1. secretory vesicles
2. peroxisomes
3. lysosomes
4. Golgi vesicles
5. vacuoles
lysosomes
32
New cards
A protein that spans the phospholipid bilayer one or more times is
a transmembrane protein
33
New cards
Water passes quickly though cell membranes because
1. it moves through aquaporins in the membrane
2. water movement is ties to ATP hydrolysis
3. it moves through hydrophobic channels
4. the bilayer is hydrophilic
5. it is a small, polar, charged molecule
1. it moves through aquaporins in the membrane
2. water movement is ties to ATP hydrolysis
3. it moves through hydrophobic channels
4. the bilayer is hydrophilic
5. it is a small, polar, charged molecule
1. it moves through aquaporins in the membrane
34
New cards
What is the voltage across a membrane called?
membrane potential
35
New cards
Which of the following types of molecules are the major structural components of the cell membrane?
1. phospholipids and proteins
2. nucleic acids and proteins
3. glycoproteins and cholesterol
4. phospholipids and cellulose
5. proteins and cellulose
1. phospholipids and proteins
2. nucleic acids and proteins
3. glycoproteins and cholesterol
4. phospholipids and cellulose
5. proteins and cellulose
phospholipids and proteins
36
New cards
You are investigating different live cells using a light microscope. The first cells you observe are part of a larger organism. They have a clear area in the middle, a defined shape, and you can see many greenish ovals pressed up along the outer edges. The movement inside the cells that you observed are a result of
1. cilia movement
2. intermediate filaments
3. cell division
4. the interaction of actin and myosin filaments
5. the extracellular matrix
1. cilia movement
2. intermediate filaments
3. cell division
4. the interaction of actin and myosin filaments
5. the extracellular matrix
4. the interaction of actin and myosin filaments
37
New cards
The evolution of eukaryotic cells most likely involved
1. endosymbiosis of an aerobic bacterium in a larger host cell-the endosymbiont evolved into mitochondria
2. an endosymbiotic fungal cell evolved into the nucleus
3. acquisition of an endomembrane system, and subsequent evolution of mitochondria from a portion of the golgi
4. anaerobic archaea taking up residence inside a larger bacterial host cell to escape toxic oxygen-the anaerobic bacterium evolved into chloroplasts
1. endosymbiosis of an aerobic bacterium in a larger host cell-the endosymbiont evolved into mitochondria
2. an endosymbiotic fungal cell evolved into the nucleus
3. acquisition of an endomembrane system, and subsequent evolution of mitochondria from a portion of the golgi
4. anaerobic archaea taking up residence inside a larger bacterial host cell to escape toxic oxygen-the anaerobic bacterium evolved into chloroplasts
1. endosymbiosis of an aerobic bacterium in a larger host cell-the endosymbiont evolved into mitochondria
38
New cards
motor proteins provide for molecular motion in cells by interacting with what types of cellular structures?
cytoskeletal structures
39
New cards
If an individual has abnormal microtubules due to a hereditary condition, in which organ or tissues would you expect dysfunction?
1. limbs, heart, areas with a good deal of contraction
2. sperm, larynx, and trachea: cells and tissues that contain flagella or cillia
3. microvilli, alveoli, and glomeruli: cellular projections that increase surface area
4. all ducts, such as those from salivary or sebaceous glands, that transport fluids
5. phagocytic cells and white blood cells that exhibit amoeboid
1. limbs, heart, areas with a good deal of contraction
2. sperm, larynx, and trachea: cells and tissues that contain flagella or cillia
3. microvilli, alveoli, and glomeruli: cellular projections that increase surface area
4. all ducts, such as those from salivary or sebaceous glands, that transport fluids
5. phagocytic cells and white blood cells that exhibit amoeboid
2. sperm, larynx, and trachea: cells and tissues that contain flagella or cilia
40
New cards
Which of the following contains hydrolytic enzymes?
1. lysosome
2. vacuole
3. mitochondrion
4. Golgi apparatus
5. peroxisome
1. lysosome
2. vacuole
3. mitochondrion
4. Golgi apparatus
5. peroxisome
1. lysosome
41
New cards
Large numbers of ribosomes are present in cells that specialize in producing which of the following molecules?
1. proteins
2. cellulose
3. lipids
4. glycogen
5. nucleic acids
1. proteins
2. cellulose
3. lipids
4. glycogen
5. nucleic acids
1. proteins
42
New cards
Which organelle often takes up much of the volume of a plant cell?
1. lysosome
2. vacuole
3. mitochondrion
4. Golgi apparatus
5. peroxisome
1. lysosome
2. vacuole
3. mitochondrion
4. Golgi apparatus
5. peroxisome
2. vacuole
43
New cards
The extracellular matrix is thought to participate in the regulation of animal cell behaviour by communicating information from the outside to the inside of the cell via which of the following?
1. plasmodesmata
2. gap junctions
3. the nucleus
4. DNA and RNA
5. integrins
1. plasmodesmata
2. gap junctions
3. the nucleus
4. DNA and RNA
5. integrins
5. integrins
44
New cards
In receptor mediated endocytosis, receptor molecules initially project to the outside of the cell. Where do they end up after endocytosis?
1. on the ER
2. on the inside surface of the cell membrane
3. on the outside of the vessicles
4. on the outer surface of the nucleus
5. on the inside surface of the vesicle
1. on the ER
2. on the inside surface of the cell membrane
3. on the outside of the vessicles
4. on the outer surface of the nucleus
5. on the inside surface of the vesicle
5. on the inside surface of the vesicle
45
New cards
Which of the following would most likely move through the lipid bilayer of a plasma membrane most rapidly?
1. an amino acid
2. K+
3. glucose
4. starch
5. CO2
1. an amino acid
2. K+
3. glucose
4. starch
5. CO2
CO2
46
New cards
Which of these are not embedded in the hydrophobic portion of the lipid bilayer at all?
1. peripheral proteins
2. integrins
3. glycoproteins
4. transmembrane proteins
5. integral proteins
1. peripheral proteins
2. integrins
3. glycoproteins
4. transmembrane proteins
5. integral proteins
1. peripheral proteins
47
New cards
Celery stalks that are immersed in fresh water for several hours become stiff and hard. Similar stalks left in a 0.15 M salt solution become limp and soft. From this we can deduce that the cells of the celery stalks are
1. hypertonic to fresh water but hypotonic to the salt solution
2. hypertonic to both fresh water and the salt solution
3. hypotonic to both fresh water and the salt solution
4. hypotonic to fresh water but hypertonic to the salt solution
5. isotonic with fresh water but hypotonic to the salt solution
1. hypertonic to fresh water but hypotonic to the salt solution
2. hypertonic to both fresh water and the salt solution
3. hypotonic to both fresh water and the salt solution
4. hypotonic to fresh water but hypertonic to the salt solution
5. isotonic with fresh water but hypotonic to the salt solution
1. hypertonic to fresh water but hypotonic to the salt solution
48
New cards
When biological membranes are frozen and then fractured, they tend to break along the middle layer of the bilayer. The best explanation for this is that
1. the integral membrane proteins are not strong enough to hold the bilayer together
2. the hydrophobic interactions that hold the membrane together are weakest at this point
3. the carbon-carbon bonds of the phospholipid tails are easily broken
4. water that is present in the middle of the bilayer freezes and i easily fractured
5. hydrophilic interactions between the opposite membrane surfaces are destroyed on freezing
1. the integral membrane proteins are not strong enough to hold the bilayer together
2. the hydrophobic interactions that hold the membrane together are weakest at this point
3. the carbon-carbon bonds of the phospholipid tails are easily broken
4. water that is present in the middle of the bilayer freezes and i easily fractured
5. hydrophilic interactions between the opposite membrane surfaces are destroyed on freezing
2. the hydrophobic interactions that hold the membrane together are weakest at this point
49
New cards
Which of the following statements is correct about diffusion?
1. it is very rapid over long distances
2. it is a passive process in which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration
3. it is an active process in which molecules move from a region of lower concentration to one of higher concentration
4. it requires integral proteins in the cell membrane
5. it requires an expenditure of energy by the cell
1. it is very rapid over long distances
2. it is a passive process in which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration
3. it is an active process in which molecules move from a region of lower concentration to one of higher concentration
4. it requires integral proteins in the cell membrane
5. it requires an expenditure of energy by the cell
2. it is a passive process in which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration
50
New cards
Which organelle is the primary site of ATP synthesis in eukaryotic cells?
1. lysosome
2. vacuole
3. mitochondrion
4. Golgi apparatus
5. peroxisome
1. lysosome
2. vacuole
3. mitochondrion
4. Golgi apparatus
5. peroxisome
3. mitochondrion
51
New cards
Ions can travel directly from the cytoplasm of one animal cell to the cytoplasm of an adjacent cell through
1. desmosomes
2. gap junctions
3. tight junctions
4. intermediate filaments
5. plasmodesmata
1. desmosomes
2. gap junctions
3. tight junctions
4. intermediate filaments
5. plasmodesmata
2. gap junctions
52
New cards
Which of the following contain the 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules, consisting of nine doublets of microtubules surrounding a pair of single microtubules?
1. both basal bodies and primary (nonmotile) cilia
2. centrioles only
3. both flagella and motile cilia
4. both motile cilia and primary (nonmotile) cilia
5. both centrioles and basal bodies
1. both basal bodies and primary (nonmotile) cilia
2. centrioles only
3. both flagella and motile cilia
4. both motile cilia and primary (nonmotile) cilia
5. both centrioles and basal bodies
3. both flagella and motile cilia
53
New cards
Which plant cell organelle contains its own DNA and ribosomes?
mitochondrion
54
New cards
The nuclear lamina is an array of filaments on the inner side of the nuclear membrane. If a method were found that could cause the lamina to fall into disarray, what would you expect to be the most likely consequence?
1. the inability of the nucleus to divide during cell division
2. failure of chromosomes to carry genetic information
3. inability of the nucleus to keep out destructive chemicals
4. a change in the shape of the nucleus
5. a loss of all nuclear function
1. the inability of the nucleus to divide during cell division
2. failure of chromosomes to carry genetic information
3. inability of the nucleus to keep out destructive chemicals
4. a change in the shape of the nucleus
5. a loss of all nuclear function
4. a change in shape of the nucleus
55
New cards
An organism with a cell wall would most likely be unable to take in materials through
1. diffusion
2. active transport
3. osmosis
4. facilitated diffusion
5. phagocytosis
1. diffusion
2. active transport
3. osmosis
4. facilitated diffusion
5. phagocytosis
5. phagocytosis
56
New cards
Which of the following is most likely true of a protein that cotransports glucose and sodium ions into the intestinal cells of an animal?
1. sodium ions can move down their electrochemical gradient through the cotransporter whether or not glucose is present outside the cell
2. a substance that blocks sodium ions from binding to the cotransport proteins will also block the transport of glucose
3. the cotransporter can also transport potassium ions
4. glucose entering the cell along its concentration provides energy for uptake of sodium ions against the electrochemical gradient
5. the sodium ions are moving down their electrochemical gradient while glucose is moving up
1. sodium ions can move down their electrochemical gradient through the cotransporter whether or not glucose is present outside the cell
2. a substance that blocks sodium ions from binding to the cotransport proteins will also block the transport of glucose
3. the cotransporter can also transport potassium ions
4. glucose entering the cell along its concentration provides energy for uptake of sodium ions against the electrochemical gradient
5. the sodium ions are moving down their electrochemical gradient while glucose is moving up
2. a substance that blocks sodium ions from binding to the cotransport protein will also block the transport of glucose
57
New cards
The phosphate transport system in bacteria imports phosphate into the cell even when the concentration of phosphate outside the cell is much lower than the cytoplasmic phosphate concentration. Phosphate import depends on a pH gradient across the membrane–more acidic outside the cell than inside the cell. Phosphate transport is an example of
1. active transport
2. osmosis
3. passive diffusion
4. facilitated diffusion
5. cotransport
1. active transport
2. osmosis
3. passive diffusion
4. facilitated diffusion
5. cotransport
5. cotransport
58
New cards
The presence of cholesterol in the plasma membranes of some animals
1. make the animals more susceptible to circulatory disorders
2. enables the animal to remove hydrogen atoms from saturated phospholipids
3. enables the animal to add hydrogen atoms to unsaturated phospholipids
4. makes the membrane less flexible, allowing it to sustain greater pressure from within the cell
5. enables the membrane to stay fluid more easily when cell temperature drops
1. make the animals more susceptible to circulatory disorders
2. enables the animal to remove hydrogen atoms from saturated phospholipids
3. enables the animal to add hydrogen atoms to unsaturated phospholipids
4. makes the membrane less flexible, allowing it to sustain greater pressure from within the cell
5. enables the membrane to stay fluid more easily when cell temperature drops
5. enables the membrane to stay fluid more easily when cell temperature drops
59
New cards
Which of the following statements about the cytoskeleton is *true*?
1. microfilaments are structurally rigid and resist compression, whereas microtubules resist tension (stretching)
2. the dynamic aspect of cytoskeletal function is made possible by the assembly and disassembly of a large variety of proteins into complex aggregates
3. transport vesicles among the membranes of the endomembrane system produce the cytoskeleton
4. chemicals that block the assembly of the cytoskeleton would cause little effect on the cell's response to external signals and stimuli
5. movement of cilia and flagella is the result of motor proteins causing microtubules to move relative to each other
1. microfilaments are structurally rigid and resist compression, whereas microtubules resist tension (stretching)
2. the dynamic aspect of cytoskeletal function is made possible by the assembly and disassembly of a large variety of proteins into complex aggregates
3. transport vesicles among the membranes of the endomembrane system produce the cytoskeleton
4. chemicals that block the assembly of the cytoskeleton would cause little effect on the cell's response to external signals and stimuli
5. movement of cilia and flagella is the result of motor proteins causing microtubules to move relative to each other
5. movement of cilia and flagella is the result of motor proteins causing microtubules to move relative to each other
60
New cards
Which type of organelle or structure is primarily involved in the synthesis of oils, phospholipids, and steroids?
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
61
New cards
In a plant cell, DNA may be found
1. only in the nucleus and chloroplasts
2. in the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and peroxisomes
3. only in the nucleus and mitochondria
4. in the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts
5. only in the nucleus
1. only in the nucleus and chloroplasts
2. in the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and peroxisomes
3. only in the nucleus and mitochondria
4. in the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts
5. only in the nucleus
4. in the nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplasts
62
New cards
The smallest cell structure that would most likely be visible with a standard (not super-resolution) research grade microscope is
1. a nuclear pore
2. a mitochondrion
3. a ribosome
4. a microtubule
5. a microfilament
1. a nuclear pore
2. a mitochondrion
3. a ribosome
4. a microtubule
5. a microfilament
2. a mitochondrion
63
New cards
Ions diffuse across membranes through specific ion channels
1. down the electrical gradients
2. down their chemical gradients
3. down the osmotic potential gradients
4. down their concentration gradients
5. down their electrochemical gradients
1. down the electrical gradients
2. down their chemical gradients
3. down the osmotic potential gradients
4. down their concentration gradients
5. down their electrochemical gradients
5. down their electrochemical gradients
64
New cards