AP - exam 3 (lymphatic)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
lymphoid organs and tissues
_________ includes. . .
- spleen
- thymus
- tonsils
- lymph nodes
lymphatic vessels
what are drainage vessels in the lymphatic system, which circulates ~3L interstitial fluid per day?
lymphatic capillaries
what are blind-ended vessels similar to blood capillaries, but are more permeable?
pathogens or cancer cells
lymphatic capillaries can act as a route for _________ to travel throughout the body, for they can take up larger molecules such as proteins and cell debris
collagen filaments1
what anchors minivalves to the matrix, where increases in ECF volume opens minivalves more?
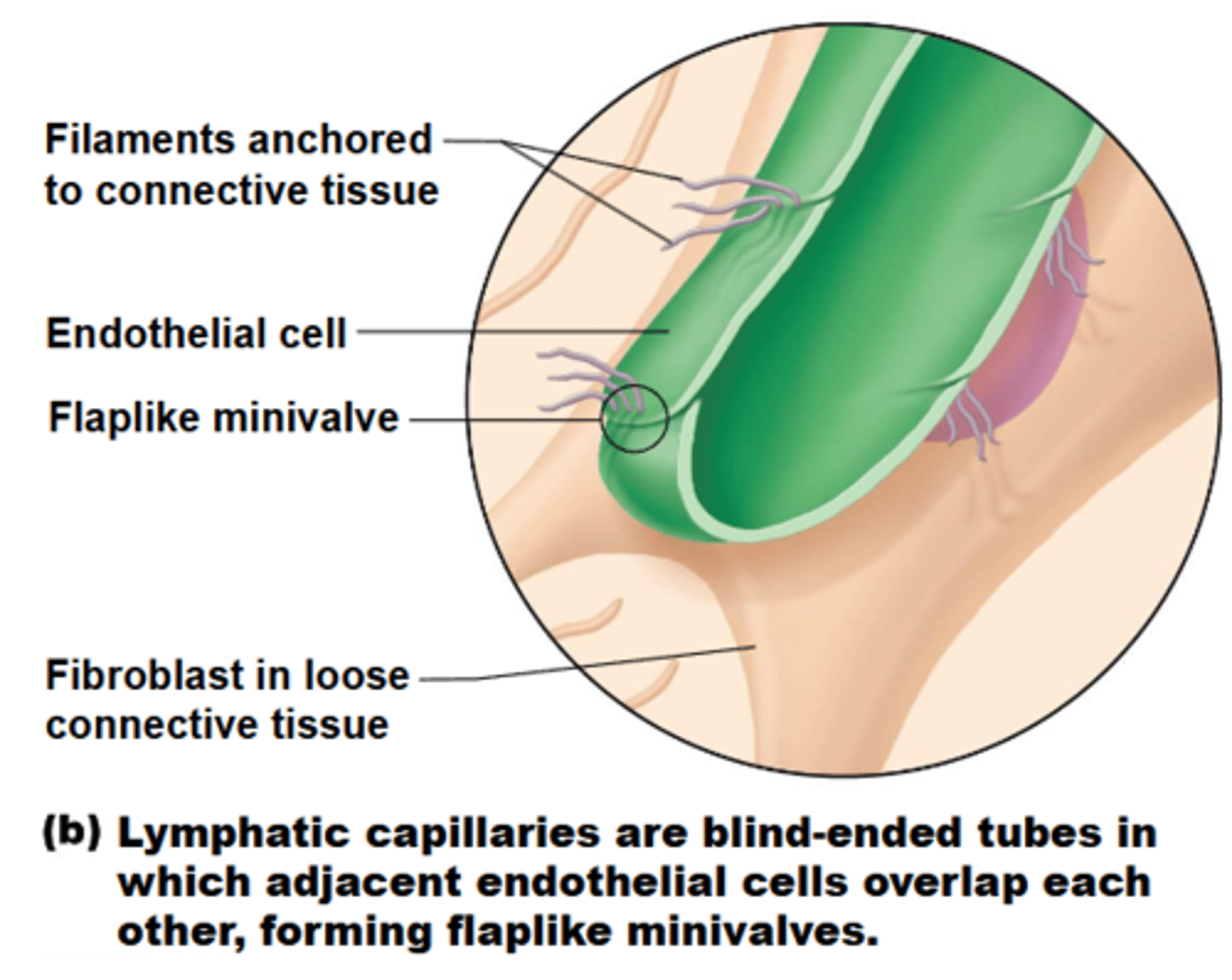
lacteals
what are specialized lymph capillaries present in intestinal mucosa that absorb digested fat + deliver fatty lymph (chyle) to blood?
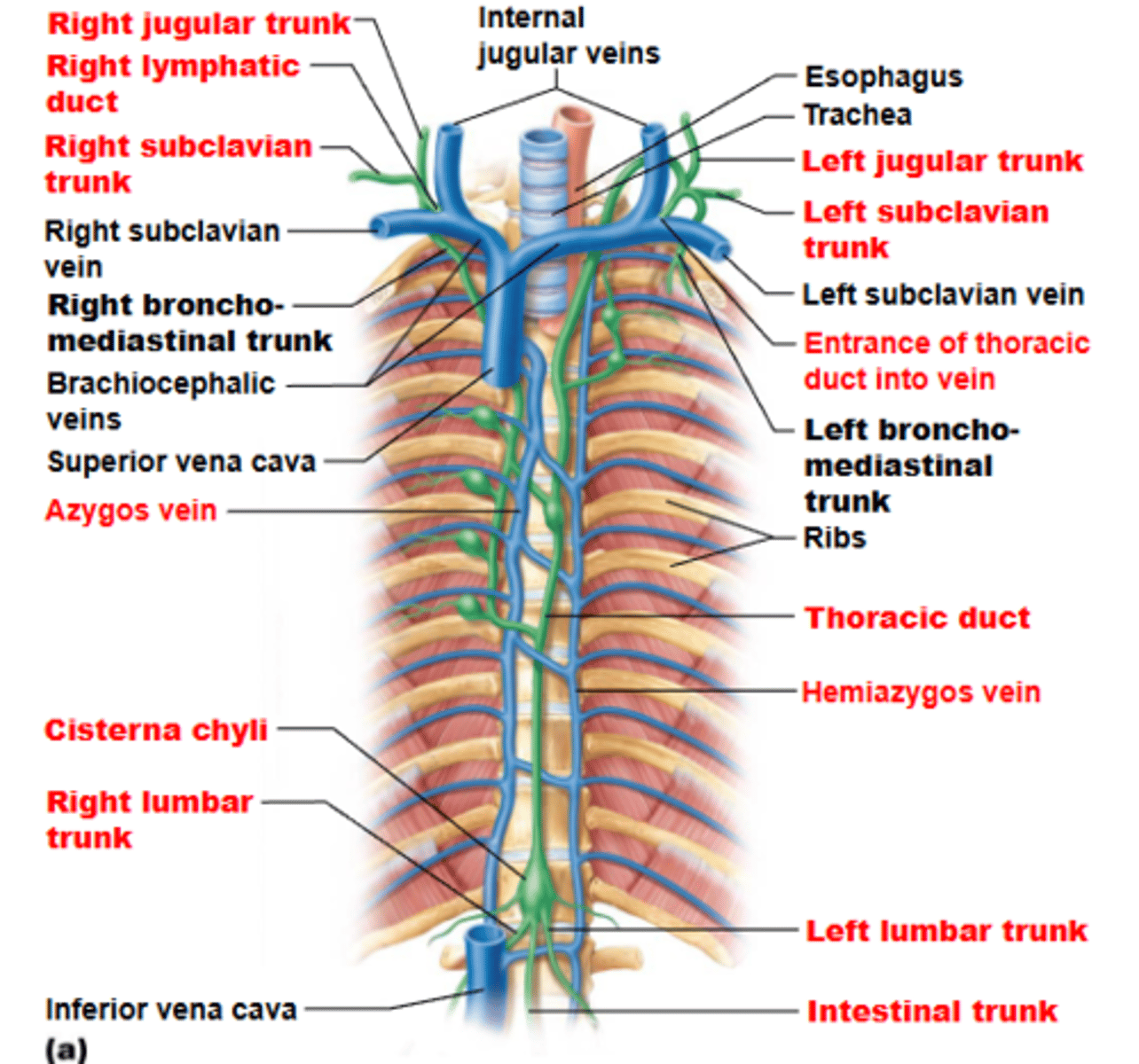
right lymphatic duct
what lymphatic duct drains the right upper arm and right side of head + thorax?
thoracic duct
what lymphatic duct drains the rest of the body, where in half of individuals, it starts off as enlarged sac called cisterna chyli?
internal jugular and subclavian veins junction
where do lymphatic ducts empty into venous circulation at?
propelled by
lymph is _______ . . .
- milking of skeletal muscle
- pressure changes in thorax during breathing
- valves to prevent backflow
- pulsations of nearby arteries
- contractions of smooth muscle in walls of lymphatics
physical activity
what increases flow of lymph?
lymphedema
_______ is defined as severe localized edema, which is caused by anything that prevents normal return of lymph to blood
bean
what is the typical shape of most lymph nodes?

cortex
what structure of a lymph node has lymphoid follicles, which are solid, spherical bodies consisting of tightly packed lymphoid cells + reticular fibers?
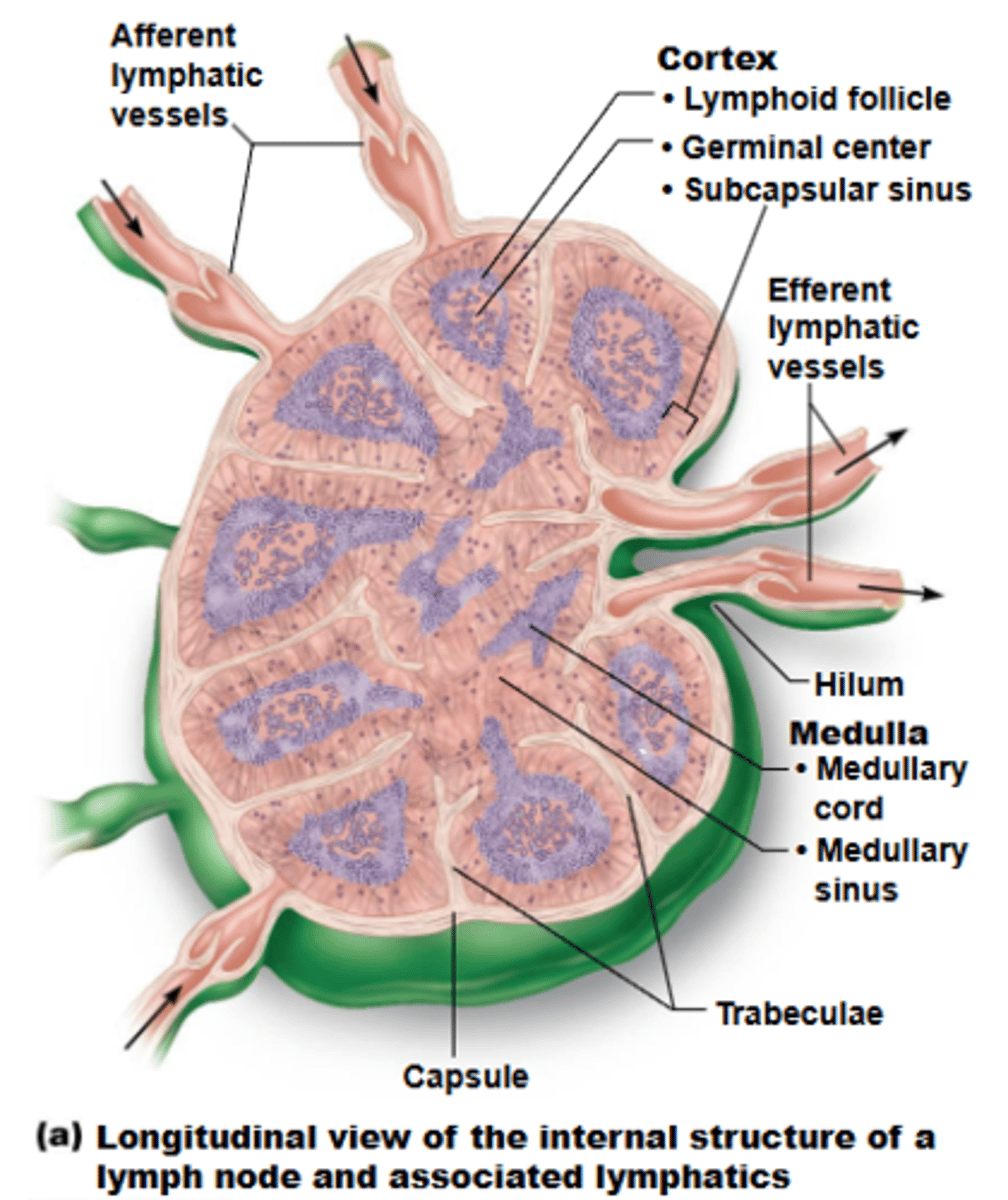
germinal centers
the cortex of lymph nodes contains ___________ of proliferating B cells
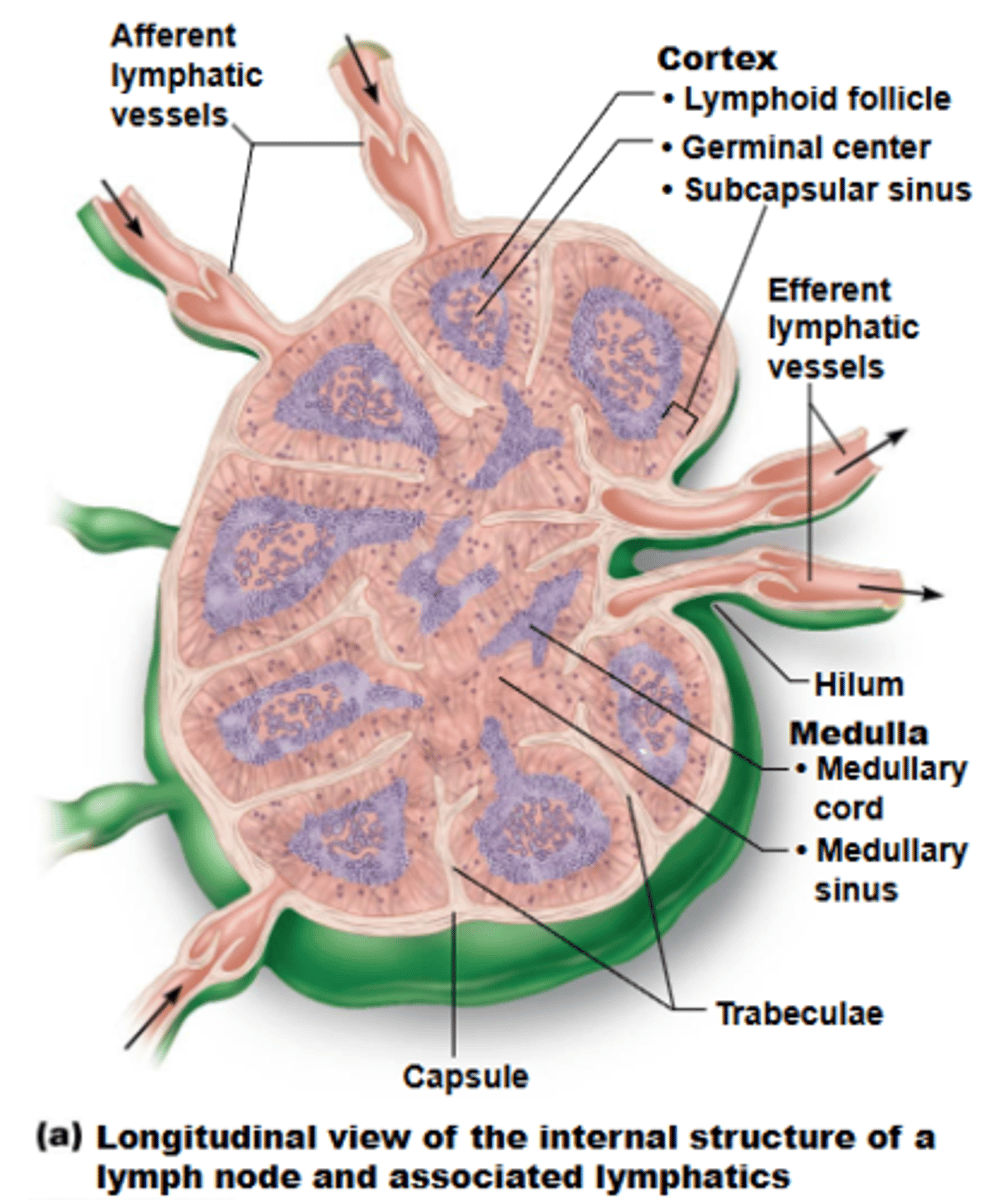
medulla
what structure of a lymph node contains cords and lymph sinuses, which contains lymphatic capillaries sustained by reticular fibers?
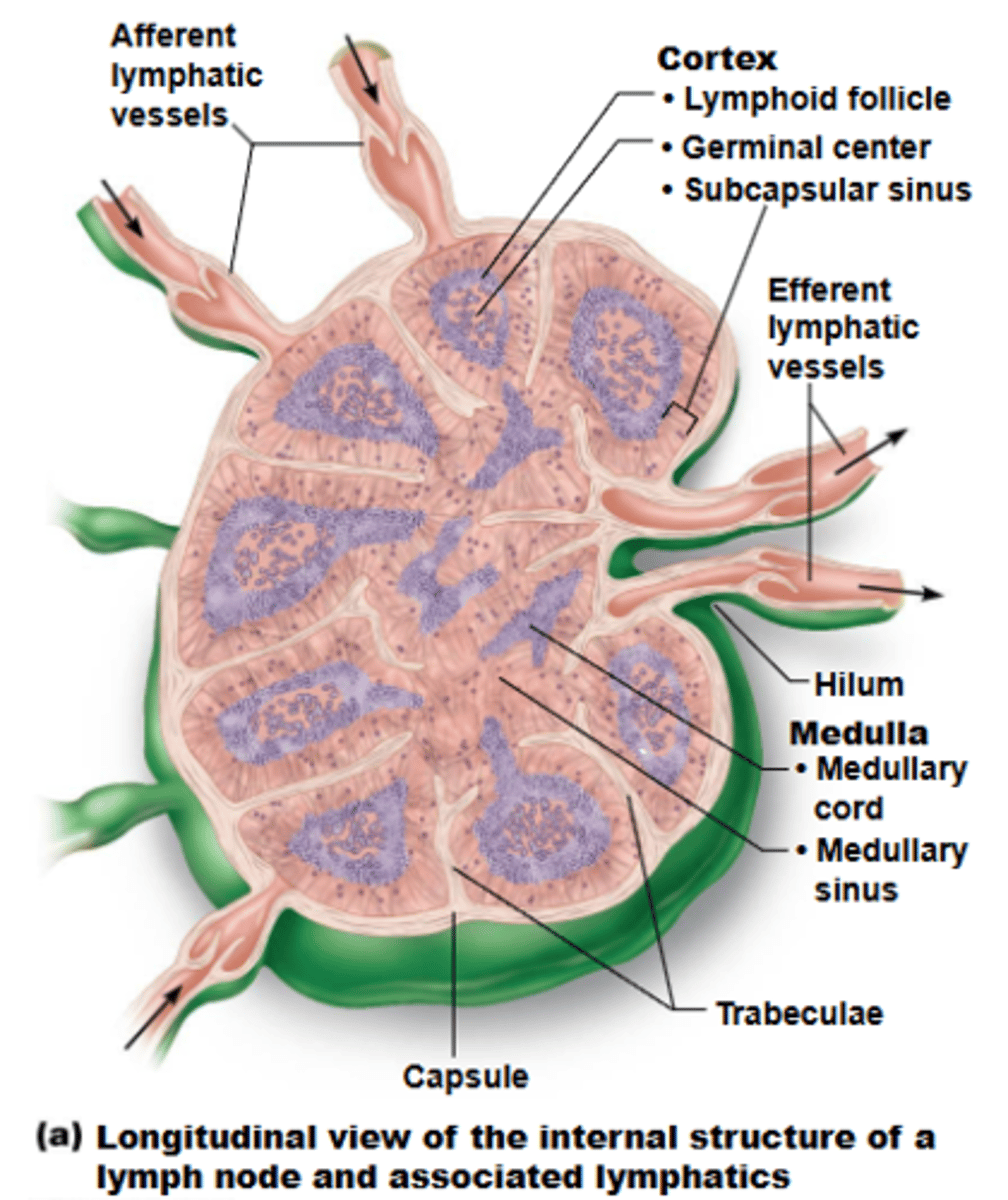
cords
the medullary ______ of the medulla of a lymph node contains B cells, T cells, and plasma cells
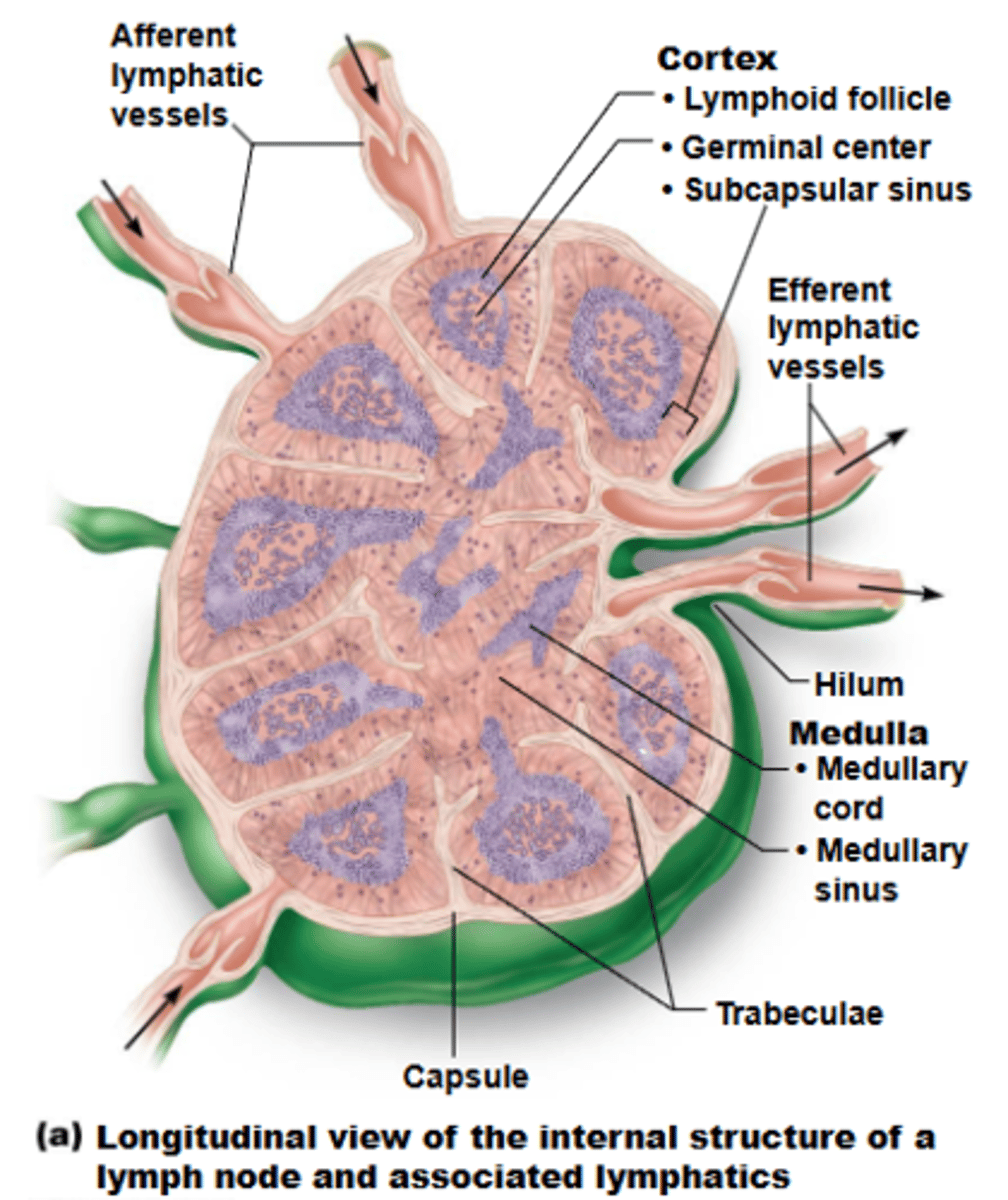
afferent lymphatic vessels
lymph enters convex side of lymph node via ___________, then travels through large subcapsular sinuses into smaller sinuses throughout cortex + medulla
efferent lymphatic vessels
lymph exits concave side at hilum of lymph node via _____________
stagnate
presence of fewer efferent vessels causes flow to somewhat ______, allowing lymphocytes + macrophages time to function
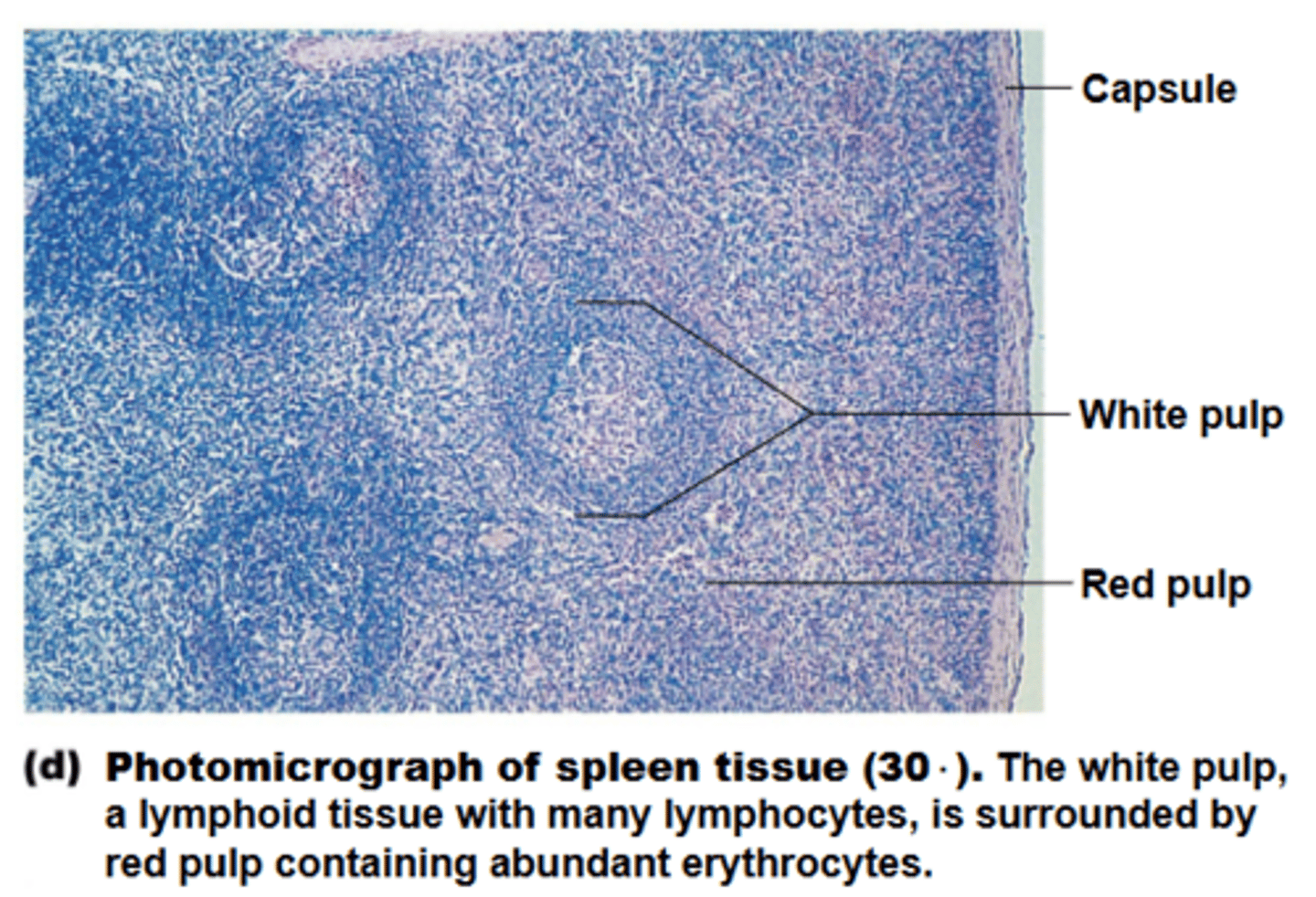
spleen
what is the largest lymphoid organ and is the site of lymphocyte proliferation + immune surveillance + response?
red blood cells
the breakdown products of ________ are stored in the spleen, such as iron, for later resue
fetal erythrocyte production
the spleen may be the site of ___________, or red blood cell formation in fetus
white pulpmucfeeee
regarding the spleen, what part contains mostly lymphocytes on reticular fibers with clusters around central arteries?
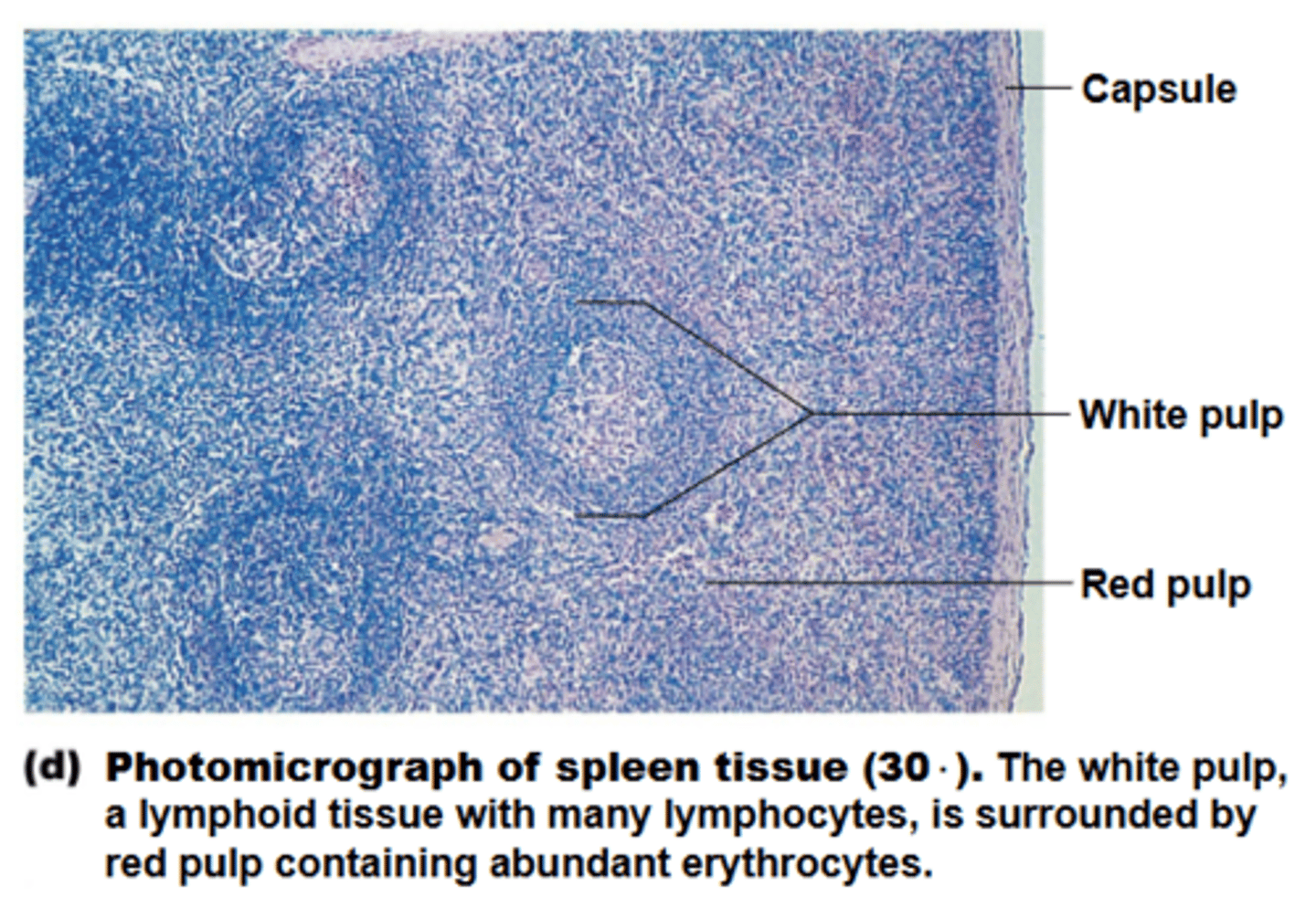
red pulp
regarding the spleen, what site is where old blood cells + bloodborne pathogens are destroyed?
mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT)
what protects pathogens from trying to enter the body and is found in. . .?
- mucosa of respiratory tract
- genitourinary organs
- digestive tract
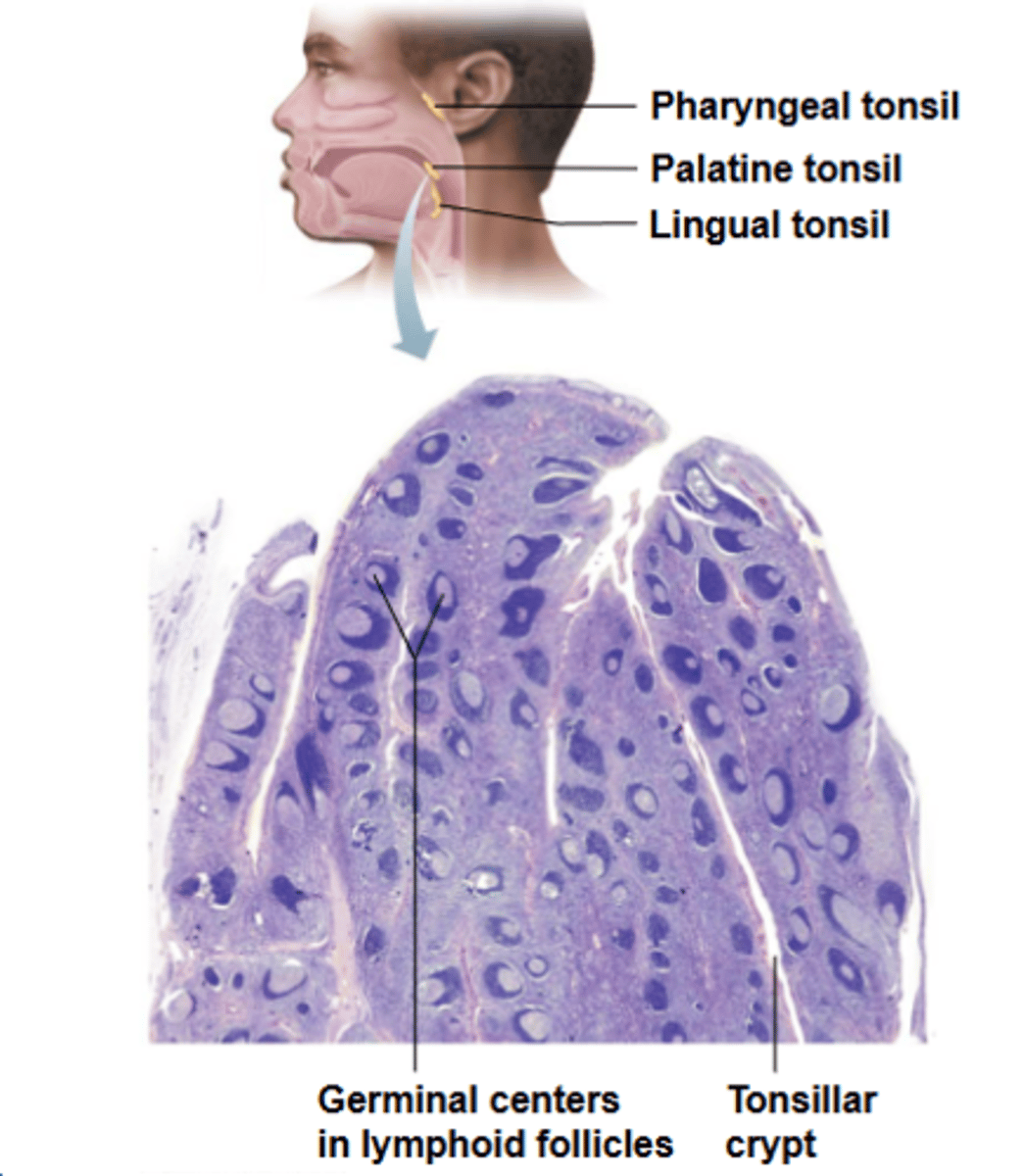
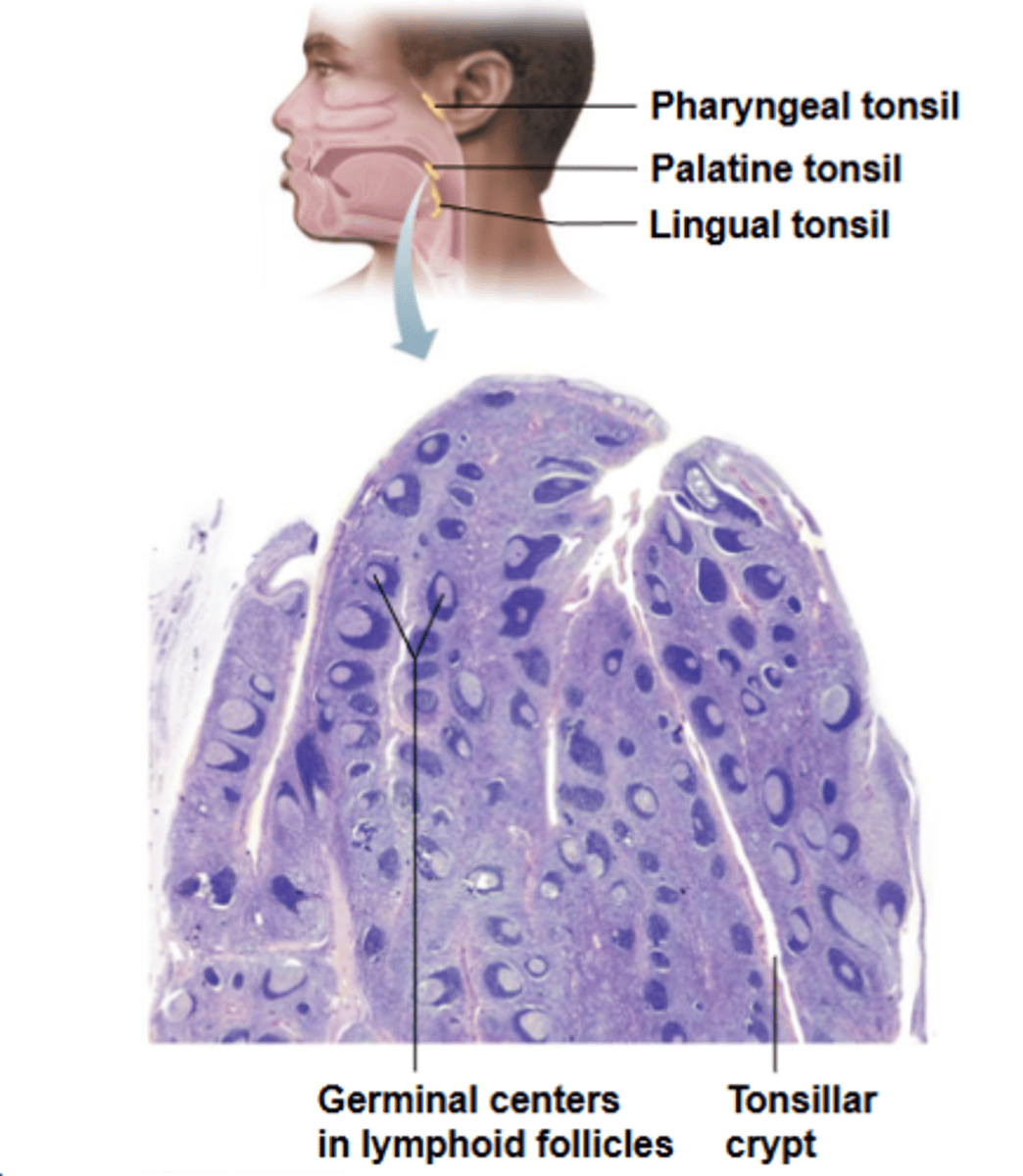
tonsils
what structure's function involves gathering and removing pathogens in food/air, where it forms a ring of lymphatic tissue around pharynx and appear as swellings of mucosa?
not
tonsils are ___________ fully encapsulated and contain follicles with germinal centers and scattered lymphocytes
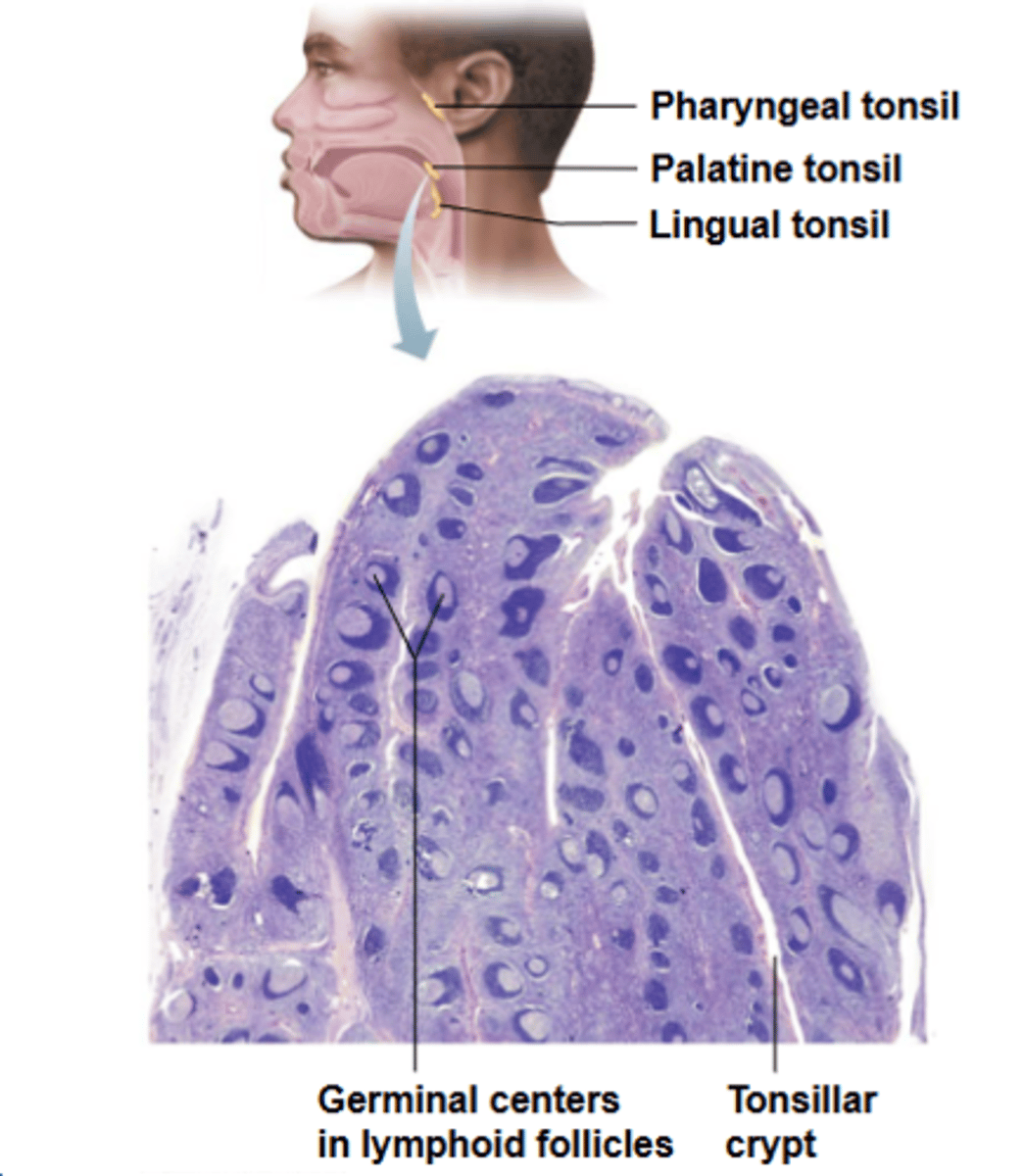
tonsillar crypts
what are small, pocket-like structures that trap bacteria or particulate matter and destroy them?
memory cells
after exposure to bacteria, immune cells activate and build what against potential pathogens?
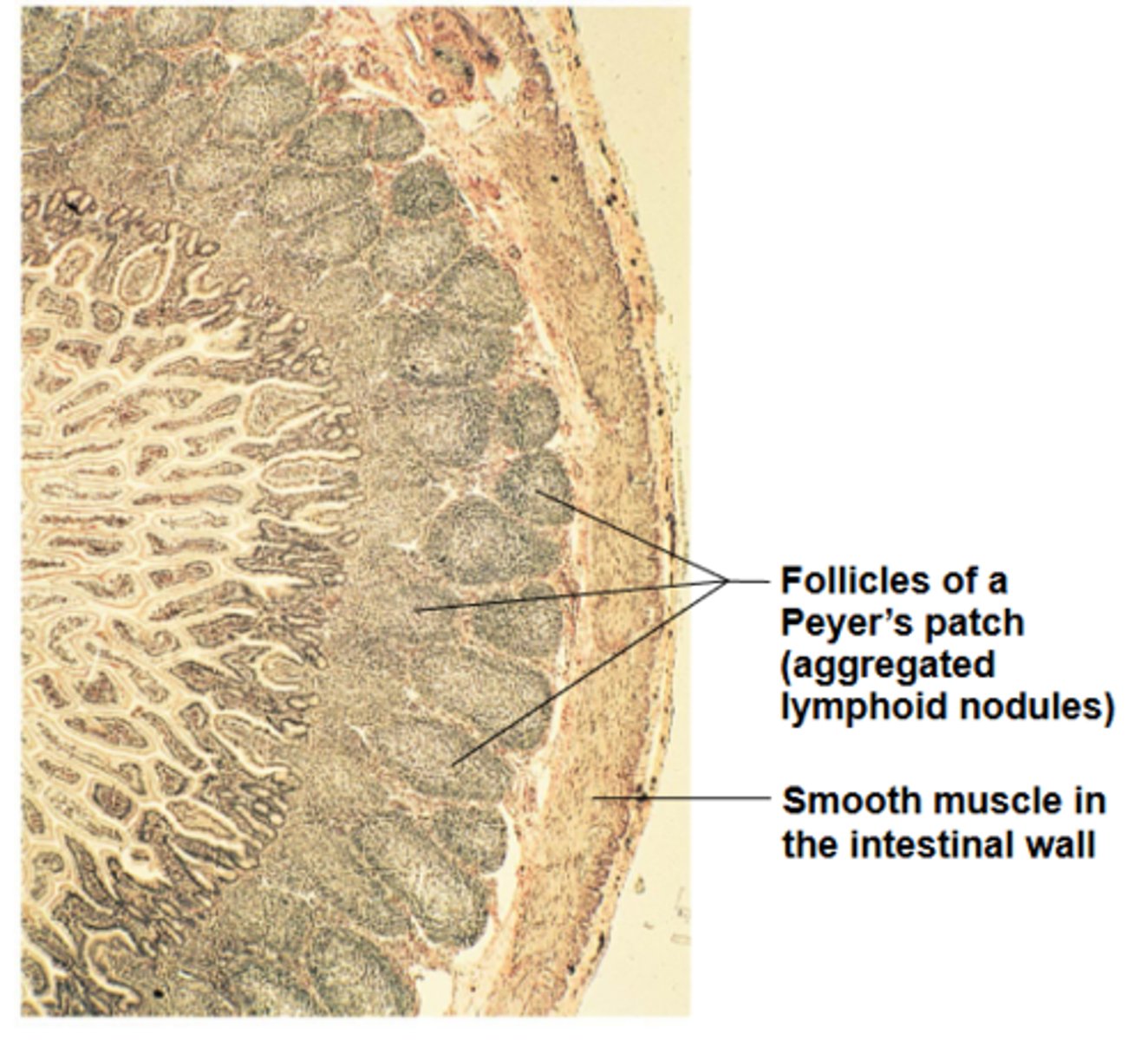
Peyer's patches
what are clusters of lymphoid follicles in wall of distal portion of small intestine that are structurally similar to tonsils?
appendix
what is the offshoot of the first part of the large intestine referred to as?
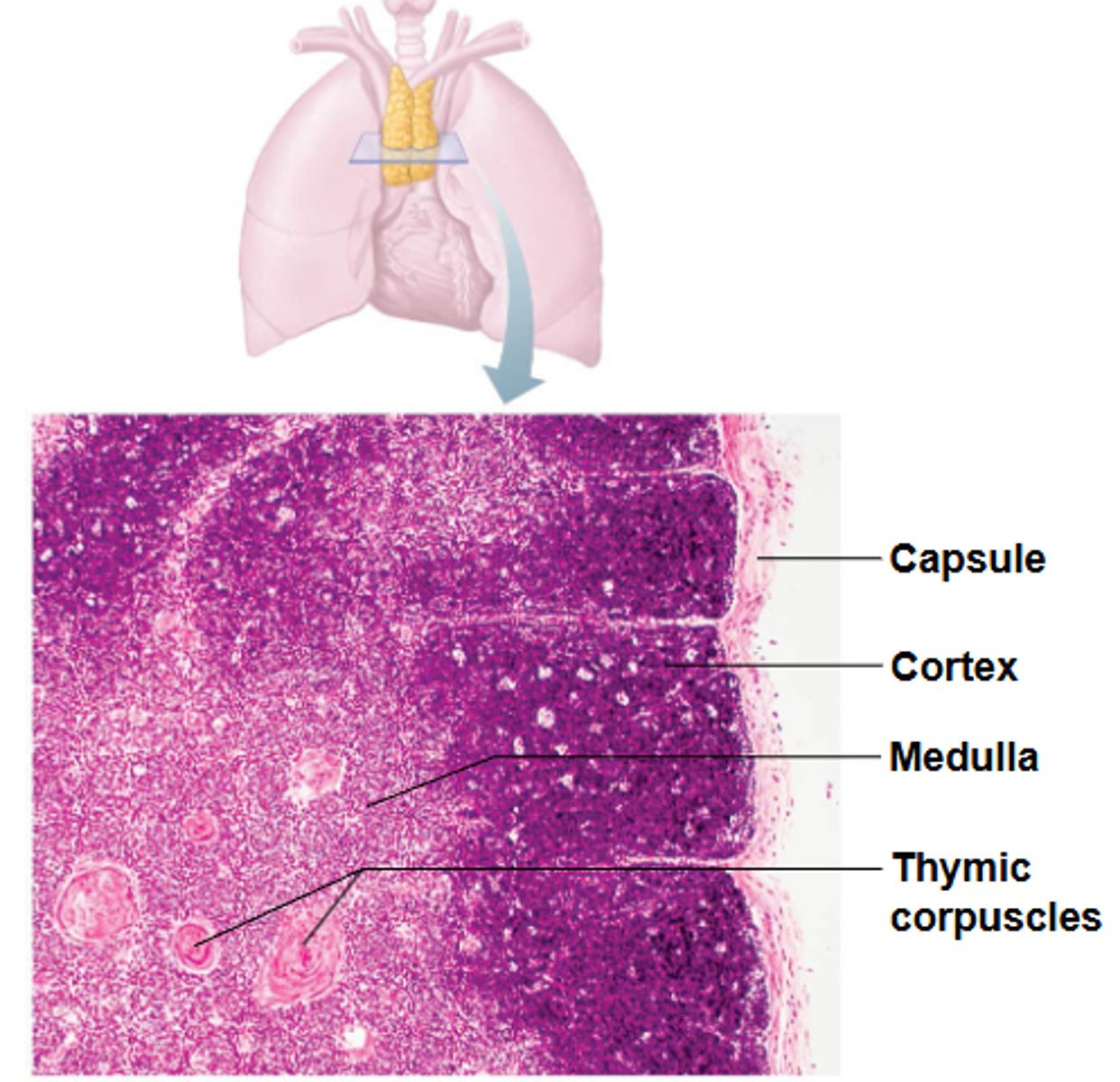
thymus
what is a lymphoid organ found in inferior neck into mediastinum and partially overlies the heart, where it stops growing during adolescence then gradually atrophies?
directly
the thymus does not ___________ fight antigens and functions strictly in T lymphocyte maturation
epithelial cells
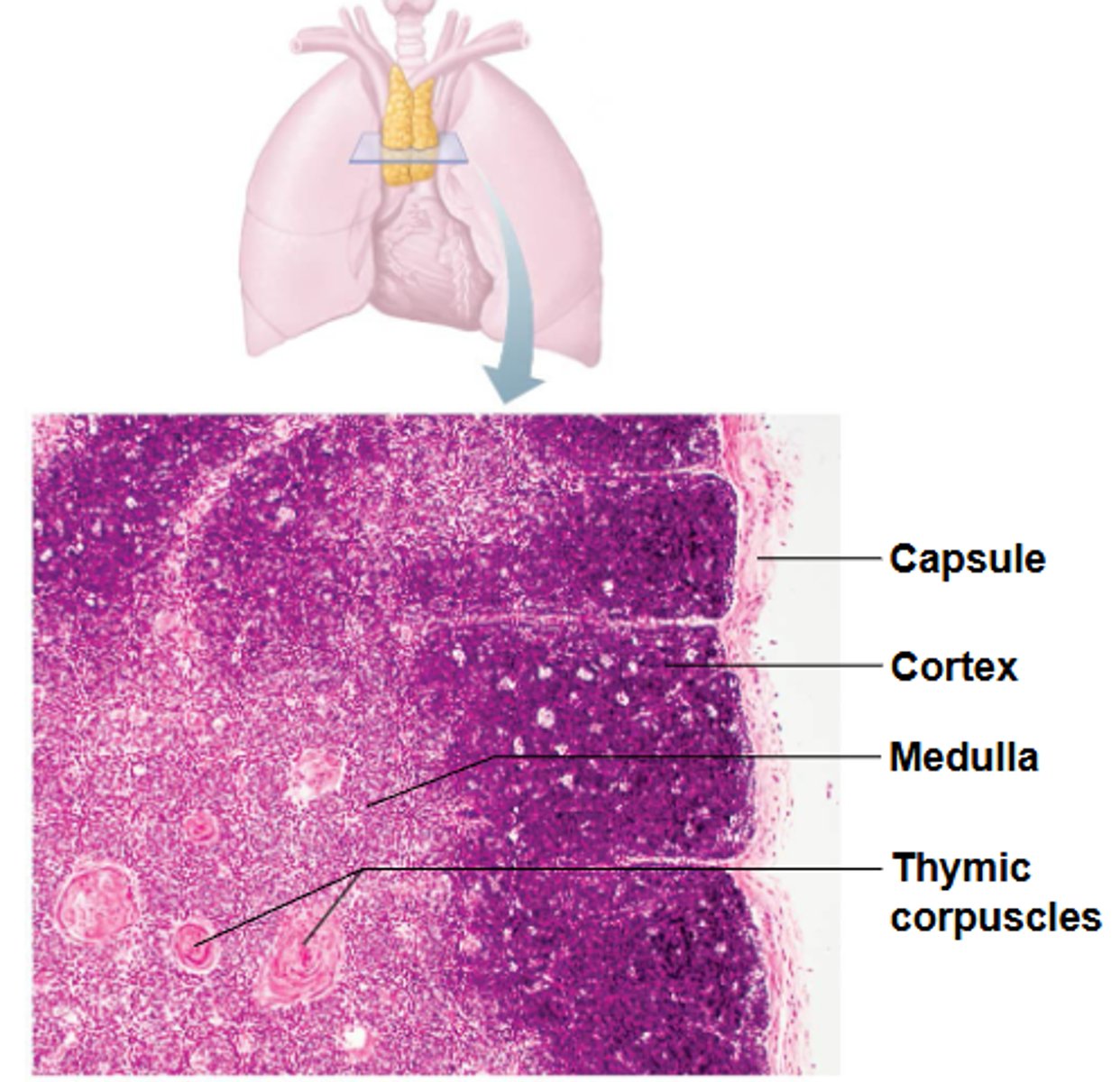
what type of cell makes up the stroma of the cortex of the thymus?
lacks
the cortex of the thymus has no follicles because it _______ B cells
thymic corpsucles
what are made of special T regulatory lymphocytes (T reg) that prevent autoinmmunity?